ISM - Lesson 12 - International Services Communication-Karteikarten | Quizlet
1/40
There's no tags or description
Looks like no tags are added yet.
Name | Mastery | Learn | Test | Matching | Spaced | Call with Kai |
|---|
No study sessions yet.
41 Terms
What is Marketing Communication?
Everything a company communicates to a customer
Marketing Communication - Definition
An audience-centered activity designed to encourage engagement between participants
Tasks of MarComms
1. To inform
2. To persuade
3. To reinforce experience
4. To act as a differentiator
Marketing Communication Mix
1. Sales promotion
2. Direct marketing
3. Public relations
4. Personal selling
5. Advertising
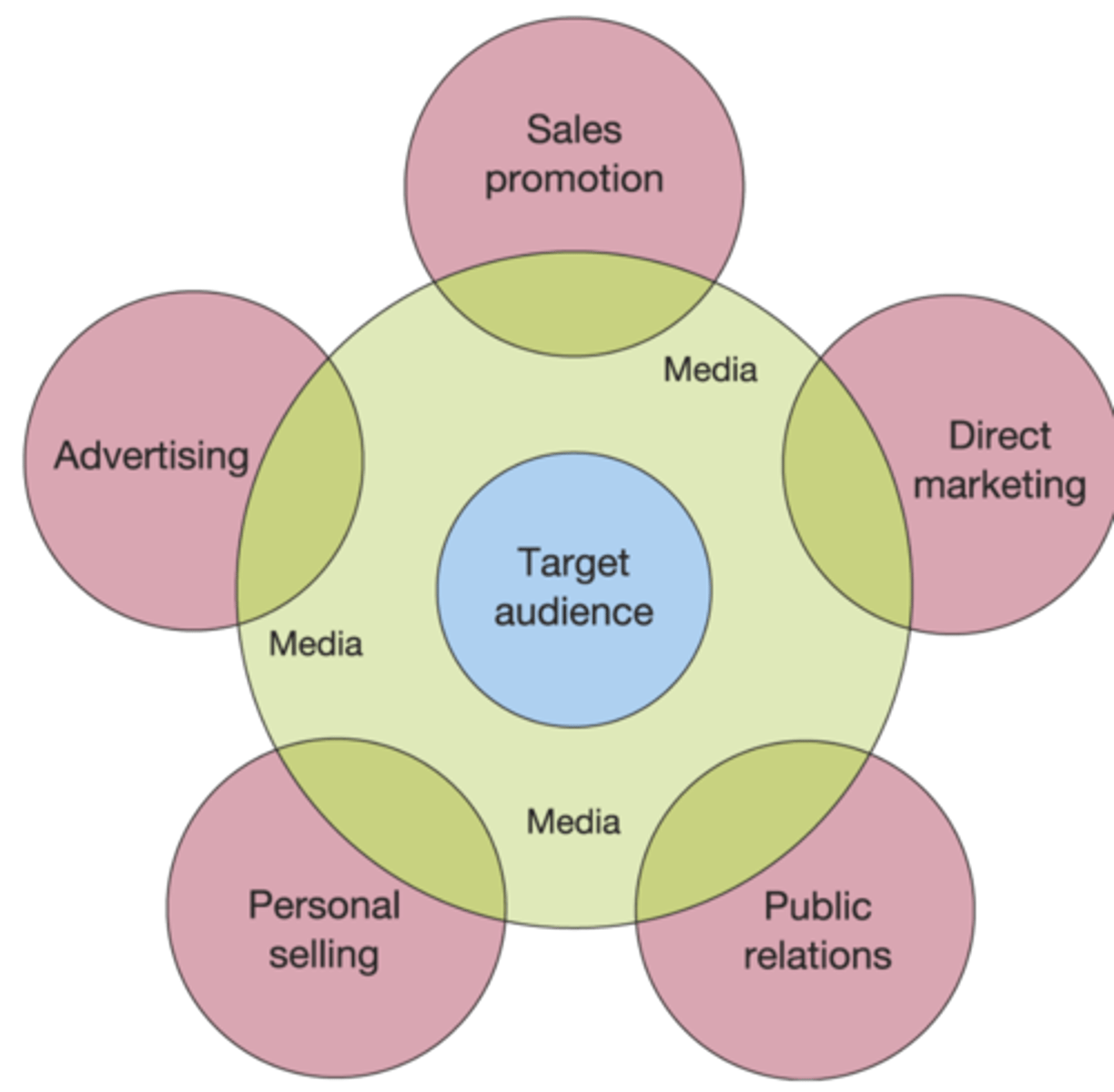
Advertising
A non-personal form of mass communication that offers a high degree of control for those responsible for the design and delivery of the advertising messages
Sales Promotion
Comprises various marketing techniques, which are often used tactically to provide added value to an offering, with the aim of accelerating sales and gathering marketing information
Personal Selling
Traditionally perceived as an interpersonal communication tool that involves face-to-face activities undertaken by individuals, often representing the company, in order to inform, persuade or remind an individual or group to take appropriate action, as required by the sponsor's representative
Public Relation
The art and social science of analysing trends, predicting their consequences, counselling organisations' leadership and implementing planned programmes of action which will serve both the organisation's and the public interest
Direct Marketing
1. Seeks to target individual customers with the intention of delivering personal messages and building a relationship with them based upon their responses to the direct communications
2. Attempts to build a one-to-one relationship by communicating with the customers on a direct and personal basis
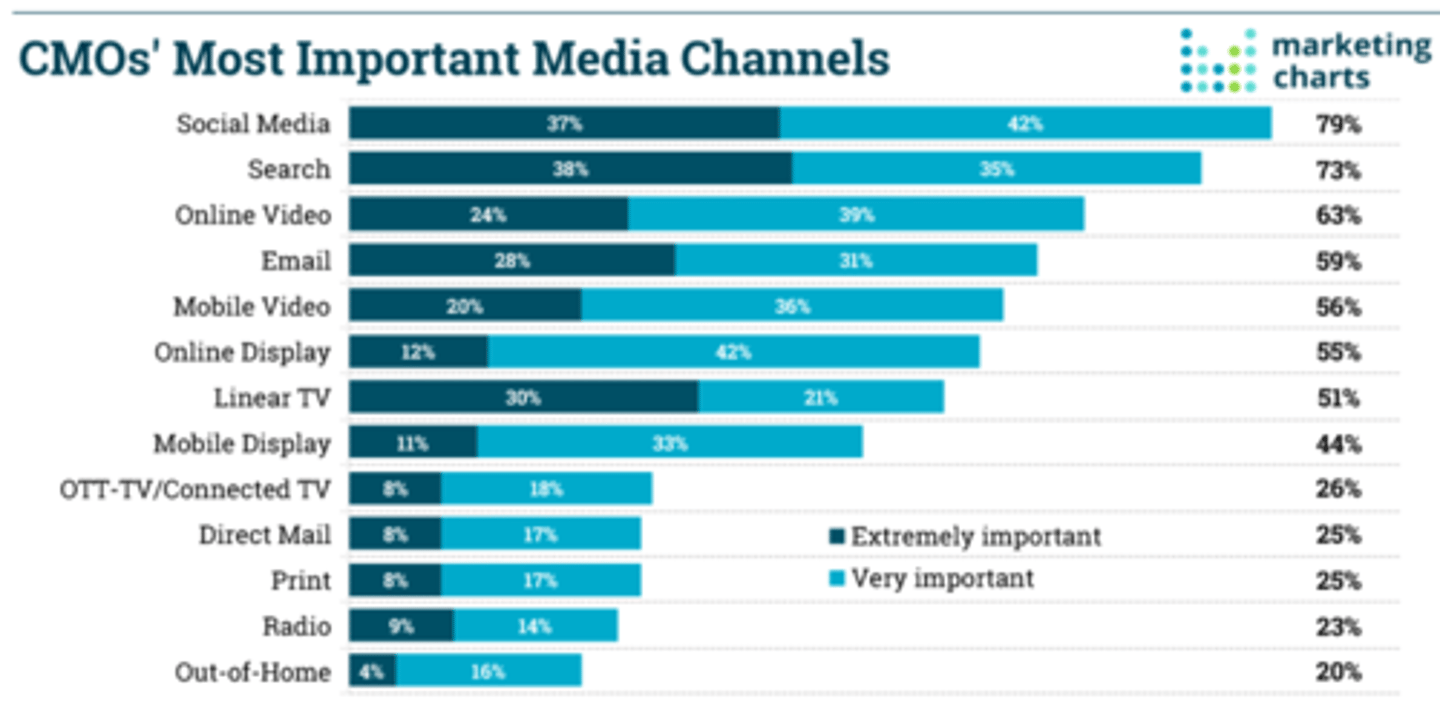
Most Important Media Channels
1. Social Media
2. Search
3. Online Video
Integrated Marketing Communication
A consistent, seamless marketing message across all media & platforms:
1. Below the line: direct marketing, press, radio
2. Above the line: advertising
3. Digital presence & social media
4. Promotion & POS
IMC Framework (Kotler et al.)
See Graph
Framework for International Promotion
1. Study the target market
2. Determine standardization
3. Determine promotional mix
4. Develop the message
5. Select effective media
6. Establish control mechanisms
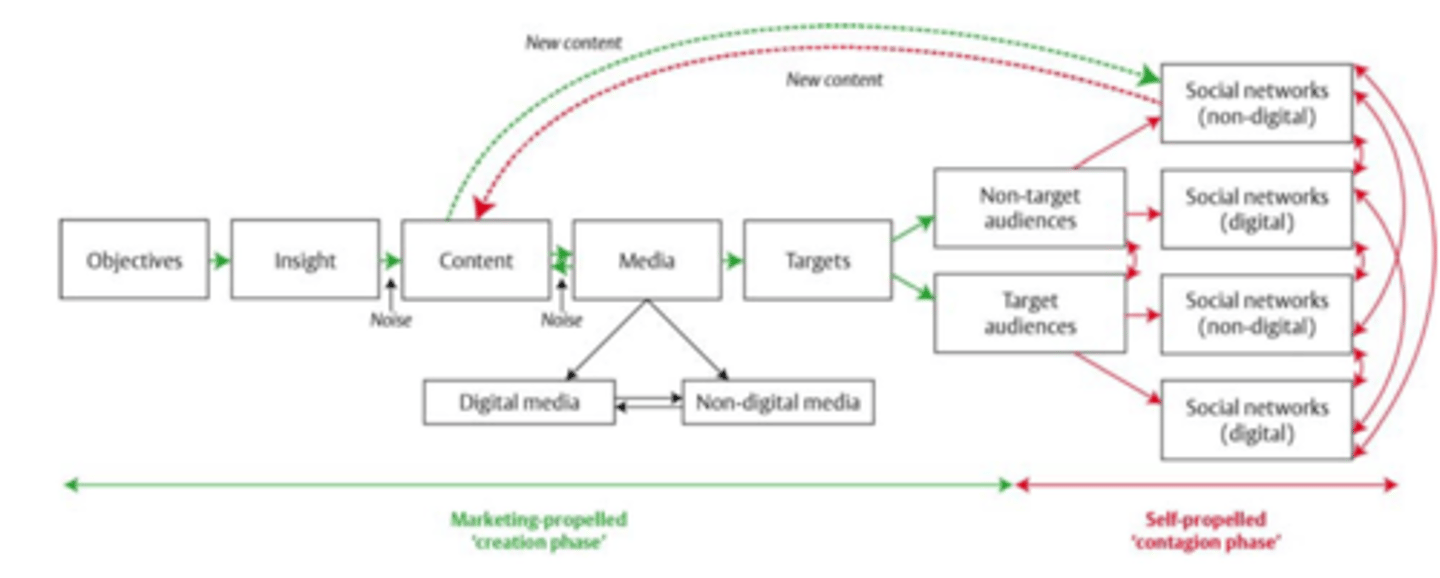
Components of International Communication Process
1. Encoding
2. Message Channel
3. Decoding
4. Receiver
5. Feedback
6. Noise
7. Information Source
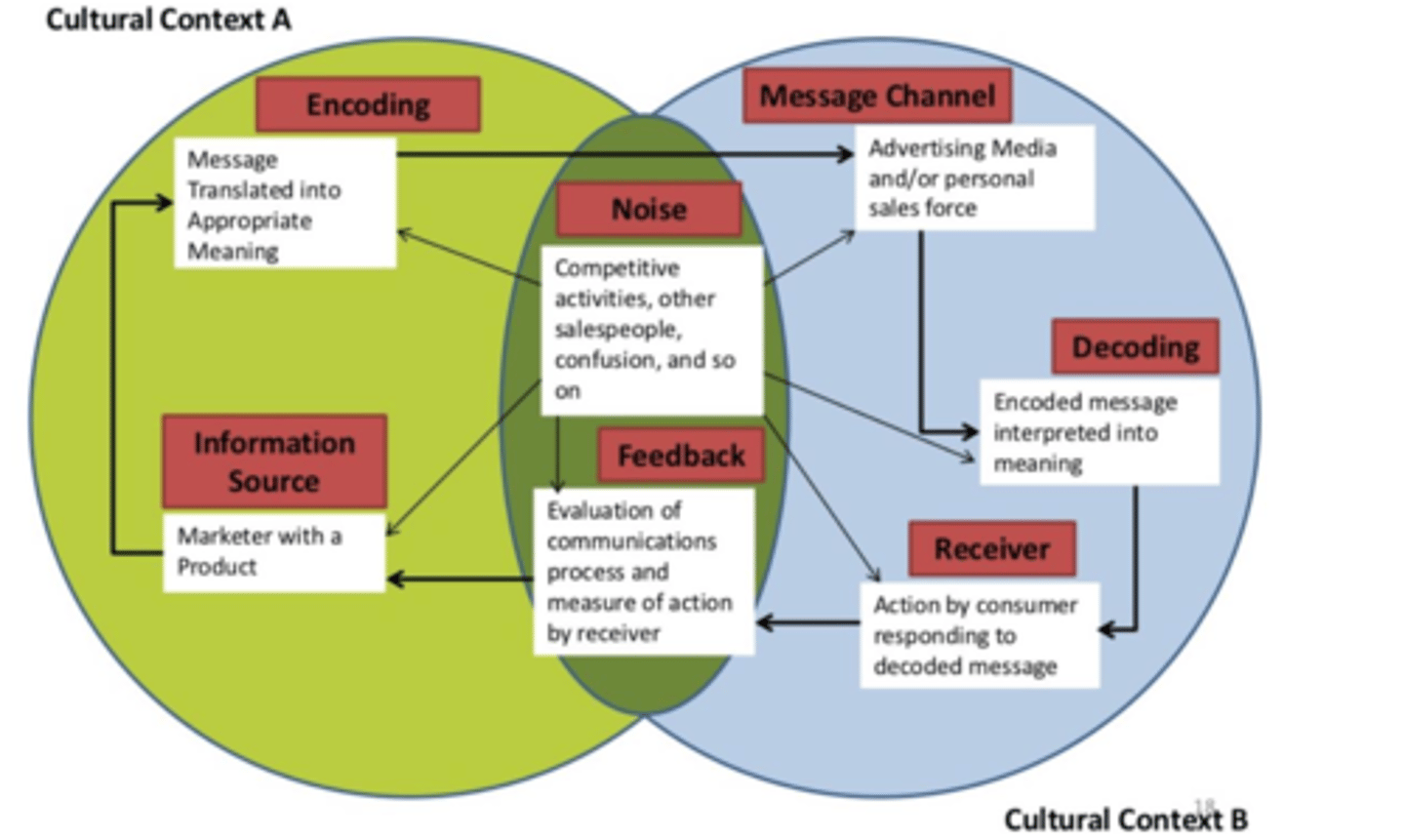
Encoding
Message translated into appropriate meaning
Message Channel
Advertising and/or personal sales force
Decoding
Encoded message interpreted into meaning
Receiver
Action by consumer responding to decoded message
Feedback
Evaluation of communications process and measure of action by receiver
Noise
1. Competitive activities
2. Other salespeople
3. Confusion
...
Information Source
Marketer with a product
Brand vs. Product
A product is 'something' made in a factory, that can be copied and can be quickly outdated, while a brand is 'something' that is bought by a customer, it is unique and timeless
Brand
A name, term, symbol, design, or combination of these, that identifies a seller's products and differentiates them from competitors
Branding
A process by which companies distinguish their product offerings from the competition
Information provided by brand names
1. Content
2. Taste
3. Durability
4. Quality
5. Price
6. Performance
Brand Names - Implication
The buyer is not required to undertake time-consuming comparison tests with similar offerings or other risk-reduction approaches to purchase decisions
Branding - Results
1. Companies with strong brand achieve 1.9 times higher returns than industry average
2. It is not about product offering or marketing effort -> it is about the customer and how to develop a meaningful relationship with the customer => CX
Components of a true brand positioning
The entire offering, encompassing both the tangible and the intangible elements to create a genuine experience and an emotional connection between the brand & customer
Brand Identity
The collection of all the core or basic characteristics of the brand from the perspective of organization
Brand Image
1. How relevant stakeholders (especially customers) perceive the brand
2. Different stakeholders can have different perceptions of the same brand -> different images may exist
Types of Brands Architecture
1. Branded House
2. House of Brands
3. Hybrid
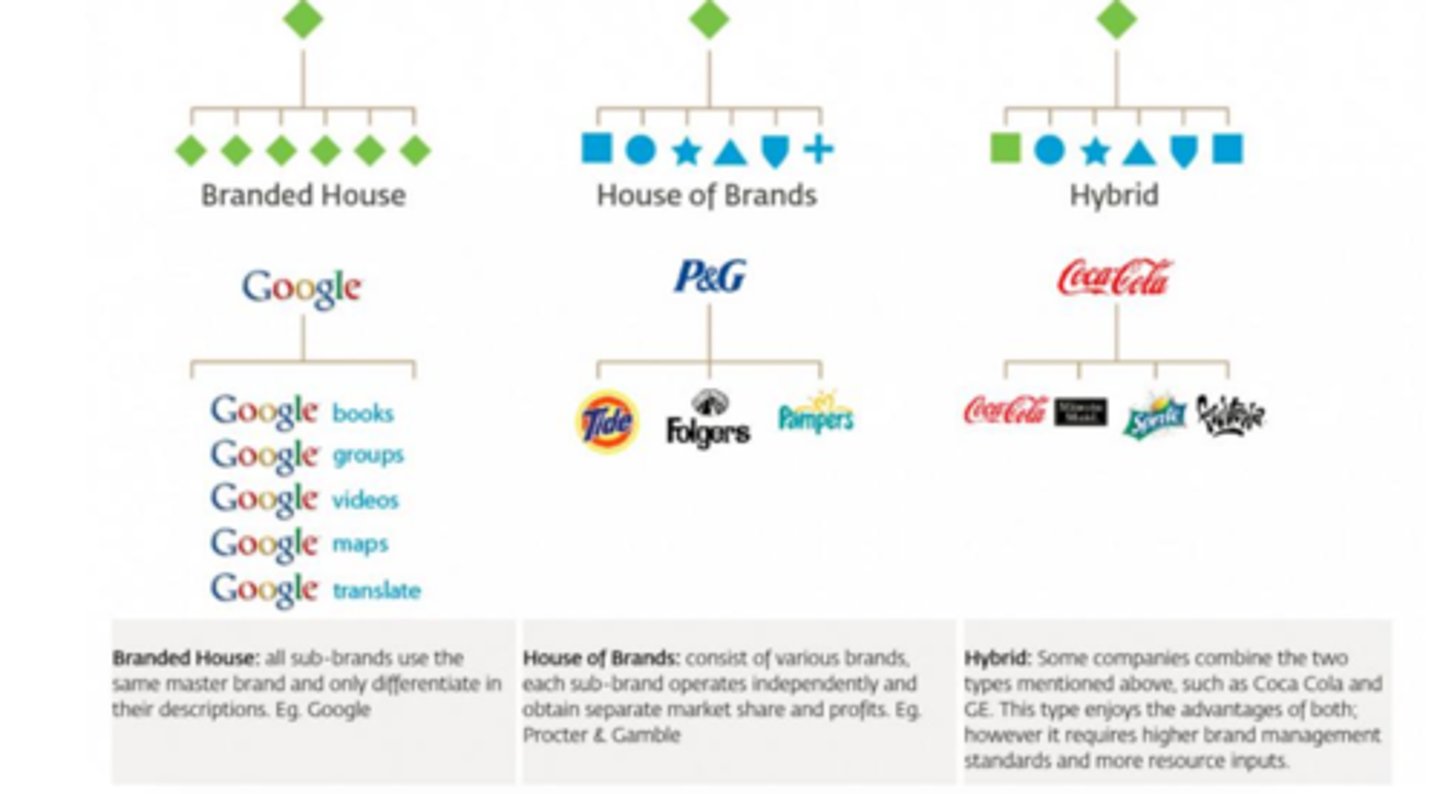
Branded House
All sub-brands use the same master brand and only differentiate in their descriptions (e.g. Google)
House of Brands
Consists of various brands, each sub-brand operates independently and obtain separate market share and profits (e.g. P&G)
Hybrid
Combination of Branded House & House of Brands (e.g. Coca-Cola)
Implications of Global Brands
1. Generally means cost saving & gives a company a uniform worldwide that enhances efficiency and costs saving when introducing new products associated with the brand name
2. Companies with successful country specific brands must balance the benefits of a global brand against the risk of loosing benefits of an established brand
Impacts on Brand Equity
Primary Impact: Brand Meaning
Secondary Impact: Brand Awareness
Impacts on Brand Awareness
Primary Impact: Company's Presented Brand
Secondary Impact: External Brand Communications
Impacts on Brand Meaning
Primary Impact: Customer Experience with Company
Secondary Impact: Company's Presented Brand & External Brand Communications
Strong Brands in Services
1. Enable customers to better visualize and understand the intangible products
2. Reduce customers' perceived monetary, social or safety risks in buying services which are difficult to evaluate before purchase
Strong Brands
Substitute when company offers no fabric to touch, no trousers to try on, no watermelons or apple to scrutinize, no automobile to test drive
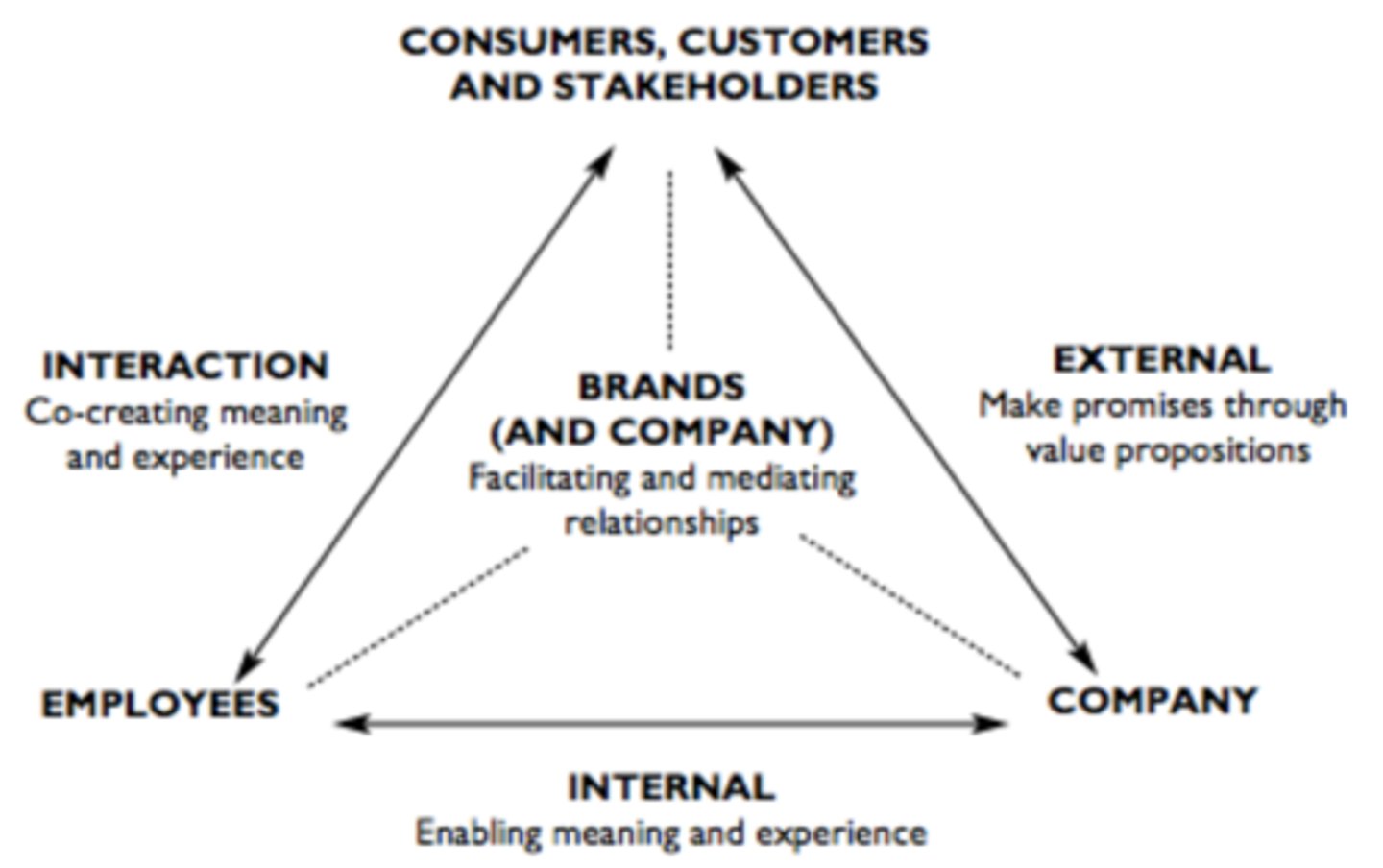
Factors of a Services Brand
1. Consumers, customers & stakeholders
2. Company
3. Employees