issues and debates
1/69
There's no tags or description
Looks like no tags are added yet.
Name | Mastery | Learn | Test | Matching | Spaced | Call with Kai |
|---|
No analytics yet
Send a link to your students to track their progress
70 Terms
define gender bias
the differential treatment and/or representation of males and females, based on stereotypes and not real differences
what is universality
when a theory is universal it can apply to all people regardless of gender and culture
what is androcentrism
theories and research that is centred or focused on males, often excluding females
what is gynocentrism
theories and research that is centred or focused on females, often excluding males
give an example of androcentrism and what are the consequences of it
Asch's research into conformity is guilty of androcentrism, as all of the participants in his study were male. This means that Asch's findings of how people conform are male-orientated.
Therefore, females are judged against a male standard of conformity behaviour.
Any behaviour from women that deviates from the male standard is seen as abnormal.
Therefore, Asch's findings aren't universal because we're unable to generalise the findings to how females will conform.
give an example of gynocentrism and explain the consequences of it
Ainsworth’s strange situation focuses on mothers as the primary attachment figure, neglecting the role of the father (Field says the father can play the role of the father).
Therefore, the findings of Ainsworth’s research represent a female orientated view on attachment where ‘normal behaviour’ is judged according to the female standard
any behaviour that deviates from the ‘female standard’ is seen as abnormal
Therefore, Ainsworth’s findings aren’t universal as we’re unable to apply them to how males will form attachments with females
what is alpha bias
refers to theories which exaggerate differences between males an females
what is beta bias
refers to theories which ignore or minimise differences between males or females
give an example of alpha bias
Freud said that females are psychologically defined by the fact that they realise they aren’t males
give an example of beta bias
Asch's study on conformity used an all male sample and Asch assumed that the findings he got from his male study applied to how females conform.
evaluate gender bias
P- gender biased research may create misleading assumptions about female behaviour
E- gender biased research may provide scientific justification for stereotyped attitudes and beliefs about women, such as being more likely to have emotional issues
E- This is an issue because women may be denied jobs and opportunities based on gender biased research
L- Therefore, it could lead to a misrepresentation of female behaviour in the real world
P- There is sexism within psychological research
E- there is a lack of females at the senior level, which means that female concerns may not be reflected in the research questions asked, although there may be female participants in studies
E- This is a weakness because, as males are asking the questions, females may be labelled as a result
L- Therefore, women may be seen as a singular group with no representation of diversity within their behaviour
P- a benefit of identifying gender bias is that it has lead to reflexivity
E- Lambert reflected on her own research and realised that her gender may have impacted the conclusions of her study
E- This is a strength, as if researchers are able to reflect on how their gender may have affected their conclusions in their research, then this should lead to a reduction of gender bias in psychological research
L- Therefore, this may increase the validity of psychological studies as gender bias won’t have as large of an impact on any conclusions drawn from studies
define culture
the values, beliefs, and patterns of behaviour shared by a group of people
define culture bias
the tendency to ignore cultural differences and judge people in terms of ones own cultural assumptions
outline what is meant by cultural relativism
the idea that a behaviour can makes sense in the context of the norms and values of the culture which it occurs in
define ethnocentrism
when one judges other cultures from the standpoint of their own culture, potentially leading to viewing other cultures as inferior
in psychological research this may be upheld by the belief that any behaviour that doesn’t conform to the dominant (normally western) model is abnormal
give an example of ethnocentrism in psychology
Ainsworth’s research only reflected the norms and values of American culture and Bowlby who was British
Ainsworth suggested that secure attachment was determined by the child showing high levels of separation anxiety when they were separated from the mother
This lead to the misrepresentation of child rearing practices in other countries- German mothers were seen as cold and rejecting rather than encouraging independence in their child, as this deviated from the ‘American norm’
Therefore, the strange situation is an inappropriate measure of attachment type for children that aren’t from the US
How do we overcome ethnocentrism/culture bias
cultural relativism
there is no global ‘right or wrong’, you must consider the behaviour of an individual from within their own culture
Scientists should be mindful of cultural relativism by using an emic approach
what is an emic approach
involves understanding a culture by using a researcher from the same culture
preconceived ideas about that culture are put aside
what is an etic approach
when a researcher tries to understand a culture that’s different from their own culture and judges the culture based upon what’s ‘normal’ in their own culture
they use preconceived ideas to understand behaviour and apply it universally
what are the consequences of using an emic approach
can lead to alpha bias where the differences between cultures are exaggerated by assuming that behaviours aren’t universal
what are the consequences of using an etic approach
can lead to beta bias where the differences between two cultures are minimised by assuming behaviours are universal
give an example of research that uses an etic approach and how could they have used an emic approach instead
Van Ijzendoorn and Kroonenberg
looked at frequencies of attachment types amongst different cultures via a meta-analysis
They should spend time in the cultures they were studying to understand the best way to measure attachment- they could also cooperate with local researchers that would make their research more appropriate
evaluate culture bias
P- the idea of culture bias is out of date
E- Osaka found that 14 out of 15 studies that compared the USA (individualist) and Japan (collectivist) found no evidence of the traditional distinction between individualism and collectivism
E- This suggests that cultural bias is less of an issue than it once was
L- Therefore, there may be less of a need for researchers to take an emic approach than previously thought
P- A limitation of culture bias is that some behaviours are universal
E- it shouldn’t be assumed that all psychology is culturally relative as some features of human attachment are universal such as interactional synchrony
E- This suggests that a full understanding of human behaviour requires the study of universal behaviour and behaviour that’s specific to a culture
L- Therefore, taking a culturally relativist approach to avoid culture bias isn’t appropriate
P- a strength of culture bias is that it may challenge typical Western ways of thinking
E- when researchers conduct cross-cultural research they take an emic approach to their research
E- This is a strength as it means that findings won’t be culturally relative as the researchers have a greater understanding of individual differences between cultures
L- Therefore, ethnic minorities will be represented fairly and appropriately in the research unlike in the past which means they won’t be denied jobs and opportunities based on biased and unrepresentative psychological research
what are ethical issues
they are problems that Aries when there are conflicts between the rights of the participants and the aims of the researcher
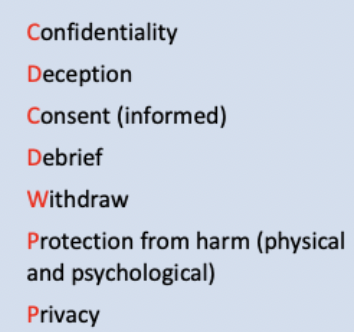
what are ethical guidelines
they are a set of guidelines that researchers must follow which helps to protect participants during research from ethical issues
what are ethical implications
the impact that the research has on society and how it influences the way which certain groups are viewed in society
what could some ethical implications of research findings be

what is socially sensitive research
any research where there are potential social consequences for either the participants involved in the research or the group of people represented by the research e.g. certain genders or ethnicities
what are the implications of socially sensitive research
socially sensitive research may be seen as giving scientific credibility to prejudice and discrimination
it can be used to justify public policy e.g. findings can be used by the government for political means
what are the ethical issues within socially sensitive research
the research question
the methodology used
the institutional context
interpretation and application of findings
how may the research question raise ethical issues in socially sensitive research
the researcher should be careful how the phrase the question asked
they should avoid questions like: ‘are there racial differences in IQ’- as this may be damaging to members of a particular group
they should rephrase their question: ‘what factors affect IQ’ as this is less problematic
how may the methodology raise ethical issues in socially sensitive research
the researcher needs to consider the treatment of the participants and their right to confidentiality and anonymity
for example, if the participant admits to committing a crime or having unprotected sex when they are HIV positive- should the researcher maintain confidentiality (ethically wrong to not report it)
how may the institutional context raise ethical issues in socially sensitive research
the researcher should be mindful of how the data collected will be used and who is funding the research
if the research is funded by a private institution- why are they funding the research and how do they intend to use it (could potentially put certain groups at harm)
how may the interpretation and application of findings raise ethical issues in socially sensitive research
the researcher needs to consider how their findings will be interpreted and applied in the real world
they could be used by the government to develop public policy- this could lead to discrimination or prejudice of certain groups in society
discuss ethical implications within research studies
There were ethical implications that came from the participants not having given informed consent
Before the study occurred Milgram didn’t inform the participants about the true aims of his study and during the study he deceived his participant into thinking that the confederates were real participants.
However, it could be argued that Milgram had to deceive the naive participant so that demand characteristics wouldn’t alter the participants behaviour and how many volts they shocked the ‘learner’ with. He made sure to debrief the participant after the study and asked them to take part in a follow up interview, where participants said that they suffered no long-term effects.
discuss ethical implications of theories
It could also be argued that Bowlby’s research had ethical implications as it could be used to coerce mothers into staying home and looking after their children.
This is because Bowlby’s research suggests that children form one special attachment bond with the primary caregiver which is usually the mother, and this must take place during the critical period.
This is a weakness because it could make mothers feel guilty about wanting to return to work after childbirth.
ETHICS EVALUATION
Strengths
P- socially sensitive research/conducting research with ethical implications can promote greater sensitivity and understanding of underrepresented groups
E- research into schizophrenia has helped to understand the causes and symptoms of schizophrenia
E- This is a strength because people are able to understand what schizophrenic people are going through and why, which helps to reduce prejudice in society
L- Therefore, this can help people with schizophrenia to lead a more normal life, as medication has been developed to reduce the positive and negative experiences associated with schizophrenia
P- socially sensitive research/conducting research with ethical implications has led to the development of an ethics society
E- today’s research must be evaluated before it takes place, where people in the committee weigh up the potential costs against the benefits
E- This is a strength as it reduces the number of unethical studies that are conducted
L- Therefore, this has real-world applications because certain groups in society won’t be at risk of being maltreated as a result of socially sensitive research
Weakness
P- socially sensitive research/conducting research with ethical implications can lead to discrimination
E- research examining racial differences in the United States was used to justify new forms of social control. Individuals were sterilized to prevent them from having children and passing on their genes
E- This is a weakness to socially sensitive research because psychologists must be mindful of how their research could be used to support unethical and discriminatory practices of social control
define free will
the notion that humans can make choices and are self determining
we are morally responsible for our own behaviour
their behaviour isn’t determined by internal or external forces
define determinism
the idea that human behaviour is controlled by internal and external forces rather than an individuals own will to do something
what is soft determinism
the view that behaviour is constrained by external and/or internal factors, but individuals still have limited free will to choose their behaviour within those contraints
what is hard determinism
we aren’t morally responsible for our actions and our actions are determined by internal and/or external factors that we can’t control
we have no free will
what is biological determinism
the idea that traits and behaviours are governed by internal biological factors like genes and neurotransmitters
give an example of biological determinism
aggression is caused by the MAOA-L gene
what is environmental determinism
the idea that traits and behaviours are governed by external forces such as experiences, learning, parenting, peers
give an example of environmental determinism
attachment type is determined by parenting style- Ainsworth
what is psychic determinism
the idea that traits and behaviours are governed by unconscious drives and that the cause of behaviour is rooted in childhood experiences
give an example of psychic determinism
Freud’s psychodynamic approach- we have unconscious defence mechanisms to stop traumatic memories from entering the conscious mind which may cause anxiety
what is scientific emphasis on causal explanations (scientific determinism)
when all other variables are controlled apart from the IV, the scientist can establish cause and effect (any change in the DV must have been due to the manipulation of the IV)
this allows the scientist to predict and control events in the future
scientific determinism directly relates to hard determinism
discuss the free will determinism debate
P- the hard determinist position isn’t consistent with the way our legal system operates
E- hard determinism states that we have no free will and that all of our behaviours have a cause and are controlled by internal and/or external forces
E- this is an issue because, in the court of law, offenders are held morally accountable for their actions but hard determinism argues that we aren’t morally responsible for our actions
L- therefore, although hard determinism may be a useful way to research certain behaviours, it doesn’t align with how behaviour is viewed in our legal system
P- One strength of the determinism side of the free will vs determinism debate is that biological determinism is that it’s useful for developing treatments.
E- For example, it has led to the development of typical and atypical drugs to treat schizophrenia. This is because a biologically determinist approach suggests that schizophrenia is caused by only internal factors such as hypodopaminergia (low levels of serotonin).
E- This is a strength because it has allowed the rates of institutionalisation to decrease.
L- Therefore, taking a biologically determinist approach to treatment has allowed individuals with mental health disorders such as schizophrenia to function more normally within society, as they don’t have as much trouble with positive and negative symptoms of schizophrenia.
P- One strength of the free will position of the free well vs determinism debate is that free will has face validity
E- Rogers client centred therapy reflects free will because it makes patients believe that they have the power to control their life and reach self actualisation
E- This supports the idea of free will because through client centred therapy patients feel as if they have control over their actions an behaviours and that they aren’t due to external forces outside of their control
define reductionism
reductionism involves explaining complex behaviour in a simple way in terms of basic units or smaller, simpler aspects of complex behaviour
define holism
any attempts to break down behaviour into its constituent parts are inappropriate and behaviour can only be explained by considering the whole person (including internal and external influences)
what is biological reductionism
behaviour should be explained by it being reduced to the physical behaviour
behaviour is reduced to the action of genes, neurotransmitters, evolution
what is environmental reductionism
all behaviour can be explained through stimulus-response links that can be measured in laboratory conditions
behaviour is as a result of interaction with the environment
what are the levels of explanation (levels of reductionism)
highest levels (less reductionist)- sociocultural explanations of how social groups affect behaviour and expectations of how to behave
middle levels- psychological explanations of behaviour
lower levels- biological explanations of aggression such as genes, neurotransmitters, hormones
give examples for each stage of the different ‘levels of aggression’
For aggression
social-cultural- media influences
psychological- SLT
biological-psychological- limbic system
biological-neurochemical- MAOA-L gene
evaluate the reductionism-holism debate
environmental reductionism strength
P- a strength of the environmental reductionism side of the reductionism-holism debate is that it’s easy to scientifically test the stimulus-response link that’s responsible for behaviour
E- For example, Skinner used Skinner’s box to empirically research operant conditioning as he had control over extraneous variables
E- This research allowed us to see how phobias are maintained
L- Therefore, having a reductionist approach allows psychologists to find causes of behaviour such as how phobias are created and maintained. This allows psychologists to help people get rid of their phobias through systematic desensitisation and live a more normal life
biological reductionism- strength
P- a strength of the biological reductionism side of the reductionism-holism debate is that it’s lead to treatments for mental illnesses
E- A typical drugs have been developed to treat the positive and negative symptoms of schizophrenia
E- This has allowed the rates of institutionalisation to decrease and has allowed individuals with mental health disorders such as schizophrenia to function within society
However- when Schooler gave patients two types of antipsychotics, only 75% of patients experienced a reduction is symptoms, so a more holistic method of treatment may be required to increase the effectiveness of treatments for mental health disorders
biological reductionism- weakness
P- taking a biologically reductionist approach may not be able to explain all behaviour
E- doesn’t focus on social factors such as expressed emotion
E- This is a weakness, because it may be the high levels that act as an environmental trigger to cause schizophrenia. Our biological factors only lead to a predisposition to schizophrenia
L- Taking a more holistic approach may be more appropriate to explain complex behaviour, even if it’s less empirical and objective
Holism
P- a strength of the holism side of the holism-reductionism debate is that certain behaviours can only be explained at the holistic level
E- For example, in Zimbardo’s Stanford prison experiment he studied conformity to social roles. It was important for him to consider the social context as the behaviour of his participants wouldn’t have been explained through reductionist means e.g. if Zimbardo looked at their genes and levels of hormones and neurotransmitters
E- This suggests that human behaviour is more complex and using a holistic approach provides a more valid explanation of behaviour than the reductionist approach could provide
what is nativism (nature)
a view that suggests the human soul was born with an understanding of certain key concepts, predispositions, and pre-programmed behaviour
what is empiricism (nurture)
we are born without any innate mechanisms and we learn from our experiences with the environment
what is meant by heredity
the process where traits/characteristics from both parents are genetically passed on and inherited by the offspring
what is the interactionist approach
the view that processes of nature and nature work together to influence behaviour, rather than in opposition
evaluate the nature-nurture debate
P- a strength of the nativist approach (nature side of the debate) is that it has research support
E- Meltzoff and Moore researched into interactional synchrony. An adult model would display different facial expressions in front of the child. The child had a dummy in its mouth during the initial display to prevent any response. Following the display the dummy was removed and the Child’s expression was filmed. An independent observer was asked to note down all gestures and expressions that the baby displayed in the film/video using a number of different behavioural categories.
E- this supports the nature side of the debate as interactional synchrony must be innate as the babies had no time to learn the response and gestures.
L- therefore, this increases the validity of the nativist/nature side of the nature-nurture explanation of behaviour
However, Isabella found that the more securely attached the infant was, the higher the levels of interactional synchrony were. This is an issue because attachment type is as a result of parenting style, which could suggest that interactional synchrony may be learnt and developed through the environment.
P- A strength of the nurture side of the nature-nurture debate is that it has research support
E- Skinner used Skinner's box to test his theory of operant conditioning where behaviour is learnt and conditioned through consequences
E- His lab experiment had high control over extraneous variables which meant that Skinner was able to establish that the rat’s behaviour was down to consequences from the environment rather than its genetics (nature)
L- Therefore this increases the validity of the nurture side of the nature-nurture debate
P- the nature-nurture debate could be better explained by the interactionist approach where nature and nurture work together to influence behaviour
E—Scarr’s theory of ‘passive gene-environment interaction’ suggests that parents pass on genes to their children and also provide the environment in which their children grow up and develop.
E- These genetic factors and environmental factors provided by the parent both work together to influence the child's behaviour.
L- Therefore, this suggests that there is a complex relationship between nature and nurture, rather than behaviour being influenced by one or the other
what is meant by the term nomothetic
focuses on the similarities between people
attempts to establish laws and generalisations about people
these provide a benchmark which people can be compared to
studies large groups of people
uses mainly quantitative data
what is meant by the term idiographic
focuses on individual insights into human behaviour
no general laws are possible because of chance, free will, ad the uniqueness of individuals
often uses case studies
gathers qualitative data that’s unique to the individual being studied
what methods are used to collect data in idiographic studies
structured observations
lab experiments
closed questions
what methods are used to gather data in idiographic studies
unstructured observations
case studies
unstructured interviews
what are the strengths of nomothetic
can generalise laws and findings to the wider population
methods are objective, measurable- so the replication, prediction and control of behaviour is easy
less time consuming than idiographic
what are limitations of nomothetic
generalised laws may not apply to an individual
understanding is often superficial- e.g. two people can both be diagnosed as depressed but for different reasons
what are the strengths of idiographic
can give detailed and insightful descriptions of behaviour
can uncover causes for behaviour that couldn’t have been identified using nomothetic methods
develops a holistic understanding of individuals
what are the limitations of idiographic
can’t generalise findings from case studies to the wider/general population
methods of gathering data are subjective and unstandardised (hard to replicate), therefore, the prediction and control of behaviour is difficult
more time consuming than nomothetic
evaluate the nomothetic-idiographic debate
P- a strength of the idiographic side of the nomothetic-idiographic debate is that it allows us to study things that we aren’t able to replicate on a mass scale
E- for example we can look into brain damaged patients such as HM who had a severe case of amnesia so his hippocampus had to be removed which resulted in HM not being able to form new memories
E- This is a strength because using case studies and studying the experiences of unique individuals helped psychologist to localise functions within the brain which wouldn’t be possible when using a nomothetic approach
L- Therefore, this increases the validity of the idiographic approach as it allows us to gather data which wouldn’t e possible with other methods
However, with idiographic studies it’s difficult to generalise the findings to the wider population as case studies have a small sample size, so we can’t be sure that behaviour will be consistent in the general population
P- a strength of the nomothetic side of the nomothetic-idiographic debate is that it’s regarded as scientific
E- Skinner studied behaviour using Skinners box which had high control over extraneous variables where he was able to replicate, predict, and control the behaviour of rats through consequences the rats faced
E- This is a strength because as Skinner had high control over extraneous variables in his lab experiment his findings were able to be replicated by others which meant that he could establish general laws about how behaviour is learnt through consequences
L- Therefore, this increases the validity of the nomothetic side of the debate as it can help us to predict and control behaviour which can be useful in real life situations such as dealing with violence and aggression in prison systems
P- a strength of the nomothetic and idiographic approaches is that they don’t have to be seen as complimentary. It’s more helpful to see them as complementary
E- Bowbly’s theory of maternal deprivation developed using a nomothetic approach states the the effects of extreme maternal deprivation are irreversible. However, and idiographic study on the Czech twins’ demonstrates that in this single case study, maternal deprivation was overcome
E- This is useful because using an idiographic approach can challenge the general principles developed when using a nomothetic approach to studying behaviour.
L- Therefore, seeing both of these approaches as complimentary can help to refine and change the general laws developed using a nomothetic approach so they can apply to more individuals