B9 - Respiration
1/16
There's no tags or description
Looks like no tags are added yet.
Name | Mastery | Learn | Test | Matching | Spaced |
|---|
No study sessions yet.
17 Terms
Aerobic Respiration Formula
Glucose + Oxygen -> Carbon Dioxide + Water + Energy
C6H12O6 + 6O2 -> 6CO2 + 6H2O + 36 ATP

Aerobic Respiration
- uses oxygen
- in the mitochondria
- constant
- exothermic
Aerobic Respiration Uses
transfers energy to the cell for
- muscle movement
- thermoregulation
- active transport
- making chemical reactions
- growth & respirations
How to Increase Oxygen Supply
- higher heart rate
- higher breathing rate
- higher breathing volume
Why does Breathing Rate/Depth Increase
- additional respiration
- for muscle cells
- for more energy
- to remove CO2 breathed in
Anareobic Respiration
respiration during vigorous exercise when there isn't enough oxygen / used for other causes
- without oxygen
- in the cytoplasm
- exothermic
- less energy than aerobic
- creates lactic acid
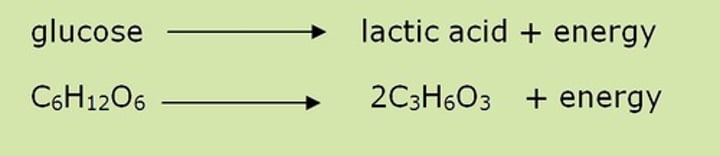
Anaerobic Respiration Formula
glucose --> lactic acid + energy
C6H12O6 -> 2C3H6O3
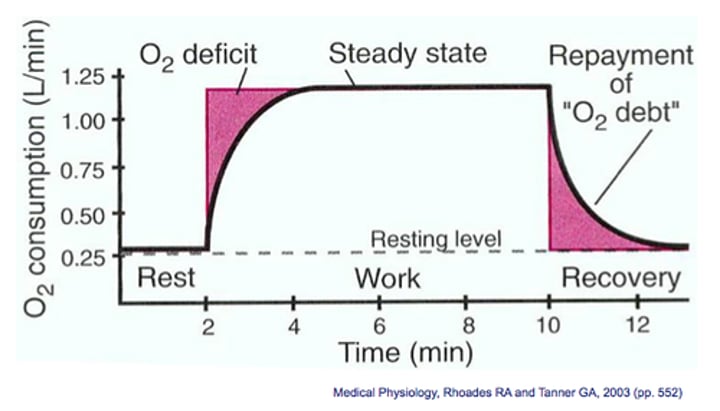
Oxygen Debt
the amount of oxygen required after physical exercise to convert / break down accumulated lactic acid to glucose
Metabolism
the sum of all chemical reactions that occur within an organism
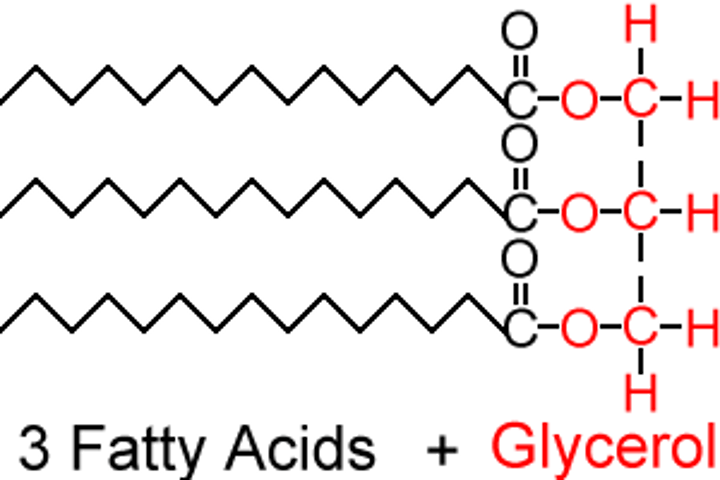
The Formation of Lipid Molecules
- one molecule of glycerol joins with three fatty acids
- in the liver
- to store energy
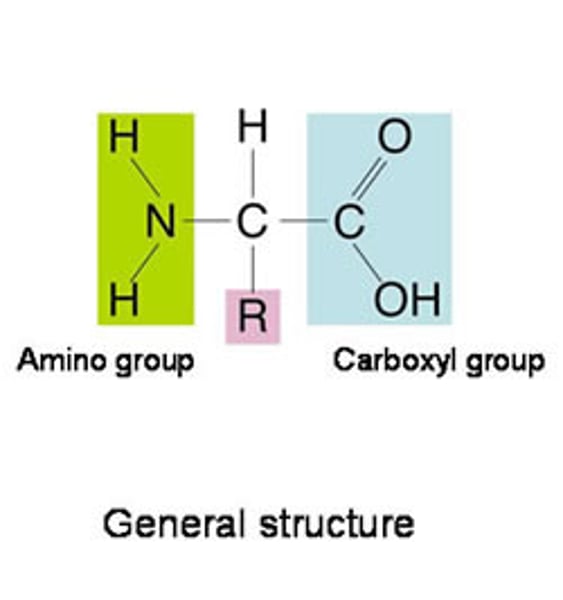
Glucose + Nitrate Ions
- form amino acids
- used to synthesise proteins
- in the ribosomes
- to grow & repair
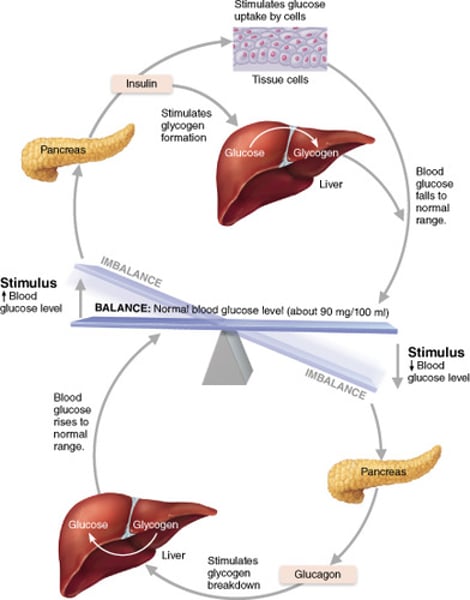
Conversion of Glucose to Glycogen
- animal
- storage of glucose
- in the liver of muscle cells
Conversion of Glucose to Starch
- plant
- long chains of glucose for storage
- made in photosynthesis
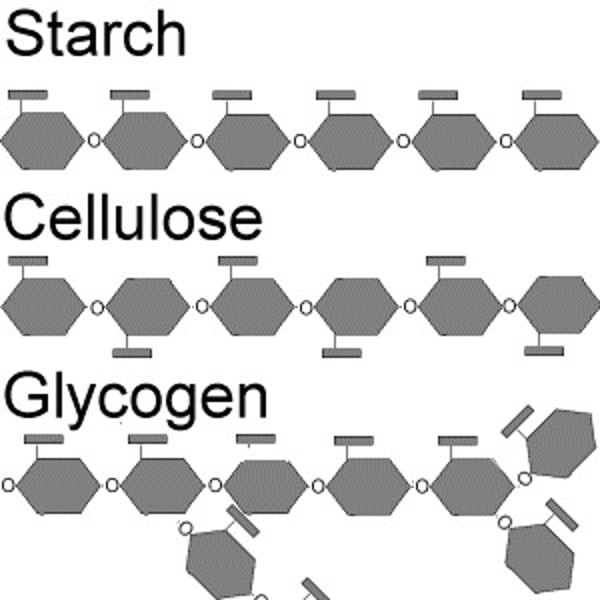
Conversion of Glucose to Cellulose
- plant
- chain of glucose
- to strengthen cell walls
Break Down of Excess Protein
- made into ammonia
- made into urea in the liver
- excreted
Fermentation in Yeast Cells
- anaerobic response
- produces alcohol and carbon dioxide
Lactic Acid
product of fermentation in many types of cells, including human muscle cells