Gene transfer and homologous recombination in bacteria
0.0(0)
Card Sorting
1/27
Earn XP
Description and Tags
Chap 6
Last updated 2:00 PM on 5/7/23
Name | Mastery | Learn | Test | Matching | Spaced | Call with Kai |
|---|
No analytics yet
Send a link to your students to track their progress
28 Terms
1
New cards
gene flow promotes --- and ---
**genetic evolution and increases the microbial diversity.**

2
New cards
**A foreign DNA entry in bacteria must be followed by a specific genetic event to be acquired.**
What are the 2 types of genetic events ?
Substitution (homologous recombination )
Addition (plasmid integration)
Addition (plasmid integration)
3
New cards
If DNA is not auto replicative or integrated, it will be diluted and lost among the bacterial population.
True or FALSE
TRUE
4
New cards
Homologous recombination is when a ==__**------**__== event occurs
==**double cross over →**== **Substituted or allelic exchange → DNA transmitted to the bacterial daughters**
5
New cards
A pair number of crossing-overs produces a ---- and ---- recombinant
circular and viable
6
New cards
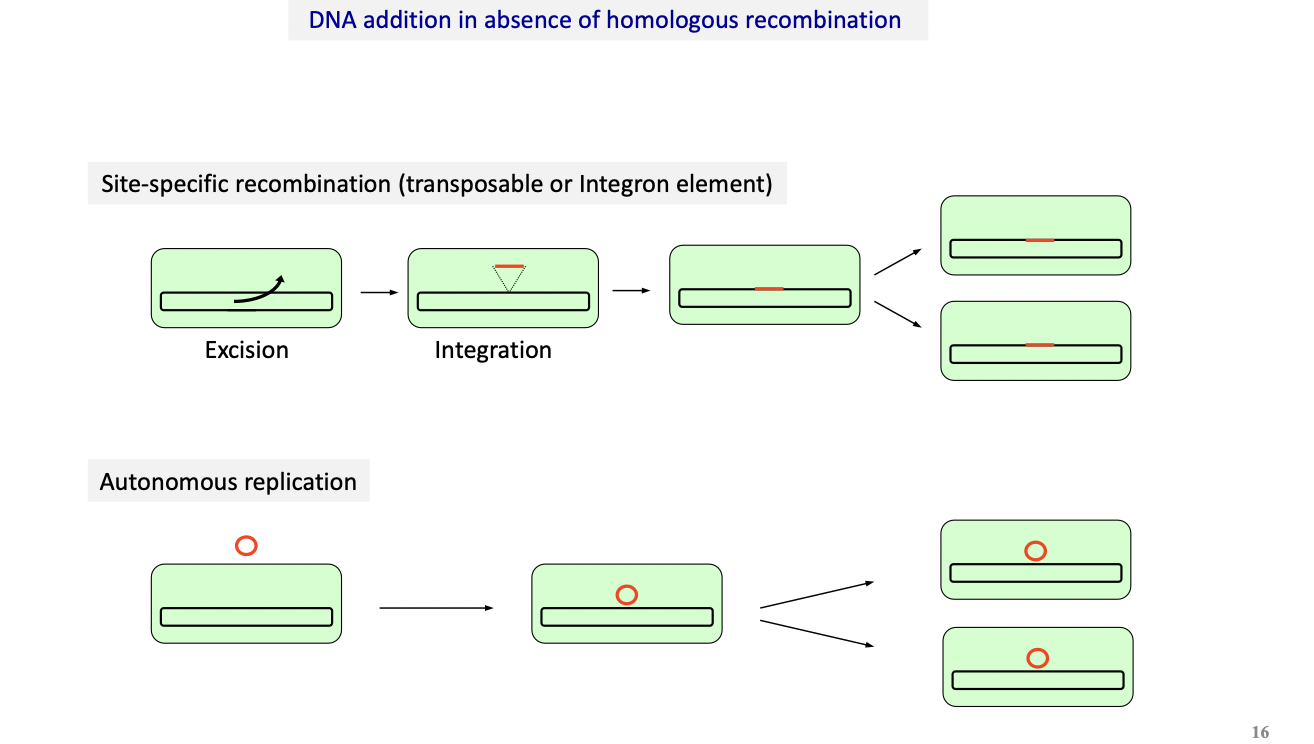
What are the different types of acquisition through a genetic element in the absence of homologous recombination ?
Site-specific recombination (Integron or transposable)
Autonomous replication
Autonomous replication
7
New cards
What is a transposon ?
DNA sequences able to __**change their location in the genome.**__
Not replicative
Have a transposase responsible for recombination .
8
New cards
Transposon may bring some new genes (resistance and virulence) and modify gene expression
True or False
True or False
True
9
New cards
Transposition implies the presence of --- and --- sequences named IR (repeated inversed sequences) Wha
Inverted and repeated
10
New cards
What do transposons carry usually?
RESISTANCE genes
11
New cards
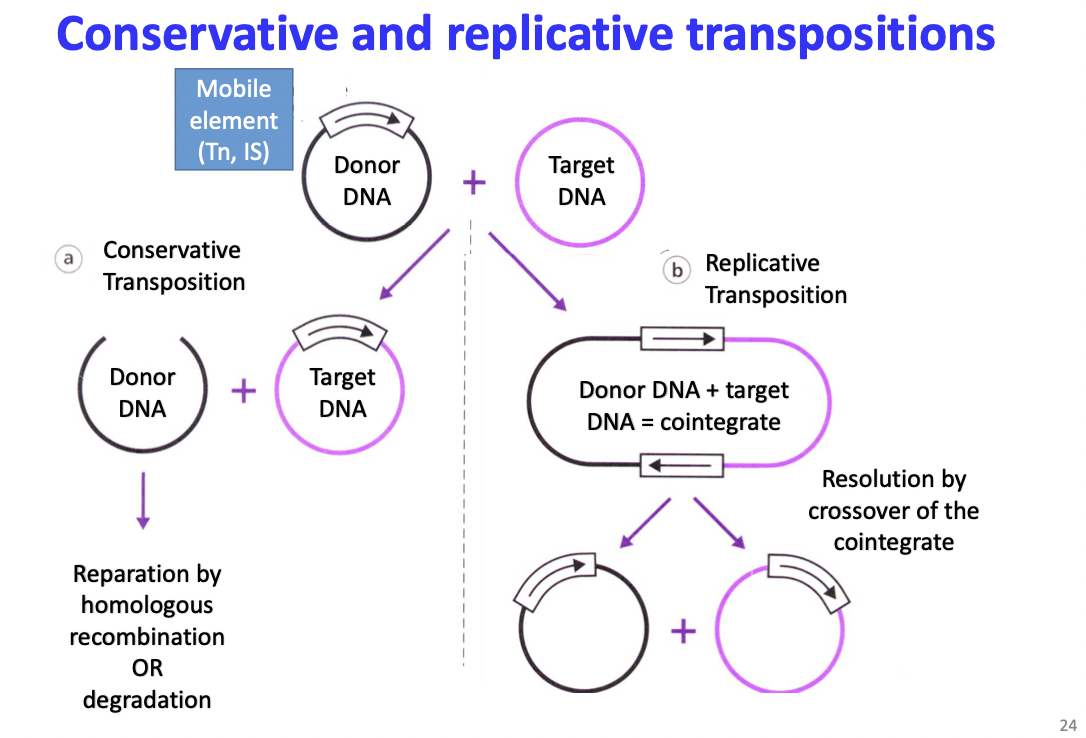
Describe the conservative and replicative transpositions
On the figure
Co-integrate → resolution by crossover of the co-integrate
Co-integrate → resolution by crossover of the co-integrate
12
New cards
What are the 3 different types of transposable elements?
* Composite
* Unitary
* Conjugative → able to transfer from b to another by conjugation between several species (BIG)
* Unitary
* Conjugative → able to transfer from b to another by conjugation between several species (BIG)
13
New cards
What is an integron?
Gene capture and expression system __**under cassettes form.**__
Integrons are __**not mobiles**__ by themselves
__**Found on transposons or plasmids**__
14
New cards
What is a cassettes ?
__**Small mobile elements**__
__**Non-replicatives**__, but able to be __**integrated or excised**__ by a specific recombination mechanism made by an __**integrase**__.
15
New cards
Do cassets contain functional gene?
Cassettes do not encode a functional gene of the integron.
16
New cards
A functional platform of integron is constituted by :
▪ *intI* (5’region) encode an __**integrase**__
▪ *attI, a* __**recombination specific site**__
▪ Pc, a __**strong promotor**__
17
New cards
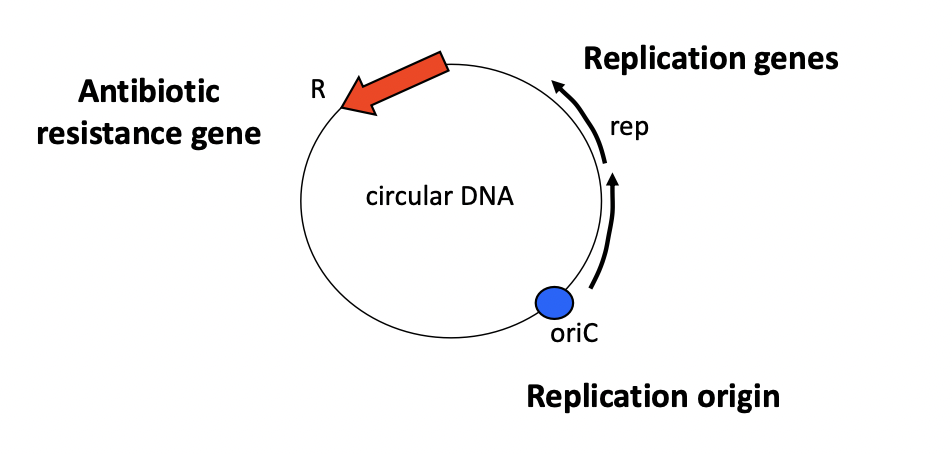
What is a plasmid?
**is a DNA molecule**:
\- Distinct from the chromosomal DNA
\- Non-essential to the cell survive
\- Able to replicate in an autonomous manner
Circular (most common) or Linear
18
New cards
What is a natural transformation?
Process by which a bacteria can actively take up and integrate an exogenous DNA thereby providing a source of genetic diversity.
19
New cards
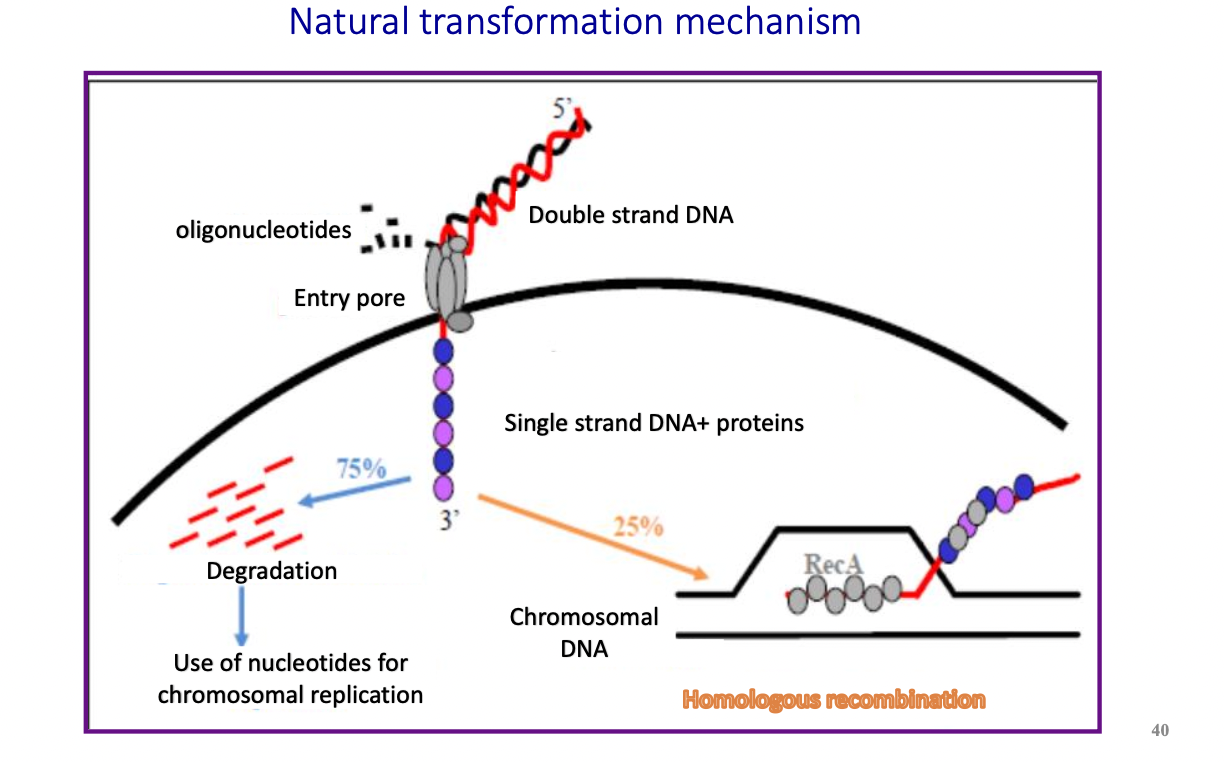
Explain the mechanism of natural trasnformation
dsDNA is taken up by a bacteria through a pore. It is tehn converted to a ssDNA which can either be __**degraded**__ (most cases) ==**or**== be integrated to __**chromosomal DNA**__ through __**homologous recombination.**__
20
New cards
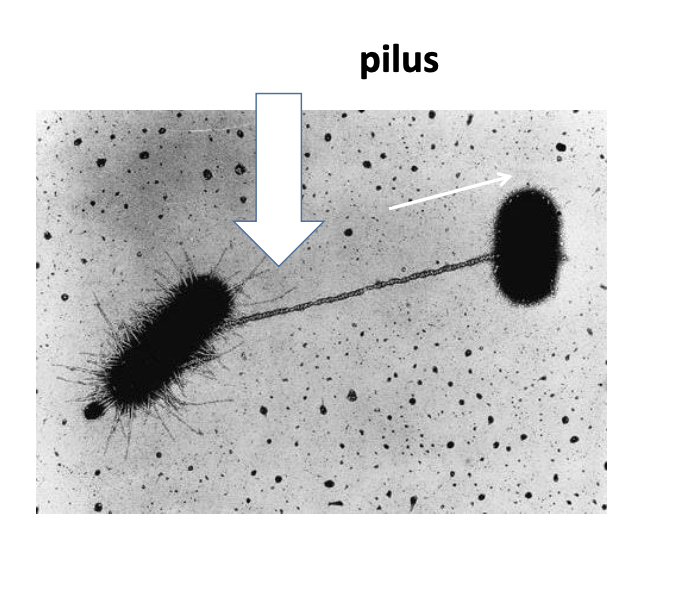
What is conjugation?
Process by which a bacteria can __**transfer genetic material**__ to each other by ==__**direct contact using a pilus**__==
21
New cards
What form of DNA is transformed during conjugation?
A ==__**plasmid**__== is received during conjugation
22
New cards
WHat is an episome?
a genetic element inside some bacterial cells, especially the DNA , that can ==__**replicate independently**__== of the host and also in association with a chromosome with which it becomes __**integrated**__.
23
New cards
What is difference between episome and plasmid?
\
\
==__**Plasmids**__== do not integrate into the genome, while the ==__**episome**__== can integrate into the genome.
24
New cards
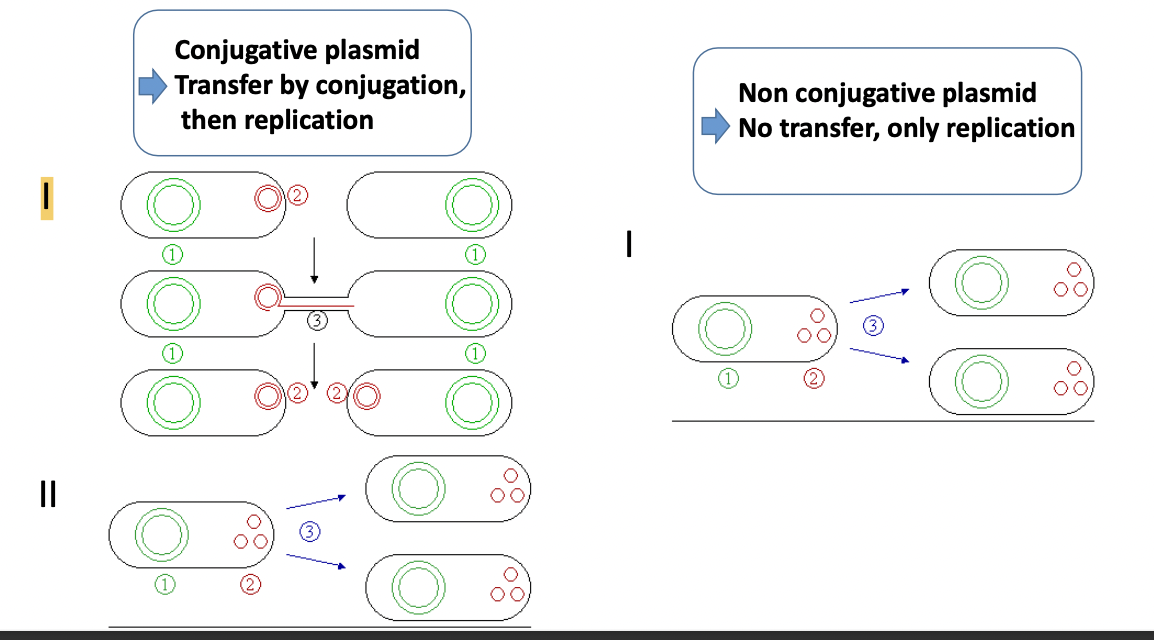
What are the 2 different groups of plasmids ?
Conjugative →transfer by conjugation then replication
Non conjugative → No transfer, only replication
Non conjugative → No transfer, only replication
25
New cards
What is transduction?
**Introduction of DNA to a recipient bacterium which is carried by a bacteriophage.**
26
New cards
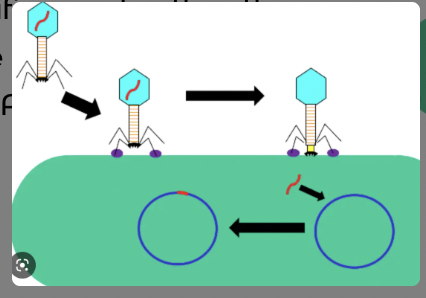
Explain the. mechanism of transduction.
When bacteriophage attach to the bacteria via a specific receptor, then there is perforation of the cell wall by the phage and injects DNA into the bacteria
27
New cards
What are the 2 type of mechanism for transduction?
**Generalized transduction or non specific →** able to transfer several bacterial genes.
**Specialized transduction →**able to transfer some metabolism properties.
28
New cards
Compare the three mechanism of DNA transfer
Natural transformation
Conjugation
Transduction
Transposition
Natural transformation
Conjugation
Transduction
Transposition
Natural transformation: bacteria take up DNA from envirnment
Conjugation: transfer of plasmid through pili
Transduction: transfer of DNA by bacteriophages
Transposition: Integration of DNA with trasnposons containing IR domains
Conjugation: transfer of plasmid through pili
Transduction: transfer of DNA by bacteriophages
Transposition: Integration of DNA with trasnposons containing IR domains