300 Things Every APUSH Student Should Know by Exam Day
1/299
There's no tags or description
Looks like no tags are added yet.
Name | Mastery | Learn | Test | Matching | Spaced | Call with Kai |
|---|
No analytics yet
Send a link to your students to track their progress
300 Terms
Columbus
Italian navigator who "discovered" the New World in the service of Spain while looking for a route to China (1451-1506)
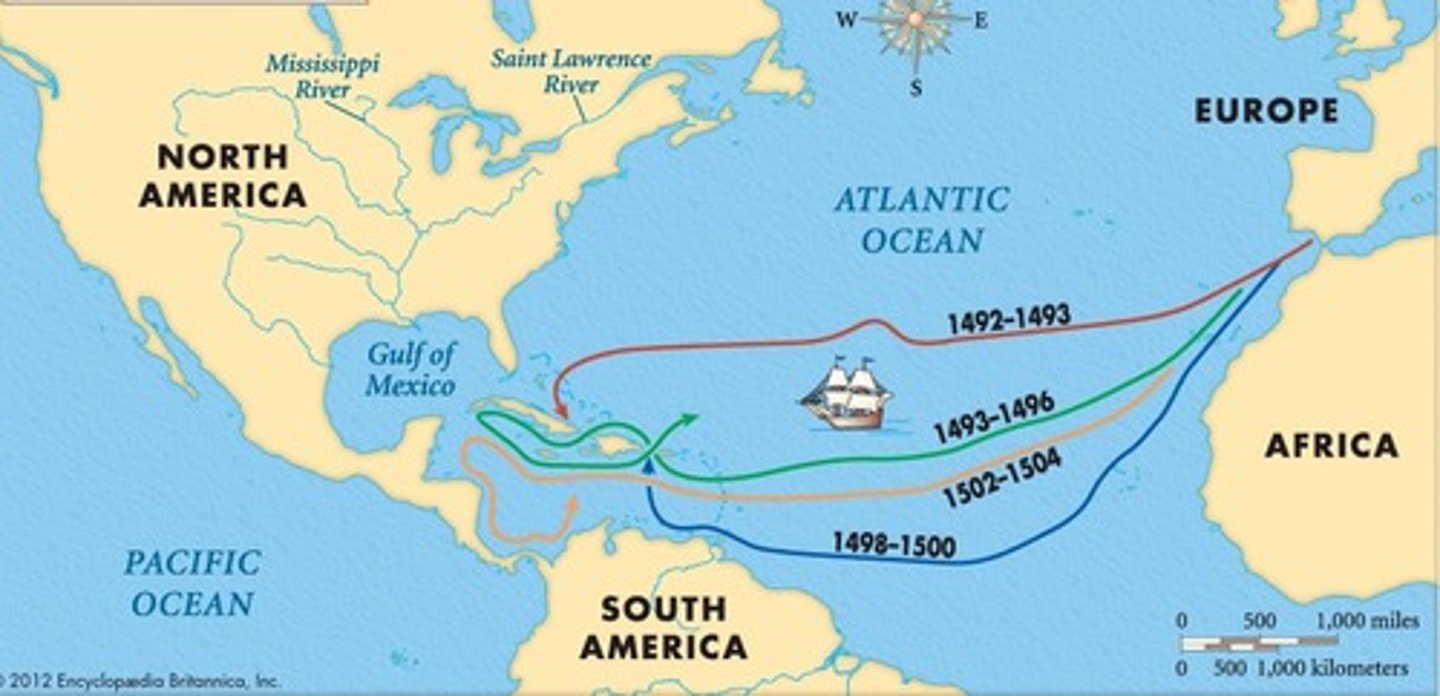
Colombian Exchange
the transfer of plants, animals, and diseases between the Americas and Europe, Asia, and Africa
Bartolomeo de Las Casas
16th Century Spanish Historian, Dominican Friar, "Protector of the Indians;" opposed atrocities by colonizers on Indigenous people

Jamestown
1607, first permanent English settlement, Virginia, John Smith, tobacco, cash crop, starving time

House of Burgesses
1619 - The Virginia House of Burgesses formed, the first legislative body in colonial America. Later other colonies would adopt houses of burgesses.

Mayflower Compact
1620 - The first agreement for self-government in America. It was signed by all men on the Mayflower and set up a government for the Plymouth colony.

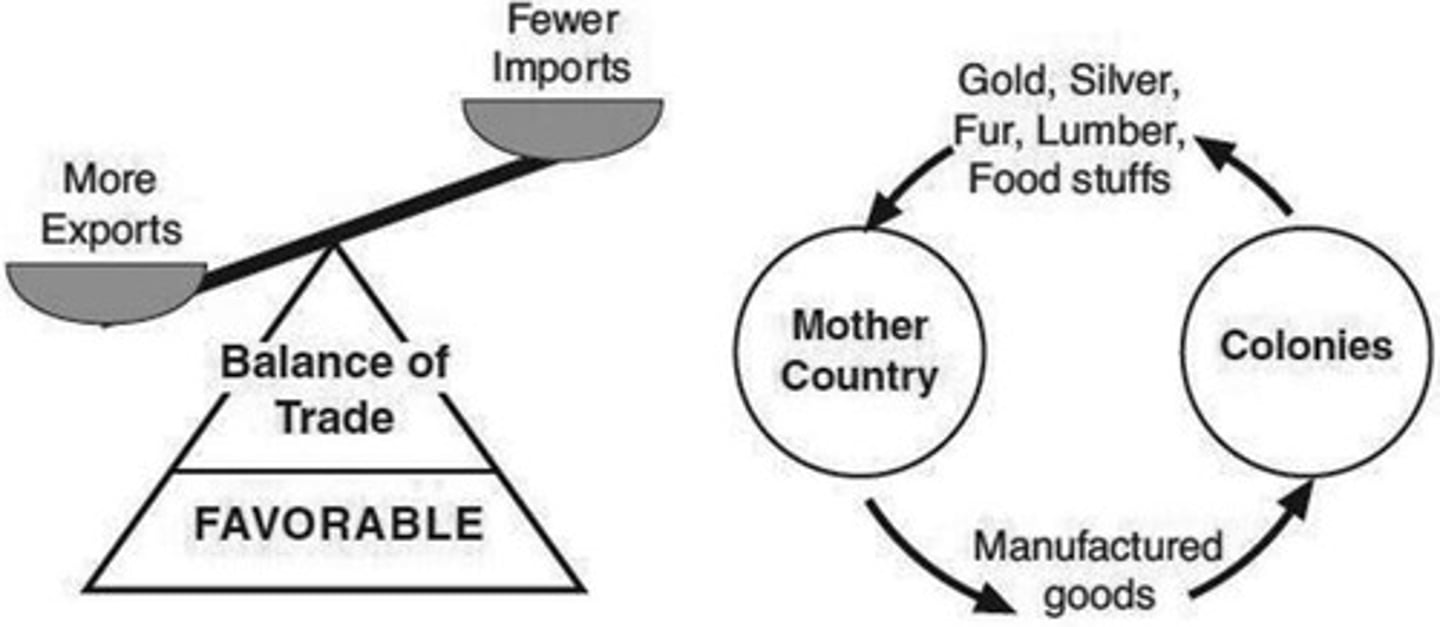
Mercantlism
an economic policy under which nations sought to increase their wealth and power by obtaining large amounts of gold and silver and by selling more goods than they bought.
Puritans
A religious group who wanted to purify the Church of England. They came to America for religious freedom and settled Massachusetts Bay in the 1630s and 1640s.

Roger William
Puritan dissenter who advocated of religious freedom, the separation of church & state, & fair dealings with Native Americans; convicted of sedition & heresy & banished from the colony; founded Providence Plantation (RI) in 1636.

Salem Witch Trials
Several accusations of witchcraft led to sensational trials in Salem, Massachusetts at which Cotton Mather presided as the chief judge. 18 people were hanged as witches. Afterwards, most of the people involved admitted that the trials and executions had been a terrible mistake.

Pueblo Revolt
Native American revolt against the Spanish in late 17th century; expelled the Spanish for over 10 years; Spain began to take an accommodating approach to Natives after the revolt

William Penn
An English Quaker, founded Pennsylvania in 1682. He launched the colony as a "holy experiment" based on religious tolerance.

Salutary Neglect
British colonial policy during the reigns of George I and George II. Relaxed supervision of internal colonial affairs by royal bureacrats contributed significantly to the rise of American self government

Cecil Calvert
English Catholic Aristocrat, founded Maryland to reap financial profits and to create a refuge for his fellow Catholics.
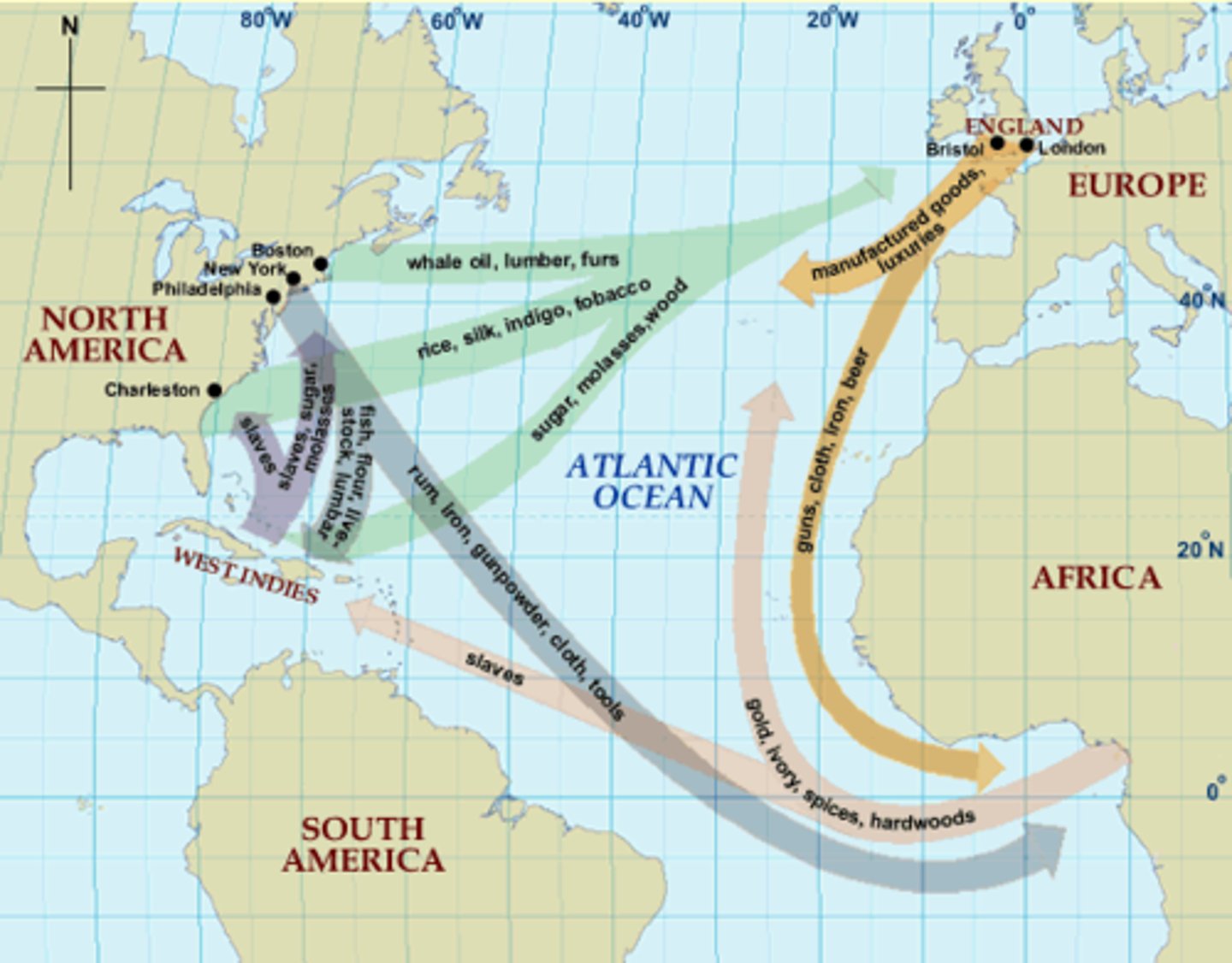
Triangular Trade
A three way system of trade during 1600-1800s Africa sent slaves to America, America sent Raw Materials to Europe, and Europe sent Guns and Rum to Africa
Jonathan Edwards
Preacher during the First Great Awakening; "Sinners in the hands of angry god"

James Oglethorpe
English leader who founded the colony of Georgia as a place where debtors from England could begin new lives

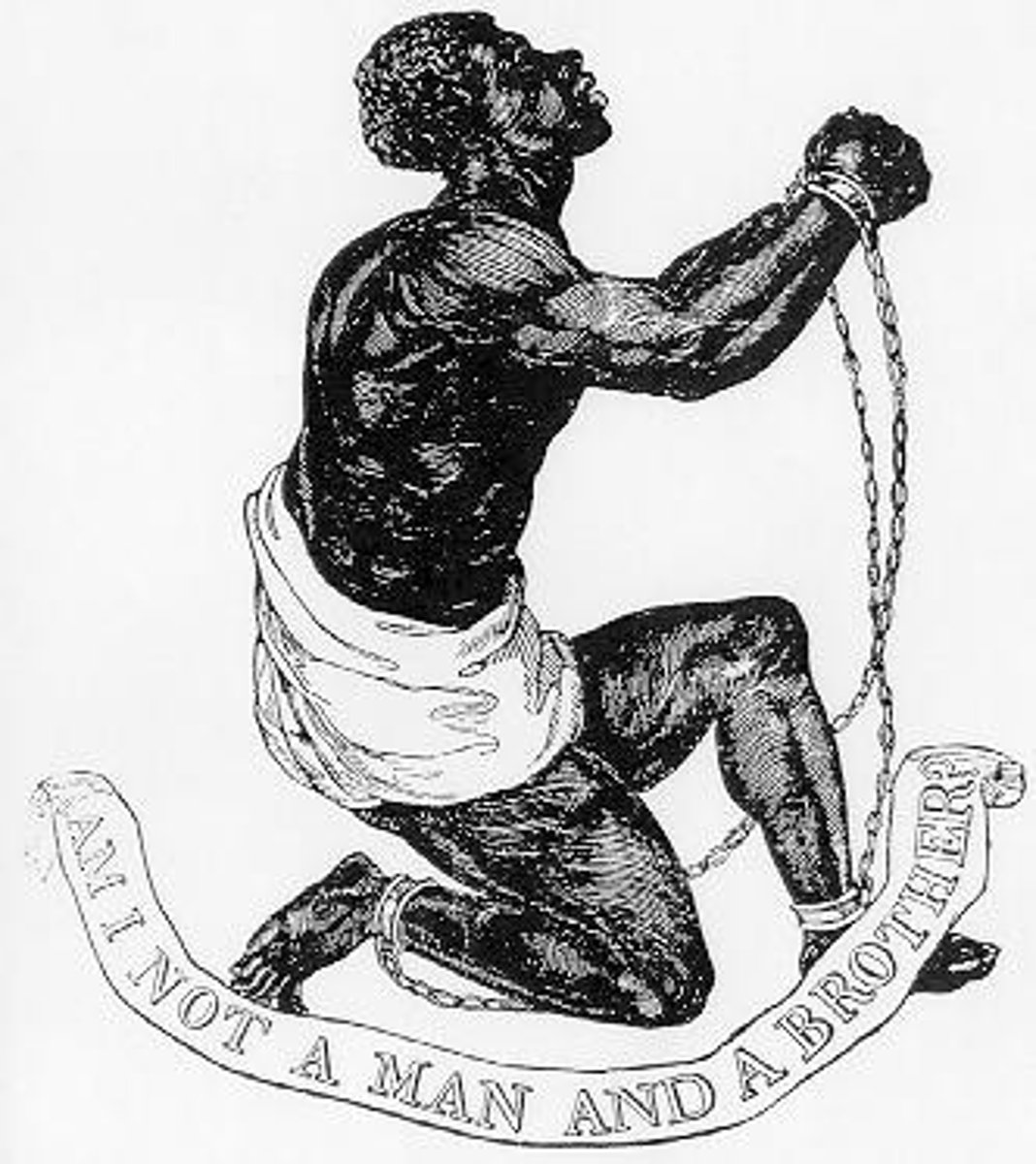
Slave Trade
European trade agreement with Africa dealing with slaves brought from Africa. Integral part of Triangle Trade between the Americas, Africa, and Europe.
1490s - 1790s. Most slaves came from West Africa. By 1790 all states except South Carolina and Georgia outlawed slave trade. Most slaves were captured by other Africans and sold to dealers on the coast.
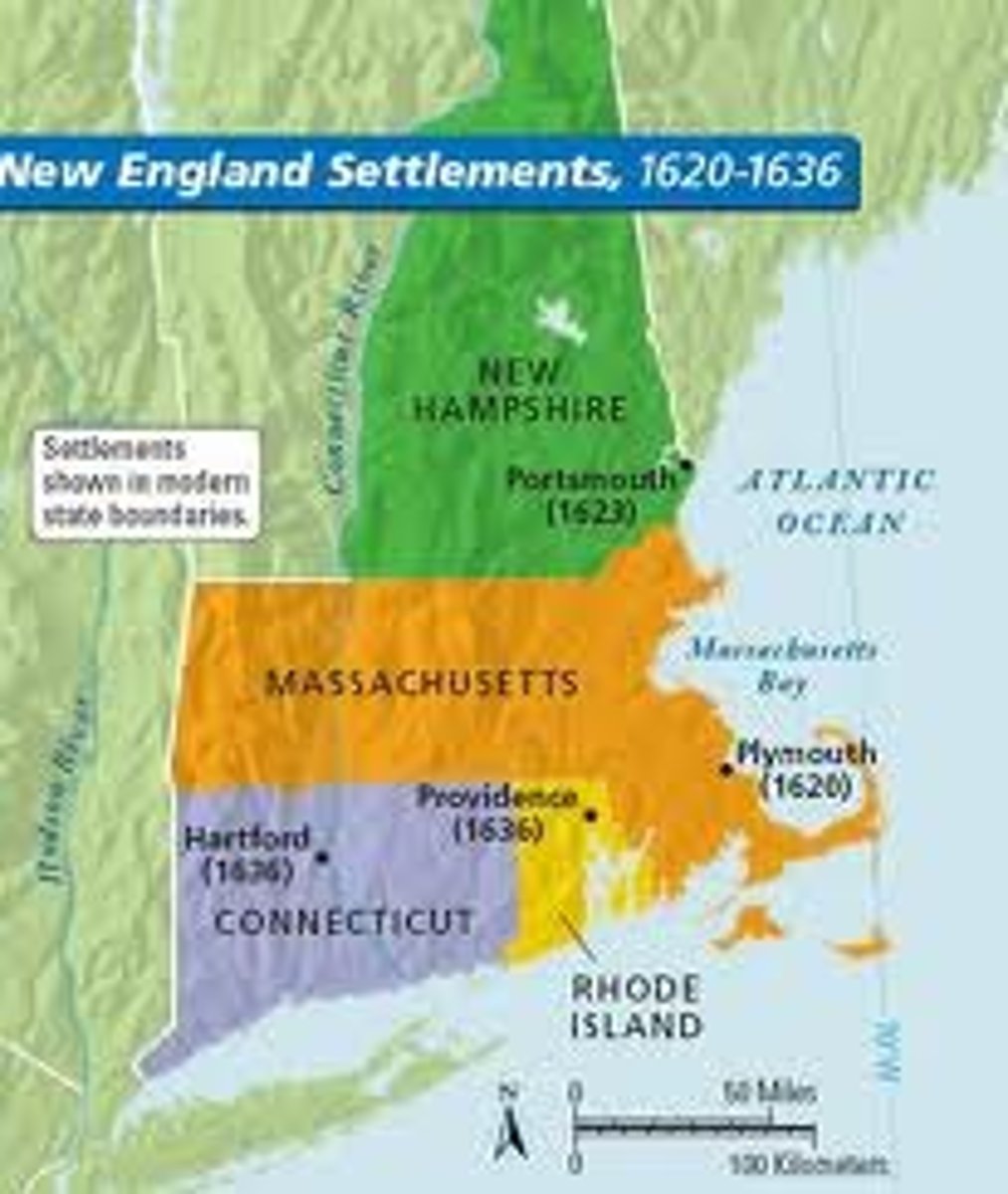
Northern Colonies ("Commercial North")
Group of American colonies made up of Connecticut, Massachusetts, Rhode Island, and New Hampshire which were characterized by having little slavery and few plantations, strong religious ties (Puritan), and fishing, lumber, shipbuilding, and furs to support the economy
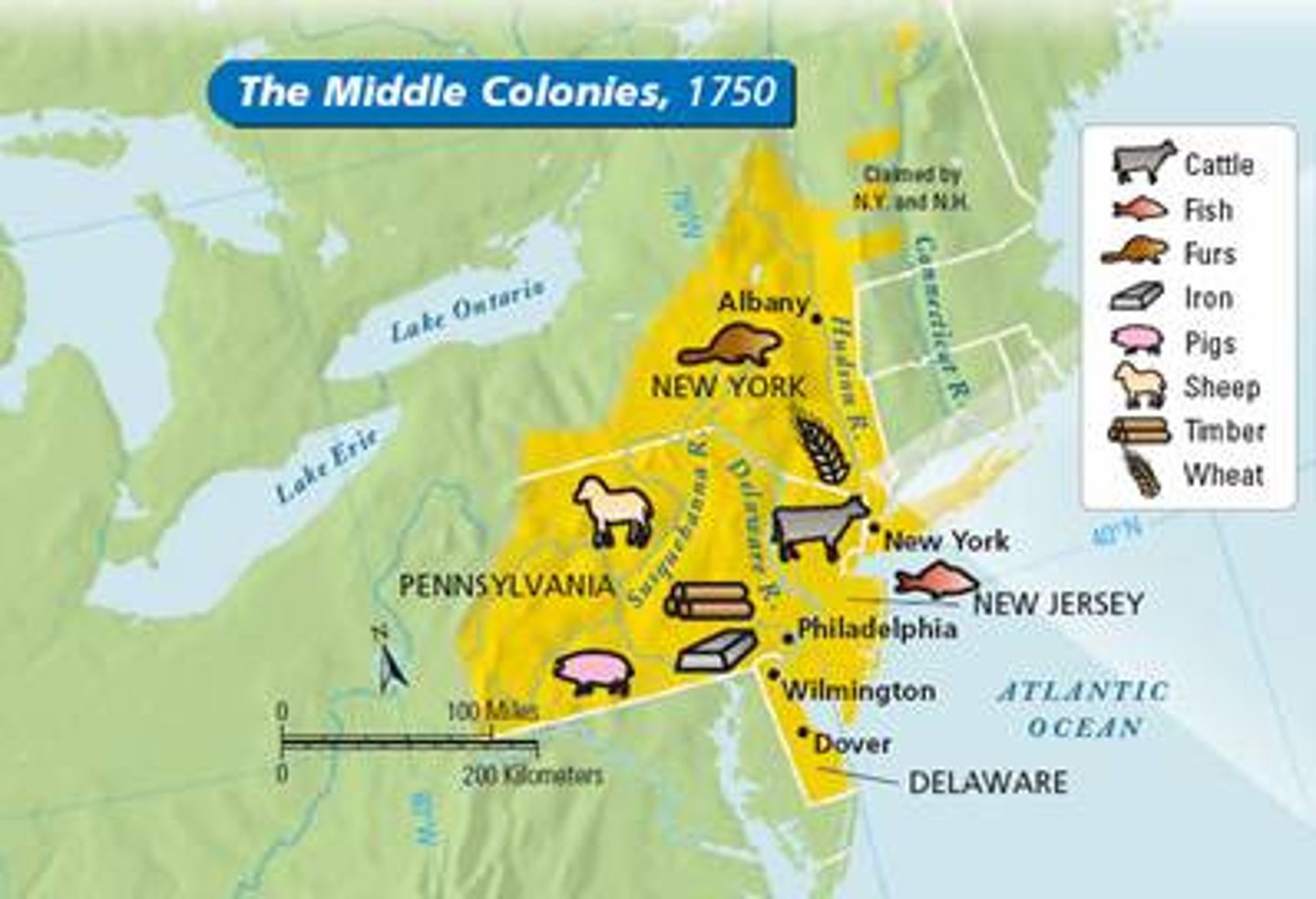
Middle Colonies ("Religious Middle")
Group of American colonies made up of Pennsylvania, Delaware, New York, and New Jersey. These were characterized by fertile river valleys, being the "bread basket" of the colonies, diversity, and harbors such as Philadelphia and New York City. The main goods here were lumber and fur
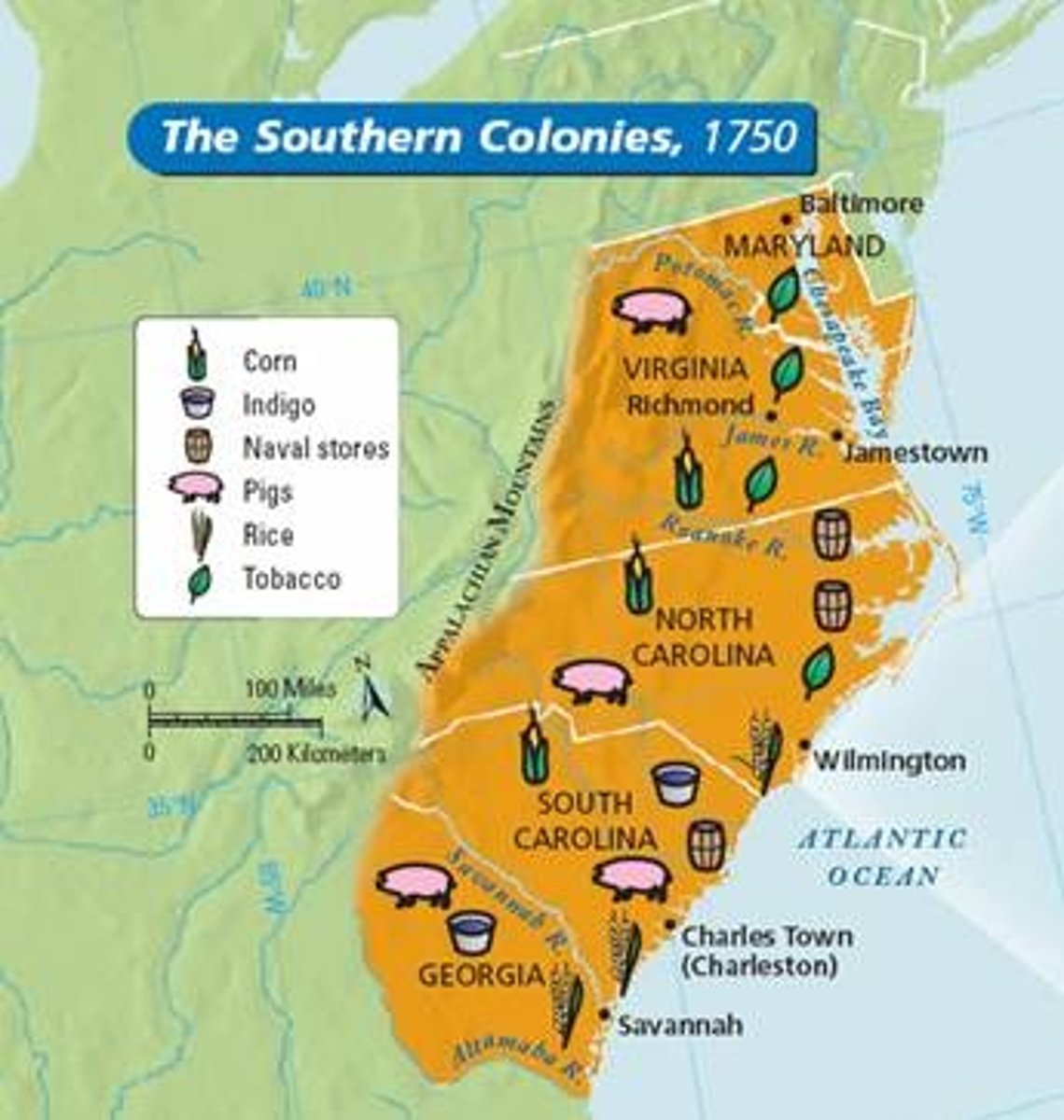
Southern Colonies ("Agricultural South")
Maryland, Virginia, North Carolina, South Carolina, and Georgia; very rural with large farms "plantations" with use of slave labor; tobacco, cotton, indigo, and rice were grown with tobacco being the largest cash crop
French and Indian War
(1754-1763) War fought in the colonies between the English and the French for possession of the Ohio Valley area. The English won.
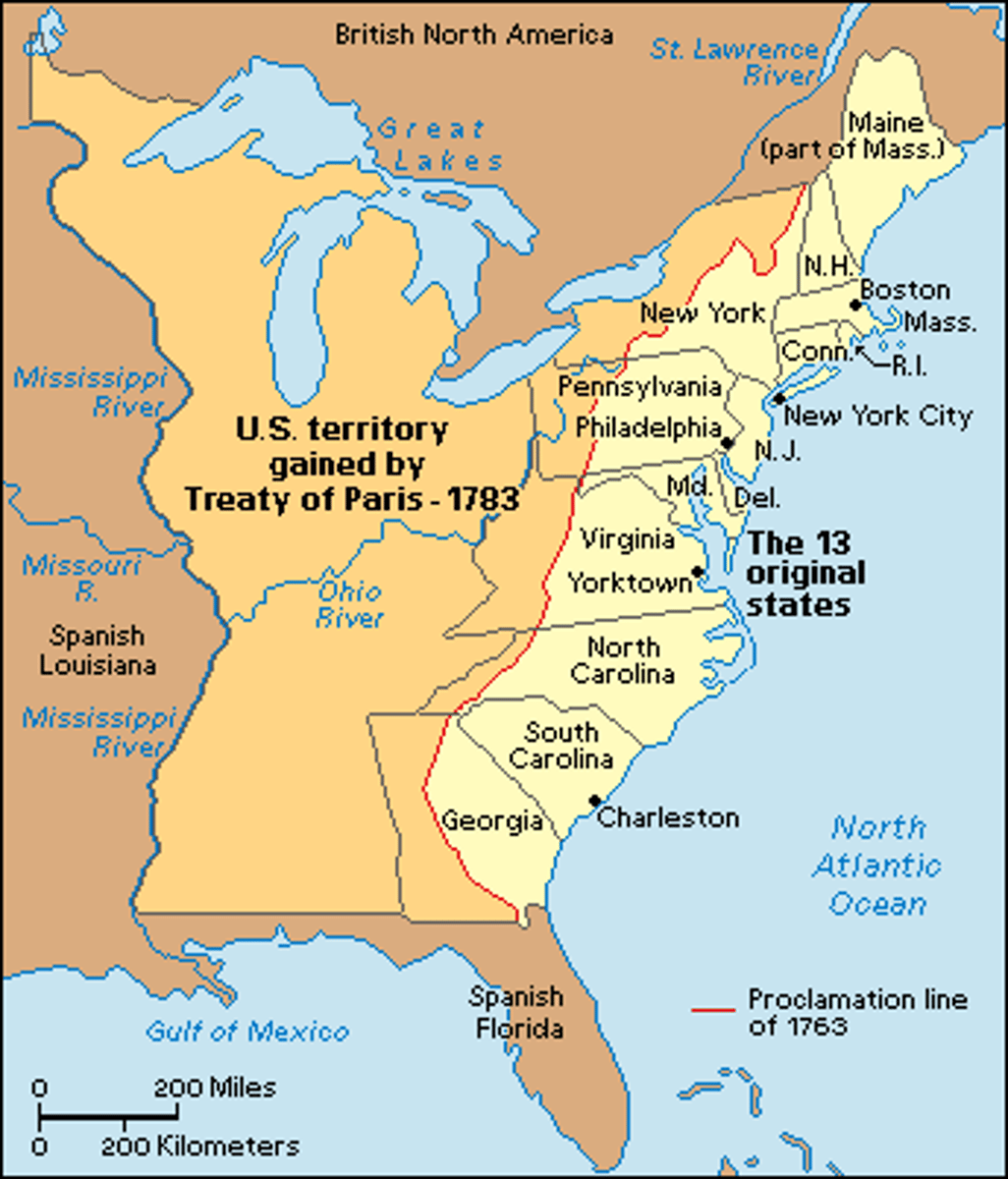
Proclamation of 1763
A proclamation from the British government which forbade British colonists from settling west of the Appalacian Mountains, and which required any settlers already living west of the mountains to move back east.
Stamp Act, 1765-66
an act of the British Parliament in 1756 that exacted revenue from the American colonies by imposing a stamp duty on newspapers and legal and commercial documents.

Declaratory Act
1766. Parliament repealed the Stamp Act of 1765. Reaffirmed Parliaments unqualified sovereignty over the North American colonies.

Townshend Acts
A tax that the British Parliament passed in 1767 that was placed on leads, glass, paint and tea

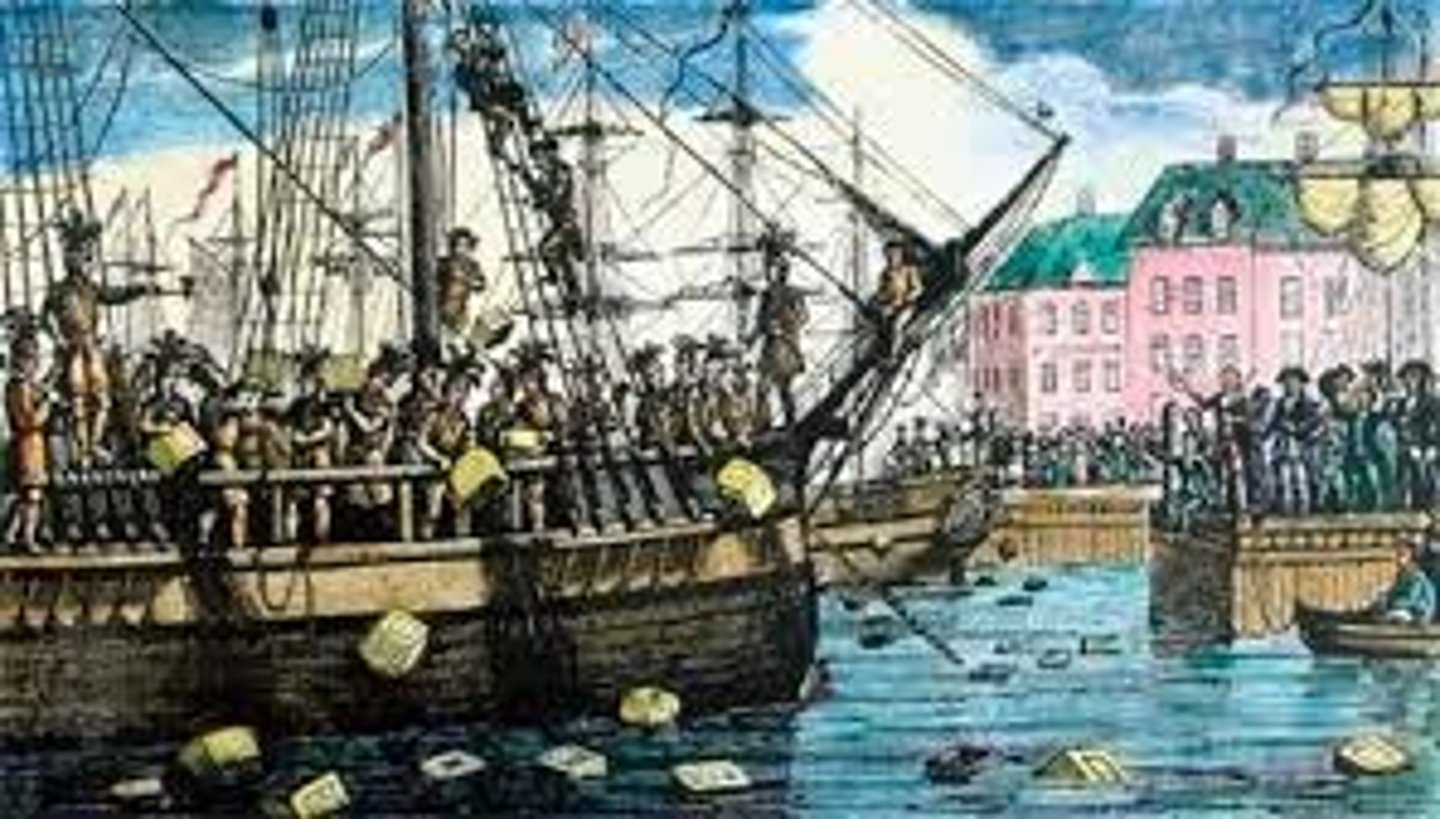
Boston Tea Party
Demonstration (1773) by citizens of Boston who (disguised as Indians) raided three British ships in Boston harbor and dumped hundreds of chests of tea into the harbor

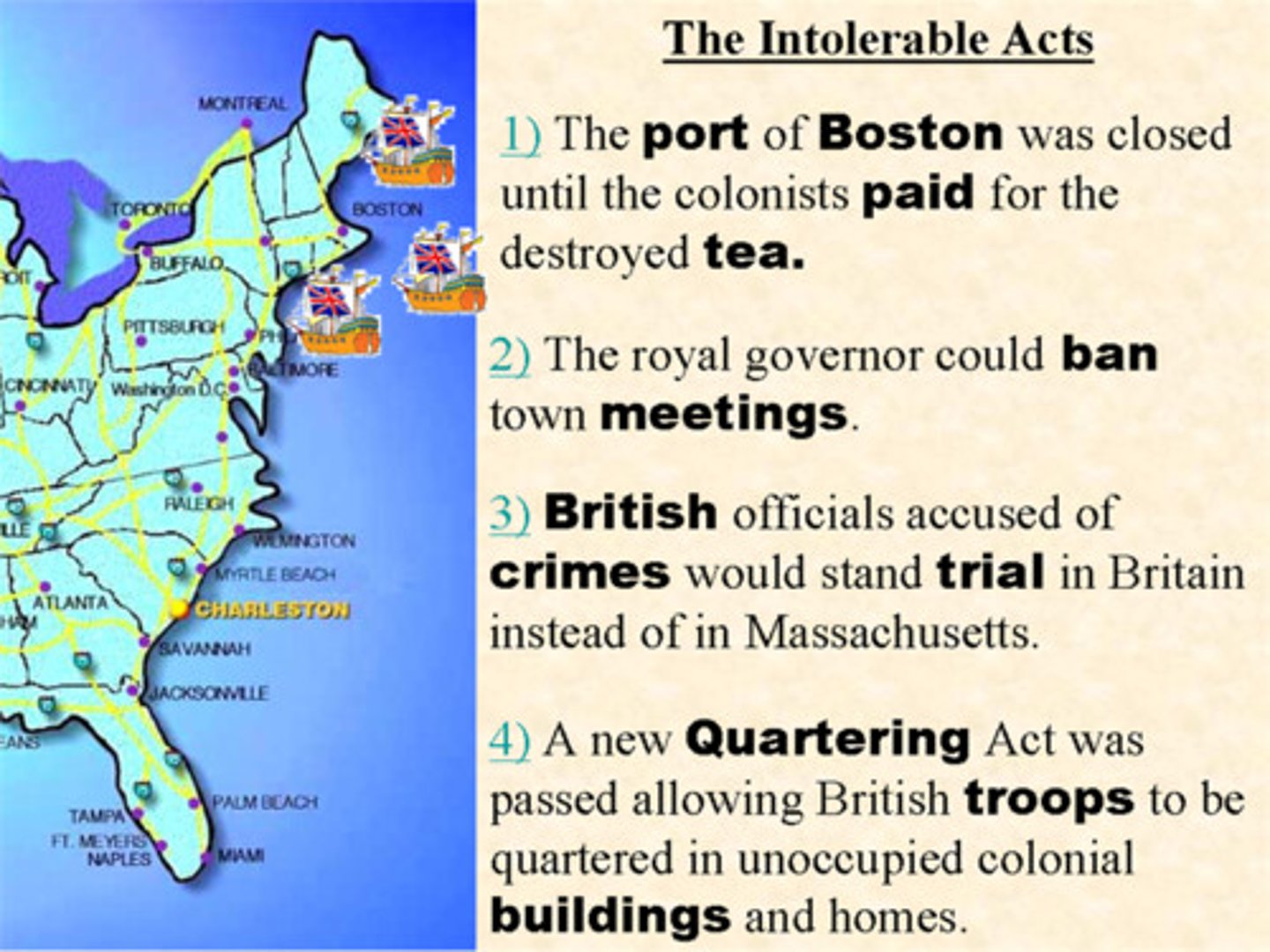
Intolerable Acts
in response to Boston Tea Party, 4 acts passed in 1774, Port of Boston closed, reduced power of assemblies in colonies, permitted royal officers to be tried elsewhere, provided for quartering of troop's in barns and empty houses
First Continental Congress
1774; response to Intolerable Acts; 55 men from 12 colonies meet on Philadelphia; called for complete halt in trade with Britain; important step towards independence.

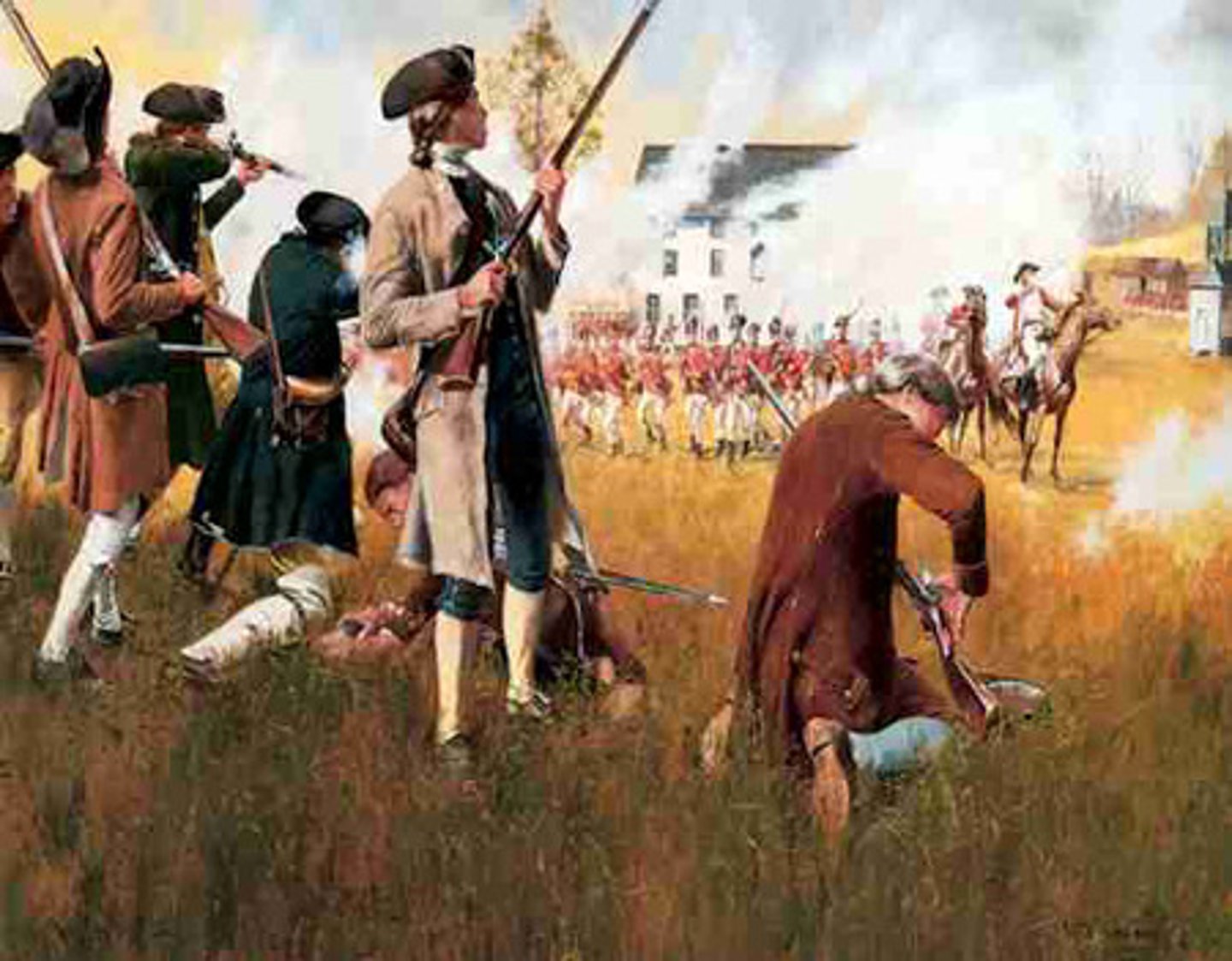
Lexington and Concord
"Shot heard round the world" (1775), conflicts between Massachusetts colonists and British soldiers that started the Revolutionary War (these are the first Battles of the Revolutionary War)

Common Sense
A pamphlet written by Thomas Paine in 1776 that criticized monarchies and convinced many American colonists of the need to break away from Britain

Second Continental Congress
It met in 1776 and drafted and signed the Declaration of Independence, which justified the Revolutionary War and declared that the colonies should be independent of Britain.
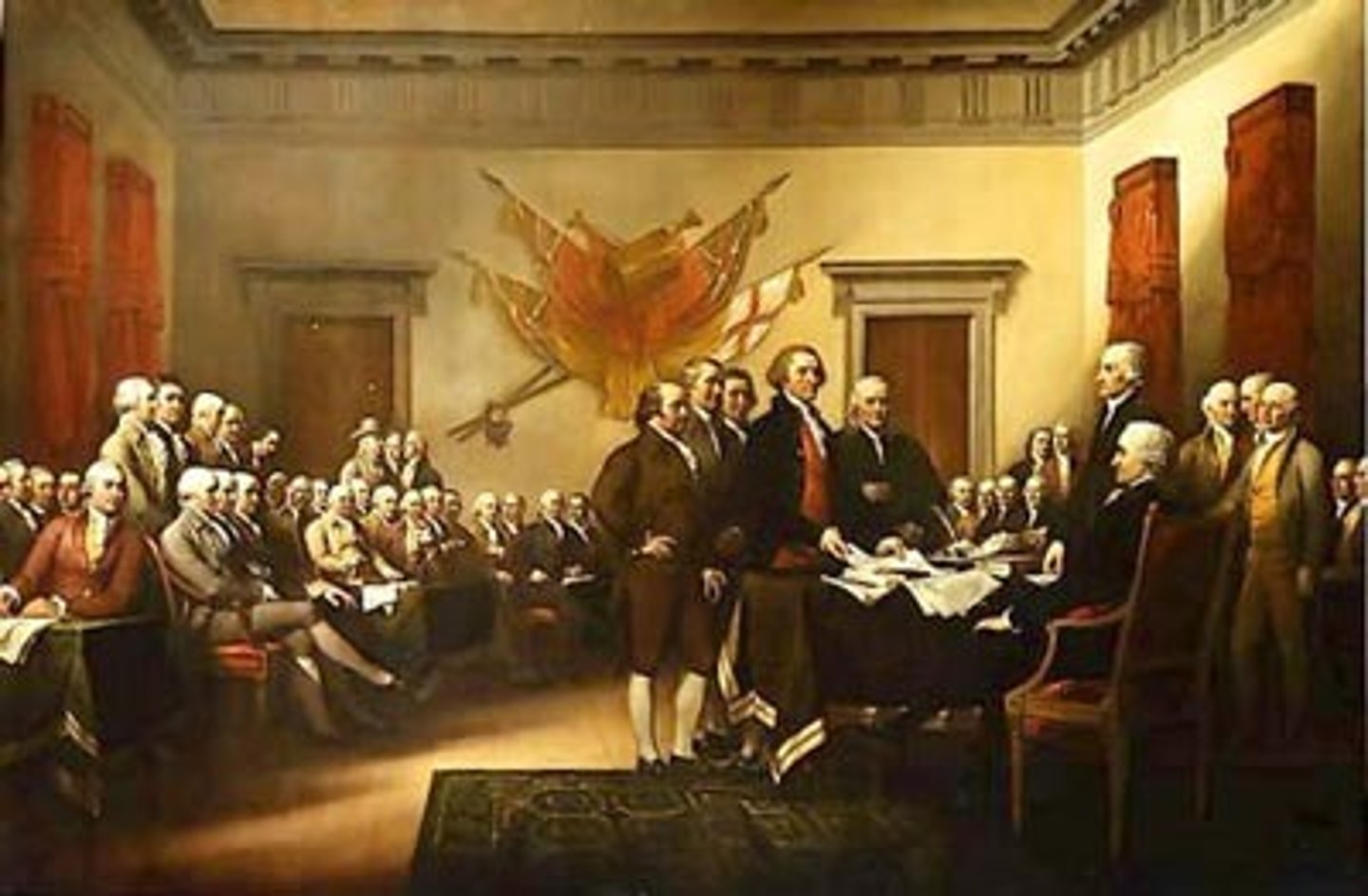

Declaration of Independence
Drafted in 1776 by T. Jefferson declaring America's separation from Great Britain (3 parts-New theory of government, reasons for separation, formal declaration of war and independence)

Treaty of Alliance
1778- In the event France and England went to war French agreed to refuse truce or peace until independence of the US shall be assured by treaty or treaties that terminate the war

Articles of Confederation
document that created the first central government forthe US; it was replaced by the constitution. weakness- placed limits. strenghts- national court system
1st Constitution of the U.S. 1781-1788 (weaknesses-no executive, no judicial, no power to tax, no power to regulate trade)

Peace of Paris
The Peace of Paris (1783) was the set of treaties which ended the American Revolutionary War.
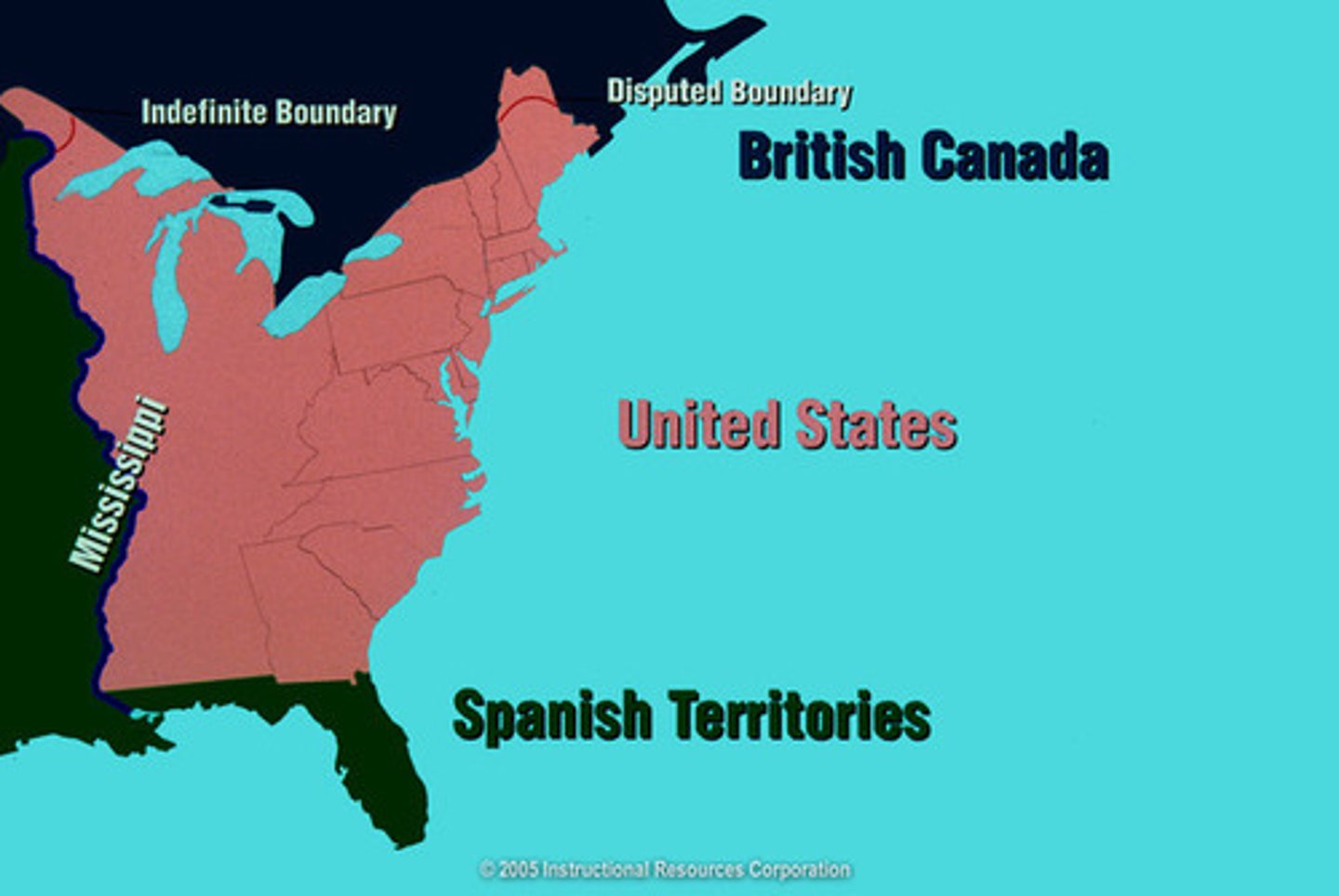
Northwest Ordinance
1787 law that set up a government for the Northwest Territory and served as a model for other new territories and as a plan for admitting new states to the Union
Shay's Rebellion
Rebellion led by Daniel Shays of farmers in western Massachusetts in 1786-1787, protesting mortgage foreclosures. It highlighted the need for a strong national government just as the call for the Constitutional Convention went out.
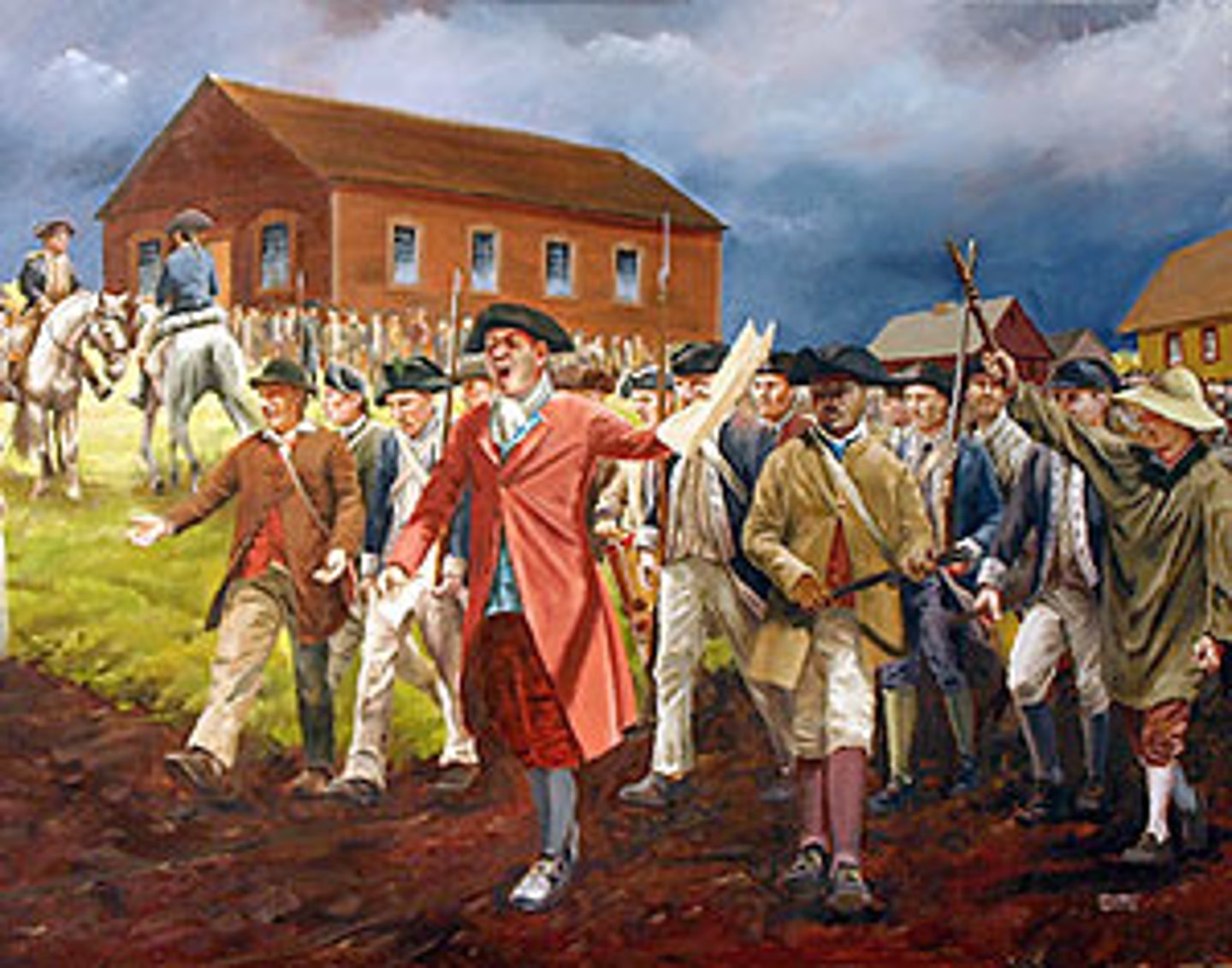

Constitutional Convention
Meeting in 1787 of the elected representatives of the thirteen original states to write the Constitution of the United States.

Constitutional Compromises
The Three-fifths Compromise; The Great Compromise; Commerce Compromise; Slave Trade Compromise; Election of the President
The Federalist Papers
This collection of essays by John Jay, Alexander Hamilton, and James Madison, explained the importance of a strong central government. It was published to convince New York to ratify the Constitution.

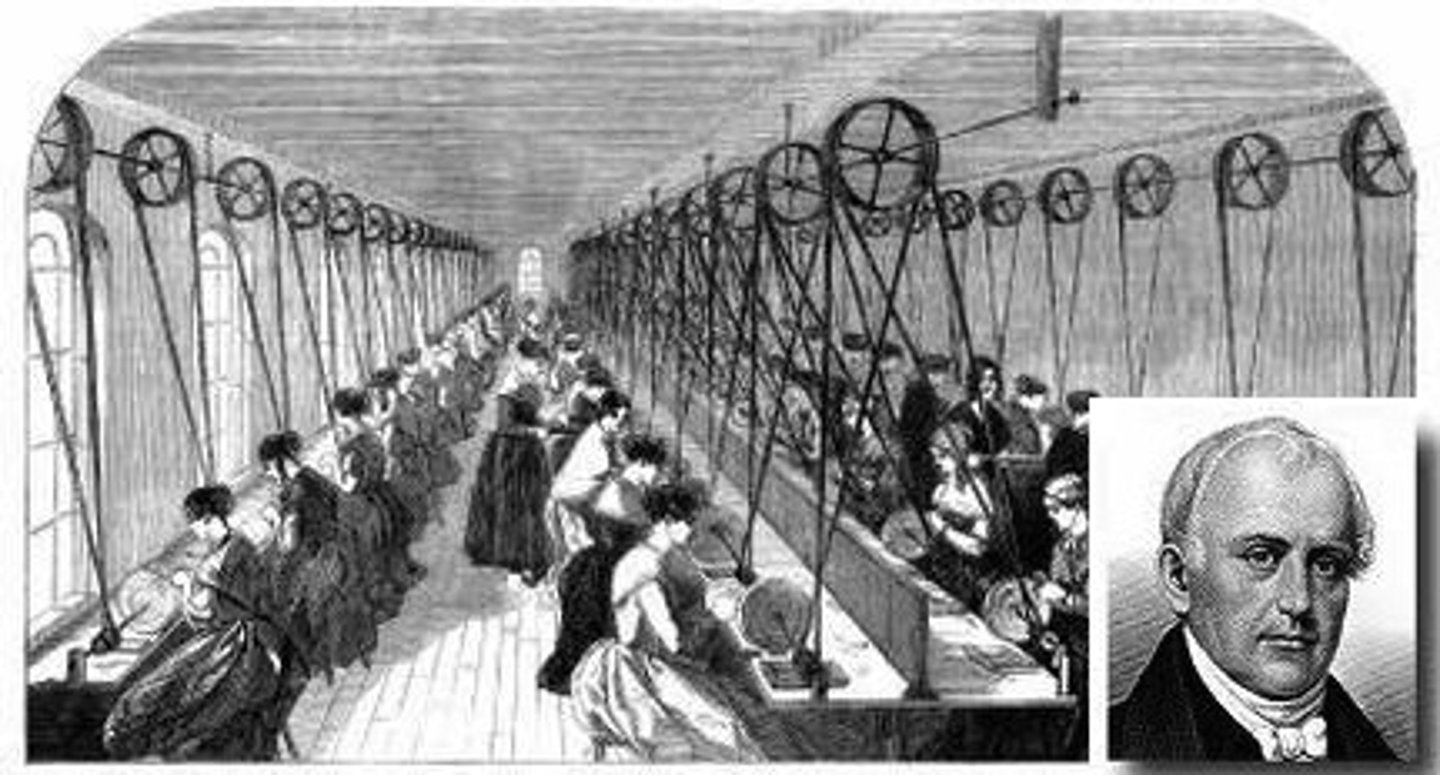
Samuel Slater
He was a British mechanic that moved to America and in 1791 invented the first American machine for spinning cotton. He is known as "the Father of the Factory System" and he started the idea of child labor in America's factories.
Alexander Hamilton
1789-1795; First Secretary of the Treasury. He advocated creation of a national bank, assumption of state debts by the federal government, and a tariff system to pay off the national debt.

Bill of Rights
Although the Anti-Federalists failed to block the ratification of the Constitution, they did ensure that the Bill of Rights would be created to protect individuals from government interference and possible tyranny. The Bill of Rights, drafted by a group led by James Madison, consisted of the first ten amendments to the Constitution, which guaranteed the civil rights of American citizens.

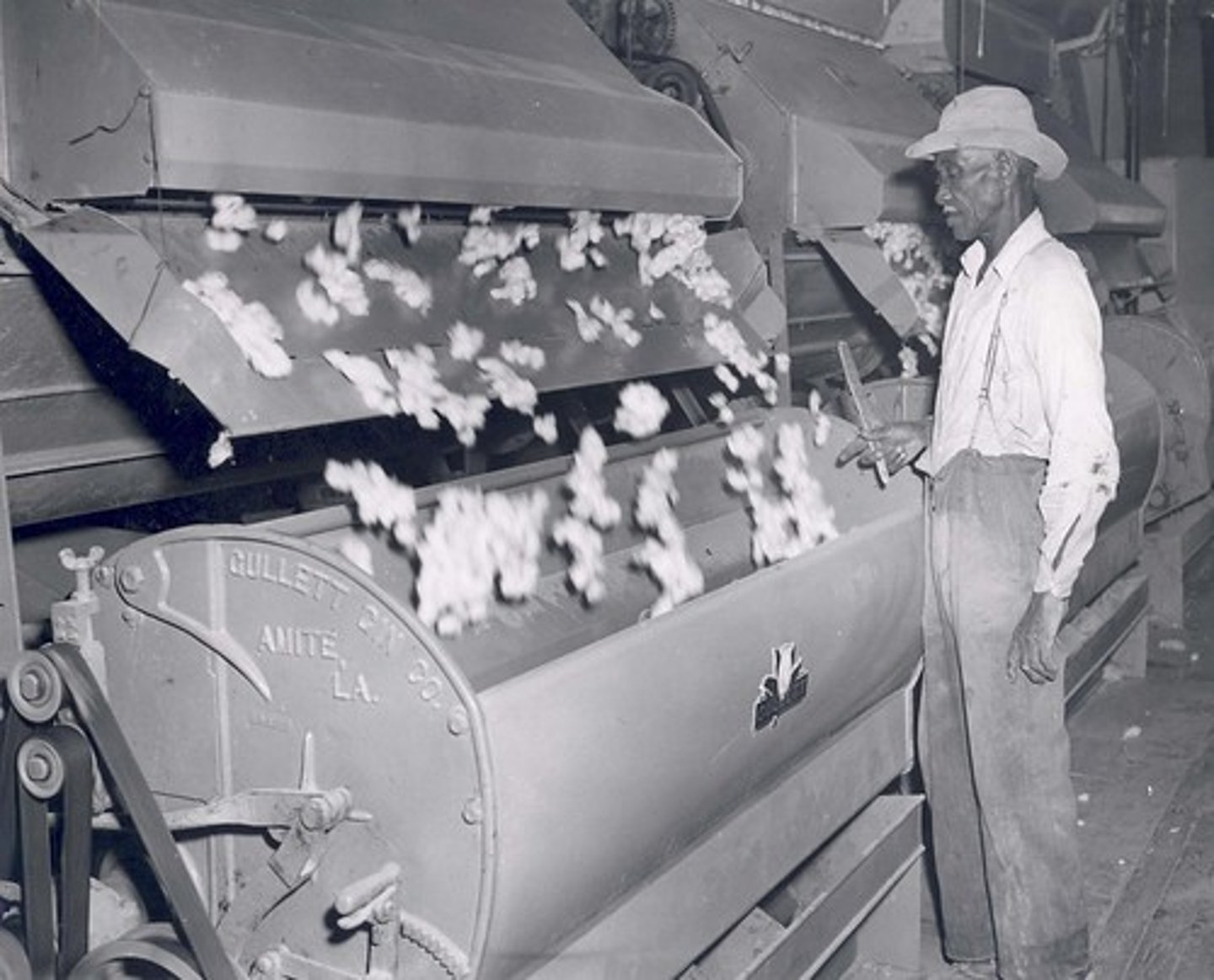
Cotton Gin
Invented by Eli Whitney in 1793. It removed seeds from cotton fibers. Now cotton could be processed quickly and cheaply. Results: more cotton is grown and more slaves are needed for more acres of cotton fields

Proclamation of Neutrality
George Washington's statement to remain neutral in the French Revolution, resulting in both British and French harassment

Whiskey Rebellion, 1784
A protest caused by tax on liquor; it tested the will of the government; Washington's quick response showed the government's strength and mercy (led an army to put down the rebellion)

Hamiltonians
thought rich educated people should lead nation; wanted strong federal government; wanted to encourage manufacturing and trade; supported loose interpretation of constitution

Jeffersonians
Democratic Republicans; small government, low taxes; wiser frugal government that would keep men from hurting each other but allow them to control their own lives for the most part and keep taxes low

Bank of the United States
Hamilton's plan to solve Revolutionary debt, Assumption highly controversial, pushed his plan through Congress, based on loose interpretation of Constitution
Washington's Farewell Address
Warned Americans not to get involved in European affairs, not to make permanent alliances, not to form political parties and to avoid sectionalism.

XYZ Affair
A 1797 French attempt to bribe the United States by demanding money before discussing French seizure of neutral American ships

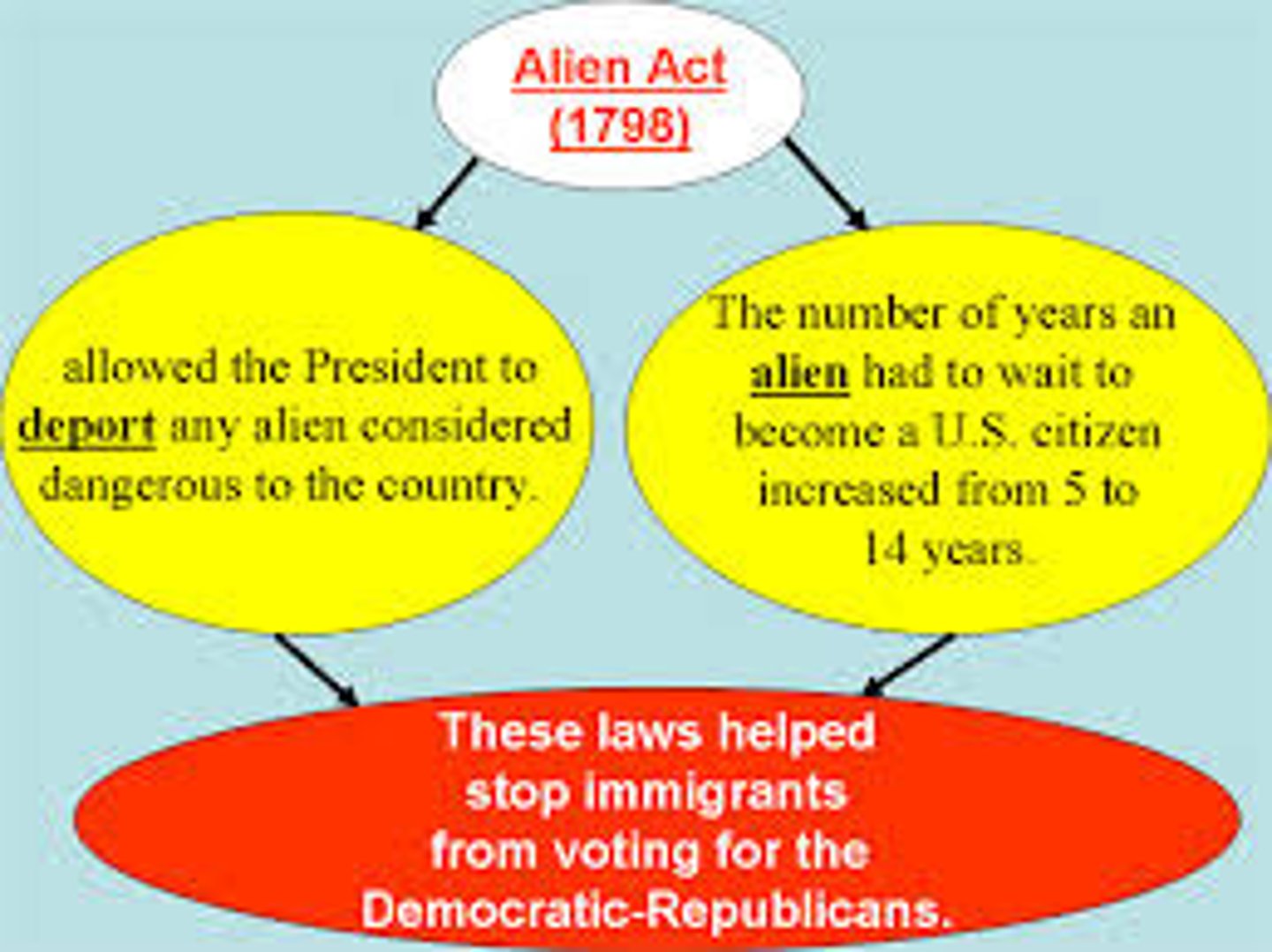
Alien and Sedition Acts
A series of laws that sought to restrict the activities of people who opposed Federalist policies (1798)
Kentucky and Virginia Resolutions
Written anonymously by Jefferson and Madison in response to the Alien and Sedition Acts, they declared that states could nullify federal laws that the states considered unconstitutional.

Election of 1800
Jefferson and Burr each received 73 votes in the Electoral College, so the House of Representatives had to decide the outcome. The House chose Jefferson as President and Burr as Vice President.

Marbury v. Madison
(1803) Marbury was a midnight appointee of the Adams administration and sued Madison for commission. Chief Justice Marshall said the law that gave the courts the power to rule over this issue was unconstitutional. established judicial review

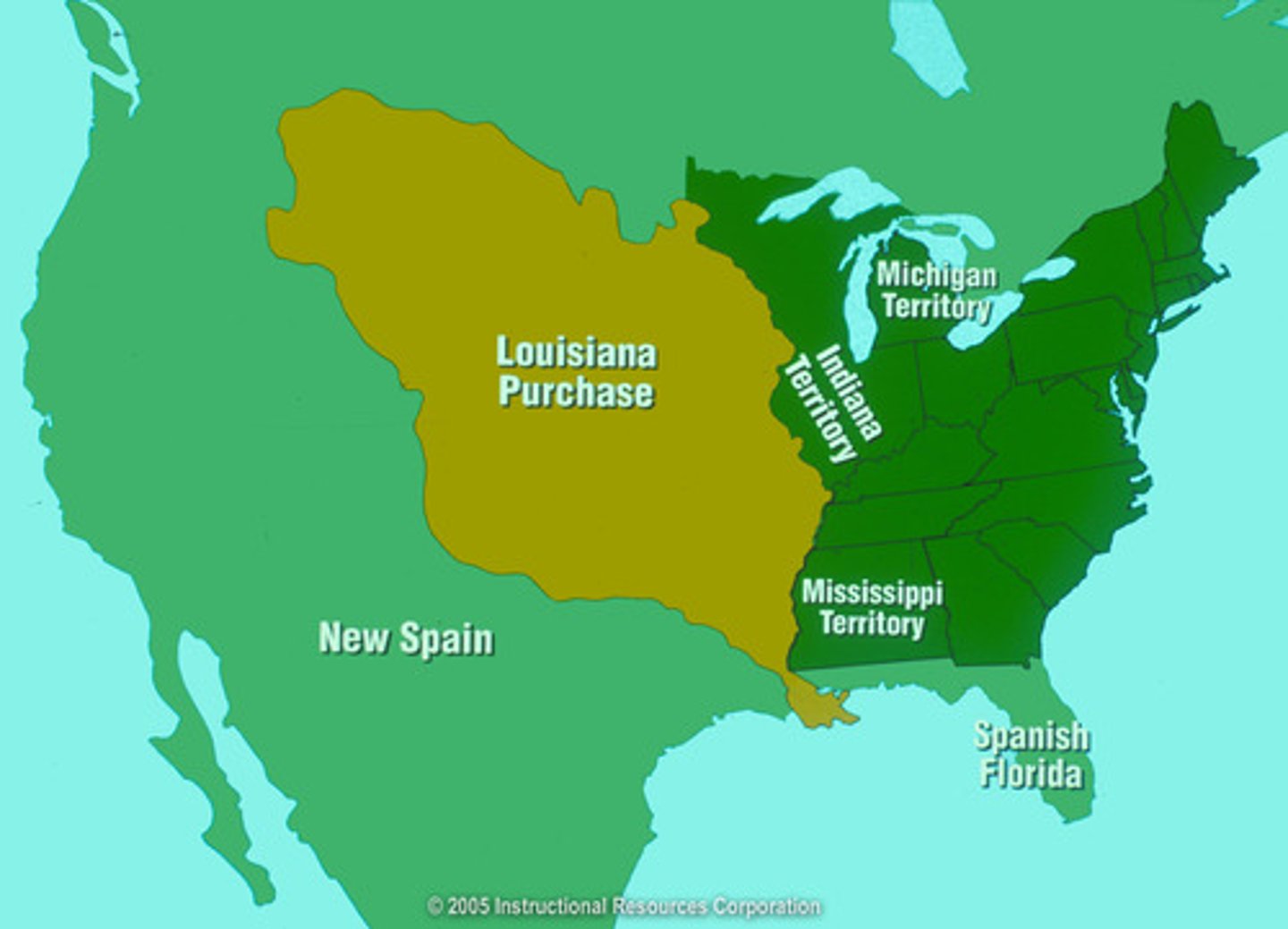
Louisiana Purchase
1803 purchase of the Louisiana territory from France. Made by Jefferson, this doubled the size of the US.
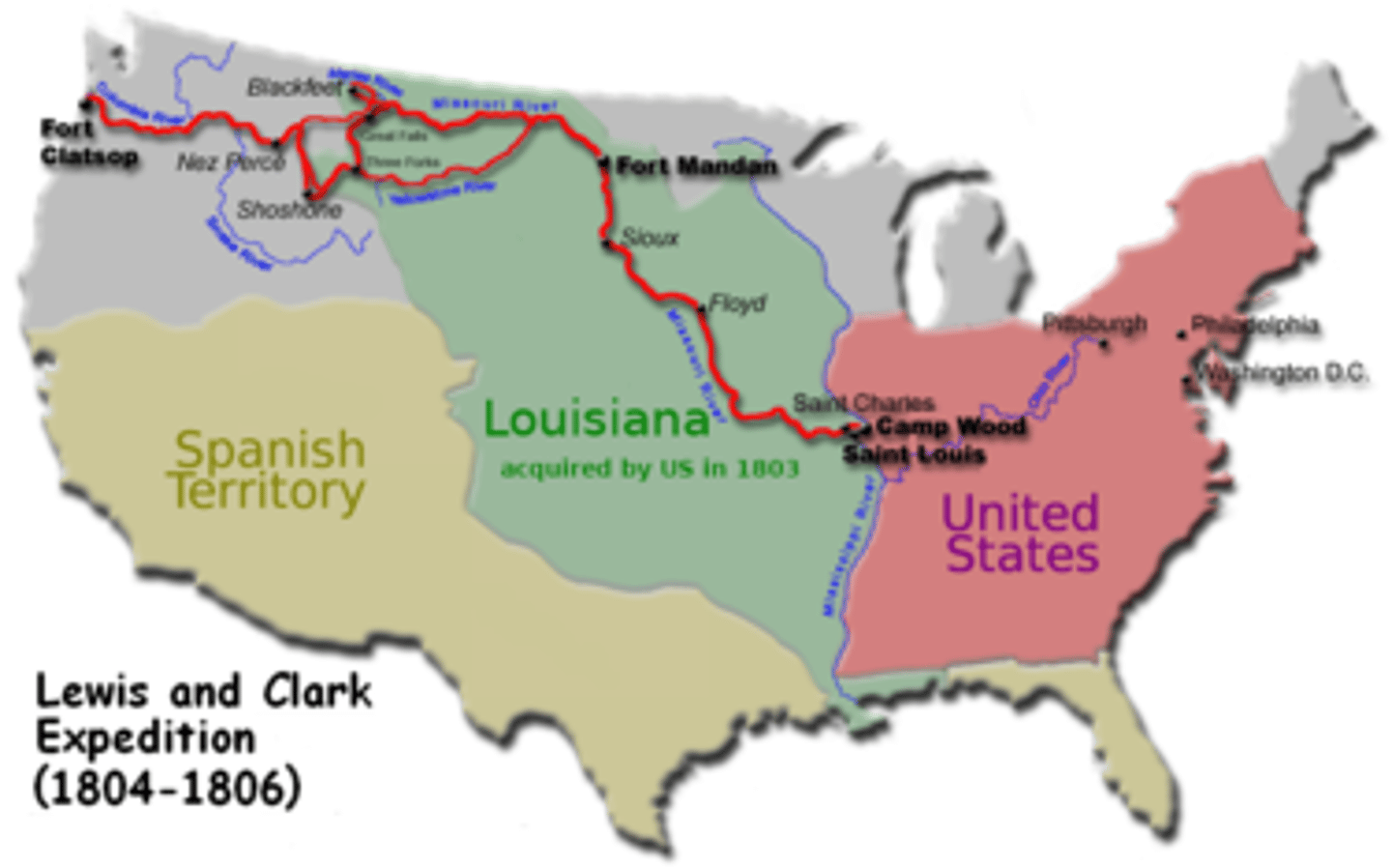
Lewis and Clark Expedition
Jefferson sent them out to explore the newly acquired Louisiana Territory; the explored as far west as the Pacific Ocean
Aaron Burr
served as the 3rd Vice President of the United States. Member of the Republicans and President of the Senate during his Vice Presidency. He was defamed by the press, often by writings of Hamilton. Challenged Hamilton to a duel in 1804 and killed him.

Embargo Act of 1807
NO TRADING. 1807, Jefferson prohibited American ships from leaving the US for any foreign port anywhere in the world. the law was widely evaded and effects created depression in the US expecially in ports and merchants/shipowners

War of 1812
A war (1812-1814) between the United States and England which was trying to interfere with American trade with France.
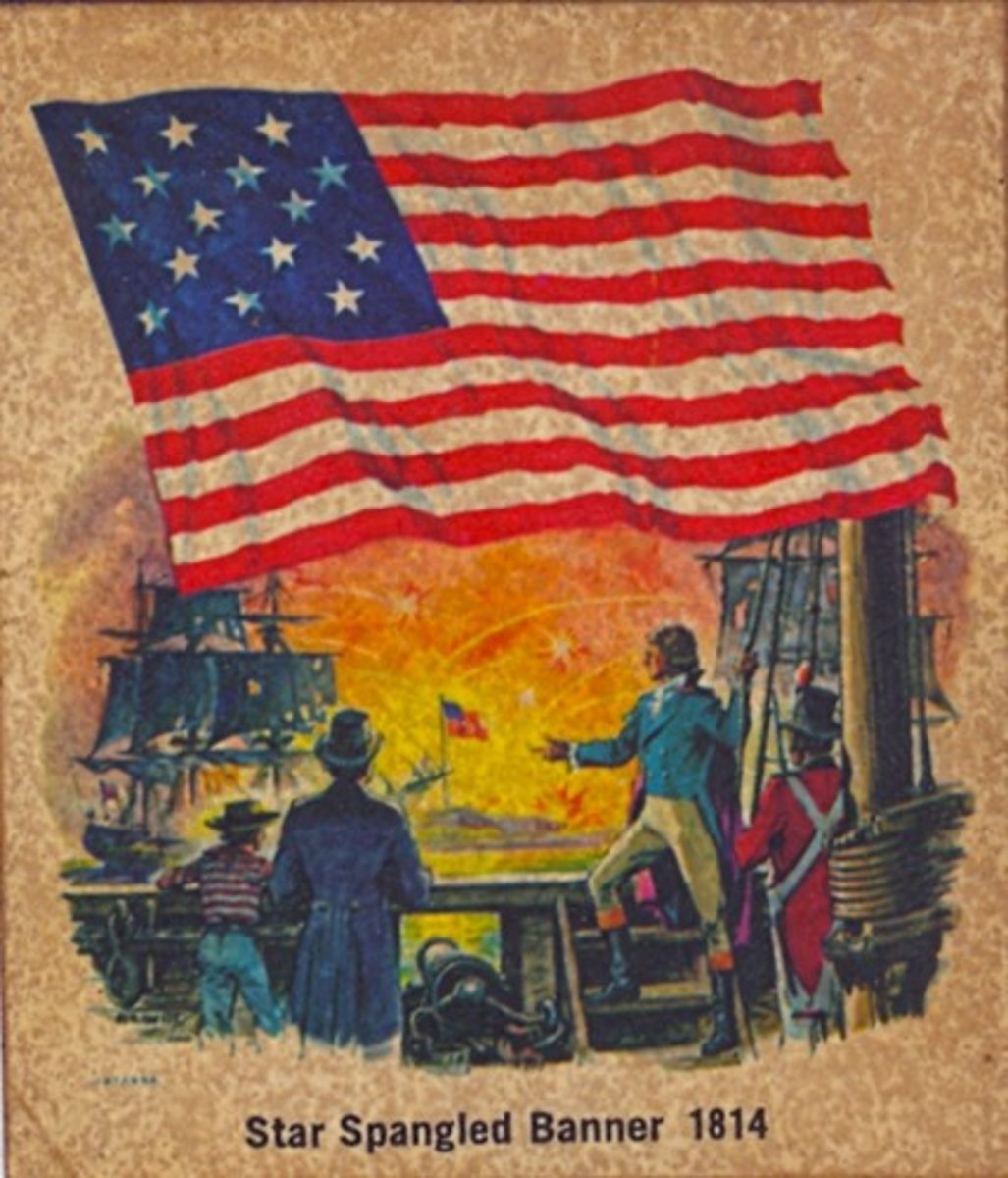

Francis Scott Key
A washington lawyer who watched the all-night battle at Fort McHenry during the War of 1812 and showed his pride by writing what became the national anthem ("Star Spangled Banner")

Hartford Convention, 1814
Meeting of Federalists near the end of the War of 1812 in which the party listed it's complaints against the ruling Republican Party. These actions were largley viewed as traitorous to the country and lost the Federalist much influence

Treaty of Ghent
(December 24, 1814) Ended the War of 1812 and restored the status quo. For the most part, territory captured in the war was returned to the original owner. It also set up a commission to determine the disputed Canada/U.S. border.(

Battle of New Orleans
Jackson led a battle that occurred when British troops attacked U.S. soldiers in New Orleans on January 8, 1815; the War of 1812 had officially ended with the signing of the Treaty of Ghent in December, 1814, but word had not yet reached the U.S. gives Jefferson huge popularity boost as a"war hero"
The American System
An economic program promoted by Henry Clay; it included a strong banking system that could provide easy credit, protective tariff to allow eastern manufacturing to grow, and a network of federally financed canals and highways to knit the country together economically and politically.

Era of Good Feelings
A name for President Monroe's two terms, a period of strong nationalism, economic growth, and territorial expansion. Since the Federalist party dissolved after the War of 1812, there was only one political party and no partisan conflicts.

McCulloch v. Maryland
(1819) Maryland was trying to tax the national bank and Supreme Court ruled that federal law was stronger than the state law

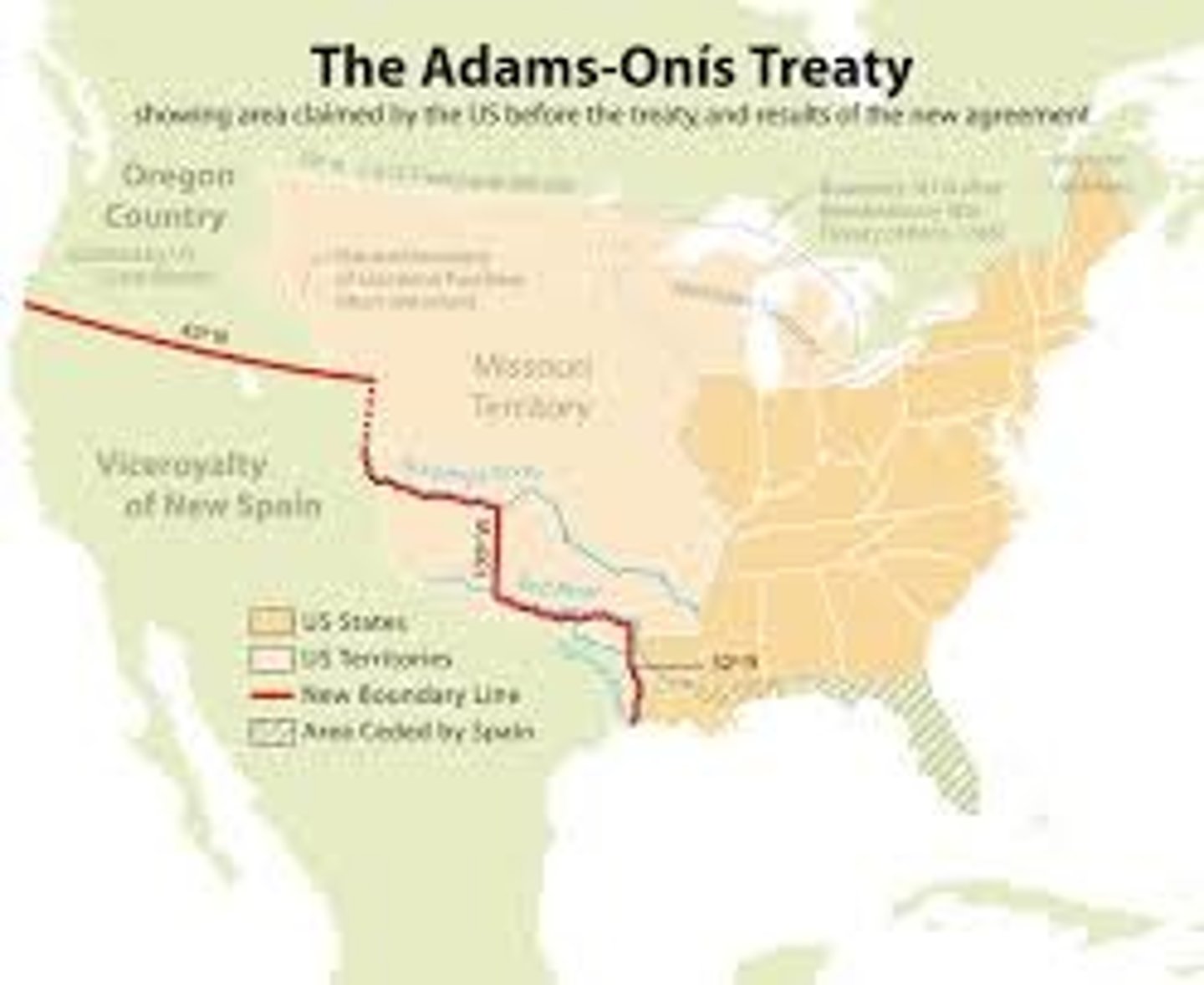
Adams-Onis Treaty
1819 treaty between the United States and Spain in which Spain ceded Florida to the United States
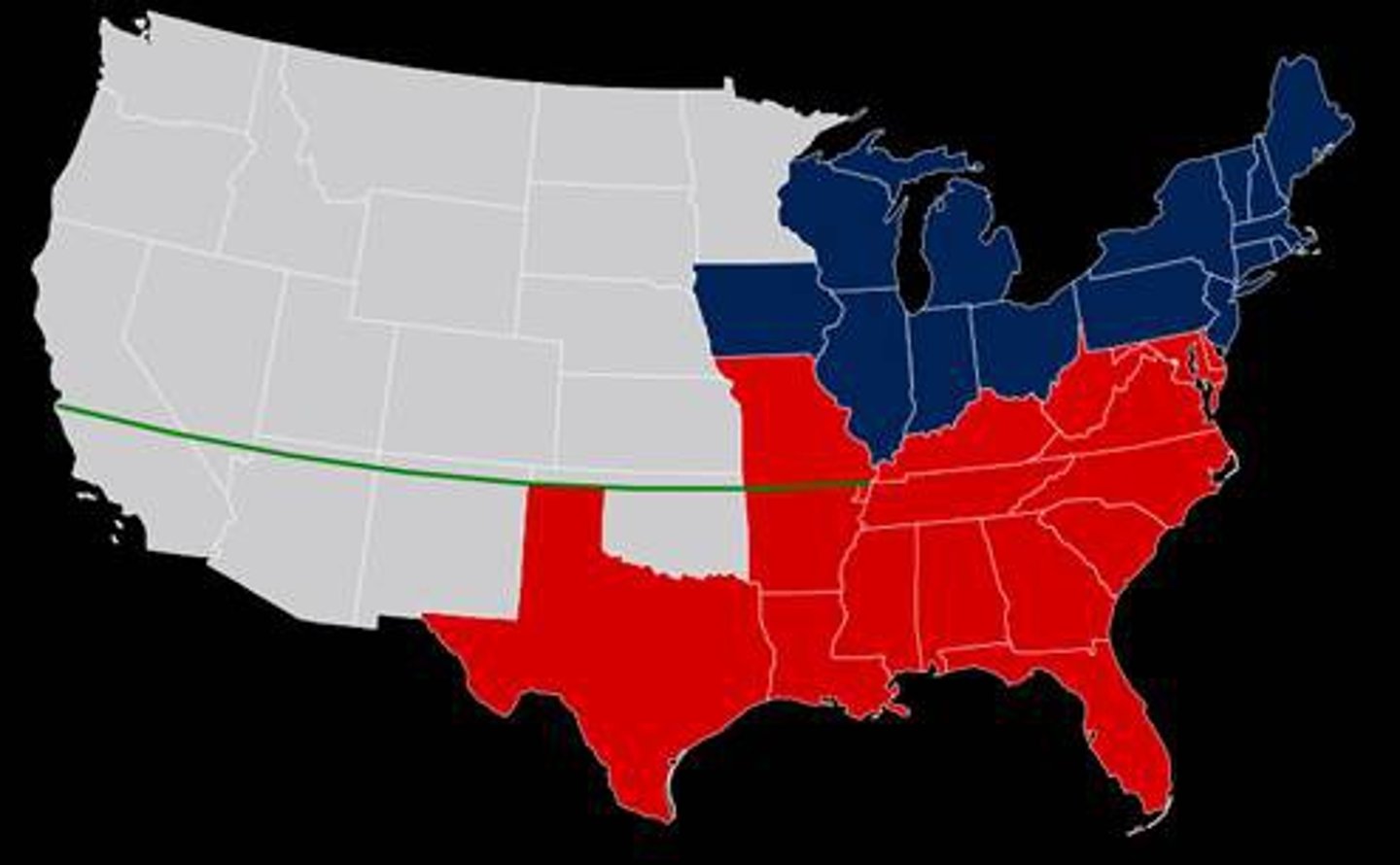
Missouri Compromise
(1820) an agreement proposed by Henry Clay that allowed Missouri to enter the Union as a slave state and Maine to enter as a free state and outlawed slavery in any territories or states north of 36°30´ latitude
Lowell Factory
Lowell created factories that employed local farm girls. This meant girls got away from the house. Before, women just stayed home and took care of their children. Then their daughters did this, and so on and so forth, creating generations of stay-at-home moms. This was broken by women who began working in the factories. However, they were soon replaced by Irish immigrants.

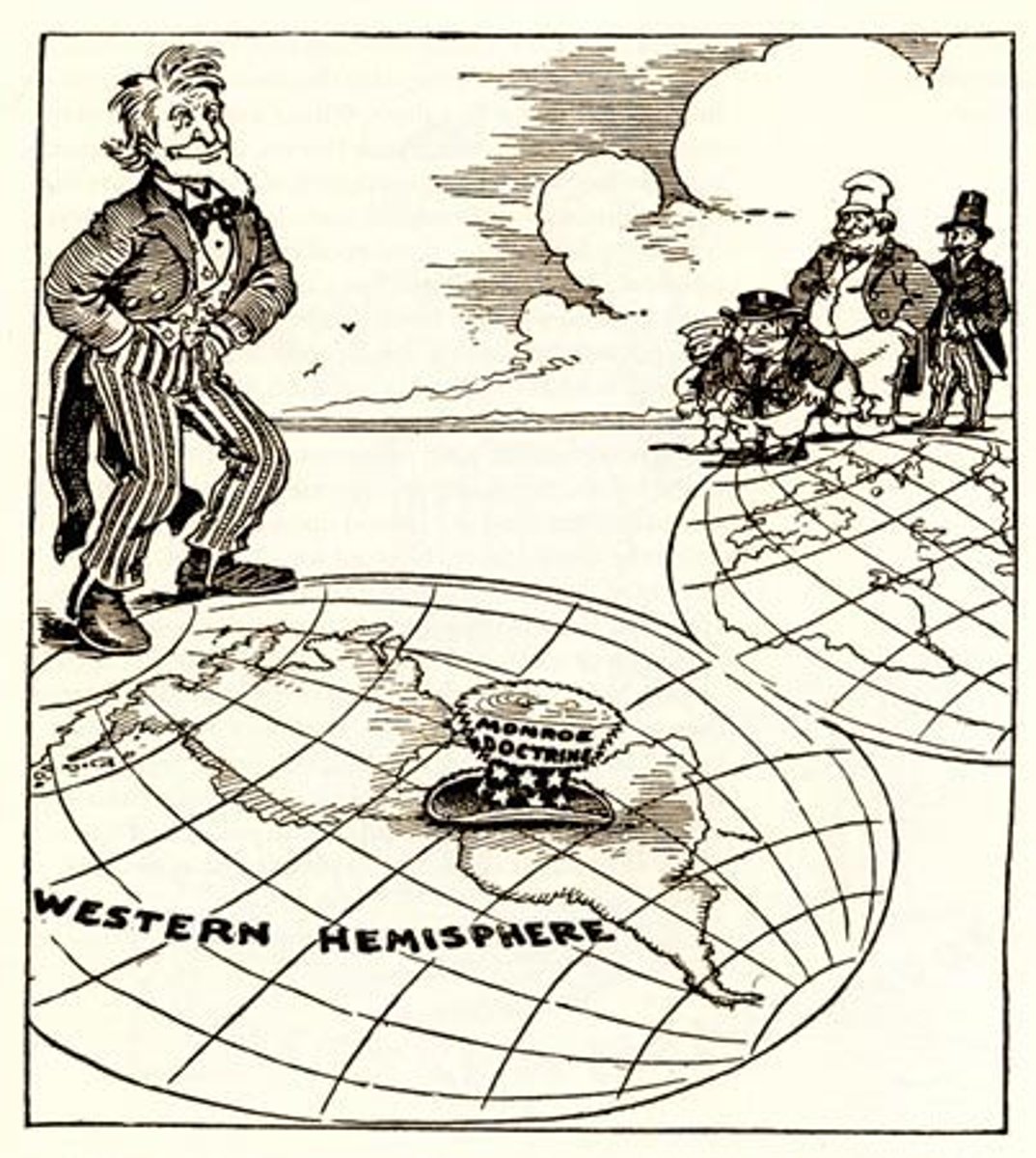
Monroe Doctrine
1823 - statement of foreign policy which proclaimed that Europe should not interfere in affairs within the United States or in the development of other countries in the Western Hemisphere.
Election of 1824
"corrupt bargain"- Adams became the president when Clay gave his support for Adams in exchange for naming Clay Secretary of State

Andrew Jackson
(1829-1833) and (1833-1837), Indian removal act, nullification crisis, Old Hickory," first southern/ western president," President for the common man," pet banks, spoils system, specie circular, trail of tears.

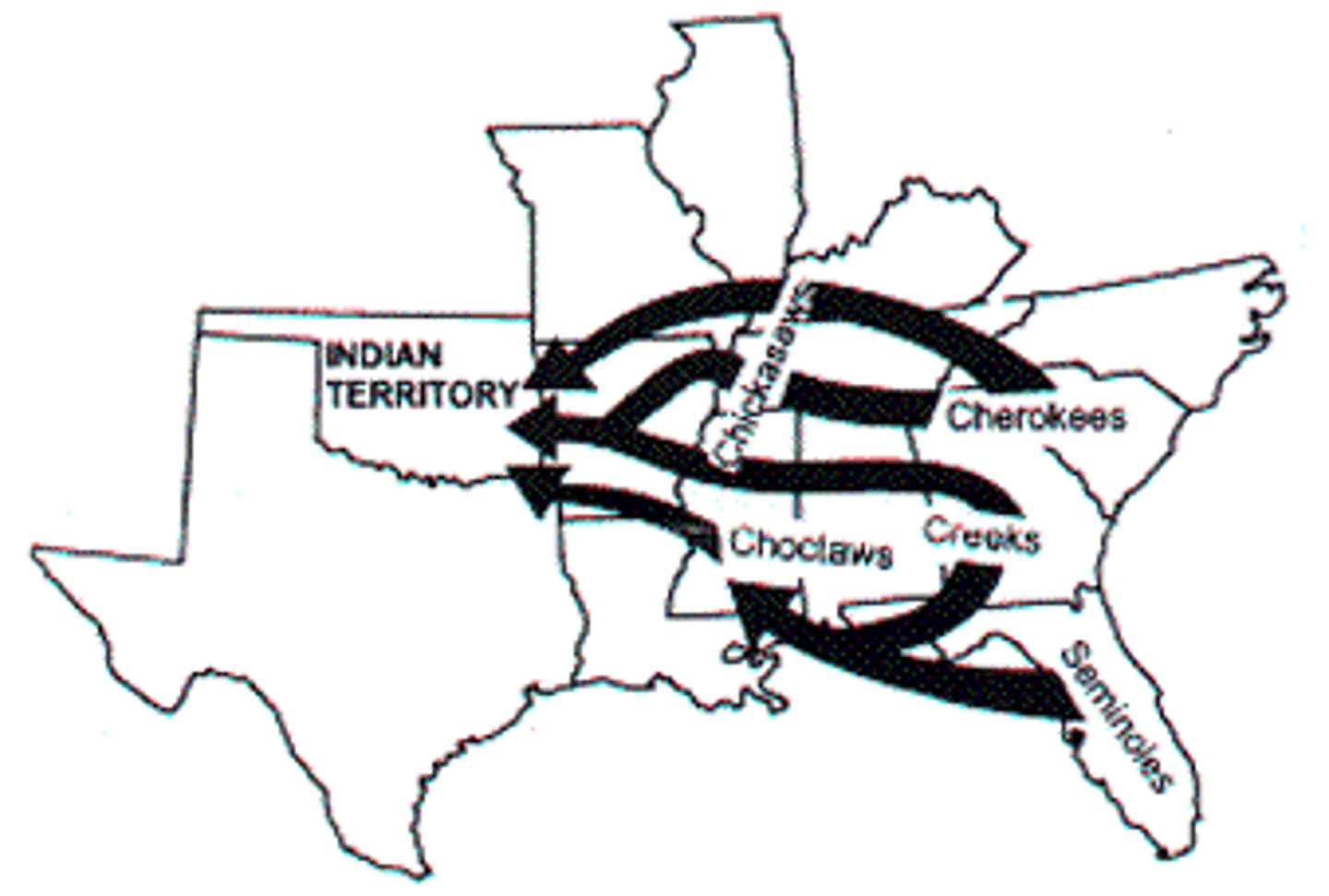
Indian Removal Act
Passed in 1830, authorized Andrew Jackson to negotiate land-exchange treaties with tribes living east of the Mississippi. The treaties enacted under this act's provisions paved the way for the reluctant—and often forcible—emigration of tens of thousands of American Indians to the West.
Nat Turner's Revolt
he led a slave revolt, slaves killed 60 whites, caused masters to be harsher
Nullification Crisis
A sectional crisis during the presidency of Andrew Jackson created by the Ordinance of Nullification, an attempt by the state of South Carolina to nullify a federal law - the tariff of 1828 - passed by the United States Congress.

Bank War
Jackson believed the Bank of US had too much power and was too rich. Vetoed the 2nd Bank charter and withdrew gov't money from the US Banks and put it into "pet banks"
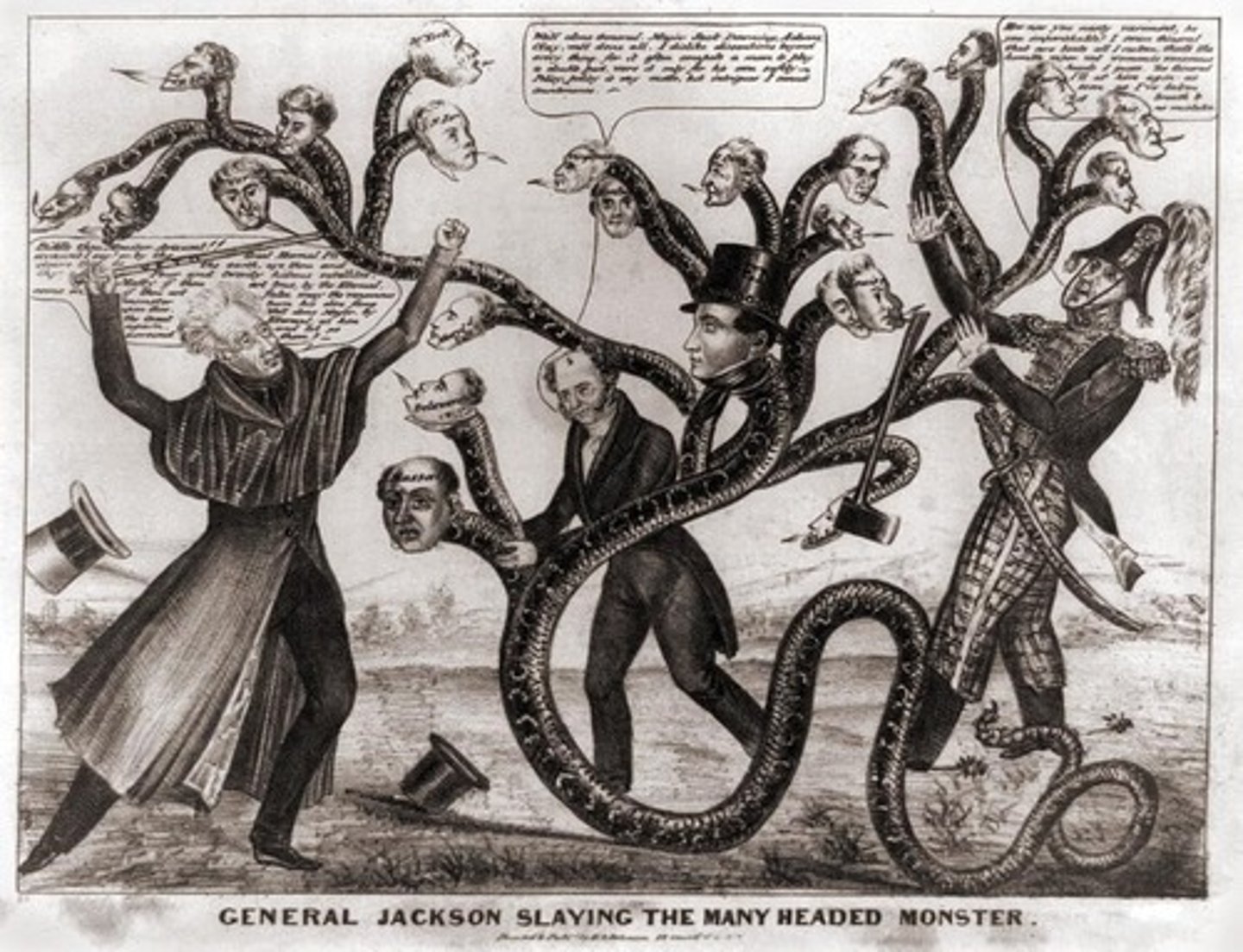

Panic of 1837
When Jackson was president, many state banks received government money that had been withdrawn from the Bank of the U.S. These banks issued paper money and financed wild speculation, especially in federal lands. Jackson issued the Specie Circular to force the payment for federal lands with gold or silver. Many state banks collapsed as a result. A panic ensued (1837). Bank of the U.S. failed, cotton prices fell, businesses went bankrupt, and there was widespread unemployment and distress.

Horace Mann
United States educator who introduced reforms that significantly altered the system of public education

Trail of Tears
The Cherokee Indians were forced to leave their lands. They traveled from North Carolina and Georgia through Tennessee, Kentucky, Illinois, Missouri, and Arkansas-more than 800 miles (1,287 km)-to the Indian Territory. More than 4, 00 Cherokees died of cold, disease, and lack of food during the 116-day journey.

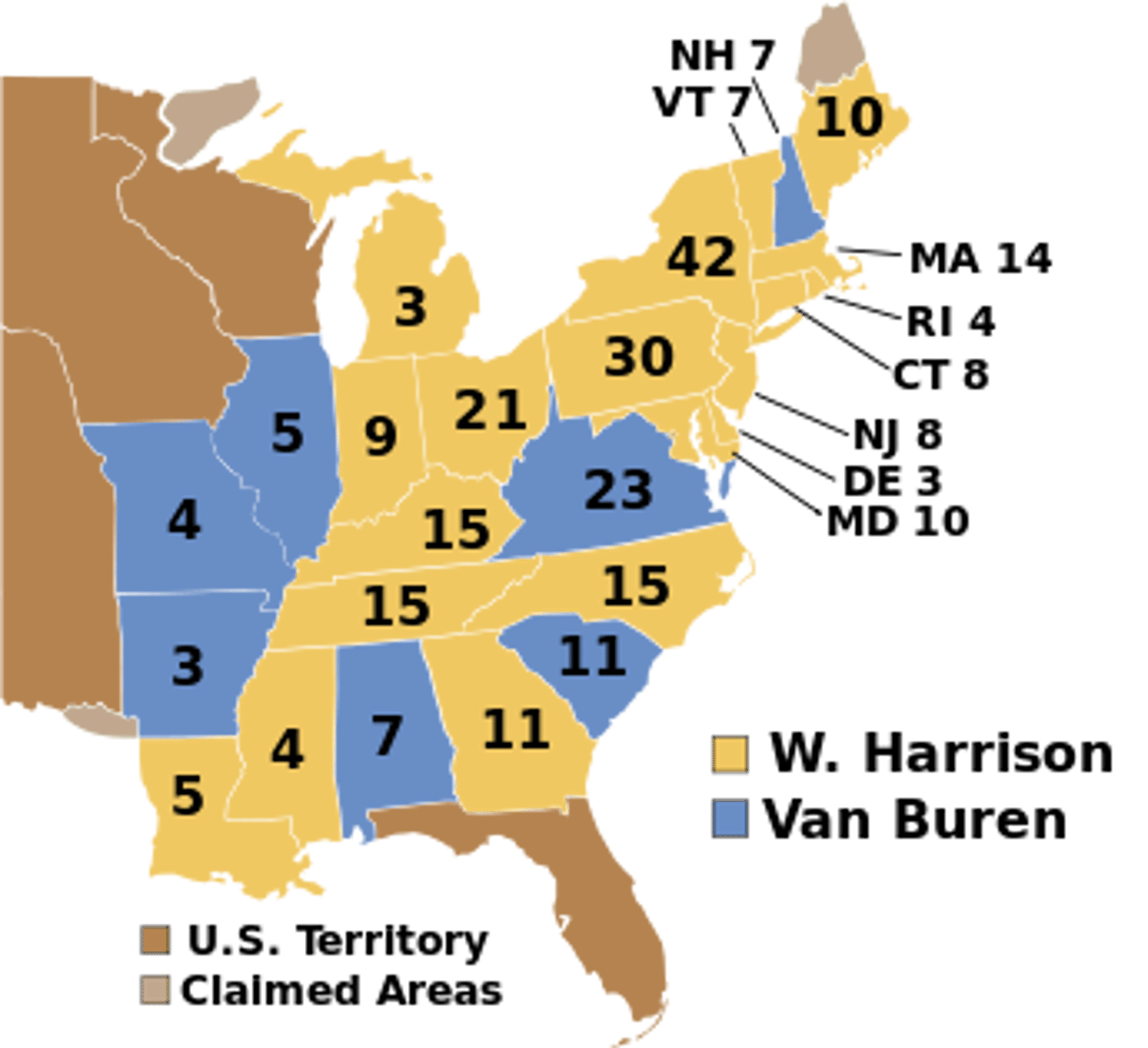
Election of 1840
William Henry Harrison (Whig) vs. Martin Van Buren (Democrat); result: Whig victory & a truly national two-party system.
Manifest Destiny
A notion held by a nineteenth-century Americans that the United States was destined to rule the continent, from the Atlantic the Pacific.

Texas Revolution
War between Texas settlers and Mexico from 1835-1836 resulting in the formation of the Republic of Texas
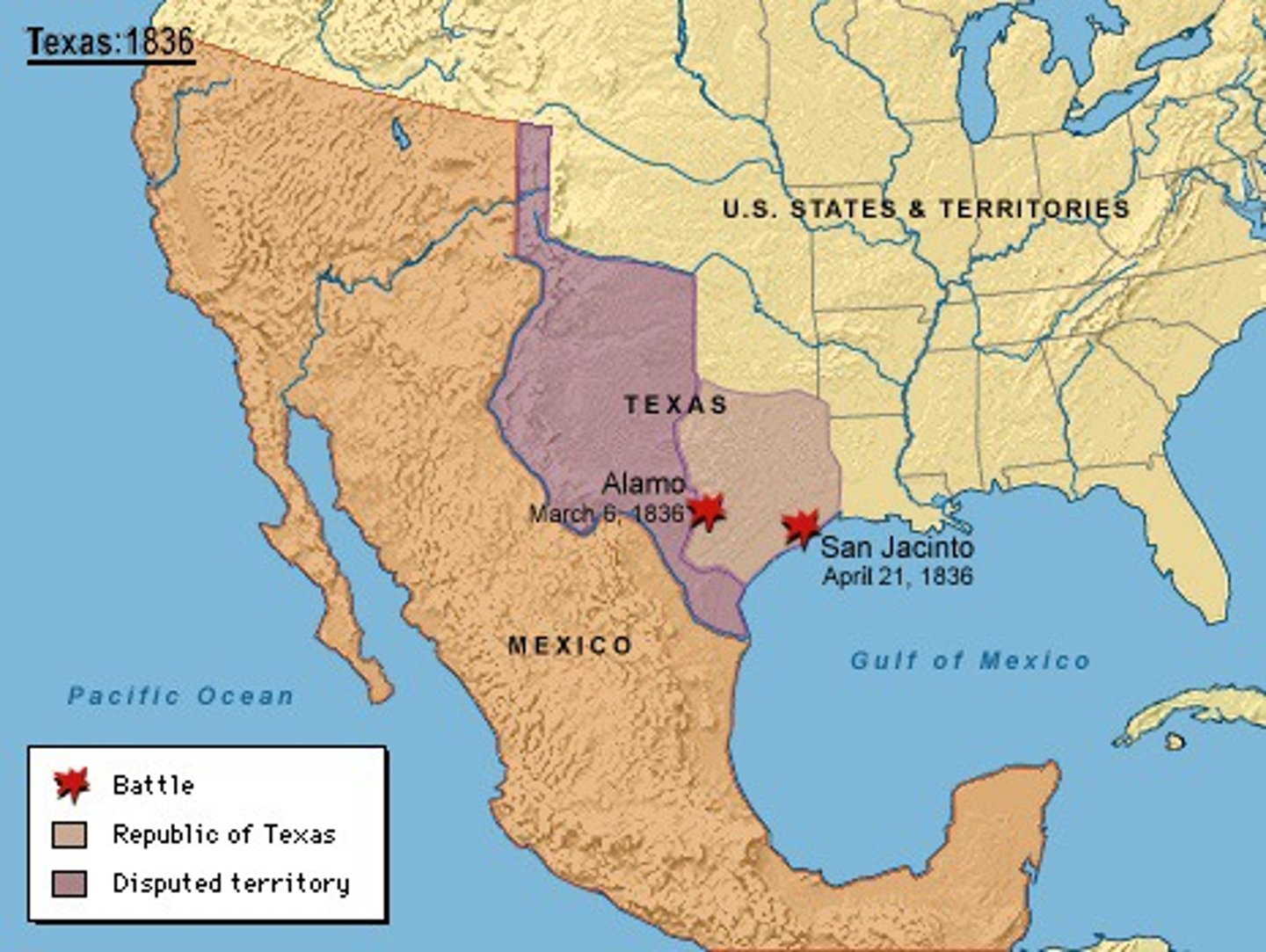
Alamo
Spanish mission in San Antonio, Texas, that was the site of a famous battle of the Texas Revolution in 1836

Texas Annexation
1845 Texas admitted as a slave state, even while Mexico claimed Texas. Mexico considered this an act of war.
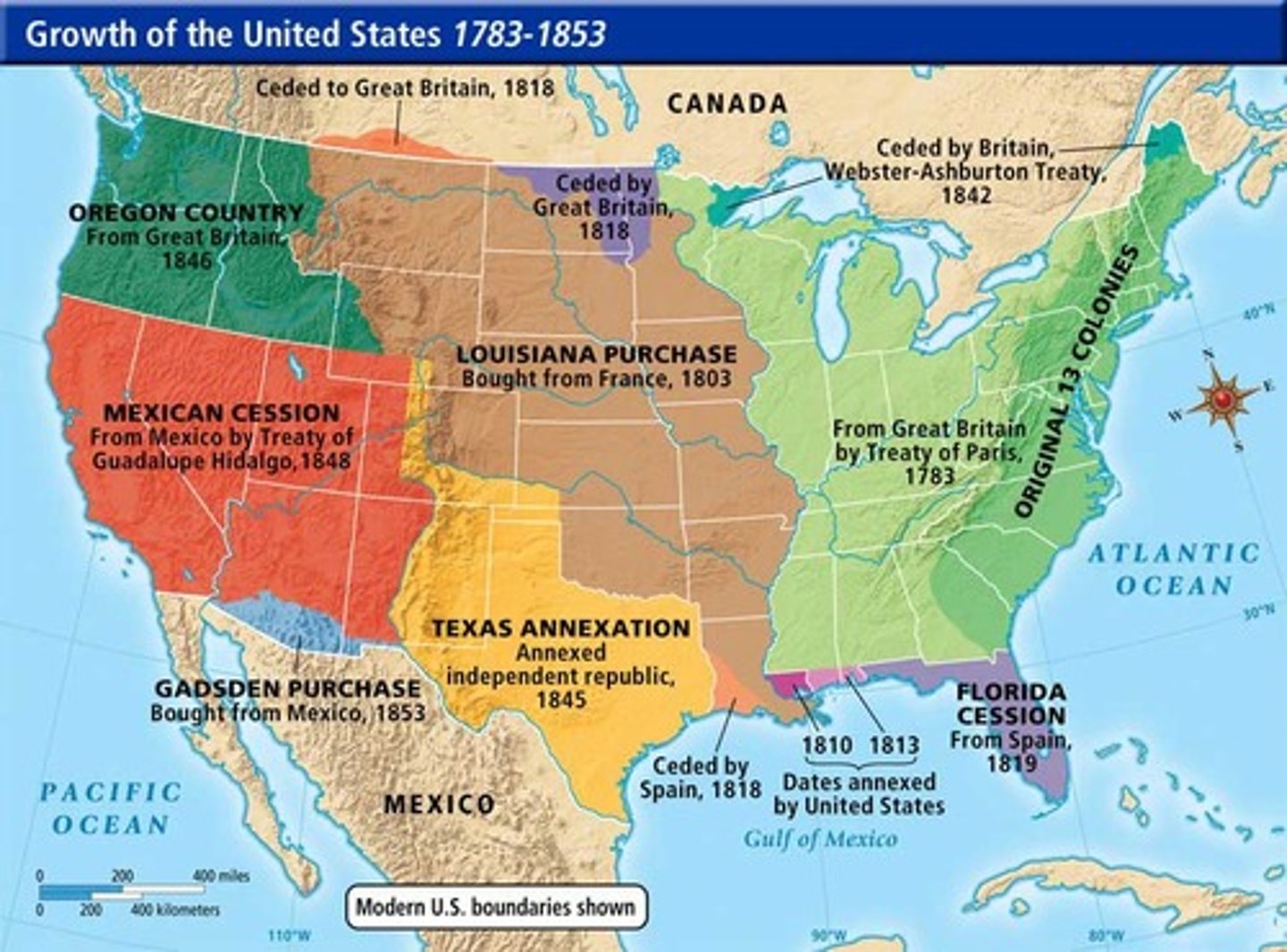
Mexican-American War
(1846-1848) The war between the United States and Mexico in which the United States acquired one half of the Mexican territory.

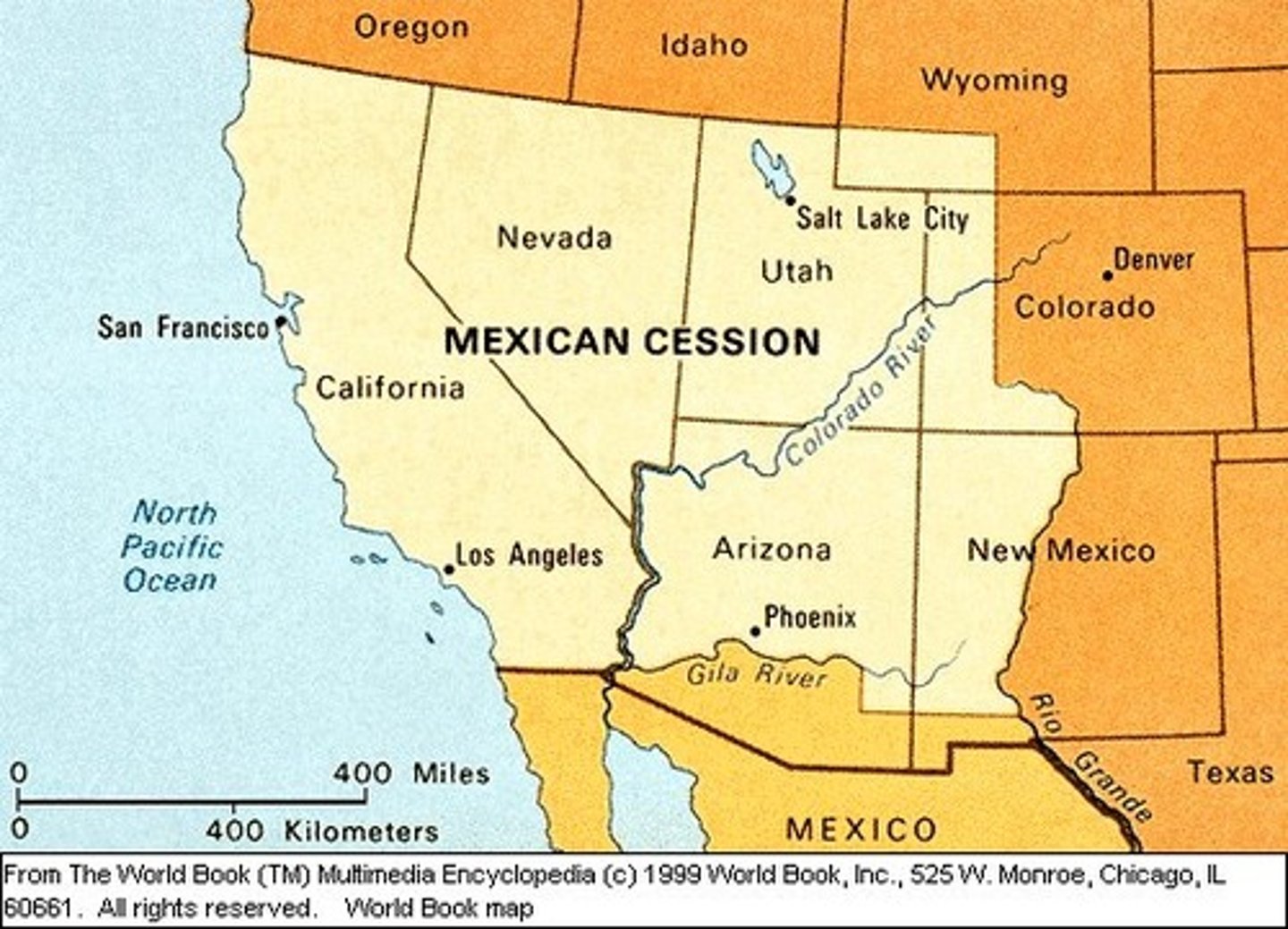
Treaty of Guadalupe Hidalgo
Treaty that ended the Mexican War, granting the U.S. control of Texas, New Mexico, and California in exchange for $15 million
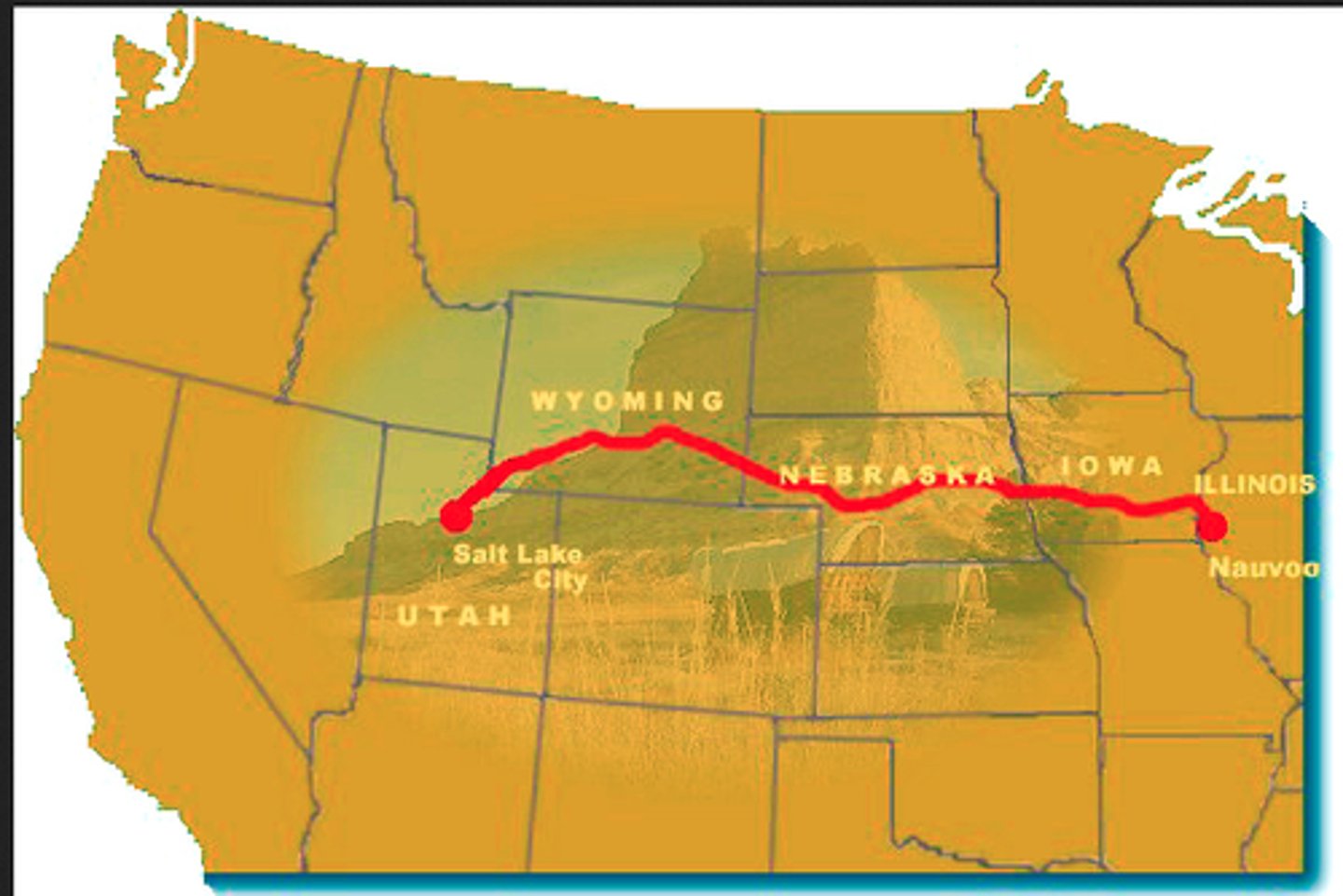
Mormon Migration
refers to the Mormons' journey to escape religious persecution; ended at Salt Lake where they established their base
Seneca Falls Convention
(1848) the first national women's rights convention at which the Declaration of Sentiments was written

California Gold Rush
1849 ("49ers") Gold discovered in California attracted a rush of people all over the country and world to San Francisco; arrival of the Chinese; increased pressure on fed gov. to establish a stable gov. in CA

Wilmot Proviso
1846 proposal that outlawed slavery in any territory gained from the War with Mexico

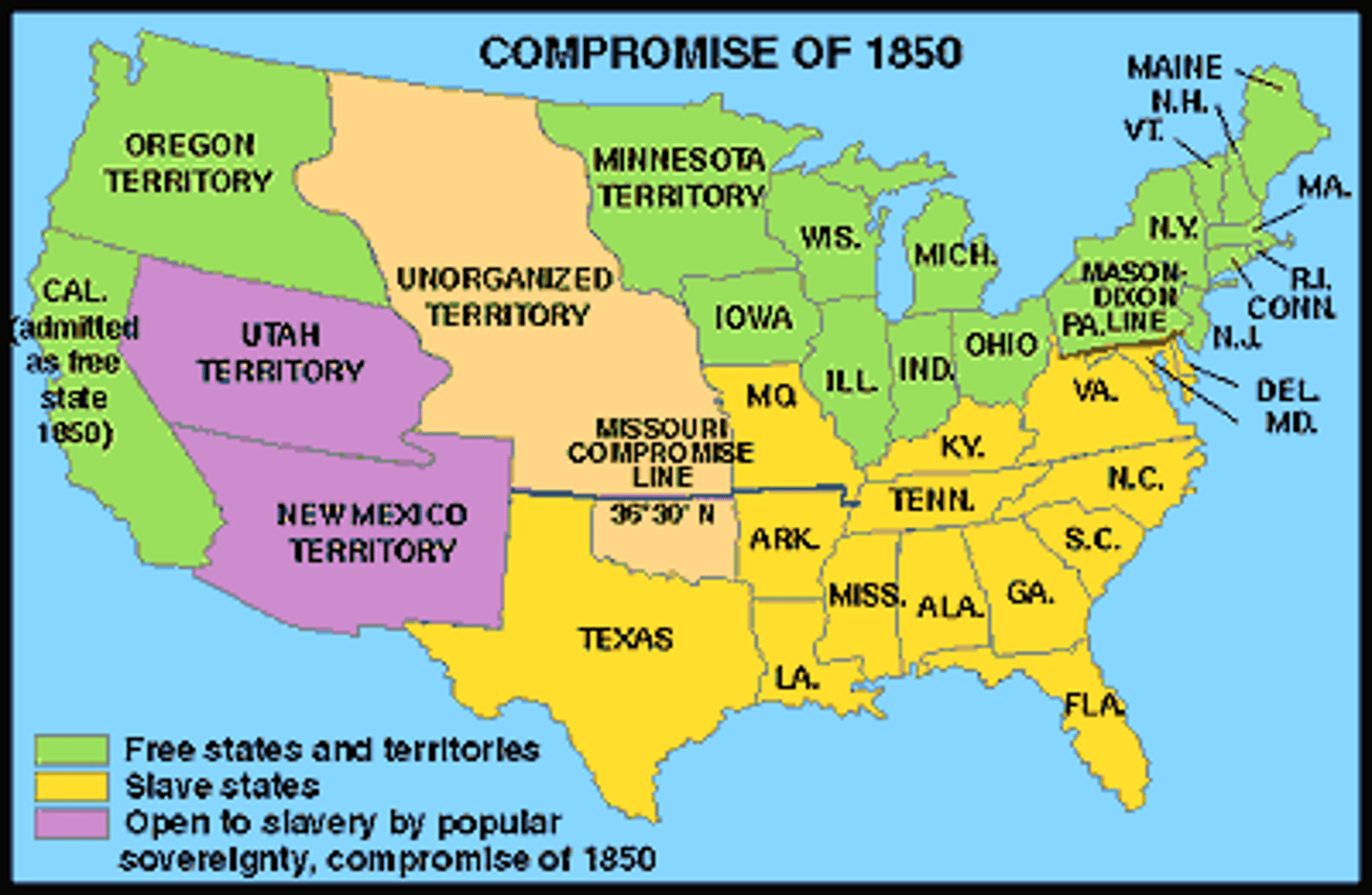
Compromise of 1850
(1) California admitted as free state, (2) territorial status and popular sovereignty of Utah and New Mexico, (3) resolution of Texas-New Mexico boundaries, (4) federal assumption of Texas debt, (5) slave trade abolished in DC, and (6) new fugitive slave law; advocated by Henry Clay and Stephen A. Douglas
Uncle Tom's Cabin
written by harriet beecher stowe in 1853 that highly influenced england's view on the American Deep South and slavery. a novel promoting abolition. intensified sectional conflict.

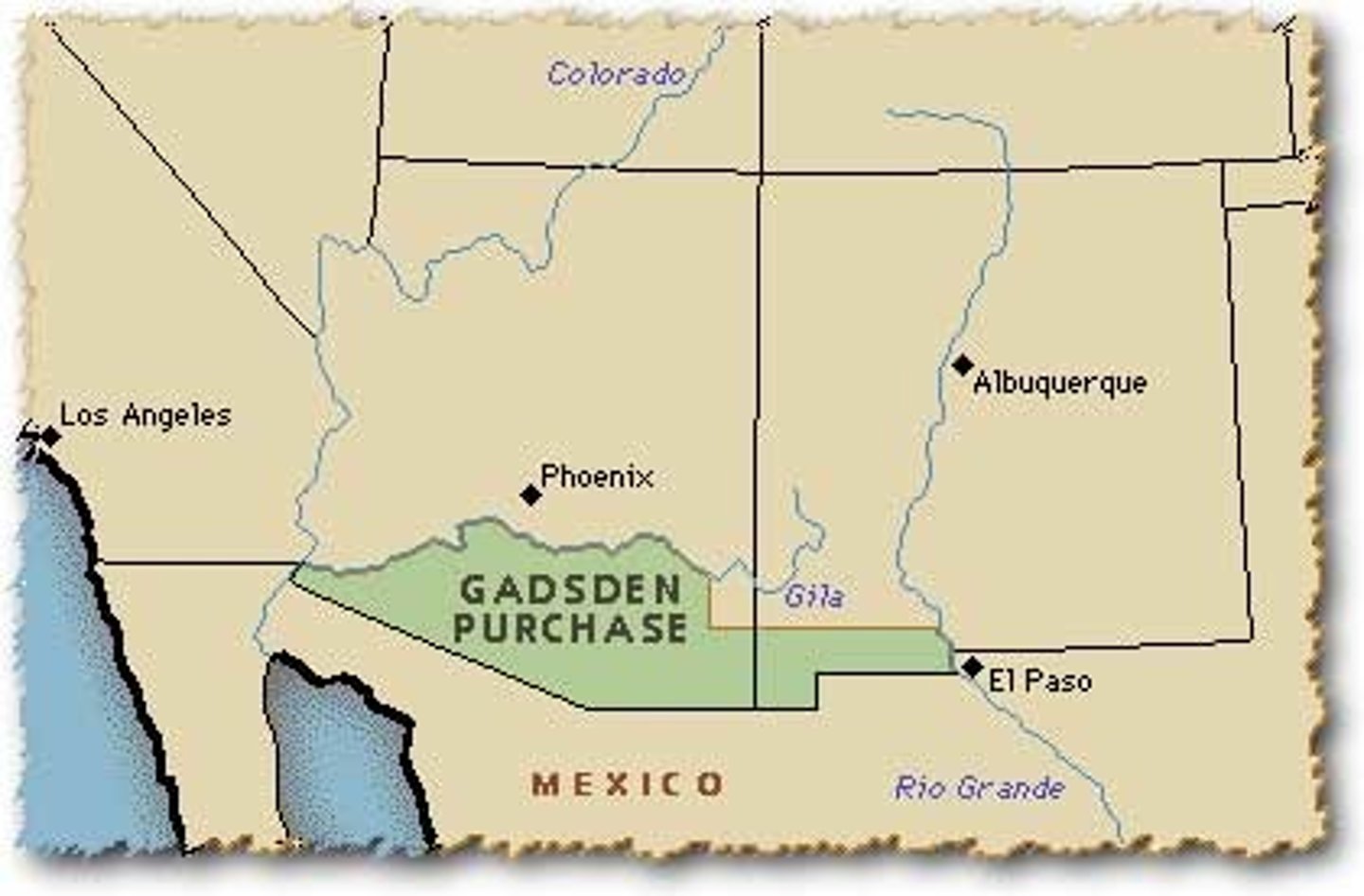
Gadsden Purchase
(1853) U.S. purchase of land from Mexico that included the southern parts of present-day Arizona and New Mexico
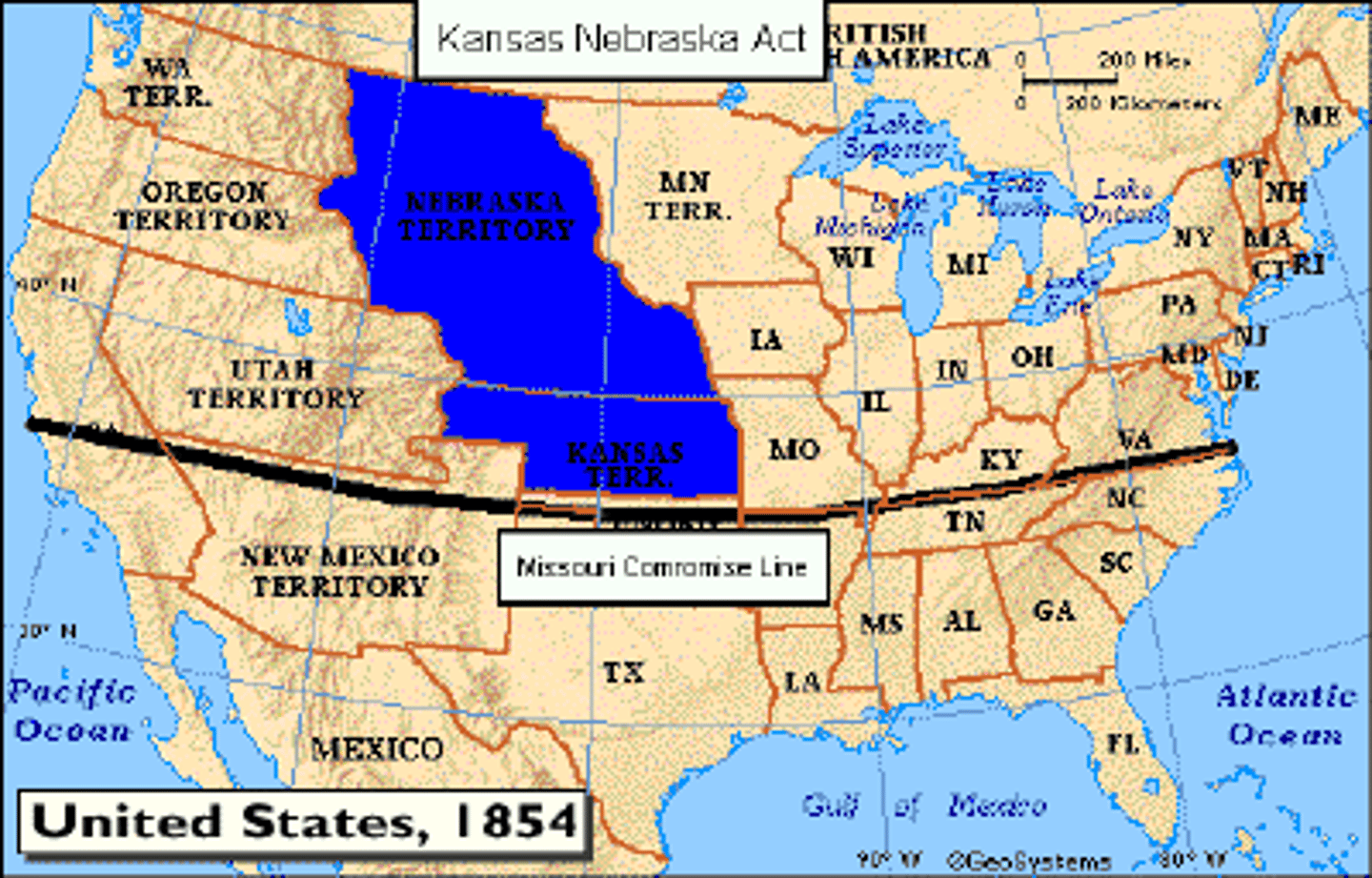
Kansas-Nebraska Act
1854-Created Nebraska and Kansas as states and gave the people in those territories the right to chose to be a free or slave state through popular sovereignty.
Creation of Republican Party
In response to kansas-nebraska act, whigs, northern democrats, free soilers, DECIATED TO STOPPING EXPANSION OF SLAVERY

Dred Scott v. Sandford
1857 Supreme Court decision that stated that slaves were not citizens; that livig in a free state or territory, even for many years, did not free slaves; and declared the Missouri Compromise unconstitional

Lincoln Douglas Debates
1858 Senate Debate, Lincoln forced Douglas to debate issue of slavery, Douglas supported pop-sovereignty, Lincoln asserted that slavery should not spread to territories, Lincoln emerged as strong Republican candidate

Abolition Movement
movement to end slavery
