equations all
1/68
There's no tags or description
Looks like no tags are added yet.
Name | Mastery | Learn | Test | Matching | Spaced |
|---|
No study sessions yet.
69 Terms
Basic discount factor

Discount factor period t+1

General present discounted value formula
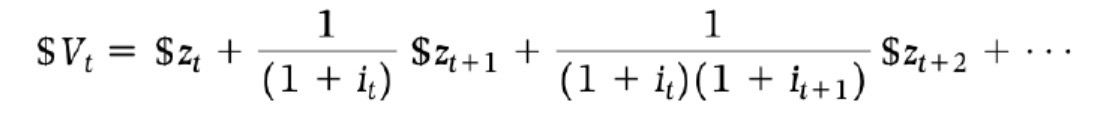
Present discounted value (expected) formula
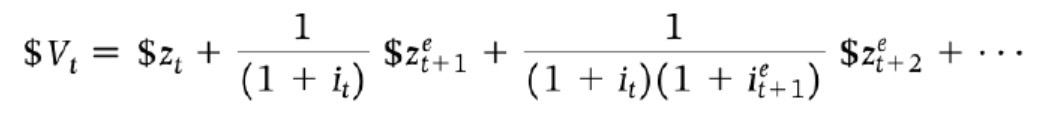
Annuity PV
(Constant returns)
N number of periods
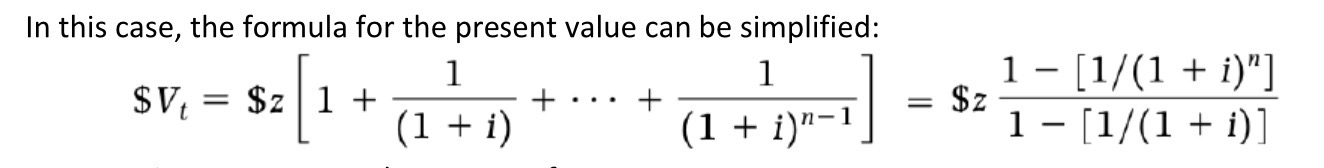
Perpetuity PV
Infinite period
Constant return & values
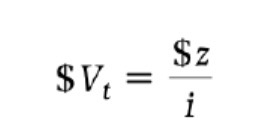
Present value with the real interest rate
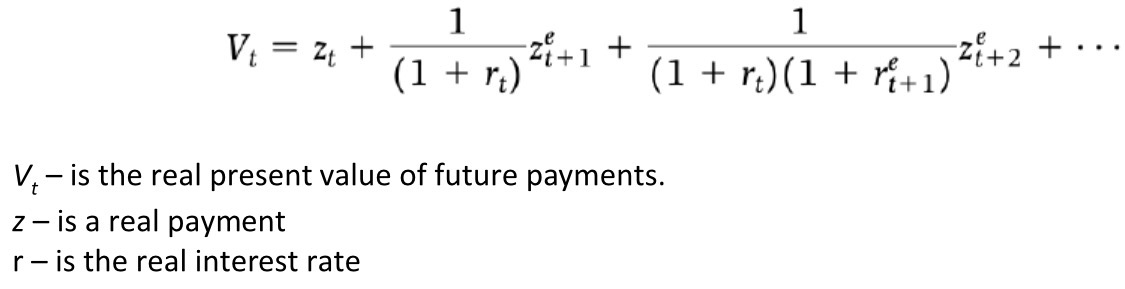
Relationship between real present value, present value, and price level
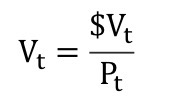
General bond price equation

Two year bond price
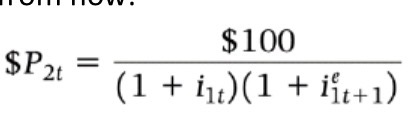
1 & 2 year arbitrage condition bond
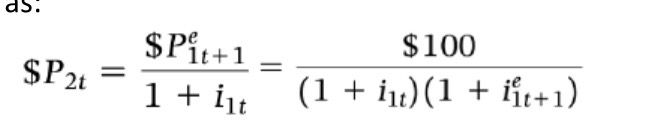
Two year bond yields (where YTM is the constant annual interest rate i)
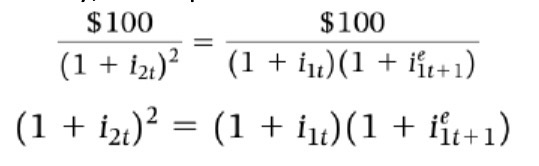
Simplified bond YTM equation
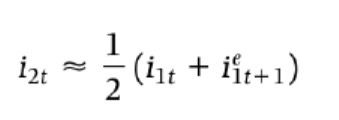
Arbitrage condition risk premium YTM
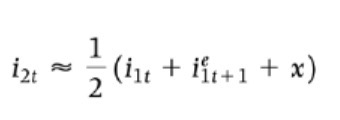
Stock (vs bond) arbitrage condition
Equity premium instead of risk premium
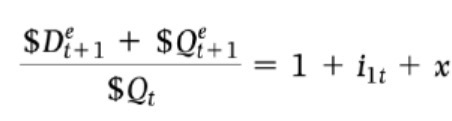
Stock dividend/interest rate annuity
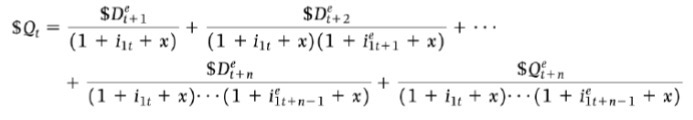
Investor reaction to increased spending (increase in IS curve)
if investors don’t believe the central bank will respond: output increases w no counter action & stock prices rise
If they believe the central bank will take interest rate (LM) action: Hence no change in output & increase interest rate = stock prices fall
Sum of expected income value (over a lifetime)
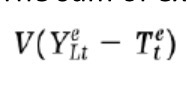
Short run consumption Function (realistic)
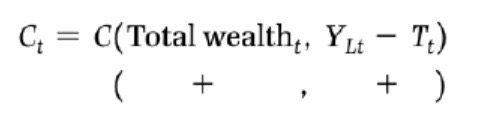
Basic present value of expected profits
Profit in t=1
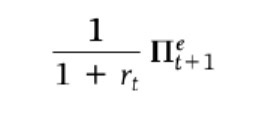
Present value of 2 periods of profit
Profit in t+1=
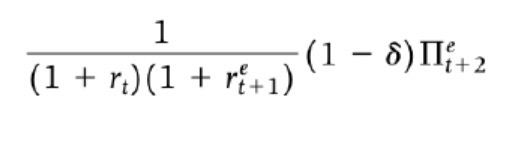
Present value of profits
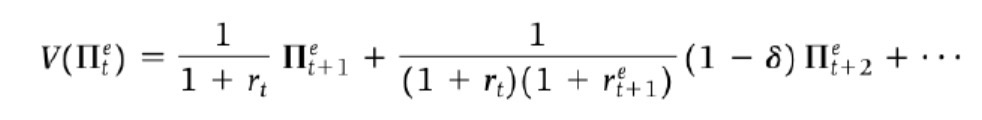
Investment function short term
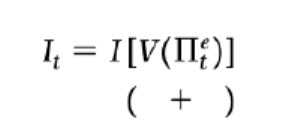
Present value of perpetuity profit
Profit_t=profit expected=t+1
Real interest rate _t = expected=t+1
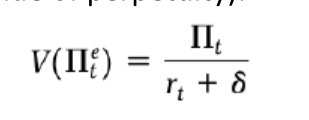
Short term investment function perpetuity case
Static expectations
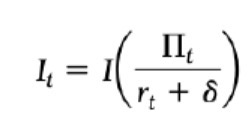
Realistic short term investment function
Adjusted for difficulty borrowing & the freedom of own/current fund reserve to utilise
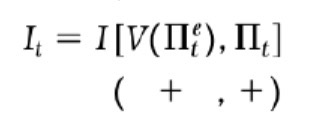
Profit/unit of capital stock
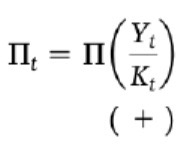
Current IS relation
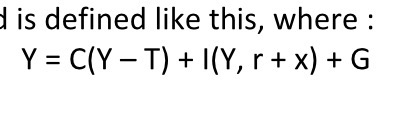
Expectations adjusted IS relation (current period)
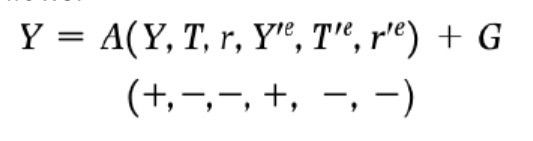
IS curve shifters
Anything except Y & r
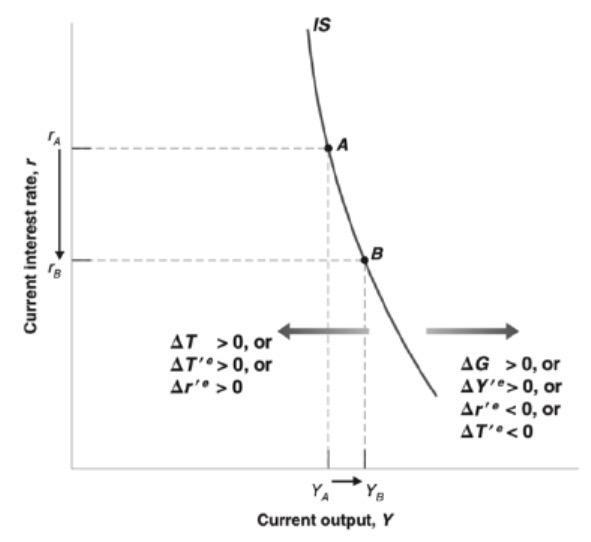
Effect of expectations on IS curve
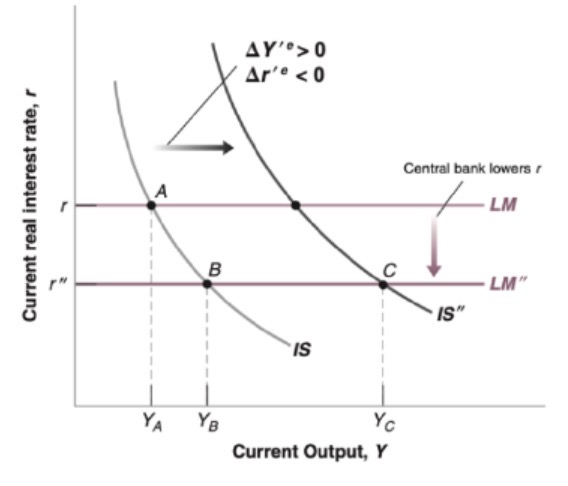
Announcement of deficit reduction affect on IS curve
Ambiguous:
Depends on :
credibility
Other fiscal/monetary policies
Political state
Plan composition
Real exchange rate (bilateral)
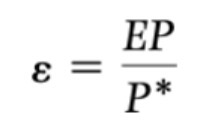
Uncovered interest relation (version 1)
Relies on assumptions
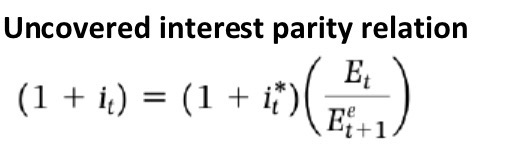
Uncovered interest parity relation (version 2)

Domestic goods demand relation
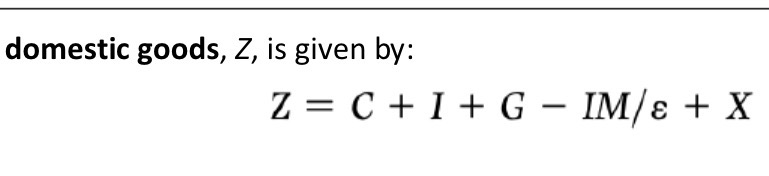
Short term import relation
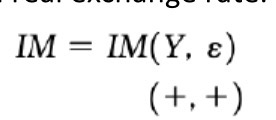
Short term export relation
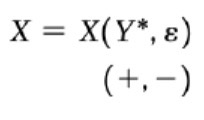
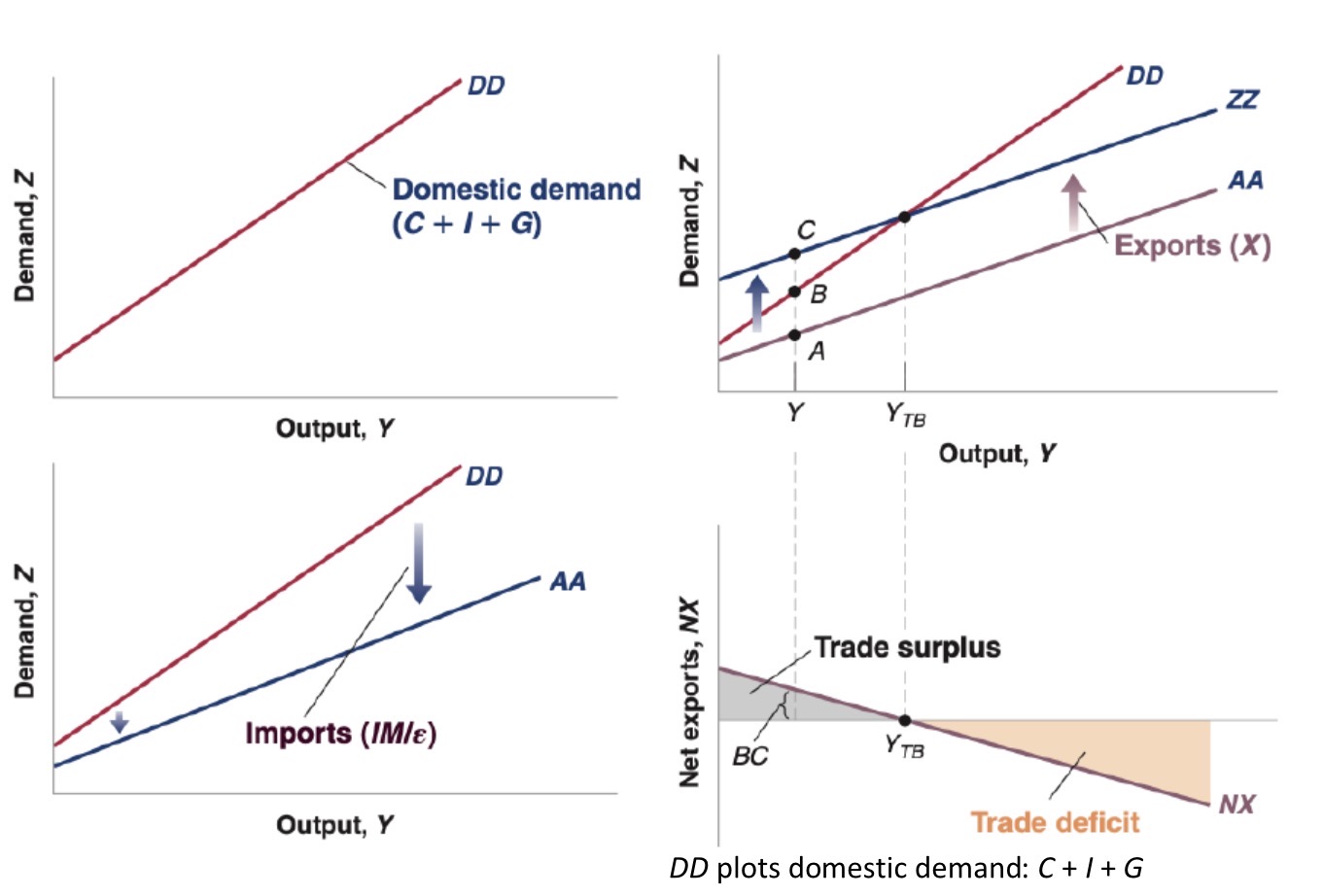
Exports, imports & domestic demand impact on trade balance
Goods market equilibrium Y=Z
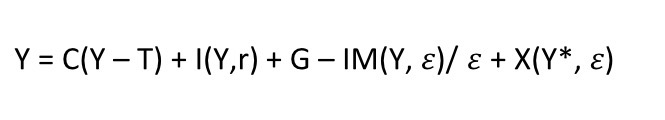
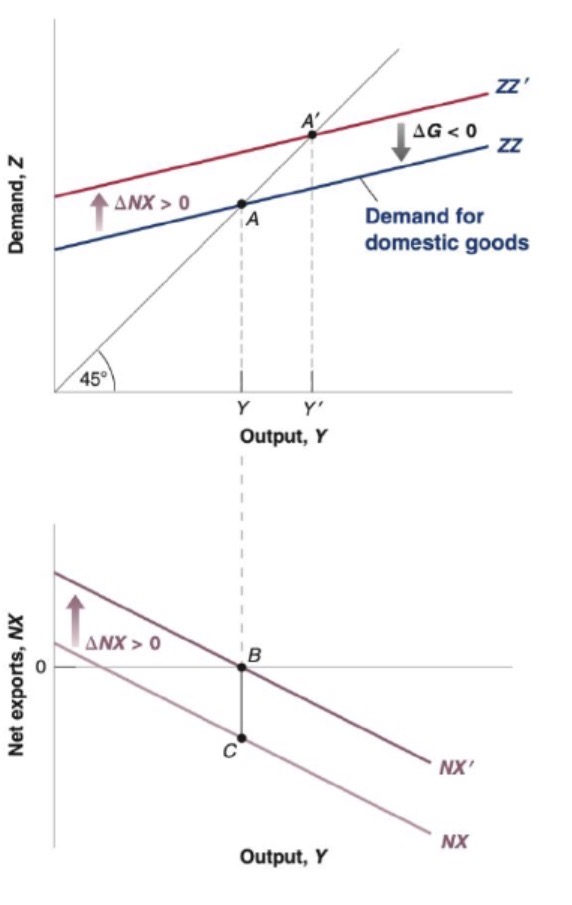
Increase in G effect on goods market
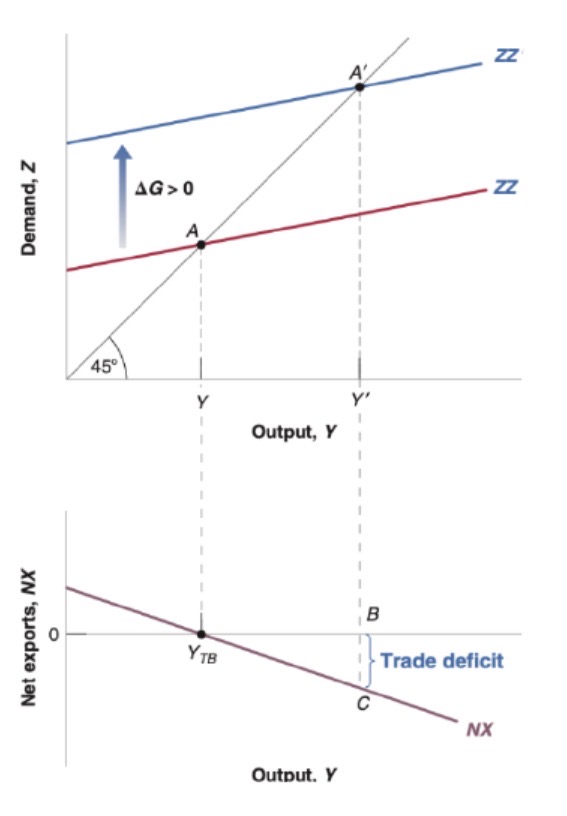
Increase in foreign Y* effect on goods market (domestic)
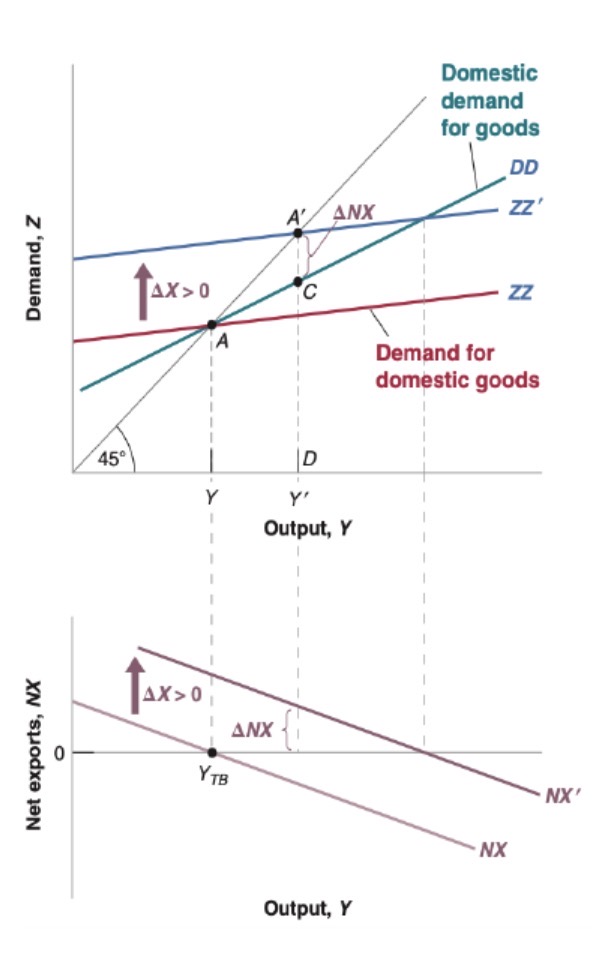
Marshall-Lerner condition
Net exports relation
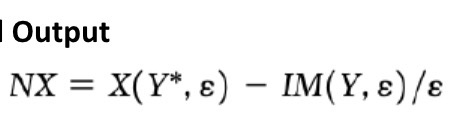
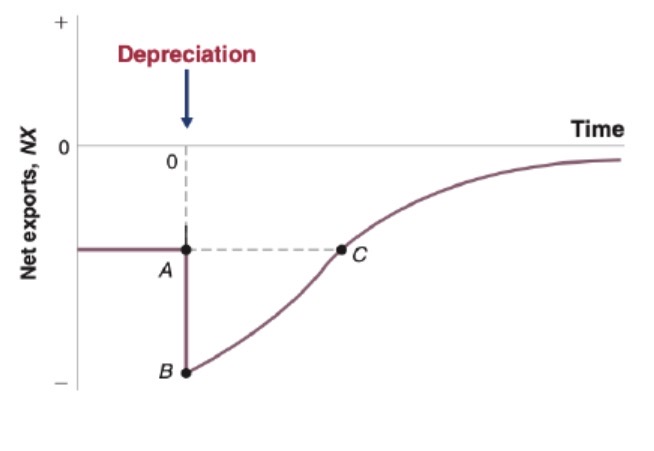
Utilizing marshall-Lerner to combat trade deficit
Current account function
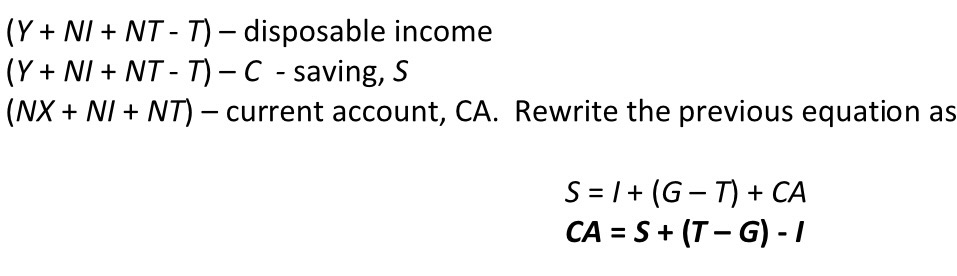
Goods market equilibrium inc. trade & exchange rate
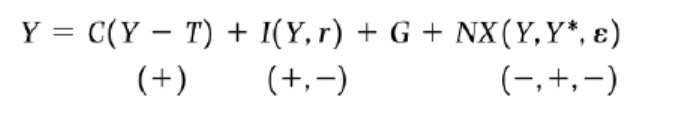
Goods market equilibrium inc. trade (if domestic & foreign Price is given & hence no Inflation )
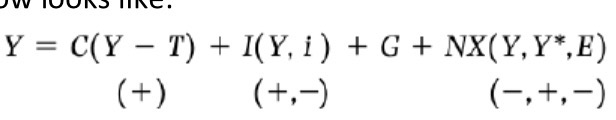
Financial market equilibrium
E is given,
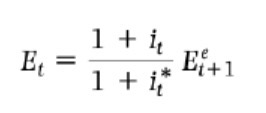
Financial & goods market equilibrium
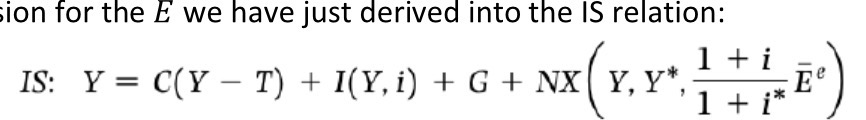
Mundell-fleming model
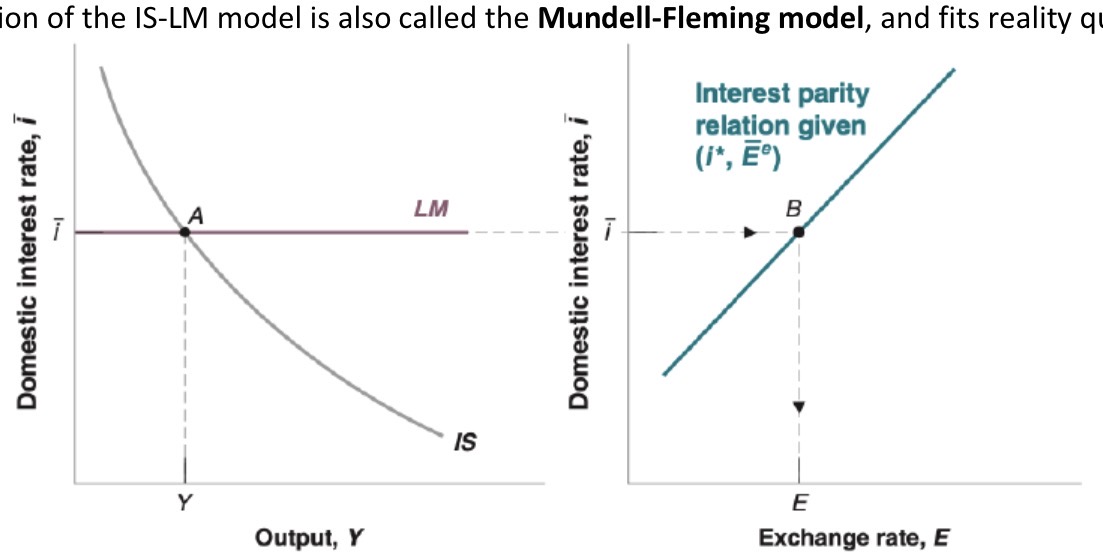
Affect of fiscal policy on open economy
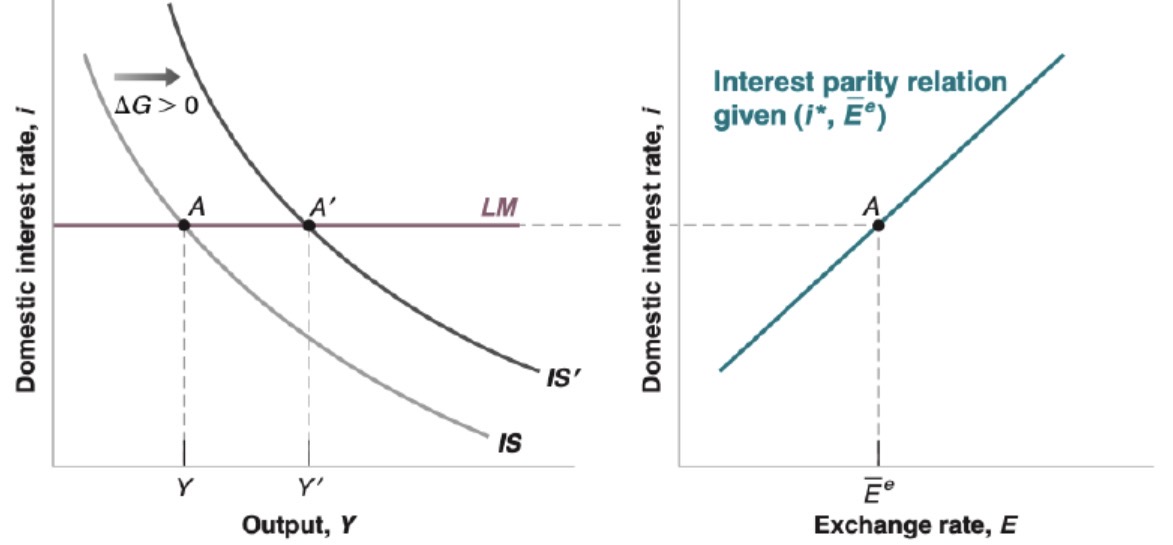
Affect of monetary policy on open economy
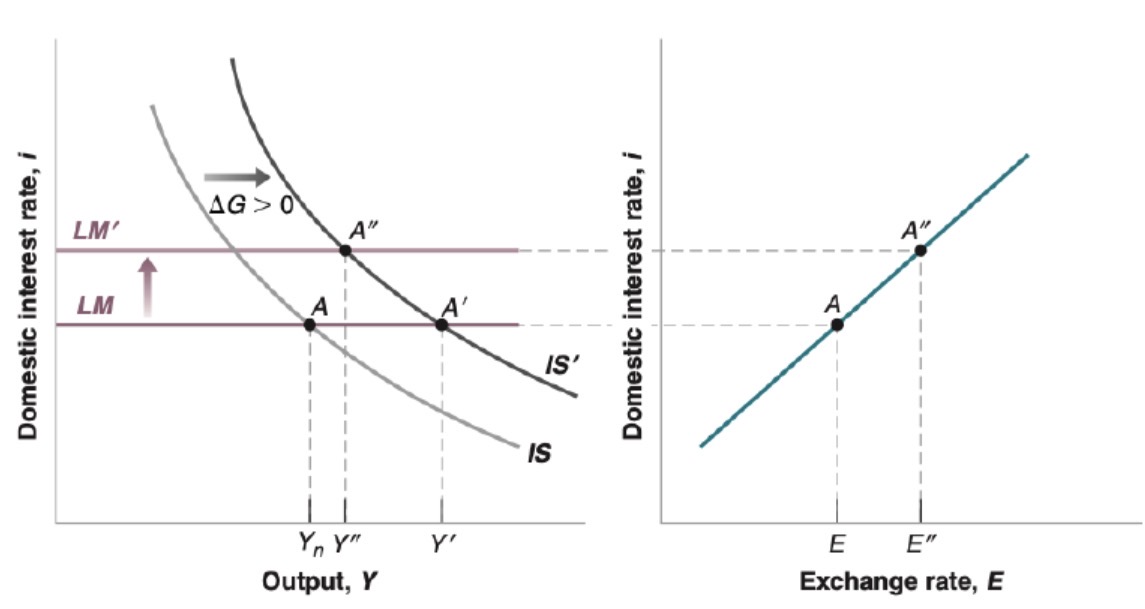
Fixed exchange rate (pegged) interest parity relation
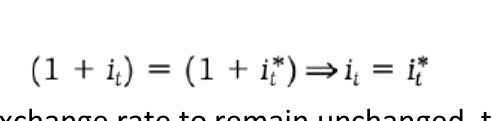
IS relation under fixed exchange rate
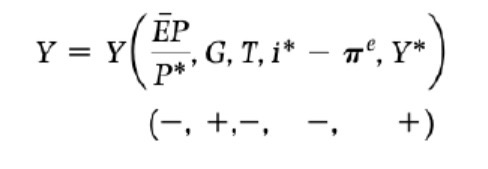
Medium run Philips curve
Expected inflation = constant
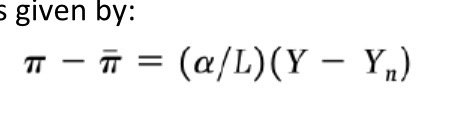
Medium run Exchange rate movement (flexible rate)
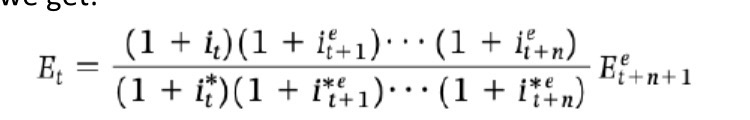
Nominal budget deficit
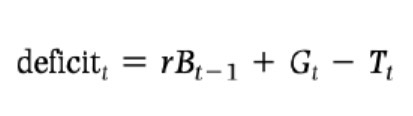
Real budget deficit
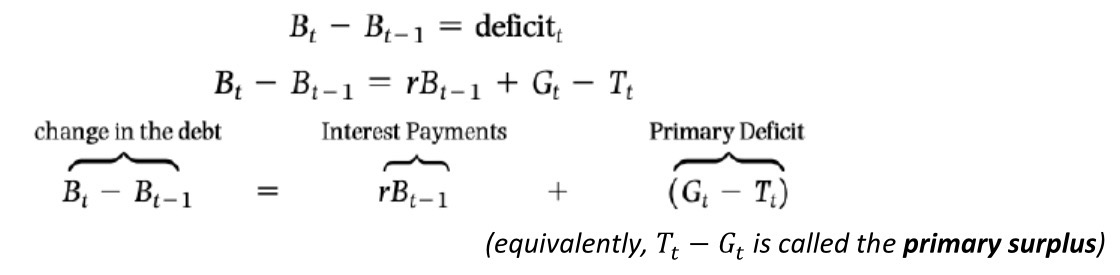
Pay back debt condition (2 year)
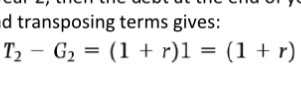
Primary deficit=zero
growth in government debt
Debt repayment condition
Surplus of (1+r)^t-1
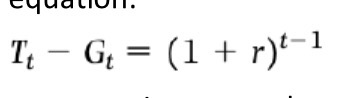
Debt to gdp ratio derivation step 1
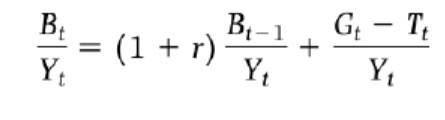
Debt to gdp ratio derivation step 2
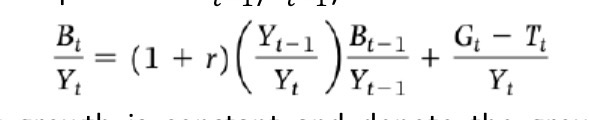
Debt to gdp ratio derivation step 3
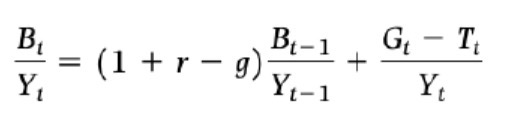
Debt to gdp ratio derivation step 4
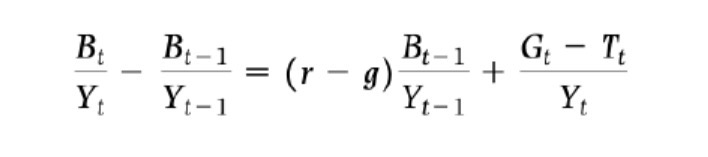
Seignorage
Govt revenue as a result of money printing
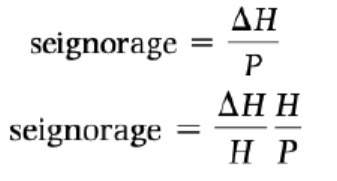
Seignorage / monthly gdp (Y)
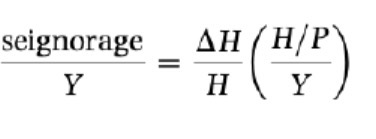
Taylor’s interest rate rule
Rules bank should follow for interest rate & inflation
