Neoplasms (Sosnowski)
1/176
Earn XP
Description and Tags
Sosnowski
Name | Mastery | Learn | Test | Matching | Spaced | Call with Kai |
|---|
No analytics yet
Send a link to your students to track their progress
177 Terms
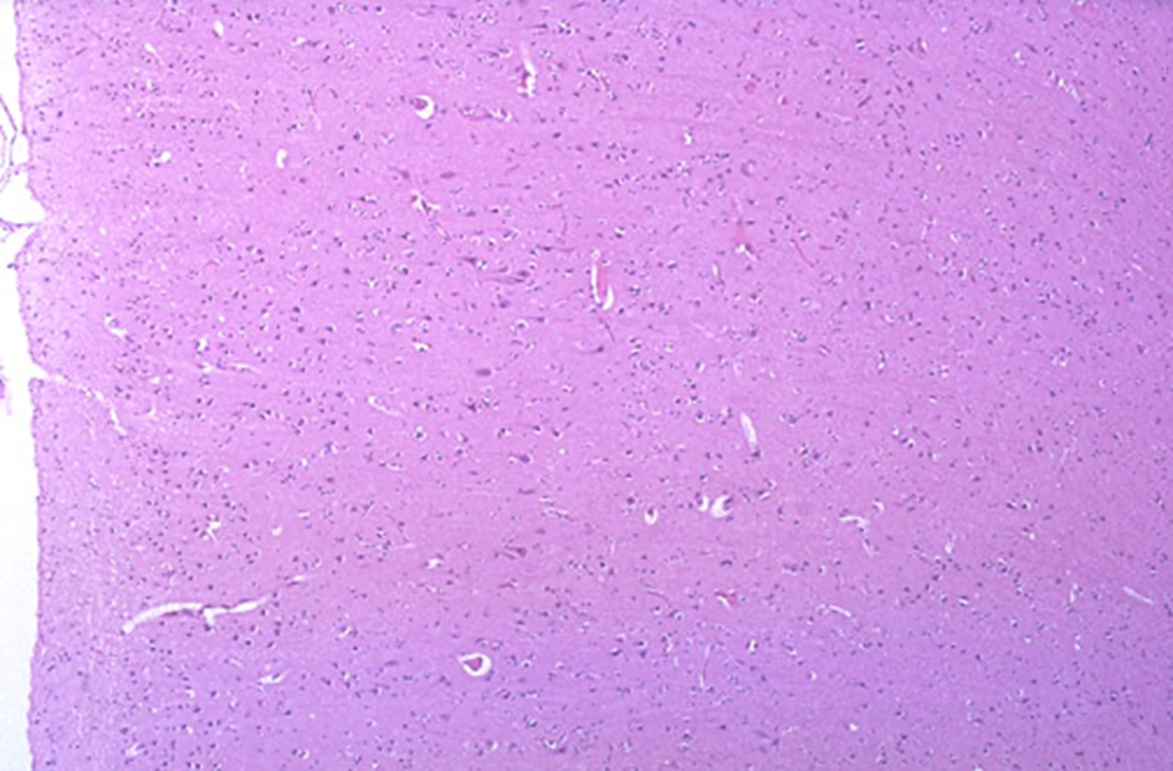
Normal
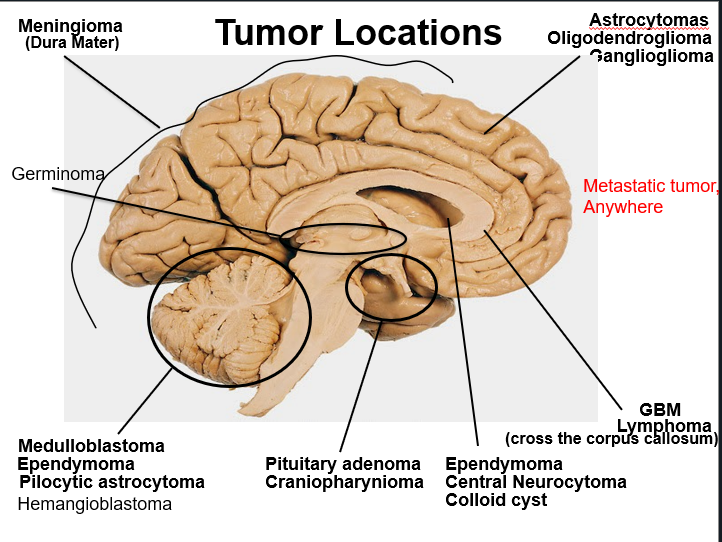
Tumor locations
Top right anywhere in cortex
Pineal gland tumor usually young kids
Germinoma
Most common metastatic neoplasms to the brain
Lung
Breast
Prostate
GI, rare
Kidney
Melanoma
Choriocarcinoma
Bloody mets to the brain
Lung
Kidney
Melanoma
Choriocarcinoma
Astrocytoma
Oligodendroglioma
Infiltrating gliomas
Infiltrating gliomas
Astrocytoma
Oligodendroglioma
Non-infiltrating gliomas
Gangliogliomas
placental tumor
Choriocarcinoma
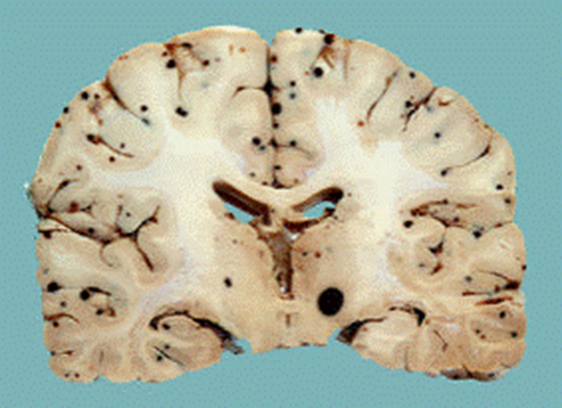
Black dots at gray white junction probably a hemorrhagic met
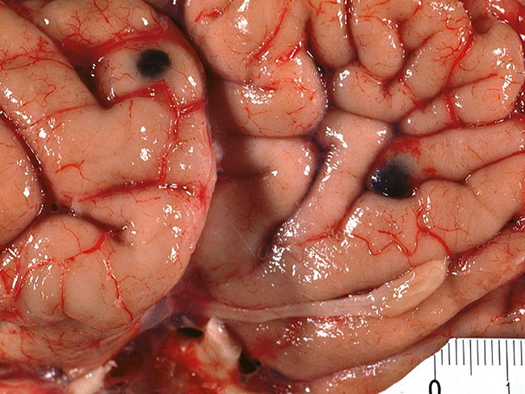
Hemorrhagic I think this one was melanoma mets
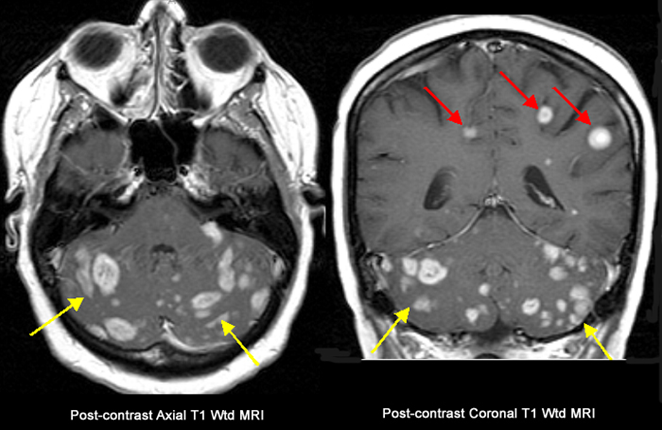
Brain mets
Bottom cerebellum loaded with mets can be silent
____ could be a presentation of metastasis to the brain
seizures
Biopsy where edema is you would see
Reactive gliosis
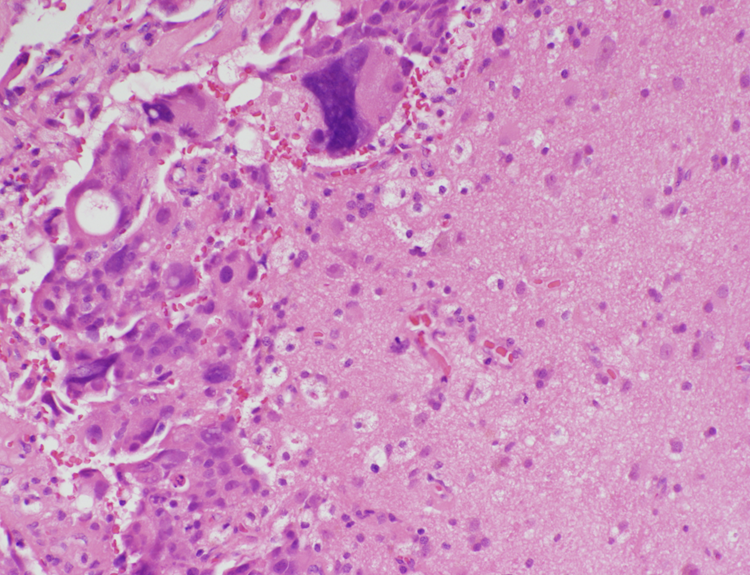
Brain met
adenocarcinoma mucin producing cell present
reactive brain with foamy macrophages
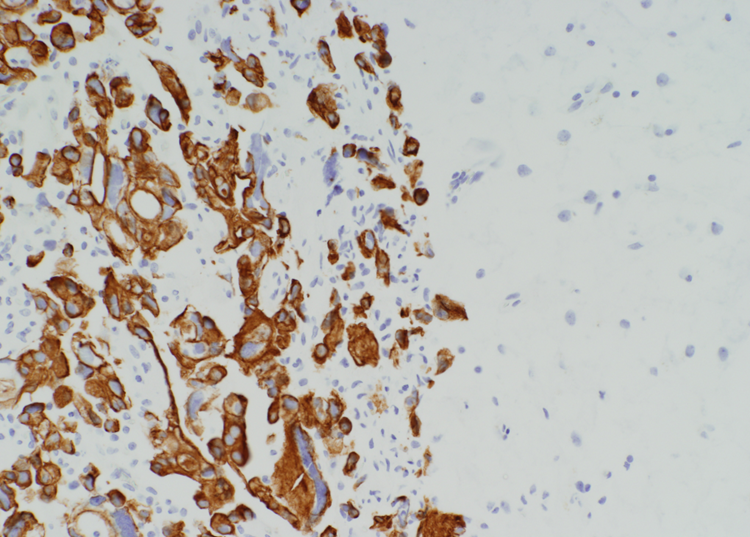
Brain met
cytokeratin stain
Stain for brain met
Cytokeratin
Brain met
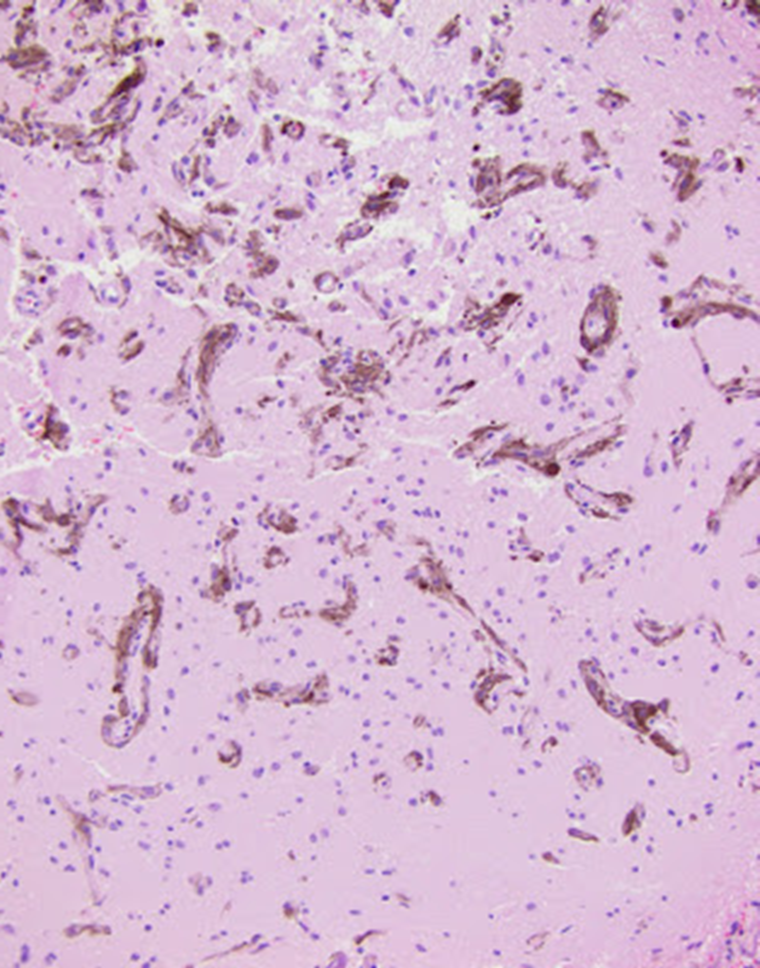
Cerebrum with pigment in it
Melanoma met
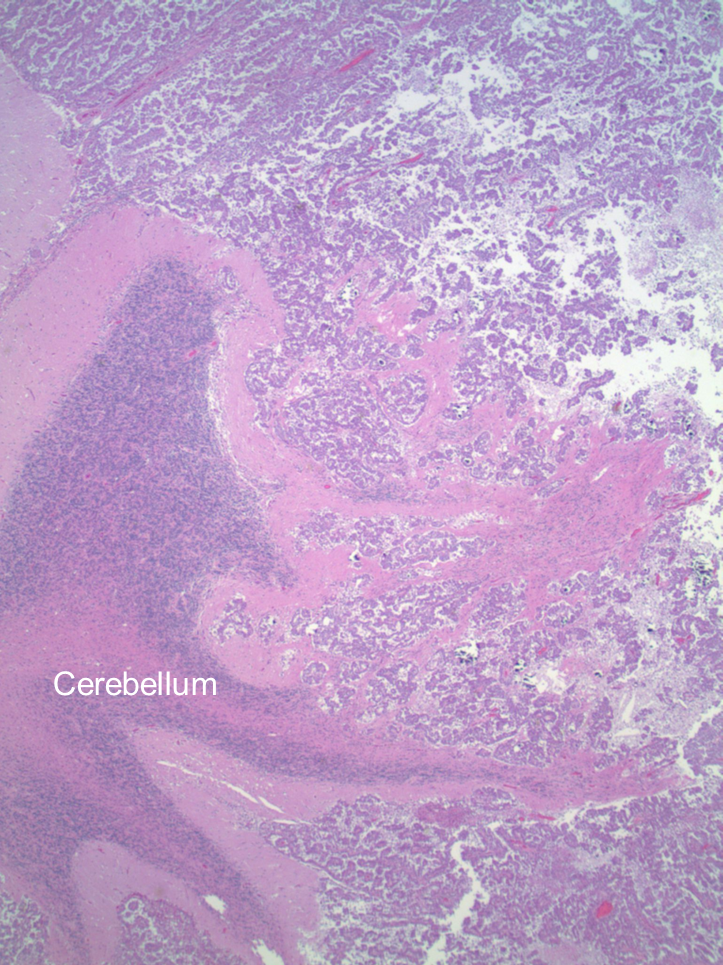
Cerebellum met
Normal cerebellum is where the word is the rest is cancer
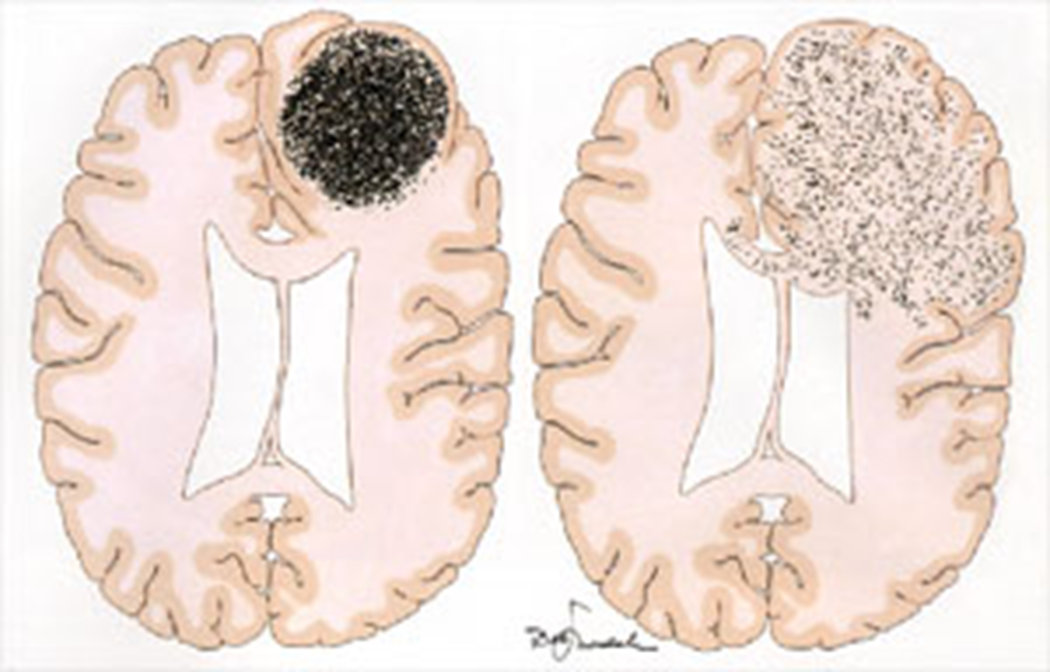
Focal vs infiltrative primary brain lesions
Focal
Pilocytic astrocytoma
PXA
Ependymoma
Subependymoma
SEGA
Infiltrative
Astrocytoma (II-IV)
Oligodendroglioma
Pilocytic astrocytoma
PXA
Ependymoma
Subependymoma
SEGA
Focal lesions
Astrocytoma (II-IV)
Oligodendroglioma
Infiltrative lesions
Arise from neoplastic astrocytes and oligodendrocytes within the white matter
Infiltrating gliomas
Infiltrate into the gray matter
Infiltrating gliomas
Can cross the corpus callosum and involve the other hemisphere
Infiltrating gliomas
Can release VEGF-like hormones producing leaky neovasculature
Infiltrating gliomas
In children, most common in brain stem or thalamus
Infiltrating gliomas
Infiltrating gliomas in children is most common the _______ or _______
brainstem or thalamus
Astrocytes and oligodendrocytes when they are neoplastic upregulate ______ on surface that bind to white matter tracts to tract along it
receptor
Arise from neoplastic astrocytes and oligodendrocytes within the white matter
Infiltrate into the gray matter
Can cross the corpus callosum and involve the other hemisphere
Can release VEGF-like hormones producing leaky neovasculature
In children, most common in brain stem or thalamus
infiltrating gliomas
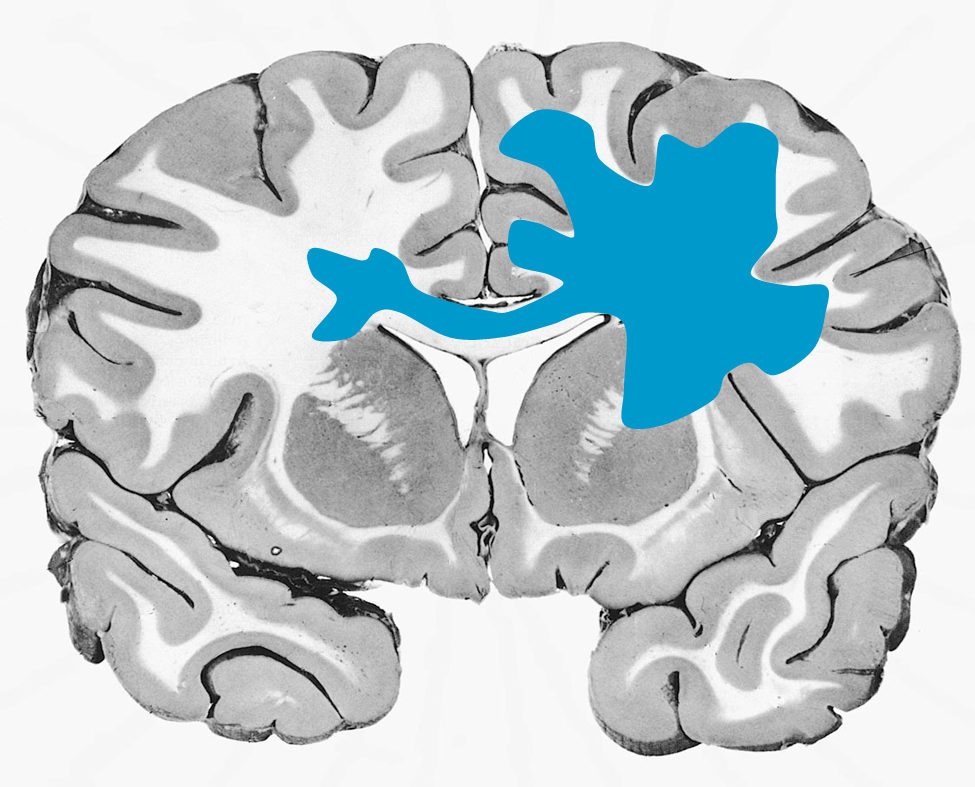
Infiltrating glioma
Astrocytoma or oligodendroglioma
Higher grade glioma tracking across corpus callosum to other hemisphere
Butterfly lesion is one hemisphere to the other
An important marker for labeling glial tumors
glial fibrillary acidic protein (GFAP), an intermediate filament protein
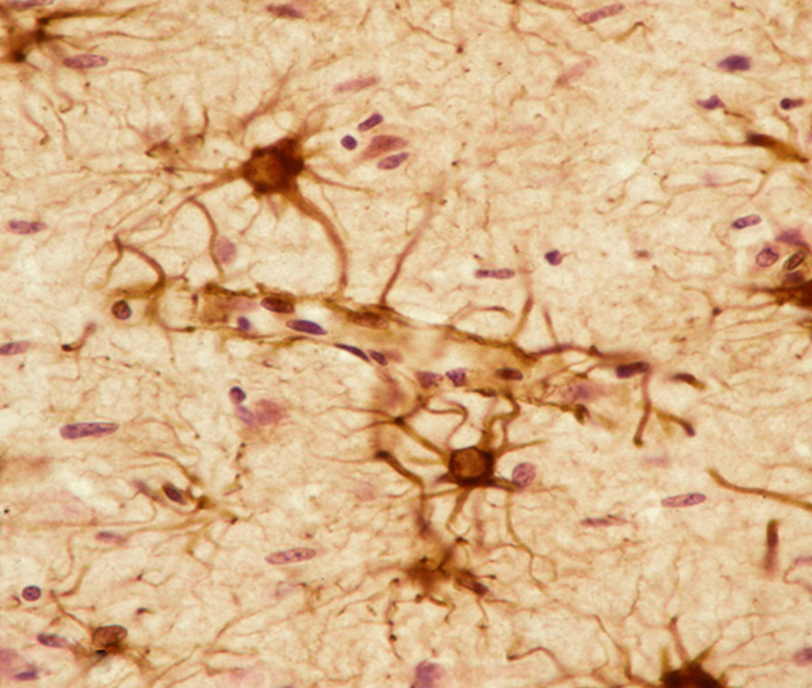
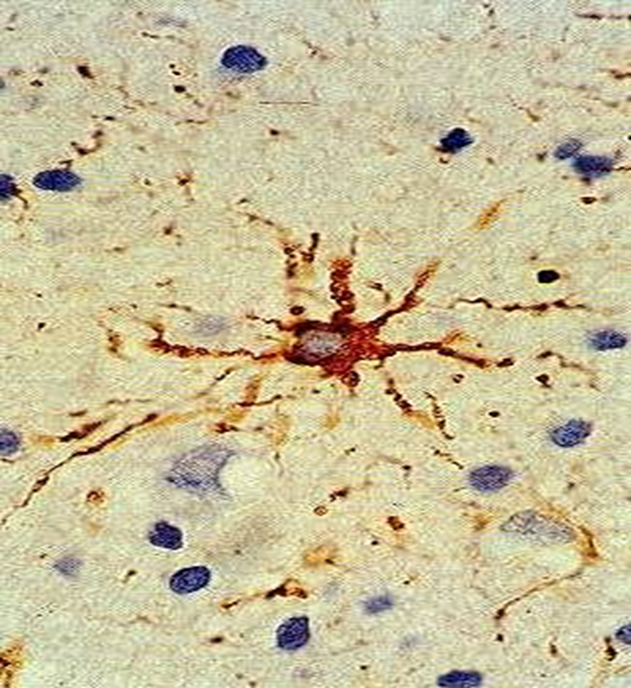
Astrocytes
GFAP stain
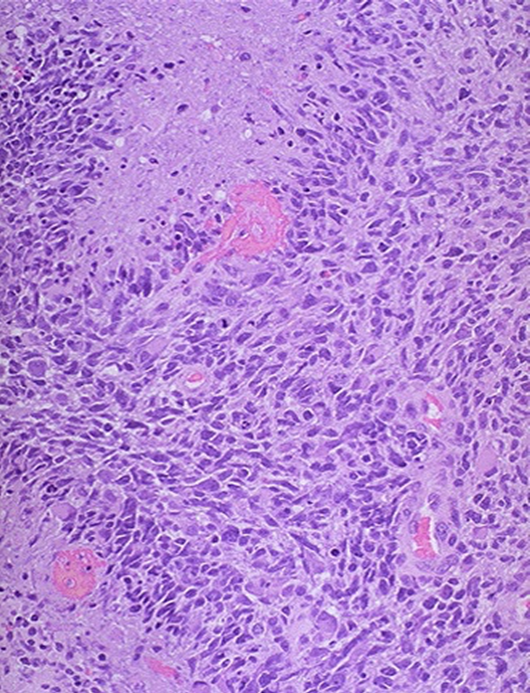
Glioma but make sure its not a met by staining with GFAP
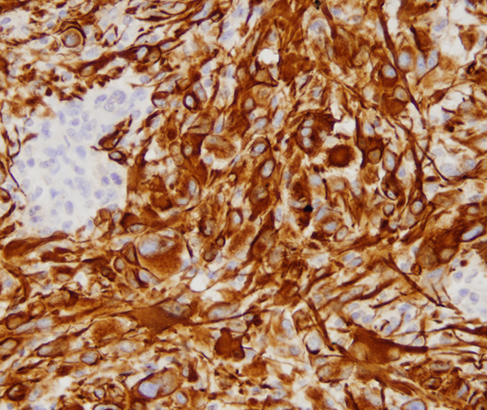
Glioma stained with GFAP
WHO grade ___
Pleomorphic astrocytes
2
astrocytoma
WHO grade ___
Pleomorphic astrocytes
Mitoses
3
anaplastic astrocytoma
WHO grade __
Pleomorphic astrocytes
Mitoses
Necrosis and/or microvascular proliferation
4
Normal astrocytoma is WHO grade
2
Anaplastic astrocytoma is WHO grade
3
Glioblastoma multiforme GBM is WHO grade
4
Glioblastoma multiforme (GBM) is an ______
astrocytoma
Found in white matter of young adults, 30-40 yrs
> 10 years survival
Astrocytoma WHO grade 2
T2-bright but lacks contrast enhancement
Prognostic factors: patient age, extent of resection, neurological status at presentation
Astrocytoma, WHO grade II
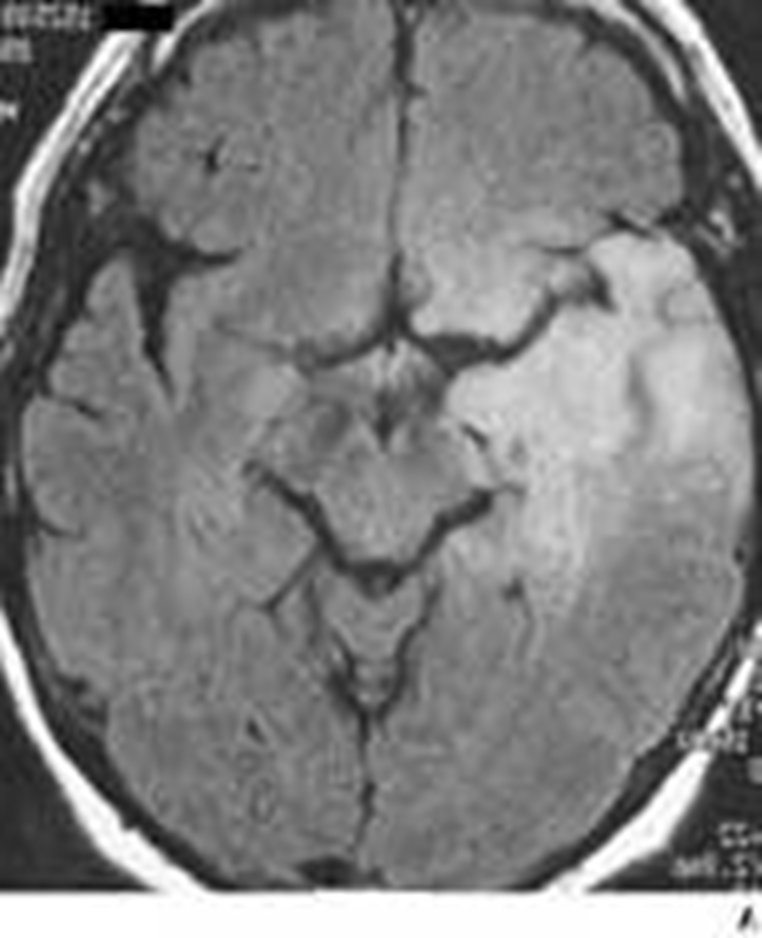
Astrocytoma, WHO grade II
Diffuse enhancement gray and white matter
Found in white matter of young adults, 30-40 yrs
T2-bright but lacks contrast enhancement
Prognostic factors: patient age, extent of resection, neurological status at presentation
May remain stable for many years or undergo anaplastic transformation
> 10 years survival
Astrocytoma, WHO grade II
Diffuse Astrocytoma, WHO Grade II
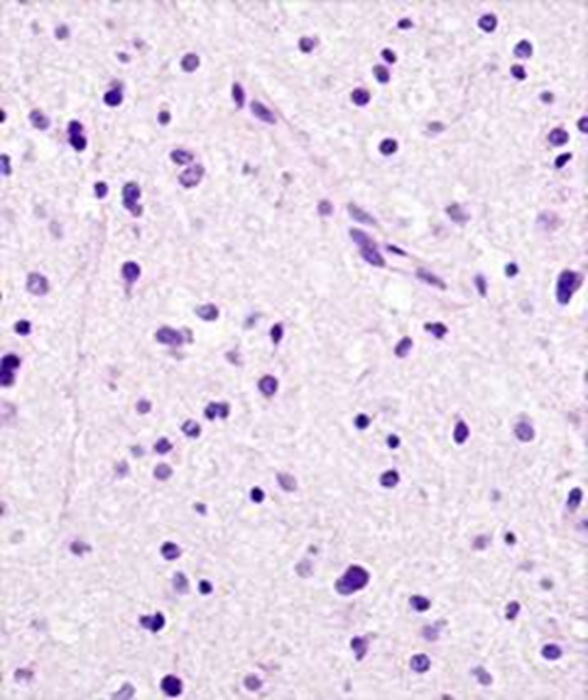
Infiltrating pleomorphic glial cells with increased cellularity
light in color edematous astrocytes
Infiltrating pleomorphic glial cells with increased cellularity
Diffuse Astrocytoma, WHO Grade II
Diffuse Astrocytoma, WHO Grade II
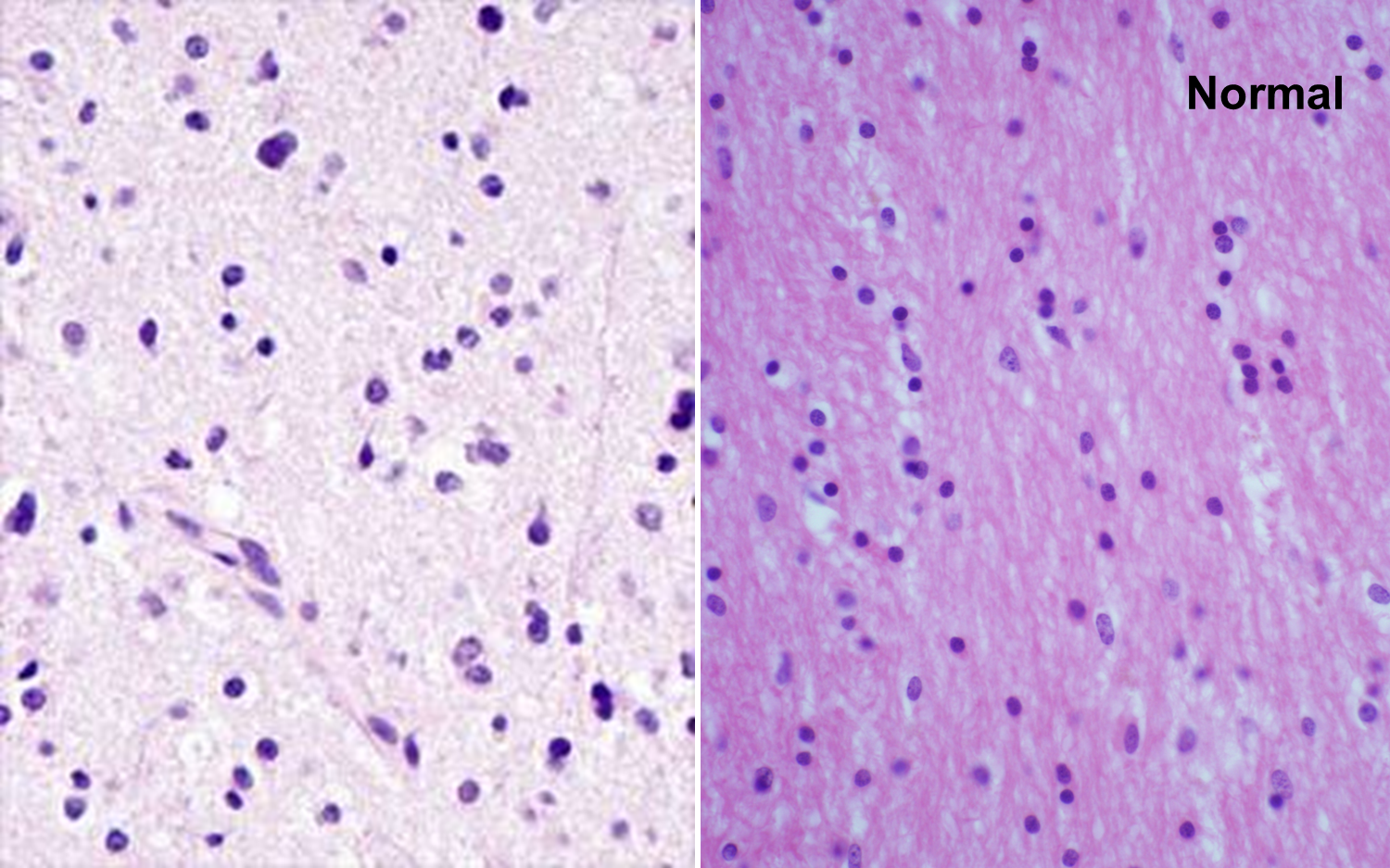
Neoplastic vs normal white matter
Astrocytoma WHO grade 2
Presents 10 years later than Grade II
Often enhance in focal or patchy pattern
2-4 year survival
Anaplastic Astrocytoma, WHO grade III
Often enhance in focal or patchy pattern WHO grade __
Anaplastic Astrocytoma, WHO grade III
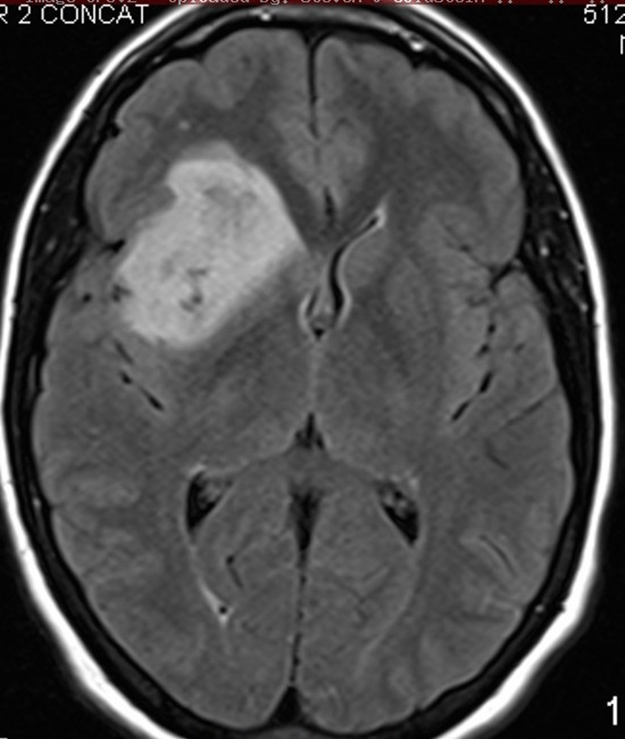
Anaplastic Astrocytoma, WHO grade III
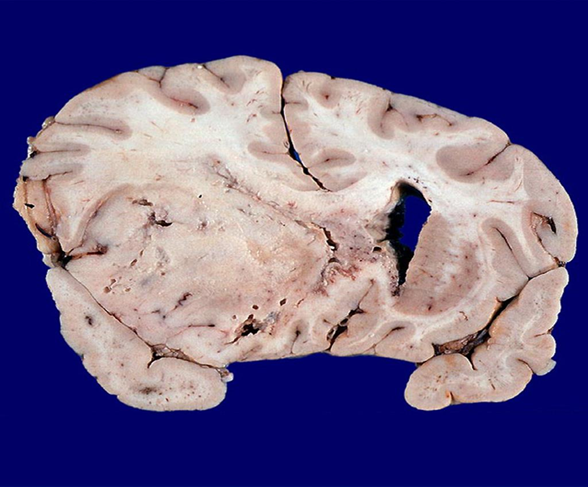
Anaplastic Astrocytoma, WHO grade III
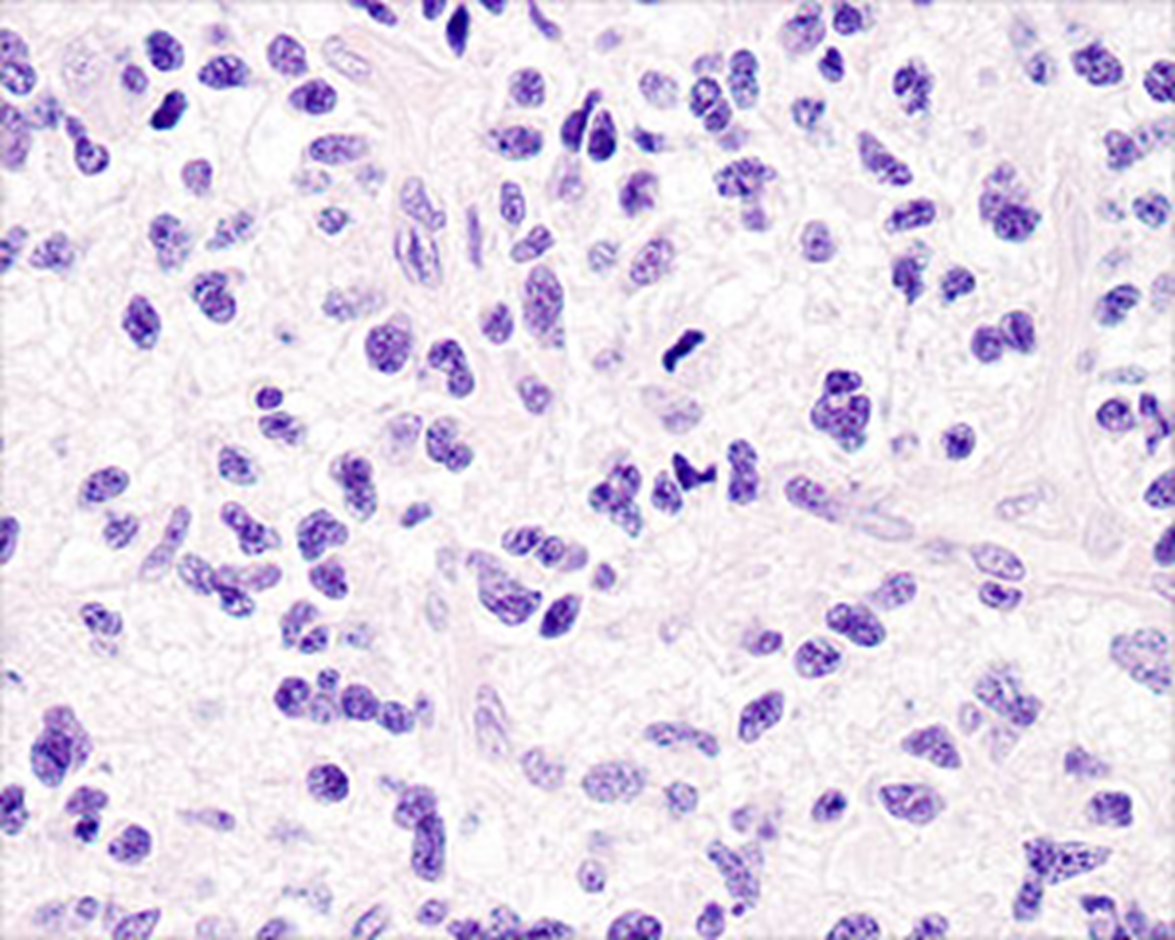
Anaplastic Astrocytoma, Grade III
Mitotic figure and pleomorphic astrocytes
Hypercellular, pleomorphic, mitotic figure so 3
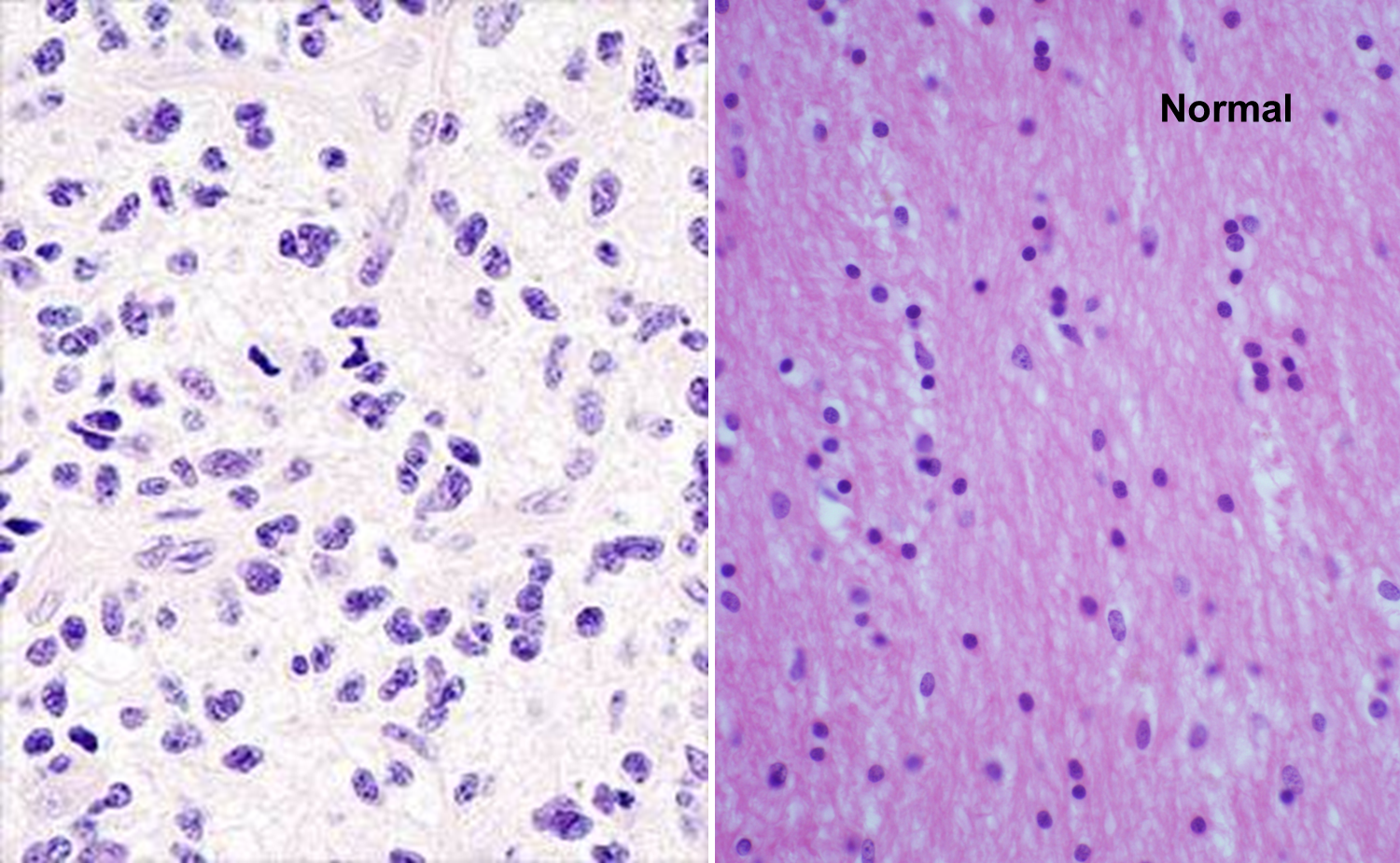
Anaplastic Astrocytoma, Grade III
Mitotic figure and pleomorphic astrocytes
What is different between grade 3 and 4 astrocytoma?
Grade 4 GBM has necrosis and/or microvascular proliferation
Peak incidence 50-60 years
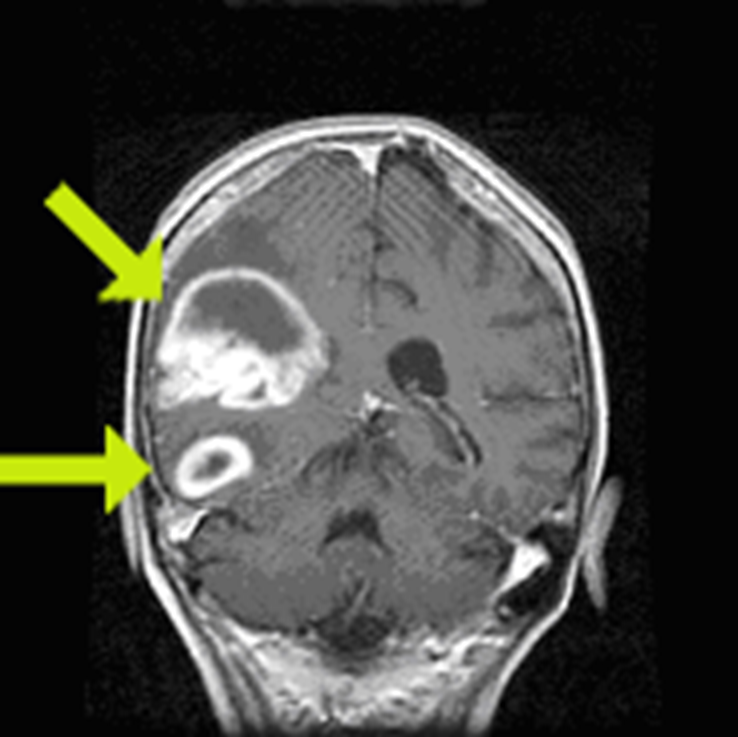
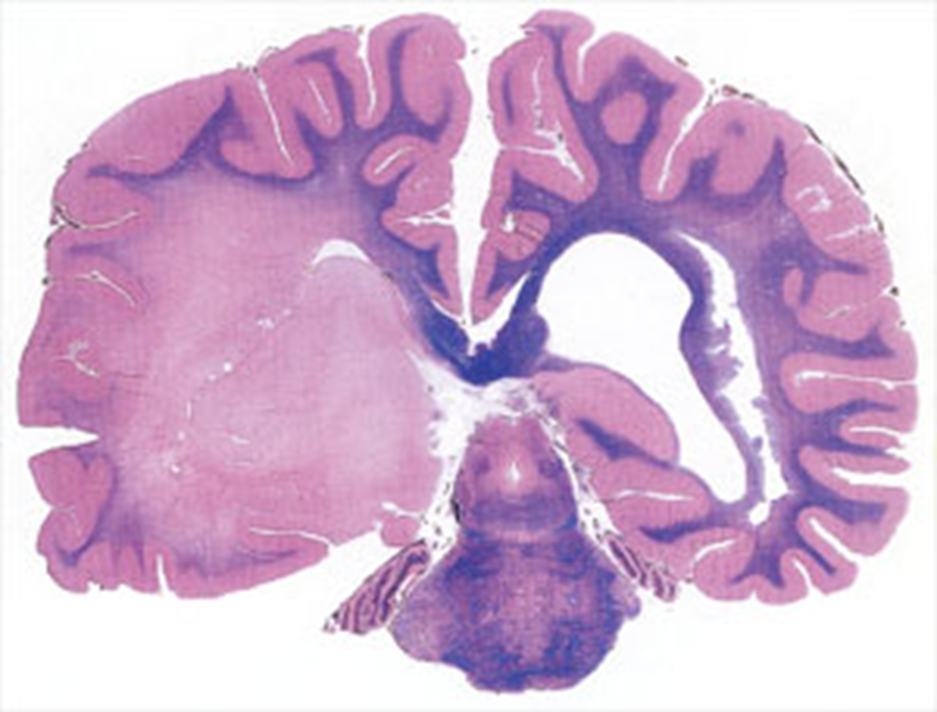
Neoplasm occupies both hemispheres through the corpus callosum
Irregular ring enhancing
Average 1 year survival
GBM
astrocytoma who grade 4
Irregular ring enhancing
GBM
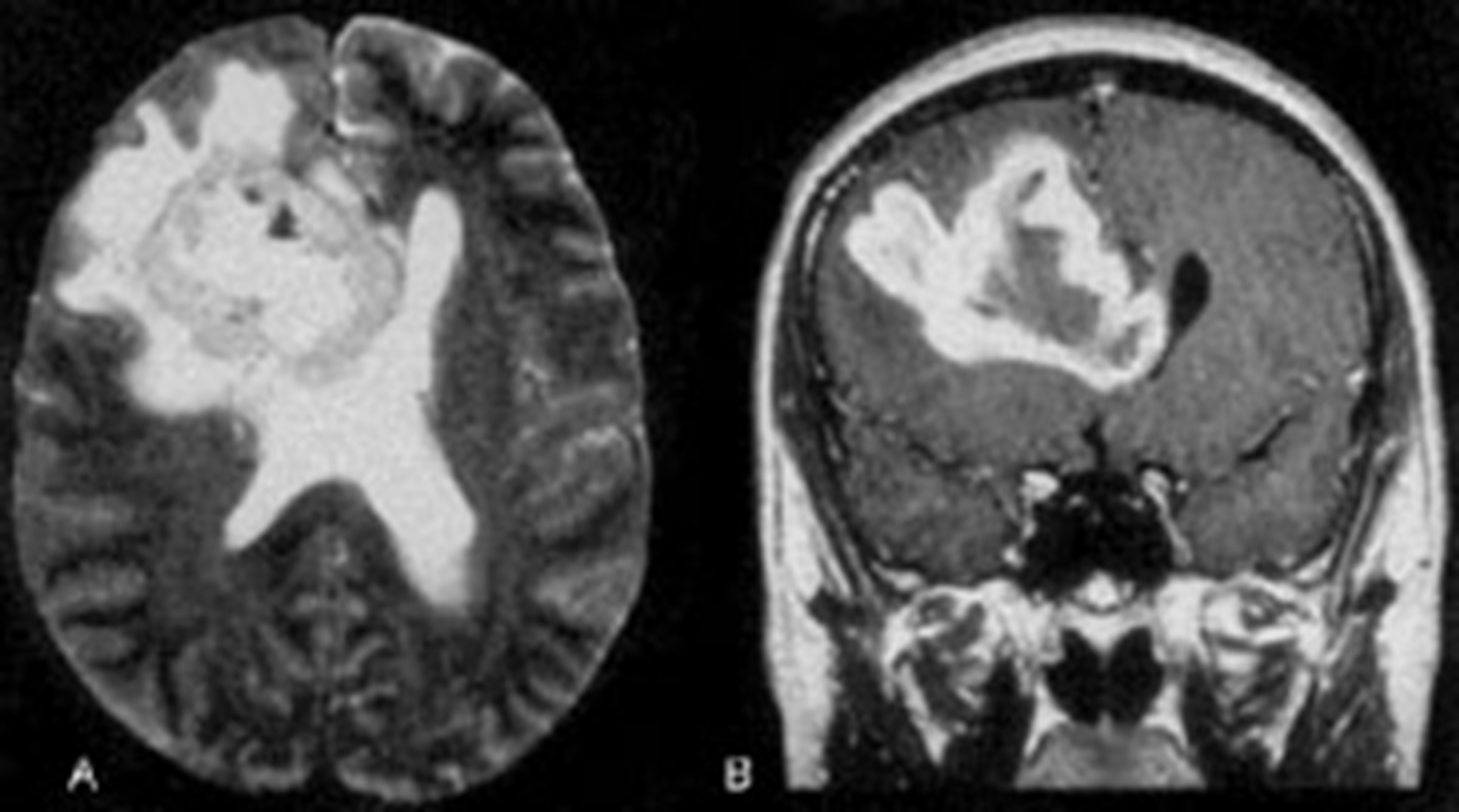
GBM
ring enhancing T1
crosses corpus callosum
necrosis in the middle
(This pattern could be GBM, abccess with correct picture of infection ,or primary CNS lymphoma, but most likely GBM)
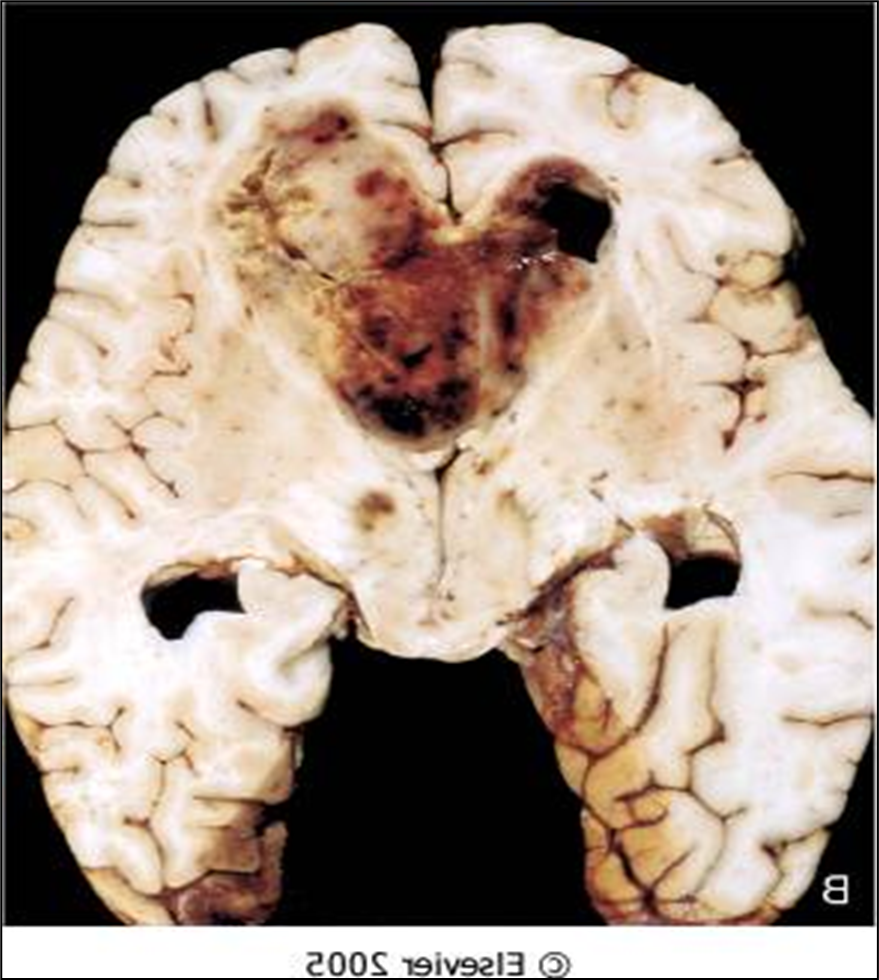
Butterfly lesion
GBM
astrocytoma grade 4
Lots of hemorrhaging, weak blood vessels, and necrosis growing fast
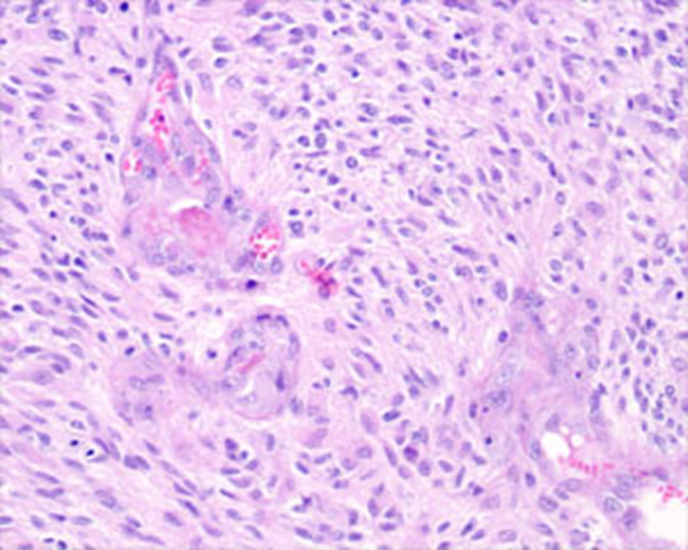
GBM
pleomorphic astrocytes
mitotic activity
vascular proliferation here
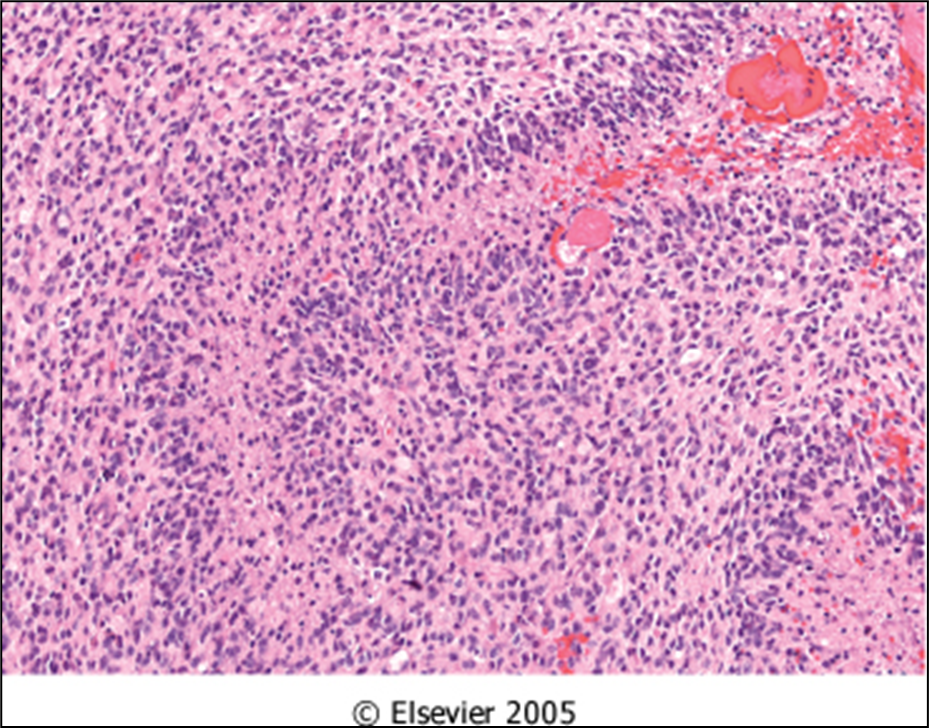
GBM
necrosis
pleomorphic astrocytes
mitotic activity
GBM
know this picture!
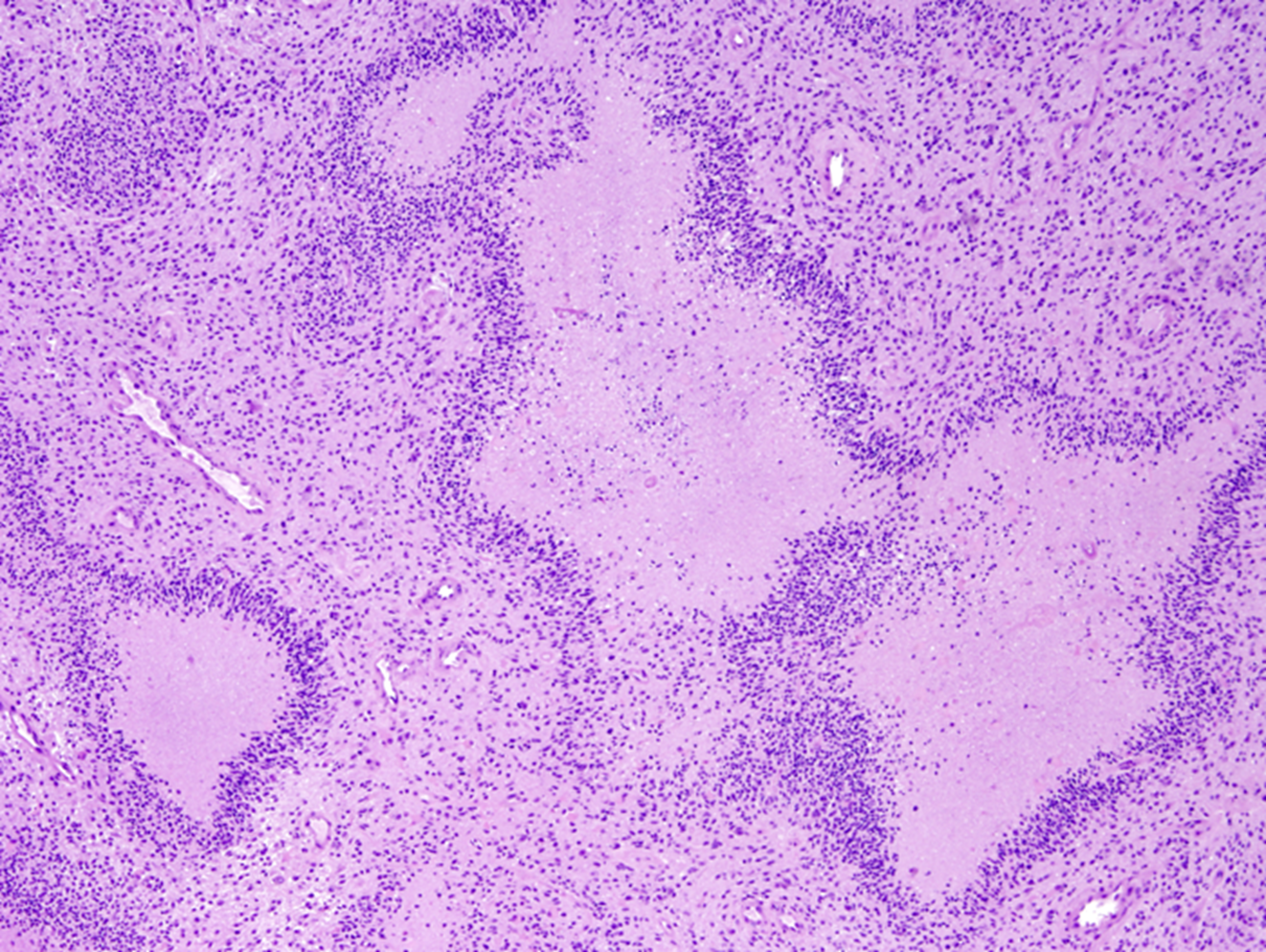
Palisading neoplastic cells surrounding necrosis
Palisading neoplastic cells surrounding necrosis
GBM grade 4 astrocytoma
Geographic pattern, a perimeter of neoplastic glial cells surrounding necrosis
GBM
Characteristic loss of chromosomes 1p,19q
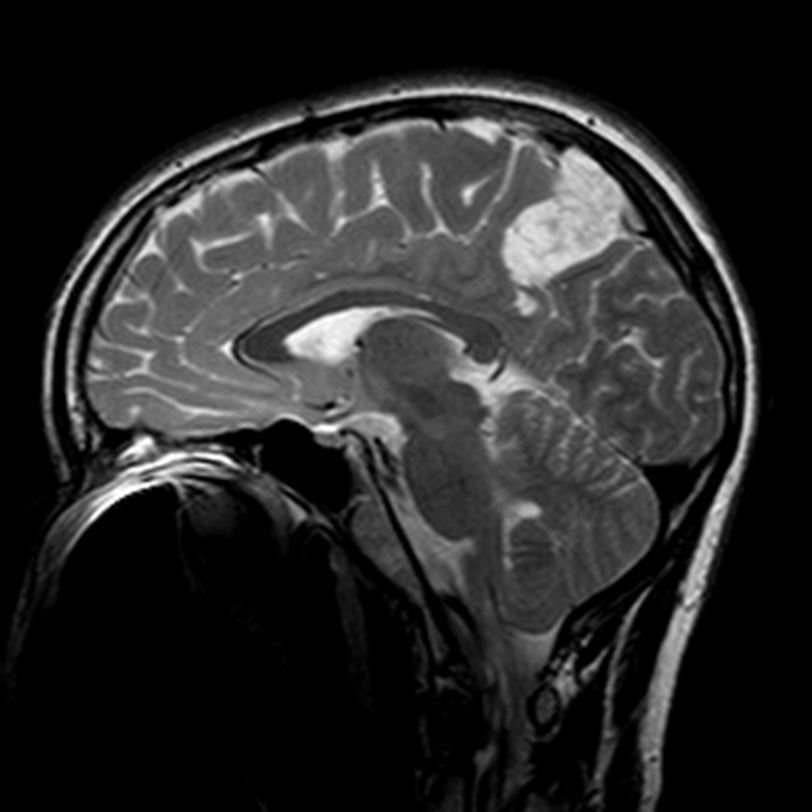
Oligodendroglioma
10-15% of all gliomas
Oligodendroglioma
Predilection for cortex
Gyriform calcification, higher grade lesions may enhance
Oligodendroglioma
Tend to like to stay in 1 of the gyri
Can have calcifications
Oligodendroglioma
Oligodendroglioma
1 gyri
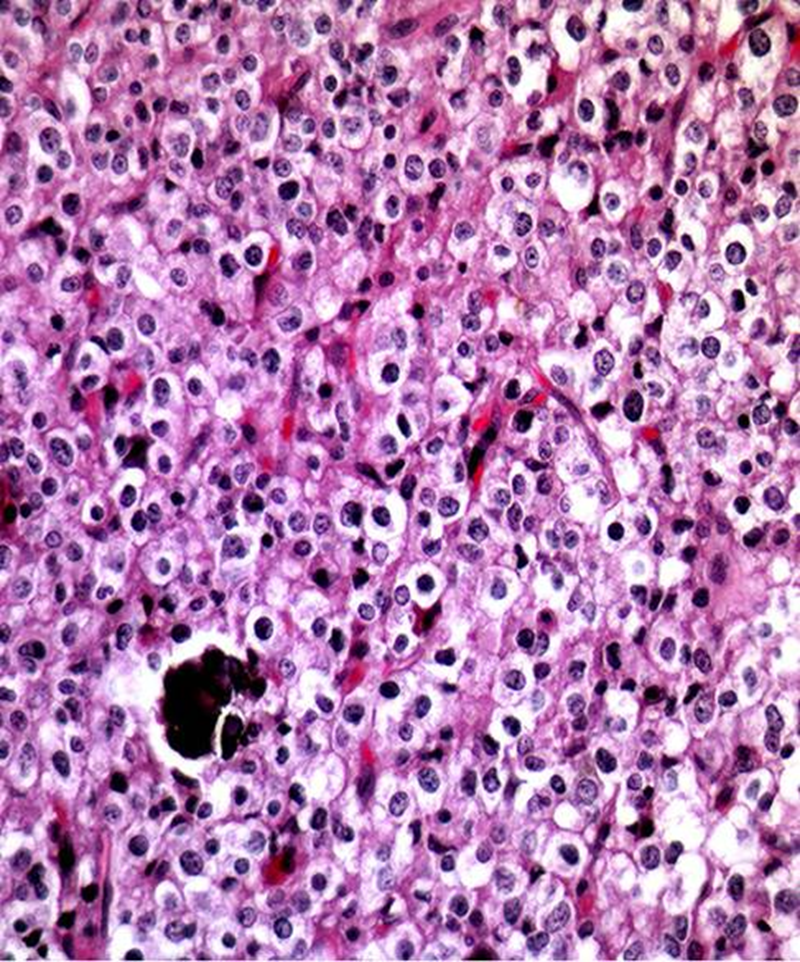
Perinuclear halos or fried egg appearance
Delicate capillaries
Calcification
Oligodendroglioma
Chicken wire vasculature
Oligodendroglioma
Perinuclear halos or fried egg appearance
Delicate capillaries
Calcification
Perineuronal satellitosis
Subpial accumulation
Oligodendroglioma
Oligodendroglioma
Perinuclear halos or fried egg appearance
Delicate capillaries (chicken wire)
Calcification
1p, 19q loss
Oligodendroglioma
Neoplasms That Infiltrate the Corpus Callosum
GBM
Primary CNS lymphoma
Primary CNS lymphoma in elder individual
Diffuse large B-cell lymphoma, enhancing (without necrosis) MRI
Primary CNS lymphoma in HIV patient
Diffuse large B-cell lymphoma, LMPEBV +, ring enhancing MRI with necrosis
HIV
Primary CNS lymphoma
HIV primary CNS lymphoma _____ +
LMPEBV
Epstein barre virus
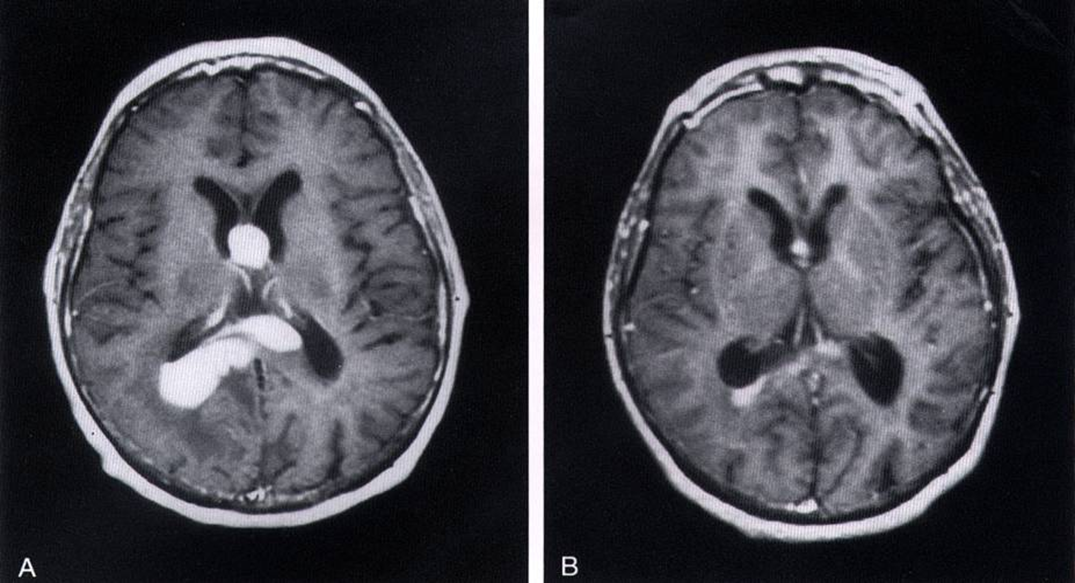
GBM vs primary CNS lymphoma biopsy to figure it out
Primary CNS lymphoma is a __ cell lymphoma
B
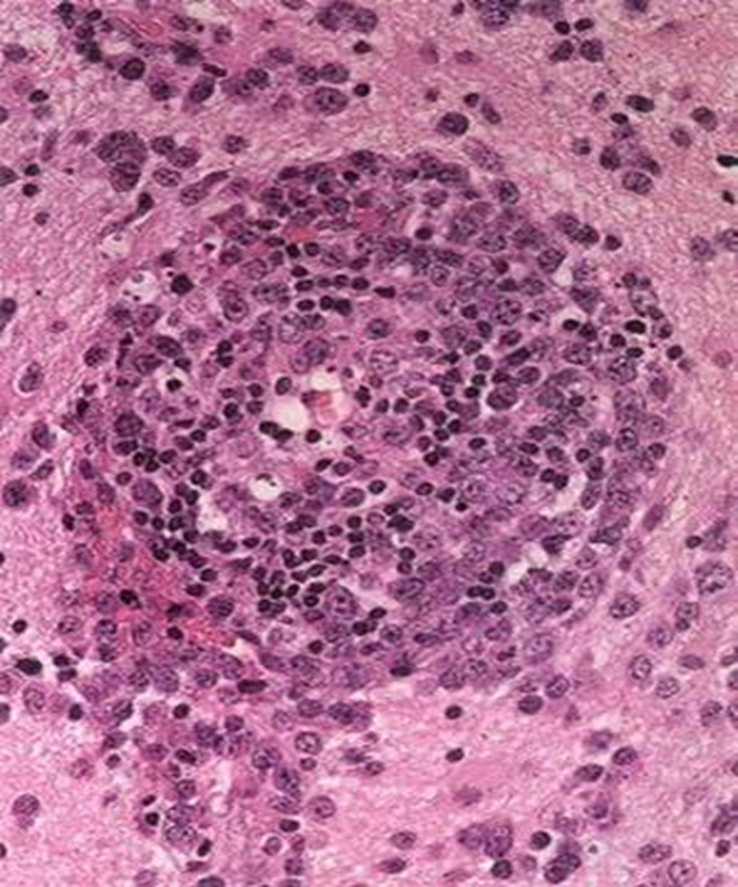
Primary CNS lymphoma
Blood vessel lots of lymphocytes popping out forming a halo
B cell membrane stain
CD20
Primary CNS lymphoma stain?
CD20
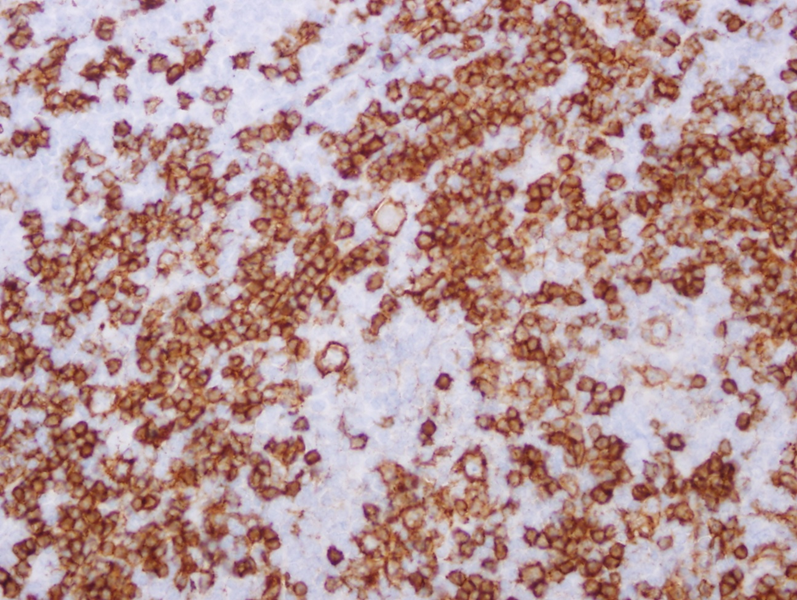
Primary CNS lymphoma
CD20 B cell stain
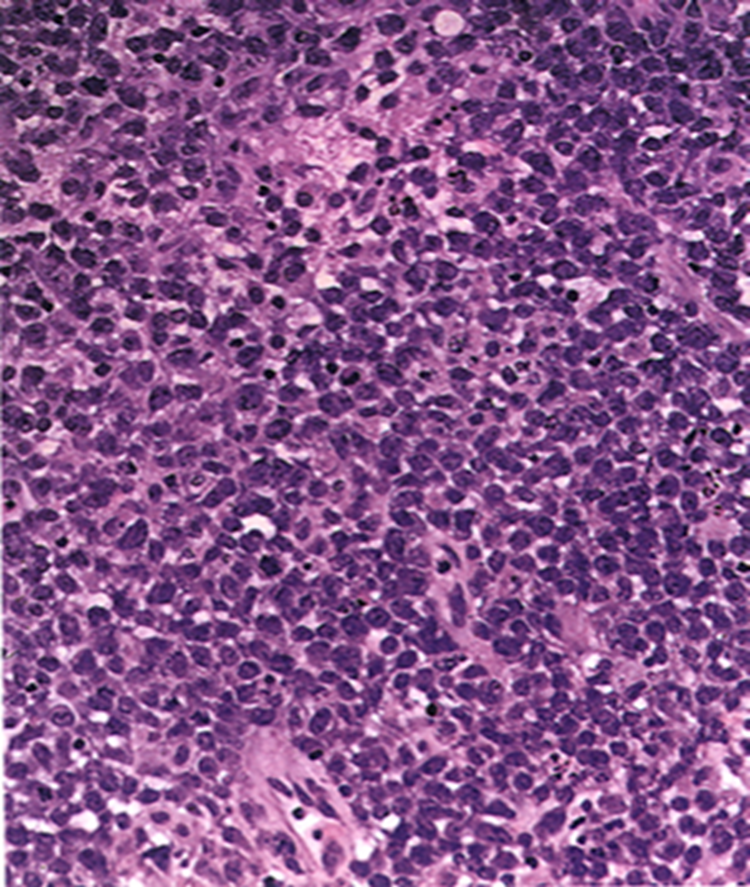
Sea of blue cells lymphocytes
Primary CNS lymphoma
Primary CNS lymphoma has a _____ prognosis
good
Periventricular Neoplasms
Ependymomas
Central neurocytomas
Colloid cyst
Ependymomas
Central neurocytomas
Colloid cyst
Periventricular Neoplasms
Ependymoma is a _______ neoplasm
periventricular
Central neurocytoma is a _______ neoplasm
periventricular
Colloid cyst is a _______ neoplasm
periventricular
Common (10-20 % of brain tumors)
ages 30-40
(Anterior) Pituitary Adenomas
Gigantism in children and acromegaly in adults from increased ____
(Anterior) Pituitary Adenomas
GH
Cushing’s disease increased _____ triggering the adrenal gland to increase production of steroid hormones
(Anterior) Pituitary Adenomas
ACTH
Hyperthyroidism from too much ___
TSH
(Anterior) Pituitary Adenomas
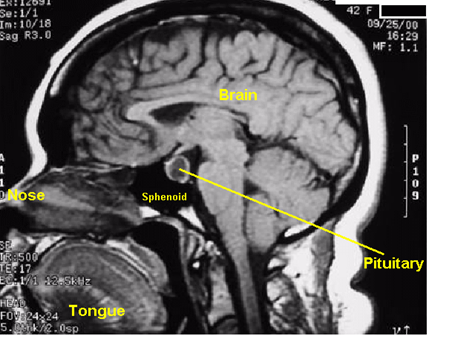
(Anterior) Pituitary Adenomas