Chapter 13 - Peripheral Nervous System
1/11
There's no tags or description
Looks like no tags are added yet.
Name | Mastery | Learn | Test | Matching | Spaced |
|---|
No study sessions yet.
12 Terms
Define Sensory Receptors
Specialized to respond to changes in environment (stimuli)
Activation results in graded potentials that trigger nerve impulses
Awareness of stimulus (sensation) and interpretation of meaning of stimulus (perception) occur in brain
List three ways to classify receptors
Type of stimulus
Body location
Structural complexity
Types of Sensory Receptors
Mechanoreceptors
Respond to touch, pressure, vibration, and stretch
Thermoreceptors
Sensitive to changes in temperature
Photoreceptors
Respond to light energy
EX: retina
Chemoreceptors
Respond to chemicals
EX: smell, taste, changes in blood chemistry
Nociceptors
Sensitive to pain-causing stimulus
EX: extreme heat or cold, excessive pressure, inflammatory chemicals
Location of Sensory Receptors
Exteroceptors
Respond to stimuli arising outside body
Receptors in skin for touch, pressure, pain, and temperature
Most special sense organ
Interoceptors (visceroceptors)
Respond to stimuli arising in internal viscera and blood vessels
Sensitive to chemical changes and temperature changes
Sometimes cause discomfort but usually person is unaware of their workings
Proprioceptors
Like interoceptors, but located in skeletal muscles, tendons, joints and muscles
Difference between Sensation and Perception
Survival depends upon:
Sensation
The awareness of changes in the internal and external environment
Perception
The conscious interpretation of those stimuli
Perception of Pain
Warns of actual or impending tissue damage so protective action can be taken
Stimuli include extreme pressure and temperature
Impulses travel on fibers that release neurotransmitter glutamate
Some pain impulses are blocked by inhibitory endogenous opioids
EX: endorphins
Pain tolerance
All perceive pain at same stimulus intensity
Pain tolerance varies
“Sensitive to pain” means low pain tolerance, not low pain threshold
Structure & Function of Nerves
STRUCTURE
Bundle of myelinated and nonmyelinated peripheral axons enclosed by connective tissue
Two types of nerves: spinal or cranial, depending on where they originate
FUNCTION
Cordlike organ of PNS
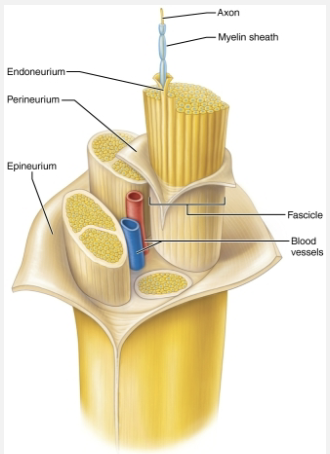
Connective Tissue Coverings
Epineurium
Tough fibrous sheath around all fascicles to from the nerve
Perineurium
Coarse connective tissue that bundles fibers into fascicles
Endoneurium
Loose connective tissue that encloses axons and their myelin sheaths (Schwann cells)
Classification of Nerves according to Direction
Mixed nerves
Contain both sensory and motor fibers
Impulses travel BOTH to and from CNS
Sensory (afferent) nerves
Impulses only TOWARD CNS
Motor (efferent) nerves
Impulses only AWAY from CNS
Pure sensory (afferent) or pure motor (efferent) nerves are rare; most are mixed
Types of Fibers in Mixed Nerves
Somatic afferent
Sensory from muscle to brain
Somatic efferent
Motor from brain to muscle
Visceral afferent
Sensory from organs to brain
Visceral efferent
Motor from brain to organs
Define Ganglia
Ganglia: contain neuron cell bodies associated with nerves in PNS
Ganglia associated with afferent nerve fibers contain cell bodies of sensory neurons
Dorsal root ganglia (sensory, somatic)
Ganglia associated with efferent nerve fibers contain autonomic motor neurons
Autonomic ganglia (motor, visceral)