Spectroscopy
1/17
There's no tags or description
Looks like no tags are added yet.
Name | Mastery | Learn | Test | Matching | Spaced | Call with Kai |
|---|
No study sessions yet.
18 Terms
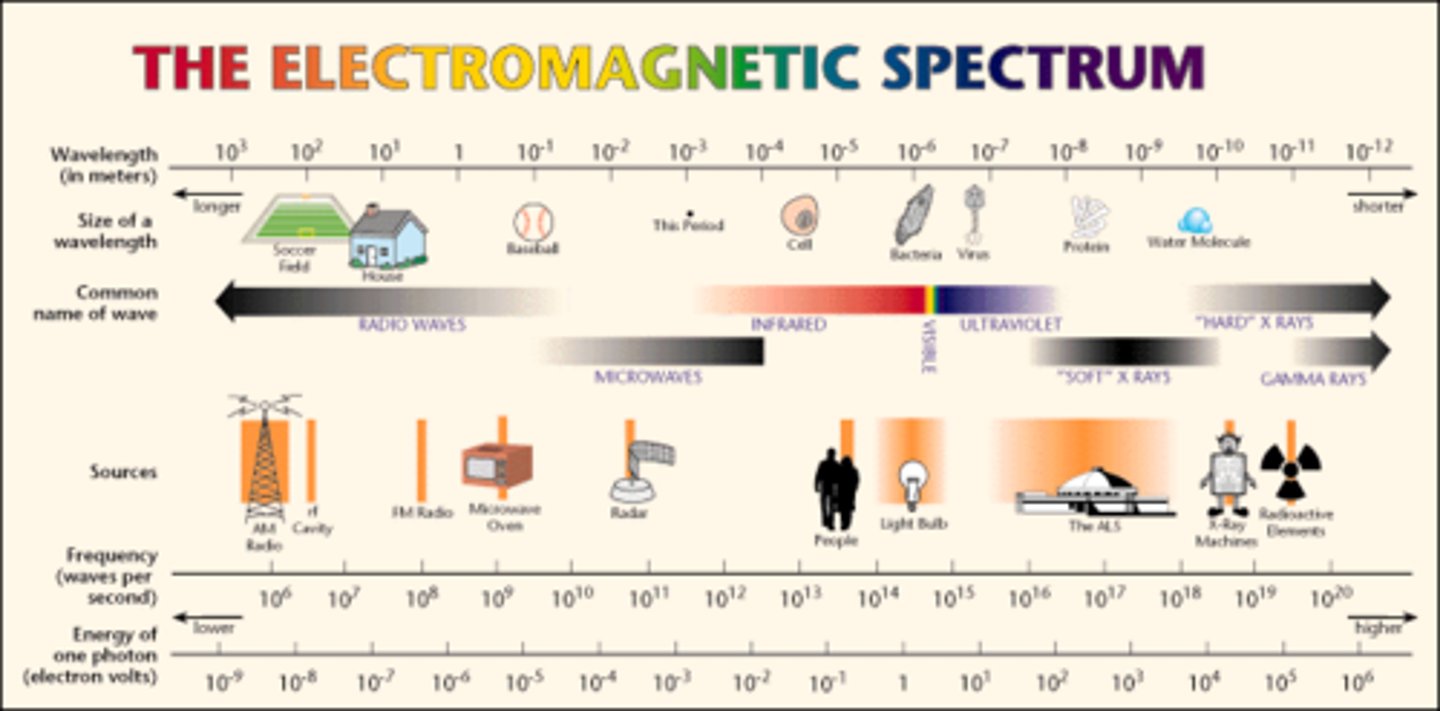
What is the electromagnetic spectrum (lowest energy to high energy)
radio, microwave, infrared, visible, ultraviolet, x-ray, gamma
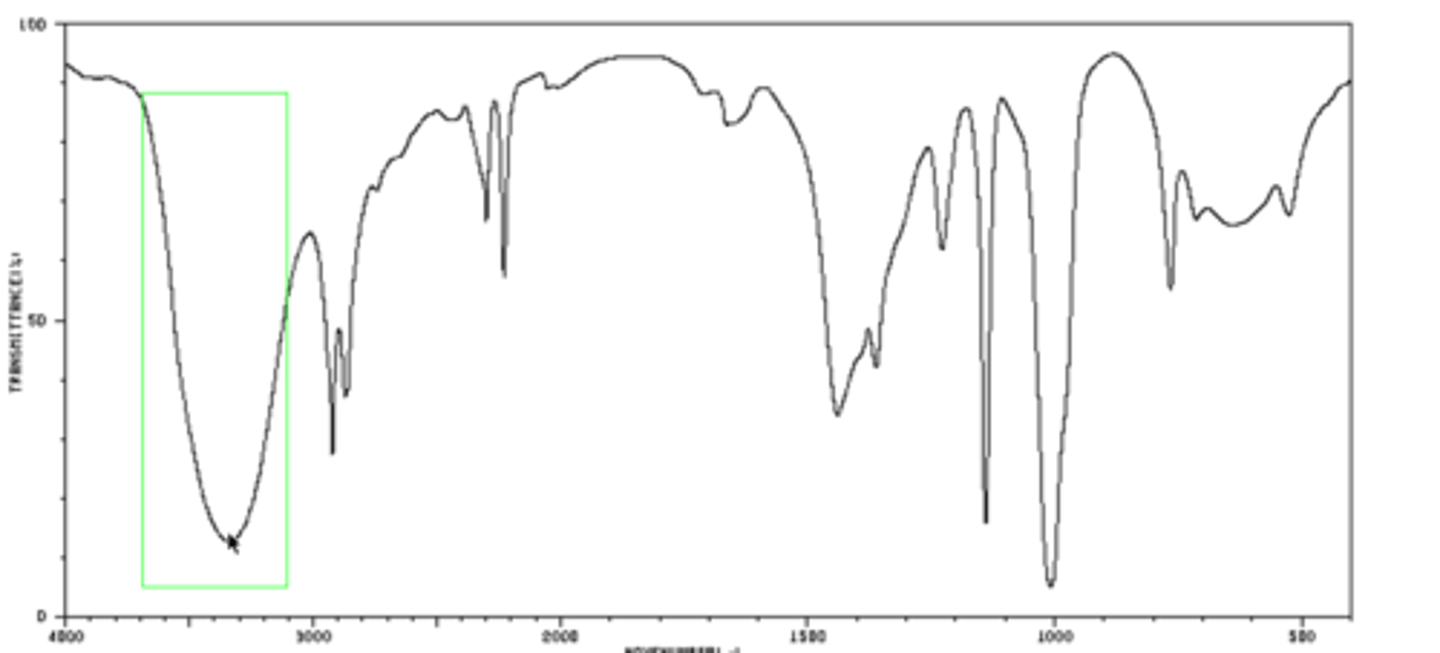
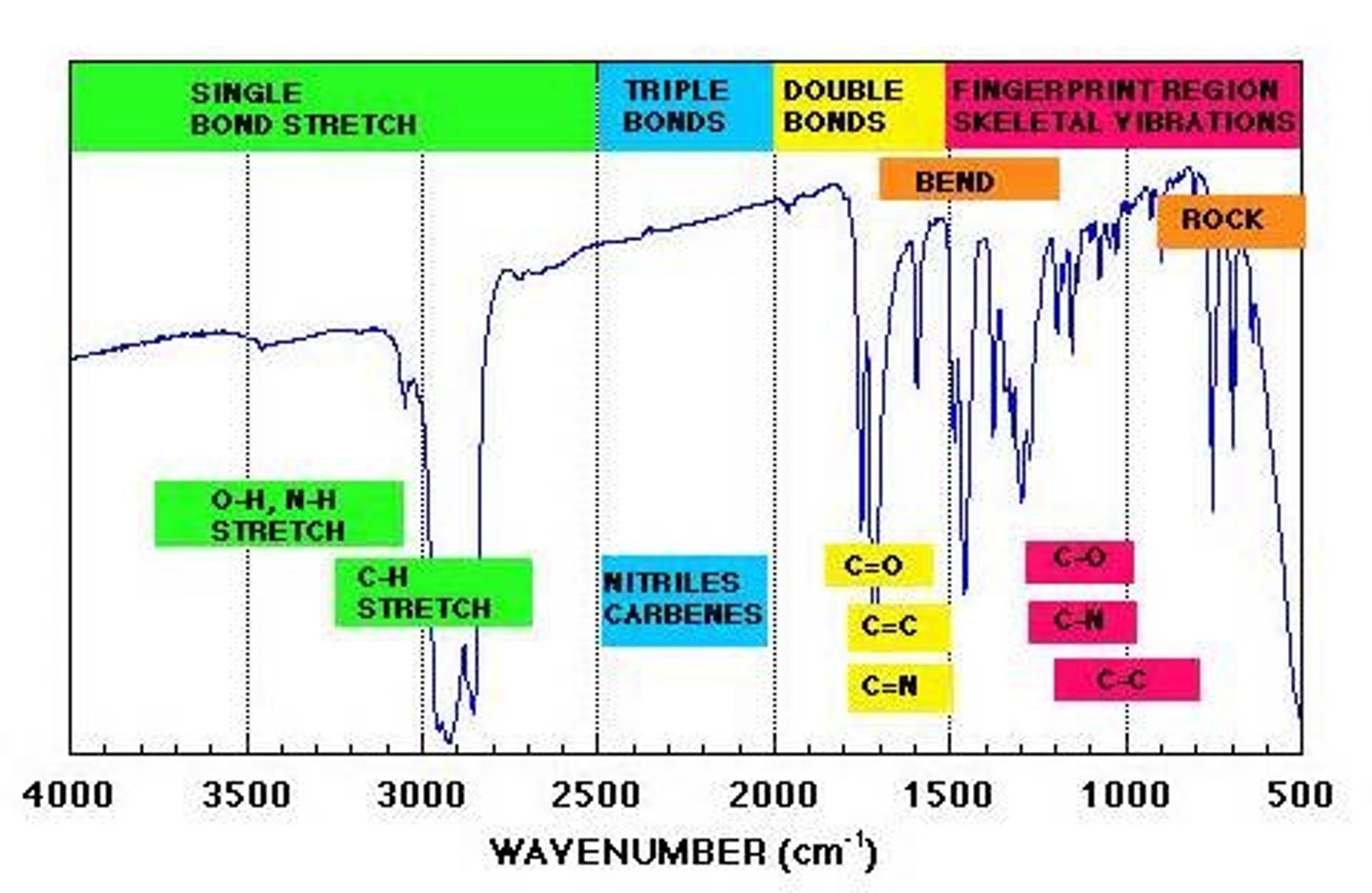
IR spectroscopy
causes bonds to vibrate at different frequencies, shows which functional groups are present
UV spectroscopy
passing uv light through a chemical sample and plotting absorbance v wavelength
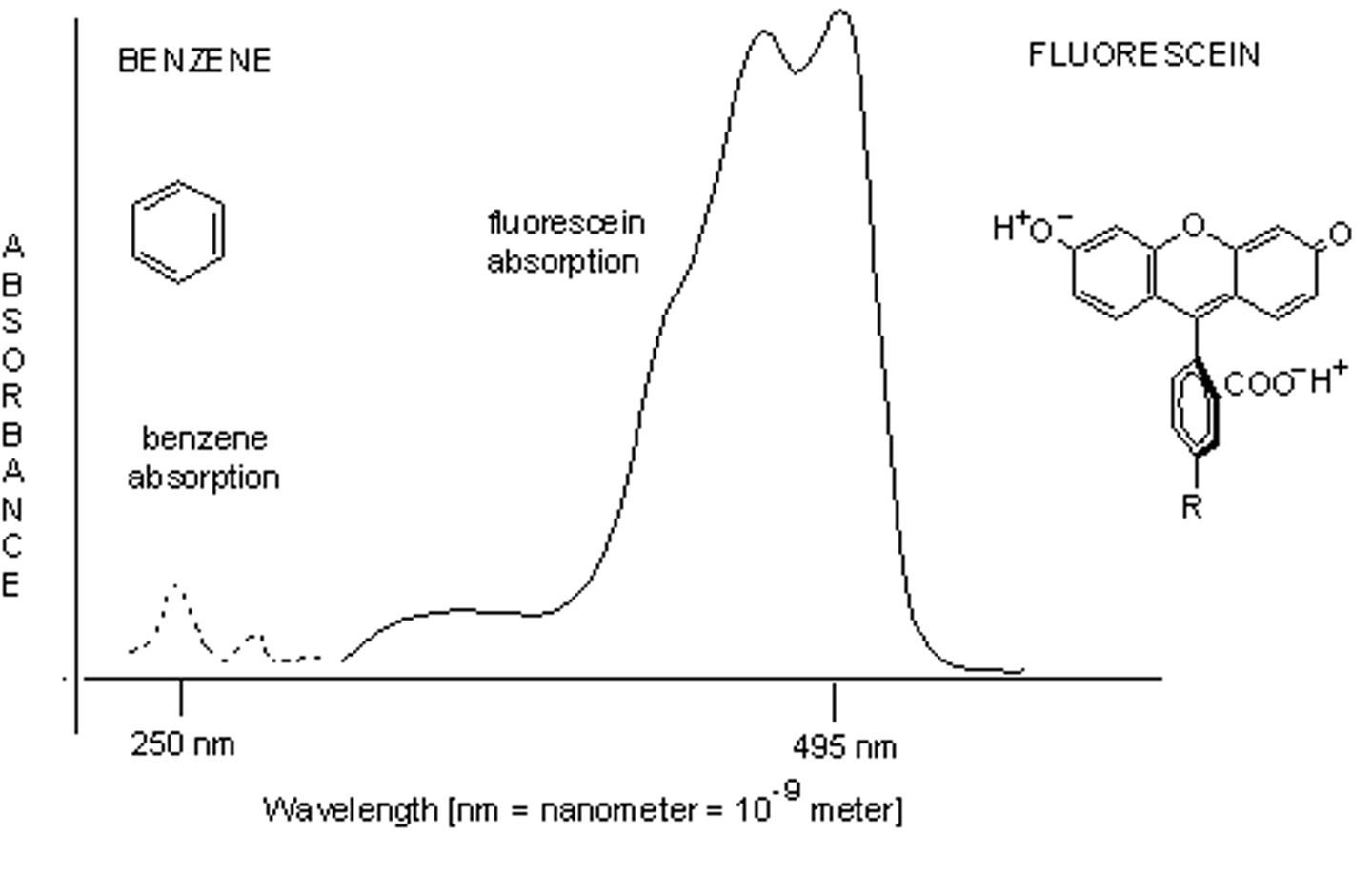
What does UV light do to molecules
provides energy for electronic transitions
IR is dependent on
change in dipole moment induced by vibrations
UV is dependent on
conjugation
batochromic shift
also known as red shift, when the absorption shifts to a lower energy
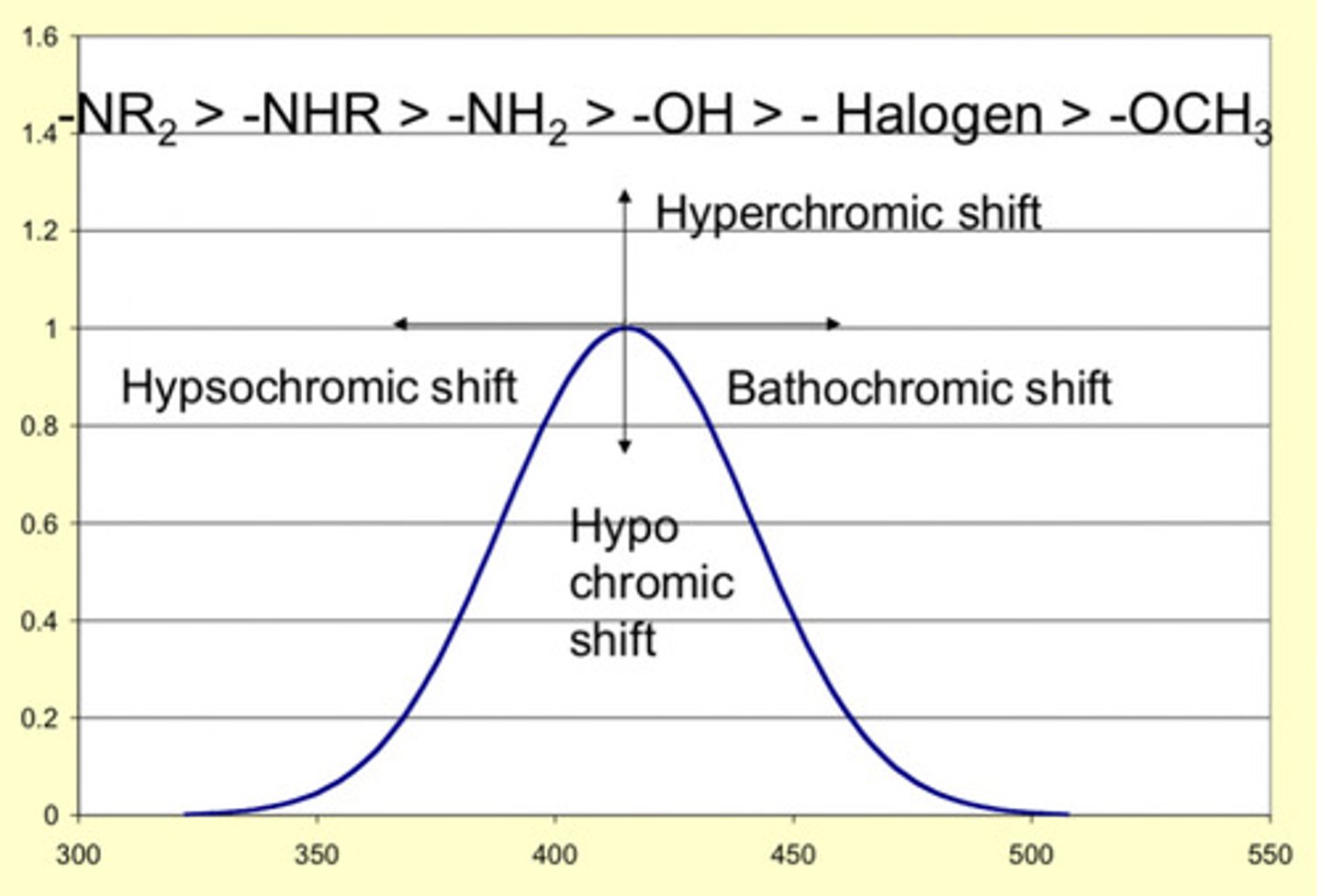
hypsochromic shift
A shift in the absorption maximum to shorter wavelength or higher energy, i.e., a blue shift.
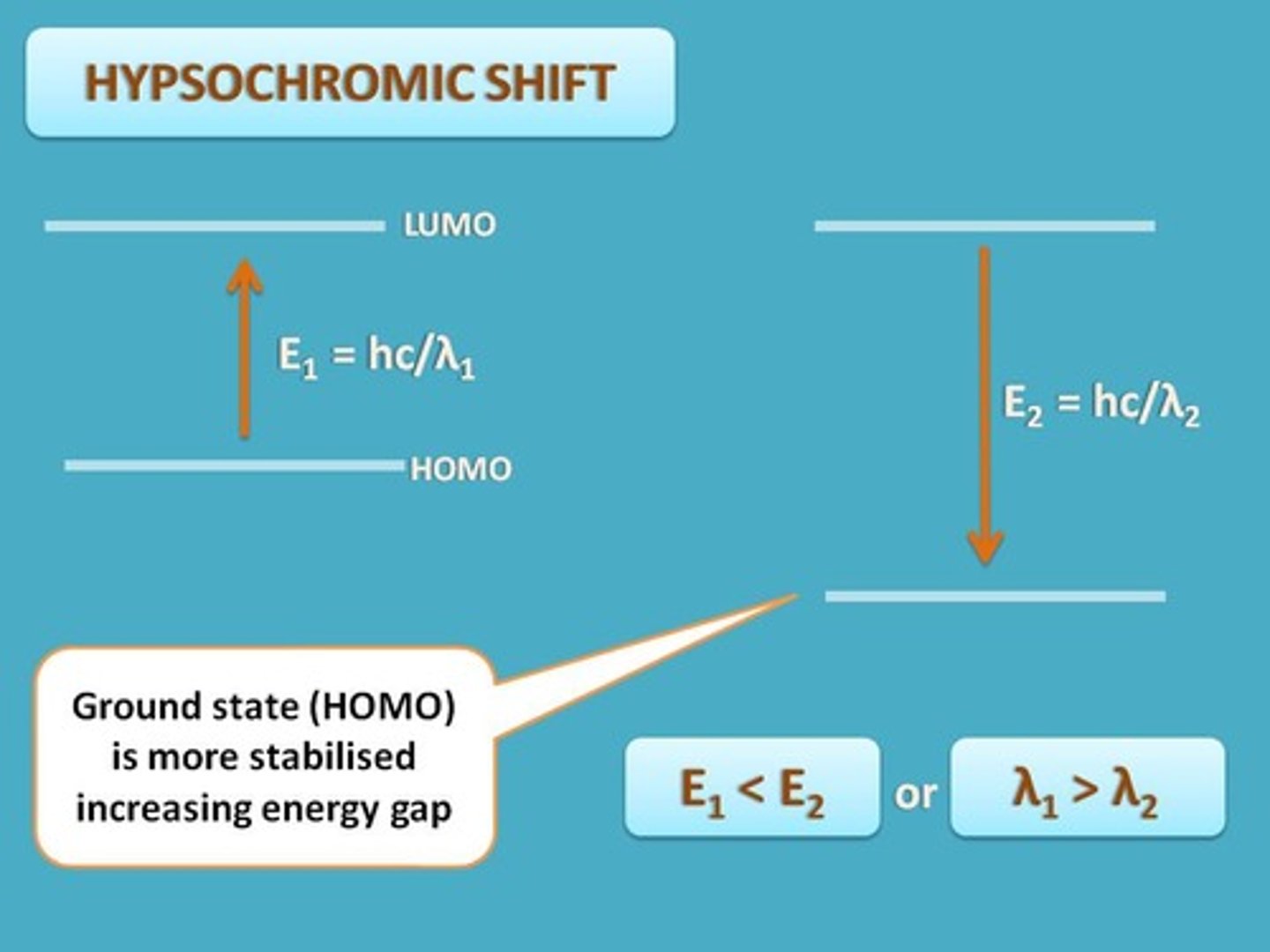
why does a blue shift occur
when there is decreased conjugation, a nonpolar solvent, and removal of auxochromes
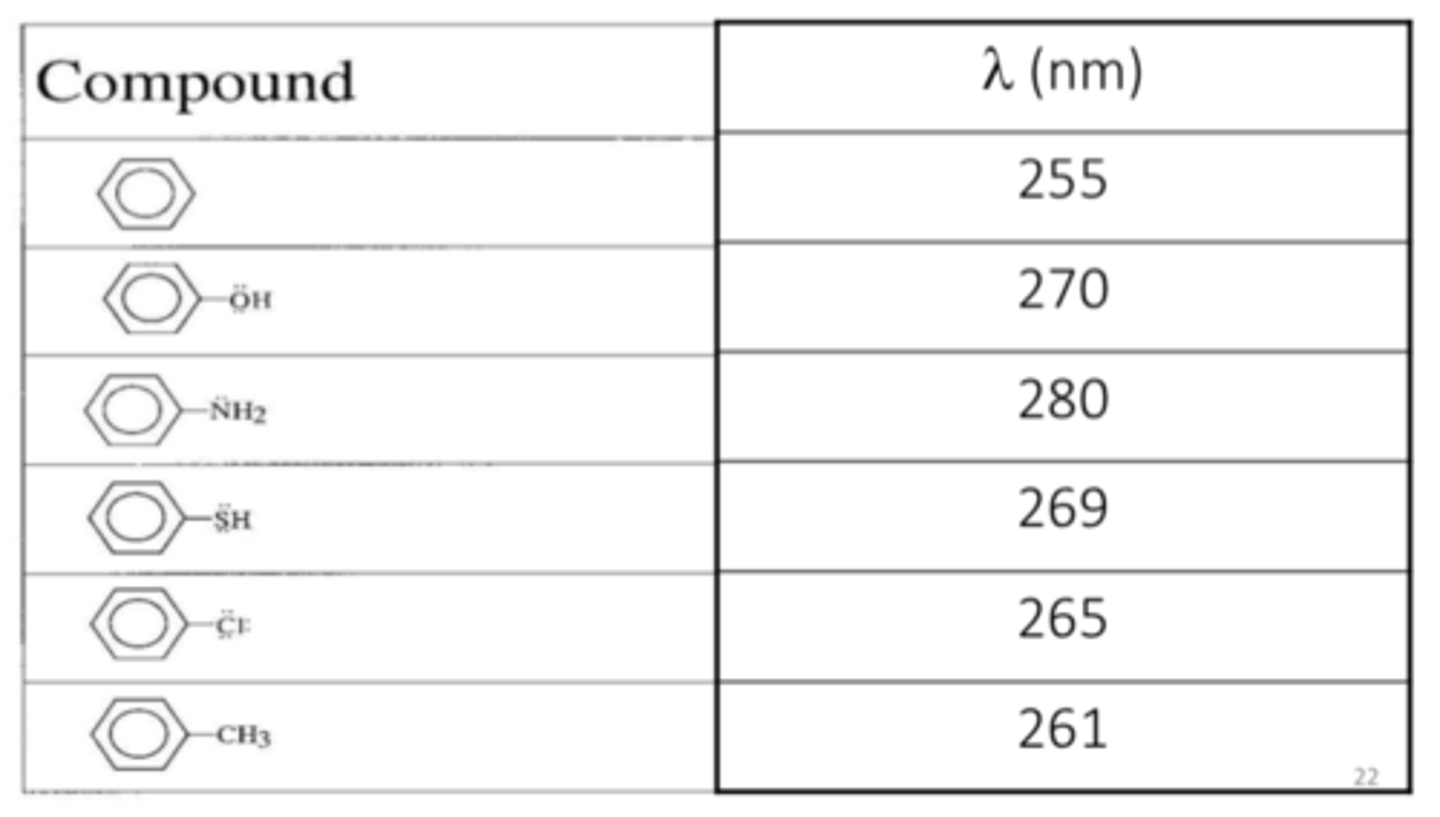
chromophore
the part of the molecule that absorbs light
auxochromes
groups attached to the chromophore
1 angstrom equals
10^-10 m
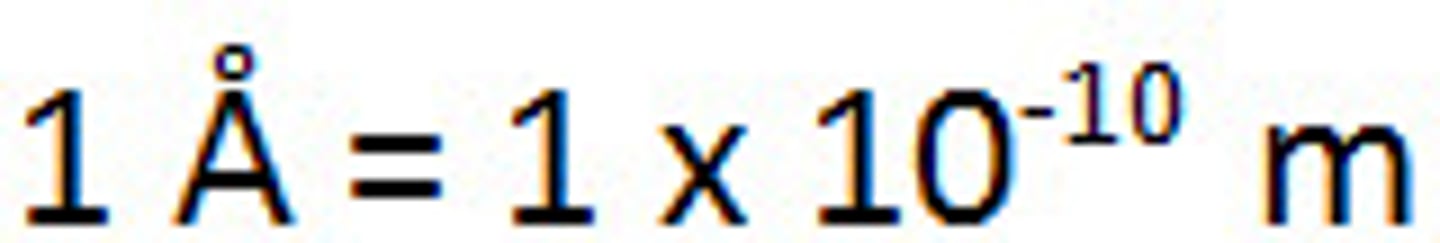
1 debeye equals
3.336 x 10^30 C x m
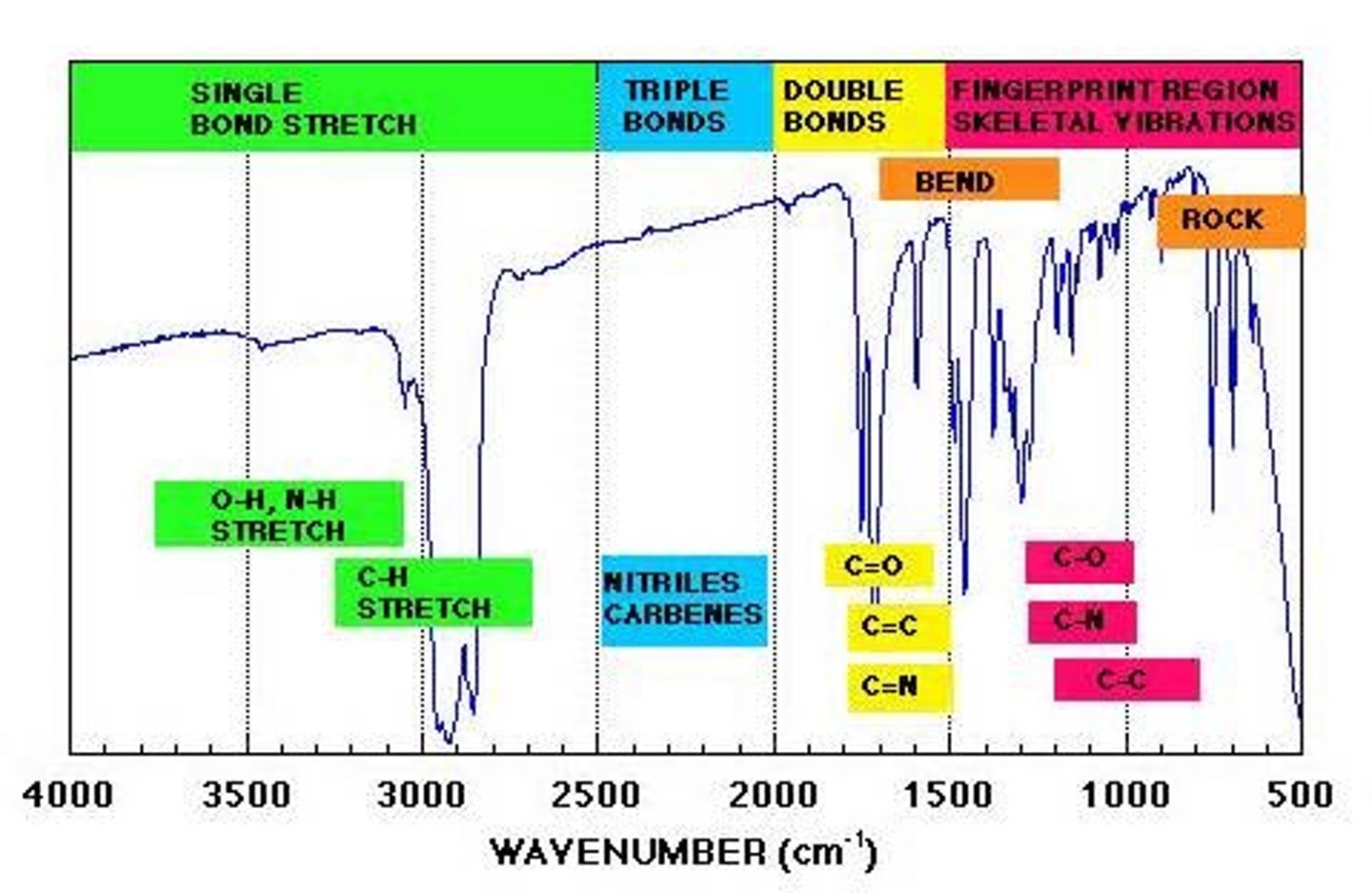
factors that affect IR frequency
dipole moment, bond strength, bond length, heavy atoms
IR frequency of carbonyls (C=O stretch)
strong intense 'V' around 1700 cm-1
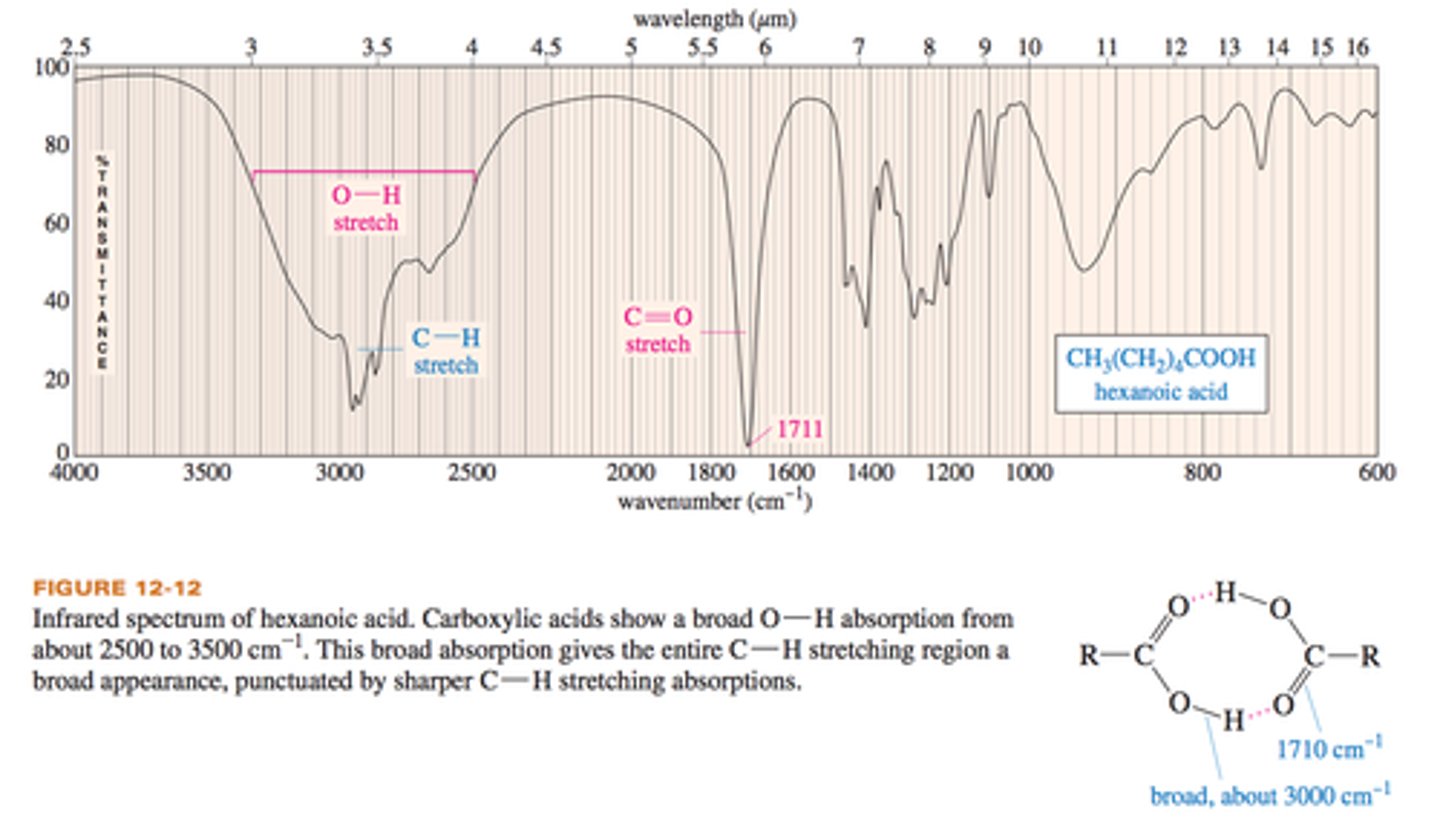
IR frequency of C-H stretches
sp3: 3000-2850 cm-1
sp2: 3150-3000 cm-1
sp: 3300 cm-1
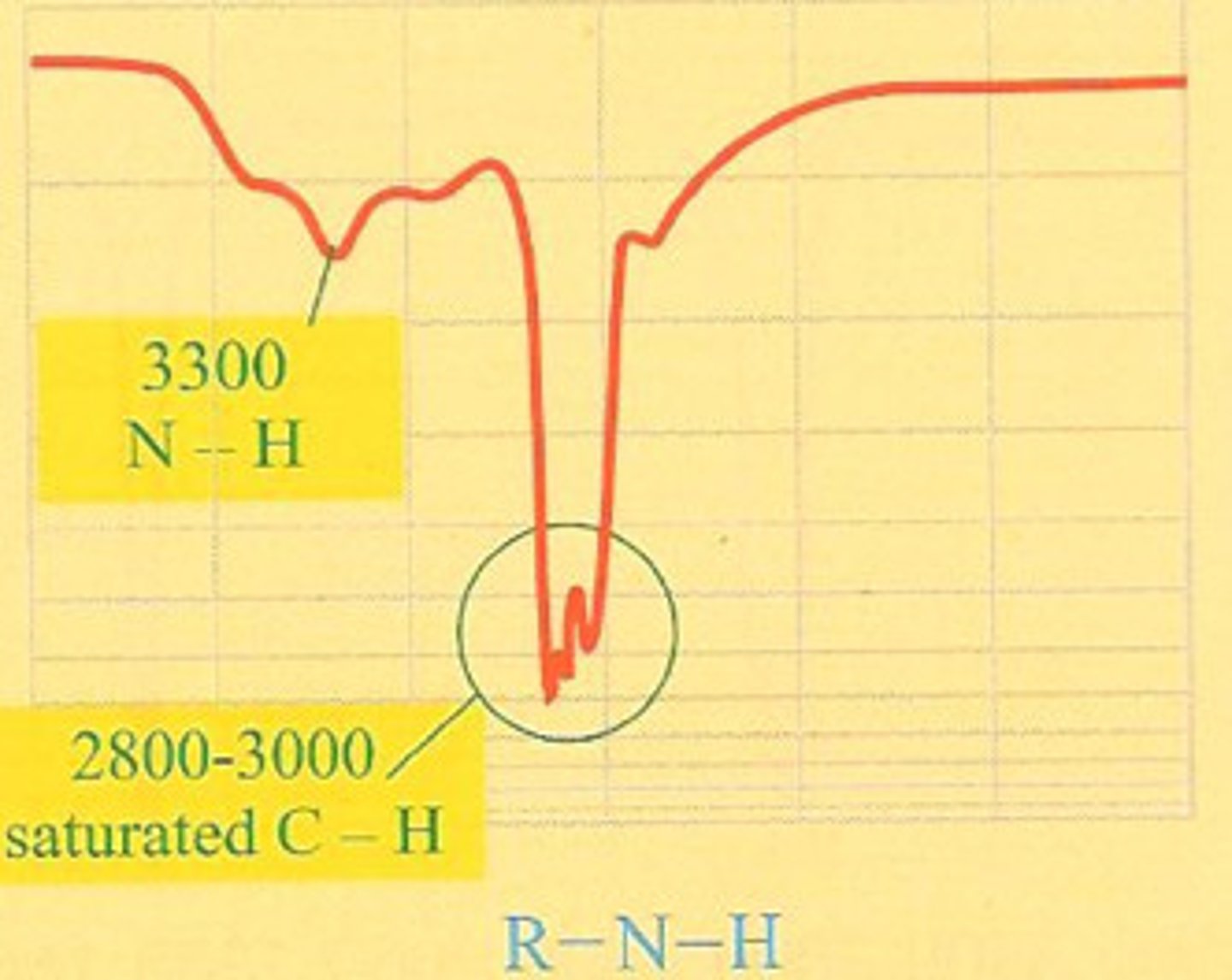
IR frequency of N-H stretch
3300 cm-1 sharp
two peak if primary
one peak if secondary
IR Frequency: O-H (alcohol)
3300 cm broad