1. Division of the nervous system
1/15
There's no tags or description
Looks like no tags are added yet.
Name | Mastery | Learn | Test | Matching | Spaced |
|---|
No study sessions yet.
16 Terms
2 main divisions of the nervous system
Central nervous system (CNS)
Peripheral nervous system (PNS)
main functions of the CNS
processes, interprets + stores information
issues orders to muscles, glands and organs
2 components of the CNS
brain
spinal chord
main functions of the brain
cognition (conscious awareness)
emotion
sensory
motor/movement
e.g. perception, attention, memory etc.
main functions of the spinal chord
bridge between brain and peripheral nerves (body)
reflex actions
Structure of the brain
Cerebral cortex- The brain's outer layer, most highly developed in humans, grey matter with many folds. Involved in a variety of higher cognitive, emotional, sensory and motor functions.
Brain hemispheres- divides into 2 symmetrical hemispheres: left: languages, rational- analytical thinking and logical abilities, right: musical and artistic abilities
Brain stem- connects the brain and spinal chord, as well as controlling involuntary processes e.g. breathing.- vital functioning and instinctive behaviour
structure of the spinal chord
white bundle of nerves which runs from the brain along a canal in the backbone. Roughly 40cm long and as wide as a thumb.
main functions of PNS
transmits information to and from CNS
2 components of PNS
somatic nervous system
autonomic nervous system
functions of somantic nervous system
controls voluntary movements of skeletal muscles (e.g moving arm)
maintains communication between CNS and outside world
nerves carry messages from eyes, ears, skeletal muscles and skin to give CNS experience of environment
posture and movement
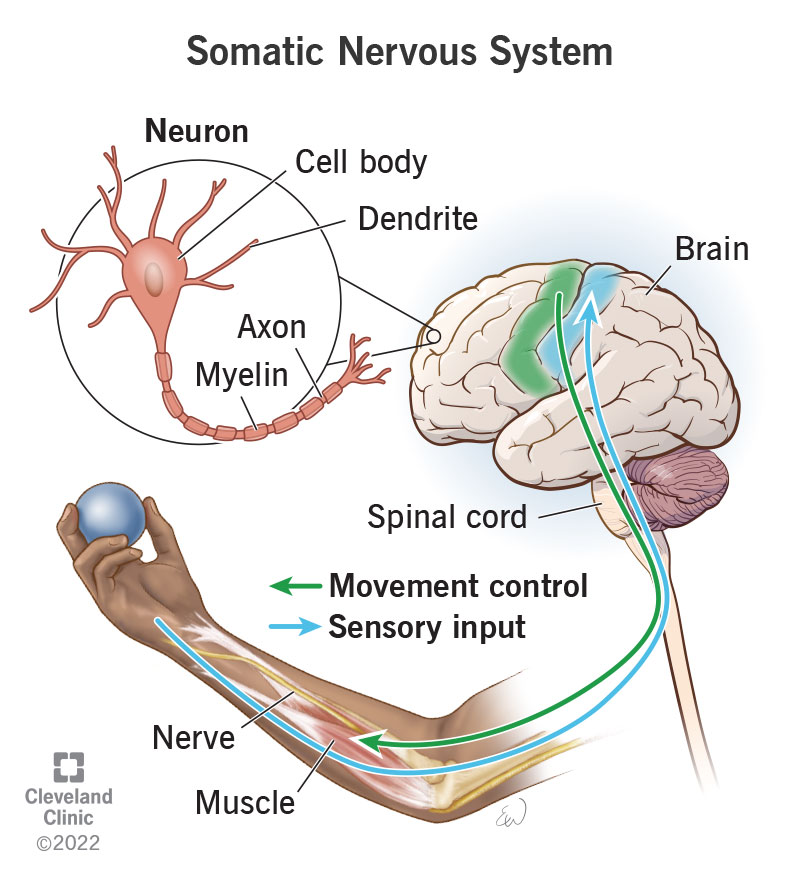
SNS consists of…
sensory receptors- carries info to spinal chord and brain
motor pathways- allows brain to control movement
functions of autonomic nervous system
regulates glands, blood vessels and internal organs
plays an important role in homeostasis (maintains internal processes) e.g. secretion and metabolism
controls involuntary movement from non-skeletal muscles (e.g. the ‘smooth muscels’ that control intestines, digestion, bladder, heart etc.)
only consists of motor pathways
2 components of ANS
sympathetic nervous system
parasympathetic nervous system
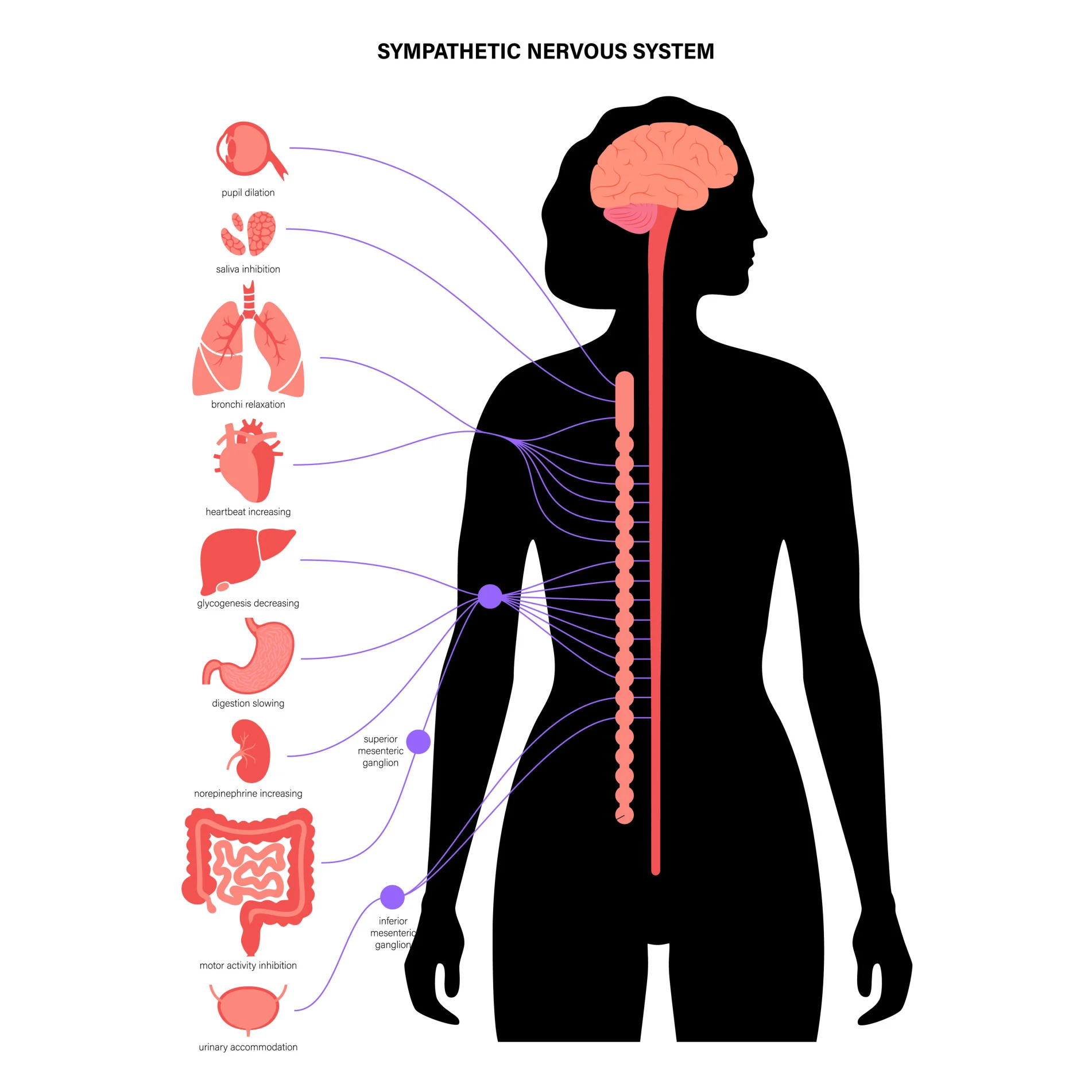
Functions of sympathetic nervous system
mobilises body for action- prepares body for fight or flight (e.g. increases heart rate and blood pressure)- activated in situations requiring arousal and energy e.g. when threatened/under stress
energy output
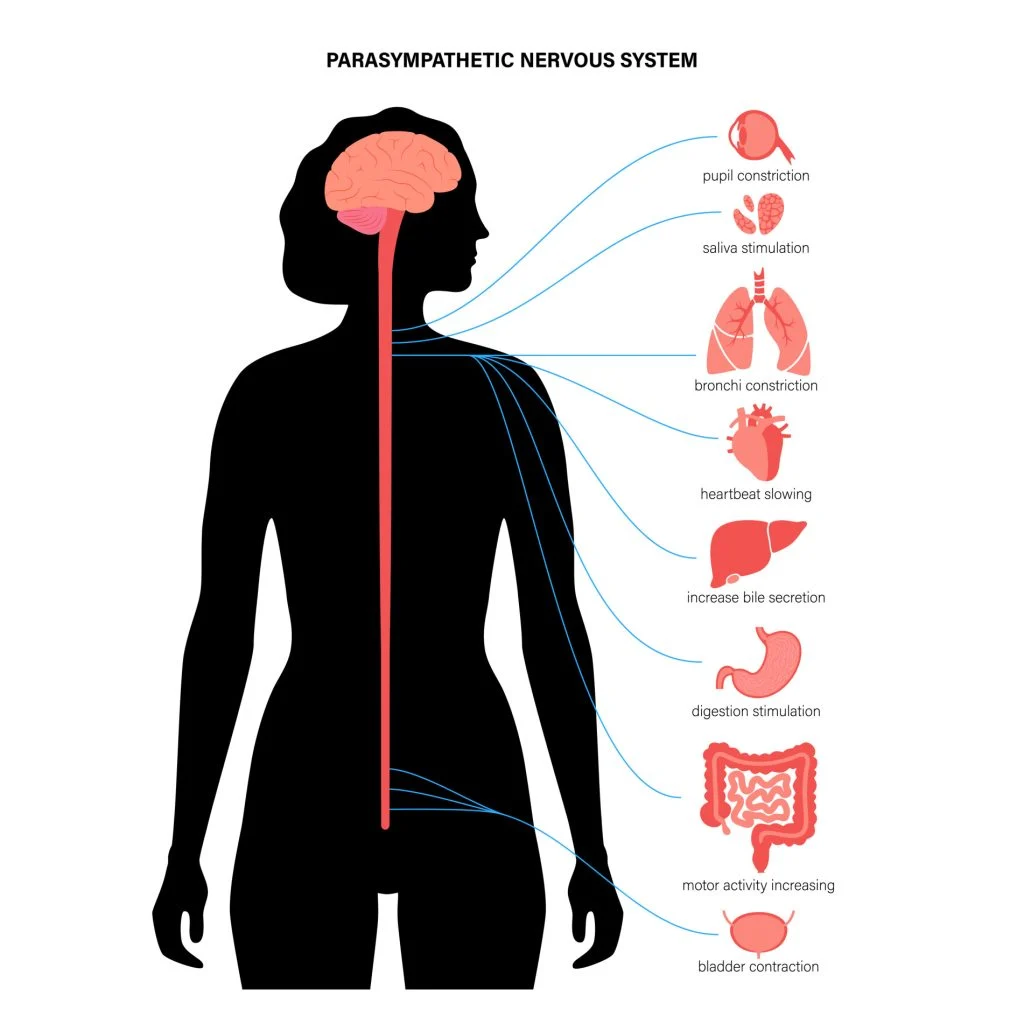
Functions of parasympathetic nervous system
conserves energy
maintains quiet state
returns body to normal resting state/homeostasis (e.g heart and respiratory rate return to normal level, blood pressure decreases)- activated soon after threat of danger has passed
Outline the structure and function of the nervous system (6 marks)
Bio-psychologists assume that thought and behaviour are caused by the activity in the nervous system. The nervous system is a specialised network of cells in the human body and is our primary internal communication system. The nervous system’s two main function are:
collect, process and respond to information in the environment
co-ordiante the working of different organs and cells
The central nervous system (CNS) is made up of the brain and spinal chord. The brain is the centre of all conscious awareness. The brain’s outer layer, the cerebral cortex, is highly developed in humans. The brain is divided in two hemispheres. The spinal chord is an extension of the brain. It is responsible for reflex actions. The PNS transmits messages via millions of nerurons (nerve cells), to and from the nervous system. The PNS is further sub-divided into:
the somatic nervous system (SNS)
the autonomic nervous system (ANS)
The SNS is the part of the PNS that is responsible for carrying sensory and motor information to and from the spinal chord. The autonomic nervous system governs vital functions in the body, such as breathing, digestion, heart rate, sexual arousal and stress responses.