AQA A level Biology Topic 1
1/155
There's no tags or description
Looks like no tags are added yet.
Name | Mastery | Learn | Test | Matching | Spaced |
|---|
No study sessions yet.
156 Terms
What is a polysaccharide?
Two or more monosaccharides are joined together by condensation reactions
What are carbohydrates?
Large, complex molecules that are made from monosaccharides
What elements are in carbohydrates?
Carbon, hydrogen, oxygen
What type of sugar is glucose?
What does this mean?
A hexose sugar.
A monosaccharide with six carbons
Beta (β) glucose molecule
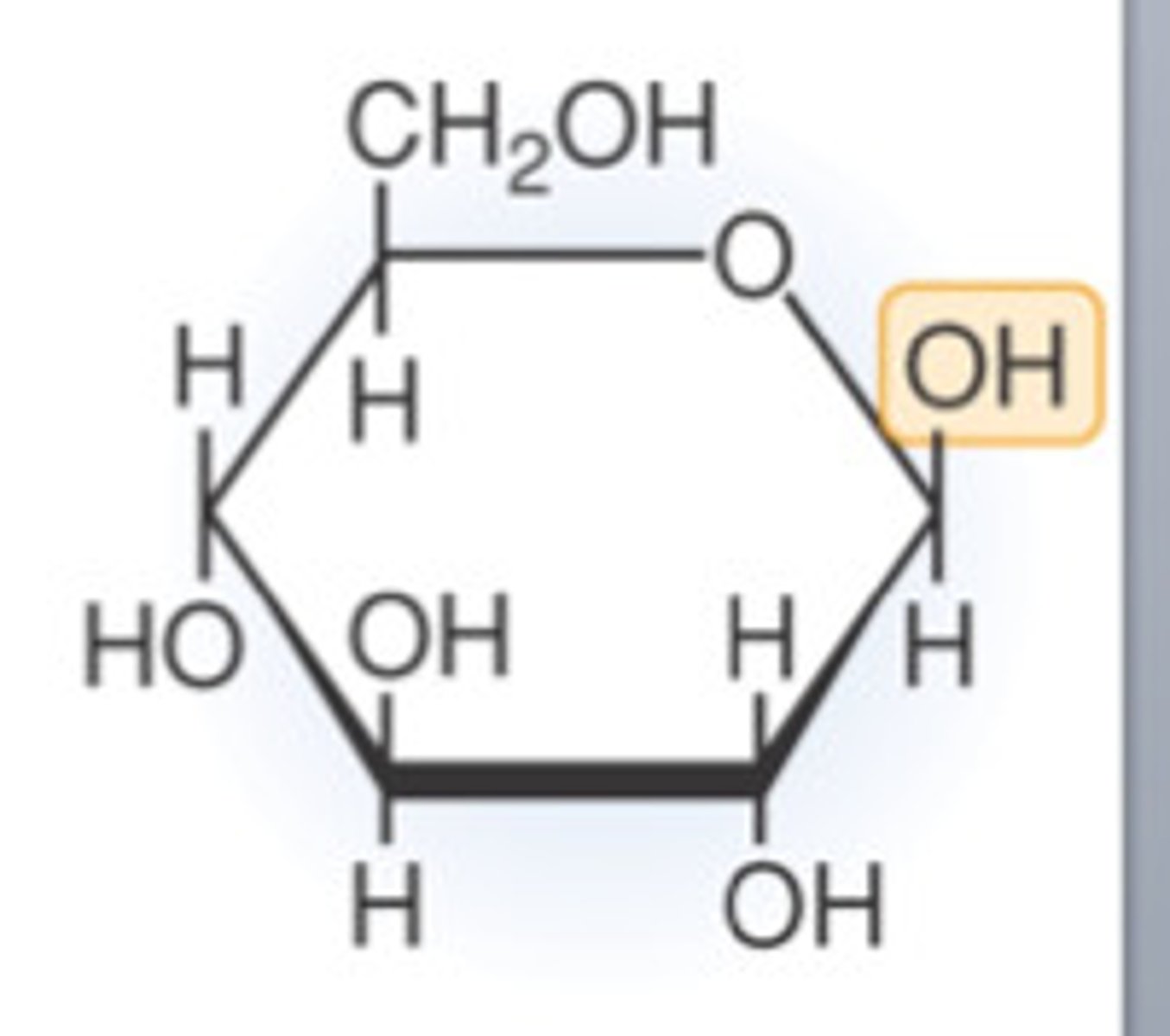
What forms between two molecules when water is released?
What forms when two monosaccharides join together?
A glycosidic bond
A disaccharide
What is the food test for sugars?
Benedict's test
Describe the food test for reducing sugars
Add Benedict's reagent to a sample then heat it in a water bath until it boils.
If reducing sugars are present then a coloured precipitate forms.
Describe the food test for non-reducing sugars
Add dilute hydrochloric acid to the sample and carefully heat in a water bath until it boils. Neutralise by adding sodium hydrogencarbonate. Then add Benedict's reagent and a colour precipitate will form
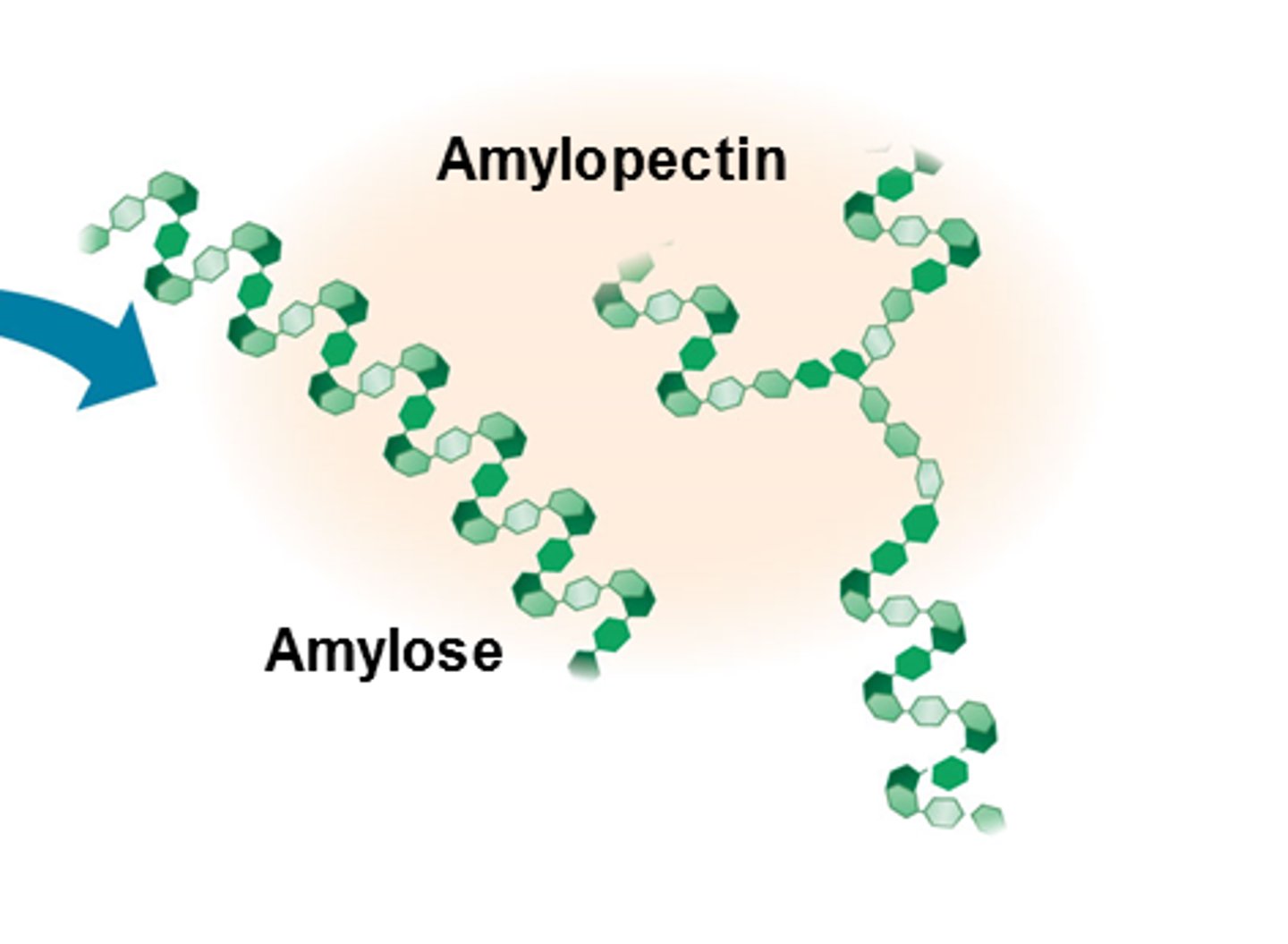
What two polysaccharides is starch made of?
amylose and andamylopectin
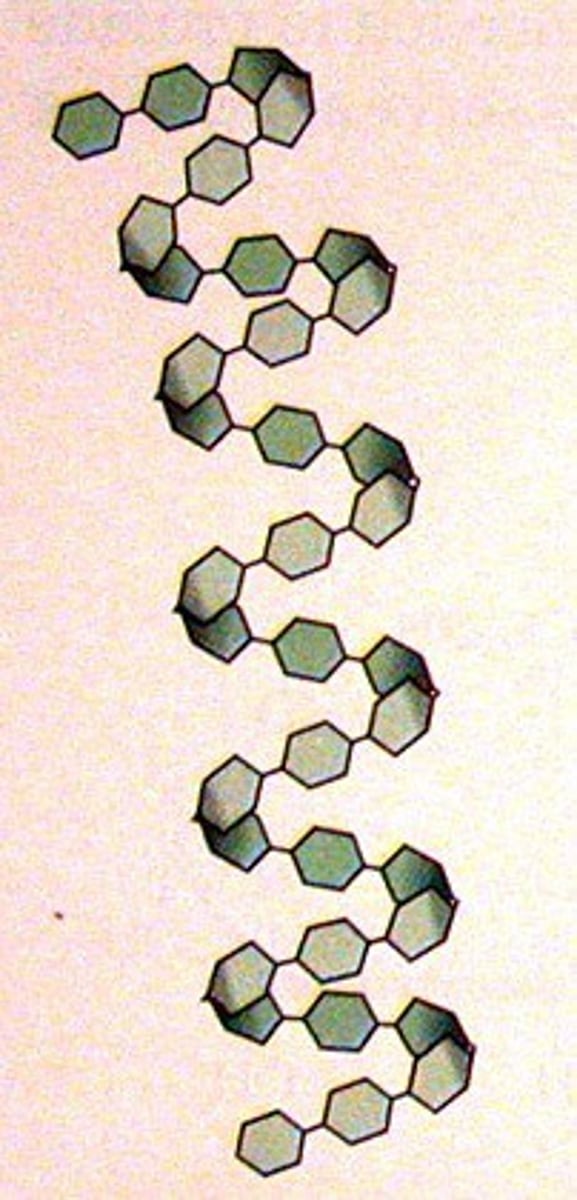
What is amylose?
A long, unbranched chain of alpha glucose.
Describe the food test for starch
To a sample, add iodine dissolved in potassium iodide solution
What are three examples of monosaccharides?
Glucose, fructose and galactose
What are the two types of glucose?
Alpha and beta
What is an isomer?
Molecules with the same molecular formulae but different connections and therefore different properties
Alpha (α) glucose molecule
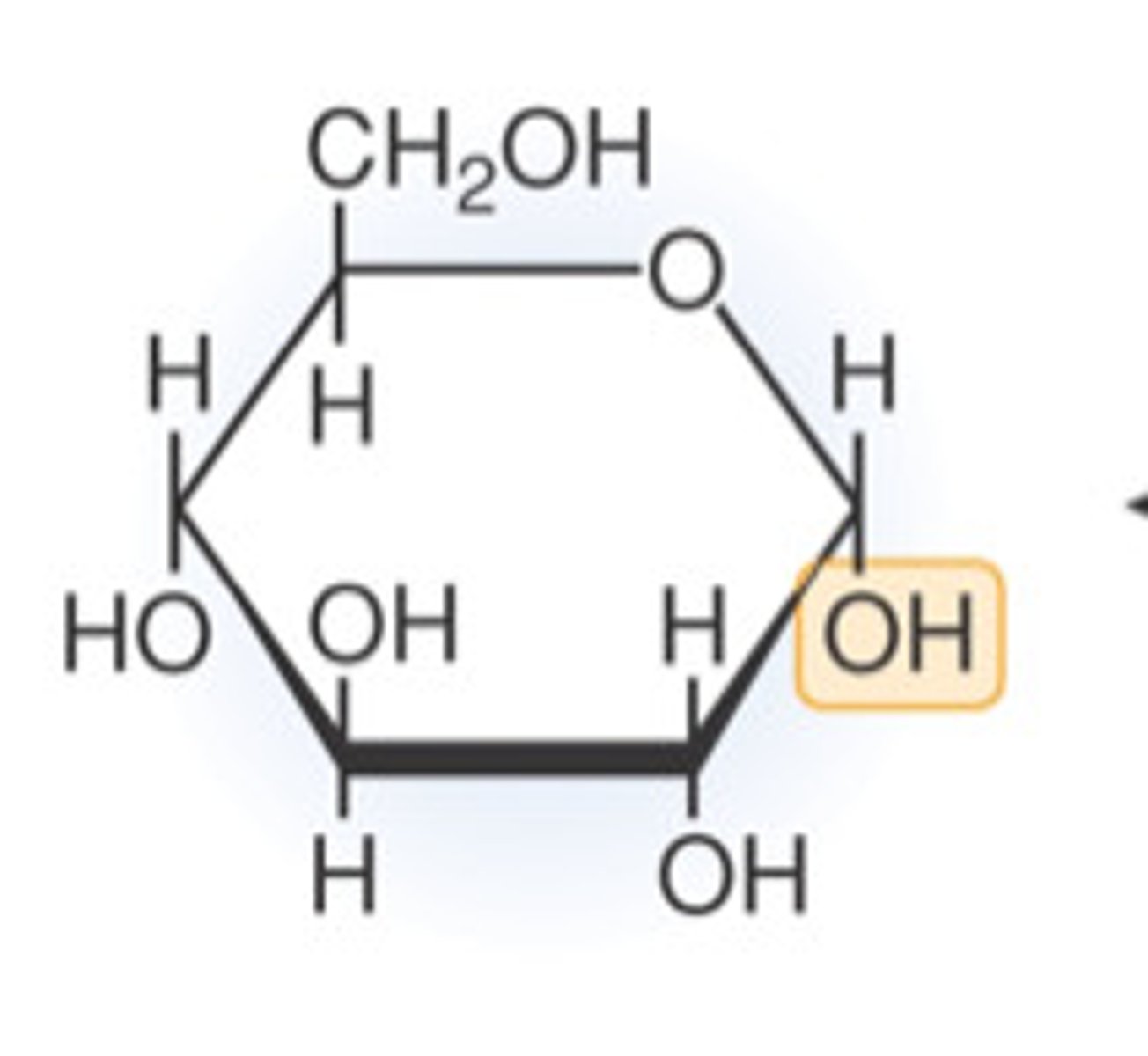
What is a condensation reaction?
Two molecules join together with the formation of a new chemical bond and a water molecule is released when the bond is formed
What is sucrose?
A disaccharide formed from a condensation reaction between a glucose molecule and a fructose molecule
What is lactose?
A disaccharide formed by condensation of a glucose molecule and a galactose molecule
How can polymers be broken into monomers?
Through hydrolysis reactions
How does hydrolysis reactions break polymers apart?
The chemical bonds between monomer is broken with a water molecule
How can sugars be classified?
Reducing or non-reducing
What is the order of the the colour change in the test for reducing sugars?
Blue, green, yellow, orange, brick red
What colour does a highly concentrated sample of reducing sugar turn?
Brick red
How can samples of reducing sugar be compared?
Filter the precipitates and then weigh the precipitates. Compare the masses
What is a negative result in the non-reducing sugar test?
The solution will remain blue
What do plants store excess glucose as?
Starch. When more glucose is needed then the starch is broken down
Describe the structure of amylose
It has a coiled structure due to the angles of glycosidic bonds. It creates a cylindrical shape due to the coils and it allows large quantities to fit into small spaces
What is amylopectin?
A long branched chain of alpha glucose
Describe the structure of amylopectin
It has side branches so enzymes can breakdown the glycosidic easily
What is a positive result for the starch food test?
The sample will turn from bowny-orange to blue-black
What do animals store excess glucose as?
Glycogen
What is glycogen?
A polysaccharide of alpha-glucose
What polysaccharide is glycogen's structure similar to? How is it different?
Amylopectin
It has many more branches
Why are there many branches on glucagon?
It means that the enzymes can reach the bonds fast so stored glucose can be released very fast.
What type glucose is cellulose made of?
Beta
How are the straight cellulose chains linked?
With weak hydrogen bonds. This forms strong fibres called microfibrils. Cellulose provides structural support for the cells which means its ideal for cell walls.
What is a triglyceride?
A kind of lipid.
What is the structure of a triglyceride?
A glycerol with three fatty acids
What are the 'tails' on fatty acids?
Hydrocarbons which are hydrophobic. This means that lipids are insoluble in water
How are triglycerides formed?
A fatty acid reacts with a sugar molecule and makes an ester bond. A water molecule is released. This happens again to form a triglyceride
What are the two types of fatty acids?
Saturated and unsaturated
How can the two fatty acids be differentiated?
The hydrocarbon tails
Saturated fatty acids don't have any double bonds between carbon acids whereas unsaturated fatty acids have at least one double bond between carbons.
What is a phospholipid?
Lipids found in cell membranes
What is the structure of a phospholipid?
A phosphate group and two fatty acids attached to glycerol
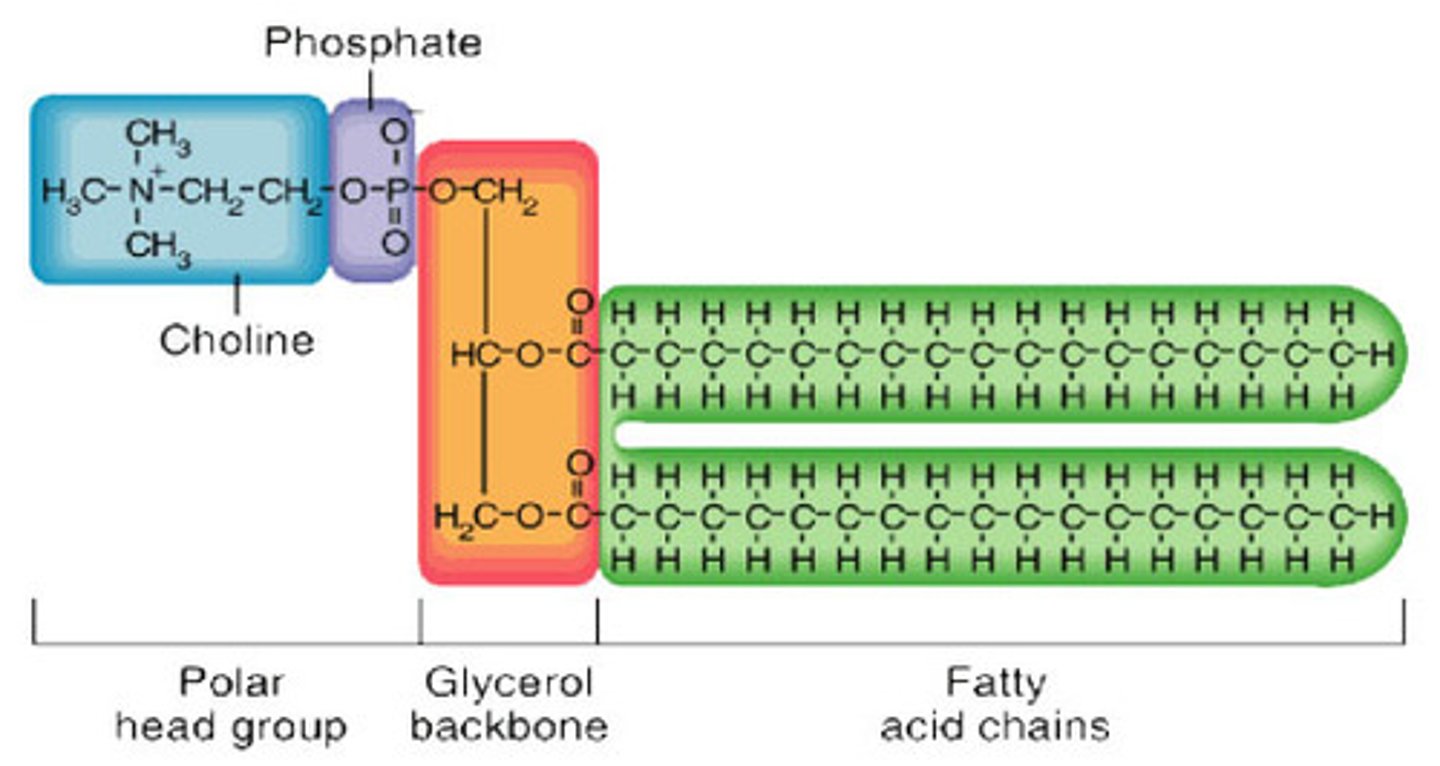
What is important about the phosphate group and fatty acids?
The phosphate group is hyrdophilic and the fatty acids are hydrophobic
What does hydrophilic mean?
Attracts water
What does hydrophobic mean?
It repels water
Why are triglycerides good energy storage molecules?
- Long hydrocarbon tails contain lots of chemical energy so it is released when broken down
-They're insoluble so water potential of the cell is unaffected
What structure does phospholipids make in a cell?
The bilayer of cell membrane
Why is are phospholipids suitable for the structure it makes?
It forms two layers with the heads which are hydrophilic and tails are hydrophobic. The heads face outwards. The centre of the bilayer is hydrophobic so water-soluble substances can't pass through easily
What is does the emulsion test check for?
The presence of fat
Describe the process of the emulsion test
Add ethanol to the substance being tested and shake the test tube for about a minute.
Pour the solution into water
What is a positive result for the emulsion test?
A milky emulsion will be visible
How many amino acids are required to form a dipeptide?
Two
What is a polypeptide?
An organic polymer than is made of more than two amino acids.
What is the general structure of amino acids?
A carboxyl group, an amino group and an R group.
How many different amino acids make up all living things?
20
What is the R group?
The variable group that differentiates the amino acids
What reactions form polypeptides?
Condensation
What is the bond between amino acids in polypeptides called?
Peptide bonds
What are the four structural levels in a protein?
Primary, Secondary, Tertiary and Quarternary
What is the primary structure in a protein?
The sequence of amino acids in the polypeptide chain.
What is the secondary structure in a protein?
Hydrogen bonds between amino acids. This forces the chain to either become an alpha coil or beta pleated sheet
What is the tertiary structure in a protein?
More bonds (hydrogen or ionic) form between parts of the polypeptide chain.
When the two molecules of the amino acid cysteine are close then disulfide bridges form. (a sulfur atom from each amino acid bonds)
This forms a 3D structure.
What is the quarternary structure of a protein?
If there are several different polypeptides then the connections between these polypeptides is the quarternary structure.
Or the quarternary structure is the final 3D structure
What is an enzyme?
A specialised protein that often has roles in metabolism
What is an antibody?
A specialised protein that is involved with immune response.
Describe the basic structure of anitbodies
Two light polypeptide chains and two heavy polypeptide chains
Where are transport proteins located?
Cell membranes
What is the role of transport proteins?
Transports molecules and ions across the cell membrane through a channel created in the proteins due to folds.
What is the structure of structural proteins?
Long, parallel polypeptide chains with cross links
What is in structural proteins?
Keratin and collagen
What test is for proteins?
Biuret Test
What is the first stage of the Biuret test?
Add sodium hydroxide solution to the test solution so it is an alkaline solution
What is the second stage of the Biuret test?
Add copper (II) sulphate solution to the alkaline test solution
What is a positive result for the Biuret test?
Purple
In terms of cells, where can enzymes function?
Both within (intracellular) and outside (extracellular)
What is the active site?
The part of the enzyme that has a particular shape which binds to the substrate molecules
How do enzymes speed up the rate of metabolic reaction?
The activation energy is lowered so reactions occur at lower temperatures.
What is an enzyme-substrate complex?
When a substrate fits into an active site on an enzyme
Why do enzyme-substrate complexes lower activation energy? (when joining molecules)
The substrate is held close to the enzyme and reduces the repulsion so bonding is easier
Why do enzyme-substrate complexes lower activation energy? (when breaking down molecules)
The bonds are strained whilst in the active siteso break quicker.
What, on the graph, is used to compare rates of reaction?
Gradient of the line (this may be a tangent at the same time point)
What type of graph is used to show enzyme-controlled reactions?
Line graphs
What does it mean on an enzyme-controlled reaction graph when the line is flat?
No more products are being produced
What is the Induced Fit model theory for enzymes?
Both the active site and substrate change shape so that the shapes completely match
What controls the shape of the active site?
The tertiary structure
What happens if the tertiary structure of the enzyme is altered?
The substrate won't fit into the active site and so the reaction will notbe catalysed.
What determines the primary structure of an enzyme?
Genes. If the genes mutate then the entire enzyme could be useless.
Why does an increase in temperature lead to enzymes working more frequently?
A higher temperature means that the substrates have a higher kinetic energy so they move faster and increases the chances of the substrate colliding with the enzyme is increased
What does denature mean?
change the shape of the active site by heat, acidity, or other effects that disrupt its molecular conformation.
What is the average optimum temperature for most human enzymes?
37°C
What is the average optimum pH of enzymes in humans?
pH7
What causes the enzyme to become denatured? (pH)
If the the pH is not the optimum then the H+ and OH- will damage the ionic and hydrogen bonds in the tertiary structure.
How does enzyme concentration affect enzyme activity?
A higher enzyme concentration means that there is a higher chance of the substrate colliding with an active site.
At what point does the rate of reaction hinder if the enzyme concentration is high?
When the concentration of substrate is less than the concentration of enzymes.
What does amylase break down?
It catalyses the breakdown of starch to maltose
What apparatus is needed to calculate the speed of breakdown of starch?
A starch solution, test tube, pipette, spotting tile, iodine in potassium iodide, stopwatch

What is the experiment to calculate the speed that substrates are broken down?
Potassium iodide is added to each well of the tile and a drop of iodine is added to each. Amylase and starch (concentrations should be know) are mixed in a test tube. A drop of this mixture is added one well. Check the colour at regular intervals (e.g every 20 seconds)