Blood Flow & Cardiomyocytes - Chapter 19
1/23
There's no tags or description
Looks like no tags are added yet.
Name | Mastery | Learn | Test | Matching | Spaced | Call with Kai |
|---|
No analytics yet
Send a link to your students to track their progress
24 Terms
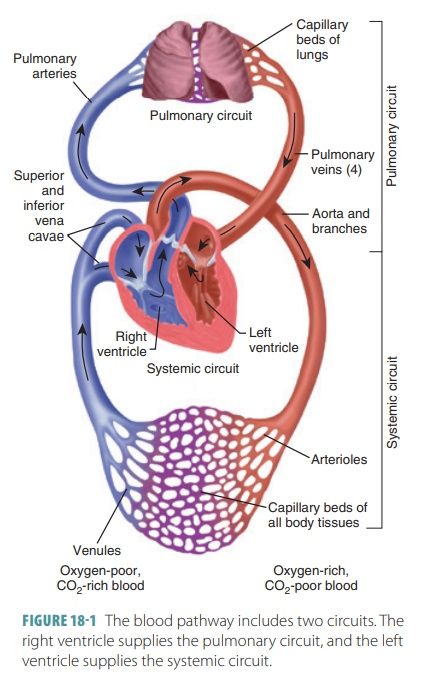
Basic pathway of blood in the body (the 2 circuits):
Pulmonary Circuit: Heart → Lungs → Heart
Systemic Circuit: Heart → Body → Heart

Pulmonary Circuit Full Pathway:
Deoxyginated blood enters into the Right Atrium
Blood travels through the tricuspid valve
Blood enters the Right Ventricle
Blood passes through the pulmonary semi lunar valve
To the pulmonary turnk
To the pulmonary artery
Into the lungs
Oxyginated blood travels to the pulmonary veins
Oxyginated blood is deposited in the left atrium.
Lower pressure
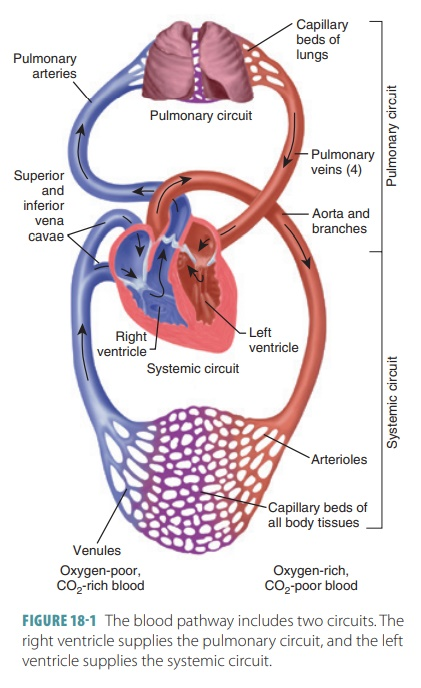
Systemic Circuit Full Pathway:
Oxyginated blood enters into the Left Atrium.
Blood travels through the mitral (bicuspid) valve
Blood enters the left ventricle
Blood passes through the aortic semilunar valve.
Blood enters the aorta
Blood enters into systemic circulation
Deoxyginated blood enters the inferior and superior vena cava
Deoxyginated blood enters into the Right Atrium.
Higher pressure
Blood Vessel Names
Arteries bring blood away from the heart.
Veins bring blood to the heart.
Coronary Circulation Overview
Blood supply for the muscles on the heart.
This blood gets delivered when the heart is relaxed, and most of it goes towards the left ventricle.
Arterial blood supply varies among individuals.
Contains many anastomoses (junctions). These provide additional routes for blood delivery, but cannot compensate for coronary artery occlusion (blocked artery)
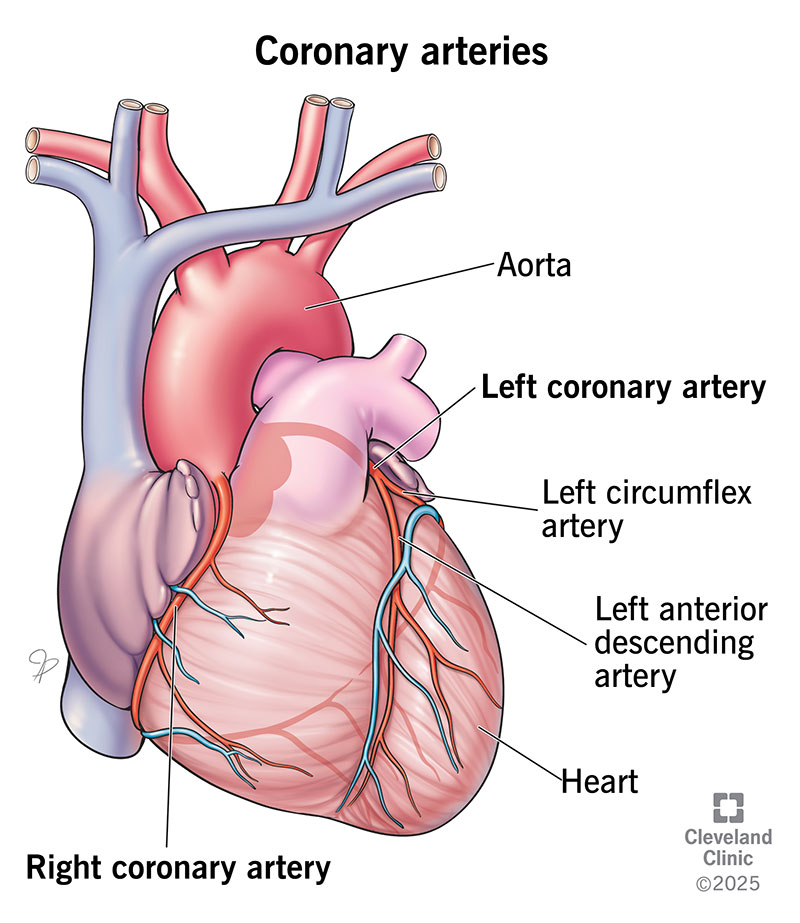
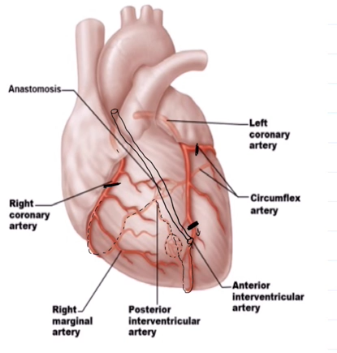
Coronary Arteries and Their Divisions
Left Coronary Artery: Anterior interventricular artery, Cirumflex Artery
Right Coronary Artery: Right interventricular artery, Posterior interventricular artery
Left Coronary Artery Supplies what
Interventricular septum
Anterior ventricular walls
left atrium
and the posterior wall of the left ventricle
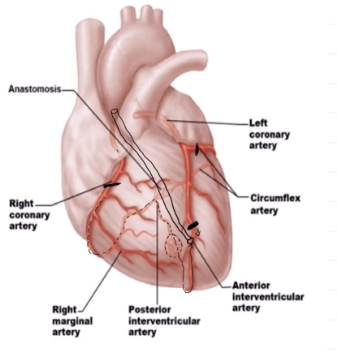
Anterior Interventricular Artery
Runs in the anterior interventricular artery
Forms an anastomosis with the posterior interventricular artery
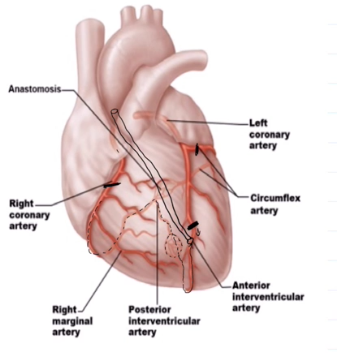
Circumflex Artery
Runs in the coronary sulcus
Forms an anastomosis with the posterior interventricular artery
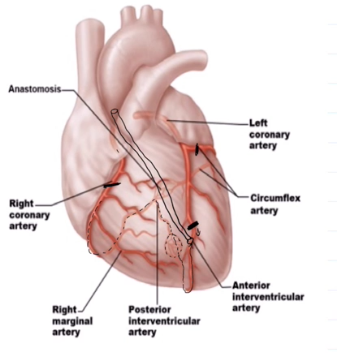
Right ventricular sulcus supplies what
Supplies the right atrium and most of the right ventricle
Right Marginal Artery
Runs in the right coronary sulcus
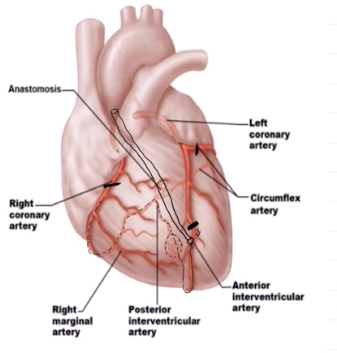
Posterior interventricular sulcus
Runs within the posterior interventricular sulcus
Forms anastomosis with both left branches
Cardiac Veins
collect blood from capillary beds
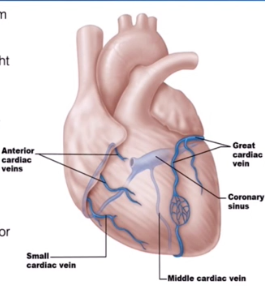
Coronary Sinuses
Empties into the right atrium
Is formed by the cardiac veins
Great Cardiac Vein
Middle Cardiac Vein
Small Cardiac Vein
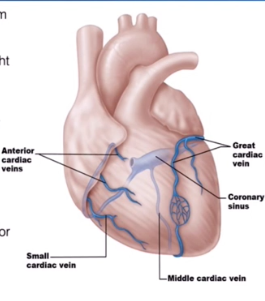
Great Cardiac Vein
Runs alongside the Anterior Interventricular Artery
Runs inside the interventricular Sulcus
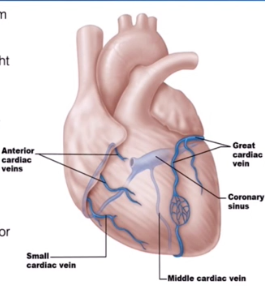
Middle Cardiac Vein
Runs with the posterior interventricular artery
Located in the posterior interventricular sulcus
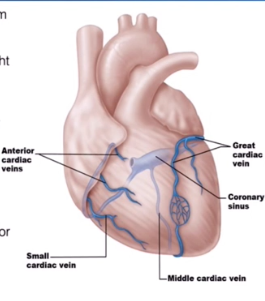
Small Cardiac Vein
Runs with the marginal artery
Located in the inferior margin
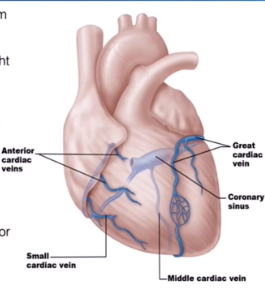
Several Small Cardiac Veins
They just drain directly into the right atrium
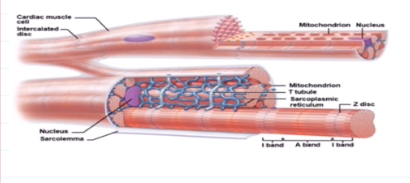
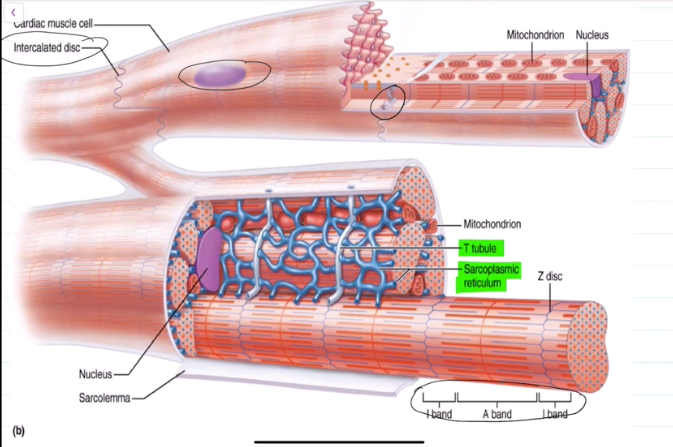
Cardiac Muscle Cells
cells of da heart muscle

Anatomy of Cardiac Muscle Cells:
They are striated, branched, and interconnected.
Is wrapped by an endomesium that provides blood supply to cardiac muscles
Contains T-Tubules, albiet wider and less numerous than skeletal muscle cells
Has many mitochondira that takes up 25%-35% of the cell
Contains intercalated discs
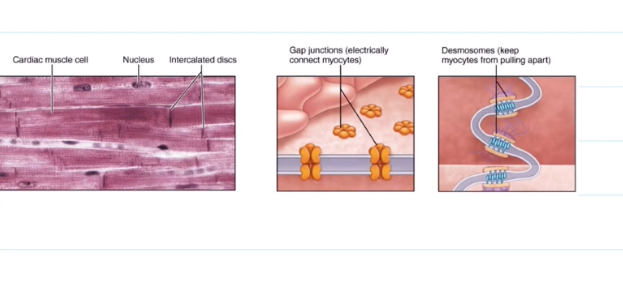
Intercalated Discs
They contain Desmosomes, which help to prevent the heart from pulling apart when contracting and relaxing.
They contain gap junctions, allowing for ions to pass in between cells. All the heart musculature contracts and relaxes at once because of this.
Three Similarities with Skeletal Muscles:
Both cells suddenly depolarize with an influx of sodium in the sarcolemma. Membrane potential from -90mv to 30mv. Brief; na+ channels close rapidly.
Depolarization wave travels down T-Tubules to triads; sarcoplasmic reticulum releases calcium
Calcium attatches to troponin, troponin pulls tropomyosin off filaments, excitation contraction coupling occurs.
Unique Features of Cardiac Muscle Functioning:
Around 1% of cardiac muscle cells have automaticity, meaning that they contrat without nervous system stimulation. Due to gap junctions, this causes the rest of the cells to contract as well.
The nervous system controls the rate at which the heart contracts, not if it does or does not.
Because of gap junctions, either all the cells contract, or all the cells relax. They work as a single unit.
Cardiac Cell Respiration
Cardiac cells use a lot of energy, so they heavily rely on aerobic respiration and do not fare well with aerobic respiraton
In an emergency, the cells can use lactic acid, fat, and even ketones, but this is not ideal and will usually lead to a heart attack.