Non-Protein Nitrogens (NPNs)
1/94
There's no tags or description
Looks like no tags are added yet.
Name | Mastery | Learn | Test | Matching | Spaced |
|---|
No study sessions yet.
95 Terms
NPNs arise from …
Catabolism (breakdown) of proteins + nucleic acids into simpler molecules that contain nitrogen but are NOT part of the protein molecule → NPNs
What organ regulates NPNs?
Kidneys filter + remove NPNs from plasma
Specimen containing NPNs
Plasma/Serum or Urine
Importance of NPNs in clinical testing
NPNs used to evalute Kidney / Renal Function → GFR = glomerular filtration rate
NPN present in Highest conc. in blood + urine =
UREA (40-50% of total plasma NPNs + 86% of total excreted nitrogen)
BUN =
Blood Urea Nitrogen
Urea production
PROTEIN metabolism
amino acids combined w/ ammonia to form Urea in Liver (UREA CYCLE)
Urea cycle
Liver : Free ammonia + amino groups (protein metabolism) → Urea
Urea travels thru blood to Kidneys
Kidney : Filters MOST Urea out of plasma + most excreted as Urine
Why is Urea cycle so important?
Without production of Urea, Free Ammonia accumulates in blood leading to toxic effects + CNS / Brain damage
Nitrogen balance depends largely on ___ levels
Urea (47% Nitrogen)
Urea levels depend on …
Diet → Protein intake
less protein = less urea
Filtrate flow thru kidneys
Slow flow = MORE reabsorption into plasma
Fast flow = LESS reabsorption + MORE excreted in urine
T/F: Most Urea is reabsorped in the kidneys
False - Most urea is FILTERED ; only a little urea is reabsorbed (depends on filtrate flow)
Importance of testing Urea
Evaluate Renal function
Monitor Dialysis
Nitrogen Balance
Azotemia =
increased urea in blood (> 20 mg/dL)
Uremia
Increased urea in blood plus renal failure
(more severe azotemia)
Prerenal Azotemia caused by …
increased blood urea due to issue BEFORE urea reaches kidneys
Increased Protein Intake / Breakdown
Decreased blood flow to kidneys
Renal Azotemia caused by …
increased blood urea due to Kidney issue
Decreased urea filtration
Acute / Chronic Renal Failure
Renal Disease (Glomerulonephritis, Tubular necrosis)
Postrenal Azotemia caused by …
increased blood urea due to issue AFTER urea exits kidneys
Urinary Obstruction
Renal calculi
Bladder / Prostate Tumors
Severe UTI (E. coli ; inflammation blocks urine flow)
Conditions causing decreased blood flow to kidneys
Dehydration, Hemorrhage, CHF, Shock
(causes of PRErenal Azotemia)
Increased urea due to Muscle wasting would fall under which category?
Prerenal azotemia
Renal azotemia
Postrenal azotemia
Prerenal azontemia
muscle wasting causing increased protein breakdown
more protein metabolized = more urea
What causes Decreased plasma urea?
Liver disease
Low protein intake
Late pregnancy
Severe vomitting, diarrhea
How does liver disease affect urea and ammonia?
Liver produces urea from free ammonia + amino acids (protein)
Damaged liver can’t make urea = Decreased urea + Increased ammonia in blood
Creatinine produced from …
Waste product from Creatine oxidation / MUSCLE metabolism
Is creatinine concentration generally high or low in blood?
Majority of creatinine FILTERED by glomeruli
Minimal reabsorption
Low Plasma levels
HIGH Clearance / High Urine levels
Creatinine levels determined by…
Muscle mass → produced from MUSCLE metabolism
Creatine turnover
NOT affected by Diet / Creatine supplements
★ GFR (Glomerular Filtration Rate)
T/F: Diet / Creatine supplements will increase serum creatinine concentrations
False - Creatine supplementation has minimal effect on serum creatinine concentrations in healthy adults
Which analyte is the most SPECIFIC measurement of Glomerular Function?
Creatinine
What is used to estimate glomerular filtration rate → ★ eGFR ★
Serum Creatinine concentration
Why is creatinine tested?
Most Specific measurement of Glomerular / Renal Function
Follow progression of Renal Disease (5 stages of CKD based off GFR)
Must be evaluated BEFORE CT scan dye administered
What can falsely affect Creatinine levels?
Icterus (bilirubin in blood)
Does a high or low Serum Creatinine indicate an issue?
HIGH SERUM Creatinine indicates Renal / GFR issue
kidneys should filter most creatinine out as urine, more in blood = kidneys NOT filtering properly / more creatinine reabsorption occuring
Causes of Elevated serum Creatinine
Decreased GFR
Renal Disease
Urinary Obstruction
How much kidney function must be lost before Creatinine levels increase?
Must lose at least 50% of kidney function BEFORE see any increase in Creatinine
What is Clearance?
Measure of how well kidneys function at filtering / “clearing” chemicals out of plasma + into urine per unit time
Used to detect how much plasma is being filtered by kidneys per unit time by comparing serum + urine concentrations of a particular analyte (Inulin, Creatinine)
Clearance units
mL / min.
Specimen used to calculate Clearance
Serum + 24 hr. Urine
Intrinsic Clearance =
Kidney Clearance measured by chemicals intrinsic to body → Creatinine
Extrinsic Clearance =
Kidney Clearance measured by chemicals extrinsic / foreign to body → Inulin
“Gold-standard” for measuring Clearance / GFR
Inulin Clearance = “GOLD-standard”
Extrinsic chemical → body naturally has NO inulin, NO reabsorption occurs, so kidneys should FILTER OUT ALL of the inulin injected
Compare serum + urine inulin concentrations
if inulin excreted does not equal amount injected into patient, means less plasma is being filtered
Why is Creatinine the next best measurement of Clearance?
★ Creatinine Clearance = MOST sensitive measure of kidney function (after than inulin)
Creatinine is steadily produced + readily excreted by kidneys
only a small amount reabsorbed
Equation to calculate CrCl

Normal Creatinine Clearance range
88-137 mL/min
(Females slightly lower than males)
Does a high or low Creatinine Clearance (CrCl) indicate an issue? What can cause this result?
LOW CrCl = LESS creatinine being FILTERED out into urine / increased creatinine reabsorbed into blood
Decreased GFR due to Acute / Chronic Glomeruli damage
What Creatinine Clearance value indicates mild, moderate, and severe renal impairment ?
Renal Impairment | Mild | Moderate | Severe |
Creatinine Clearance (mL / min.) | 50 - 79 | 10 - 49 | < 10 |
First Step in calculating Creatinine Clearance
Calculate V (volume of urine)→ Convert 24 hr. Urine Volume into mL / min
Divide total 24 hr. Urine volume by 1440 min. in 24 hrs
What factor must be taken into account in order to accurately calculate Creatinine Clearance?
patients’ BSA (Body Surface Area)
calculate BSA using pt Height + Weight
OR use Nomagram
multiply original equation (UV / P) by ( 1.73 m2 / BSA m2 )
1.73 m2 = average adult BSA
Modification of Diet in Renal Disease (MDRD) equation
equation used to calcuate eGFR using
Serum creatinine concentration
Age
Gender
Ethnicity
Issue w/ MDRD equation
uses Ethnicity to calculate eGFR
OVERestimates GFR in Black pop. which UNDERestimates progression of kidney disease
Cystatin C
small protein that functions as cysteine protease inhibitor
used to detect decreased GFR
High blood levels = Low GFR
eliminated exclusively by glomerular filtration
Produced by cells at constant rate
Not altered by age, sex, nutrition
How do Azotemia conditions affect BUN : Creatinine Ratio?
Azotemia Condition | Ratio | Description |
Pre-Renal | ↑ | BUN ↑ Creatinine N |
Renal | N | BUN + Creatinine ↑ proportionally |
Post-Renal | ↑ | BUN ↑↑ Creatinine slightly ↑ |
Uric Acid produced by..
Purine metabolism
purines = nucleotides
uric acid waste product of cell turnover / DNA breakdown
“Alert” / “Critical” Uric Acid value
> 10 mg/dL
(normal = 3.5 - 7.2 mg/dL)
Increased Uric Acid due to ___ or ____
Increased Production OR Decreased Excretion of Uric Acid
Conditions associated w/ elevated uric acid
Idiopathic Gout
Renal calculi (kidney stones)
Cancer (leukemia)
increased cell turnover = increased DNA breakdown + purine release = increased purine metabolism into uric acid
Renal Failure
Acute Infxn
Inherited Purine disorders
Gout
increased uric acid in plasma deposits around joints (commonly big toe) + develops sharp, painful Uric acid crystals
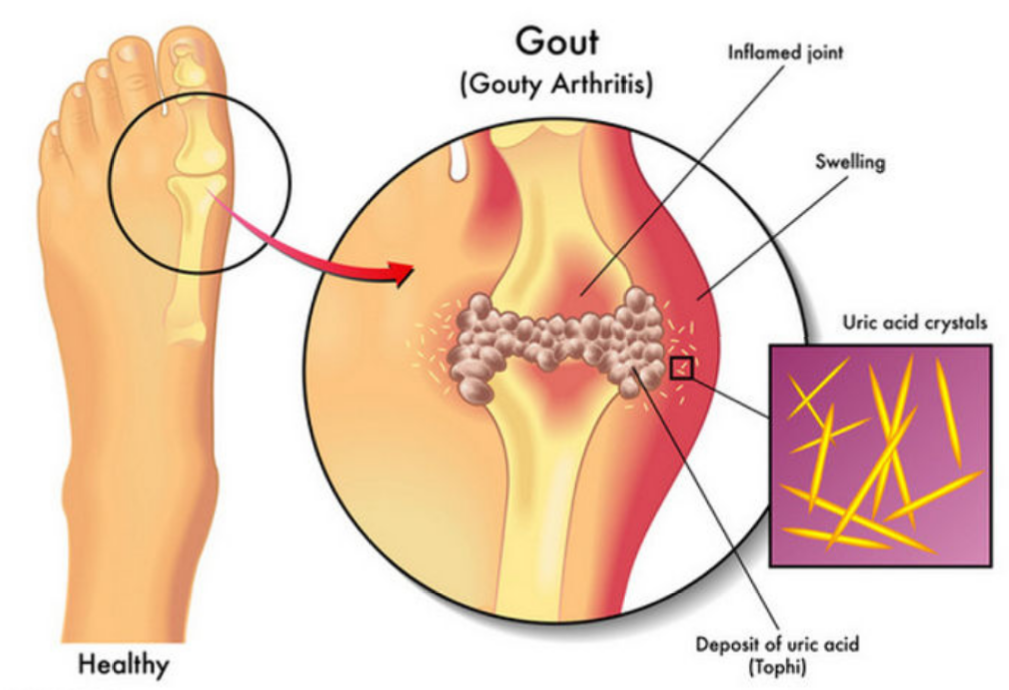
Gout usually develops in what population?
What are some risk factors?
Older Males diagnosed between 30-60 yrs old
Alcohol consumption
Purine-rich diet
Ammonia formed from…
Amino Acid breakdown + Bacterial metabolism
Ammonia metabolized by what organ?
Liver - turns ammonia + amino groups into Urea (Urea Cycle)
Ammonia Elevations most commonly caused by …
Severe Liver disease
Liver makes urea from free ammonia → liver disease = decreased urea synthesis → leaves incr. Ammonia in body
Effect of increased ammonia
Ammonia = Toxic to CNS (brain)
What can interfere w/ ammonia results?
Smoking several hrs prior to blood collection contaminates sample
Hemolysis falsely increases ammonia (2-3x more ammonia in RBCs than plasma)
How should Ammonia samples be transported + processed?
Collect samples on ice + process w/in 20 min.
First sign of glomeruli damage =
Leaking protein into urine
Loss of protein in blood results in …
Decreased osmotic pressure → water leaks out of cells into interstitial space (between tissues) → Edema
Glomerular Disease
Acute or Chronic damage to the glomeruli = filtering unit of nephron (kidneys)
Acute Glomerulonephritis (AGN)
Acute = Rapid onset of symptoms
Glomerulonephritis = damaged glomeruli
AGN most commonly affects what population?
Childen + Young adults
AGN caused by…
GAS infxn (Group A Streptococcal)
Circulation of immune complexes trigger inflammatory response in the glomerular basement membrane → temporary leakage of protein in urine
Toxins / Drugs. Acute kidney infxns, Systemic / Autoimmune diseases
Key symptoms of AGN (Acute Glomerulonephritis)
Rapid Onset of …
Proteinuria
Na+ and H2O retention
Edema
Hypertension
Hematuria
Oliguria (low urine output)
AGN Lab Results
Proteinuria
Hematuria
Decreased GFR
Increased BUN + Creatinine
Urine Casts
AGN + CGN stand for …
AGN = Acute Glomerulonephritis
CGN = Chronic Glomerulonephritis
CGN
Chronic Glomerulonephritis
End stage of persistant glomerular damage
Irreversible renal tissue loss
results in Renal Failure
Nephrotic Syndrome
Increased permeability of GBM (glomerular basement membrane)
causes kidneys to “leak” protein + lipids in urine
causing not enough protein in blood (Hypoalbuminemia)
Causes of Nephrotic Syndrome
Glomerulonephtritis complications
Circulatory disorders affecting Kidneys
Key lab findings in Nephrotic Syndrome
Massive Proteinuria (>3 g/day)
Albuminuria (>1.5 g/day)
Hypoalbuminemia
Pitting Edema
Lipiduria (Oval fat bodies in urine)
Hyperlipidemia
liver nonspecifically increases lipid production due to excess loss of proteins + lipids
What condition is associated w/ Massive Proteinuria, Hypoalbuminemia, Hyperlipidema, Pitting Edema, and Oval fat bodies in urine?
Nephrotic Syndrome
increased GBM permability allows LOTS of protein + lipids to leak out into urine
What condition is associated w/ Proteinuria, Hematuria, Oliguria, Edema, Hypertension, Decreased GFR, Increased BUN + Creatinine, and Casts in urine ?
Acute Glomerulonephritis (AGN)
Dmaged glomeruli =
decreased GFR = low urine output ; casts form
proteins + RBCs leak into urine
Decr. Urea + Creatinine filtration = Increased serum levels
Pyelonephritis =
Acute vs Chronic =
Kidney inflammation / infection caused by UTI
Acute = non-permanent damage
Chronic = permanent damage, possible renal failure
Cystitis =
Bladder inflammation / infection caused by UTI
UTI Lab results
Pos. Nitrite on urine dipstick
common bacteria causing UTIs = Enterobacteriaceae = mostly all convert nitrate to nitrite
Hematuria
Pyuria
WBC Casts
Causes of Renal Obstructions
Renal Calculi (stones)
Tumors
Urethral strictures
Most common cause of Renal Calculi
Calcium oxalate
GFR in Acute Renal Failure
GFR < 10 mL/min
2 most common conditions associated w/ CKD =
Hypertenstion + Diabetes
Complications of CKD
Anemia
kidneys secrete EPO
decr. kidney function = decr. EPO = decr. blood cells
Vit D deficiency
kidneys convert calcidiol into calcitriol (active Vit D)
Mineral + Bone disorders
kidneys increase calcium reabsorption
Hyperparathyroidism
due to kidney damage causing less Vit D produciton + Less Calcium reabsorption , Parathryoid glands secreate more PTH to increase Calcium in blood
Stage 1 of CKD
Kidney damage w/ normal - increased GFR > 90 mL/min.
Stage 2 CKD
Kidney damage w/ normal - decreased GFR (60-89 mL/min.)
Stage 3A + 3B CKD
3A = Moderate - Decreased GFR (45-59 mL/min.)
3B = Modertate - SEVERELY Decreased GFR (30-44 mL/min.)
Stage 4 CKD
Severely Decreased GFR (15-29 mL/min.)
Stage 5 CKD
Kidney FAILURE = GFR < 15 mL/min.
Normal GFR
90 -120 mL/min/1.73 m2
CKD staging is dependent on what measurment?
GFR
As Chronic Kidney disease progresses, GFR gradually declines
Hemodialysis
removal of waste from blood
Hemofiltration
ultrafiltration of blood
decreases fluid volume
For patients with kidney failure, ____ are the only options
dialysis and/or kidney transplant