AP Psychology: Topic 4.1 - Attribution Theory and Person Perception
1/16
There's no tags or description
Looks like no tags are added yet.
Name | Mastery | Learn | Test | Matching | Spaced | Call with Kai |
|---|

17 Terms
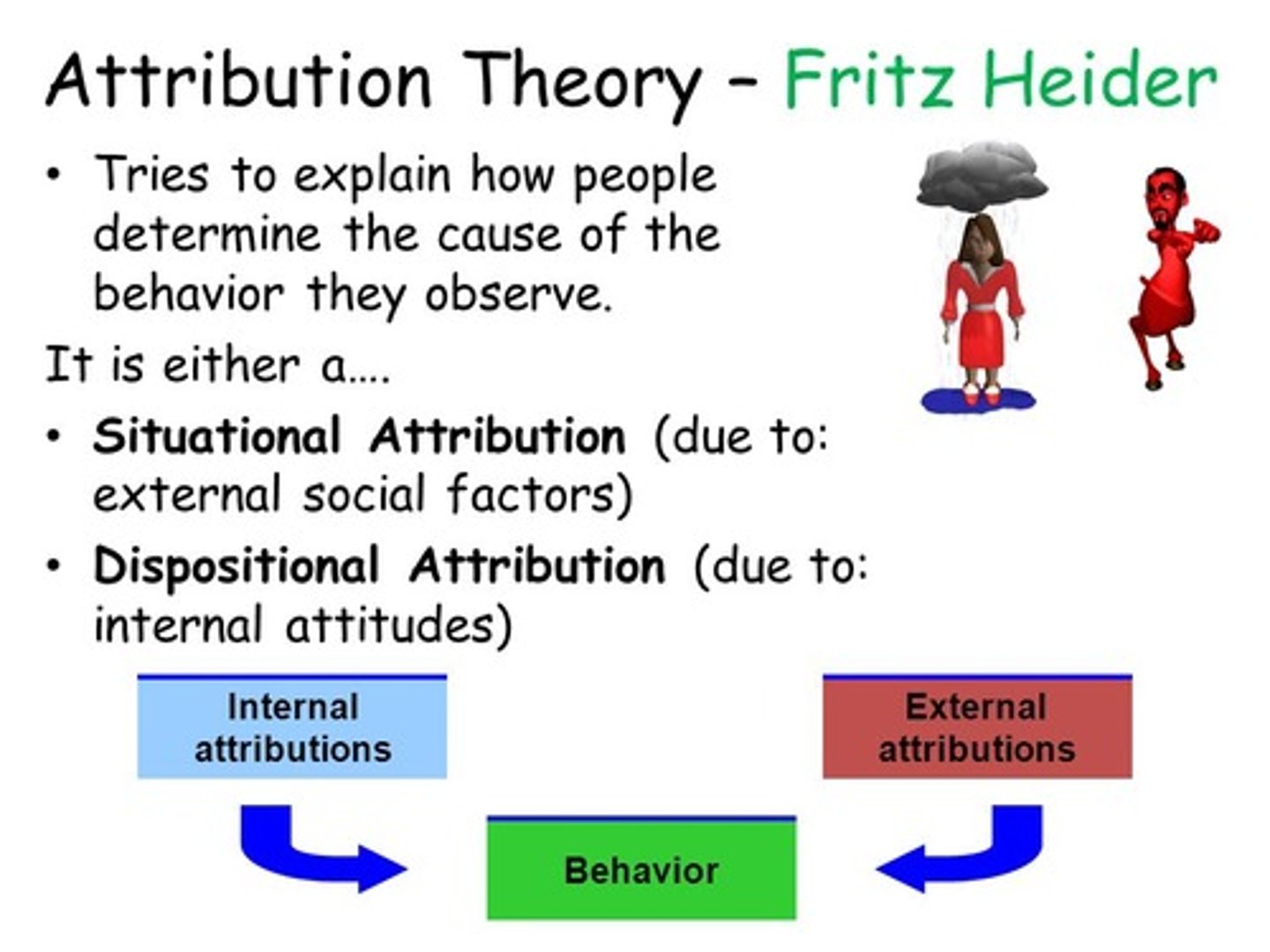
Attributions
refers to how individuals perceive the causes of everyday experience, as being either external to themselves or internal
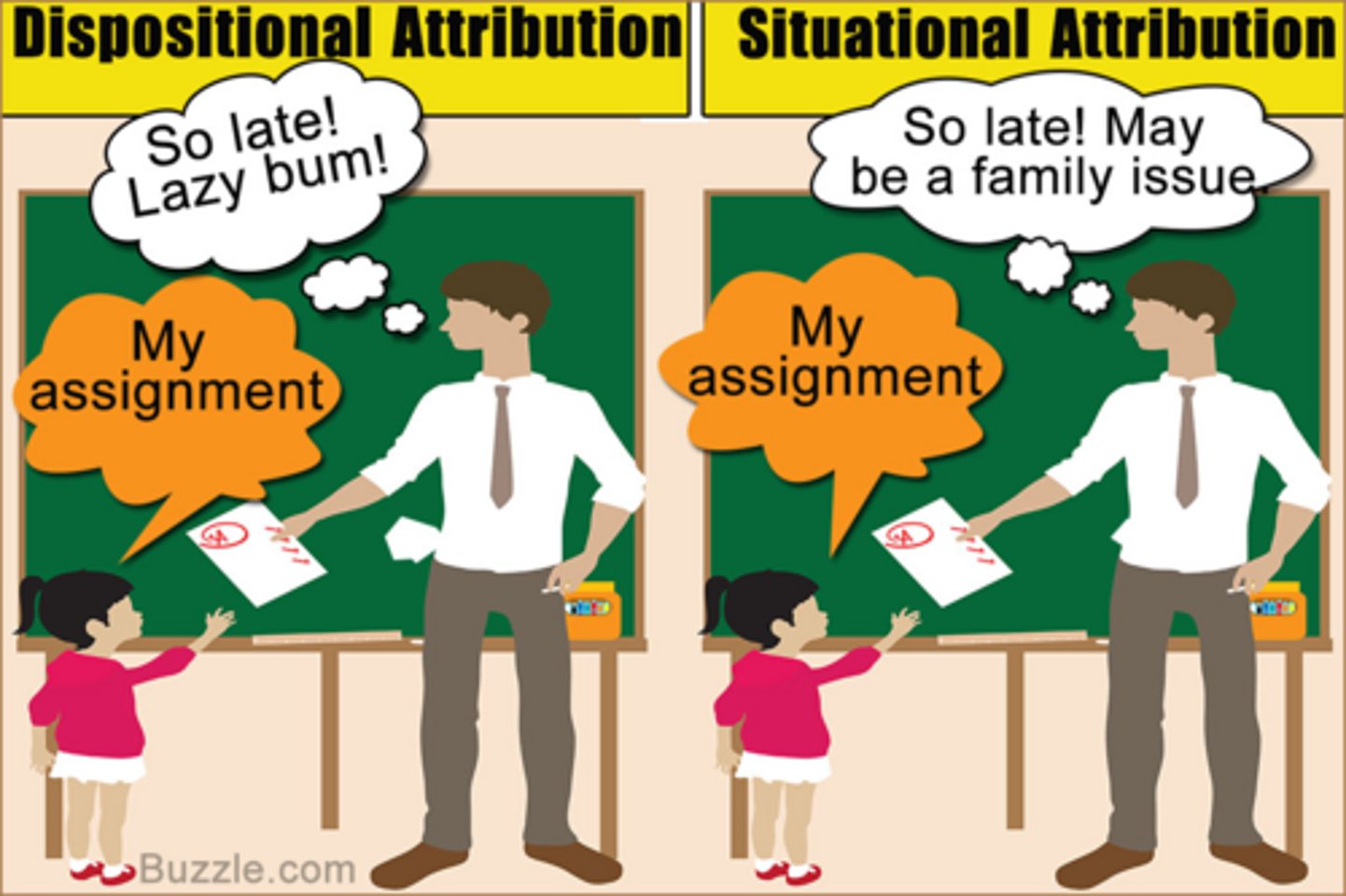
Dispositional attributions
refers to attributing someone's behavior to their personality or character

Situational attributions
when a person believes an event is caused by factors that are outside of themselves (external attribution)
Explanatory style
how people explain to themselves why they experience a particular event-- this can either be categorized as positive (optimistic) or negative (pessimistic)
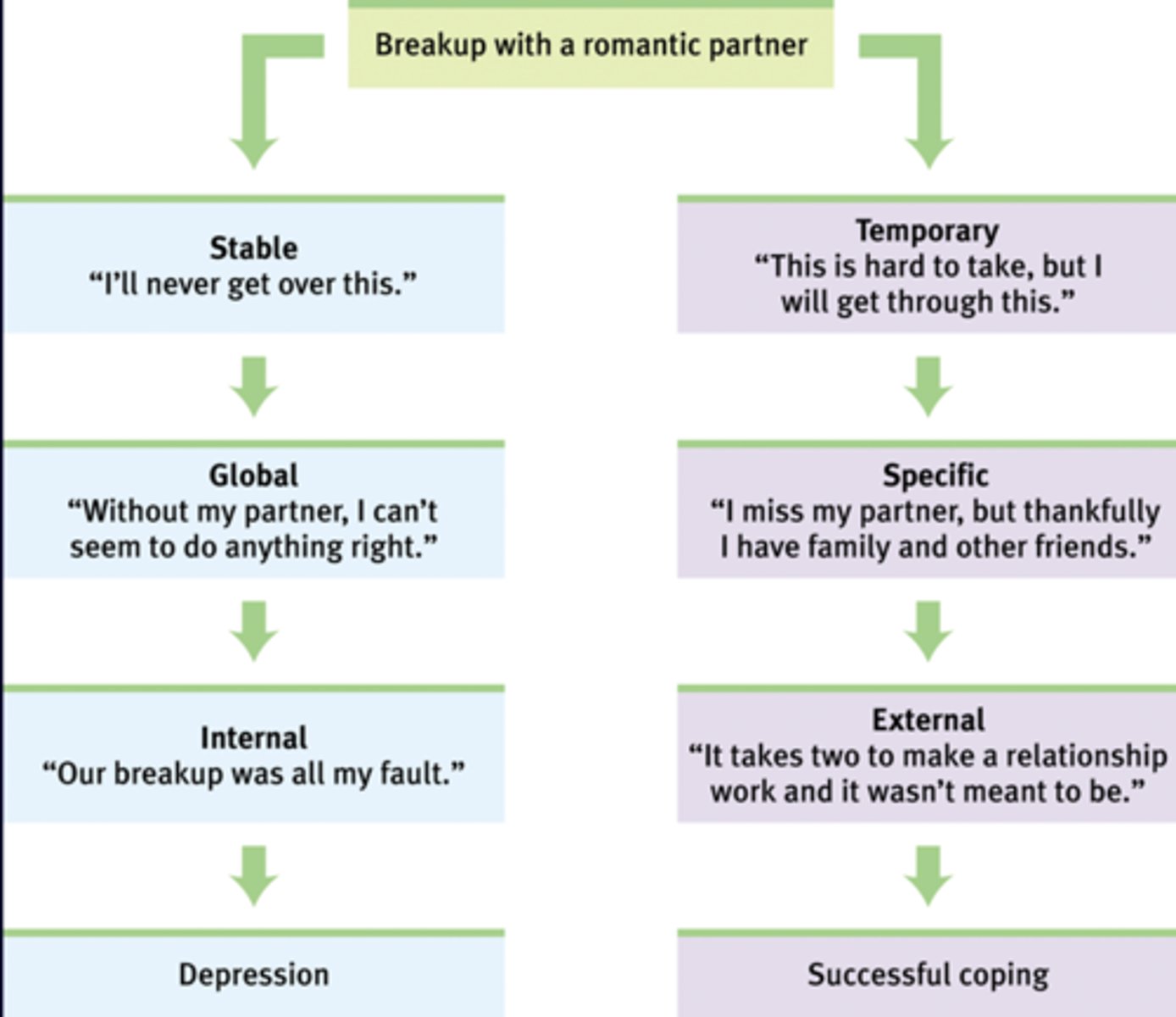
Optimistic explanatory style
the perspective that a challenging situation is temporary, there are aspects the person can control, and it's not their fault
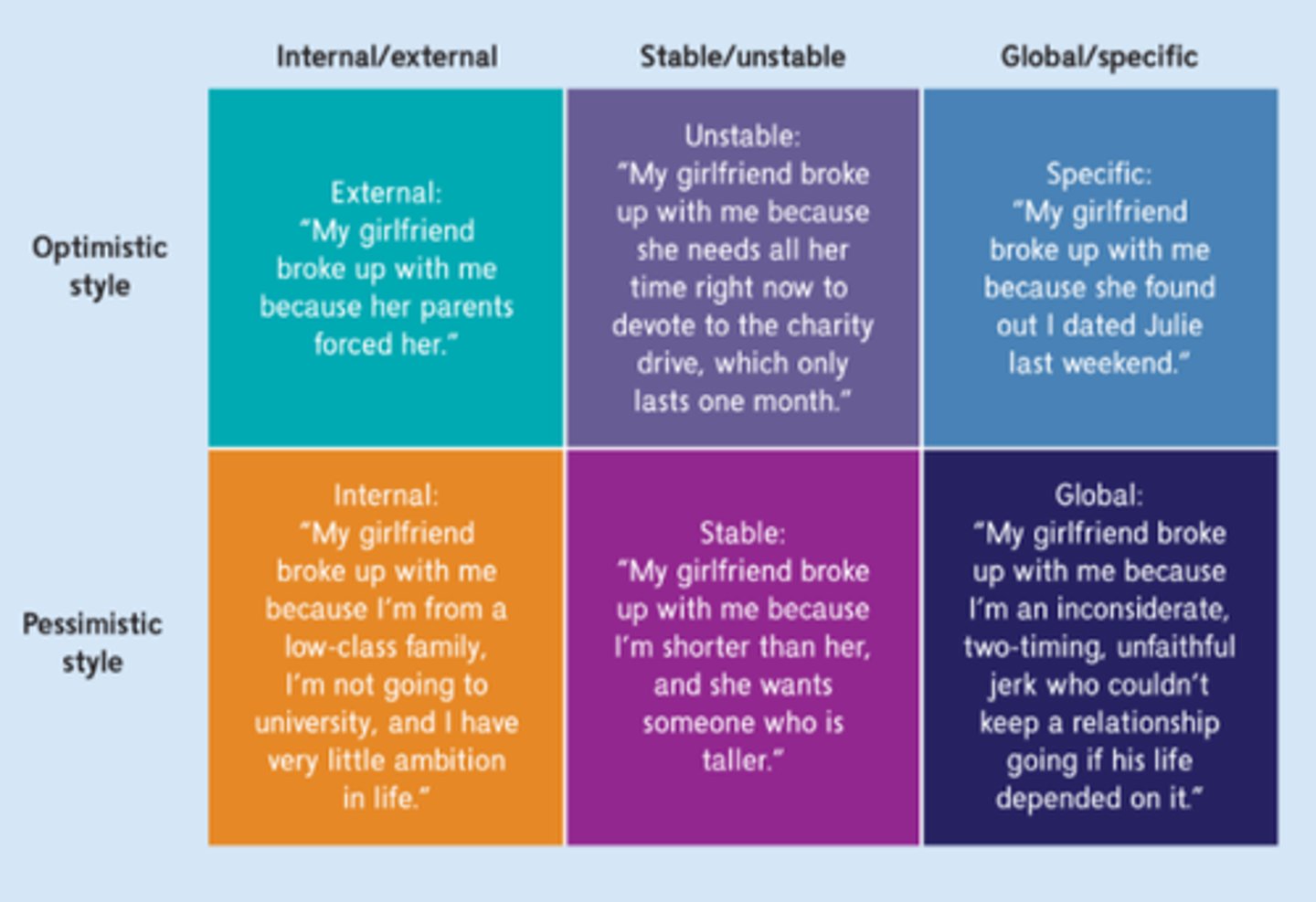
Pessimistic explanatory style
the tendency to explain bad events in a self-blaming manner, viewing the causes as global (affecting many aspects of life), stable (likely to happen again) and internal (caused by the self)

Fundamental attribution error
the tendency to overemphasize personal characteristics and ignore situational factors in judging others' behavior

Actor/observer bias
the tendency to attribute the behavior of others to internal causes, while attributing our own behavior to external causes

Self-serving bias
the tendency for people to take personal credit for success but blame failure on external factors

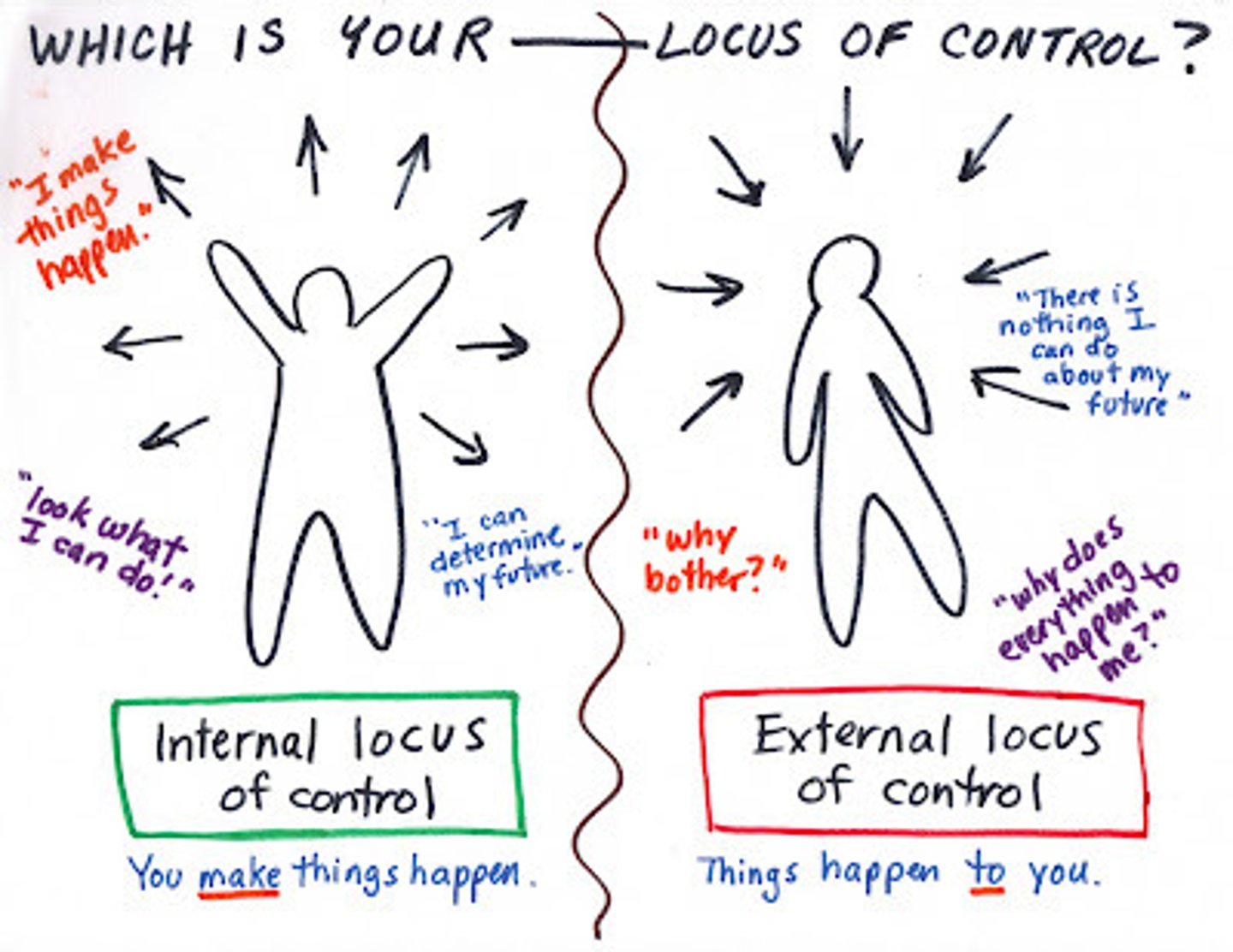
Internal locus of control
the belief that an individual has control over their own actions and outcomes in life

External locus of control
the perception that chance or outside forces beyond one's control determine their fate
Mere exposure effect
the tendency of people to like things or people they are exposed to more often rather than things they have only been exposed to a few times

Self-fulfilling prophecy
a prediction that motivates a person's behavior to cause itself to become true

Social comparison
when an individual evaluates their abilities and attitudes based on how they see themselves in comparison to others
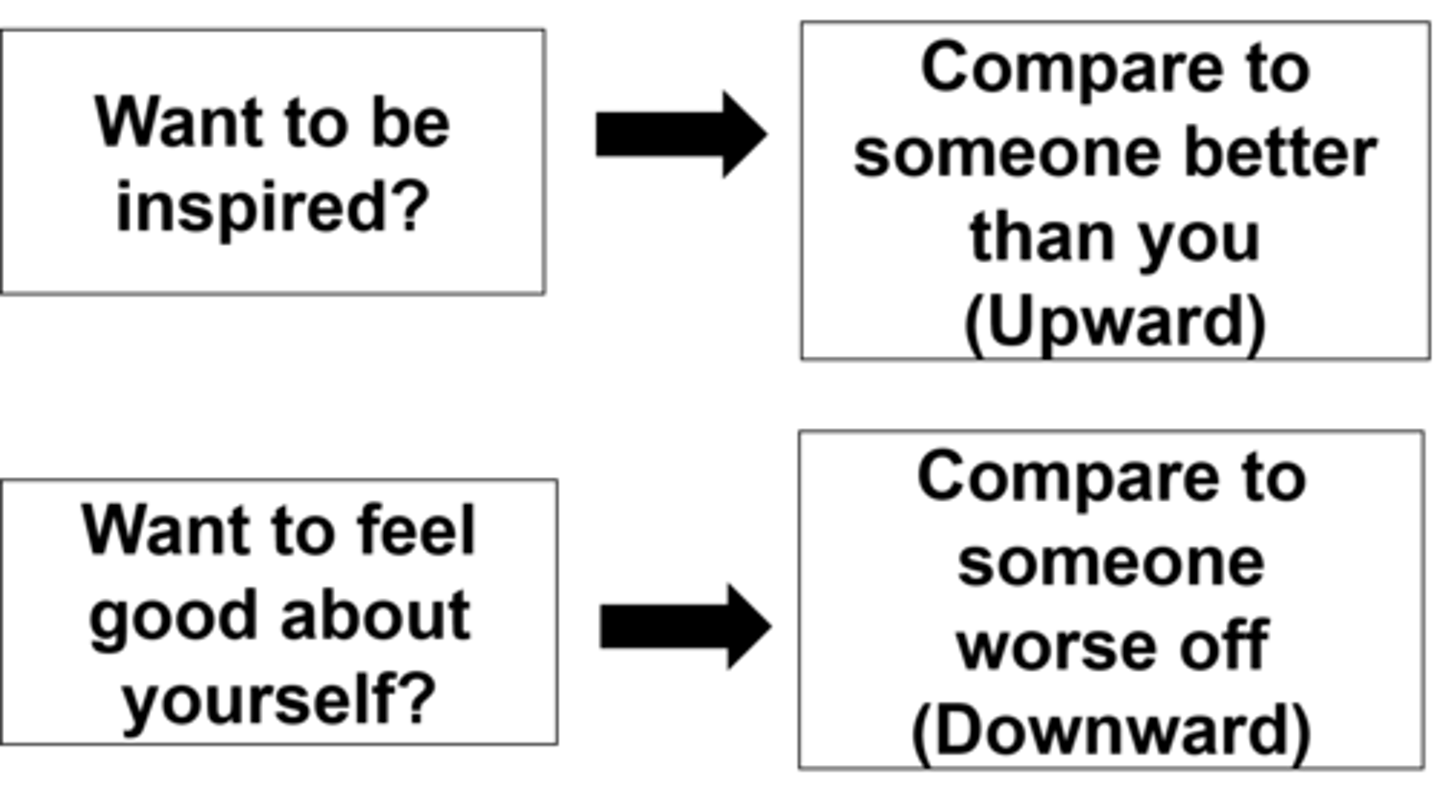
Upward social comparison
comparing oneself with someone who is perceived as being better in a particular area

Downward social comparison
comparing oneself with someone who is perceived as being worse in a particular area
Relative deprivation
A perception by an individual that they are not doing well (e.g., wealth, social status) in comparison to others
