Lab Quiz #1
1/51
There's no tags or description
Looks like no tags are added yet.
Name | Mastery | Learn | Test | Matching | Spaced | Call with Kai |
|---|
No analytics yet
Send a link to your students to track their progress
52 Terms
What does the CNS contain?
Brain and Spinal cord
What does the PSN contain?
12 pairs of cranial nerves, 31 pairs of peripheral nerves
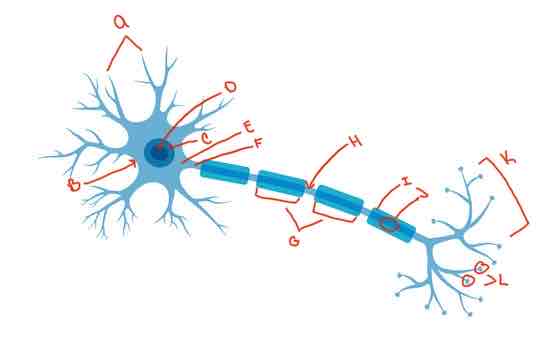
What is letter A?
Dendrite
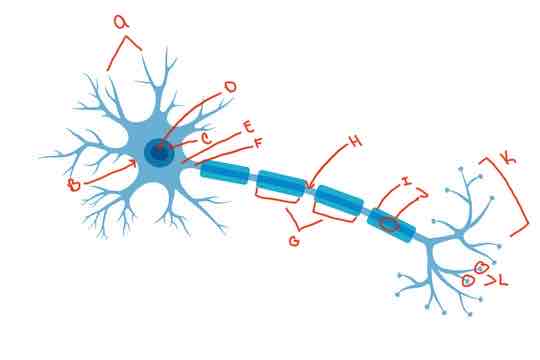
What is letter B?
Soma
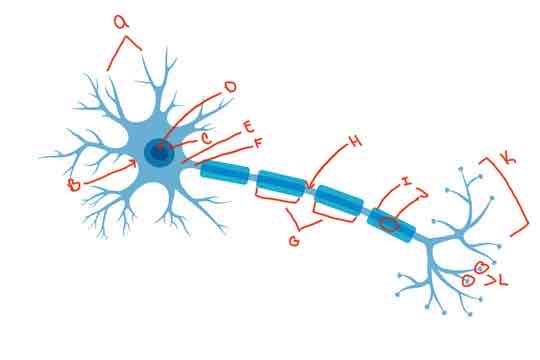
What is letter C?
Nucleus
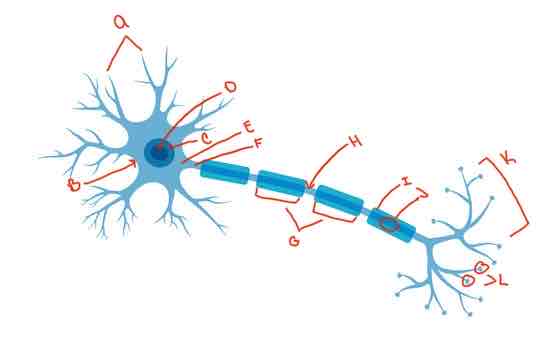
What is letter D?
Nucleolus
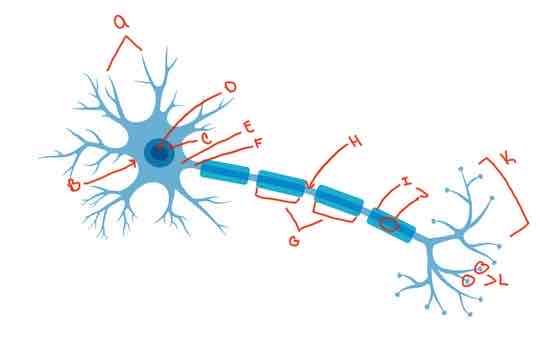
What is letter E?
Axon hillock
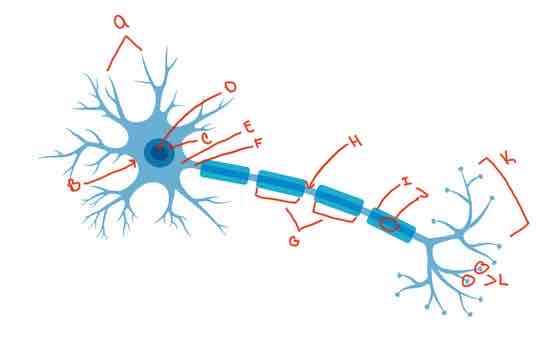
What is letter F?
Axon
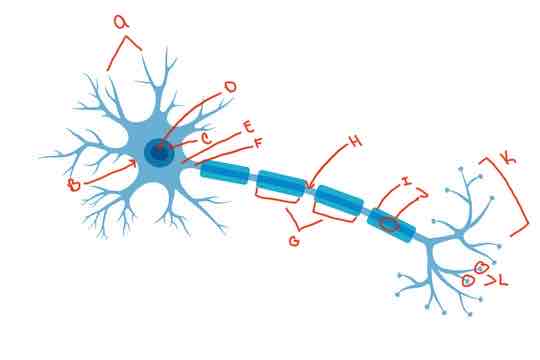
What is letter G?
internodes
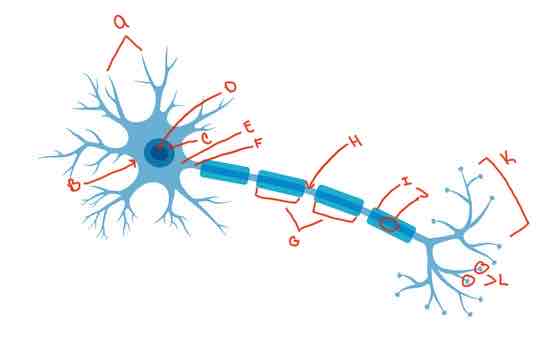
What is letter H?
Nodes of Ranvier
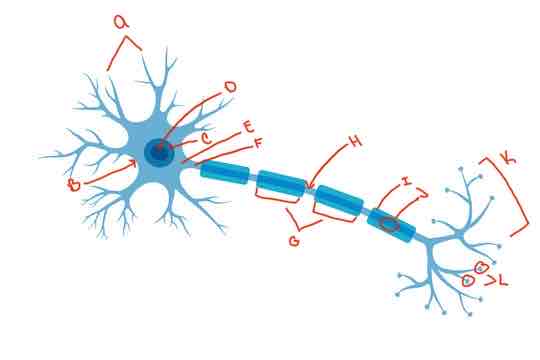
What is letter i?
myelin sheath
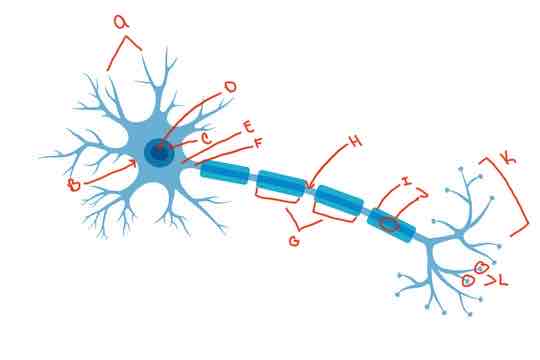
What is letter J?
Schwann cells
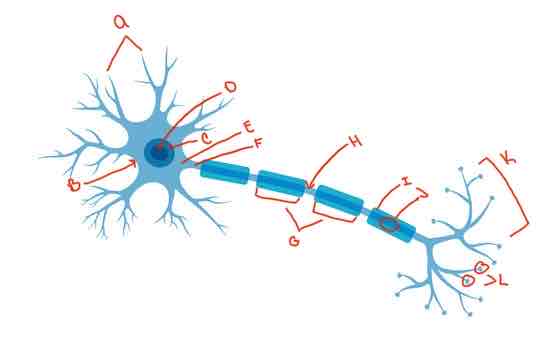
What is letter K?
Terminal arborization
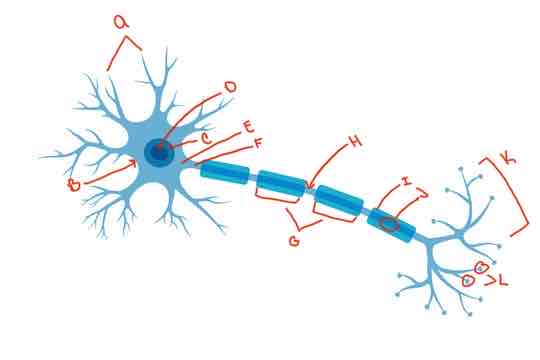
What is letter L?
synaptic knobs
Function of axon
transmit impulses
function of dendrites
receives signals
function of Nissl bodies
protein synthesis
function of neuroplasm
provides support and nourishment to the neuron
function of neurolemma
insulates the axon
function of nucleolus
produces ribosomes for protein synthesis
Schwann cells
produce myelin sheath, regeneration of damages axons (PNS)
Satellite cells
regulate environment around neurons (PNS)
Astrocyte
Provide structure and blood brain barrier (CNS)
Microglia
Act as the primary immune defense in CNS
Oligodendrocyte
Form myelin sheath around axons in CNS
Ependymal Cells
Line the ventricles of the brain and produce cerebrospinal fluid (CNS)
What are plexus?
bundle of nerves w function
Grey matter
neuron cell body w/o myeline
White matter
myelinated axons
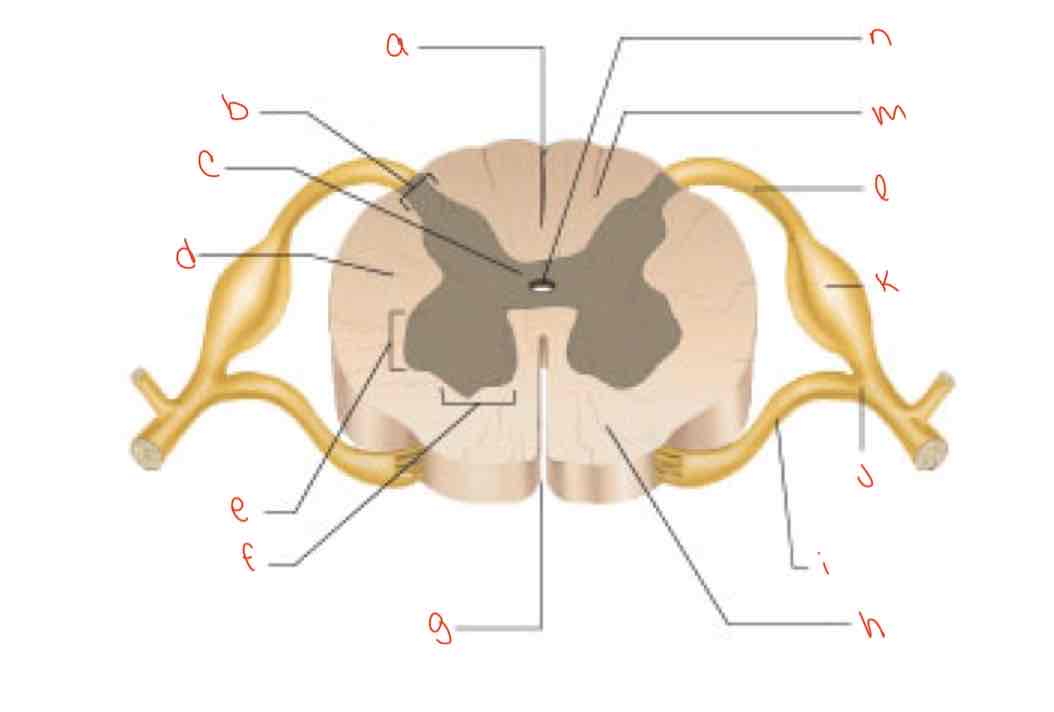
What is letter a?
posterior median sulcus
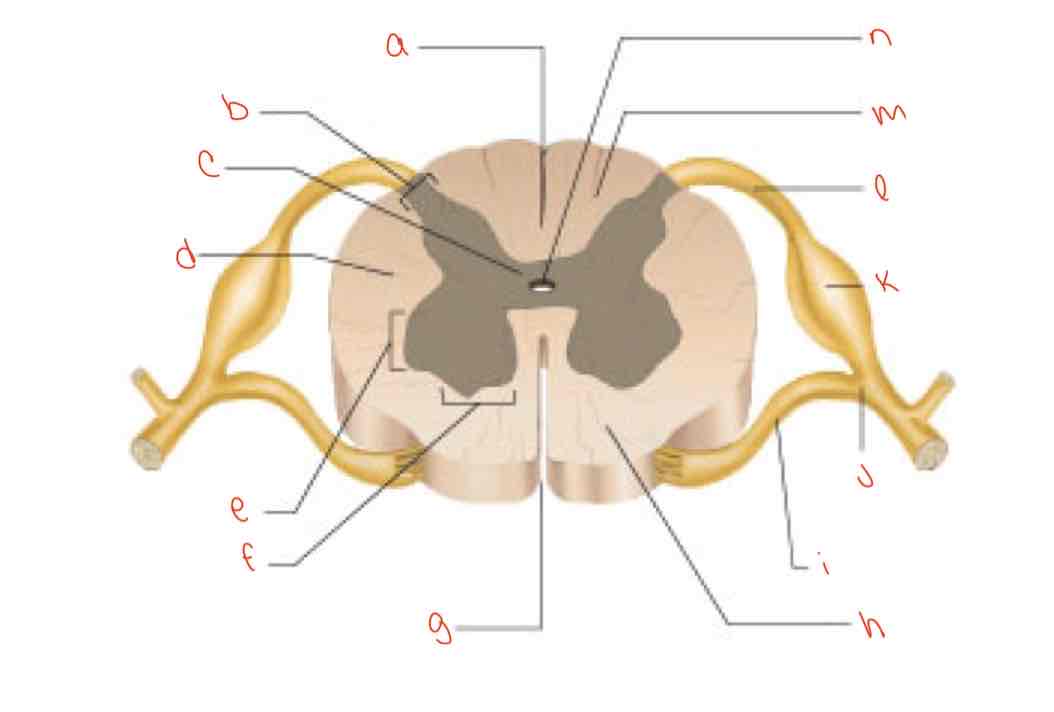
What is letter b?
dorsal horn
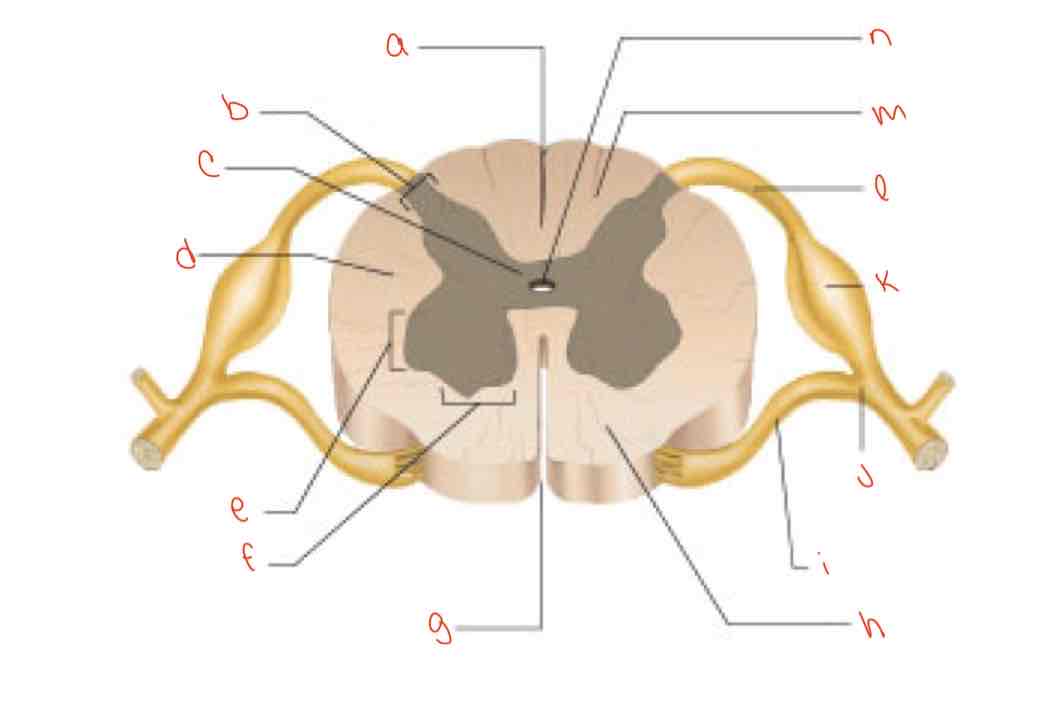
What is letter c?
gray commissure
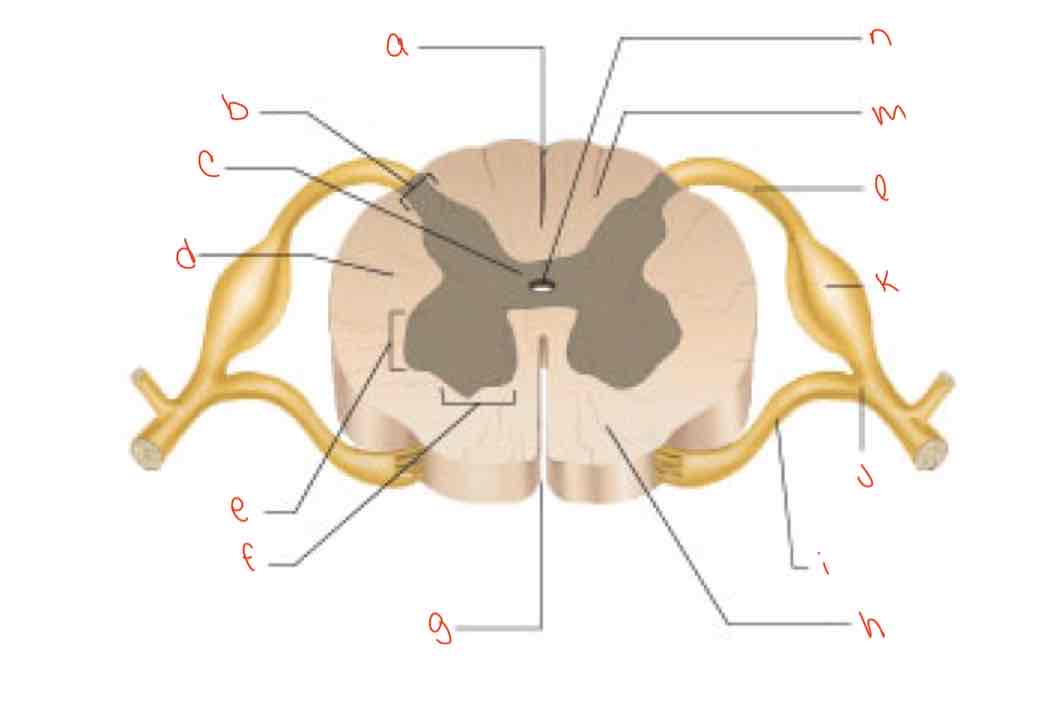
What is letter d?
lateral column
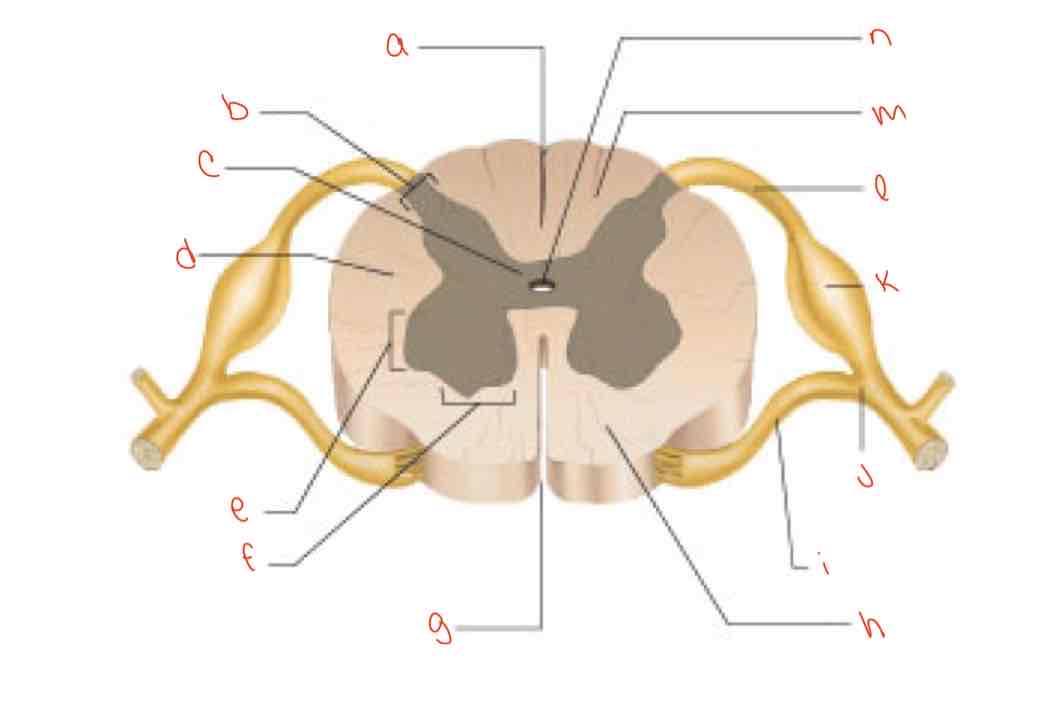
What is letter e?
Lateral horn
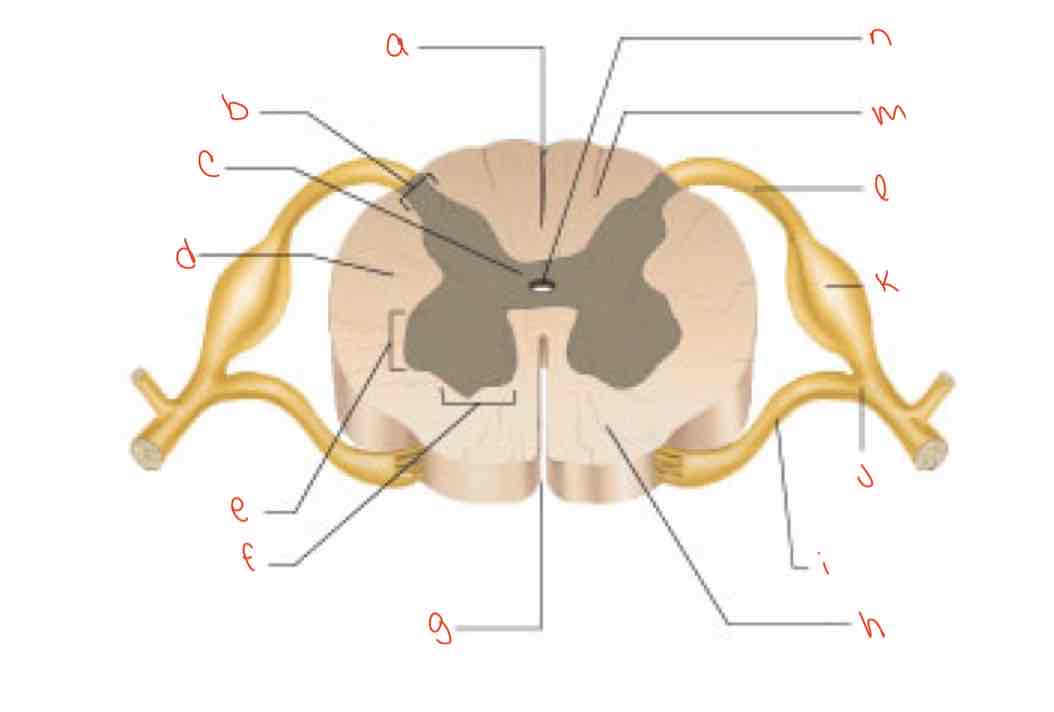
What is letter f?
Ventral horn
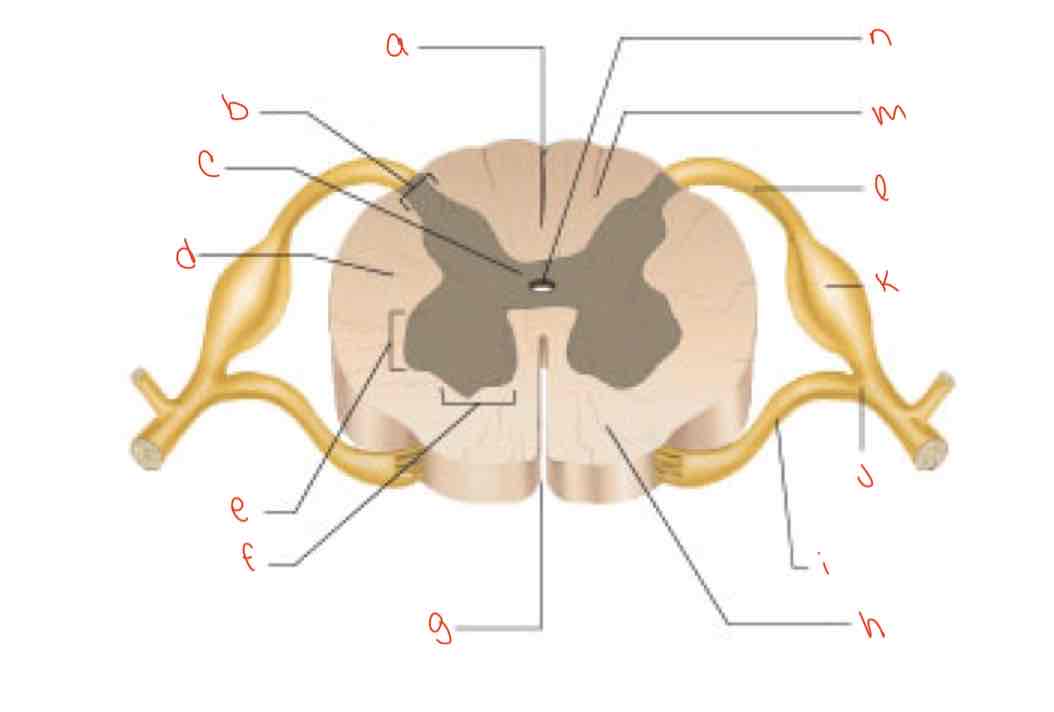
What is letter g?
anterior median fissure
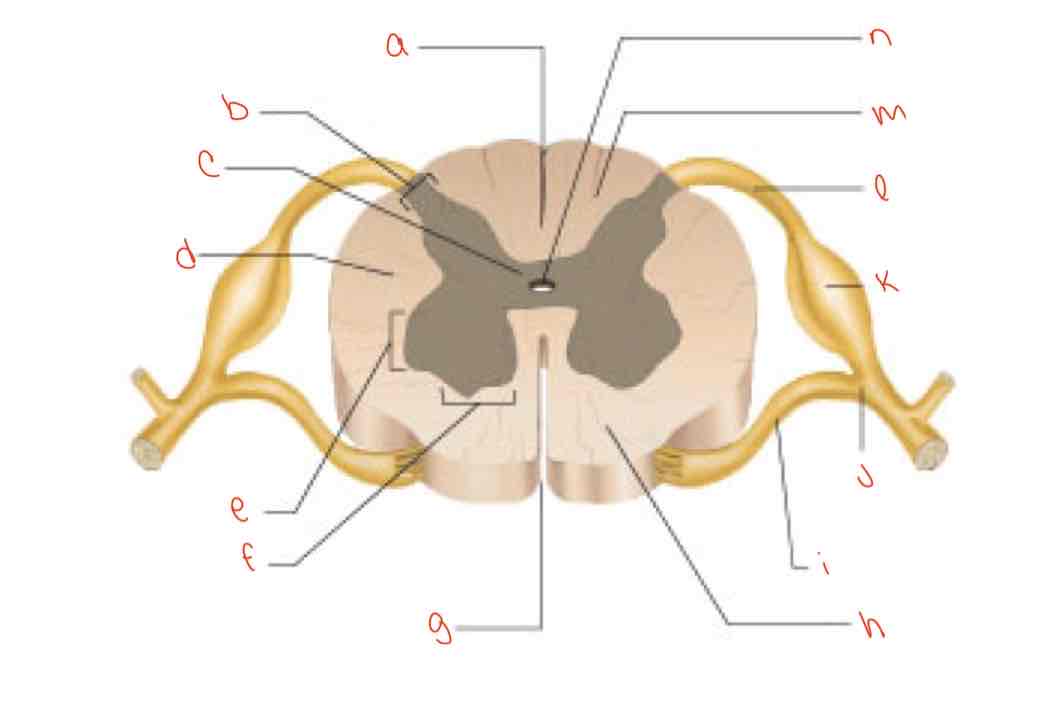
What is letter h?
ventral column
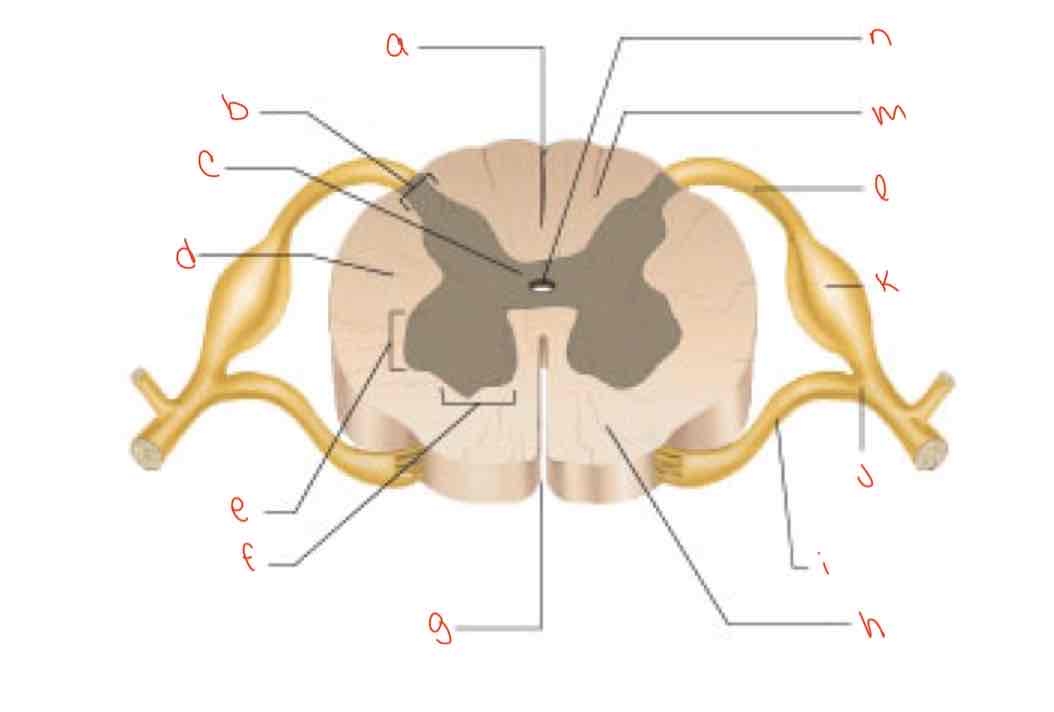
What is letter i?
Ventral root of spinal nerve
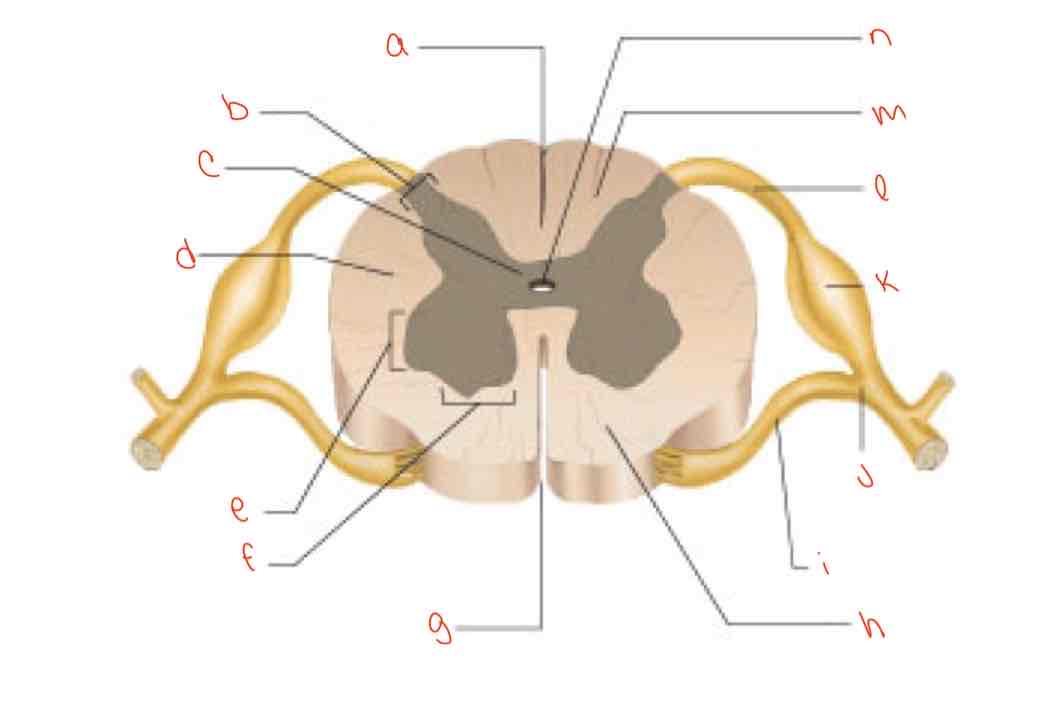
What is letter j?
spinal nerve
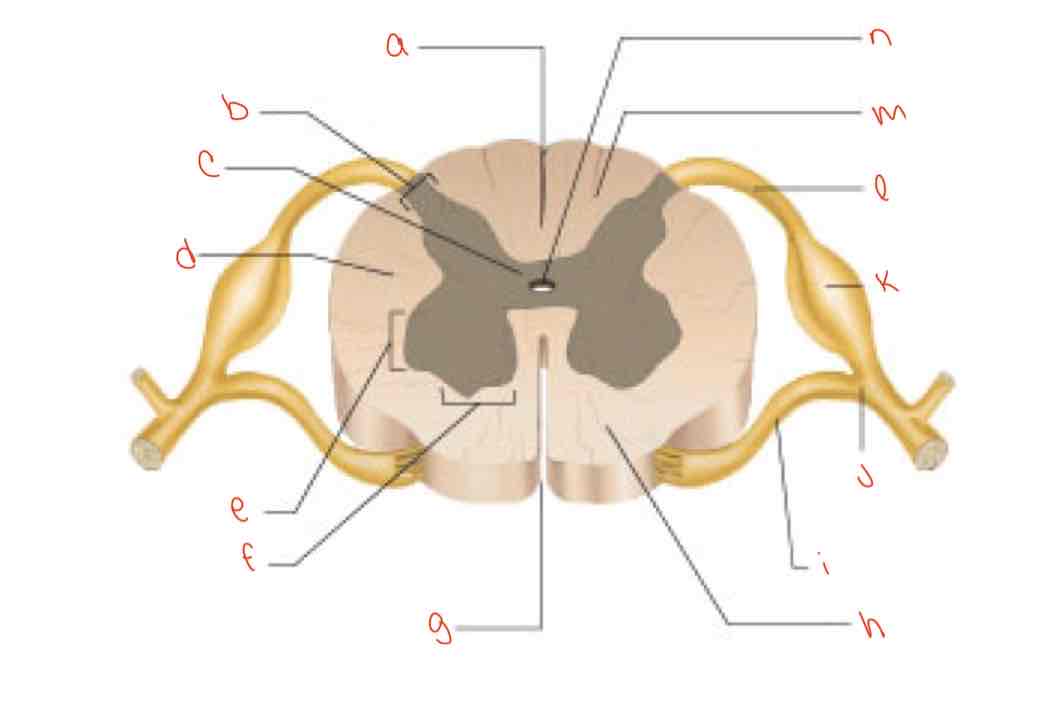
What is letter k?
dorsal root ganglion
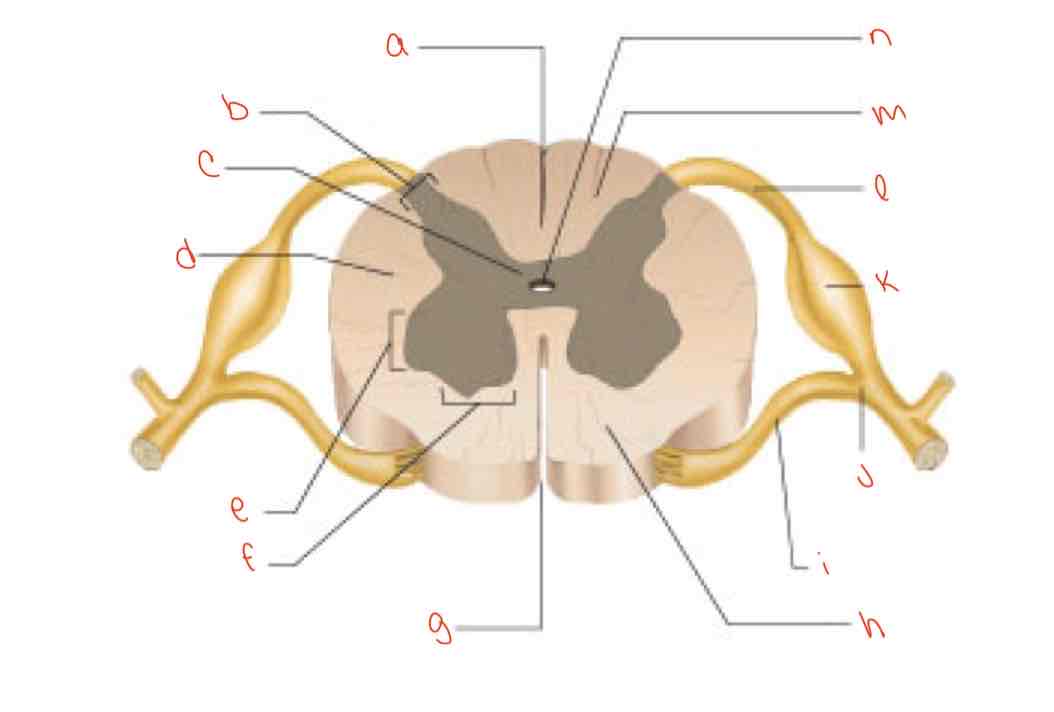
What is letter L?
dorsal root of spinal nerve
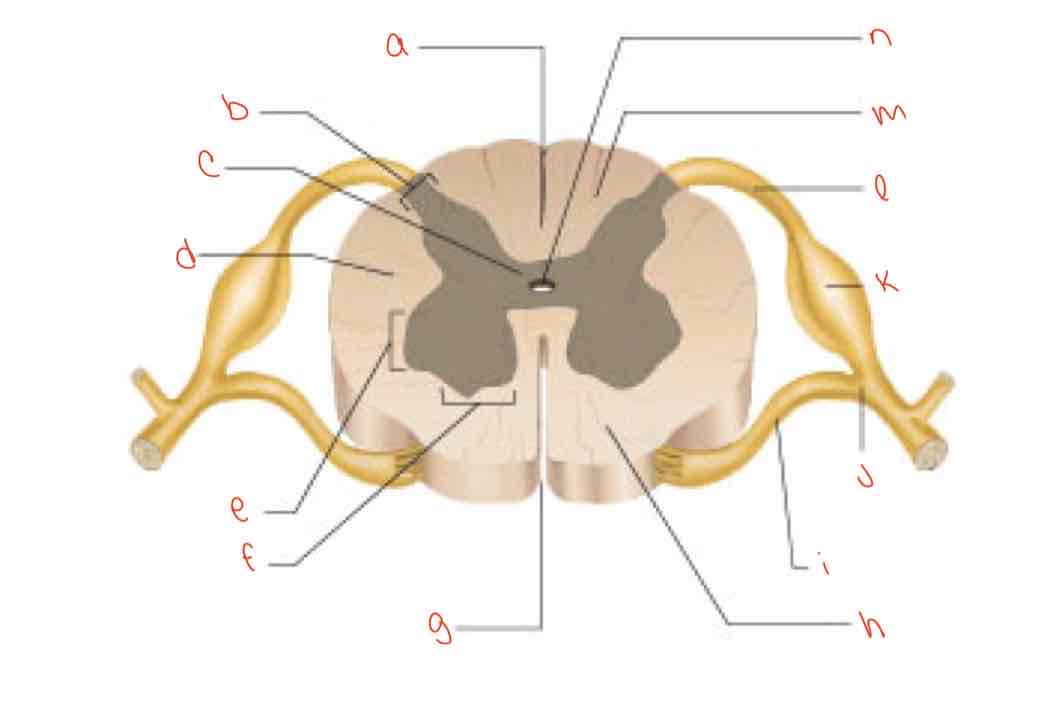
What is letter m?
dorsal column
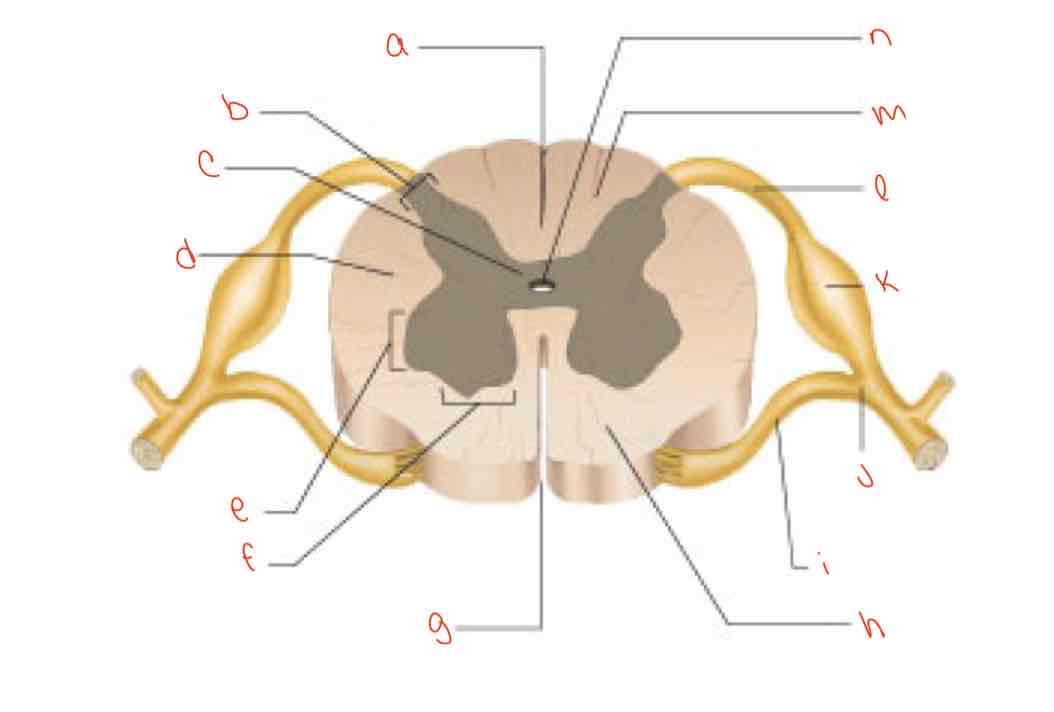
What is letter n?
central canal
afferent neurons
transmit sensory info from receptors in body to CNS
efferent neurons
transmits info from CNS to muscles, glands, etc + allows for voluntary and involuntary actions