Kinesiology Vocab and Notes -- Unit 5 p.2
1/27
There's no tags or description
Looks like no tags are added yet.
Name | Mastery | Learn | Test | Matching | Spaced |
|---|
No study sessions yet.
28 Terms
Heartbeat
The rhythmical contraction of the wall of the heart (pulse in a distal area)
Heart Rate
The number of times the heart beats in a minute
Cardiac Output
The amount of blood that flows to the peripheral circulation (the entire body)
Carotid and Radial
What are the most common sites for pulse?
Temporal artery
Carotid
Apical Pulse
Branchial
Radial
Femoral
Popliteal
Posterior tibial artery
Pedal (Dorsalis Pedis)
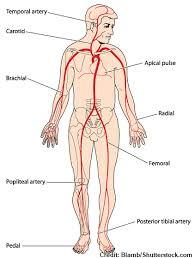
Where can one check the pulse in the body?
60-100 bpm
What is the average heart rate?
Enters from SVC/IVC
Right Atrium
Tricuspid Valve
Right Ventricle
Pulmonary Valve
Pulmonary Artery
Goes to the lungs for oxygenation
Pulmonary vein
Left atrium
Bicuspid Valve
Left ventricle
Aortic valve
Aorta
Travels to the entire body
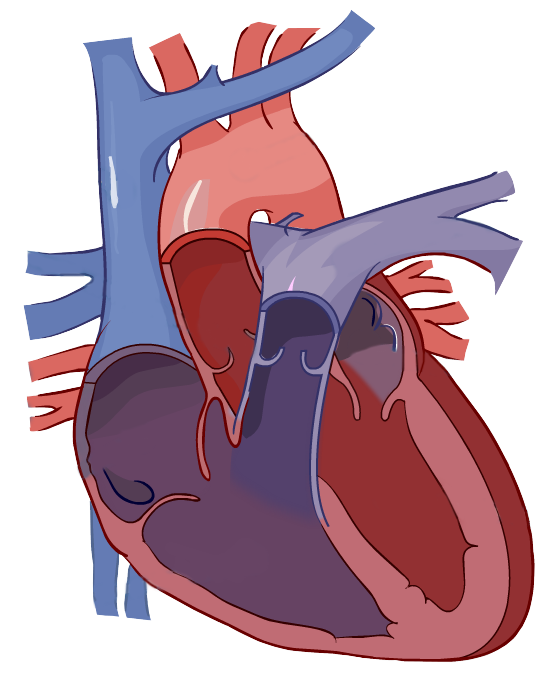
What is the journey of a drop of blood?
Heart attack
Circulation problem, typically a blockage in an artery
Damaged or Killed cardiac tissue is known as acute coronary syndrome
Cardiac Arrest
Electrical problem, typically caused by an irregular heartbeat (ventricular fibrillation)
The widowmaker
Left Anterior Descending artery (LAD)
Supplies the left chamber, meaning an issue is fatal as it interrupts blood flow to the entire body.
Nausea/vomiting
Jaw/neck/back/chest pain
Shortness of breath
What are the common symptoms of a heart attack?
Varies in Men vs. Women
Fainting, indigestion, and extreme fatigue
What are the symptoms of a heart attack in women?
Arteries
Veins
Capillaries
What is the peripheral circulatory system composed of?
Arteries
Branch into arterioles and then into capillaries.
Carry blood away from the heart (Oxygenated)
Capillaries
Allow for the exchange of oxygen and nutrients
Blood picks up waste products (co2)
Width of ONE RBC
Veins
Capillaries connect to form larger vessels into VENULES, which then merge into VEINS
Contain valves that prevent back-flow and helps blood return to the heart against the flow of gravity.
Soleus + gastrocnemius
What is the second heart of the body?
Helps get blood back to the heart
Blood Pressure
One of the vital signs and is made up of two numbers
Systole/Diastole
Systole
Pressure in the arteries when the heart contracts
High during intense movement
Diastole
Pressure in the arteries when the heart is resting
120/80
What is the normal blood pressure?
Red Blood Cells (Erythrocytes)
Transports oxygen from the lungs to tissues and CO2 from the body back to the lungs
Lifespan of 90-120 days (3-4 months)
Hermatocrit
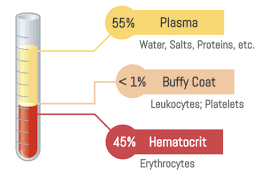
The percentage of blood made up of RBC (should be 45%)
Hemoglobin
A molecule made up of proteins and iron
Can bond and transport 4 oxygen molecules (oxygen or co2)
Erythropoietin
What hormone stimulates rbc production in the red bone marrow?
Oxygenated: Bright red
Deoxygenated: Deep Red
NO!
IS your blood ever blue?
Carbon Dioxide (CO2)
A by-product of metabolism and, once formed, transports to the lungs
Dissolves into blood plasma
Bonds to the hemoglobin molecule through partial pressure
Plasma (55%)
White blood cells and platelets (1%)
Red Blood Cells (45%)
What is the composition of blood?