Enzymes and Activation Energy
1/17
There's no tags or description
Looks like no tags are added yet.
Name | Mastery | Learn | Test | Matching | Spaced | Call with Kai |
|---|
No study sessions yet.
18 Terms
What is metabolism?
Metabolism refers to all the reactions of the body.
Give examples of metabolic reactions.
Respiration
Digestion
Photosynthesis
State one way in which reactions can be sped up and suggest reasons as to why it may not be most effective.
Reactions can be sped up by increasing temperature.
However, high temperatures can cause damage to cells:
Melt lipids- lipids make up the cell membrane; this would destroy the cell.
Denatures proteins- changes shape- cannot function properly.
In industry, generating very high temperatures is very expensive.
State a better way in which reactions can be sped up.
Using catalysts.
What is a catalyst?
A chemical that speeds up the rate of reaction but remains unchanged / reusable at the end of the reaction.
Enzymes are…
Biological catalysts.
Explain how enzymes are specific.
They will catalyse only one particular reaction.
Explain how enzymes are efficient.
Enzymes are very efficient and have a high turnover number; this means that they can convert many molecules of substrate into product per unit time.
Any molecule that can bind to an enzyme / have a reaction catalysed by an enzyme is a…
Substrate.
What affects the ability of an enzyme to function?
The 3D shape of the active site.
Substrate molecules bind to the reactive part of an enzyme i.e. the active site.
Substrates can only bind if it is the correct shape.
∴ Each enzyme is specific for the substrate it binds to.
What is complementary binding?
When 2 molecules fit together to complete each other.
What is the activation energy?
The minimum amount of energy needed for a reaction to happen.
The activation energy is the energy needed to break existing chemical bonds inside molecules.
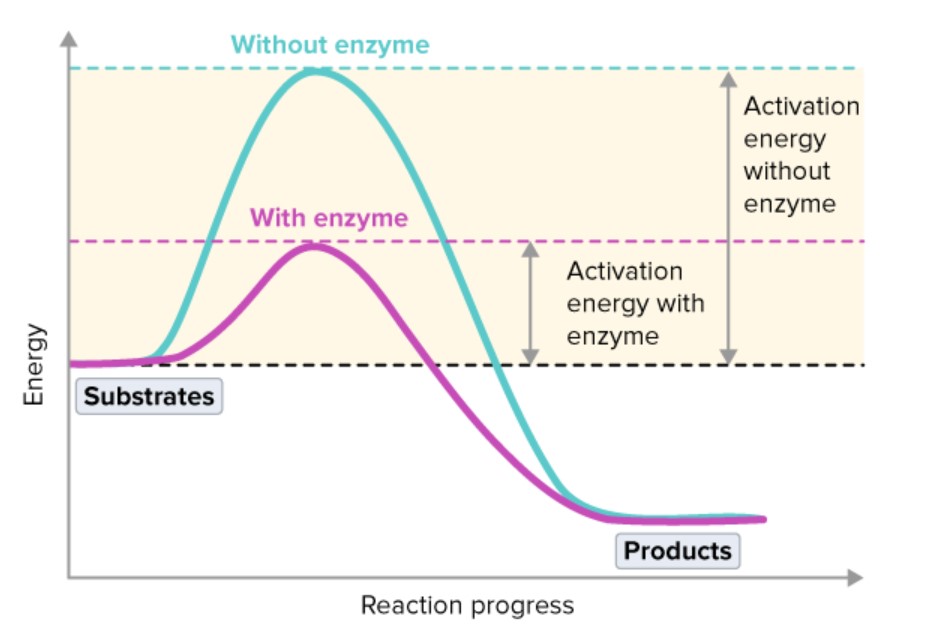
How do enzymes affect activation energy?
In the body, enzymes lower the activation energy of a reaction.
How does an enzyme lowering the activation energy affect the rate of a reaction?
Lowering the activation energy reduces the input of energy needed to allow reactions to take place; which means they can take place at lower temperatures.
As a result, the reaction will occur at a faster rate.
How do you calculate rate from given data?
To calculate rate, you must have time as one of the given values.
From data:
If the dependent variable is time: rate = 1 / time
If the dependent variable is a quantity: rate = quantity / time
How can you improve an experiment to ensure that the accurate optimum pH / temperature is measured?
The optimum pH/temperature is given by the shortest time / highest rate.
BUT:
If the time or rate at two values of the independent variable are close, then the optimum is likely to be between these values.
You can improve the method by investigating values of the IV between these two values.
If the shortest time or fastest rate is at the highest or lowest value of the independent variable, then you don’t know what would happen at values of the IV higher or lower than this.
You can improve this by extending the range of the IV.
If there is a large difference between two values of the independent variable, then the same points apply – you don’t know what is happening between those points so you would need to investigate a range of values between them.
What are the 3 different rates that can be calculated from a graph?
From a graph, there are three different rates that can be calculated:
rate between two times
initial rate – i.e. at the instant that substrate and enzymes are mixed
rate at a particular time.
Why is the initial rate always highest?
The initial rate is always highest as the concentration of substrate is the highest, so there is the highest frequency of successful collisions and the highest rate.
As the reaction progresses, substrate is converted to product so concentration decreases. There is a lower frequency of successful collisions and the rate decreases.
When all the substrate has been converted to product, the rate will decrease to zero.