AP Lit Common Literary Terms
1/58
There's no tags or description
Looks like no tags are added yet.
Name | Mastery | Learn | Test | Matching | Spaced | Call with Kai |
|---|
No analytics yet
Send a link to your students to track their progress
59 Terms
simile
a comparison of two seemingly unlike things that uses comparative words (such, like, as,etc)
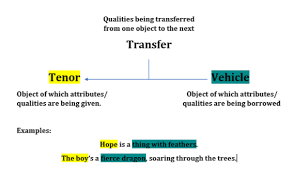
vehicle
the aspect of a comparison (metaphor/simile/analogy, etc) that coneys (“drives”) intended understanding of the subject; the thing being used to describe the subject
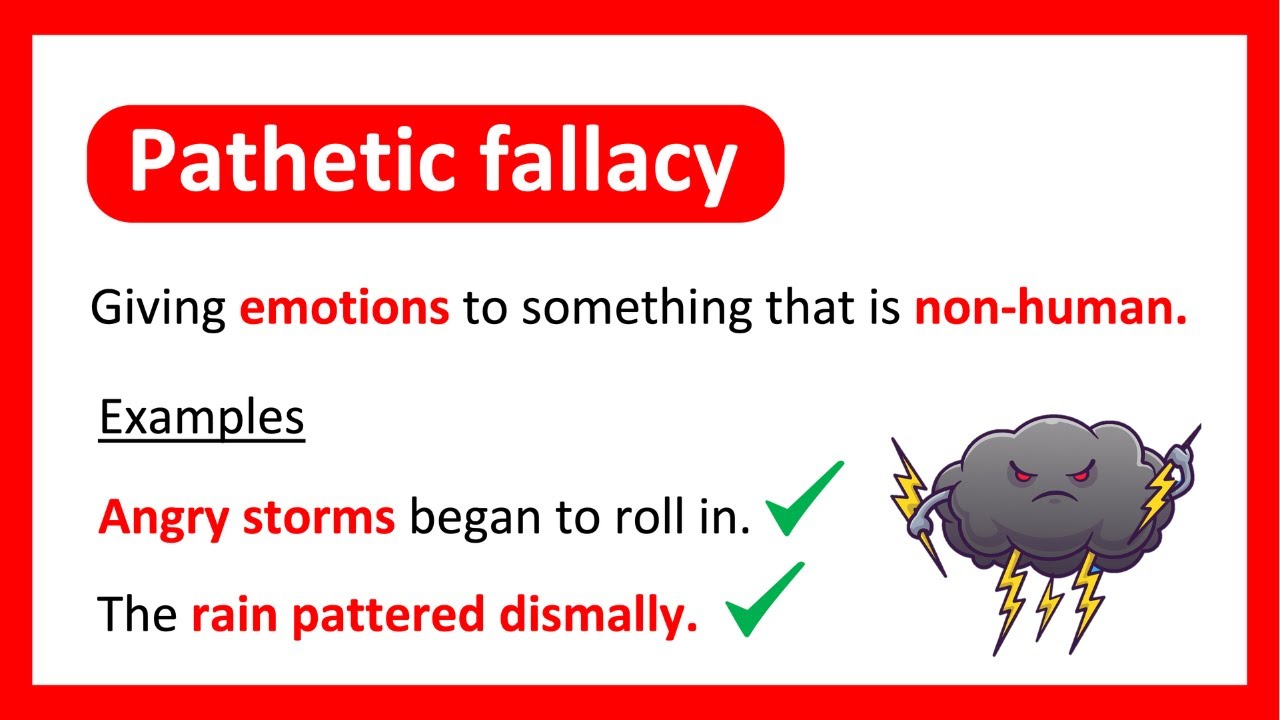
pathetic fallacy
a type of personification in which inanimate aspects of nature (weather, landscape) are given human qualities or feelings. Usually reflects or foreshadows events and contributes to tone

mixed metaphor
when two or more incongruous vehicles are used to describe the same tenor
metaphor
a comparison of two seemingly unlike things that does not use comparative words
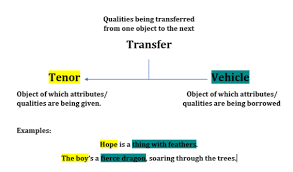
tenor
the aspect of a comparison (metaphor/simile/analogy, etc) that is the literal subject; the thing that is being described
rhetorical question
a question is asked not to get answered but to emphasize an already implied conclusion
figurative language
words or phrases that are not intended to be interpreted literally
synecdoche
a part is used to designate the whole or the whole is used to designate a part.
For example, the phrase “all hands on deck,” means “all men on deck,” not just their hands
understatement
a form of irony in which a point is expressed as lesser in some way than it really is
1st POV
indicated by pronouns I, me, we, etc. Narrator tells a story in which they are a character
2nd POV
indicated by pronoun you. Narrator tells a story in which the reader is a character
3rd Omniscient POV
indicated by pronouns they, he, she, it, etc. Narrator is not a character in the story but knows everything about all the characters and events including inner thoughts, full backgrounds, etc.
3rd Objective POV
indicated by pronouns they, he, she, it, etc. Narrator is not a character in the story but knows only what is visible; does not know the thoughts or feelings of any characters
3rd Limited POV
indicated by pronouns they, he, she, it, etc. Narrator is not a character in the story but knows the thoughts and feelings of only one or a select few characters
Verbal irony
implying a different meaning from, and often opposite of, what is actually stated. Can be misconstrued as sincere (ex. “Die early, and avoid the fate [of being famous].”)
Situational irony
that which is expected is not what occurs (not necessarily the opposite of what’s expected)
Dramatic irony
when the audience knows something that one or more of the characters do not know
Cosmic irony
outcome of character action seems to be controlled by forces larger than the self (fate, the universe, the gods)
metonymy
one word is substituted for another with which it is closely associated.
For example, in the expression The pen is mightier than the sword, the word pen is used for “the written word,” and sword is used for “military power”
intrusive narration
the narrator offers commentary on characters and events in a clear effort to influence the perceptions of the audience
parallelism
repetition of syntactical structure of a line or phrase
periphrasis
the point is stated by deliberate circumlocution rather than directly
*circumlocution - the use of many words where fewer would do, especially in a deliberate attempt to be vague or evasive
personification
nonhuman things or abstract ideas are given human attributes
unreliable narration
the narrator interprets events and intentions in their narration and thus influences (intentionally or unintentionally) the perceptions and attitudes of the audience. First person narrators are more likely to be unreliable. Tone is meant to be seen as exaggerated or misleading
alliteration
repetition of initial consonant sounds
atmosphere
the predominant mood in all or part of literary work (established through setting, dialogue, diction, etc)
speaker
the voice that “speaks” a poem; as opposed to the “narrator” of a book or story
diction
word choice; phrasing
syntax
the order/arrangement of words in a line of poetry (or in a sentence)
theme
the central idea that a work conveys; that which the author intended the reader to understand, think about or know as a result of having read the work, established through plot, characterization, motif, and other elements
assonance
repetition of internal vowel sounds
apostrophe
spoken to a person who is absent or imaginary, or to an object or abstract idea
antithesis
words or phrases with opposite ideas or meanings are balanced against each other. Example: “To err is human, to forgive divine” (Alexander Pope)
sarcasm
taunting use of approval or praise when the opposite is what is felt. More crude than verbal irony and is intended to cause emotional pain
anaphora
intentional repetition of words or phrases at the beginning of successive lines, stanzas, sentences or paragraphs
hyperbole
a deliberate and purposeful exaggeration
litotes
a positive is stated by negating its opposite; e.g. no small victory, not a bad idea, not unhappy; a form of understatement that requires the negative statement rather than just the understatement
enjambment
a line of poetry which is not end-stopped, in which the thought continues into the next line without any pause
tone
the attitude that a literary speaker expresses toward their subject matter and audience
(term is derived from spoken discourse in which listeners attend to a speaker's voice in order to assess feelings about the topic at hand and about the speaker’s relationship to their audience / the speaker’s conception of the audience’s intelligence, sensitivity, receptivity, etc. In written discourse, must be inferred via diction, syntax, POV, selection of detail)
verisimilitude
writing that tries to be close to the truth (real-seeming) as possible
stanza
a grouping of lines of poetry, indicated by an empty space before the next one begins
rhyme
The repetition of the end sounds of nearby words
oxymoron
a kind of paradox that links seemingly contradictory elements that turn out to make sense together
repetition
the reiterating of a word or phrase within a poem
allusion
a reference to another work, an historical or mythical event, person, etc
paradox
a statement that appears contradictory or impossible but turns out to express a striking truth
onomatopoeia
words that sound like the idea or thing they represent
imagery
descriptive language that relies on at least one of the five senses
symbol
anything (word, phrase, person, action, etc) that represents itself but also stands for a more abstract idea
mood
the overall feeling of a text often created by the author’s use of imagery and word choice
motif
a recurring idea found in a work. Established through plot and symbols. Contributes largely to theme
chiasmus
a verbal pattern (a type of antithesis) in which the second half of an expression is balanced against the first with the parts reversed. Example: You forget what you want to remember, and you remember what you want to forget
pun
a play on words in which an effect is produced by using a word that suggest two or more meanings or involves words with similar sounds
analogy
a comparison of two seemingly different things so that a larger point can be made based on the comparisons
foreshadowing
allusion to a later point in the story
in media res
beginning “in the middle”
*Latin phrase meaning “in the midst of things” used to describe when a story opens with the character already in the middle of things
flashback
an interruption to the chronological order of the plot in order to provide context, information, or a scene that took place before the timeline of the current plot sequence
frame narrative
narrative technique in which there is a story within a story