mechanics and formulae
1/177
There's no tags or description
Looks like no tags are added yet.
Name | Mastery | Learn | Test | Matching | Spaced | Call with Kai |
|---|
No analytics yet
Send a link to your students to track their progress
178 Terms
What is a scalar quantity?
A quantity that has only magnitude and no direction, e.g., mass, temperature.
What is a vector quantity?
A quantity that has both magnitude and direction, e.g., force, velocity.
Define Newton's First Law of Motion.
An object remains at rest or in uniform motion unless acted upon by a net external force.
What is the principle of conservation of momentum?
In a closed system, the total momentum before and after an event remains constant.
What is work done?
Work done is the transfer of energy when a force causes displacement, calculated as W = F × d × cos(θ).
Define kinetic energy (KE).
The energy possessed by an object due to its motion
What is the law of conservation of energy?
Energy cannot be created or destroyed, only transformed from one form to another.
What is the formula for gravitational potential energy?
Gravitational potential energy (PE) is calculated as PE = mgh, where m is mass, g is gravity, and h is height.
Define tension in a string.
Tension is the force transmitted through a string or rope when it is pulled tight by forces acting from opposite ends.
What is a free body diagram?
A graphical representation showing all the forces acting on an object.
Define uniform acceleration.
Acceleration that is constant in magnitude and direction throughout the motion.
What is the equation of motion for an object under uniform acceleration?
s = ut + 1/2 at², where s is displacement, u is initial velocity, a is acceleration, and t is time.
What does 's' stand for in kinematic equations?
's' stands for displacement.
What is the definition of friction?
The force that opposes the relative motion of two surfaces in contact.
What is the coefficient of friction?
A dimensionless value that describes the ratio of the force of friction between two bodies to the force pressing them together.
Define momentum.
The product of an object's mass and its velocity, calculated as p = mv.
What is an elastic collision?
A collision in which kinetic energy is conserved before and after the event.
What is an inelastic collision?
A collision in which kinetic energy is not conserved; some energy is transformed into other forms.
Define impulse.
Impulse is the change in momentum resulting from a force applied over time; calculated as Impulse = F × t.
What is uniform circular motion?
Motion of an object traveling at a constant speed on a circular path.
What is centripetal force?
The net force that acts on an object moving in a circular path, directed towards the center.
What is the equation for centripetal acceleration?
Ac = v²/r, where v is the linear speed and r is the radius of the circular path.
Define torque.
Torque is a measure of the force that can cause an object to rotate about an axis, calculated as τ = rF sin(θ).
What is the center of mass?
The point where the mass of a body or system is concentrated and the whole mass can be considered to act.
Define gravitational field strength (g).
The force per unit mass experienced by a small test mass placed in the field, g = F/m.
What is the principle of moments?
For an object in equilibrium, the sum of clockwise moments about any point equals the sum of anti-clockwise moments.
What is the definition of a wave?
A disturbance that transfers energy through matter or space without transferring matter itself.
What are the two main types of waves?
Transverse and longitudinal waves.
Define frequency (f) of a wave.
The number of waves that pass a point in a given period of time, measured in hertz (Hz).
What is wavelength (λ)?
The distance between consecutive crests or troughs of a wave.
Define amplitude.
The maximum displacement of points on a wave from its rest position.
What is the Doppler effect?
The change in frequency or wavelength of a wave in relation to an observer moving relative to the wave source.
What does Hooke's Law state?
The force exerted by a spring is directly proportional to the displacement of the spring from its equilibrium position, F = kx.
What is a projectile?
An object that is thrown into the air with an initial velocity and is subject only to the forces of gravity and air resistance (if significant).
What is the formula for the range of a projectile?
Range (R) = (v^2 sin(2θ)) / g, where v is the initial velocity, θ is the launch angle, and g is gravitational acceleration.
What is the definition of a moment of inertia?
A measure of an object's resistance to angular acceleration, depending on the mass distribution relative to the axis of rotation.
Define energy conservation in mechanics.
The total mechanical energy (kinetic + potential) of a closed system remains constant.
What is the work-energy principle?
The work done on an object is equal to the change in its kinetic energy.
Define mechanical advantage.
The factor by which a machine multiplies the force applied to it; is calculated as output force/input force.
What is angular velocity?
The rate of change of angular displacement with time, usually measured in radians per second.
What is the law of universal gravitation?
Every point mass attracts every other point mass with a force that is directly proportional to the product of their masses and inversely proportional to the square of the distance between their centers.
What does 'g' represent in mechanics?
The acceleration due to gravity, approximately 9.81 m/s² near the Earth's surface.
SUVAT
Equations of motion that can be used when an object is moving at uniform acceleration
Distance
Scalar quantity that describes the amount of ground the object has covered
Displacement
Vector quantity that describes the overall distance travelled from the starting position
Speed
Scalar quantity that describes the distance travelled per unit time
Velocity
Vector quantity that describes the rate of change of displacement
Acceleration
Vector quantity that describes the rate of change of velocity
Uniform acceleration
Where the acceleration of an object is constant
Area under acceleration-time graph
Velocity
Gradient of velocity-time graph
Acceleration
Area of velocity-time graph
Displacement
Gradient of displacement-time graph
Velocity
Instantaneous velocity
The velocity of an object at a specific point in time
Resolving vectors
Splitting a vector into its vertical and horizontal components
Adding vectors using trig
Used when two vectors are perpendicular to each other. Use Pythagoras’ theorem to find the magnitude and trigonometry to find the direction
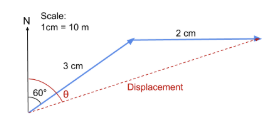
Adding vectors using a scale drawing
Used when vectors are at angles other than 90°. Use a ruler and protractor to find the magnitude and direction, making sure to note the scale used
Projectile motion
Vertical and horizontal components of a projectile’s motion are independent. Use SUVAT in two dimensions, ignoring air resistance so acceleration is constant
Free-body diagrams
A diagram which shows all the forces that act on an object
Newton’s first law
An object will remain at rest or travelling at a constant velocity, until it experiences a resultant force
Newton’s second law
The acceleration of an object is proportional to the resultant force experienced: F=ma
Newton’s third law
For each force experienced by an object, the object exerts an equal and opposite force
Terminal velocity
Frictional forces acting on an object are equal to the driving forces, so there’s no resultant force and no acceleration
Gravitational field strength
The force per unit mass exerted by a gravitational field on an object: g=F/m
Weight
The gravitational force that acts on an object due to its mass: W=mg
Momentum
The product of the mass and velocity of an object: p=mv
Principle of conservation of momentum
Momentum is always conserved in a closed system. Total momentum before = Total momentum after
Moments
The turning effect of a force. Force multiplied by the perpendicular distance from the line of action of the force to the point: Moment=Fx
Principle of moments
For an object in equilibrium, the sum of anticlockwise moments about a pivot is equal to the sum of clockwise moments
Centre of gravity
The point at which gravity appears to act
Uniform object
Centre of gravity is exactly at its centre
Work
The force causing a motion multiplied by the distance travelled in the direction of motion: W=FΔs
Kinetic energy
The energy an object has due to its motion
Gravitational potential energy
The energy an object has due to its position in a gravitational field
Principle of conservation of energy
Energy cannot be created or destroyed, only transferred from one form to another
Power
The rate of energy transfer
Efficiency
A measure of how efficiently a system transfers energy
What is the acceleration when using suvat equations?
Constant
On a displacement time graph what is the gradient?
Velocity
On a displacement time graph where is the starting point?
On the x axis
On a displacement time graph when is it below the x axis?
Past the starting point
What does a velocity time graph have when it is a straight line?
A constant velocity
What is the area under a velocity time graph?
Displacement
What is the gradient on a velocity time graph?
Acceleration
What does it mean when the graph goes below the x axis on a velocity time graph?
The velocity is in the other direction so the object moves backwards
On a displacement time graph, what does it mean when the graph is horizontal?
The object is stationary
What does a positive curve mean on a displacement time graph?
Gradient/Velocity increasing so the object is accelerating
On a displacement time graph, how do you find the average velocity?
Divide the total displacement s by the time taken t
On a displacement time graph, how do you find the instantaneous velocity at a point?
Gradient at a point. You find this by drawing a tangent to the curve and calculating its gradient.
How do you find the area under the curve/ total displacement on a velocity time graph?
Count the squares by putting a dot in every square so you get the marks for counting them. The displacement = the area of 1 square x total number of squares.
Where should the hunter aim to hit the monkey?
The hunter should aim directly at the monkey as vertical and horizontal motion are independent of each other.
What do I need to remember when drawing a vector polygon?
When one vector ends, the next vector starts.
What does a closed vector polygon mean?
The quantities are in equilibrium.
What does an open vector polygon mean?
There is a resultant vector.
Why is acceleration due to gravity always negative on a velocity time graph?
Weight acts downwards
What is the displacement like for the first bounce on a velocity time graph of a bouncing ball?
Equal
What is the displacement like for the second bounce on a velocity time graph of a bouncing ball?
Smaller as energy is lost
What is the maximum height on a velocity time graph of a bouncing ball?
0ms^-1
What is the gradient when the ball is falling on a velocity time graph of a bouncing ball?
-9.81ms^-2