Edexcel A-level Geography - Tectonics
1/59
There's no tags or description
Looks like no tags are added yet.
Name | Mastery | Learn | Test | Matching | Spaced | Call with Kai |
|---|
No analytics yet
Send a link to your students to track their progress
60 Terms
Tectonic location
Most earthquakes and volcanoes occur near plate boundaries
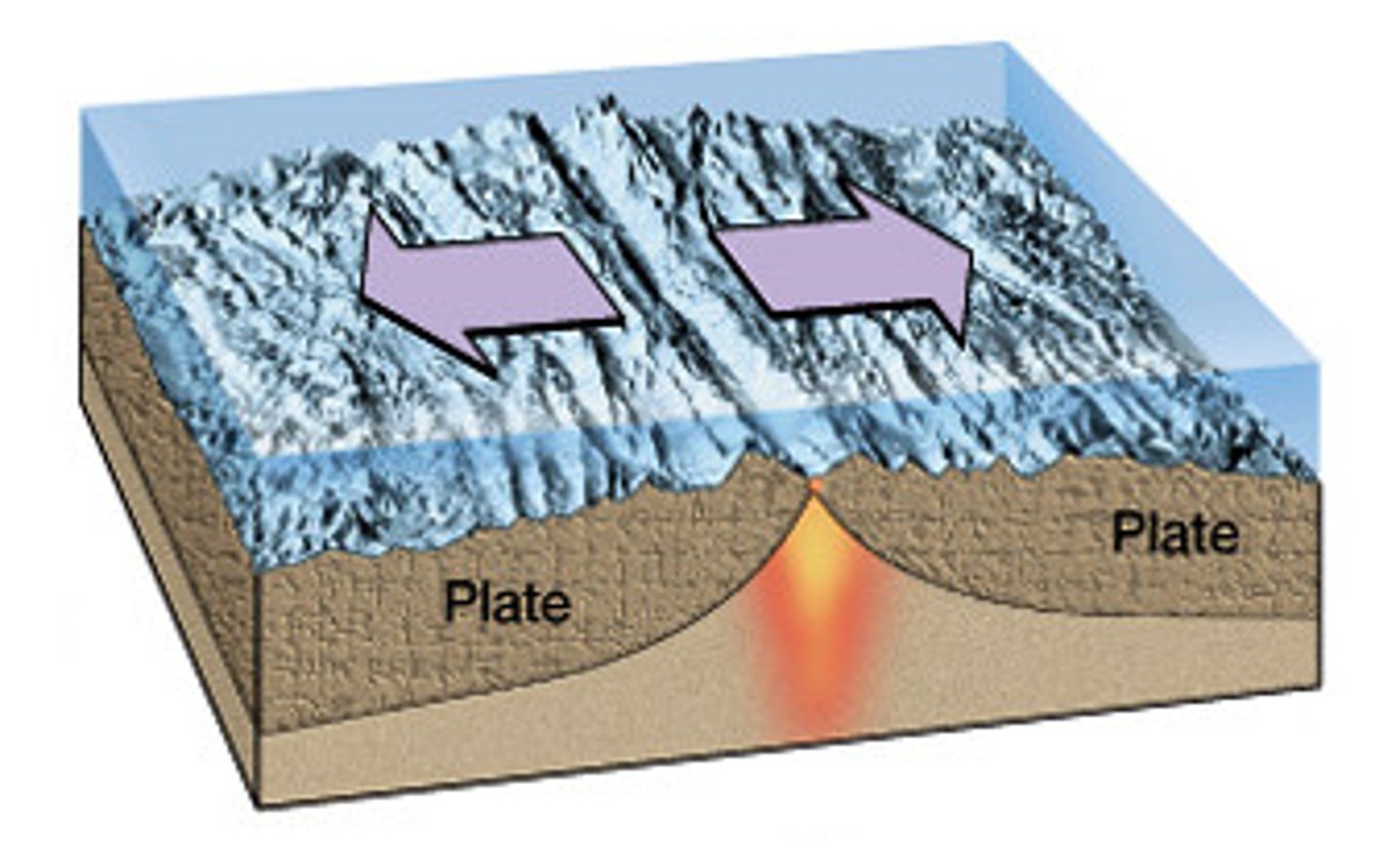
Divergent Plate Boundary
Cause effusive basaltic eruptions and rare shallow earthquakes (Mid-atlantic ridge - Iceland)
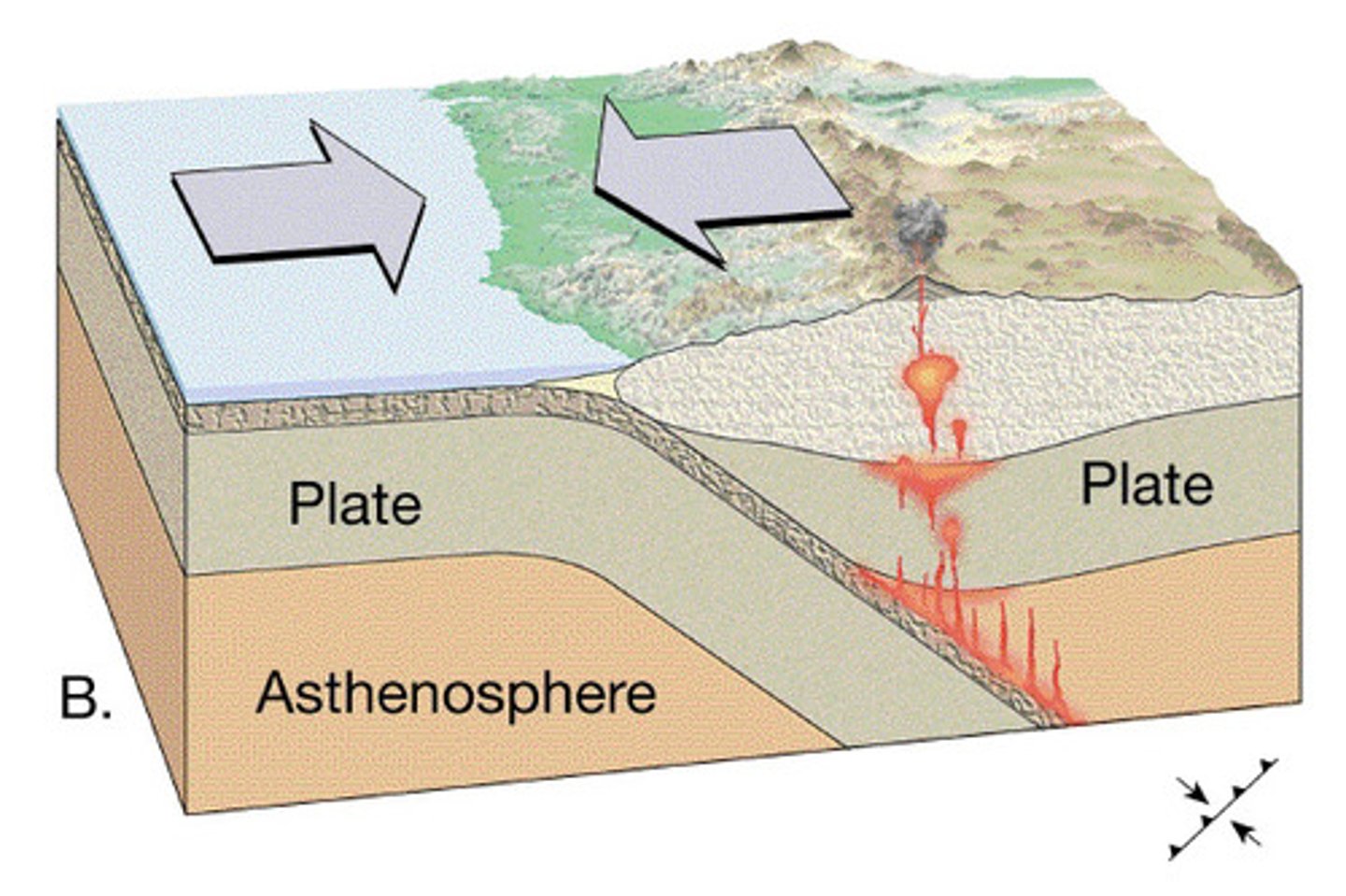
Convergent Plate Boundary
Cause violent andesitic eruptions and shallow, deep powerful earthquakes, volcanic cones, ocean trenches and mountains (Japan - Pacific plate moving NW under Okhotsk plate)
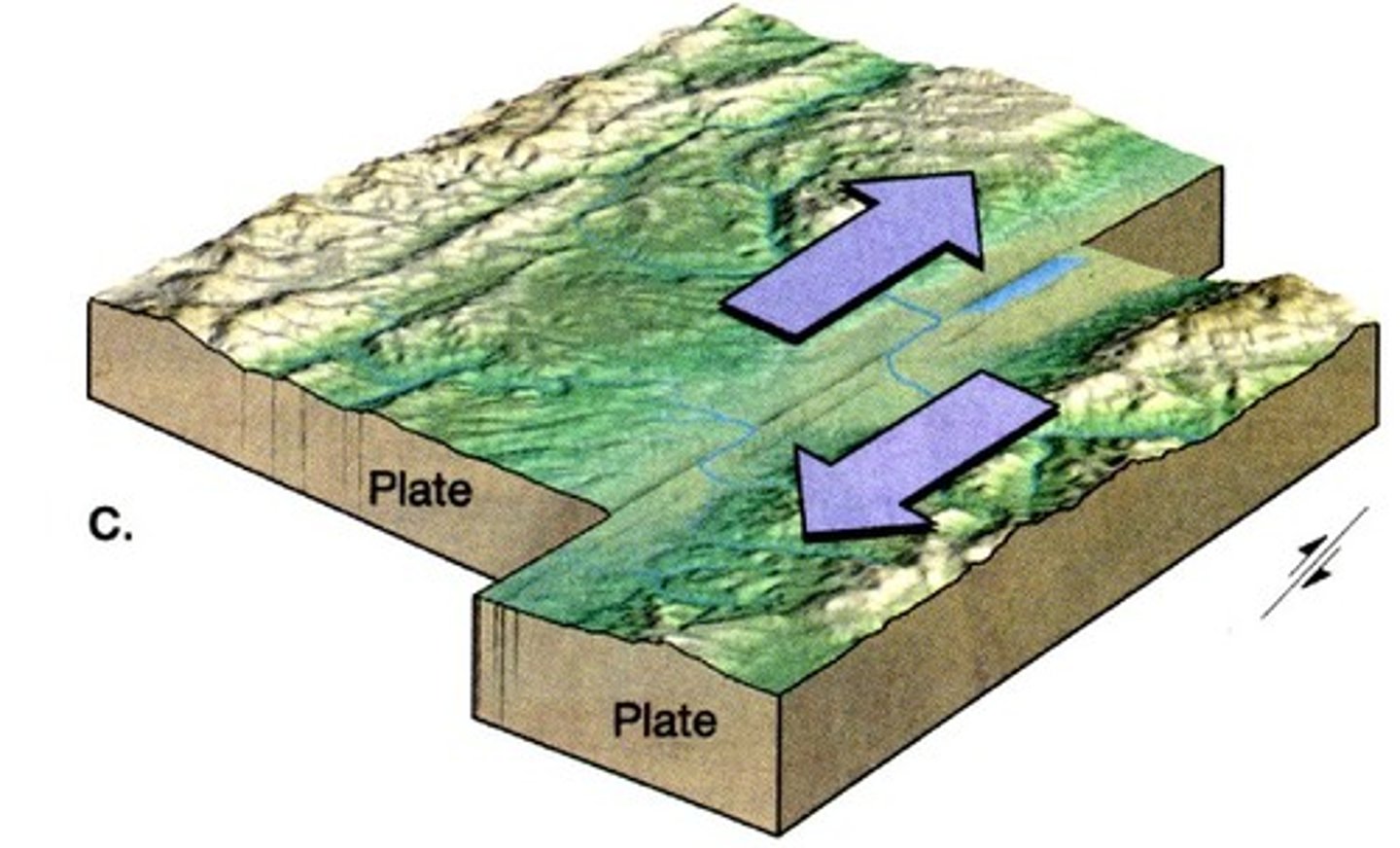
Conservative Plate Boundary
Cause powerful shallow earthquakes and diverted rivers along faults (San Andreas fault)
Infra-plate earthquakes
Caused by solid crust cracking over millions of years and primary collision at a plate boundary (New Madrid, Missouri)
Infra-plate volcanoes
Caused by hot spots from molten upwelling (Hawaii) or from mantle plume under crust (Cape Verde)
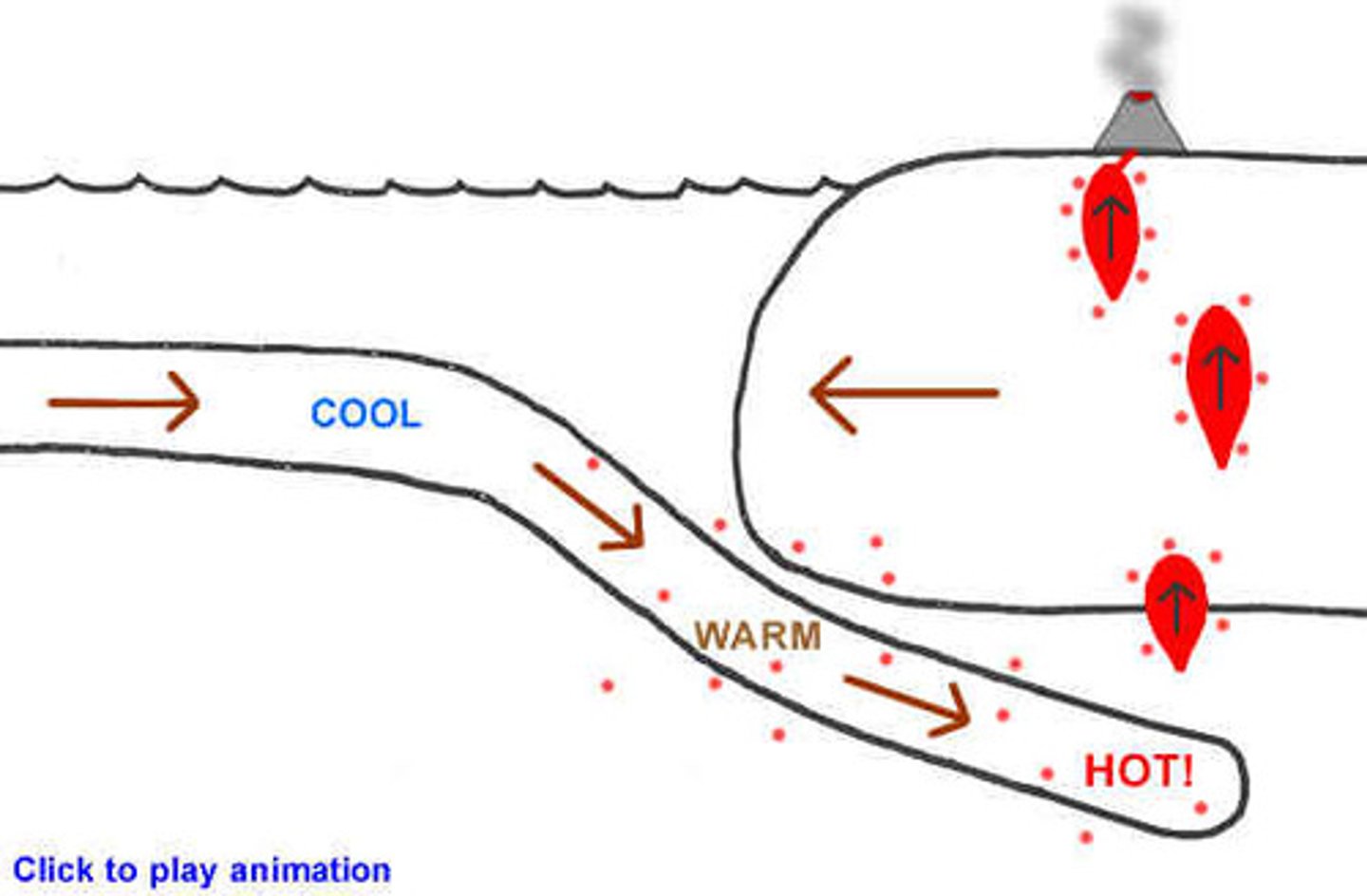
Convection currents
Caused by heat radiating outwards from core that occur due to mantle behaving like a viscous liquid
Earths structure
Core (Nickel/Iron), Mantle (870C solid and liquid), Crust (solid 1-75km)
Slab pull
When denser oceanic plates are subducted at cold downwellings by gravity
Ridge push
When magma rises at constructive margin and pushes the plates apart (Mid-atlantic ridge)
Paleomagnetism
Movement of plates apart identified by magnetic pattern caused by magnetic field reverse (every 4 million years). Mid-oceanic ridge contains iron that lines itself parallel to magnetic field and 'sets' after it cools, permanently marking magnetic field
Constructive processes
Activity = shallow, low magnitude earthquakes and effusive basaltic eruptions
Create = Rift valley, M.O.R, volcanic isle and transform faults
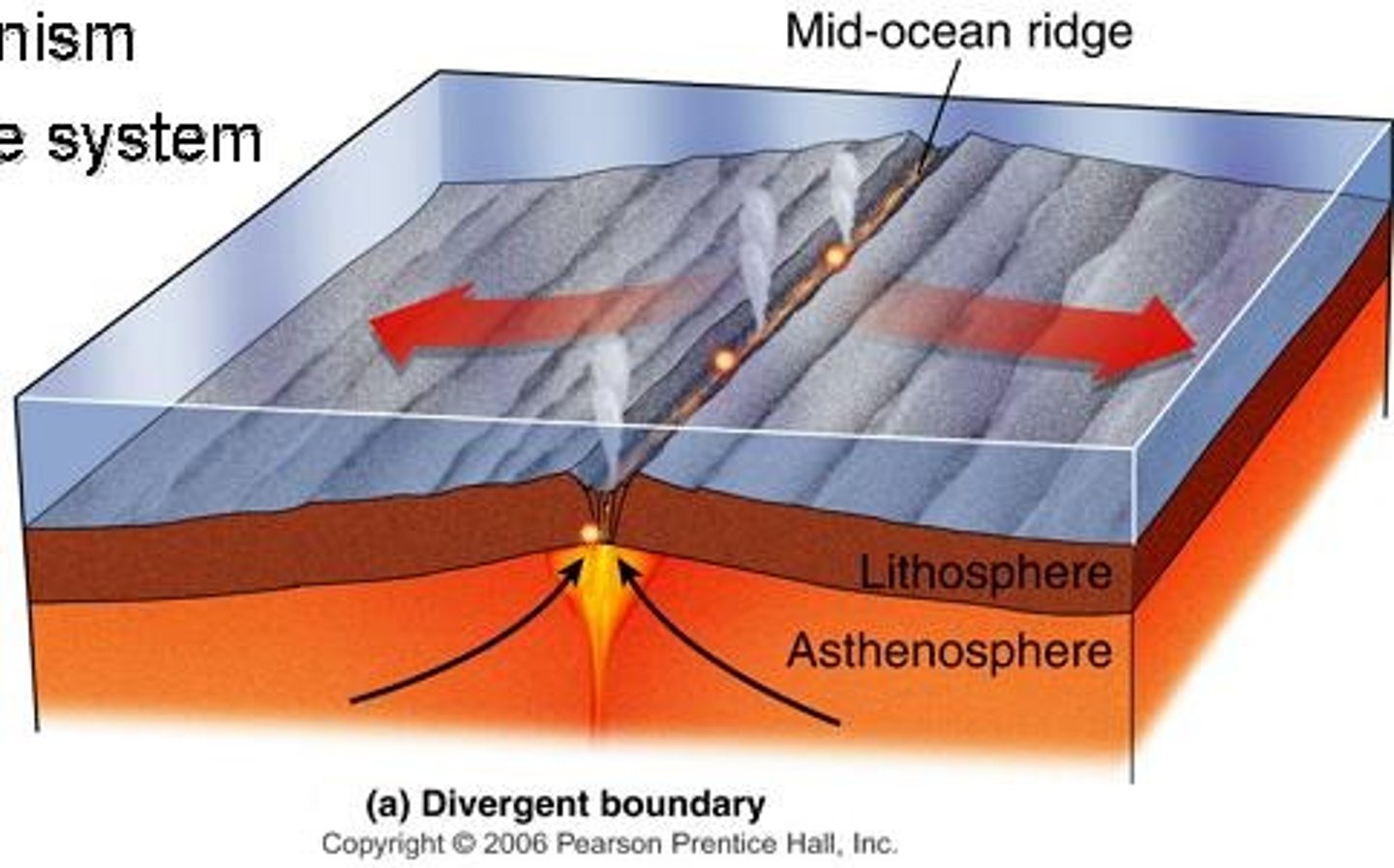
Destructive processes
Activity = shallow to 700km, high magnitude earthquakes (ocean-ocean plates)/ moderate magnitude (ocean-continent), explosive eruptions
Create = ocean trench, fold mountains (ocean-cont') or volcanic isle and ocean trench (ocean-ocean)
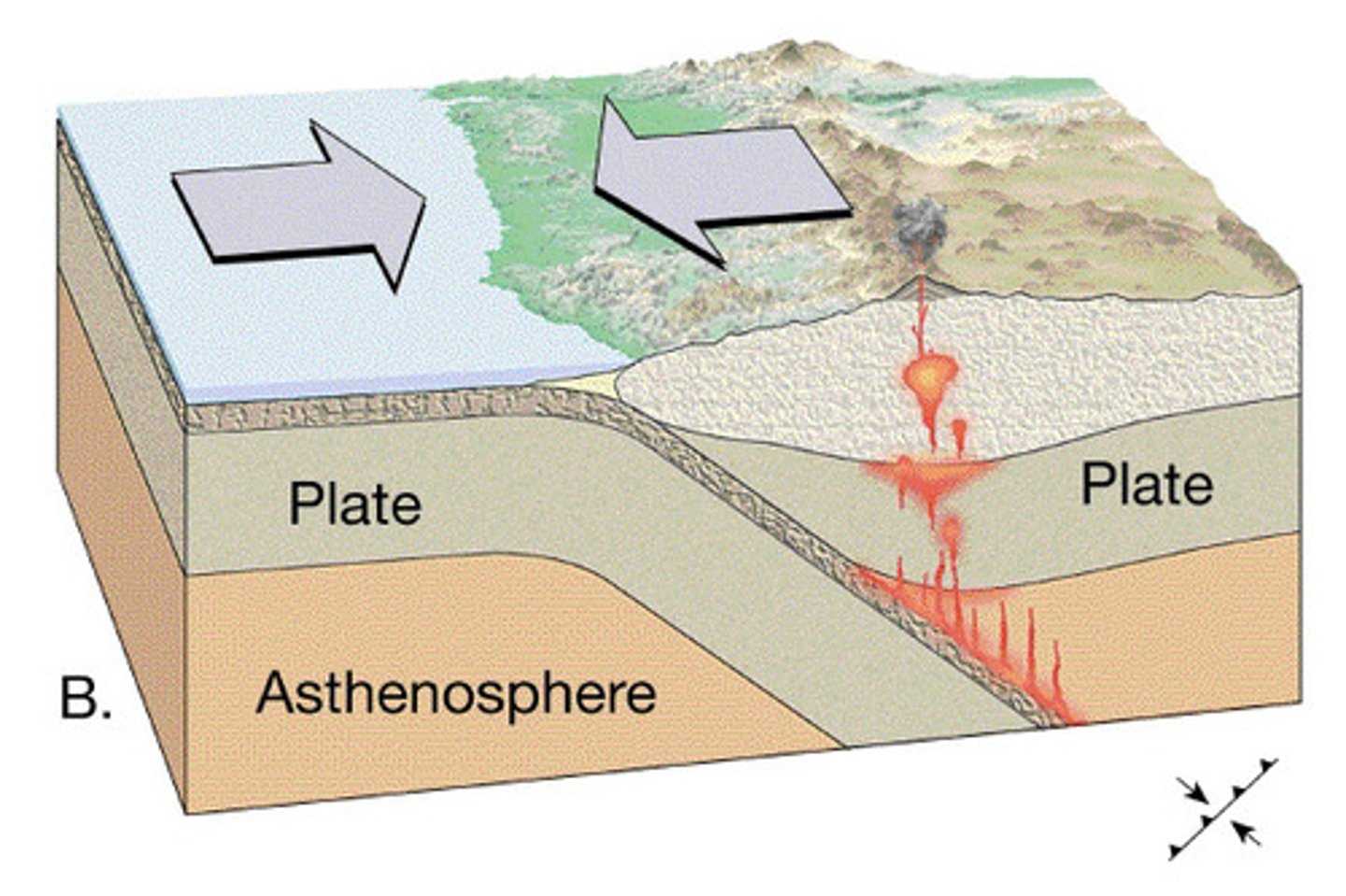
Transform processes
Activity = shallow, moderate magnitude earthquakes with usually no volcanic activity
Create = ridges and scars on the surface
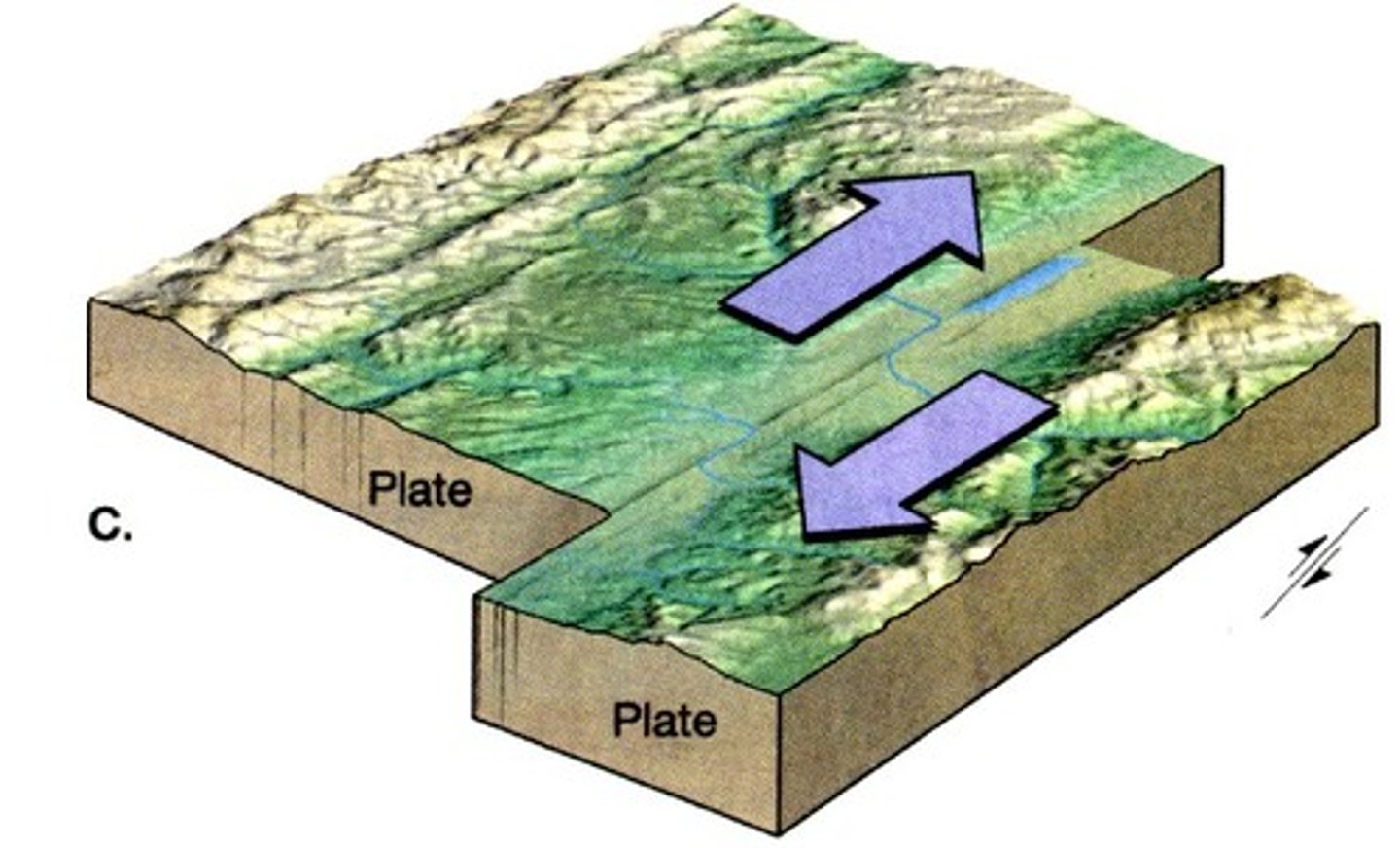
Collision processes
Activity = shallow to middle, moderate magnitude earthquakes with usually no volcanic activity
Create = plateaus and fold mountains (Himalayas)
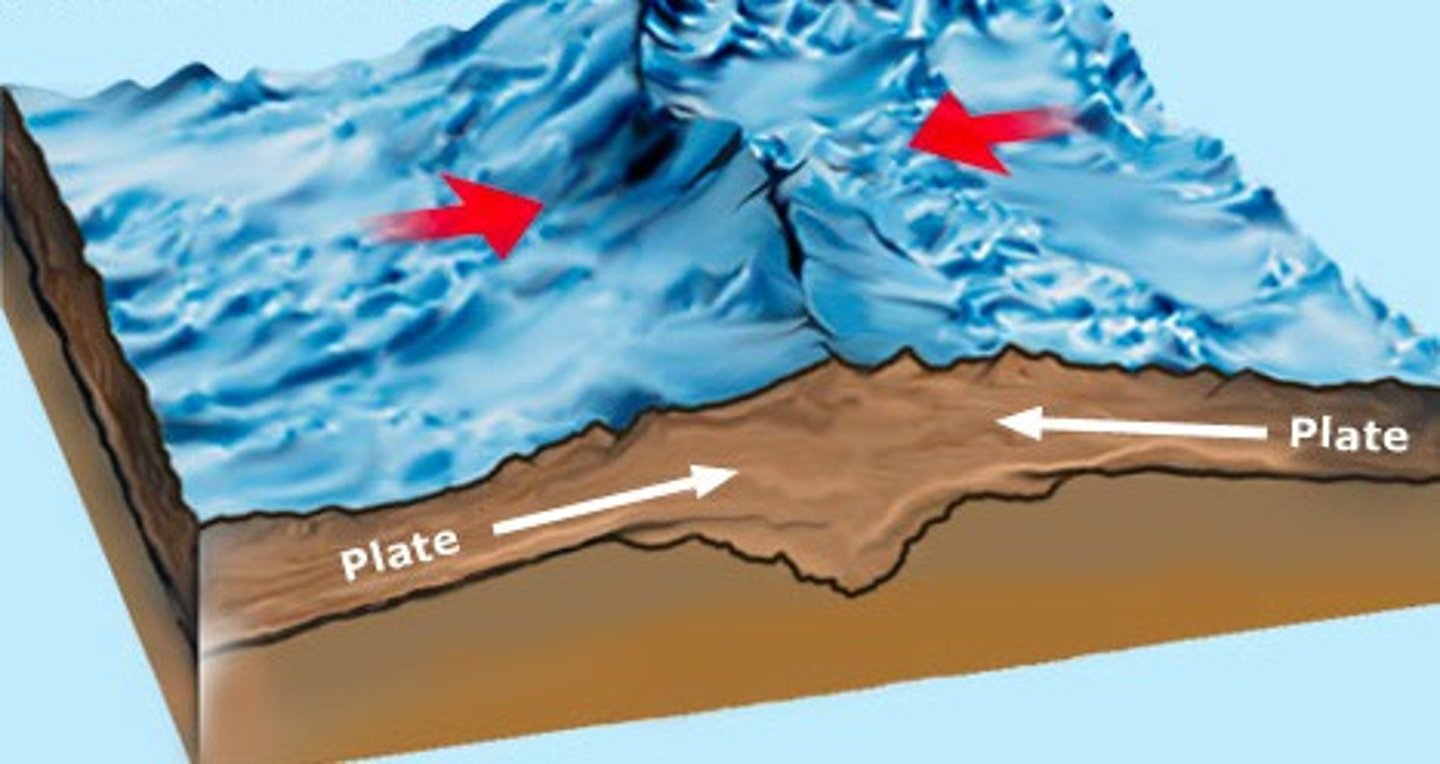
Magnitude factors
Seismic gap (time since last earthquake)
Depth of focus (0-75km)
Types of movement (subduction, collision, etc.)
Primary waves
Arrives first and fast, moves through rock and fluids whilst pushing and pulling (compresses) in travel
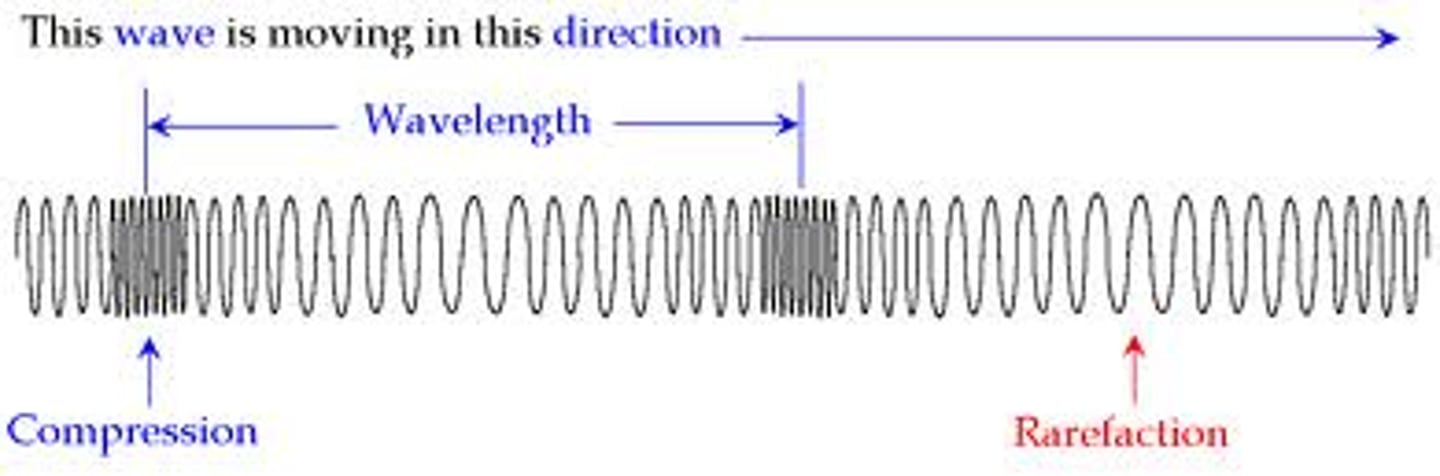
Secondary waves
Arrives second and slower than P waves, only move through rock in up and down movement
Love waves
Arrives last but moves fastest (only through crust surface), most damaging
Liquefaction
Earthquake secondary hazard; shaking sorts sediment that makes it act as a fluid
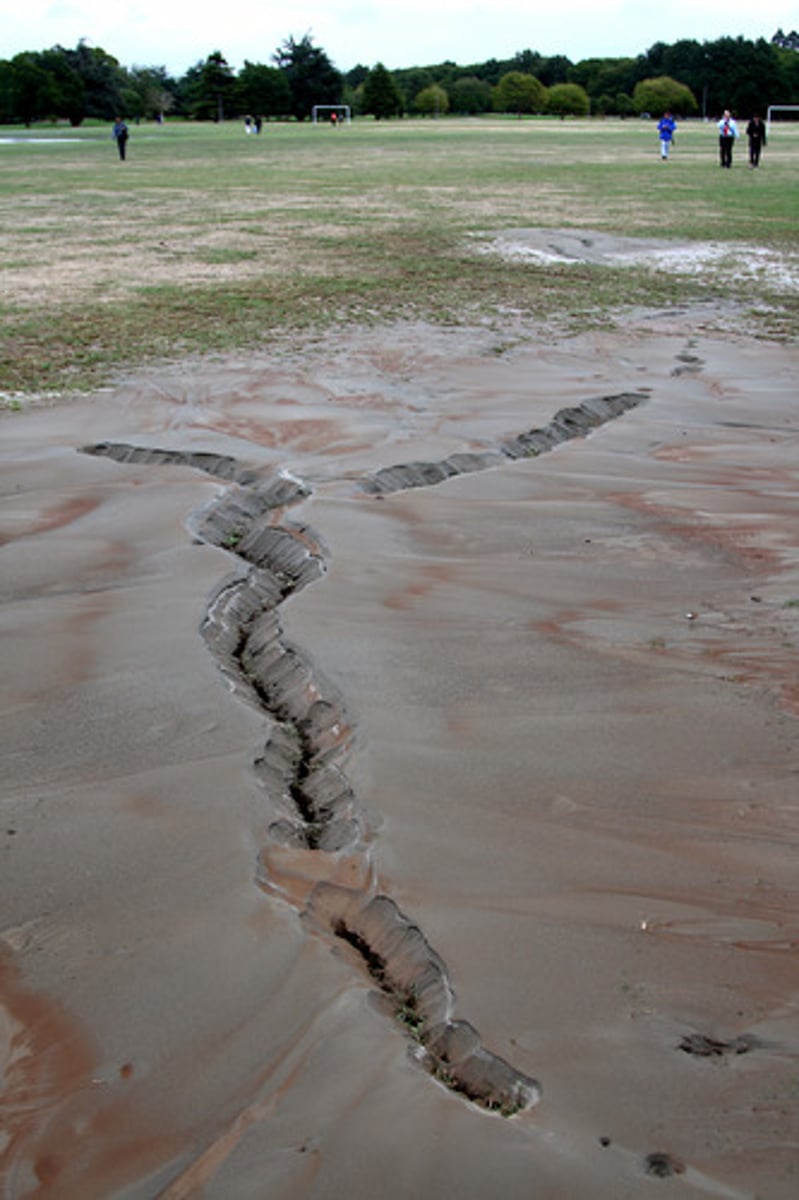

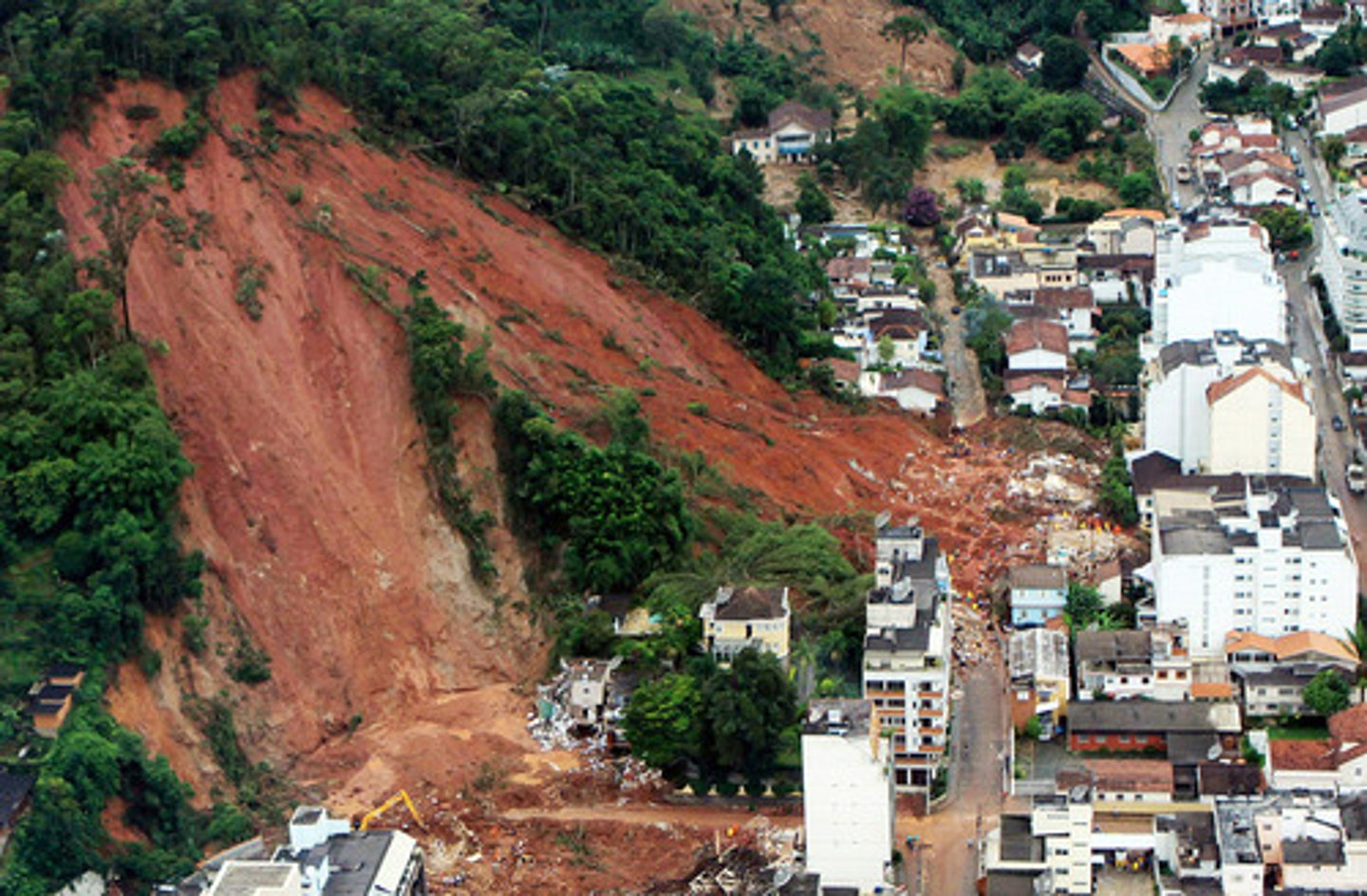
Landslides
Earthquake secondary hazard; mass material moves downslope (Kashmir 2005)

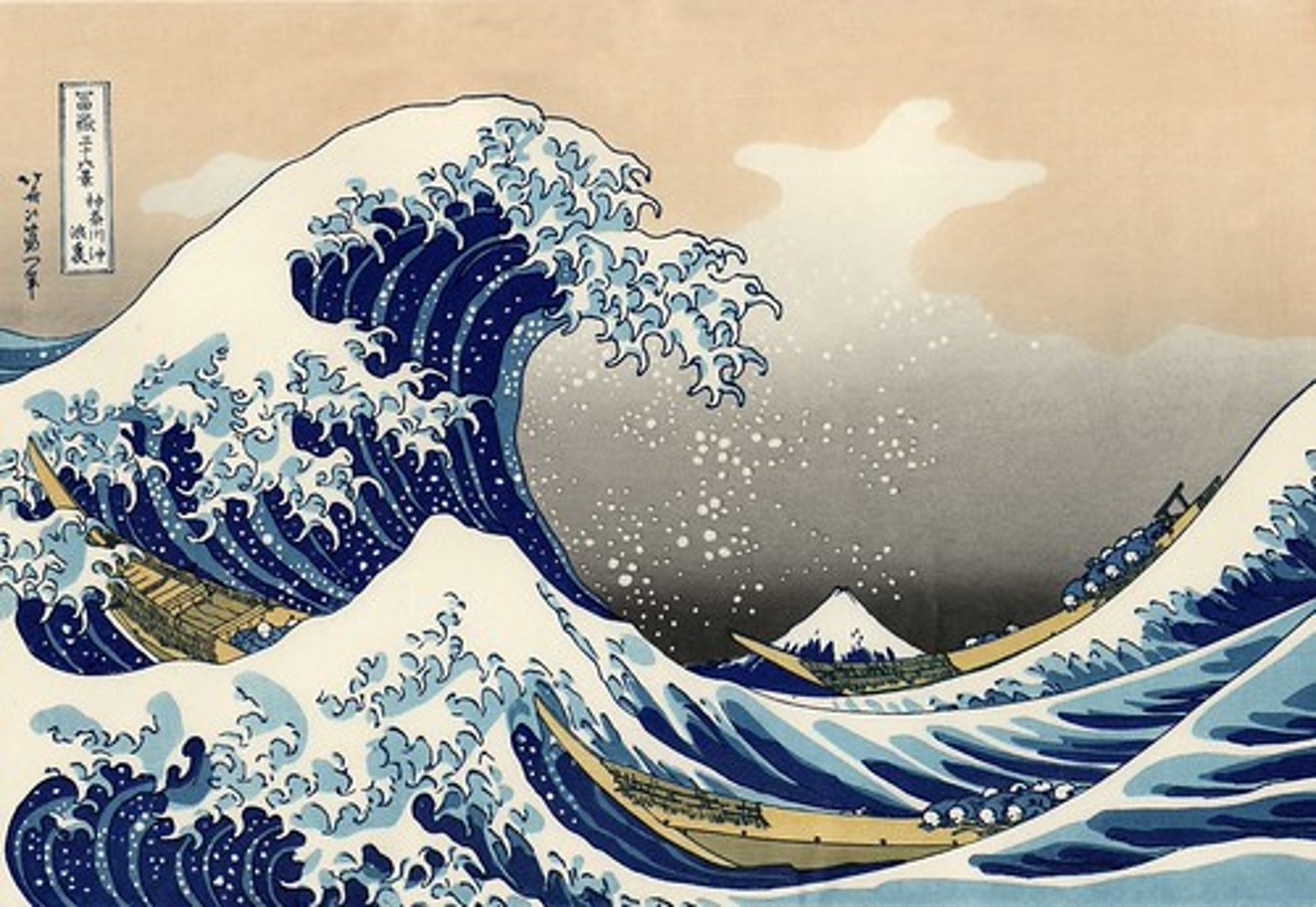
Tsunamis
Earthquake secondary hazard; water column displacement by plate thrust/volcano

Volcanic primary hazards
Lava flows, gas emissions, ash and pyroclastic flows
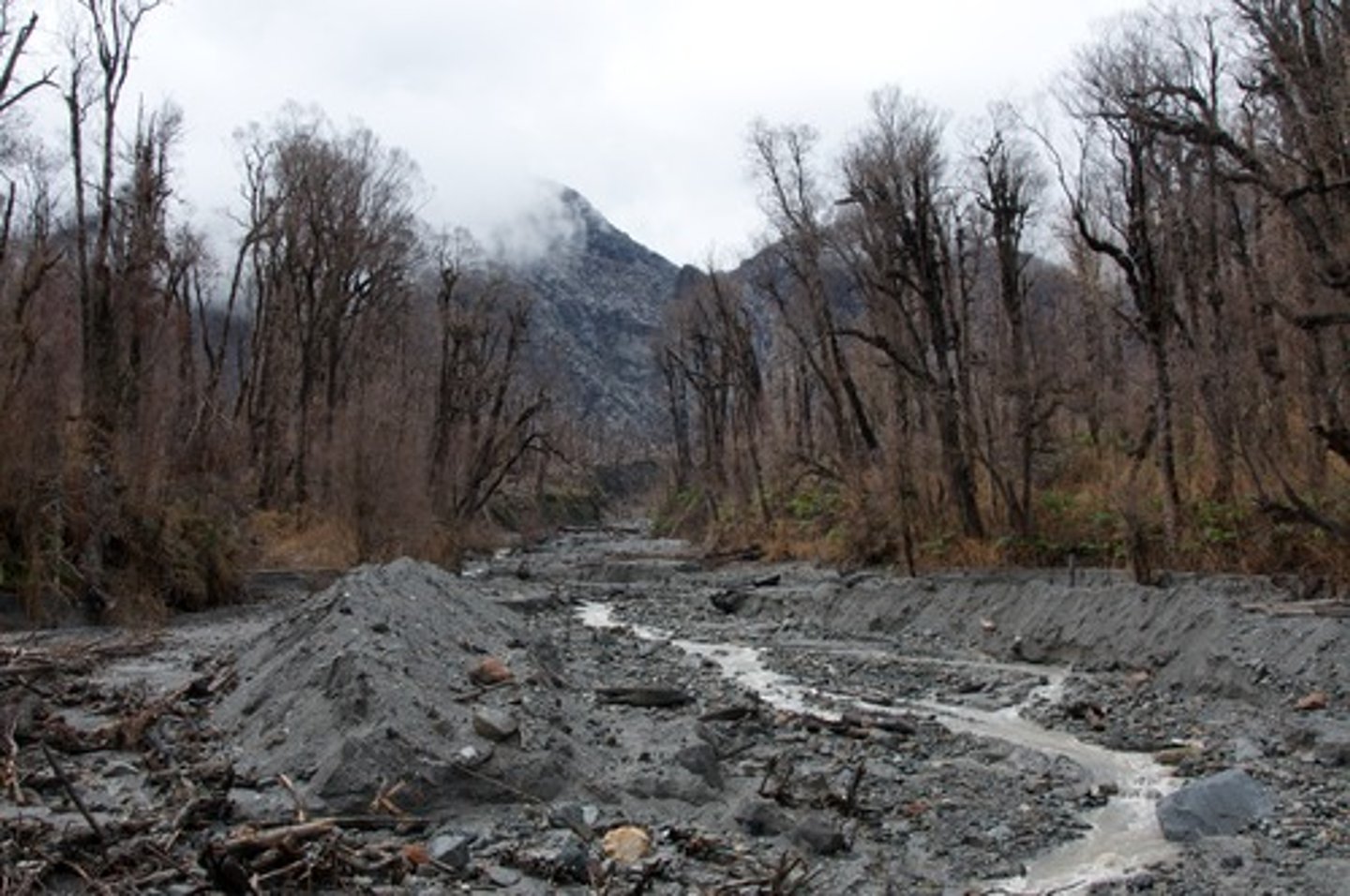
Lahars
Volcanic secondary hazard; mudflows

Jokulhlaups
Volcanic secondary hazard; meltwater floods
Basaltic lava
Hottest (1000-1200C), low silica/gas content, low viscosity (runny), gentle/effusive
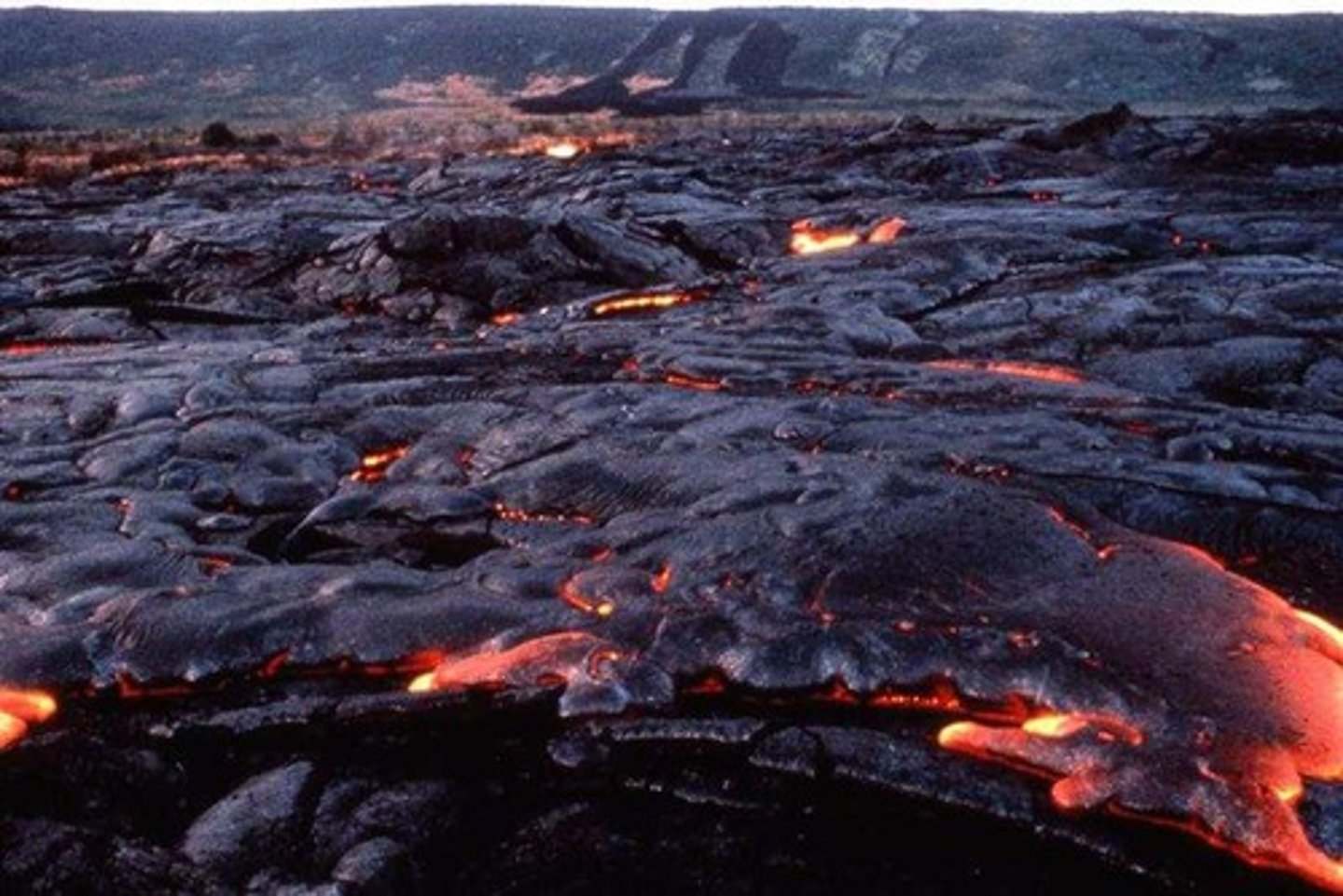

Andesitic lava
Medium heat (800-1000C), intermediate silica/gas content, medium viscosity, violent
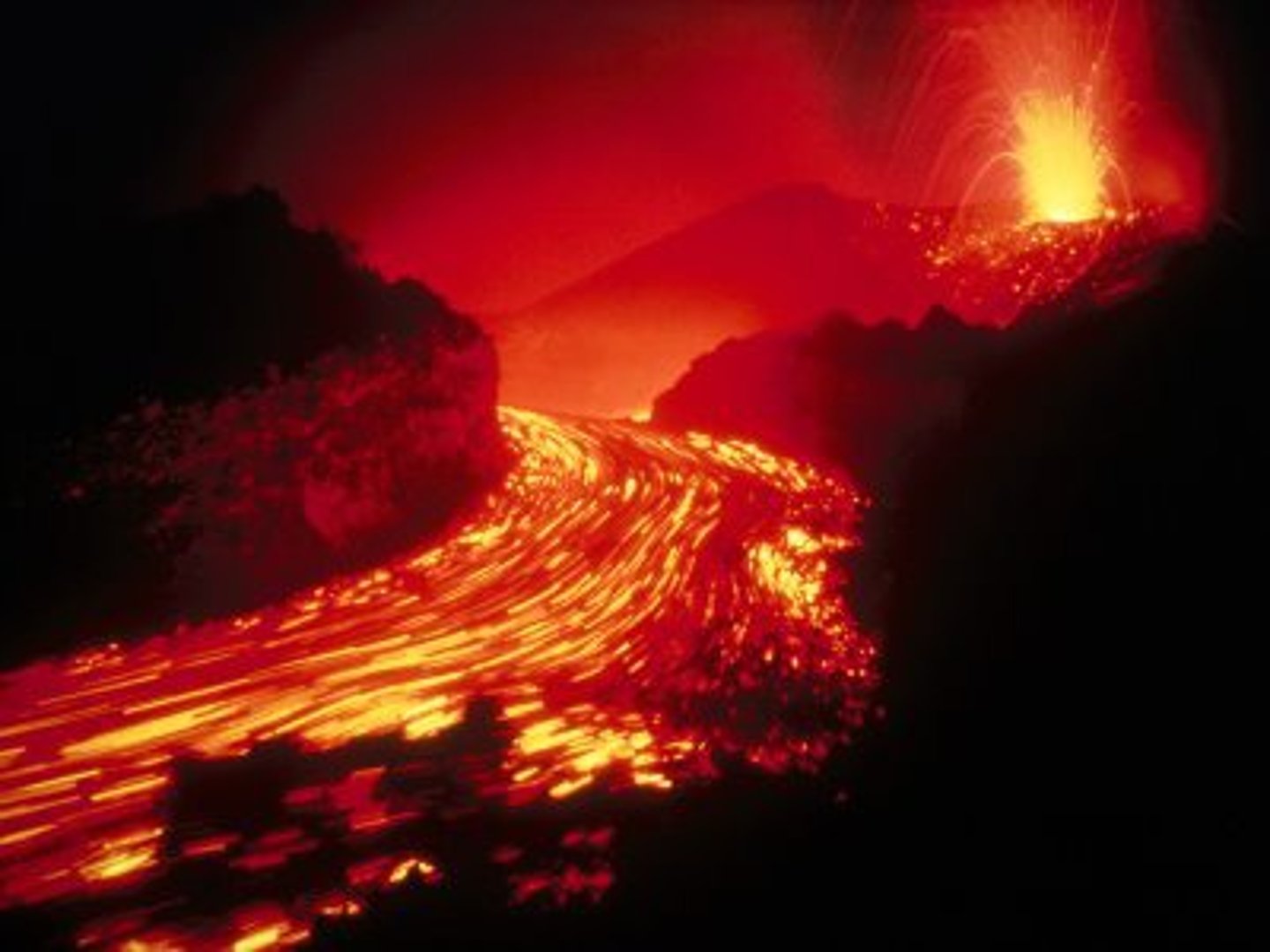

Rhyolitic lava
Coolest (650-800C), high silica/gas content, high viscosity, very violent
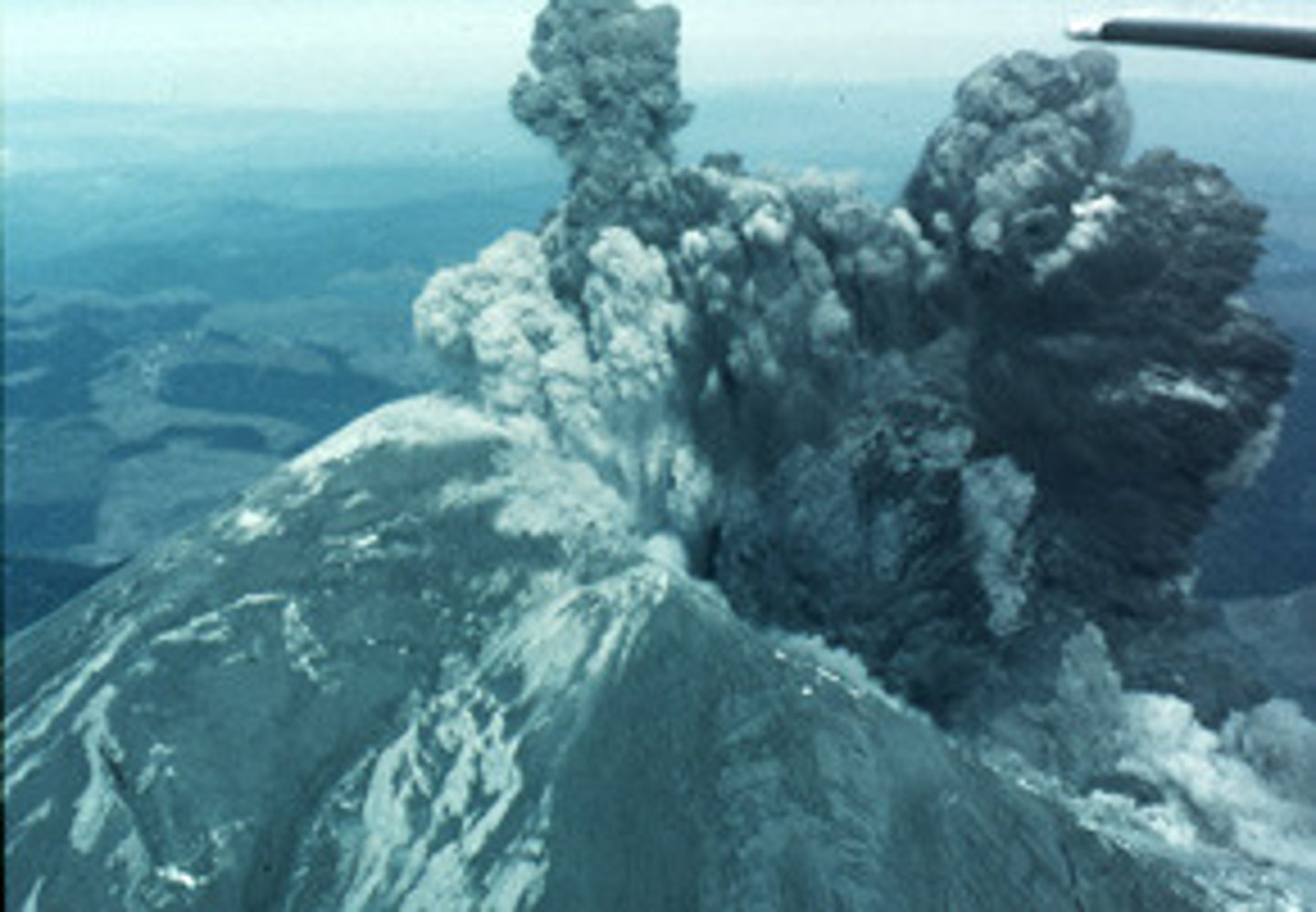

Hazard
Tectonic event with potential to threaten life and property
Disaster
When hazard causes significant impact (more than 10 deaths and over 100 affected)
Vulnerability
Ability to anticipate, cope, resist and recover
Resilience
Ability of a community to resist the impacts of a hazard by adapting and recovering
Factors affecting ability to cope
Location, resilience, preparedness, tech, knowledge of threat, community adaptation/ability to react and governance
Hazard risk equation
Risk = hazard x exposure x vulnerability / manageability (resilience)
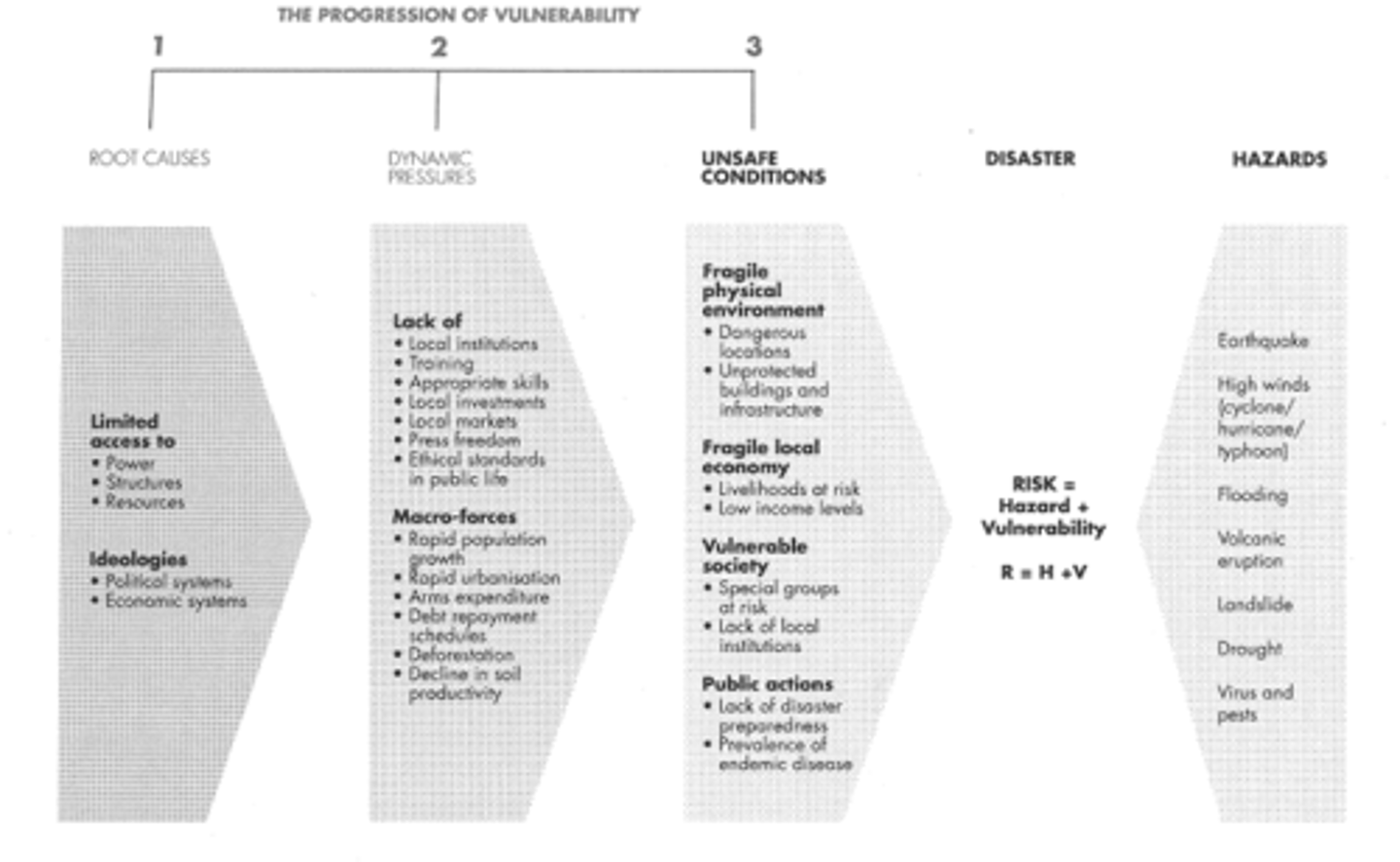
Pressure and Release Model
New Zealand 2010
Event = 7.1 magnitude, 10km focus on Aus.- Pac plate boundary
Responses = 1 death and 2 major injuries, 16 operational ambulances, Hospital used emergency generators, 90% power back on by 6pm
Vulnerability/resilience = 14.3% elderly, GDP/C $30,500, reinforced houses, water boiled before use, $20 million spent on soil compaction 2005
Haiti 2010
Event = 7 magnitude, 13km focus on Carib - N.A plate boundary
Responses = 230,000 dead, all hospitals/services destroyed, roads damaged
Vulnerability/resilience = 34% 0-14 years, GDP/C $674, no reinforced buildings, high levels of poverty/disease, poor governance
Volcanic Explosivity Index
Measure explosiveness (1 = small and gentle ==> 8 = colossal)
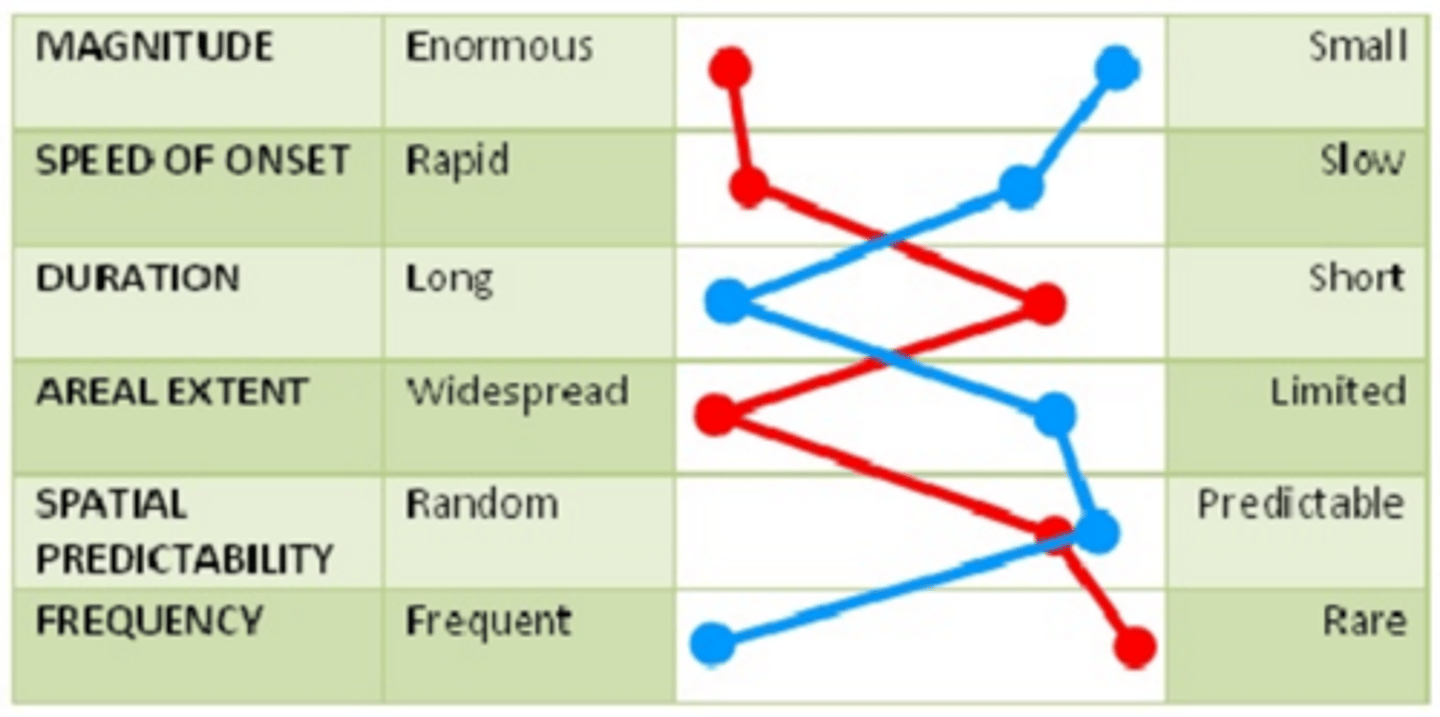
Hazard Profiling
Resilience/vulnerability
Education, housing, healthcare, income, food, utilities/governance, age and disability
Haiti poor governance
61% school attendance
7% HIV
Poor sanitation (Diarrhoea)
90% capital buildings collapsed
Heimaey, Iceland 1973
Evacuation = 5,000 evacuated under 6 hours due to contingency plan
Dealt by = Lava stopped by spraying seawater, ash clearance from roofs, $2 million gov't funds, rebuilt property and monitoring seismometers
Bam, Iran 2003
Event = magnitude 6.6 at 5.52am, 7km focus
Response = 3 hospitals destroyed/services struggled and 70% houses gone
Governance = 1989 building code ignored as not enforced, lack of specialised medical training
Disaster trends since 1960
Steep exponential rise until decline 2000, most likely due to increased resilience and reduced vulnerability by government
Accuracy = most disasters recorded due to better global reporting network, ancient records less reliable, location may be remote/not reported
Spatial variation = Asia experienced far more disasters 2004-2013 (population)
Tectonic mega-disaster
Large scale by area or socio-economic impact - serious problems for management (may need international support)
High impact low probability event
Impossible to predict but very likely to occur over long time scales - require rapid global response and less resilience from globalisation
Multiple hazard zone
Philippines 2013, 2018:
Hazards = Earthquakes (7.2 2013), Typhoons (Haiyan 2013) and Volcanoes (Mayon 2018)
Resilience = stilt houses adapted for floods/storms but broken by earthquakes, buildings more resilient in capital
Vulnerability = hot and humid climate makes typhoons occur regularly, on active Philippine and Sunda plates, dense 102 million people, 74% vulnerable to multiple hazards, 18 active volcanoes
Tiltmeters
Earthquake indicator; react to change in ground levels
Gas measure
Earthquake indicator; radon gas can be released before 'quake
Parks Model
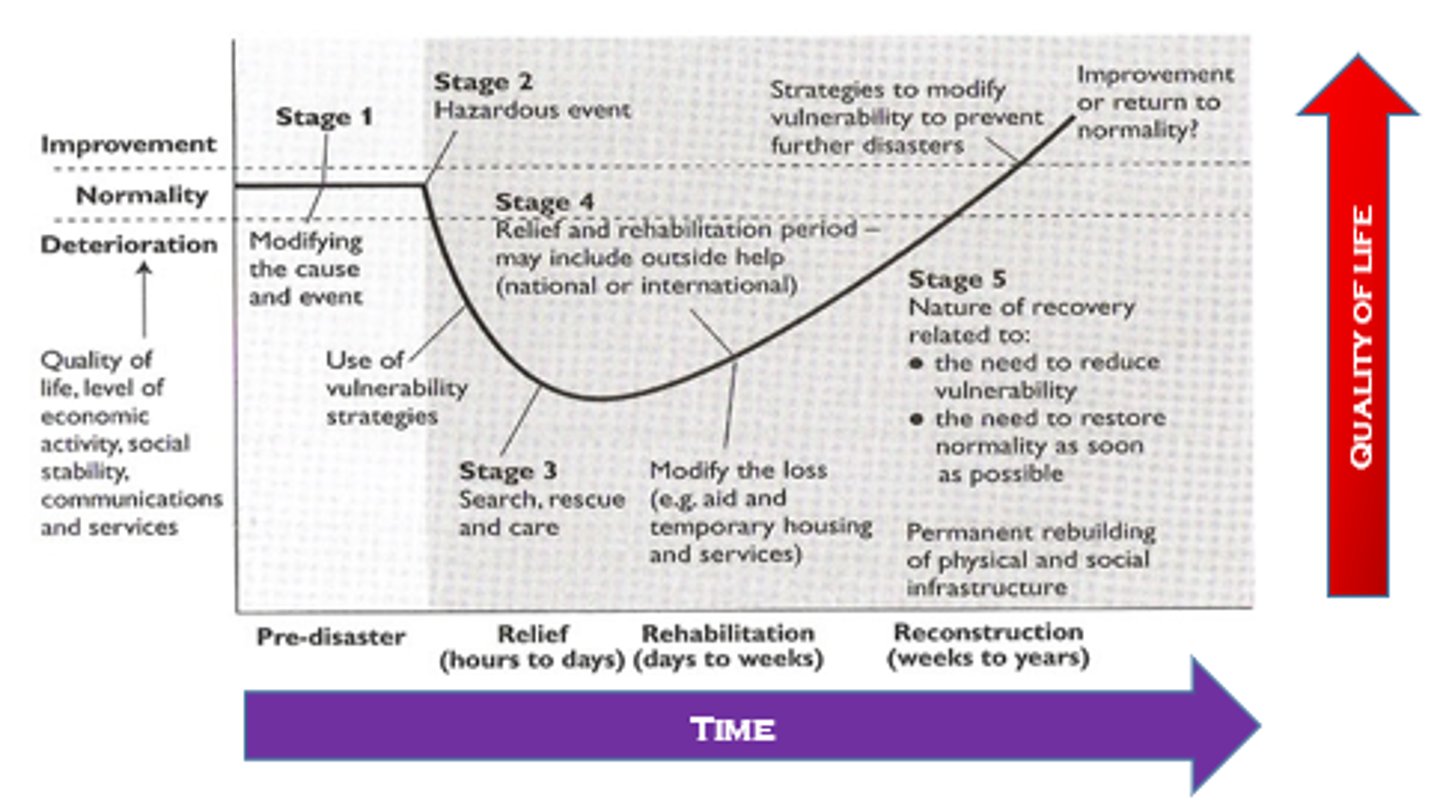
Mitigation
Land use zoning (California), Volcanic use zoning (New Zealand), Lava walls/channels
Preparedness
Modify vulnerability (monitoring systems, diverse economy, increase food production)
Response
After event; evacuation, immediate assistance and asses damage (by charity, services and insurers)
Recovery
After event; restoration of services, rebuilding infrastructure and socio-economic recovery
Micro management strategy
Strengthen individual buildings
Macro management strategy
Large scale protective measures
Hazard resistant engineering
Reinforced concrete and steel crossbracing
Internal Pendulum to decrease displacement
Base isolation, shock absorbers
Retrofitting old buildings

Cheap engineering
Lighter materials and single story (dome)
Sloped roofs to prevent ash build-up
Elevated buildings
Insurers
Protect economic livelihoods (compulsory in Turkey)
Emergency services
Reduce the loss after a tectonic event