MCAT Biochemistry Review
1/94
Earn XP
Description and Tags
Name | Mastery | Learn | Test | Matching | Spaced |
|---|
No study sessions yet.
95 Terms
What configuration are all amino acids found in (in eukaryotic cells)?
All of them are in the L configuration.
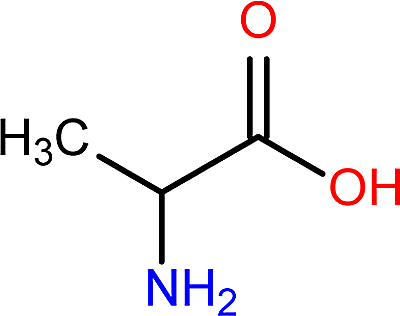
Alanine
Structure of Alanine:
Ala: A
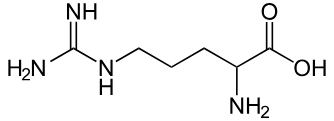
Arginine
Arg: R
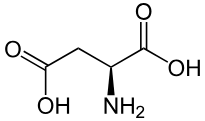
Aspartic Acid (deprotonated OH is aspartate)
Asp: D
Cysteine
Cys: C

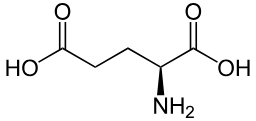
Glutamic acid (deprotonated OH is glutamate)
Glu: E
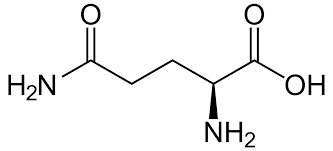
Glutamine
Gln: Q
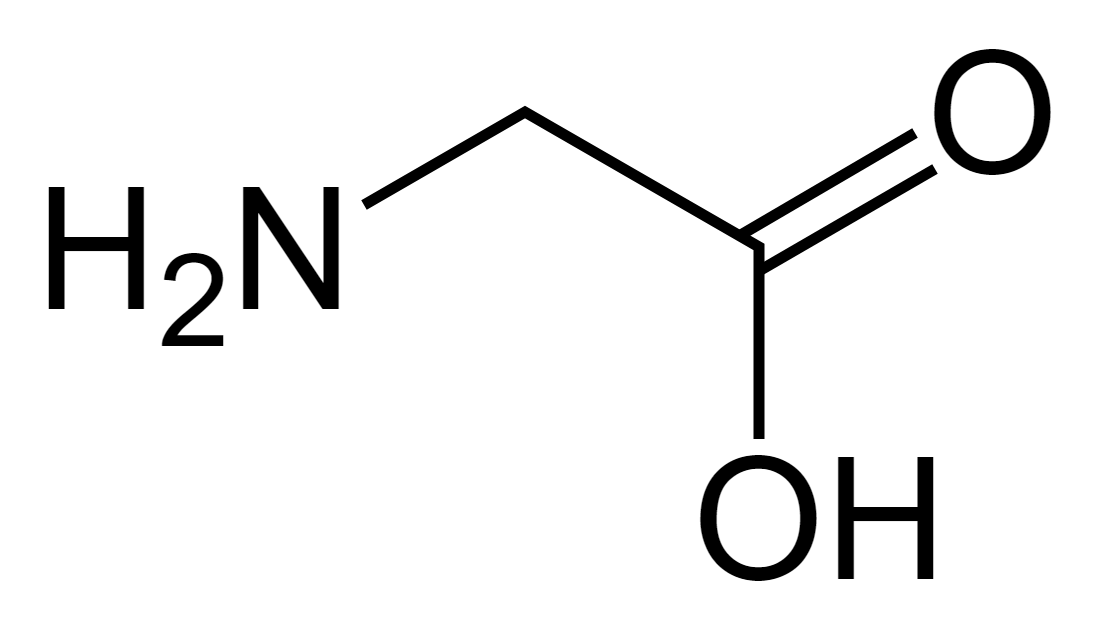
Glycine
Gly: G
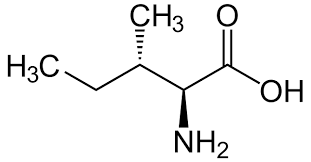
Isoleucine
Ile: I
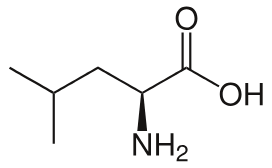
Leucine
Leu: L
Lysine
Lys: K
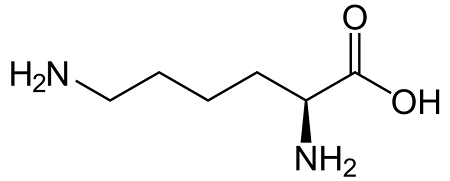
Methionine
Met: M
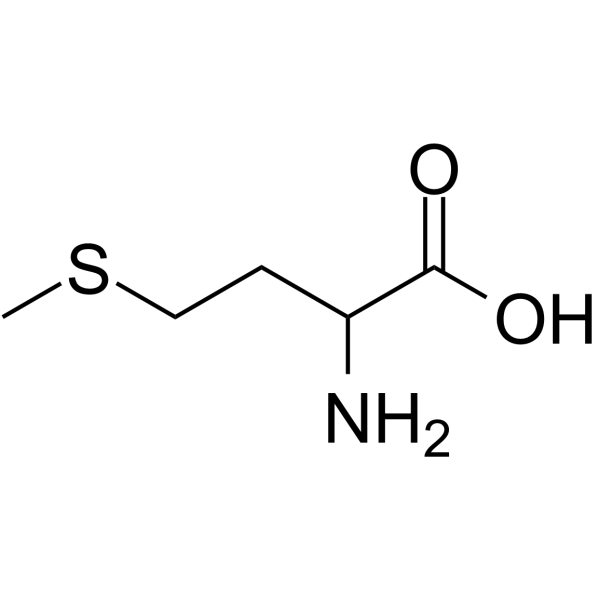
Phenylalanine
Phe: F
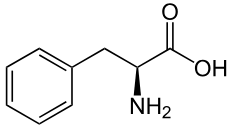
Proline
Pro: P
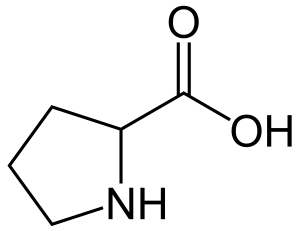
Serine
Ser: S
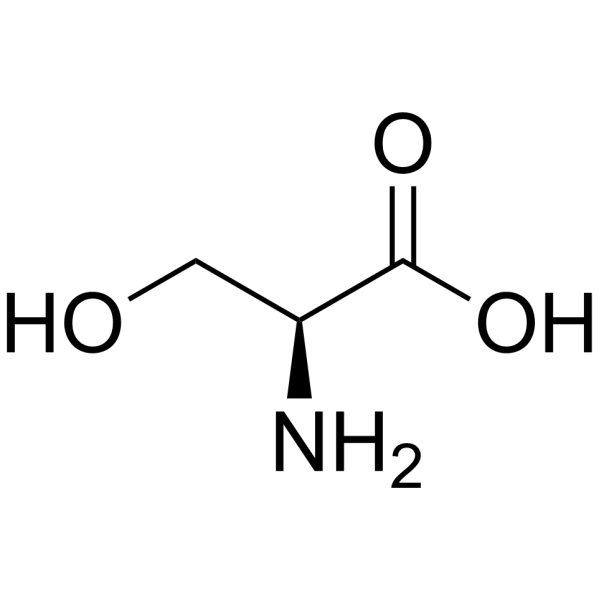
Threonine
Thr: T
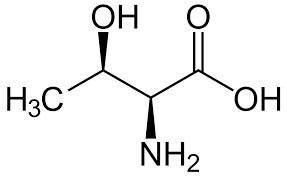
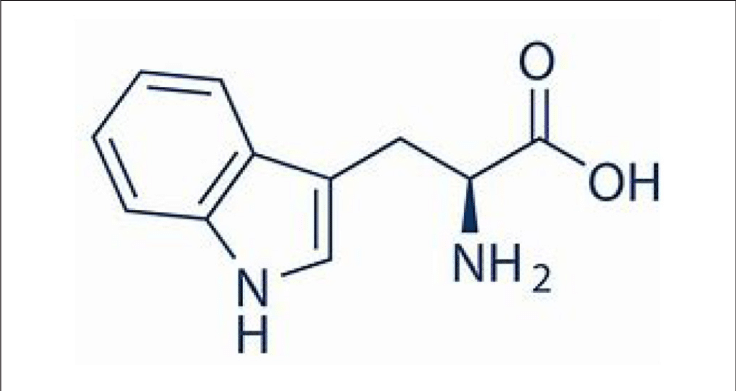
Tryptophan
Trp: W
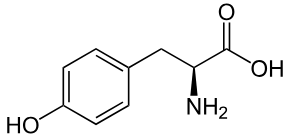
Tyrosine
Tyr: Y
Valine
Val: V
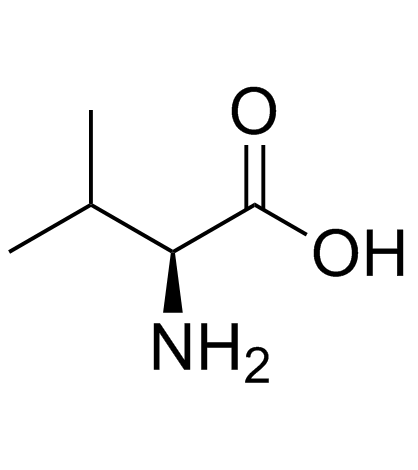
All chiral amino acids have the S absolute configuration except for…
Cysteine (CH2SH takes priority over COOH, making it R)
Which amino acids have aromatic side chains?
Tryptophan, phenylalanine, tyrosine
Which amino acids have polar side chains?
Serine, threonine, asparagine, glutamine, cysteine
Which amino acids have a negatively charged (acidic) side chain?
Aspartate (aspartic acid), glutamate (glutamic acid)
Which amino acids have a positively charged (basic) side chain?
Lysine, arginine, histidine
What is the only achiral amino acid?
Glycine
Disulfide bonds occur between what two amino acids? What is the resulting molecule called?
Disulfide bonds occur between two cysteine molecules through oxidation. The result is cystine.
pI of alanine
6.11
pI of arginine
10.76
pI of asparagine
5.43
pI of aspartic acid
2.98
pI of cysteine
5.15
pI of glutamine
5.65
pI of histidine
7.64
pI of isoleucine
6.04
pI of leucine
6.04
pI of phenylalanine
5.76
pI of proline
6.30
pI of serine
5.70
pI of threonine
5.60
pI of tryptophan
5.88
pI of tyrosine
5.63
pI of valine
6.02
pI of lysine
9.47
Asparagine
Asn: N
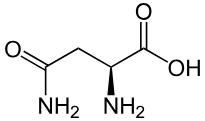
pI of glycine
6.06
Which amino acids have nonpolar, nonaromatic side chains?
Glycine, alanine, valine, leucine, isoleucine, methionine, proline
Histidine
His: H
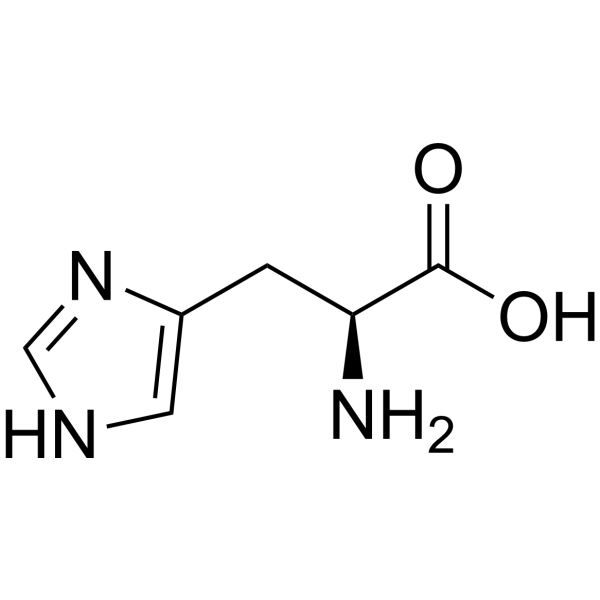
pI of methionine
5.71
pI of glutamic acid
3.08
What is a micelle?
A micelle is a small ball of soap with the hydrophobic tails turned inwards and the hydrophilic heads turned outwards (similar to the plasma membrane)
What is a colloid?
A colloid consists of small particles dispersed evenly in another medium. The medium may be of a different state of matter. The particles are uniform and do not separate. Examples include gels, foam, milk, and emulsions.
What happens in saponification?
A triacylglycerols undergoes an ester hydrolysis with a strong base (usually NaOH). The result is a glycerol molecule as well as the sodium salt of the fatty acid (the soap). 
What is a triglyceride (aka triacylglycerol)?
Triglycerides have a glycerol backbone that is bonded to three (usually different) fatty acid chains. They are a form of energy storage and are stored in adipocytes in the human body.
What is Vitamin K?
Vitamin K refers to a group of compounds including phylloquinone and the menaquinones. These vitamins are important after translation to form prothrombin, a clotting factor in our blood (the aromatic ring undergoes oxidation and reduction). It is also necessary for certain calcium requiring proteins to bond to calcium. 
What is Vitamin E?
Vitamin E is the name used for certain lipids called tocopherols and tocotrienols. They are hydrophobic, and have a substituted aromatic ring and an isoprenoid side chain. The aromatic ring destroys free radicals, and this makes Vitamin E an important antioxidant.
What is Vitamin D?
Vitamin D (cholecalciferol) can be consumed or our bodies can make it when exposed to UV light. It is converted into calcitriol in the liver and kidneys, and this increases calcium and phosphate uptake in the intestine. A lack of Vitamin D can cause rickets (underdeveloped, curved long bones). 
What is Vitamin A?
Vitamin A (carotene) is an unsaturated hydrocarbon. It is vital for vision, growth, development, and the immune system. Retinal is an aldehyde metabolite of Vitamin A that allows the retina to sense light. Retinol is the storage form of Vitamin A and it can be oxidized to retinoic acid, which is a hormone that regulates gene expression during epithelial development.
What are prostaglandins?
Prostaglandins are 20 carbon unsaturated carboxylic acids derived from arachidonic acid. They are paracrine and autocrine signaling molecules. They help synthesize cAMP.
What is cholesterol?
Cholesterol is a steroid that is a major part of the phospholipid bilayer, and makes sure the bilayer is not too liquid at high temperatures and not too solid at low temperatures. It is also a precursor to steroid hormones, bile acids, and vitamin D.
What is a steroid? What is the structure of a steroid?
Steroids are derivatives of terpenes consist of four fused carbon rings. Some steroids are hormones, but not all. 
What is a terpene?
A terpene is made up of two isoprene units. They often have strong smells. Terpenes are named by the number of terpene units in the molecule (double that number for the number of isoprene units). They are also steroid precursors. 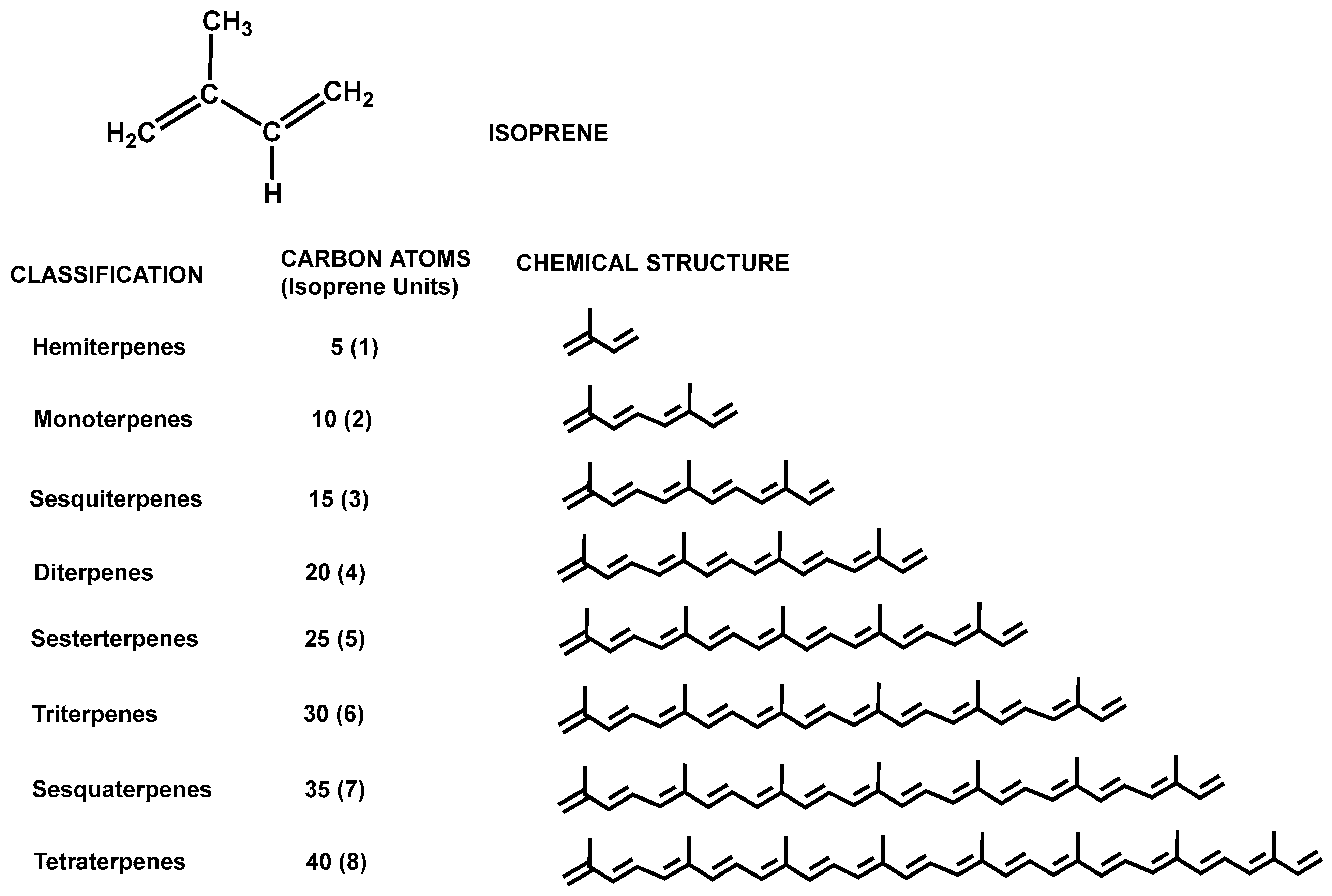
What are waxes?
Waxes are esters of long-chain fatty acids with long-chain alcohols.
What is an ester?
An ester is a carboxylic acid derivative where the H in the -COOH has been replaced with a hydrocarbon R group.
What is a phospholipid?
A phospholipid has a phosphate and alcohol head and a hydrophobic fatty acid tail.
What are glycerophospholipids?
Glycerophospholipids (phosphoglycerides) are a subcategory of phospholipids. A glycerol backbone holds two fatty acids and a very polar head group (the head group always contains a phosphate group and an R group). They are named according to their head group. For instance, phosphatidylethanolamine has an ethanolamine head group. 
What are sphingolipids?
Sphingolipids are like glycerophospholipids, as they have long fatty acid tails and polar head groups. However, sphingolipids have a sphingosine or spingoid backbone instead of the glycerol backbone that is present in glycerophospholipids. Some sphingolipids contain phosphodiester links and are therefore phospholipids, but others contain glycosidic links to sugars, making them glycolipids instead.
What is a sphingosine backbone?

What is ceramide?
Ceramide is the simplest sphingolipid. It has a hydrogen atom as its head group. 
What are sphingomyelins?
Sphingomyelins are a subcategory of sphingolipids that are also phospholipids. They contain a phosphodiester bond and are found in the plasma membranes of cells that produce myelin. Their heads have no net charge. 
What are glycosphingolipids? What are the subcategories cerebroside and globoside?
A glycosphingolipid is not a phospholipid. It is a subcategory of sphingolipids that contains a sugar in its head. They are often found on the outer surface of plasma membranes. A cerebroside has a single sugar, and a globoside has two or more sugars. Their heads have no net charge.
What is a ganglioside?
A ganglioside is the most complex sphingolipid. It has a polar head group made of oligosaccharides and one or more N-acetylneuraminic acid (NANA, aka sialic acid) at the end and a negative charge. They are glycolipids. They play a major role in cell interaction, recognition, and signal transduction.
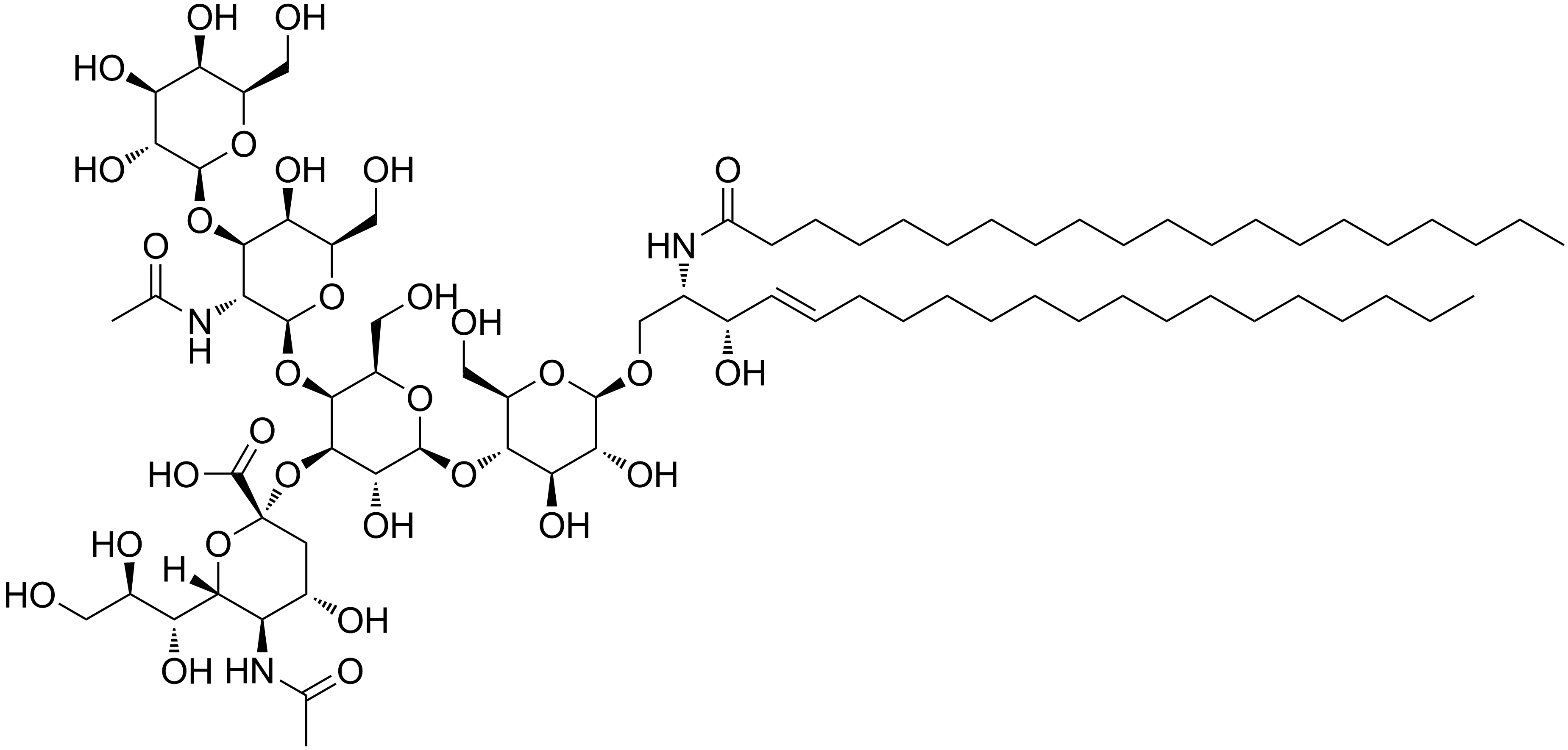
Which of the following is NOT a glycolipid? Cerebroside, Globoside, Sphingomyelin, Ganglioside
Sphingomyelin is a phospholipid, not a glycolipid.
Soap bubbles form because fatty acid salts organize into structures known as…
Micelles

Why are triacylglycerols used in the body for energy storage?
The carbon atoms of the fatty acid chains are highly reduced, which means they release plenty of energy upon oxidation.
Which lipids are used in the ABO blood typing system?
Sphingolipids are used.
What are nucleosides?
Nucleosides are made up of 5-carbon sugars (pentose) bonded to a nitrogenous base (the base is bonded to C-1’ of the sugar.
What are nucleotides?
Nucleotides are formed when one or more phosphate groups are attached to C-5’ of a nucleoside. Nucleotides are the building blocks of DNA, but they are found in other places, like ADP and ATP, which are named according the number of phosphate groups present.
Typically, bond breaking is endothermic (needs energy to happen) and bond forming is exothermic (releases energy when it happens). What is the important exception to this rule?
ATP contains plenty of negative charges in close proximity. Removing the terminal phosphate for ATP releases energy, which powers our cells.