Prosocial Behavior - Ch. 11
1/22
There's no tags or description
Looks like no tags are added yet.
Name | Mastery | Learn | Test | Matching | Spaced | Call with Kai |
|---|
No analytics yet
Send a link to your students to track their progress
23 Terms
altruism
selfless or at a cost to ones self
no benefit to helping the other person
intrinsic motivation only
egoism
does things only for the benefit to the self
for reward/good feeling
social exchange theory
if we do something good for someone, we expect to get something good out of it from the other person
Empathy Altruism Hypothesis
we are driven to help people more when we feel some sort of empathy towards them
‘slacktivism’
doing the bare minimum to show your pro-socialness
private token activism promotes more prosocial behavior than public token activism
observing prosocial behavior/being observed
we want to be seen in a pro-social light, so when we see people do prosocial things and get rewarded, we also do those things when other people are watching
feel good-do good hypothesis
we are more prosocial when in a better mood
negative state release hypothesis
we do prosocial things to make ourselves feel better
most commonly triggered by guilt, least triggered by grief and anger
kin selection
we prioritize helping our family first
evolutionarily: to preserve genes and the ‘in-group’
social responsibility norm
says that you should help others when they need it
universal
evolutionary!!
reciprocity norm
direct: you help when you’ve been helped
indirect: you help with no expectation of help in return
evolutionary!!
signaling theory
evolutionary!!
we act prosocially to signal to others that you are a good person
attracts partners or an ingroup
contributing to public good shows you have plenty of resources for yourself (are doing well)
Fairness norm
everyone puts in their fair share
we need to feel our effort is justified
recipient characteristics
Attributions made to assess if person ‘deserves’ help
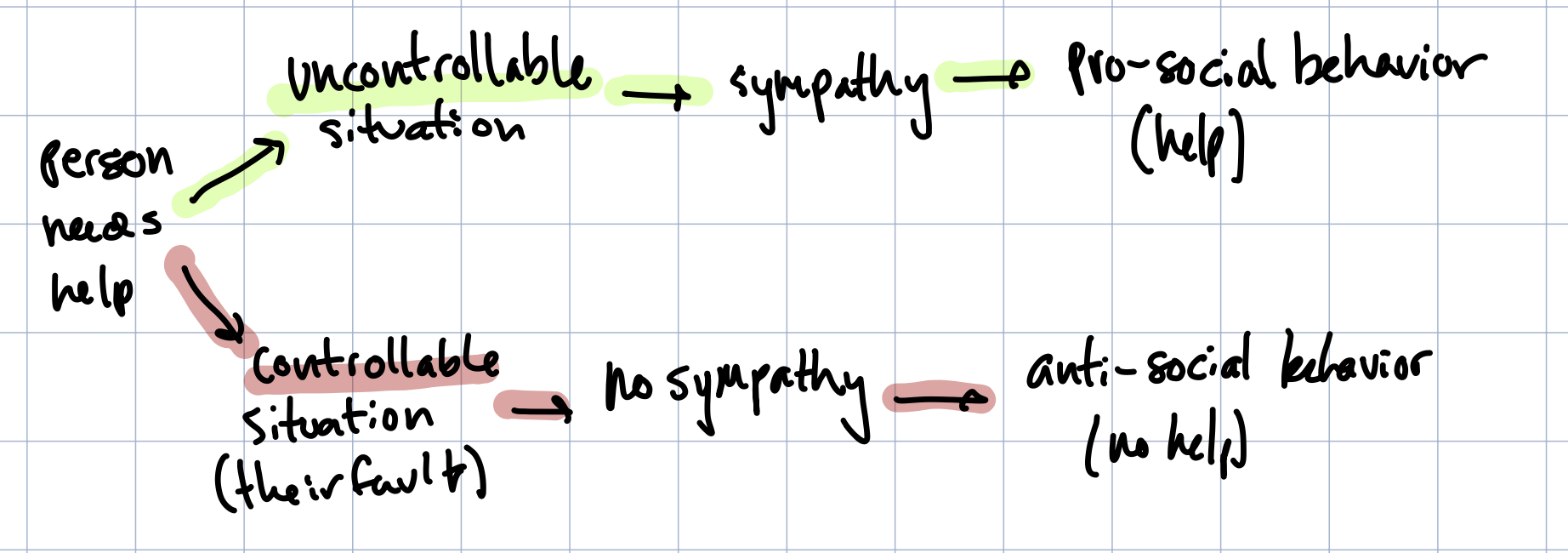
social identity and percieved group membership
we are more likely to help people in our in group
especially if you are recently thinking about why you value being in that group
prosocial gender roles
men likely to be heroic, chivalrous
women likely to be helpful longterm and nurturing
culture
when more value is placed on helpfulness people are more prosocial
religion
we are more prosocial towards same-religion
kitty genovese story
attacked in NYC at night, no one called first responders until it was too late (BYSTANDER EFFECT)
urban vs rural impediments to helping (hypothesis)
less likely to get help when more people are around because responsibility is dispersed too thinly
urban overload hypothesis
so much sensory input in urban environments makes us focus more and more on ourselves
bystander effect
The more people witnessing an emergency, the less likely it is that the victim will receive help
awareness of the bystander effect decreases the likelihood of it
bystander intervention tree
notice emergency
interpret it as an emergency
assume responsiblity
know how to implement help
decide to help