6.1 operant conditioning (learning) & 6.2 classical conditioning (learning)
1/31
There's no tags or description
Looks like no tags are added yet.
Name | Mastery | Learn | Test | Matching | Spaced |
|---|
No study sessions yet.
32 Terms
learning
a relatively permanent change in behavior that arises from practice or experience.
learning is demonstrated by changes in behavior, but learning itself is a mental process
Operant Conditioning
Operant Conditioning (Burrhus Fredrick Skinner, 1904-1990)
The study of how behavior is affected by its consequences.
An association is made between a VOLUNTARY behavior and its consequence.
Operant conditioning examples!
• Text a person, they rarely respond = negative reinforcement
• Post on Facebook, everyone comments = positive reinforcement
• Someone does something nice, they don’t get thanked = negative reinforcement
• Cat meows at front door, door opens = negative reinforcement
Timing is key (in order to pair behavior with consequences)!
Immediate consequences are more effective than delayed
consequences in acquiring a brand new behavior.
– You call your dog (he doesn’t come)
– When he finally does come, you swat him.
– What did you just teach him?
operant learning
the organism has to be able to do the behavior for learning to occur.
behaviors become habits with sufficient consequences
-you learned to eat
– You learned to drive
– You learned to brush your teeth!
reinforcer:
Any stimulus which increases the probability of the response happening again in the future
positive reinforcers: +
Something that is added or applied to increase the
probability the behavior.
– child receives a toy when well behaved
negative reinforcers: -
Something that is taken away to increase the the
probability of a behavior.
– Child does not have to clean his or her room when
s/he behaves well.
punishers
anything that decreases the probability of a response happening again in the future is a punishment
positive punishment: +
Imposing something unpleasant to decrease behavior.
– Child gets a spanking when misbehaves
negative punishment: -
Taking a pleasant thing away to decrease behavior.
– Child gets time out when misbehaves
learned helplessness
When an individual believes that unpleasant stimuli are
inevitable and gives up trying to change the situation
• The belief that one has no control over the outcome
• The belief that all actions are futile
• Give up
• Associated with depression
extinction burst
A sudden increase in the frequency of behavior just before the
behavior stops.
negative reinforcement trap
1. Parent requests child to do something
2. Child’s behavior escalates by crying or whining until parent
gives in.
3. Child repeats this behavior in the future because it works!
learned behavior can escalate quickly!
observational learning
learning by observing others

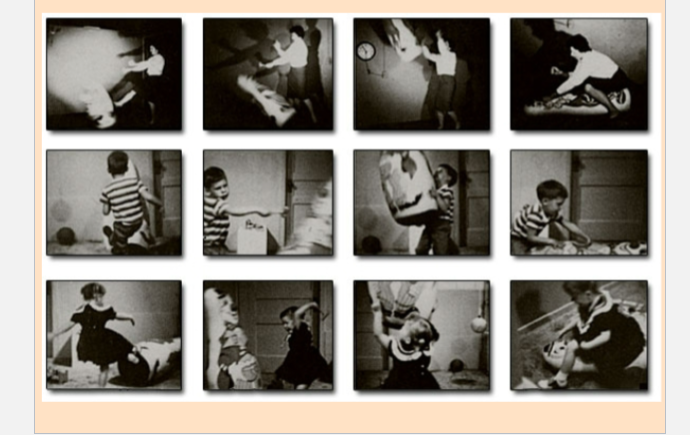
observational learning
• (Bandura, Ross and Ross, 1963) conducted a study using a
BoBo doll.
– They found that children who had observed the
aggressive model showed significantly more aggressive
behavior toward the doll themselves.

observational learning via TV
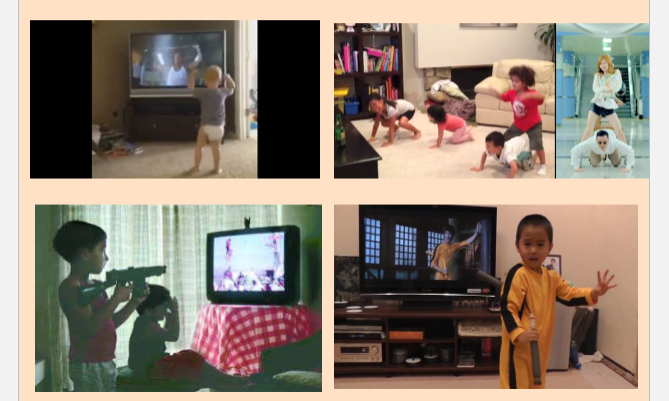

life connections: violence in the media and aggression
teaching children not to imitate media violence
-children who watch violent shows act less aggressively when they are informed that:
• Media does not represent the behavior of most people.
• The behaviors they see are not real.
• Most people resolve conflicts by nonviolent means.
• Real-life consequences of violence are harmful to the victim.
newborn observational learning
even cross species
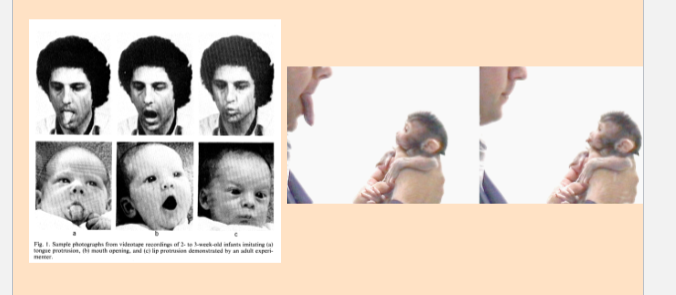
Acquire attitudes via observation and mimicry.
Mikey Wilson 5-years-old
Picture taken at a soccer final between two teams.

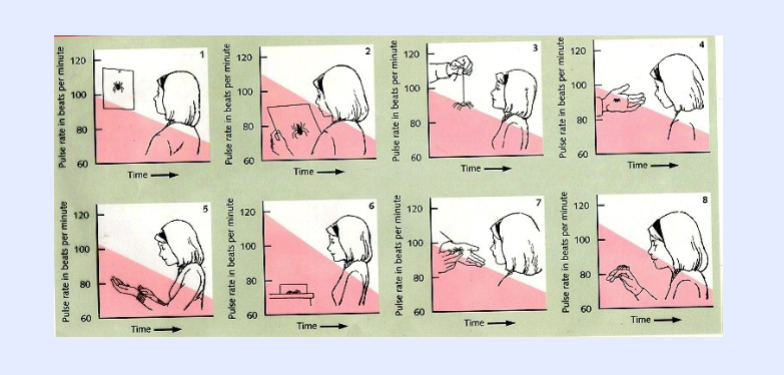
stimulus
an environmental condition that evokes a natural
reflexive, unconscious response from an organism.
• (Ex. Puff of air)
reflex:
simple automatic responses to stimuli either physical or
mental.
• (Ex. Eye blink)
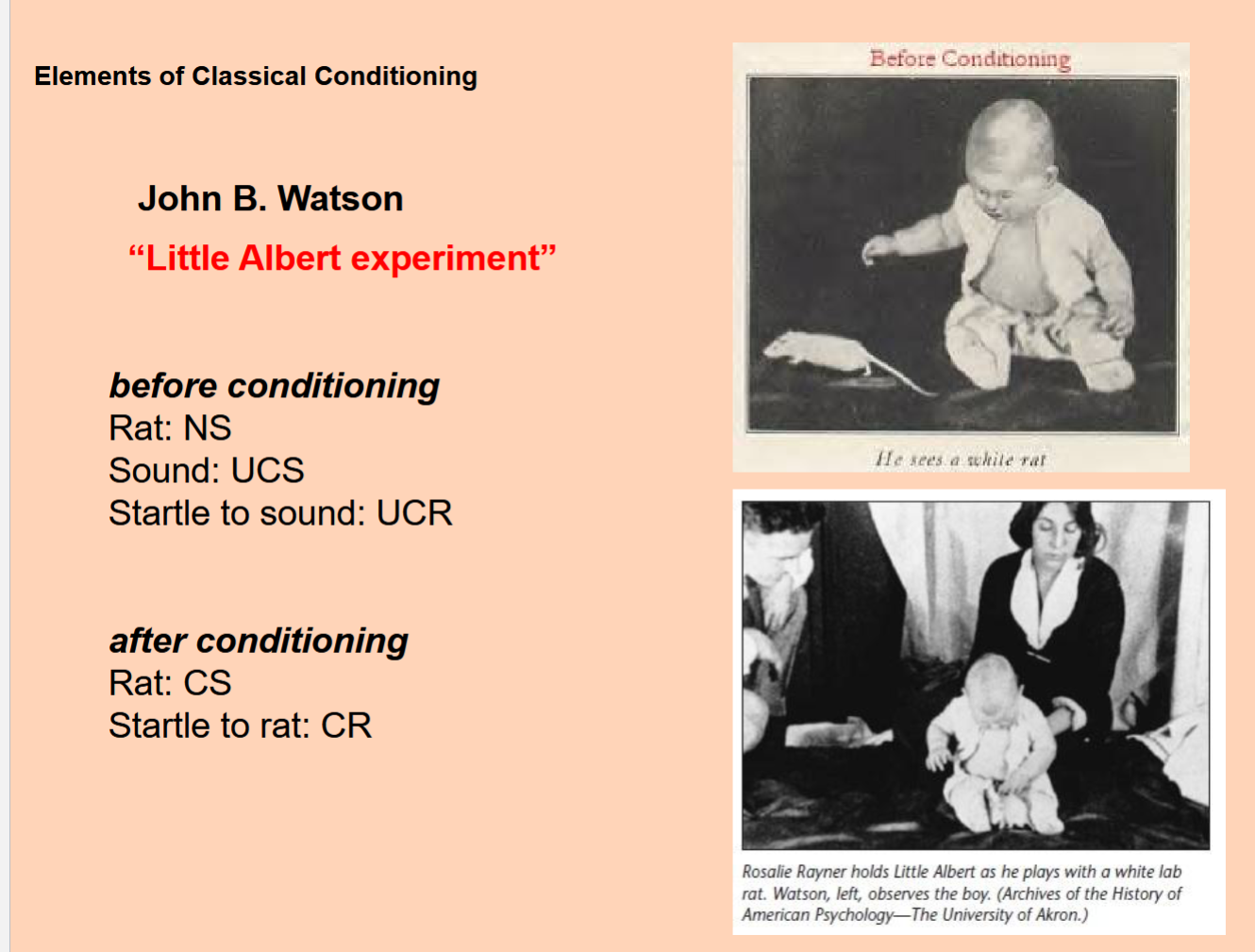
Ivan Pavlov (1890)
discovered that reflexes can also be learned through association.
– learned reflexes are “conditioned.”
some examples of classically conditioned stimuli
1. Smelling food and salivating
2. Smelling certain food and becoming nauseated or sick
3. Brown liquids and alertness
4. Jasmine flowers and amore
5. Hospitals and feeling sick
6. Being in Lowes and feeling happy
7. The smell of rotting seaweed and playfulness
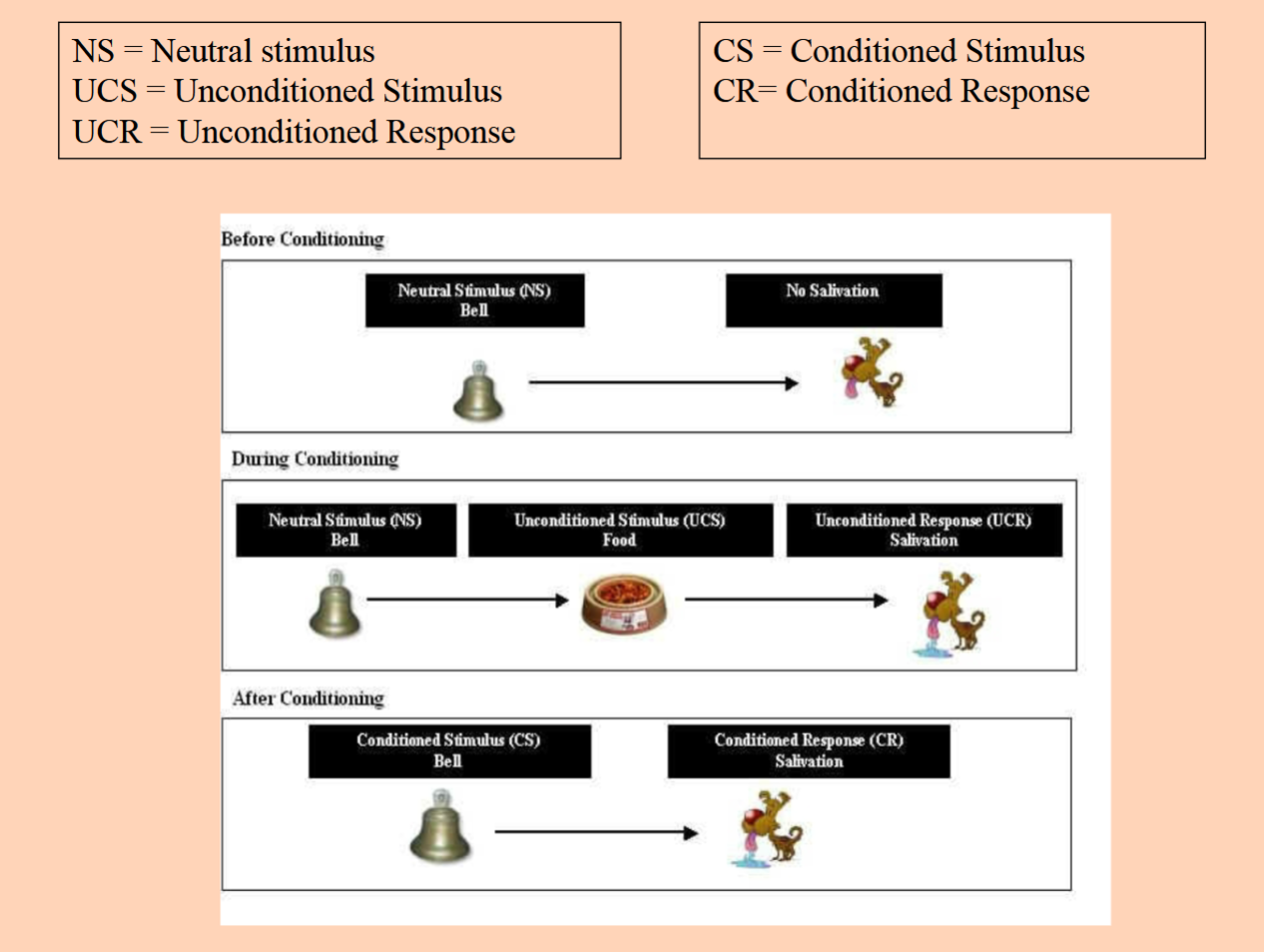
classical conditioning defined
Organisms form associations between stimuli because the stimuli
are contiguous – that is, they occur at about the same time
classical conditioning
associative learning that enables organisms to anticipate events.
Or
– Learning to link stimuli together in order to anticipate events
Likely to become reflexive and automatic*
principals classical conditioning
Generalization
The tendency for a conditioned response to be evoked by
stimuli similar to the stimulus to which the response was
conditioned.
applications of classical conditioning
counterconditioning
– a pleasant stimulus is repeatedly paired with a fear-evoking
object, thereby counteracting the fear response.
• Ex. Mary Cover Jones, 1924; Peter: Candy and Bunnies

exposure therapy
-Exposing individuals to the fear/anxiety evoking event until the
fear is extinguished.
• Flooding & Systematic Desensitization
flooding
the client is exposed to the fear-evoking
stimulus until the fear response is extinguished.
• Flooding is usually effective but unpleasant.
systematic desensitization
the client is gradually exposed to fear-evoking stimuli under
circumstances in which they remain relaxed.