6.1.3 Carboxylic acids and esters
1/47
There's no tags or description
Looks like no tags are added yet.
Name | Mastery | Learn | Test | Matching | Spaced |
|---|
No study sessions yet.
48 Terms
functional group of carboxylic acid
-cooh
how to name carboxylic acid
suffix oic acid and takes priority
if there is carboxylic aid and alcohol present how to name
use alcohol prefix carbonyl and oic acid as suffix
what takes prioirty when naming
carboxylic acid,aldehyde,ketone
solubility of carboxylic acids in water
they are soluble as form hydrogen bonds with water molecules
polarity of carboxylic acids
polar molecules since electrons are drawn from the carbon atoms in the carbonyl groups towards the more electronegative oxygen atoms
how does solubility of carboxylic acids change as get bigger
as they get bigger they get less soluble as length of non polar hydrocarbons chain length increases lowering interaction between carboxylic acid molecule with water molecule
how can carboxylic acids be prepared
oxidation of primary alcohols or aldehydes under reflux using acidified pottasium dichromate or hydrolysis of nitrile compounds,hydrolysis of esters
what type of acids are carboxylic acids
weak acids
what happens to carboxylic acids in water
partially dissociate into a carboxylate ion and a H+ ion
reaction of carboxylic acid to carboxylate ion and H+ ion
the reaction is reversible but equilibrium lies to left as most of molecules dont dissociate
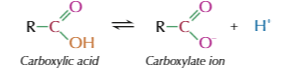
neutralisation reaction of carboxylic acids
react with bases in a neutralisation reaction to produce a salt
reaction of carboxylic acis with metal
salt and hydrogen
reaction of carboxylic acid with carbonates
forms salt,carbon dioxide and water
reaction of carboxylic acid with metal oxides/hydroides/base
form salt and water
what is the salt called from carboxlic acid
carboxylate salt
how is carboxylate salt shown
negative ion first then positive showing charge
functional group of esters
COO
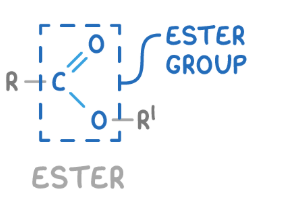
how to name ester
the alcohol becomes the prefix and the carboxylic acid gains the -oate suffix
name of ester for methanoic acdid and ethanol
ethyl methanoate
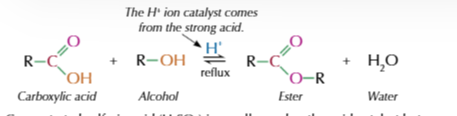
esterifcation reaction
ester formed by reacting an alcohol with a carboxylic acid in the presence of strong acid
conditions for esterification
-H+ catalyst - conc H2SO4
warm-reflux
example of esterification
as esterifcation is reversible what needs to be done
you need to seperate out product as it forms
how to seperate small esters compared to large
small are very volatile so just warm mixture and distil of the ester
large esters are harder to form so heat under feflux and use distillation to seperate
acid anhydrife
formed from removing a molecule of water from 2 carboxylic acid molecules
functional group of acid anhydride
O=C-O-C=O
example of acid anhydrides formed
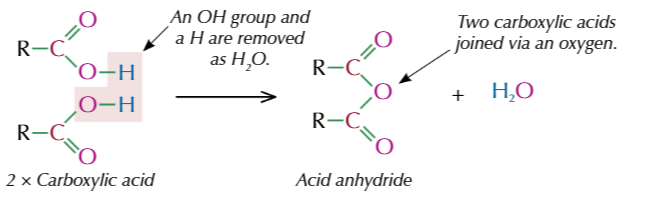
how to name acid anhydride
take away acid and add anhydride
esters formed from acid anhydride
acid anhydride react with alcohol to make esters
warm
example of formation of ester from acid anydride and alcohol
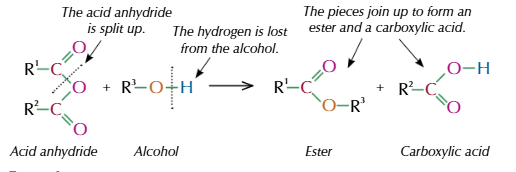
what is the other product of acid anydride and alcohol
carboxylic acid
how is carboxylic acid and ester seperated from acid anydride reaction
distillation
advantage of acid anhydride producing ester
non reversible
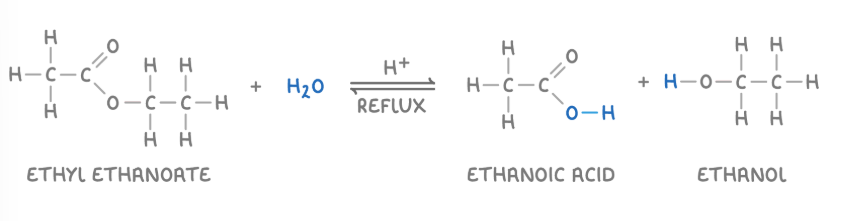
hydrolysis of ester with acid
the ester is heated under reflux with a dilute acid, such as HCl or H2SO4, to produce a carboxylic acid and an alcohol.
acid hydrolysis of ethyl ethanoate
hydrolysis of ester with alkali
When the ester is heated under reflux with a dilute base like NaOH, the products are a carboxylate salt and alcohol. This method is generally irreversible due to the stability of the carboxylate salt.
alkali hydroylsis of ethyl ethanoate

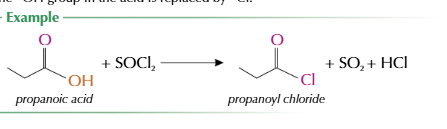
how are acyl chlorides fromed `
when carboxylic acid reaccts with sulfur dichloride oxide/thionly chloride SOCl2
oh group replaced by cl
formation of acyl chloride equation
functional group of acyl chloride
COCl
what do acyl chloride names end in
-oyl chloride
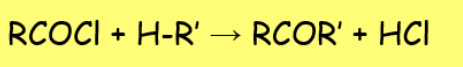
general acyl halide reactons
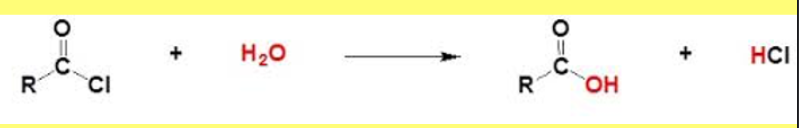
reaction of acyl chloride with watter
produces a carboxylic acid
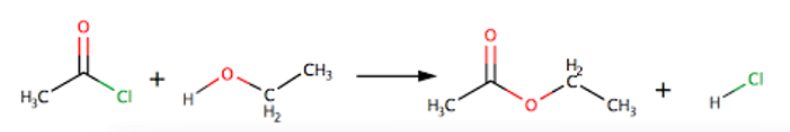
reaction of acyl chloride with alcohol
produces ester
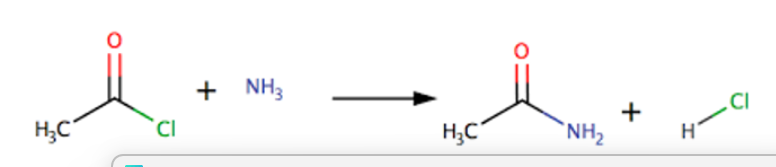
reaction of acyl chloride with ammonia
produces a primary amide
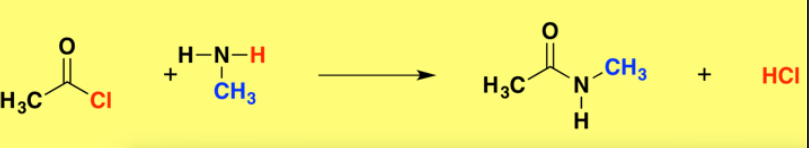
reaction of acyl chloride with amine
oroduces a secondary amide
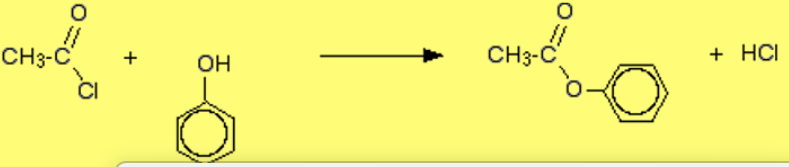
reaction of acyl chloride with phenol
produces ester