Phys Lecture 16 Endocrine, Hormones
1/28
There's no tags or description
Looks like no tags are added yet.
Name | Mastery | Learn | Test | Matching | Spaced |
|---|
No study sessions yet.
29 Terms
Long distance signaling (Nervous system )
Nervous system
Rapid
Voluntary and involuntary control
Neurotransmitters (close, cell to cell)
Exocytosis of all neurotransmitters
All have extracellular receptors
Excitatory and inhibitory neurotransmitters
Long distancing signaling (endocrine system)
Slow and long lasting
Involentary
Hormones (cells are very far apart)
Transported in blood vessels, lymph vessels
Exocytosis or simple diffusion of hormones
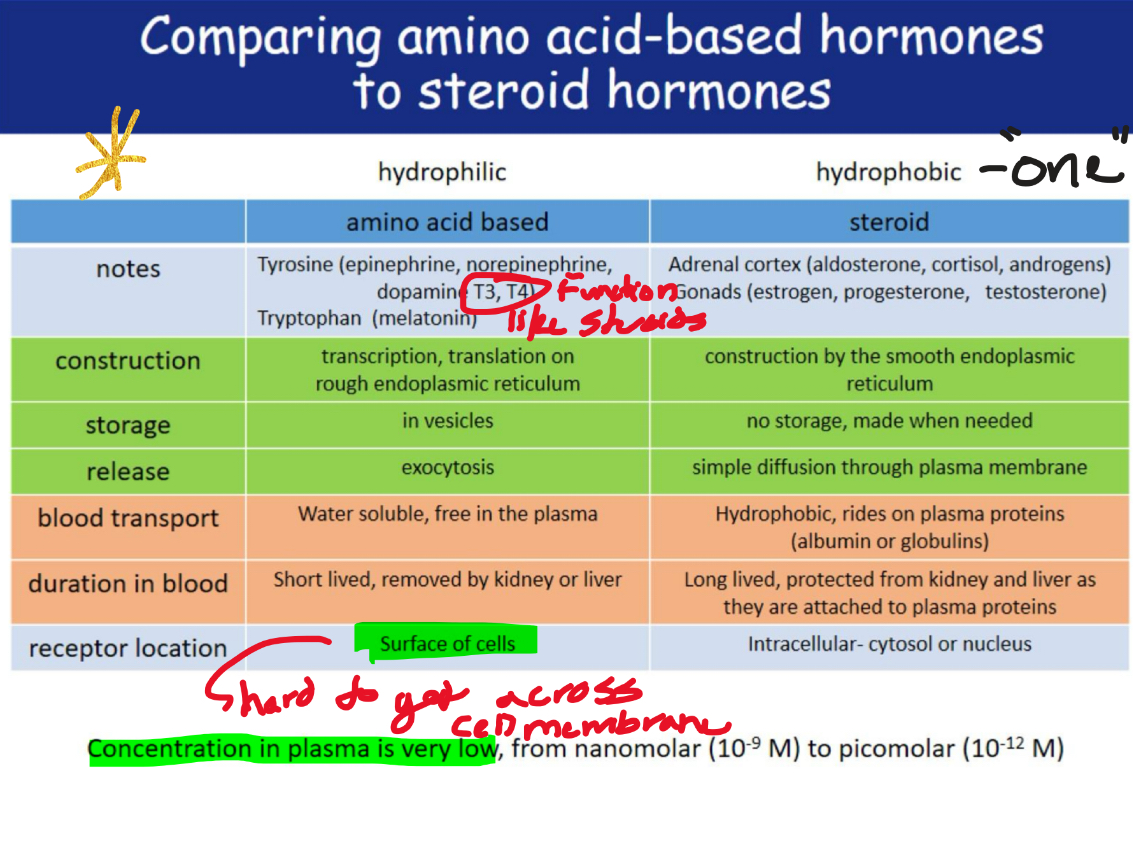
Have extracellular receptors or intracellular resceptors STEROIDS (T3, T4)
Excitatory and inhibitory hormones
Endocrine system
20 endocrine glads, 9 we have to know in this section
Hormones 2 types
Amino-Acid- based hormones (hydrophillic)
amino acid derivatives, peptides, and proteins
Steroids (hydrophobic)
Synthesized from cholesterol
What determines strength of the signal
Amount of available hormone (amount released)
HYPOsecretion
HYPERsecretion
Rate of breakdown (Number of receptors)
HYPOresposivness
HYPERresposivness
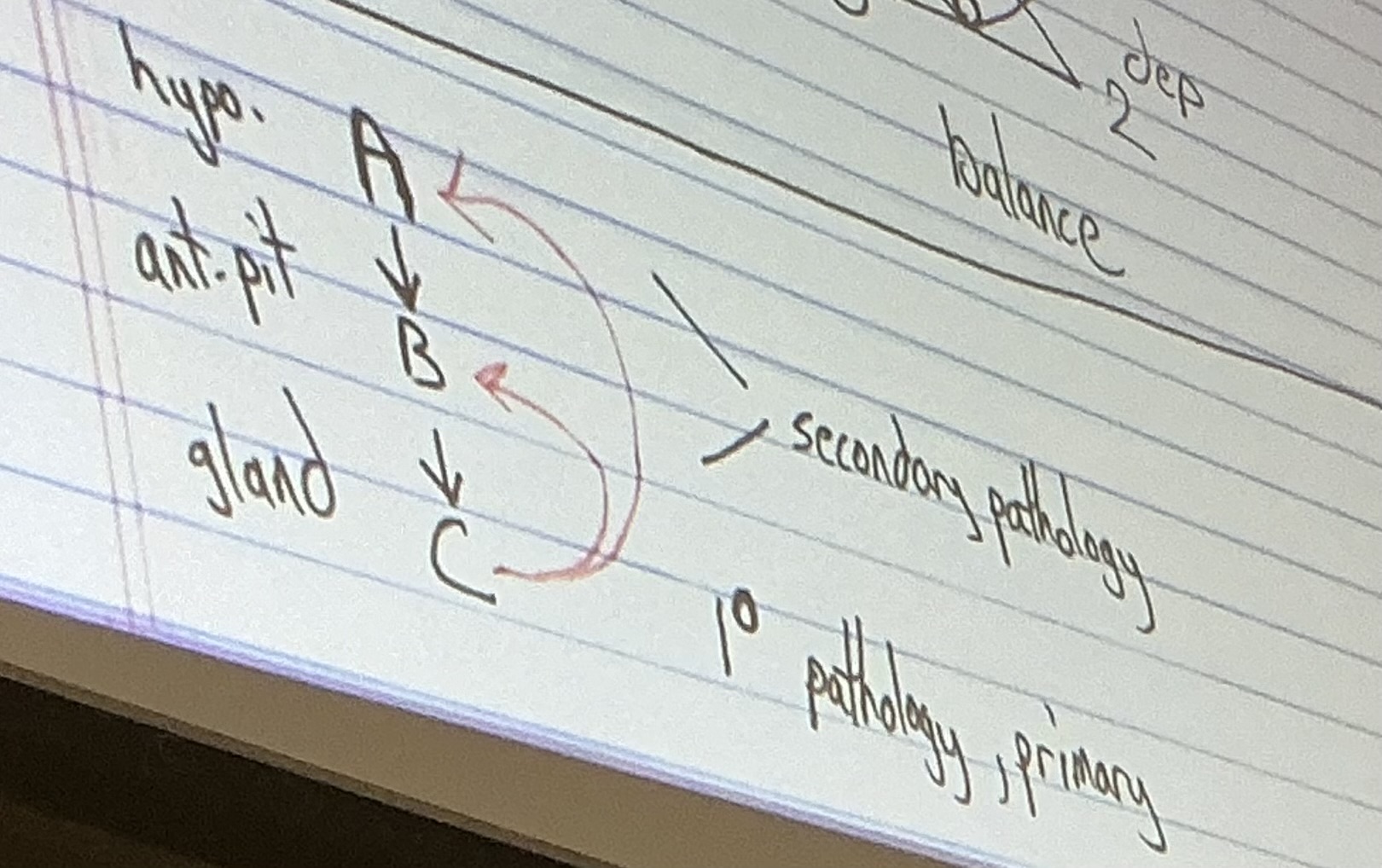
Classification when things break: Primary pathology
Damage occurs to the LAST gland in the pathway
Classification of when things break: secondary pathology
Damage occurs to a gland EARLIER in the pathway
Blood levels of hormones
Vary only within narrow, desirable range
Controlled by NEGATIVE FEEDBACK SYSTEMS
Endocrine glands stimulated to synthesize and release hormones in response to
Humoral stimuli
Neural stimuli
Hormonal stimuli
Humoral stimuli
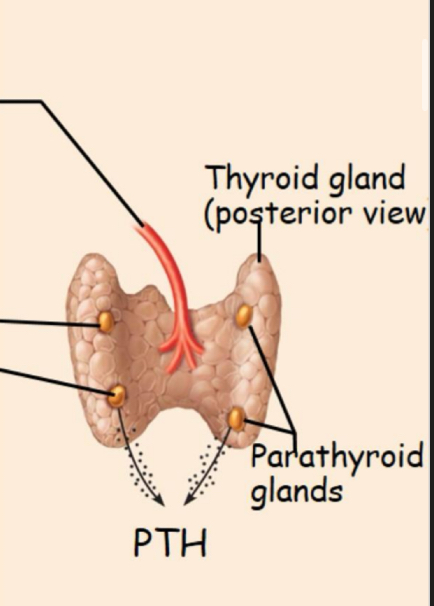
Hormones release caused by altered levels of certain critical ions/nutrients (O2, Na+, K+, Ca2+)
Stimulus: low concentration of Ca2+ in capillary blood
Response: PARATHYROID GLANDS
secrete parathyroid hormone (PTH) which increases blood Ca2+
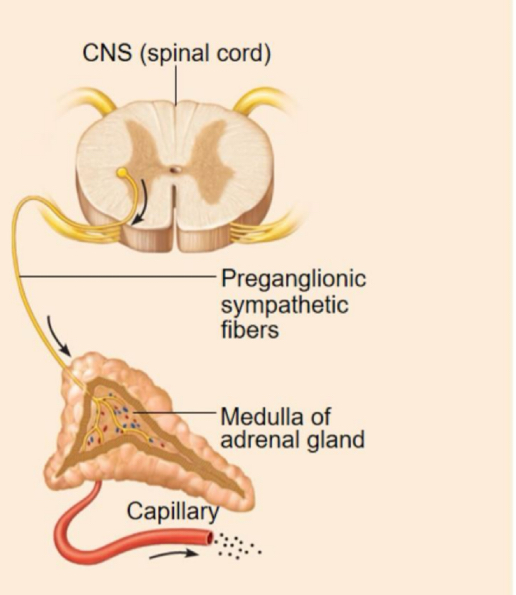
Neural stimuli
Hormone release cause by neural input
Stimulus: action potentials from sympathetic fibers to adrenal medulla.
Response: adrenal medulla cells secrete epinephrine and norepinephrine.
FLIGHT OR FIGHT RESPONSE
Hormonal stimuli
Hormone release is controlled by another hormones (tropic hormone)
Stimulus: hormones from hypothalamus
Response: anterior pituitary gland secretes hormones that stimulate other endocrine glands to secrete hormones
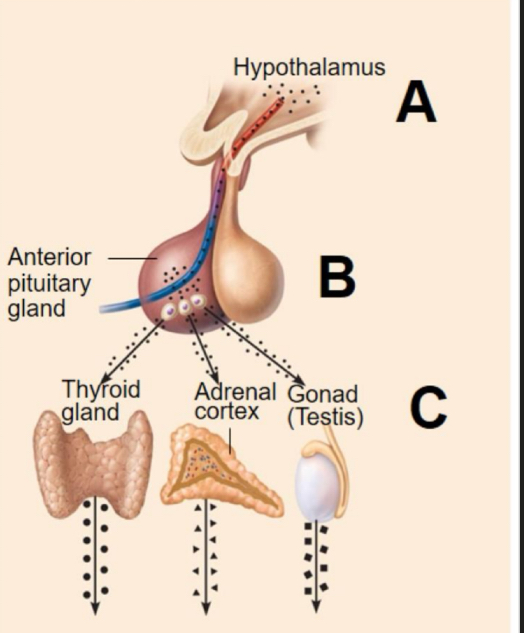
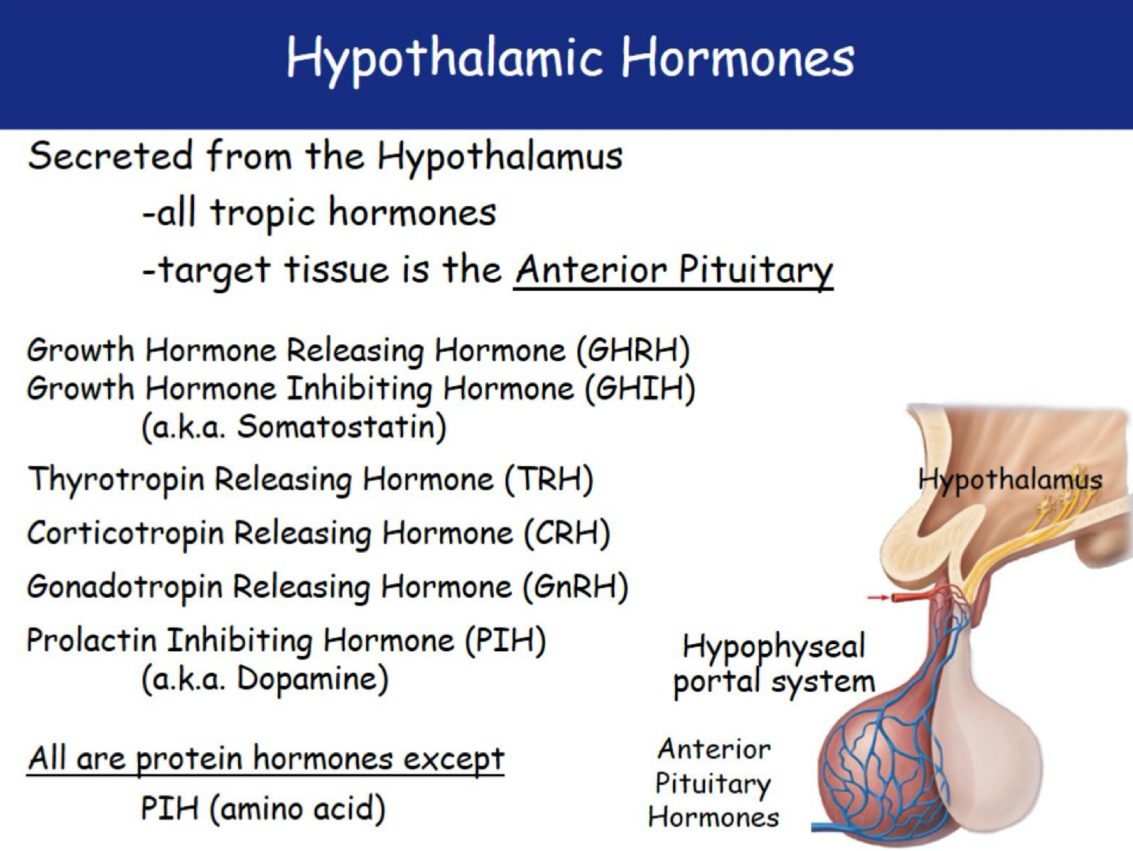
Hypothalamic Hormones
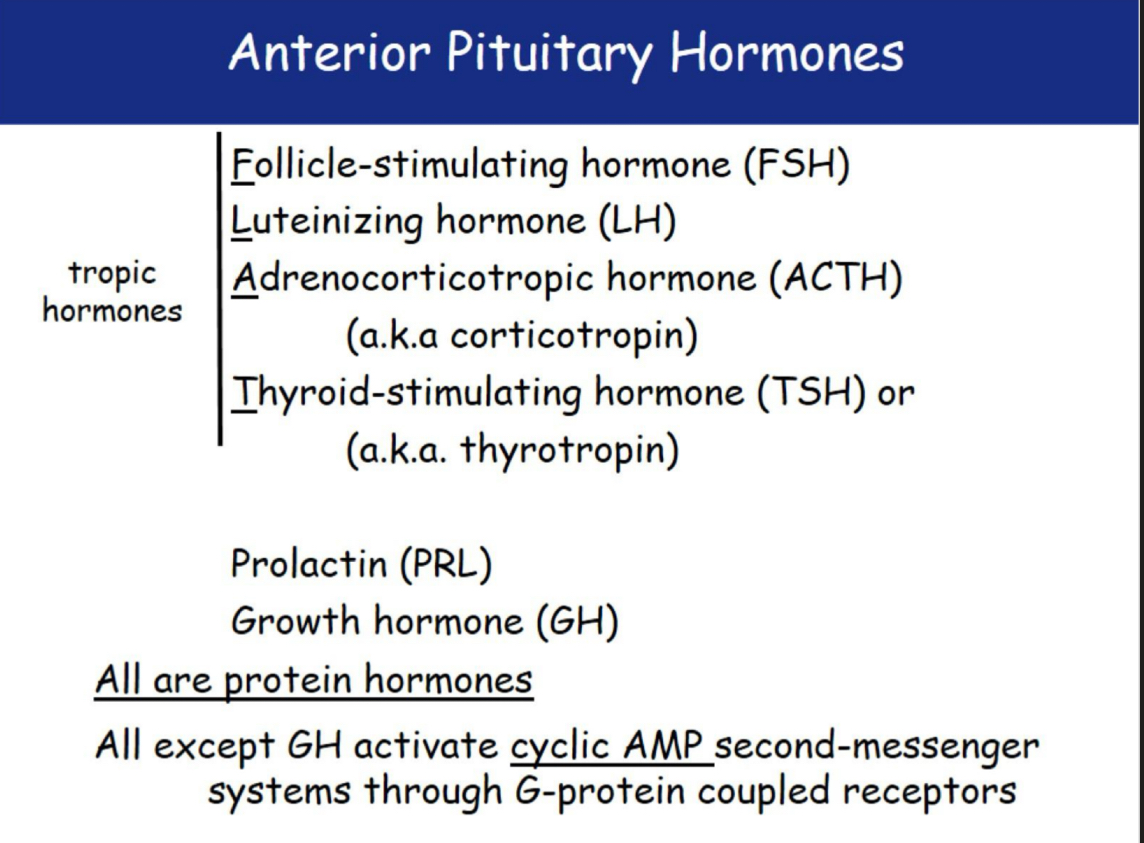
Anterior pituitary hormones
FSH and LH (Gonadotropins)
FSH stimulates gamete production (egg and sperm) by stimulating granulosa cells (female) and sertoli cells (male)
LH promotes production of gonadal hormones (sex steroids)
THECA calls make androgens, GANULOSA cells convert androgens to estrogen and LEYDIG cells make testosterone
Both: lead to maturation of human egg and sperm (granulosa and Sertoli cells have receptors for BOTH FSH and LH hormones)
LH spike triggers ovulation (release of egg)
Gonadotropins are absent from the blood of prepubescent children
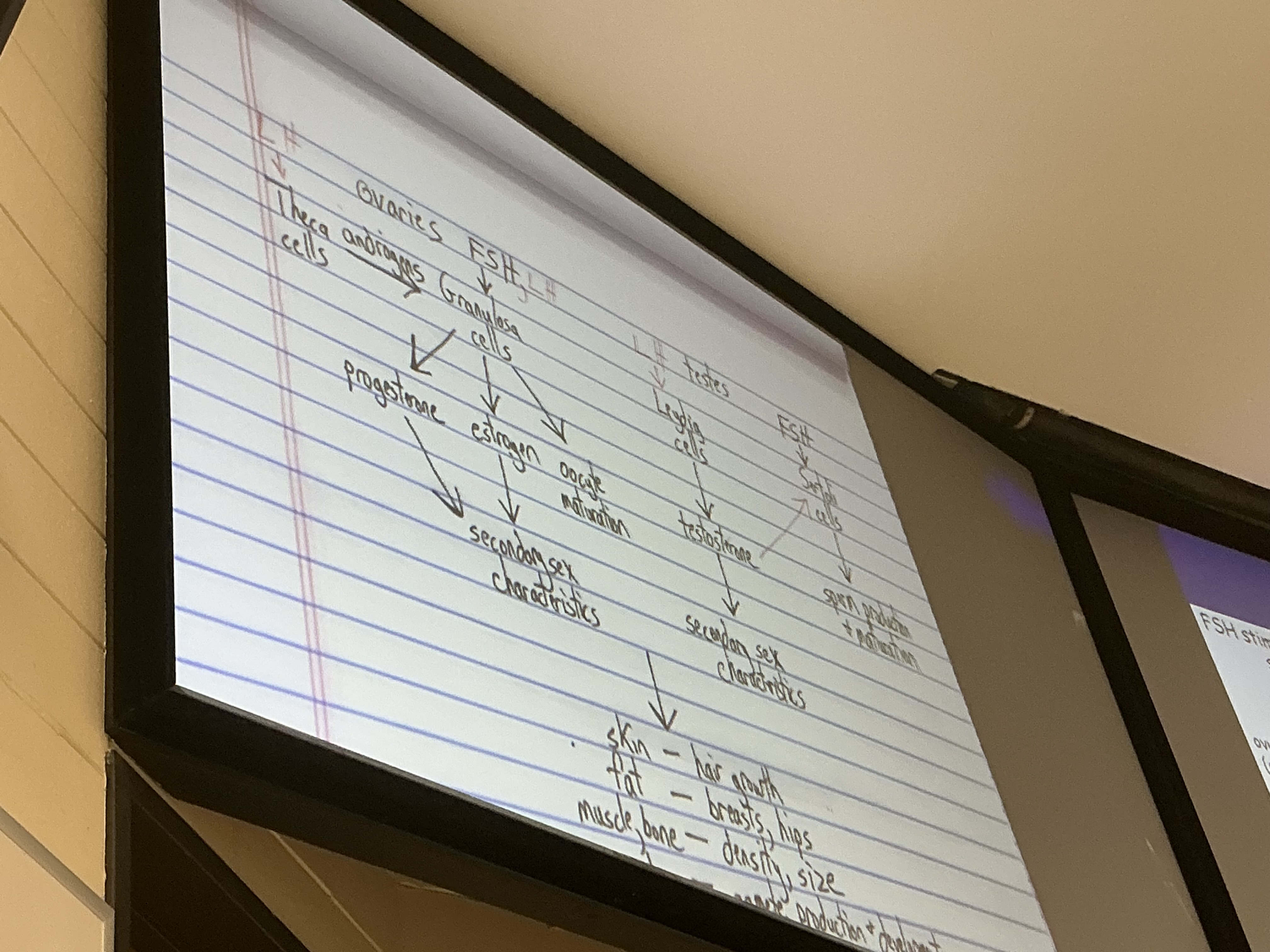
Ovaries
Produce ESTROGENS and PROGESTERONE
Testes
Produce testosterone
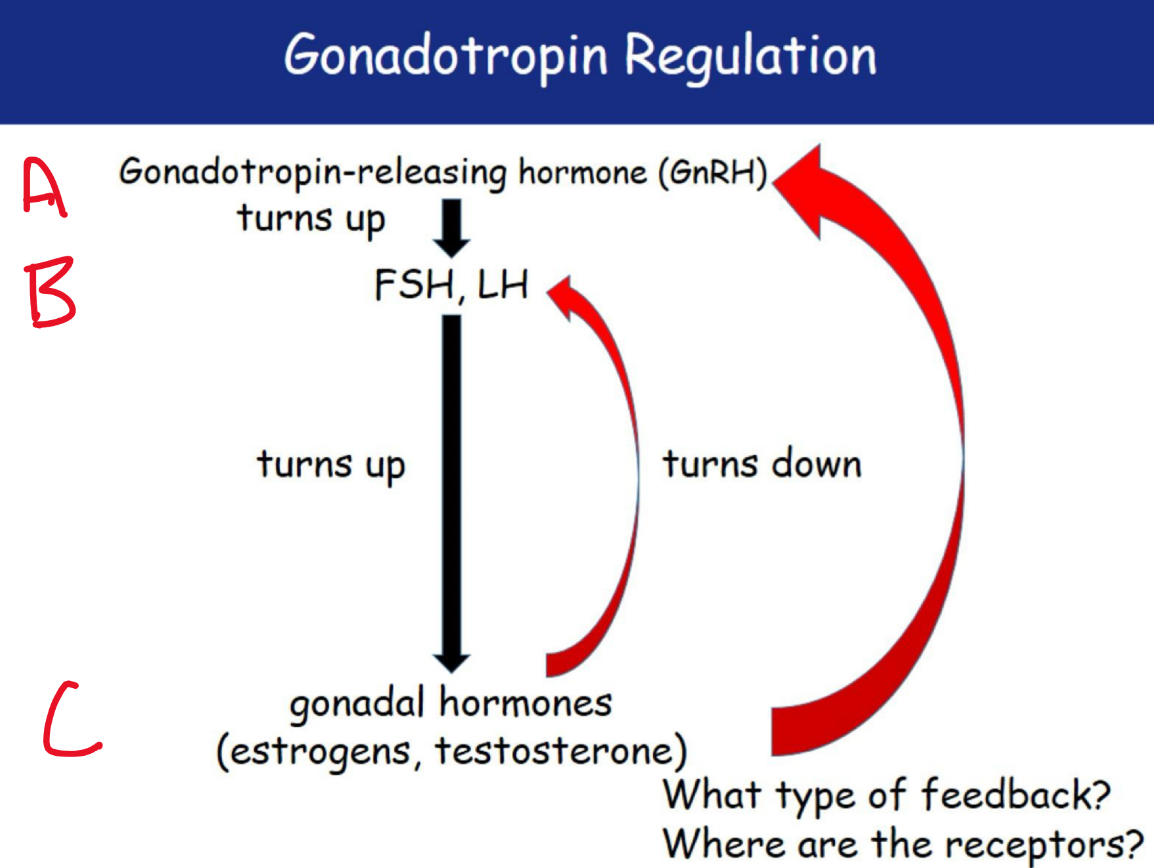
Gonadotropin regulation
NEGATIVE FEEDBACK
Adrenocorticotropic hormone (Corticotropin)
Stimulates ADRENAL CORTEX to release cortisol (resist stress)
Feedback loops
NEGATIVE FEEDBACK

Prolactin (PRL)
Lactation: production (milk production)
Regulation of PRL release is controlled by prolactin inhibiting hormone (PIH) (DOPAMINE)
BLOOD LEVELS RISE TOWARDS END OF PREGNANCY
Suckling stimulates PRL release and promotes continued milk production
HYPER-SECRETION CAUSES:
Inappropriate location
Lack of menses and infertility in females
INHIBITS RELEASE OF GONADOTROPIN RELEASE HORMONE (natural birth control)
Impotence and sterility in males (if experiencing PRL)
Growth Hormone (GH)
Direct actions on metabolism (promotes mitosis ** more production of cells)
Encourages use of fat for fuel and promote protein synthesis
Decrease rate of glucose storage and promotes glycogen breakdown (raises blood glucose similar to glucagon)
Indirect actions of growth:
Mediates growth via growth-promoting proteins - Insulin like growth factors (IGFs)- promotes growth (IGF is a hormone)
GH and IGF promote:
uptake of nutrients —> DNA and proteins
Build collagen and deposits bone matrix
Major targets- bone and skeletal muscle
Growth hormone HYPERsecretion (gigantism and acromegaly)
in children results in GIGANTISM
In adults results in ACROMEGALY
pituitary tumor (many more cells releasing GH to other cells)
Growth hormone HYPOsecretion (dwarfism)
in children results in PITUITARY DWARFISM
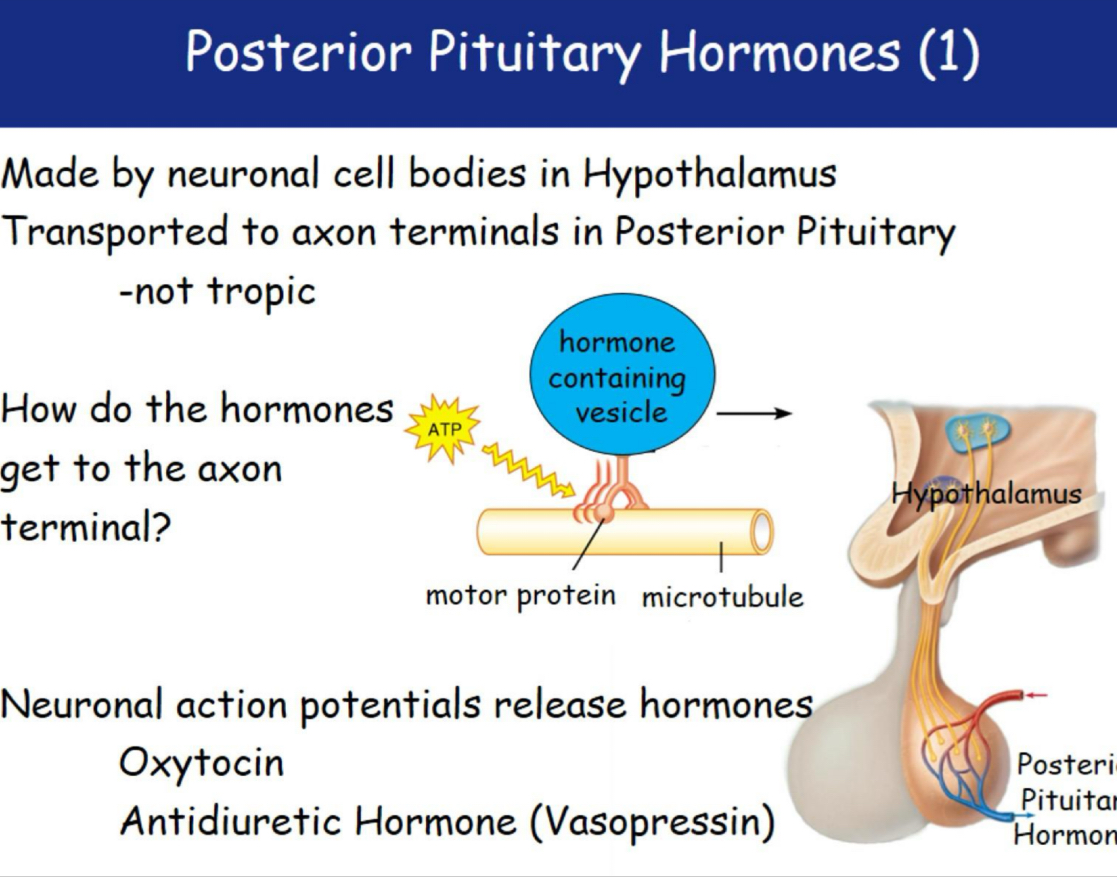
Posterior pituitary hormones
Neural Hormone
OXYTOCIN: stimulates uterine CONTRACTION
Oxytocin
1) strong stimulate of uterine CONTRACTIOn
dissension of the cervix and uterus during labor (promotes release)
2) hormonal trigger for MILK EJECTION
Mammary glands promote milk release
POSITIVE FEEDBACK
ANTIdiuretic hormone vasopressin
inhibits or prevents urine formation (regulates water balance)
Increased by low blood pressure (targets kidney collecting ducts —> reabsorb more filtrate)
A high concentrations—> VASOCONSTRICTION (increase blood pressure)
Inhibited by alcohol (diuretics- make you want to pee)
ADH Disorders
Diabetes insipidus (lacking flavor)
ADH defeiciency due to hypothalamic or posterior pituitary damage
Kidney insensitive to ADH (receptor problem)
Excess urination: (DIULUTE URINE)
Treatment: hydration
Syndrome of inappropriate ADH secretion (SIADH)
retention of fluid (headache disorientation leading to hyponaterimia)
Treatment: fluid restriction (blood sodium monitoring)