Principles of Genetics
5.0(1)
Card Sorting
1/55
Earn XP
Description and Tags
Last updated 3:33 PM on 2/15/23
Name | Mastery | Learn | Test | Matching | Spaced | Call with Kai |
|---|
No analytics yet
Send a link to your students to track their progress
56 Terms
1
New cards
Blending hypothesis
the idea that genetic material from the two parents blends together
2
New cards
Particulate hypothesis
the idea that parents pass on discrete heritable units (genes) o Mendel documented a particulate mechanism through his experiments with garden peas
3
New cards
Character
Heritable feature that varies among individuals ▪ Ex. Flower color
4
New cards
Trait
Each variant for a character ▪ Ex. Purple or white color for flowers
5
New cards
Short generation time ▪ Large numbers of offspring ▪ Mating could be controlled
Why did Mendel use peas as the subject?
6
New cards
Hybridization
process of mating two contrasting, true-breeding varieties
7
New cards
P - generation
the true breeding parents
8
New cards
F1 generation
hybrid offspring of the P generation
9
New cards
F2 generation
offspring of F1 individuals that self-pollinate or cross-pollinate with other F1 hybrids
10
New cards
Law of Segregation
each individual that is a diploid has a pair of alleles (copy) for a particular trait
11
New cards
all purple flowers were yield in the f1 gen
(Mendel experiment) crossing the true breeding parents yield what type of f1 gen of hybrids?
12
New cards
purple and white flowers in the f2 gen
(Mendel experiment) he then cross the purple f1 gen flowers ; the f2 gen showed what type of flowers
13
New cards
3 : 1 ratio (purple to white flowers)
(Mendel experiment) what is the ratio of the f2 gen flowers
14
New cards
the purple flower color is a dominant trait, while white is recessive trat
(Mendel Experiment) what does the amount of purple and white flowers tell us?
15
New cards
Gene
heritable factor is also known as
16
New cards
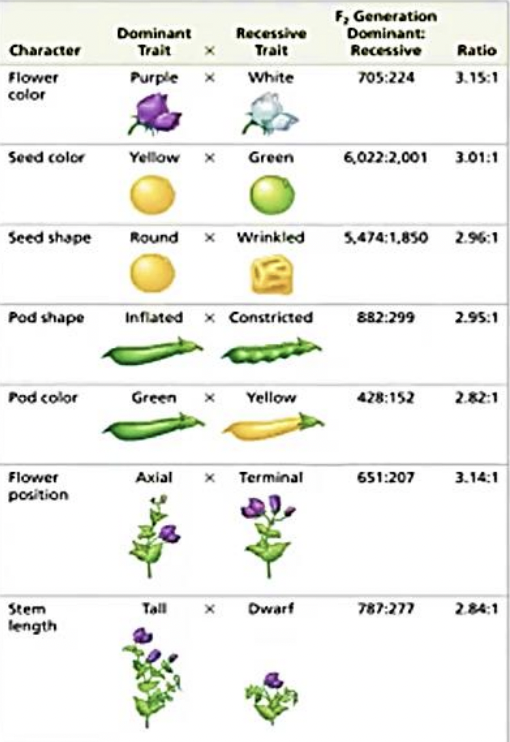
Flower color, seed color, seed shape, pod shape, pod color, flower position, and stem length
What characteristics did Mendel observe in his experiment?
17
New cards
Punnett square
can show possible combinations of sperm and egg
18
New cards
Dominant allele
capital letter represents what allele
19
New cards
Recessive allele
lowercase letter represents what allele
20
New cards
Homozygous
An organism with 2 identical alleles for a character
21
New cards
Heterozygous
An organism that has 2 different alleles for the gene controlling that character
22
New cards
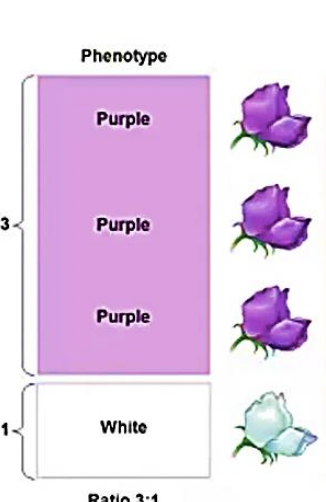
Phenotype
physical appearance
23
New cards
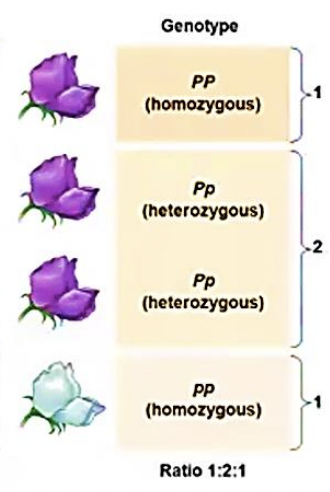
Genotype
genetic makeup
24
New cards
Testcross
dominant phenotype could be either homozygous dominant or heterozygous
25
New cards
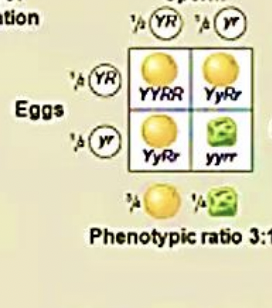
Monohybrid Cross
cross between heterozygotes following one trait only (ex. seed color)
26
New cards
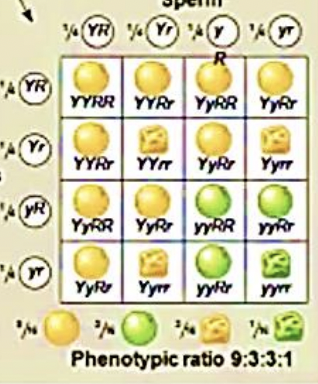
Dihybrid Cross
cross following two traits at the same time (ex. seed color and seed shape)
27
New cards
Law of Independent Assortment
the alleles of two (or more) different genes get sorted into gametes independently of one another
28
New cards
Dihybrid cross (between F1 dihybrids)
this cross can determine whether two characters are transmitted to offspring as a package or independently
29
New cards
Complete Dominance
Occurs when phenotypes of the heterozygote and dominant homozygote are identical
30
New cards
Incomplete Dominance
The phenotype of F1 hybrids is somewhere between the phenotypes of the two parental varieties
31
New cards
Codominance
Two dominant alleles affect the phenotype in separate, distinguishable ways
32
New cards
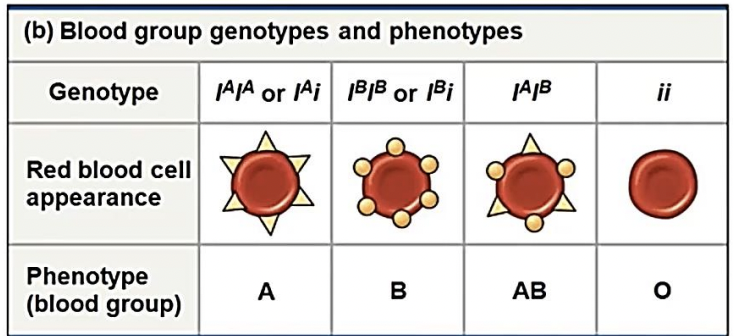
multiple alleles
Most genes exist in populations in more than two allelic forms (ex. blood type)
33
New cards
Pleiotropy
Most genes have multiple phenotypic effects called (ex. Sickle Cell Disease)
34
New cards
Epistasis
a gene at one locus alters the phenotypic expression of a gene at a second locus
35
New cards
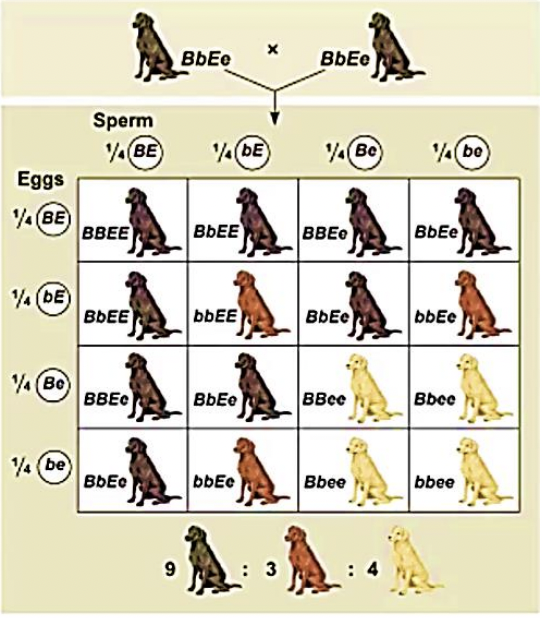
Polygenic Inheritance
An additive effect of two or more genes on a single phenotype (ex. skin color of humans)
36
New cards
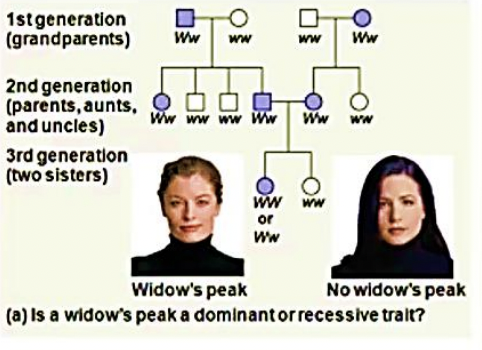
Pedigree Analysis
a family tree that describes the inter-relationships of parents and children across generations ; can predict the future offspring
37
New cards
Recessively Inherited Disorders
Show up only in individuals homozygous for the allele ; genetic disorders that are inherited in a recessive manner
38
New cards
Carriers
are heterozygous individuals who carry the recessive allele but are phenotypically normal
39
New cards
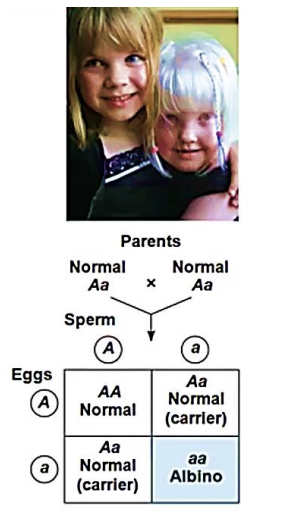
Albinism
a recessive condition characterized by a lack of pigmentation in skin and hair
40
New cards
Dominantly Inherited Disorders
human disorders are caused by dominant alleles
41
New cards
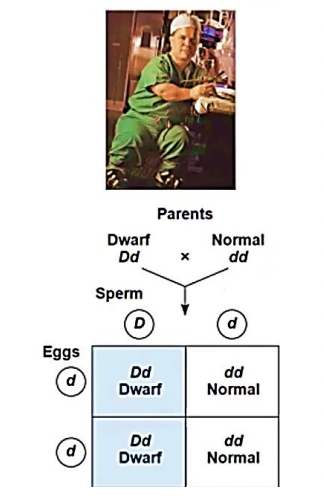
Achondroplasia
is a form of dwarfism caused by a rare dominant allele
42
New cards
Multifactorial Disorders
Many diseases, such as heart disease, diabetes, alcoholism, mental illness, and cancer have both genetic and environmental components (lifestyle and genotype are the factors for diseases)
43
New cards
Thomas Hunt Morgan
provided the first solid evidence associating a specific gene with a specific chromosome came in the early 20th century
44
New cards
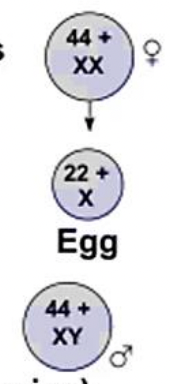
Female
a person with two x chromosomes is
45
New cards
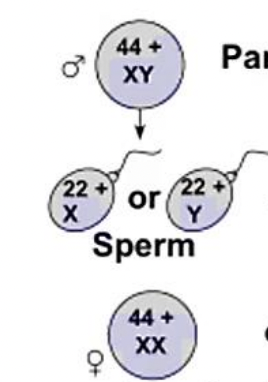
Male
a person with one x and y chromosome is
46
New cards
Sex- linked gene
gene that is located on either sex chromosome
47
New cards
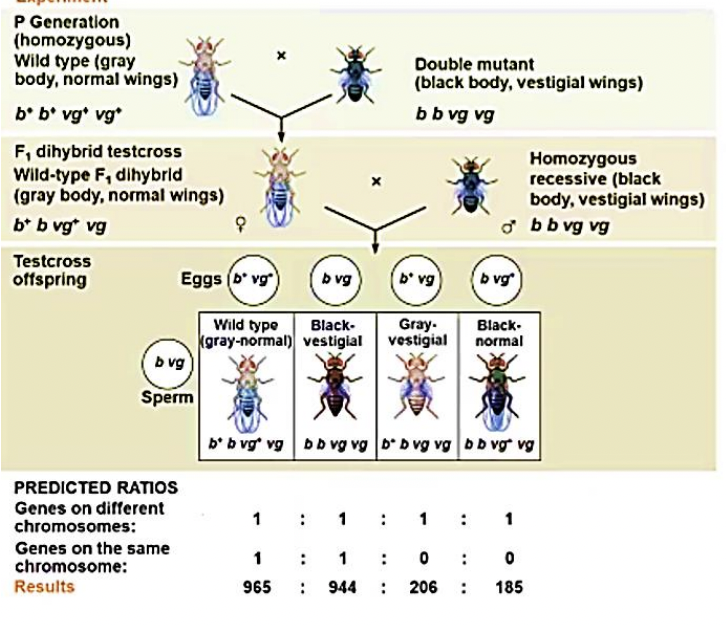
Linked genes
Genes located on the same chromosome that tend to be inherited together
48
New cards
Parental Types
Offspring with a phenotype matching one of the parental phenotypes are called
49
New cards
Recombinants / Recombinant types
Offspring with non-parental phenotypes (new combinations of traits) are called
50
New cards
crossing over of homologous chromosomes
genes can be linked, but the linkage was incomplete, because some recombinant phenotypes were observe ; this mechanism is called
51
New cards
Deletion, Duplication, Inversion , Translocation
Breakage of a chromosome can lead to four types of changes in chromosome structure
52
New cards
Down Syndrome
is an aneuploid condition that results from three copies of chromosome 21
53
New cards
Klinefelter syndrome
the result of an extra chromosome in a male, producing XXY individuals
54
New cards
Monosomy X, / Turner Syndrome,
produces X0 females, who are sterile; it is the only known viable monosomy in humans
55
New cards
cri du chat (“cry of the cat”)
specific deletion in chromosome 5 ; A child born with this syndrome is severely intellectually disabled and has a catlike cry; individuals usually die in infancy or early childhood
56
New cards
chronic myelogenous leukemia (CML)
cancer caused by translocations of chromosomes