Test 3 Microbiology Dr. Moore
1/175
There's no tags or description
Looks like no tags are added yet.
Name | Mastery | Learn | Test | Matching | Spaced |
|---|
No study sessions yet.
176 Terms
Nucleotides
Basic units of DNA molecule, composed of a sugar, a phosphate, and one of 4 DNA bases
5' end
The free phosphate end of the sequence is the ____________
3' end
The free hydroxyl end of the sequence is termed ___________
deoxyribonucleotides
polymer of DNA
Double stranded
Conformation of DNA
Doexyribose
Sugar in DNA
Adanine and Guanine
Purine bases in DNA
Cytosine and Thymine
Pyrimidine bases in DNA
Adanine and Guanine
Purine bases in RNA
uracil and thymine
Pyrimidine bases in RNA
Antiparallel
The opposite arrangement of the sugar-phosphate backbones in a DNA double helix.
Genes
The entire DNA sequence necessary for the production of a functional RNA or Protein
One
Number of chromosomes in Prokaryotes
Haploid
Copy number of Prokaryotes
Circular
Conformation in DNA in Prokaryotes
No introns
Are there intervening sequences in Prokaryotes
Multiple
Number of chromosomes in Eukaryotes
Haploid/Diploid
Copy numbers in Eukaryotes
Linear
What is the conformation in DNA for Eukaryotes
Yes introns
Are there intervening sequences in DNA for Eukaryotes
Microbial genome
sum of all genetic material in a cell
-Chromosome
-Plasmid
-F plasmid
-R plasmid
- Virulence factor plasmid
-Bacteriophage
Fertility
What does "F" stand for in F plasmid
(contained by cell donor that allows the synthesis of a conjugation (sex) pilus.)
Resistant
What does the "R" stand for in R plasmid
(resistant to antibiotics)
semiconservation replication
replication where each daughter cell receives one original (parent strand) in the newly synthesized strand.
Plasmids
Small rings of DNA found naturally in some bacterial cells in addition to the main bacterial chromosome. Can contain genes for antibiotic resistance, or other "contingency" functions.
semiconservative DNA replication
Replication:
-requires a Template
-requires a Primer
-needs an Origin of replication
-replication always 5' to 3'
Okazaki fragments
Small fragments of DNA produced on the lagging strand during DNA replication, joined later by DNA ligase to form a complete strand.
Steps for DNA repliaction
1) unwind DNA
2) strand separation
3) stabilization of ssDNA
4) polymerization of leading and lagging strand
5) repair and ligation
ssDNA
single stranded DNA
ssDNA binding proteins
prevent unwound DNA strands from snapping back
RNA primer
short segment of RNA used to initiate synthesis of a new strand of DNA during replication
-needs a free OH group
One
Leading strands only need ___________ primer
Multiple
Lagging strands need __________ primer
5' to 3'
mRNA is synthesized in a _______ direction
3' to 5'
mRNA is read __________
Topoisomerase I
relaxes supercoiled DNA
Topoisomerase II
supercoils the DNA back together
Helicase
Melts the H2 bonds in DNA
Primase
An enzyme that joins RNA nucleotides to make the primer.
DNA polymerase I
removes the RNA primer and replaces it with DNA
DNA polymerase II
DNA repair
DNA polymerase III
synthesizes new DNA only in the 5' to 3' direction
DNA ligase
an enzyme that eventually joins the sugar-phosphate backbones of the Okazaki fragments
rolling circle replication
a DNA replication mechanism in which one strand is nicked and unrolled for use as a template to synthesize a complementary strand
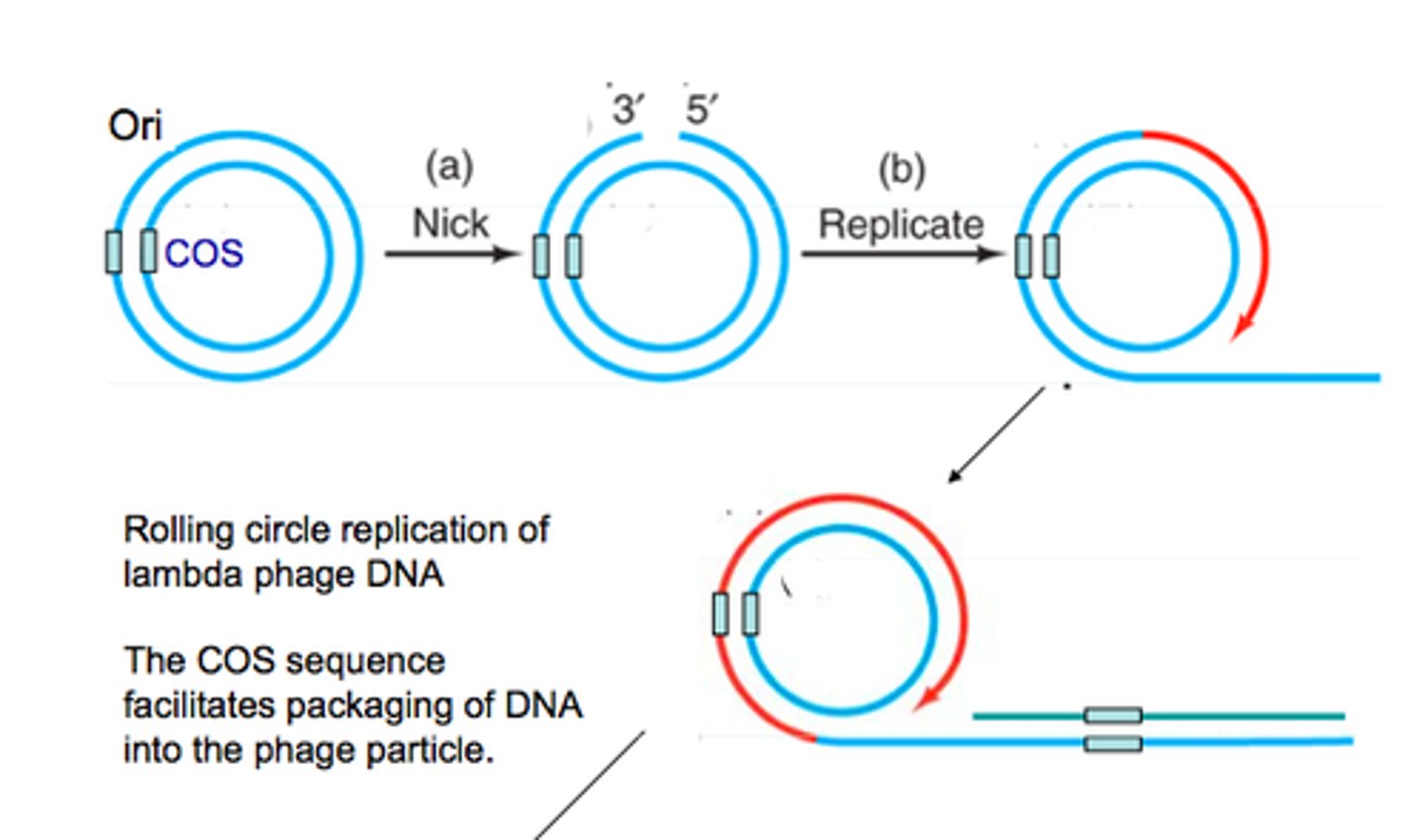
OriC
origin of replication
polymerase chain reaction
A method to amplify DNA in vitro by using many cycles of DNA denaturation, primer annealing, and DNA polymerization with a heat-stable polymerase
(Offers a way to detect pathogens present in patients who have nor shown symptoms)
PCR
polymerase chain reaction
Taq polymerase
A DNA synthesis enzyme that can withstand the high temperatures of PCR
Thermus aquaticus
Taq polymerase
Electrophoresis
The movement of suspended particles through a fluid or gel under the action of an electromotive force applied to electrodes in contact with the suspension.
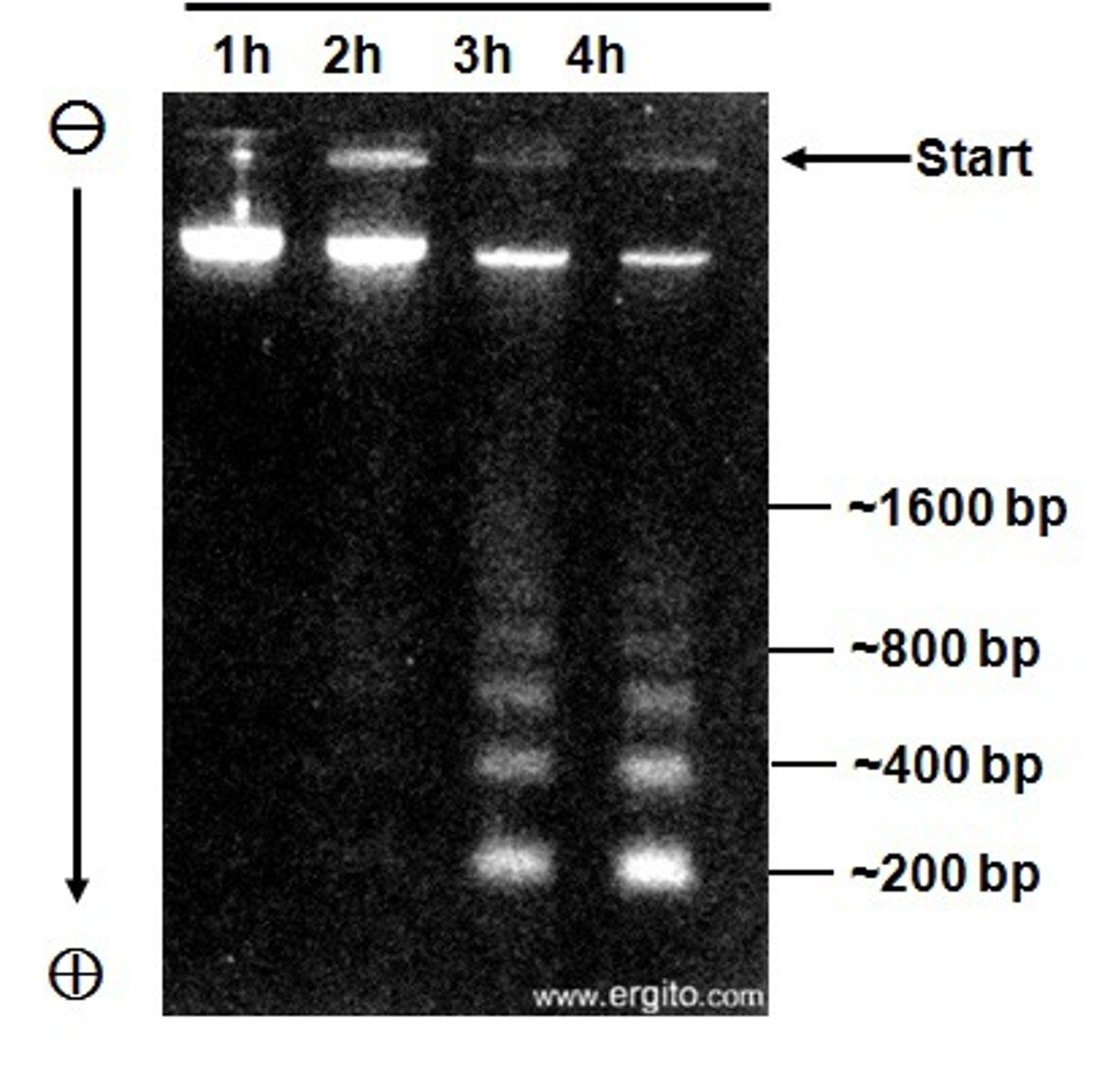
Top
In electrophoresis larger DNA is on the ________
Bottom
In electrophoresis smaller DNA is on the _____________
PCR buffer, MgCl2, Taq polymerase, DNA specific primer, original DNA, dioxynucleotides
List the materials necessary to achieve a successful PCR reaction
gene expression
process by which a gene produces its product and the product carries out its function
constitutive genes
genes that are expressed all the time
inducible genes
Genes that are expressed only when their products are needed.
Transcription
synthesis of an RNA molecule from a DNA template
mRNA
A type of RNA, synthesized from DNA, that attaches to ribosomes in the cytoplasm and specifies the primary structure of a protein.
tRNA
An RNA molecule that functions as an interpreter between nucleic acid and protein language by picking up specific amino acids and recognizing the appropriate codons in the mRNA
rRNA
type of RNA that combines with proteins to form ribosomes
miRNA
a class of functional RNA that inhibits the translation of mRNA
Sense strand
in viruses mRNA is called _____________
Translation
______________ can occur simultaneously as transcription
Translation
Process by which mRNA is decoded and a protein is produced
polyribosomal complex
assembly line for mass production of proteins
Transcriptome
the sum total of all the messenger RNA molecules expressed from the genes of an organism.
Shine-Dalgarno sequence
In prokaryotes, what is the name of the RNA sequence that ribosomes bind to so translation can occur?
Codons
A three-nucleotide sequence of DNA or mRNA that specifies a particular amino acid or termination signal; the basic unit of the genetic code.
degenerative code
When more than one series of three nucleotides codes for any amino acid.
AUG
start codon
UAA, UAG, UGA
stop codons
formylmethionine
first amino acid in protein synthesis in a bacteria
Operon
A unit of genetic function common in bacteria and phages, consisting of coordinately regulated clusters of genes with related functions.
-Consist of regulatory gene, control sites, and structural genes
Sponataneous mutations
NO outside influences, they are permanent, usually caused by errors in replication in DNA polymerase.
Mutations
Random errors in gene replication that lead to a change in the sequence of nucleotides. The source of all genetic diversity.
Inducible mutations
Changes in gene replication due from outside sources like Physical or Chemical.
physical mutagens
radiation-x-rays, UV light
frameshift mutation
mutation that shifts the "reading" frame of the genetic message by inserting or deleting a nucleotide
insertion mutation
a mutation in which one or more nucleotides are added to a gene
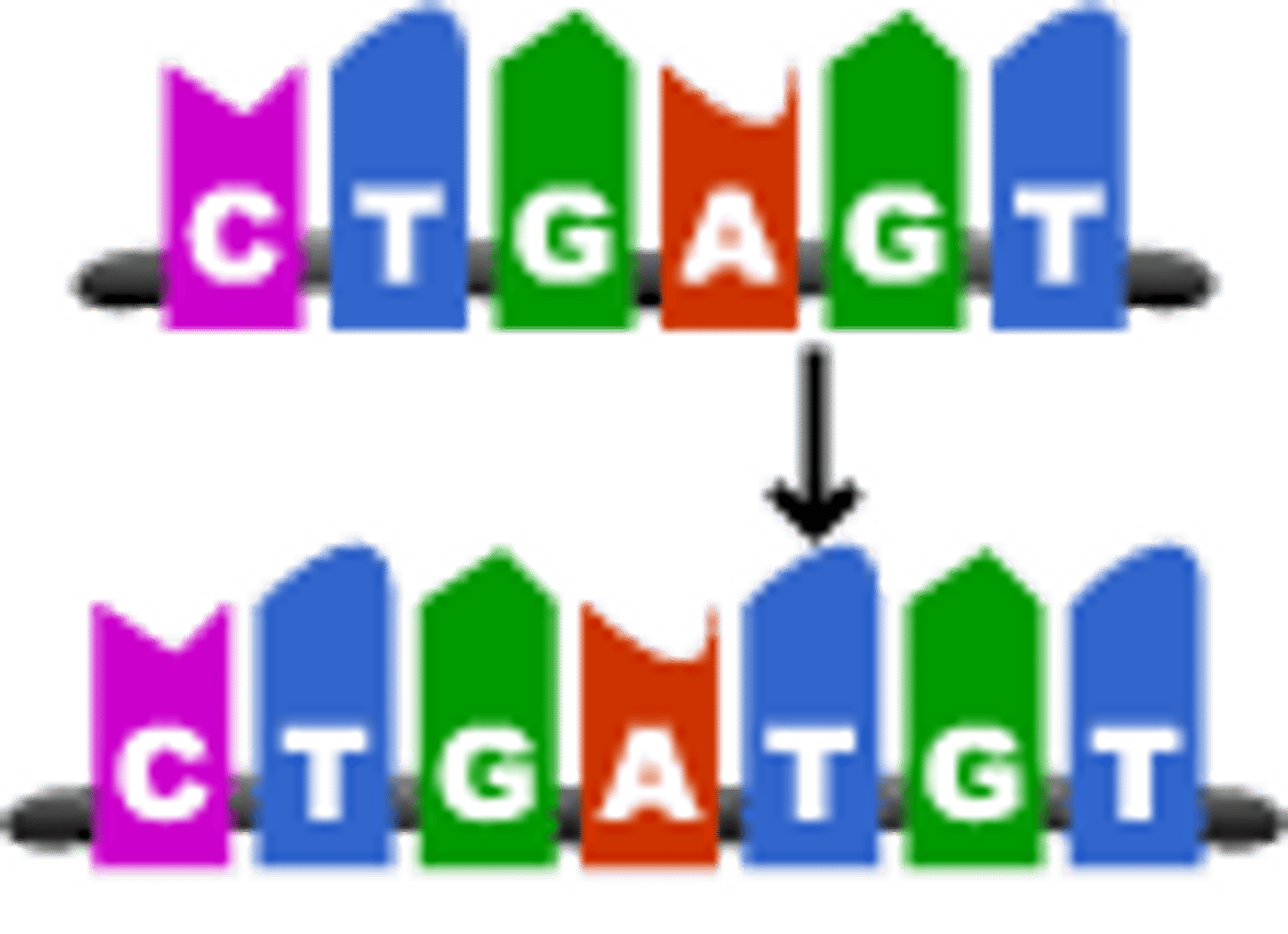
deletion mutation
a mutation in which one or more pairs of nucleotides are removed from a gene

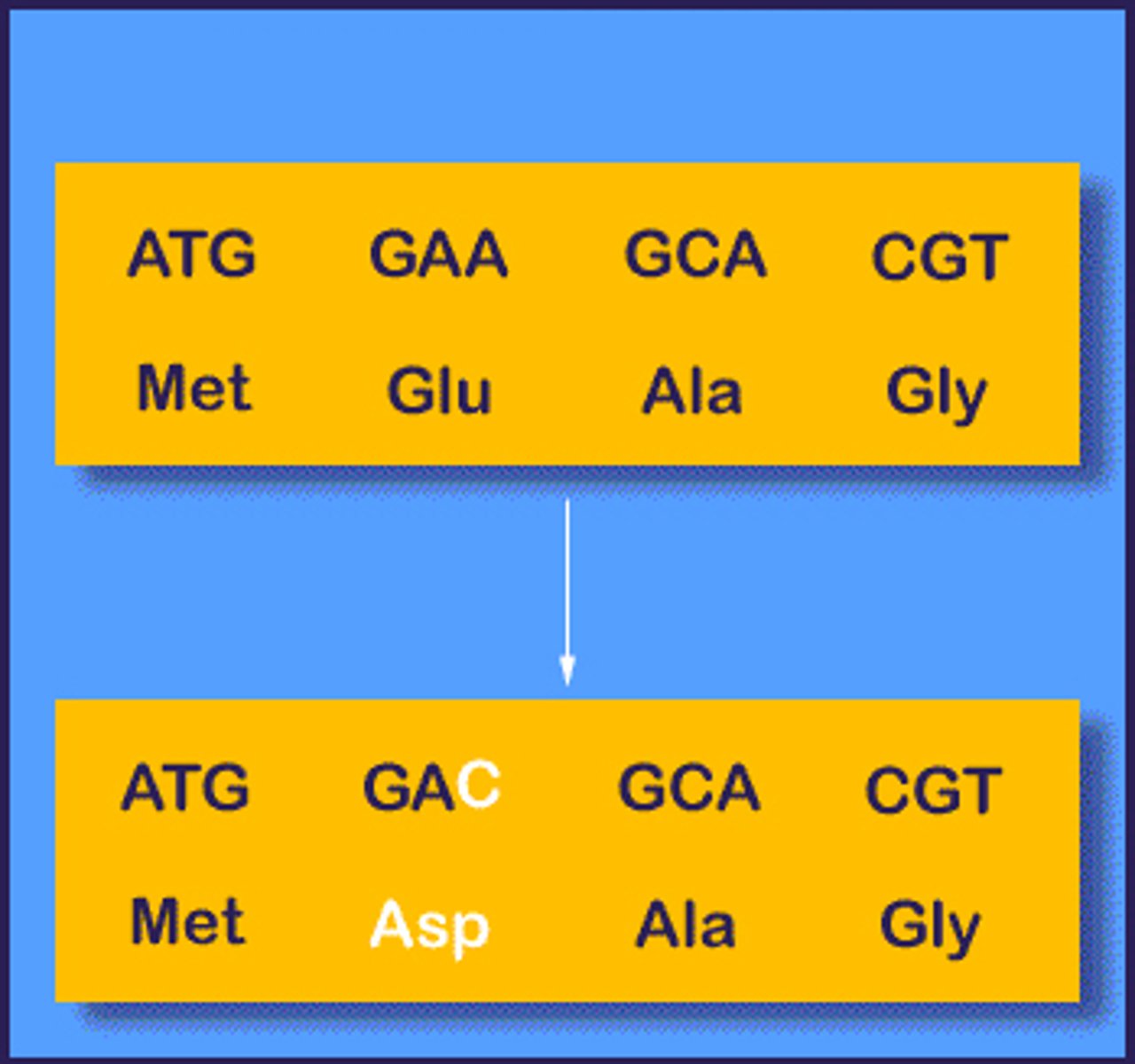
substitution mutation
Mutation in which a single base is replaced, potentially altering the gene product.
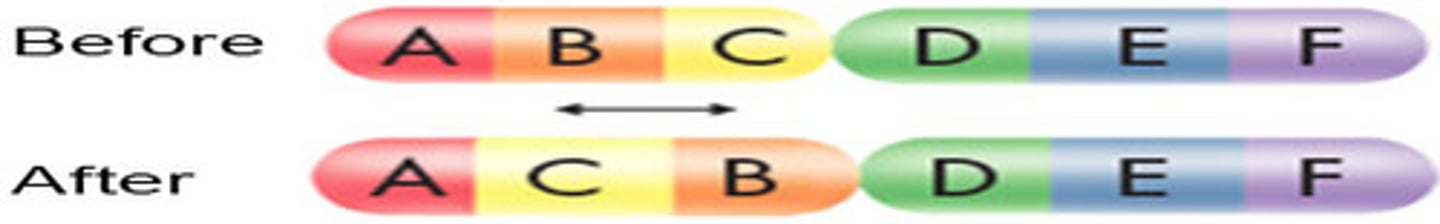
inversion mutation
Mutation in which a chromosome piece reattaches to original chromosome but in reverse orientation
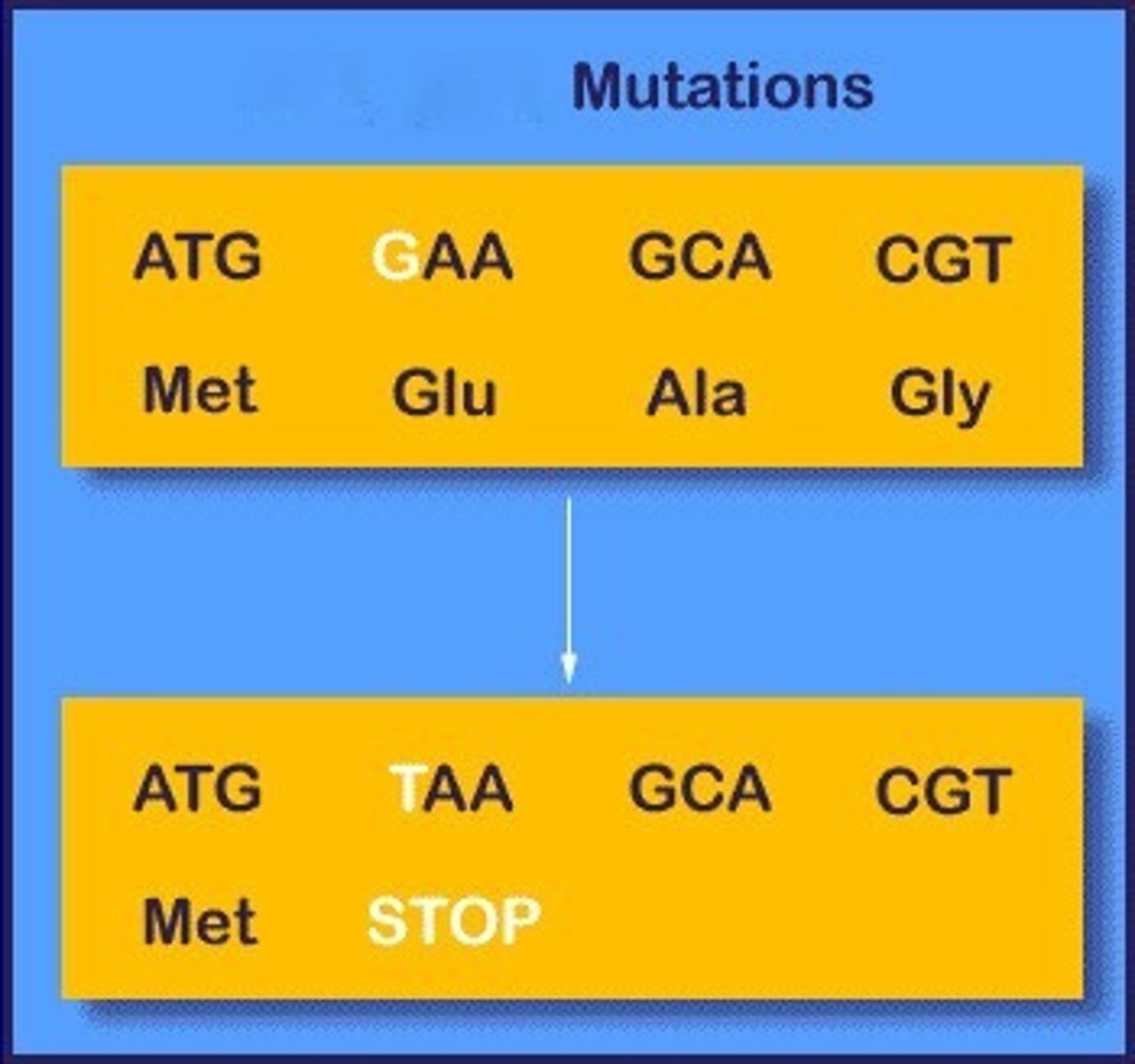
nonsense mutation
changes a normal codon into a stop codon
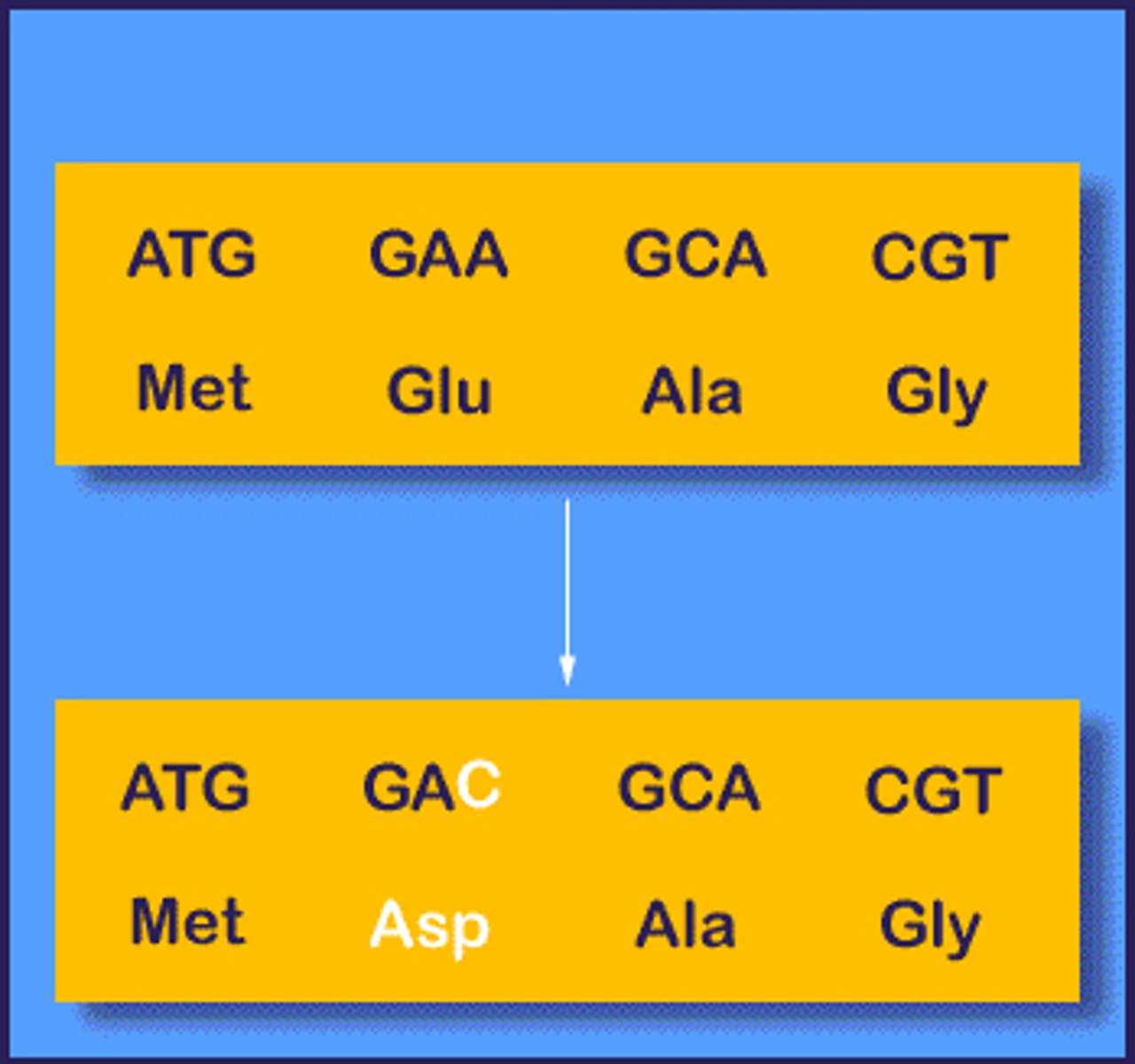
missense mutation
A base-pair substitution that results in a codon that codes for a different amino acid.
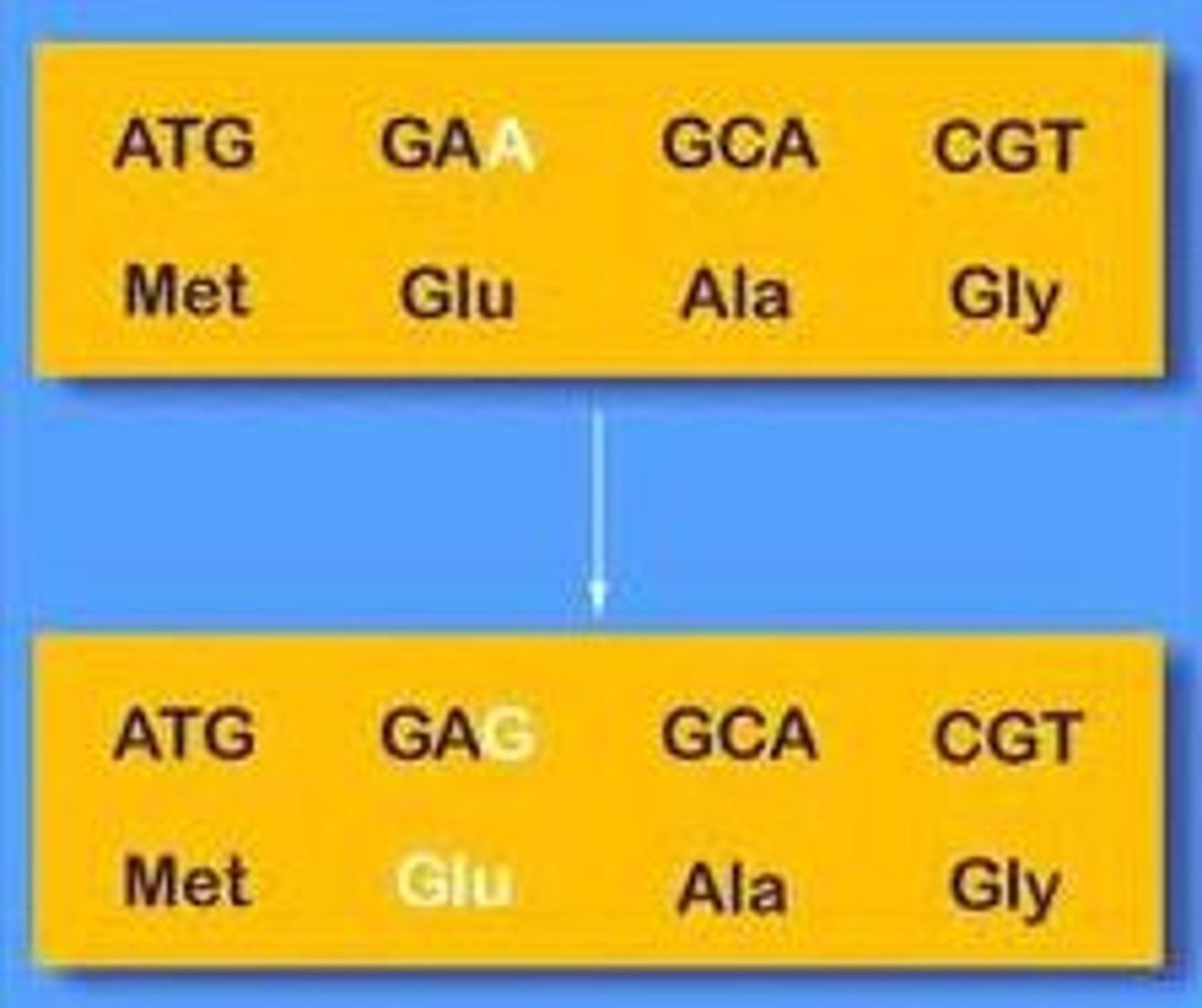
silent mutation
A mutation that changes a single nucleotide, but does not change the amino acid created.
Induced operon
Operon that turns on upon introduction of specific substrate
Repressed operon
Operon that gets turned off by products it has produced
Lac operon
a gene system whose operator gene and three structural genes control lactose metabolism
-governs catabolsim
-normally turned off
absense of lactose
Lac repressor binds to the operator region and blocks RNA polymerase from transcribing DNA
presence of lactose
Lactose binds to the repressor; the repressor cannot bid to the operator and transcription occurs
catabolite repression
System of gene control in some bacterial operons in which glucose is used preferentially and the metabolism of other sugars is repressed in the presence of glucose.
Glucose
In the presence of Lactose and Glucose the cell will metabolize ________________
cAMP
In the presence of Lactose and absence of glucose the cell will produce ____________
catabolic activator protein
CAP stands for
Alarmone
a chemical alarm signal that promotes a cell's response to environmental or nutritional stress
presence of lactose and absence of glucose
Transcription at high affinity due to the CAP-cAMP complex
Low glucose and High cAMP
Presence of lactose and glucose
Transcription at normal (low) affinity
High Glucose and low cAMP
Bends the DNA
CAP-cAMP complex binds before the Plac region, the complex then ________________ which increases the affinity for the RNA polymerase
trp operon
tryptophan binds to the repressor protein and enables it to repress gene transcription.
absence of tryptophan
Trp repressor is inactive so the RNA polymerase can transcribe and translate the mRNA