Option A: Freshwater
1/38
There's no tags or description
Looks like no tags are added yet.
Name | Mastery | Learn | Test | Matching | Spaced | Call with Kai |
|---|
No analytics yet
Send a link to your students to track their progress
39 Terms
Drainage Basin
The area drained by a river and its tributaries
Freshwater
Freshwater includes rivers, lakes, wetlands, groundwater, glaciers and ice caps
Hydrological cycle
A conceptual model that describes the storage and movement of water between the bio/atmo/litho/hydrosphere
Watershed/Drainage divide
Imaginary line defining the boundary of a river/stream drainage basin separating it from adjacent basin(s)
Discharge
The volume of water passing a given a point over a set time
Physical water scarcity
Lack of water scarcity where water resource development is approaching/has exceeded unsustainable levels. Relating to availability to demand and implies that arid areas are not necessarily water scarce.
Economic water scarcity
lack of water where water is available locally, but not accessible for human, institutional or financial capital reasons
Storm hydrograph
A graph showing how a river changes over a short period, such as a day/couple of days
Flood
A discharge great enough to cause a body of water to overflow its channel and submerge surrounding land
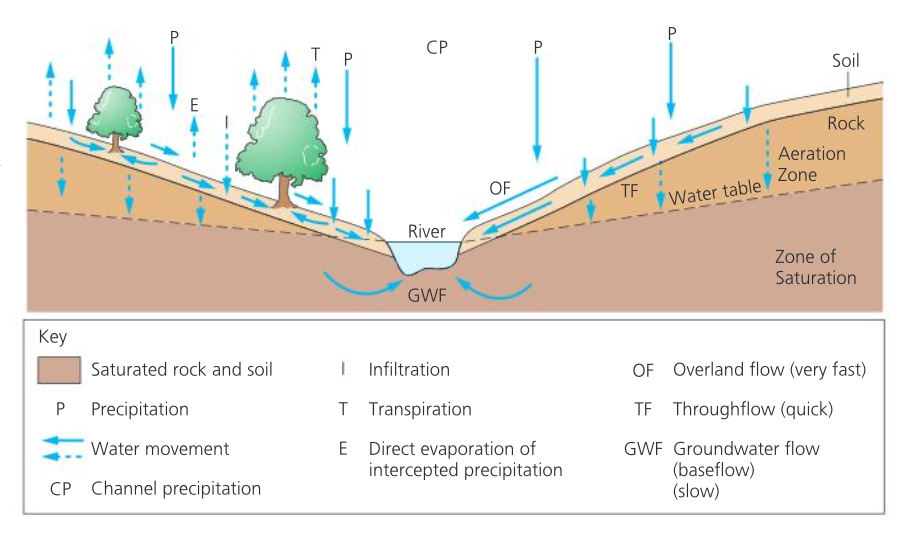
drainage basin as an open system
Cycle has single input/ percipitation (PPT) and two major losses (output), evapotranspiration and run-off. A third output, leakage, may also occur from the deeper subsurface to other basins. The drainage basin system is an open system as it allows the movement of energy and matter across its boundaries.
Infiltration flows
the process bt which water soaks into or is absorbed by the soil.
Infiltration capacity
Maximum rate at which rain can be absorbed by a soil in a given condition
Overland flow
Water flows over the land’s surface
Overland flows occurs in 2 ways
When percipitations exceeds the infiltration rate
When the soil is saturated (all the pores spaces are filled with water)
Inputs
Percipitation ; forms of rainfall/snow/frost/hail/dew
Outputs
Corrasion/Abrasion
the wearing away of the bed and bank by the load carried by a river.
Attrition
is the wearing away of the load carried by a river. It creates
smaller, rounder particles.
Hydraulic action
Force of air and water on the sides of rivers and in cracks
Load
The heavier and sharper the load, the greater the potential for erosion
Velocity
The greater the velocity, the grater potential for erosion
Gradient
Increased gradient increases the rate of erosion
Geology
Soft, unconsolidated rocks such as a sand and gravel are easily eroded
pH
rates of solution are increased when the water is more acidic
Human impact
Deforestation, dams, and bridges interfere with the natural flow of a river and frequently end up increasing the rate of erosion.
Types of erosion
Attrition/abrasion/hydraulic action.
Corrasion
the mechanical impact produced by the debris eroding the bed and banks of the stream
Transport
The load is transported downstream in a number of ways
Types of transport
Suspended/saltated/tacted/flotation
suspended transport
small particles like silts and clays are carried in suspension
Saltated load
Larger particles like sand/gravels/veru small stones are transported in a series of “hops”
Tracted load
Pebbles are shunted along the bed
Causes of deposition
shallowing gradient → decreases velocity
Decrease in volume of water in channel
Increase in friction between water and channel
formation of typical river landforms
waterfalls
Waterfalls
Occur on horizontally bedded rocks.
Soft rock is undercut by hydraulic and abrasion.
Water weight + lack of support = waterfall to collapse and retreat
Main features of deposition
flood plains, meanders, levers, oxbow lakes and deltas
Flood plains
los relief formed by deposition when river floods
generally a mixture of sand and gravel, eroded on outside of meander & built up by channel deposition
Meanders
Normal behaviour of fluids and gases in motion.
Occur on variety of materials, ice→ rock
Develops when channel slope, discharge, and load combine create meander