Drug Allergy and Dermatologic Drug Rxns Pt. 1
1/93
There's no tags or description
Looks like no tags are added yet.
Name | Mastery | Learn | Test | Matching | Spaced | Call with Kai |
|---|
No analytics yet
Send a link to your students to track their progress
94 Terms
What is released during hypersensitivity reactions (ex: drugs) & cellular injury?
histamine
What are the key sites of histamine synthesis and storage in secretory granules?
basophils: blood
mast cells in most tissues but especially concentrated in skin, bronchioles, and intestinal mucosa
Which histamine receptor is blocked by the classic antihistamines?
H1
Which histamine receptor is primarily involved in acid production of parietal cells (more about this with GI topics) but has minor role in the treatment of certain allergy conditions?
H2
When do we use H2 receptor antagonists?
reduce GI acid production
What is a product of choice for an H2 receptor antagonist?
Ranitine (Zantac)
Cimetidine (Tagamet HB 200®)
Famotidine (Pepcid®)
Nizatidine (Axid®)
"Nerds Call Ralph Funny"
all end in "TIDINE"
What is the MoA for H2 receptor antagonists?
block histamine receptor on parietal cell blocking secretion of acid & pepsin resulting in increasing pH
What is the MoA for antihistamines?
block the H1 receptor
What is the therapeutic effect for antihistamines (H1 blockers)?
blocks action of histamine; blocks wheal and flare, flushing, edema, pain and itching associated with localized release of histamine.
What is the principle difference between the first generation antihistamines and second generation antihistamines, 1st gen > 2nd gen?
sedation
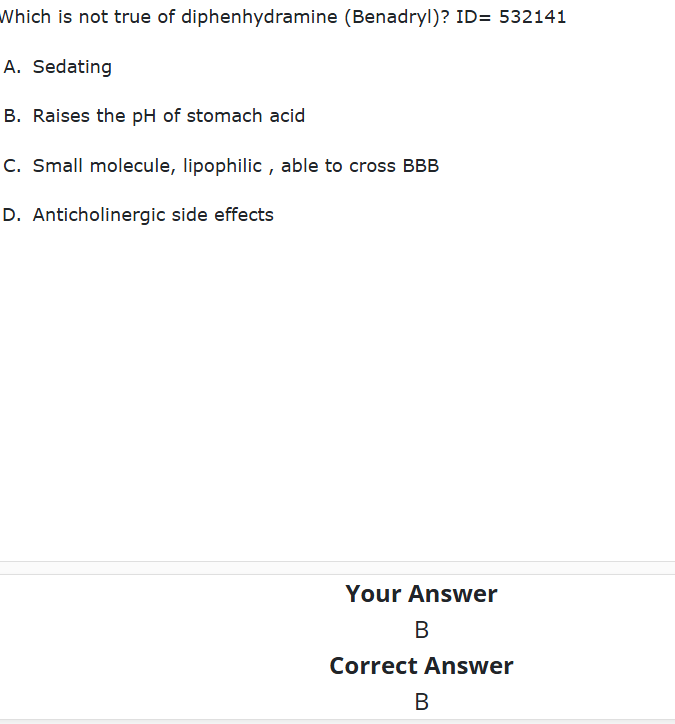
What generation H1 blocker is relatively small molecules with high lipid solubility able to cross CNS BBB and can cause SEDATION?
ex: benadryl
1st
These are key side effects of which generation antihistamine H1 blocker:
Dry mouth, dry secretions, dry eyes, urinary retention, constipation
1st gen
What generation H1 blocker is big molecules with low lipid solubility?
2nd
What H1 receptor antagonist has a BBW for respiratory depression contradicted in <2yrs old?
Promethazine
What are two important H1 receptor antagonists that block the H1 receptor, are very sedative, and have the anticholinergic response?
diphenhydramine (benadryl) and hydroxyzine (atarax)
What are 4 hormones produced by the adrenal gland?
glucocorticoids (cortisol)
mineralocorticoids (aldosterone)
adrenal androgens (DHEA)
and catecholamines (Epi)
What adrenal gland hormone:
Focus is glucose & anti-inflammation
Cortisol = hydrocortisone
glucocorticoids
What adrenal gland hormone:
aldosterone
- focus is in minerals Na+ and K
mineralocorticoids
What adrenal gland hormone:
DHEA, focus is sex hormones
adrenal androgen
What adrenal gland hormone:
Epi, produced in the medulla
catecholamines
What are the key glucocorticoid (anti-inflammatory) activity?
-Stabilizes the liposomal membrane inhibiting the release of inflammatory mediators resulting in decreased vascular response
•↓ inflammation
•↓ swelling
-Inhibits the dilation of small blood vessels
-Inhibits cellular immunity
Activity of what corticosteroid regulates salts and promotes the reabsorption of sodium and increased excretion of potassium by the kidney?
mineralcorticoid
Activity of what corticosteroid increases glucose?
glucocorticoid
What are 2 short acting systemic corticosteroids that are low potency?
cortisone and hydrocortisone cortisol)
What are 3 intermediate acting systemic corticosteroids that are medium potency?
methylprednisone, prednisone, and triamcinolone
What are 2 long acting systemic corticosteroids that are high potency?
betamethasone and dexamethasone
What is a mineralocorticoid acting systemic corticosteroids that regulates salt/potassium?
fludrocortisone
true or false: the longer-acting the drug, the higher the potency of the drug
TRUE
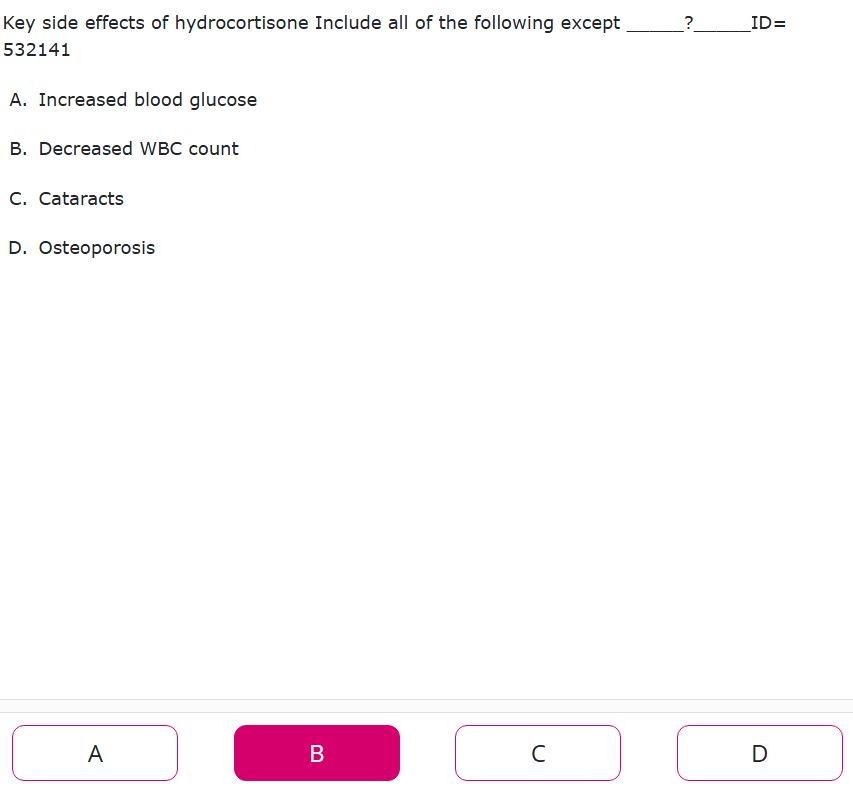
These are key side effects of what??
•Elevated glucose levels (acute)
•Increased WBC count (acute)
•Impaired immune response
•Myopathy
•Cataracts
•Osteoporosis
•Psychosis
glucocorticoid
What is defined as "immunologically mediated” drug hypersensitivity reaction, hyper-response to antigenic drug leads to organ-specific or systemic reaction, and is responsible for 6-10% of all adverse drug reactions?
drug allergy
What defines a more heterogenous reactions that resemble allergy but may not be or NOT proven to be mediated via an immune response and brings occurrence up to 15% if included?
drug hypersensitivity rxn (DHR)
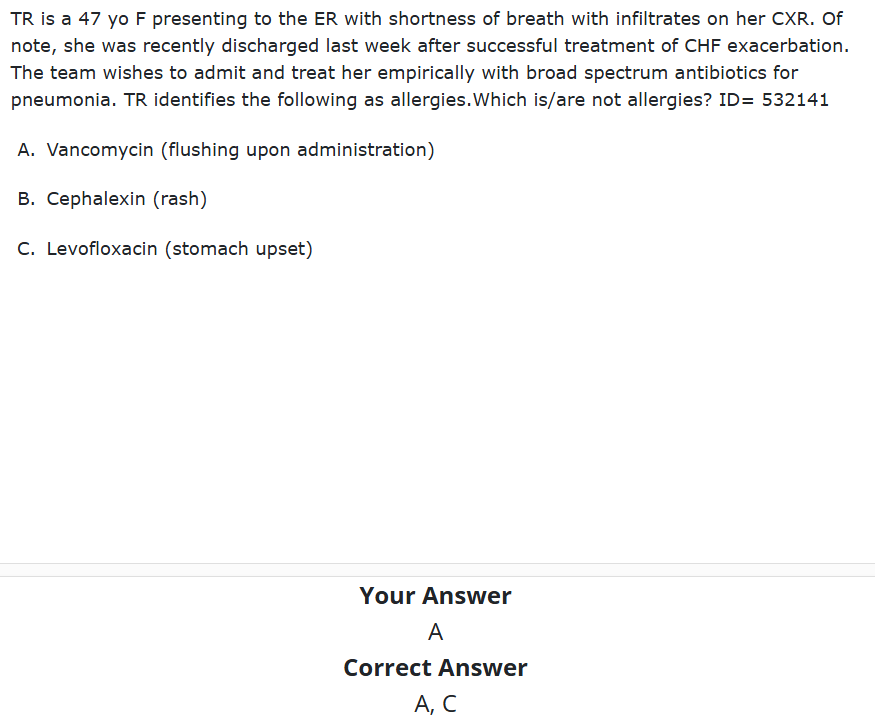
What drug causes ____ flushing syndrome also known as “red man’s syndrome” that is NOT an allergic reaction but rather, caused by a histamine release in response to infusion rate
Vancomycin
the solution is to slow the rate of infusion
What classification is IMMEDIATE and IgE mediated which causes the release of inflammatory mediators?
type I
Which classification is anaphylaxis?
Type I
What classification is delayed (>72hrs) and is regulated by IgG and complement?
type II
What classification is delayed (>72 hours) that is regulated by antigen-antibody complexes that activate complement and deposit on BVs?
type III
What classification is delayed (1day-6weeks) and is T cell mediated?
type IV
What causes vasodilation of capillaries/capillary permeability , contraction of bronchial smooth muscle, and hypersecretion?
histamine
What is a metabolite of arachidonic acid and and is a major component of mast cells (therefore causes BRONCHOCONSTRICTION)?
prostaglandin
What is a metabolite of arachidonic acid that is more potent and causes a LONGER LASTING bronchoconstriction?
leukotrienes
What drugs are involved in ~43% of all severe drug induced anaphylaxis?
penicillin and cephalosporins
What can have a cross reactivity due to: sharing a common beta lactam ring, and having different chemical side chains (LOOK AT R group!)?
penicillin and cephalosporins
If you are a 1st or 2nd generation cephalosporin will you be allergic to PCNs?
yes
Pts who have a reaction to penicillin will have the GREATEST change or HIGHEST reaction to which cephalosporin rxn?
1st generation (ex: cephalexin)
What generation cephalosporin has the SMALLEST rxn to penicillins?
3rd, 4th, 5th (ex: ceftriaxone, cefdinir, etc.)
An allergy to what group of drugs is almost never a contraindication to cephalosporins?
Look for a documented history of rash, anaphylaxis or other serious reaction (angioedema, bronchospasm, Stevens-Johnson syndrome or TEN)
Penicillin allergy
The penicillin skin test is determined to be not cost effective, except for pts with a history of beta lactam allergy and is ONLY indicative for the presence of _____.
IgE
A negative result for the penicillin skin test indicates what?
extremely low risk of life-threatening immediate reactions
What can resemble a drug allergy, but not proven IgE-mediated, immediate or delayed in onset?
DHR (drug hypersensitivity rxn)
What drugs typically can have these type of reactions:
–asthma/rhinitis, urticarial, angioedema, meningitis, pneumonitis, anaphylaxis
aspirin (ASA), NSAIDs
9-20% of those with asthma are sensitive to ___ and ____.
Aspirin (ASA) and NSAIDS
There is a LOW cross- reactivity between antibiotics and non-antibiotic ______ due to their chemical structure differences and reactive metabolite differences
sulfonamides
What are the 4 basic principles of tx for anaphylaxis?
1.Early Recognition
2.Discontinuation of offending agent
3.Symptomatic treatment
4.Substitution, if necessary
What is an acute onset, multi-organ, life-threatening reaction most commonly caused by penicillin's, aspirin, NSAIDs, or insulin?
Presentation:
-flushing, urticaria, pruritis, and angioedema
-throat/chest tightness, cough, dyspnea, dysphonia, rhinorrhea
-dizziness, hypotension
-GI symptoms (n/v/d)
anaphylactic
What is the first line tx for anaphylaxis?
intramuscular epinephrine
- can repeat every 10-15 minutes
What drug MoA is described:
adrenergic agonist of receptors alpha, beta1, beta2 agonist
intramuscular epinephrine (first line tx for anaphylaxis)
What should you do if 1st line anaphylaxis tx is ineffective to restore BP?
fluids to restore volume or IV vasopressor drips
how often can a REPEAT dose of self-administered epinephrine be administered?
every 5 to 15 minutes
What is the lower dose for Epinephrine Auto-injectors )ex: Epipen Jr)?
0.15mg delivery
What is the adult (>30kg) dose for Epinephrine Auto-injectors?
0.3mg delivery
What is another drug used for anaphylaxis tx that is a inhaled beta-adrenergic agonist?
albuterol
What drug has this MoA:
• relaxes bronchial smooth muscle, β-2 agonist
albuterol
What drug has these SE:
tachycardia, excitement and nervousness
albuterol
What is another tx for anaphylaxis with usage of glucocorticoids?
methylprednisolone (Solumedrol) IV
What drug has this MoA:
-regulate gene expression → effect not immediate
-repress genes encoding cytokines
-decrease inflammation by suppression of migration of leukocytes and reversal of increased capillary permeability
methylprednisolone (glucocorticoid) IV
What are 2 antihistamine txs for anaphylaxis?
diphenhydramine (Benadryl) and famotidine (Pepcid)
What drug has this MoA:
-competes with histamine receptor sites on effector cells in GI tract, blood vessels, and respiratory tract
antihistamines -diphenhydramine and famotidine
What drug are known to cause angioedema?
ACE inhibitors and ARBs
What is the caution and wash out period for angioedema?
36 hr wash out period BETWEEN ACE inhibitor -> Entresto
What type of rxn is not mediated by immune mechanism, is released of mast cell-and basophil derived mediators, and presents with pain, localized swelling, inflammation, ↑ vascular permeability, vasodilation?
anaphylactoid reaction (ANGIOEDEMA)
What is done so there is no IgE reaction, has many rapid 12 step methods depending on the agent that allows for TEMPORARY safe drug therapy?
- TEMPORARY and not for patients with history of serious cutaneous adverse rxns (SCARS)
-only do in hospital setting w/ resuscitation equipment available
-PO > IV
desensitization
What is a stepwise process of incremental dosing that TEMPORARILY allows safe drug therapy?
Induction of Drug Tolerance
What induction of drug tolerance has no standardization and starts with 1/10th to 1/100th of final dose which can be useful to challenge dissimilar R1 side chain cephalosporins?
graded challenge
What are some dermatological drug rxn signs?
localized:
-exanthematous
-urticarial
-pustular eruptions
-blistering
•fixed drug eruptions
•Stevens-Johnson Syndrome and Toxic Epidural Necrolysis
-hyperpigmentation
-photosensitivity
Systemic
presence of fever
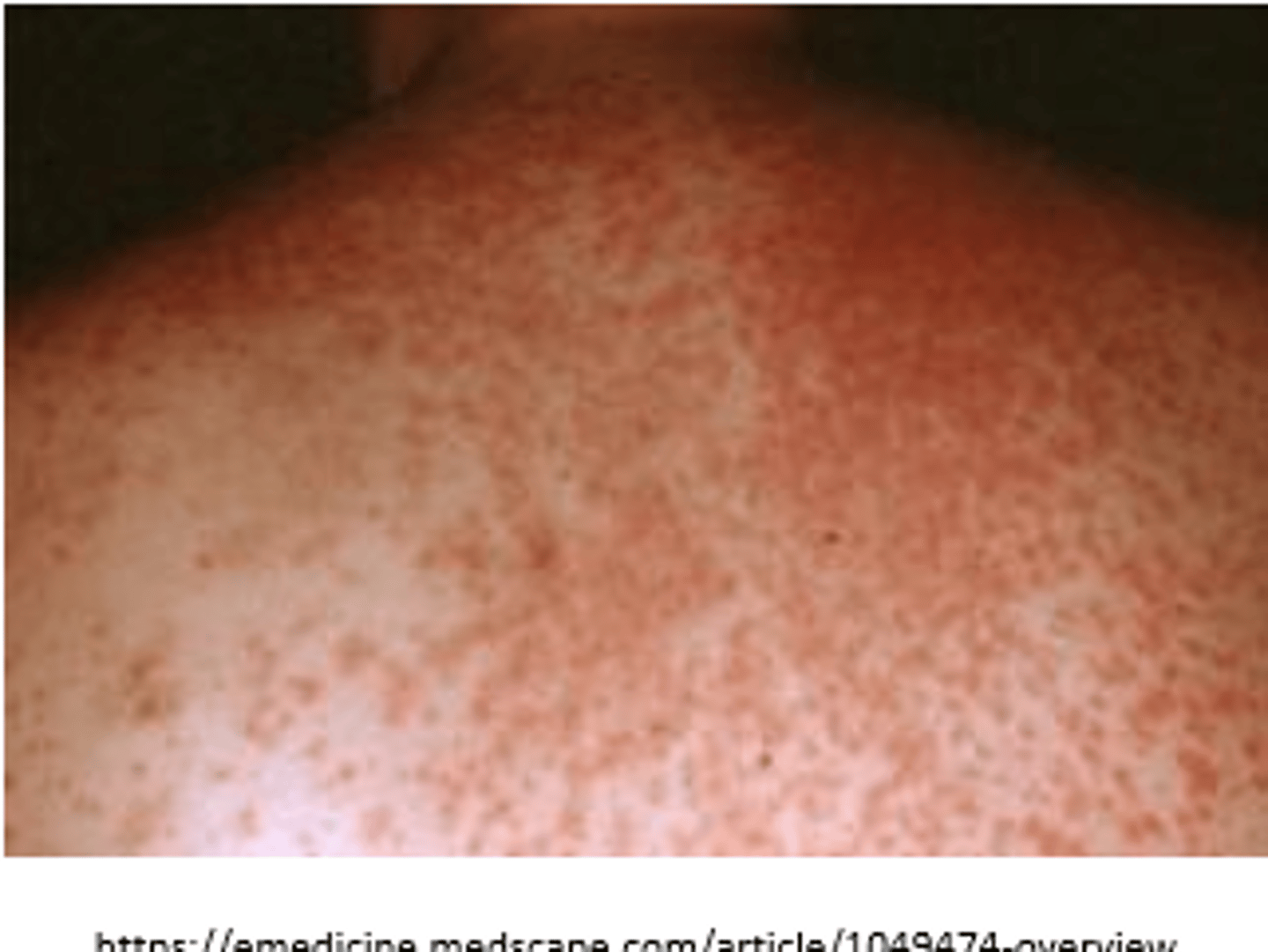
exanthematous drug eruption (aka morbilliform or maculopapular)
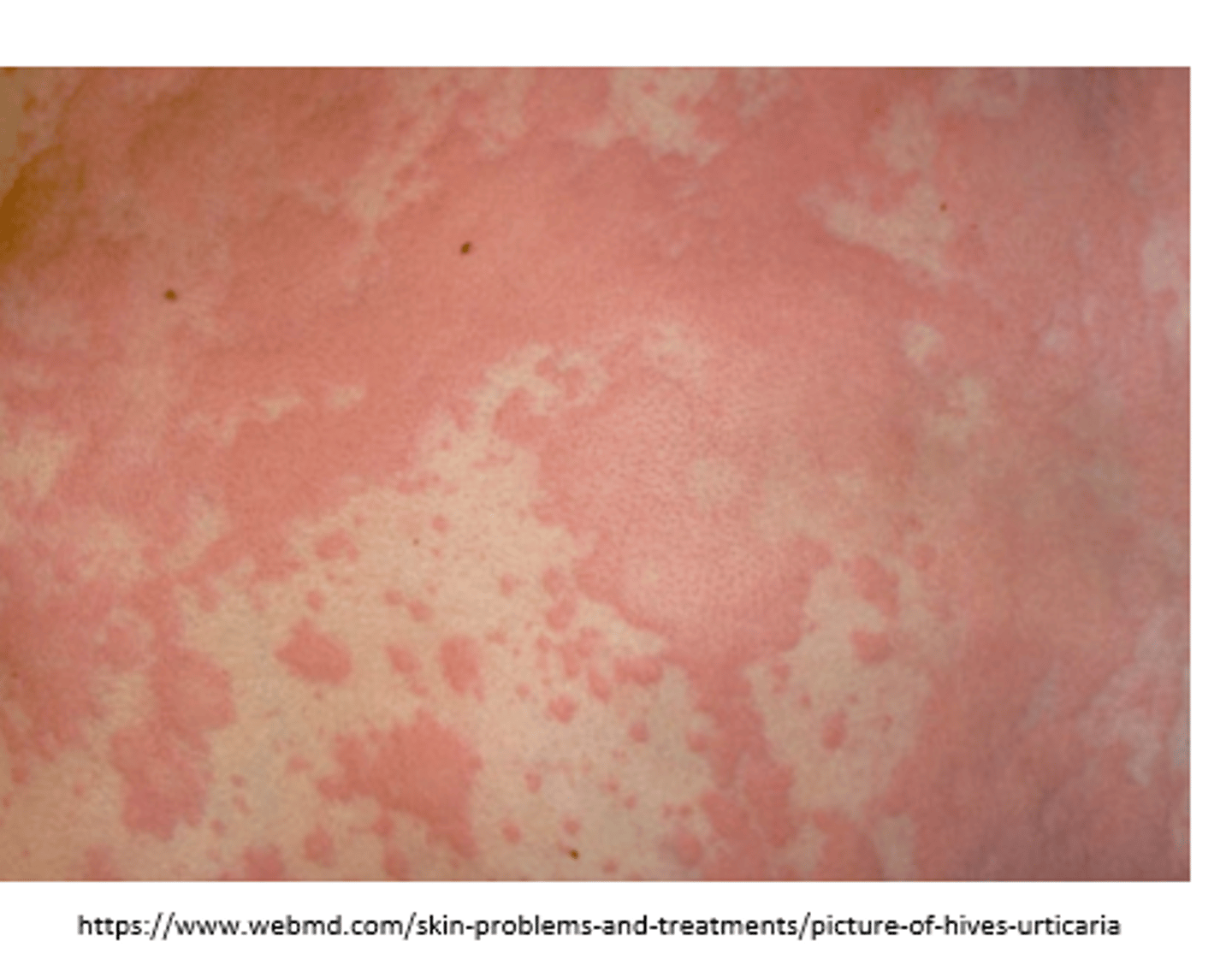
urticaria- hives
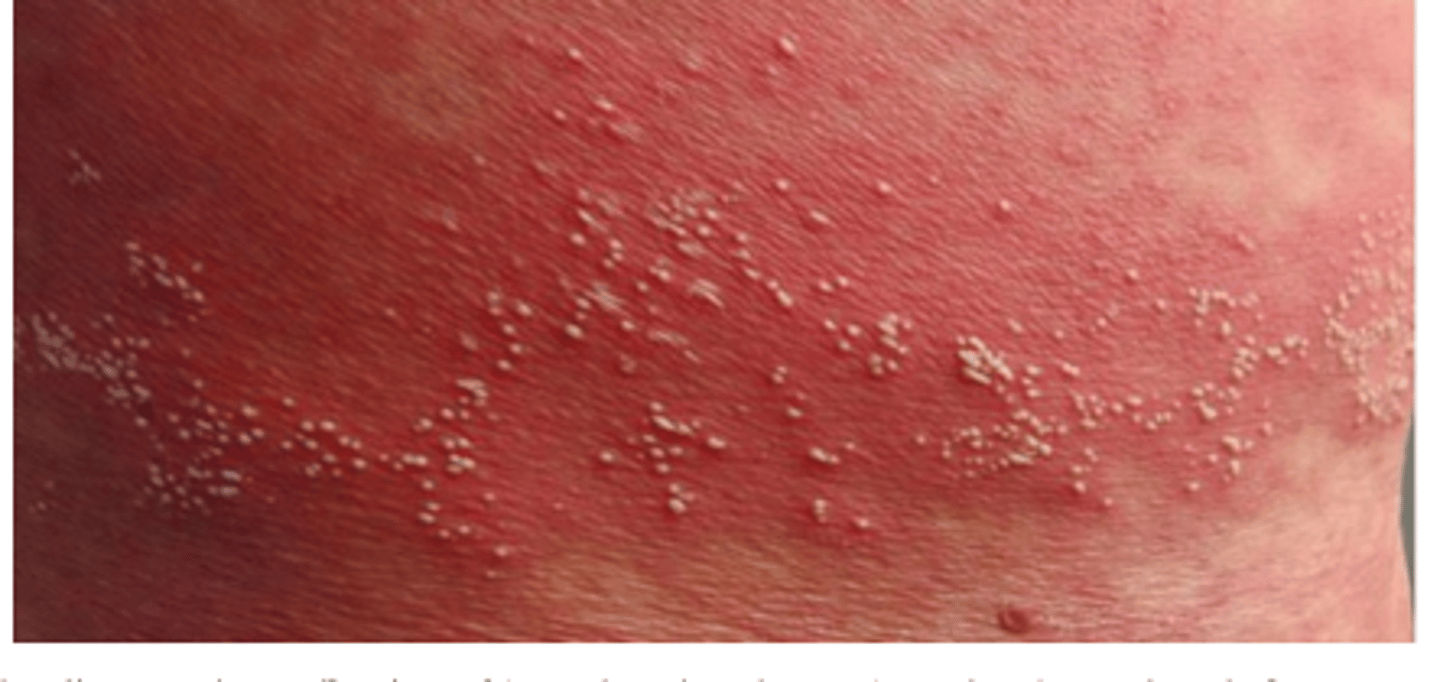
pustular drug eruption
What are these symptoms of
-rare, severe, and life-threatening
-extent defines which designation (<10%, 10-30%, >30%)
-blister eruptions
that present with:
-tender/painful bullous formation, fever, headache, and respiratory symptoms
-extensive necrosis and detachment of the skin
-presents within ~7-14 days
SJS or TEN
What are some associated medications for serious cutaneous adverse reactions (SCAR) like SJS or TEN?
–sulfonamides, PCNs, carbamazepine (and increased risk with HLA alleles), lamotrigine, NSAIDS, allopurinol
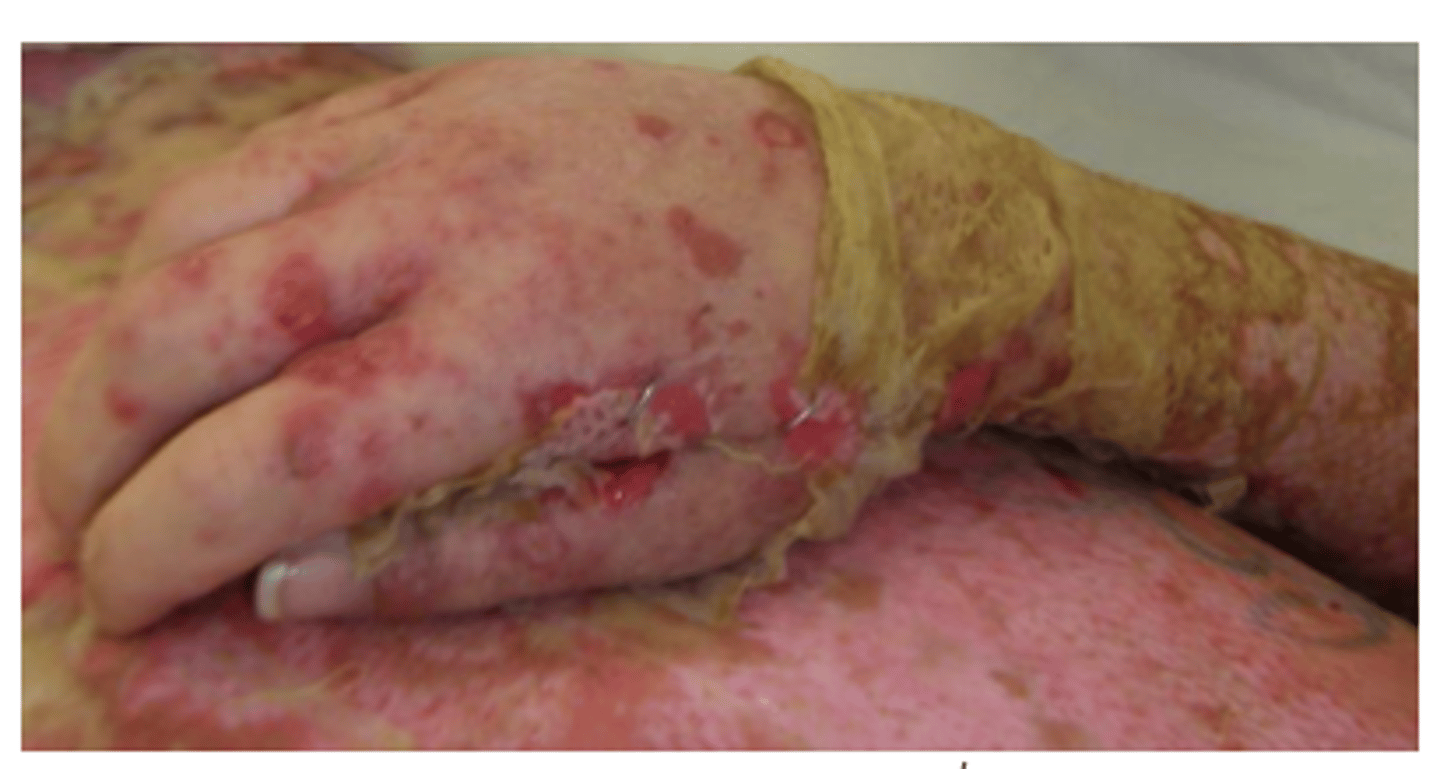
SJS
What is the management for dermatologic rxns for mild to moderate?
-discontinue the suspected offending agent (in any severity)
What is the management for severe dermatologic rxns?
-short course of systemic steroids
- antipyretic for fever
In a severe case of dermatologic rxn what should be AVOIDED?
AVOID ASA and NSAIDs - USE ACETAMINOPHEN
What is the management for life threatening dermatologic rxns?
-monitoring and support
•blood pressure
•fluid and electrolytes
-prevent/treat secondary bacterial infections
-corticosteroids controversial (high initial dose, rapid taper)
-IVIG
What are severe adverse drug rxns are associated with what:
–exanthematous eruption
–accompanied by fever
–lymphadenopathy
–multiorgan involvement
•including kidneys, liver, lung, bone marrow, heart and brain
drug hypersensitivity syndrome
What are some associated medications that can cause drug hypersensitivity syndrome?
–allopurinol
–sulfonamides
–carbamazepine
–lamotrigine
"ACLS"
Where should you report ADEs?
to FDA