Parasitology Lab - Protozoans
1/141
There's no tags or description
Looks like no tags are added yet.
Name | Mastery | Learn | Test | Matching | Spaced | Call with Kai |
|---|
No study sessions yet.
142 Terms
Hemoflagellates
A parasitic flagellate found in the circulatory system of its host
delivered to human host via vector (kissing bug, flies, mosquitoes, etc)
kinetoplast
a mass of mitochondrial DNA lying close to the nucleus in some flagellate protozoa.
heteroxenous
Infects more than one host
monoxenous
infects only one host
amastigote
trophozite round, no external flagellum, intracellular form within host cells
choanomastigote
flagellum emerges from a collarlike process
promastigote
motile, elongated form of protozoans
opisthomastigote
trophoziote involved in the life cycle of protozoans
epimastigote
It is found in the vectors responsible for transmitting the Trypanosoma species.
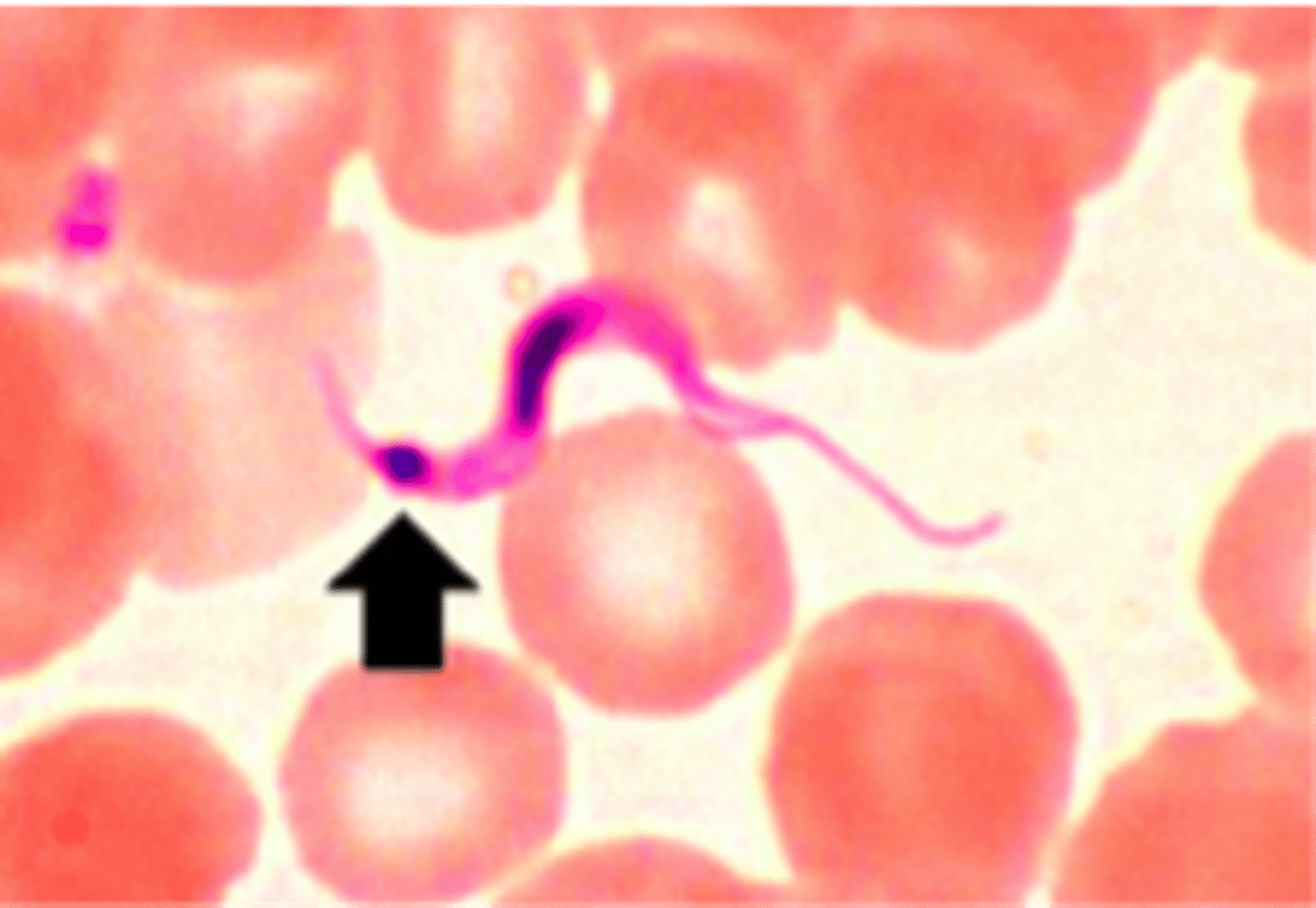
trypomastigote
Infective stage of Trypanosomes
what is the simple life cycle of protozoans
1. cysts
2. excyst --> trophozoites
3. Trophozoites mature
4. trophozoites undergo binary fission
5. encyst
protozoans have no
eggs
protozoans have two life phases:
cysts
trophozoites
cysts
dormant stage of protozoans
not metabolically active
trophozoites
active stage of protozoans
metabolically active
what are the different types of protozoans
amoebas
flagellates
ciliates
sporosoans
protzoans characteristics:
single-cell organisms
two life phases
One nucleus for trophozoites
cytoplasm
heterotrophic
heterotrophic
Organisms that obtain their nutrients or food from consuming other organisms.
what are the different types of movements for protozoans
- pseudopodia
- single flagella
- multiple flagella
- cilia
What are the protozoans covered in lab
- Entamoeba histolytica
- Entamoeba coli
- Endolimax nana
- Iodamoeba butschili
- Balantidium coli
- Chilomastic mesnili
- Trichomonas vaginalis
- Giardia lambila
- Dientamoeba fragilis
- Trypanosoma sp
- Trypanosoma cruzi - found in tissue
- Trypanosoma brucei - found in blood
- Trypanosoma brucei rhodesiense
- Trypanosoma brucei gambiense
- Leishmania sp.
- Leishmania donovani - found in blood
- Toxoplasma gondii
- Plasmodium sp.
- Plasmodium malariae
- Plasmodium ovale
- Plasmodium vivax
- Plasmodium falciparum
What are the protozoans that have no cysts in their life cycle
- Leishmania sp.
- Leishmania donovani
- Trypanosoma sp
- Trypanosoma cruzi
- Trypanosoma brucei
- Trypanosoma brucei rhodesiense
- Trypanosoma brucei gambiense
- Dientamoeba fragilis
- Trichomonas vaginalis
what are the protozoans that have cysts in their life cycle
- Entamoeba histolytica
- Entamoeba coli
- Endolimax nana
- Iodamoeba butschili
- Balantidium coli
- Chilomastic mesnili
- Giardia lambila
- Toxoplasma gondii
- Plasmodium sp.
what were the cysts observed in lab?
- Entamoeba coli
- Iodamoeba buschielli
- Endolimax nana
- Giardia lamblia
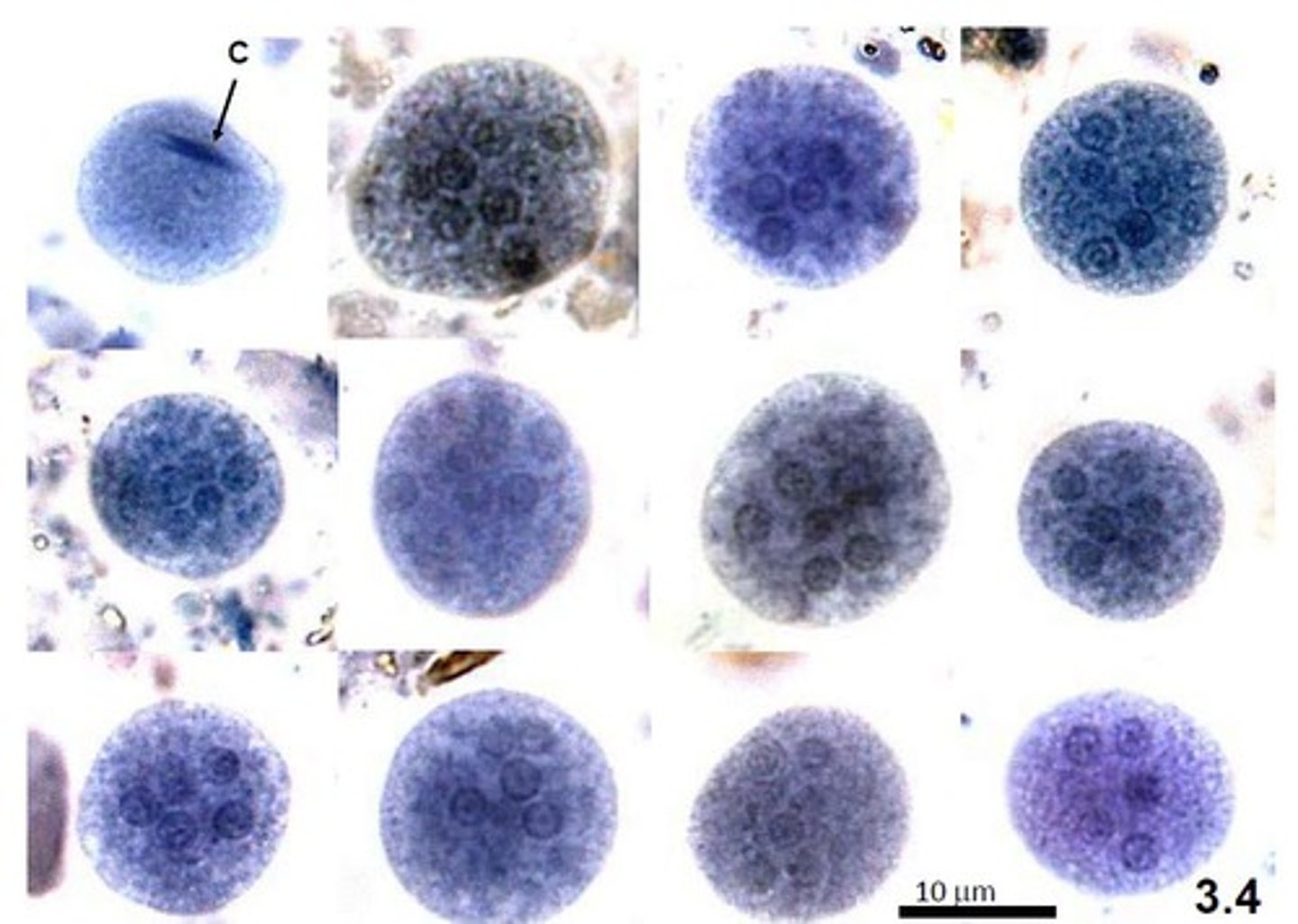
Entamoeba coli cysts (observed on the slides - description)
- methylene blue (blue or purple look)
- 8 nuclei
- round in shape perfect circle
Iodamoeba buschielli cysts (observed on the slides - description)
- iodine (brown or yellow look)
- 1 nuclei
- abnormal round shape
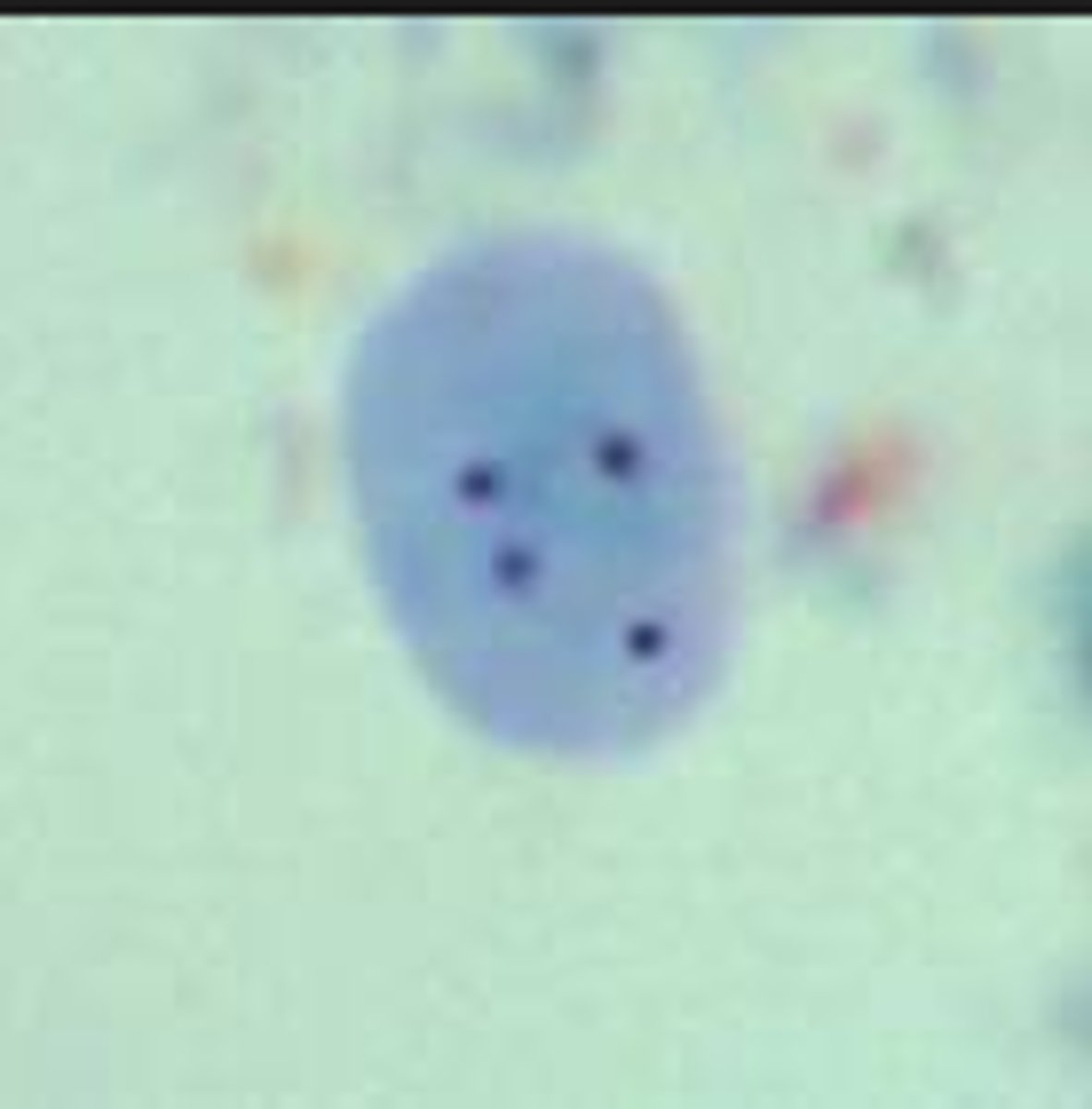
Endolimax nana cysts (observed on the slides - description)
- methylene blue (blue or purple look)
- four nuclei
- round shape
Giardia lamblia cysts (observed on the slides - description)
- methylene blue (blue or purple look)
- four nuclei
- circular shape
- transparent circle around the blue circle
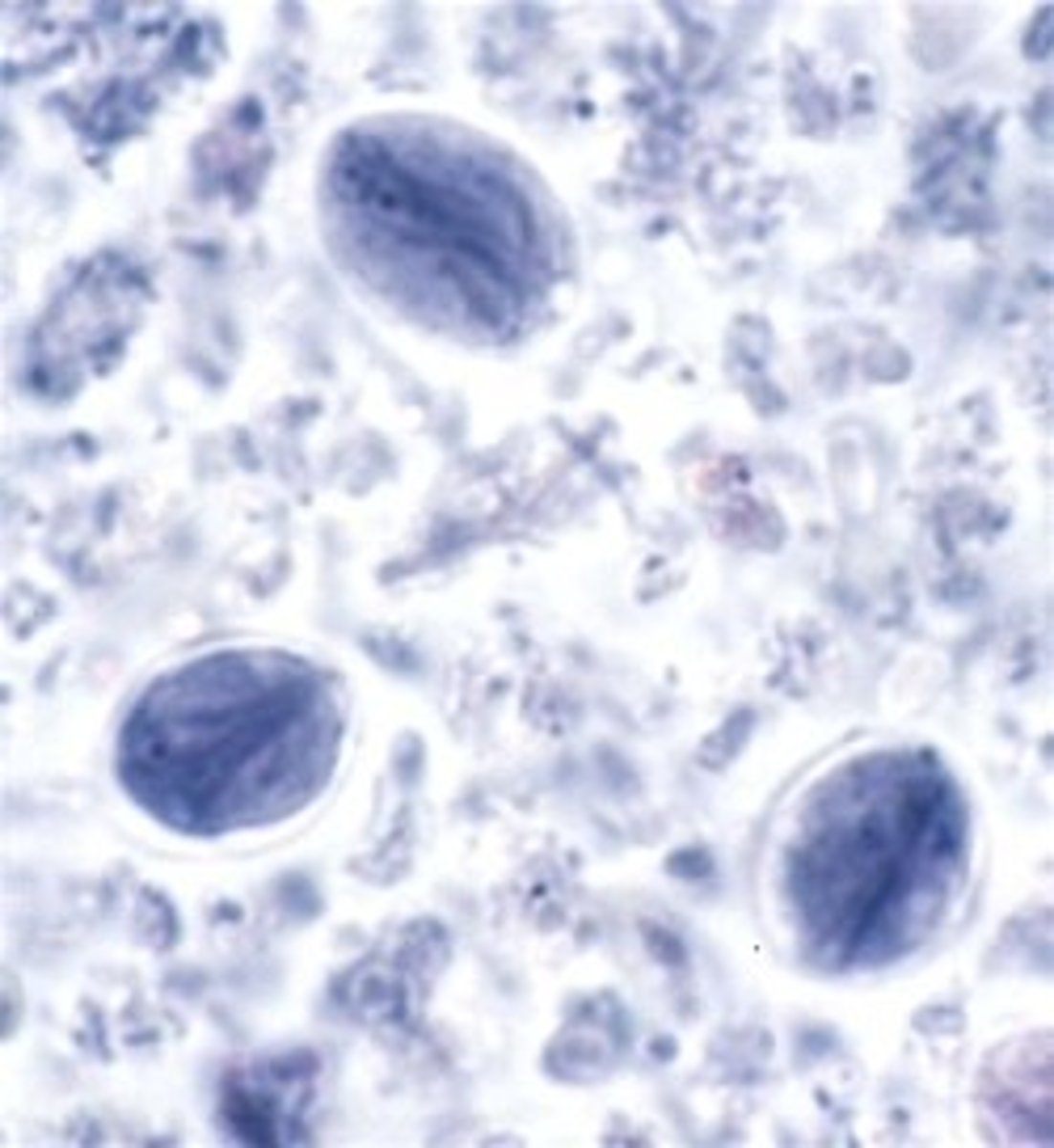
What are the differences between Trypanosoma cruzi and Trypanosoma brucei
- different vectors
- shape (cruzi is c shaped)
- amastigotes in cruzi life cycle and procyclic in brucei life cycle
- brucei is found in blood
- cruzi is found in blood and tissues
Entamoeba histolytica has how many nuclei in the cyst
4 nuclei
Entamoeba coli has how many nuclei in the cyst
8 nuclei
Endolimax nana has how many nuclei in the cyst
4 nuclei
Iodamoeba buetschili has how many nuceli
one nucleus
based on the nuceli in the cysts: which of these organisms is larger?
Iodamoeba buetschili
Endolimax nana
Entamoeba coli
Entamoeba histolytica
Entamoeba coli because the cyst has 8 nuclei
which of the organisms are amoeba
- Entamoeba histolytica
- Entamoeba coli
- Endolimax nana
- Iodamoeba butschili
- Dientamoeba fragilis
which of the organisms are flagellates
- Chilomastix mesnili
- Trichomonas vaginalis
- Giardia lamblia
- Trypanosoma spp.
- T. cruzi
- T. brucei
- T. brucei rhodesiense
- T. brucei gambiense
- Leishmania spp.
- L. donovani
which of the organisms are ciliates
- Balantidium coli
which of the organisms are sporosoans
- Toxoplasma gondii
- Plasmodium sp.
life cycle of Entamoeba histolytica
1. cysts and trophozoites passed in feces
2. mature cyst ingested
3. excystation --> trophozoite
4. The trophozoite undergoes binary fission
5. encystation
6. exits host via feces
what is the infective stage of Entamoeba histolytica
mature cysts ingested
what is the diagnostic stage of Entamoeba histolytica
cysts and trophozoites in feces
what is the life cycle of Entamoeba coli
1. cysts and trophozoites passed in feces
2. mature cyst ingested
3. excystation --> trophozoite
4. The trophozoite undergoes binary fission
5. encystation
6. exits host via feces
infective stage of Entamoeba coli
mature cyst ingested
diagnostic stage of Entamoeba coli
cysts and trophozoites in stool
life cycle of Endolimax nana
1. cysts and trophozoites passed in feces
2. mature cyst ingested
3. excystation --> trophozoite
4. The trophozoite undergoes binary fission
5. encystation
6. exits host via feces
infective stage of Endolimax nana
mature cyst ingested
diganostic stage of Endolimax nana
cysts and trophozoites in feces
life cycle of Iodamoeba butschlii
1. cysts and trophozoites passed in feces
2. mature cyst ingested
3. excystation --> trophozoite
4. The trophozoite undergoes binary fission
5. encystation
6. exits host via feces
infective stage of Iodamoeba butschlii
mature cysts ingested
diagnostic stage of Iodamoeba butschlii
cysts and trophozoites in feces
life cycle of Balantidium coli
1. cysts and trophozoites passed in feces
2. mature cyst ingested
3. excystation --> trophozoite
4. The trophozoite undergoes binary fission
5. encystation
6. exits host via feces
infective stage of Balantidium coli
cysts ingested
diagnostic stage of Balantidium coli
Trophozoites or cysts in stool
where does Entamoeba histolytica reside
large intestine
where does Entamoeba coli reside
large intestine
where does endolimax nana reside
large intestine
where does Iodamoeba butschili reside
large intestine
where does balantidium coli reside
large intestine
Chilomastic mesnili life cycle
1. cysts and trophozoites passed in feces
2. mature cyst ingested
3. excystation --> trophozoite
4. The trophozoite undergoes binary fission
5. encystation
6. exits host via feces
infective stage of Chilomastic mesnili
mature cysts ingested
diagnostic stage of Chilomastic mesnili
cysts and trophozoites in stool
where does the Chilomastix mesnili reside
large intestine, mainly cecum
Trichomonas vaginalis life cycle
1. trophozoites in vaginal and prostatic secretions and urine
2. binary fission
3. trophozites in vagina or urethra
4. sexual intercourse
5. infects new host
infective stage of Trichomonas vaginalis
trophozoites in the vagina or urethra
diganostic stage of Trichomonas vaginalis
trophozoites in vaginal and prostatic secretions
where does the Trichomonas vaginalis reside
vagina - women
urethra and prostate - men
Giardia lamblia life cycle
1. cysts and trophozoites passed in feces
2. mature cyst ingested
3. excystation --> trophozoite
4. The trophozoite undergoes binary fission
5. encystation
6. exits host via feces
infective stage of Giardia lamblia
mature cysts ingested
diagnostic stage of Giardia lamblia
cyst and trophozoites in feces
where does Giardia lamblia reside
small intestine
Dientamoeba fragilis life cycle
1. trophozoites passed in feces
2. trophozoite ingested
3. The trophozoite undergoes binary fission
4. exits host via feces
Infective stage of Dientamoeba fragilis
trophozoite ingested
diagnostic stage of Dientamoeba fragilis
trophoziotes in stool
where does Dientamoeba fragilis reside
large intestine
Trypanosoma cruzi life cycle
1. Kissing bug takes its blood meal (bites human)
2. release metacyclic trypomastigotes into human host
3. enters blood stream of humans
4. Metacyclic trypomastigotes loses flagella and becomes Amastigotes
5. Amastigotes deposit into tissue and undergo binary fission
6. Amastigotes --> trypomastigotes
7. another kissing bug takes its blood meal (bites human)
8. uptake of trypomastigotes
9. trypomastigotes enters gut of bug
10. trypomastigotes --> epimastigotes
11. Epimastigotes undergoes binary fission
12. epimastigotes --> metacyclic trypomastigotes
what are the different types of trophozoites involved in the Trypanosoma cruzi life cycle
metacyclic trypomastigotes
Amastigotes
trypomastigote
Epimastigotes
infectious stage of Trypanosoma cruzi
metacyclic trypomastigote
diagnostic stage of Trypanosoma cruzi
trypomastigotes in blood
where does Trypanosoma cruzi reside
bloodstream and wihtin tissues
which trophozoites of the Trypanosoma cruzi occurs within the human
Amastigote
Trypomastigote
which trophozoites of the Trypanosoma cruzi occurs within the bug
epimastigote
metacyclic trypomastigote
what is the vector of Trypanosoma cruzi
kissing bug or Reduvidae bug
Trypanosoma brucei sp. life cycle
1. Glossina fly/tsetse fly takes its blood meal (bites human)
2. release metacyclic trypomastigotes into a human host
3. enters bloodstream of humans
4. Metacyclic trypomastigotes --> blood stream trypomastigotes
5. 2nd glossina fly/tsetse fly takes a blood meal
6. bloodstream trypomastigotes enters gut of glossina fly/tsetse fly
7. bloodstream trypomastigotes → procyclic trypanostomgote
8. procyclic trypomastigotes → epimastigote
9. Epimastigote undergo binary fisson
10. epimastigotes --> metacyclic trypomastigotes
infectious stage of Trypanosoma brucei sp.
metacyclic trypomastigotes
diagnostic stage of Trypanosoma brucei sp.
trypomastigotes in blood
where does Trypanosoma brucei sp. reside
blood stream
what are the different trophozoites in Trypanosoma brucei sp.
metacyclic trypomastigotes
trypomastigotes
procyclic trypomastigotes
epimastigote
which are the trophozoites that occur in humans for Trypanosoma brucei sp
metacyclic trypomastigotes
trypomastigotes
which are the trophozoites that occur in the vector for Trypanosoma brucei sp
metacyclic trypomastigotes
trypomastigotes
epimastigoites
procyclic trypomastigotes
What is the vector for Trypanosoma brucei sp.
Glossina fly
Leishmania donovani life cycle
1. Sand fly takes its blood meal (bites human)
2. release promastigotes into a human host
3. enters bloodstream of humans
4. Promastigotes engulfed by the macrophages in the blood stream
5. Promastigotes --> amastigotes
6. Amastigotes undergo binary fission in macrophage
7. Amastigotes in the blood stream
8. 2nd sand fly takes a blood meal
9. uptake of bloodstream amastigotes
10. Amastigotes enter gut of sand fly
11. amastigotes --> promastigotes
12. Promastigotes undergo binary fission
infectious stage of Leishmania sp.
promastigotes
diagnostic stage of Leishmania sp.
amastigotes in blood stream
what are the trophozoites of Leishmania sp.
Promastigotes
amastigotes
what is the vector of Leishmania sp.
sand fly
where does the Leishmania sp. reside
in the bloodstream (specifically the macrophages)
Toxoplasma gondii life cycle
1. Unsporulated cysts in cat feces
2. Exposed to surroundings/ environment (soil)
3. Cysts become sporulated
4. Intermediate host (rat, bird, sheep, pig) ingests sporulated cysts
4. Inadvertent host (human) ingests sporulated cysts
5. Definitive host ingests intermediate host cysts in tissue
6. Sporulated cysts in the gut
7. spotulated cysts enter tissue
8. In the tissue the sporulated cysts become trophozoites (excystation)
8. Trophozites → bradyzoites or tachyzoites via schiogony
9. Bradyzoites enter tissue (brain or pancreas)
10. Reproduce schizonts (cell that has multiple nuclei) formed and releases trophozites
infective stage of Toxoplasma gondii
sporulated cysts ingested
diagnostic stage of Toxoplasma gondii
tissue cyst (bradyzoites and tachyzoites)
where does the Toxoplasma gondii reside in humans
within tissues
Plasmodium sp. life cycle
1. mosquito takes blood meal, injects sporozoites into humans
2. sporozoites enter the circulation
3. passes through the liver
4. sprorzoites enter liver cell
5. liver cells are infected
6. infected liver cells --> schizont
7. schizont ruptures and releases merozoites
8. merozoites infects RBC
9. RBC --> Immature trophozite (ring stage)
10. Ring stage --> mature trophozites --> schizont --> ruptures and infects other RBC
10. Or ring stage --> gametocytes (sex cells)
11. mosquito take blood meal with the gametocytes
12. microgamete enters macrogamete to form ookinete
13. okinete --> oocyst
14. oocyst ruptures releasing sporozoites