OIA1012 ALKENES
1/22
Earn XP
Description and Tags
Name | Mastery | Learn | Test | Matching | Spaced | Call with Kai |
|---|
No analytics yet
Send a link to your students to track their progress
23 Terms
Q:What are alkenes?
A:Alkenes are unsaturated hydrocarbons containing at least one C=C double bond.
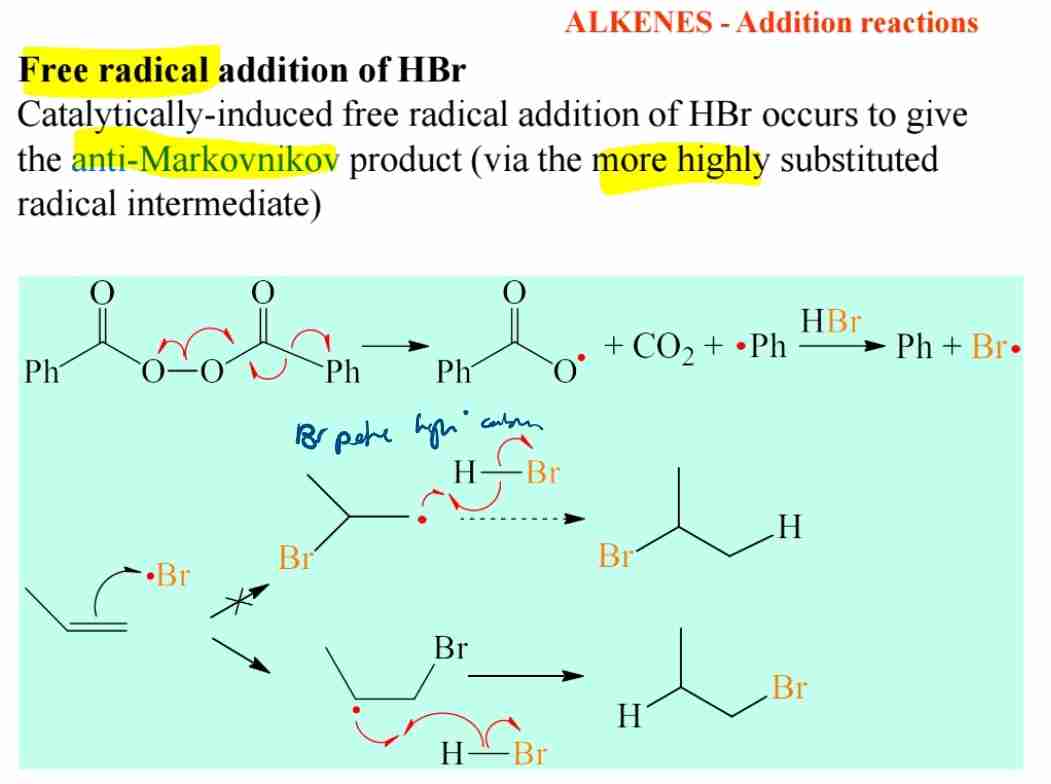
Explain free radical addition of HBr.
If HBr, then H is added to less substituted C atom (anti-Markovnikov rule), producing more highly substituted carbocation intermediate.
Q:What is the general formula for alkenes?
A:The general formula for alkenes is CₙH₂ₙ.
Q:What type of isomerism is associated with alkenes?
A:Alkenes exhibit geometric isomerism due to restricted rotation around the C=C bond.
Q:How do you name an alkene?
A:Identify the longest carbon chain containing the C=C bond, replace the -ane ending with -ene, and number the chain to indicate the position of the double bond.
Q:What is Markovnikov’s rule?
A:In the addition of an electrophile to a C=C bond, the electrophile adds to the less substituted carbon atom.
Q:What is the effect of alkyl substitution on the stability of carbocation intermediates?
A:Reactivity increases with increasing alkyl substitution due to electron-donating effects, stabilizing the carbocation.
Q:What are addition reactions in alkenes?
A:Addition reactions involve the addition of atoms or groups across the C=C bond, resulting in the formation of saturated products.
Q:What is the outcome of the ionic addition of halogens to alkenes?
A:The outcome is the formation of vicinal dibromides, such as trans-1,2-dibromocyclohexane from cyclohexene.
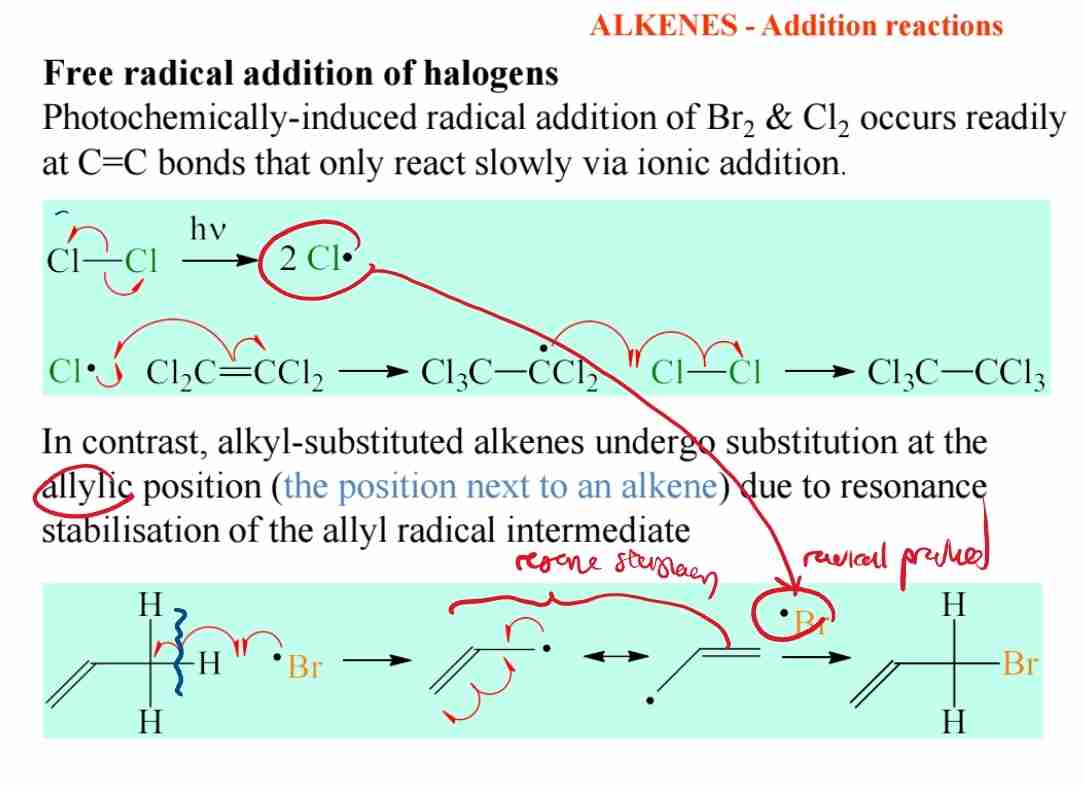
Q:Describe the free radical addition of halogens.
A:Free radical addition involves the formation of radicals and occurs under light conditions, leading to substitution at the allylic position.
Q:What is the role of KMnO₄ in alkenes?
A:KMnO₄ is a powerful oxidizing agent used for oxidative cleavage of C=C bonds.
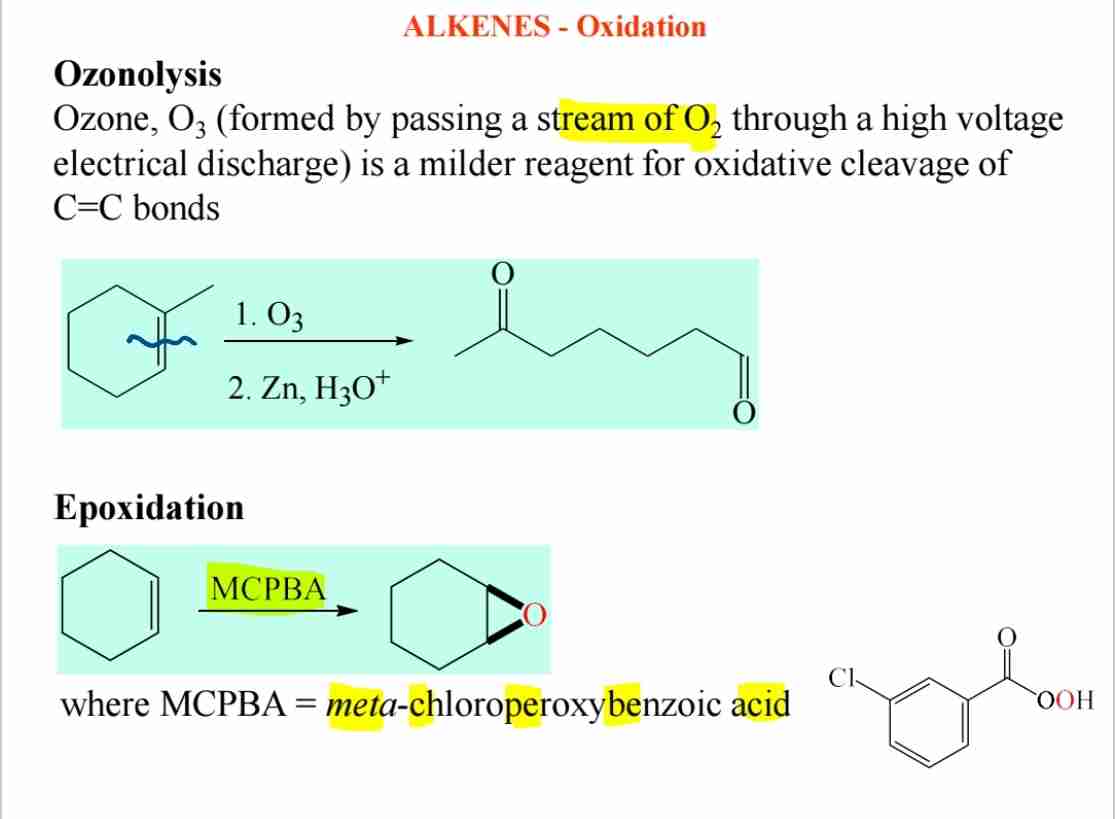
Q:Explain the concept of ozonolysis.
A:Ozonolysis is the oxidative cleavage of C=C bonds using ozone (O₃), resulting in carbonyl compounds.
Q:What is the significance of hydrogenation in alkenes?
A:Hydrogenation is the addition of hydrogen across the C=C bond, converting alkenes into alkanes, often used in food processing.
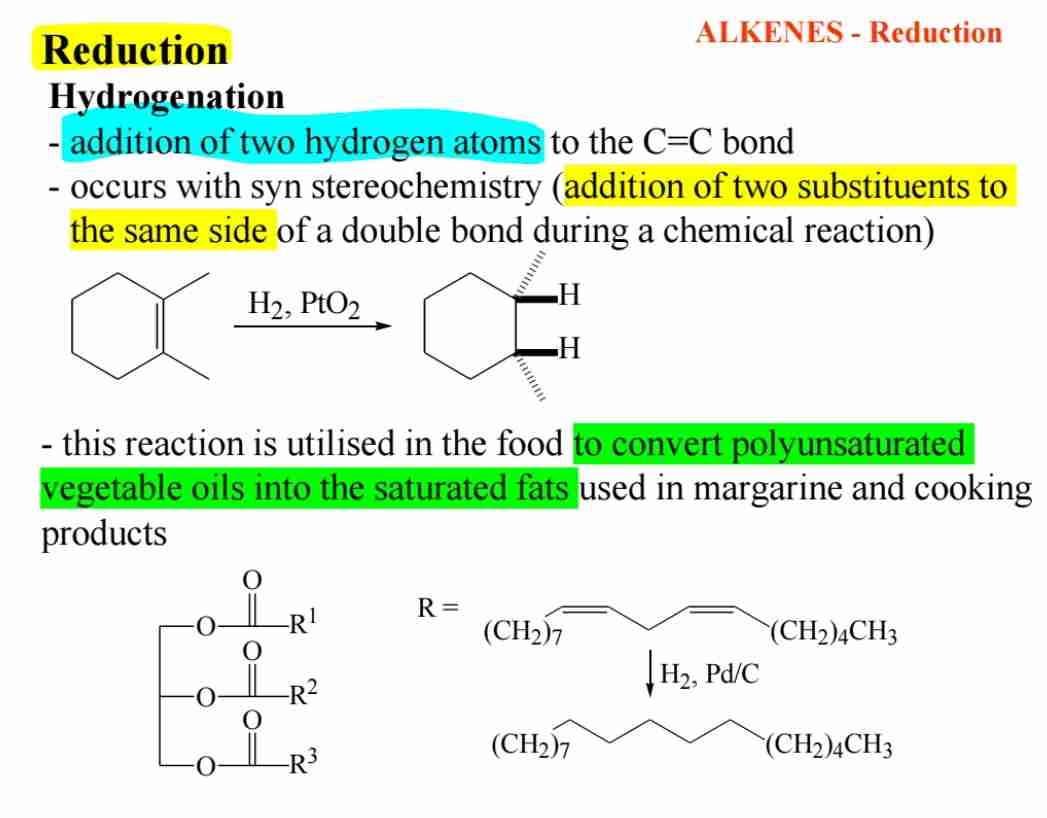
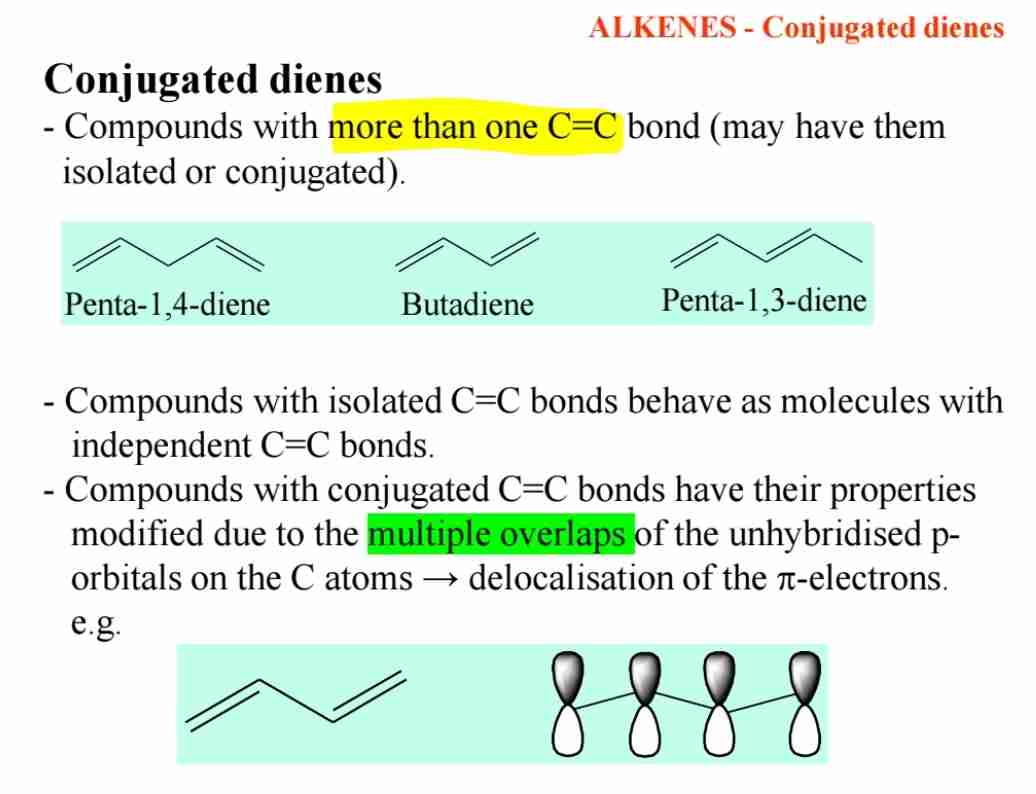
Q:What are conjugated dienes?
A:Conjugated dienes are compounds with two C=C bonds that are separated by a single bond, allowing for delocalization of π electrons.
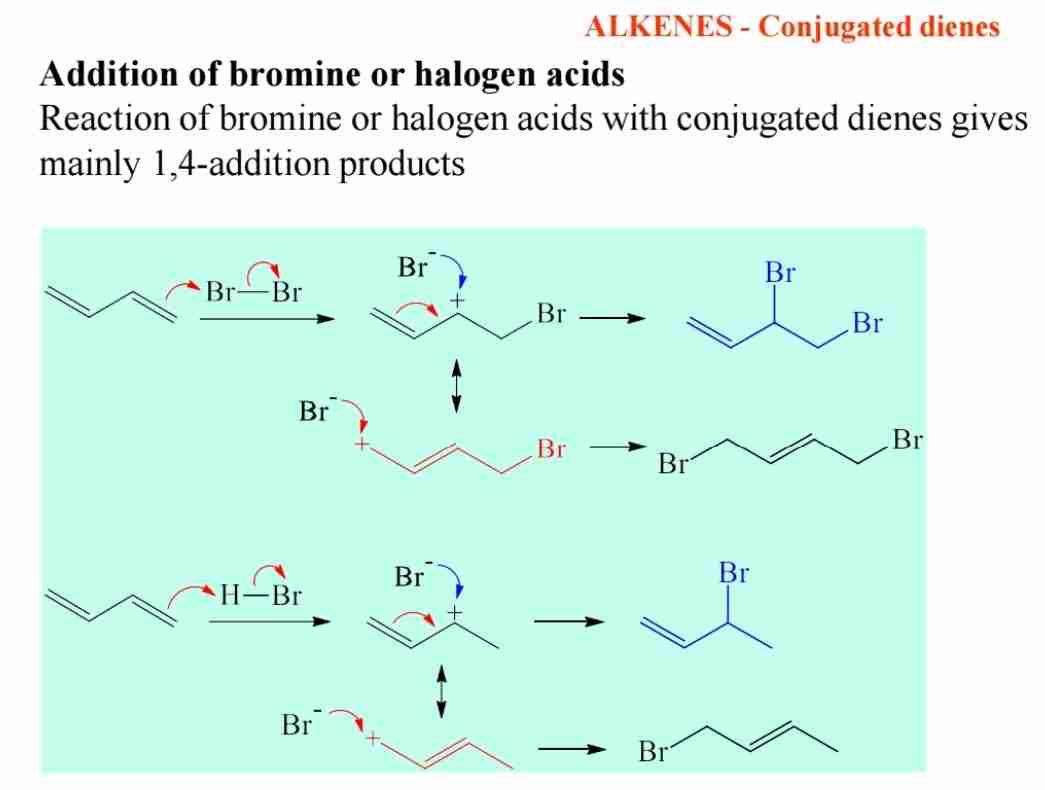
What is product of bromine/halogen acid addition in conjugated dienes?
Mainly 1,4-addition products.
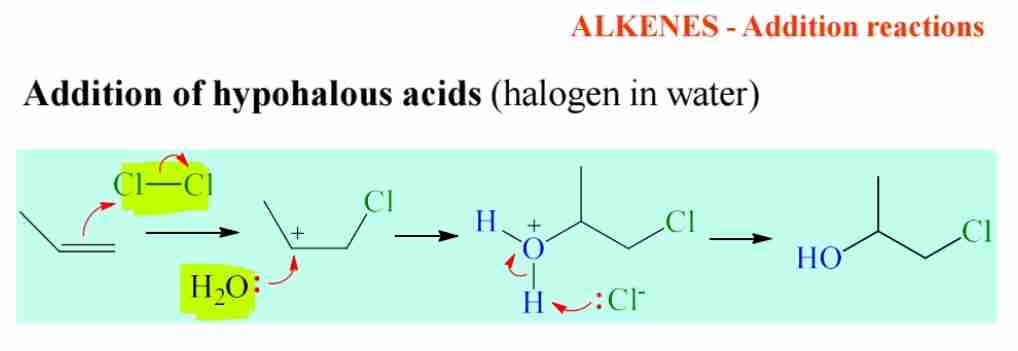
Show mechanism of addition of hypohalous acid (halogen in H2O).
C=C attack Cl form carbocation & other Cl form radical
water attack carbocation
Cl radical attack H of H2O and the bond attack O+
H2O+ form OH
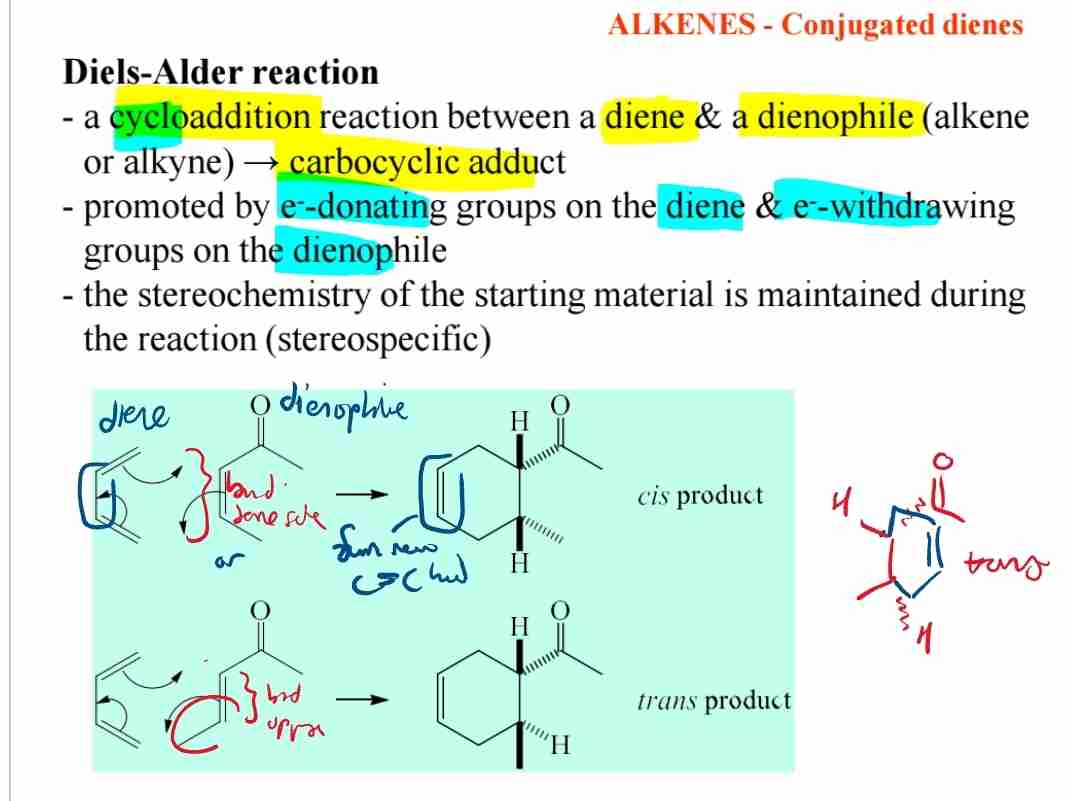
Q:What is the Diels-Alder reaction?
A:The Diels-Alder reaction is a cycloaddition reaction between a diene and a dienophile, producing a cyclic compound.
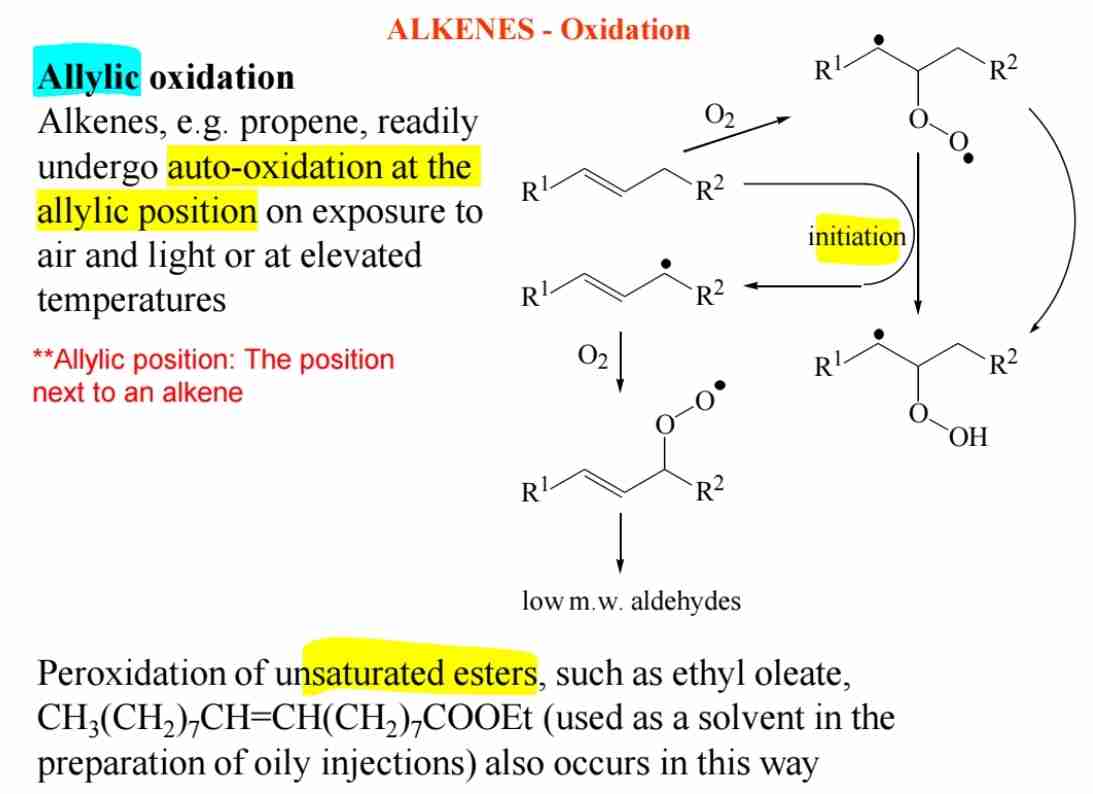
Q:How do alkenes undergo auto-oxidation?
A:Alkenes can undergo auto-oxidation at the allylic position when exposed to air or light, leading to allylic oxidation products.
Q:What is the significance of trans fatty acids formed from partial hydrogenation?
A:Trans fatty acids can raise blood cholesterol levels and contribute to coronary heart disease.
Q:Describe the process of polymerization of alkenes.
A:Polymerization involves the radical-induced reaction of alkenes at high temperatures and pressures to form long-chain polymers like polyethylene.
Q:What are the physical properties of alkenes?
A:Alkenes resemble alkanes in physical properties, being gases or low-boiling liquids, and are insoluble in polar solvents.
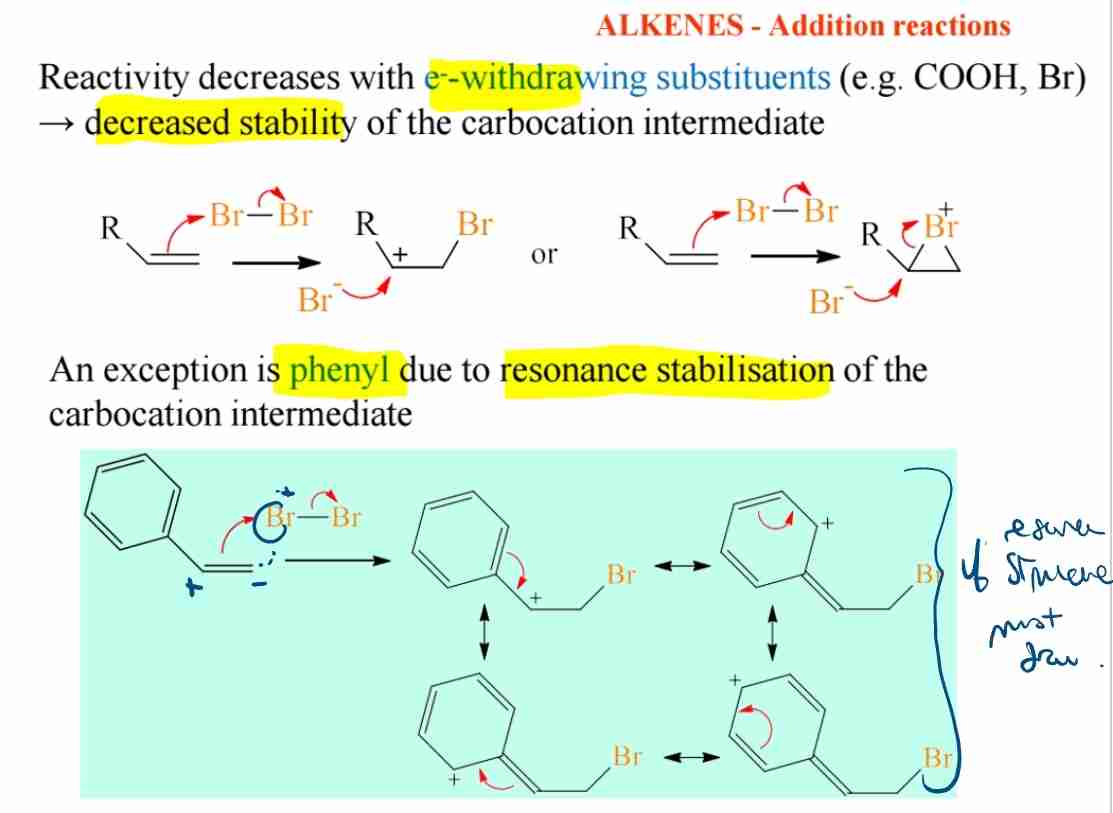
Q:Explain the role of electron-withdrawing groups in alkene reactivity.
A:Electron-withdrawing groups decrease the stability of carbocation intermediates, reducing the reactivity of alkenes except for phenyl as carbocation intermediate due to resonance stabilisation .
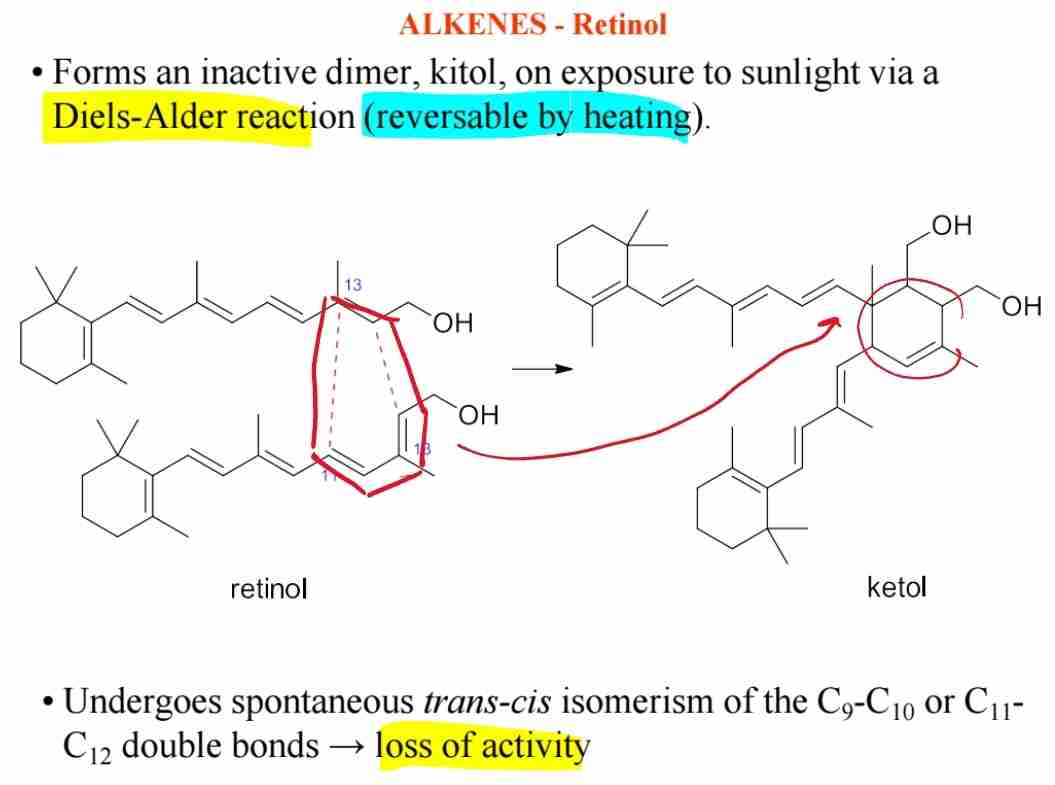
Q:What is the biological significance of retinol (Vitamin A)?
A:Retinol is crucial for vision and is sensitive to oxidation, forming inactive dimers upon exposure to light.