AP Bio Cell Test
1/41
Earn XP
Description and Tags
10/6/25
Name | Mastery | Learn | Test | Matching | Spaced |
|---|
No study sessions yet.
42 Terms
Origin of Life is
CHNOPS
Abiogenesis
life from no life
Proto cell
transitional step between non-living matter and the first cells, membrane barrior forms around macromolecules , forms bubble of chemistry: CHNOPS
1st living cell
Simple prokaryotic cell, Self replicating RNA + RNA based, simple membrane
Characteristics that make something alive
Reproduction, Metablize, Grow + Develop, response to environment, Homeostasis (Barrier)
Prokaryotic Cell
SImple, unicellular, has a cell wall, no membrane bound organnelles, lacks a distinct, membrane-bound nucleus, has RNA + Circular DNA
Endosymbiosis
Explains the origin of eukaryotic cells ( engulfing the other cell )
What does endosymbiosis provide
Symbiotic relationship, protection, ATP due to aerobic cellular respiration
Endosymbiotic theory
Mitochondria and chloroplasts (Plastids) evolved in eukaryotic cells after endosymbiosis and contain their own circular DNA and Ribosomes which are seen in modern day plant cells.
Eukaryotic cells
Membrane bound nucleus that holds genetic material, membrane bound organelles ( ER, lysosome, etc), lipid membrane, complex
Nucleus
Houses DNA and directs synthesisi of proteins + lipids
Smooth Endoplasmic Reticulum
Synthesizes lipids
Rough Endoplasmic Reticulum
Synthesizes proteins ( has ribosomes)
Golgi Apparatus
“Warehouse, package & ship”, process and transport molecules like lipids and proteins
Mitochondria
Power house of the cell, performs cellular respiration
Lysosome
Digest food and breaks down waste
peroxisome
Oxidize + break down fatty acids and amino acids
Vacuoles
Storage
Central Vacuole
Stores water in plant cells
Chloroplast
performs photosynthesis to produce ATP
Translation
the process where genetic information encodid in mRNA is used to synthesize protein.
Transcription
The process where genetic info from a specific segment of DNA is copied into a mRNA molecule ( matches with top strand of DNA )
mRNA
messanger RNA - carries genetic info from nucleus to cytoplasm
tRNA
Transfer RNA - delivers during translation
Ribosomes
builds proteins by translating mRNA into sequences amino acid.
osmosis
The diffusion of free water molecules across a selectively permeable membrane
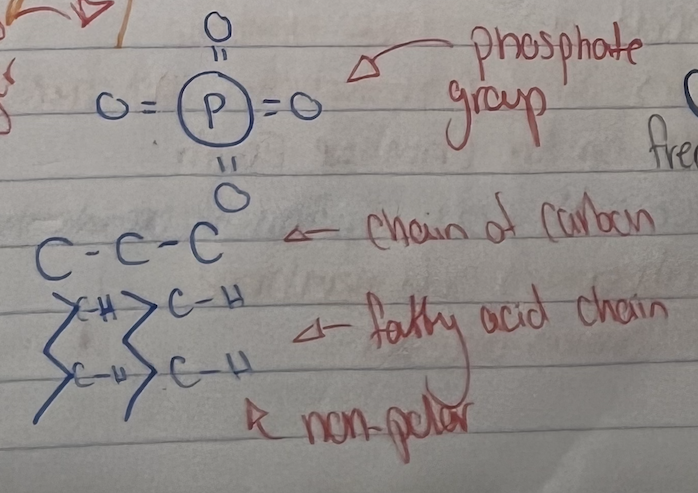
What is this form?
Phospholipid bi-layer
Hypertonic solution
causes cell to lose water
Hypotonic solution
causes cell to gain water
Isotonic solution
doesnt lose or gain water
Cytoskeleton
maintains cell shape & provides mechanical strength
cyanobacteria
microrganisms related to bacteria but can photosynthesis
Archae
Single-celled prokaryotes - extremist
aerobic cellular respiration
metabolic process that breaks down nutrients (glucose) in the presence of oxygen to provide large amounts of ATP
What was present on primitive earth
Amino acids, nucleus, simple carbohydrates, and free standing liquid water were present on the primitive Earth.
what makes eukaryotic and prokaryotic cells common ancestors
have ribosomes = Comman ancestor
DNA, RNA Cell membrane + ribosomes