Physics for Life Sciences Exam II Practice Questions
1/26
There's no tags or description
Looks like no tags are added yet.
Name | Mastery | Learn | Test | Matching | Spaced | Call with Kai |
|---|
No analytics yet
Send a link to your students to track their progress
27 Terms
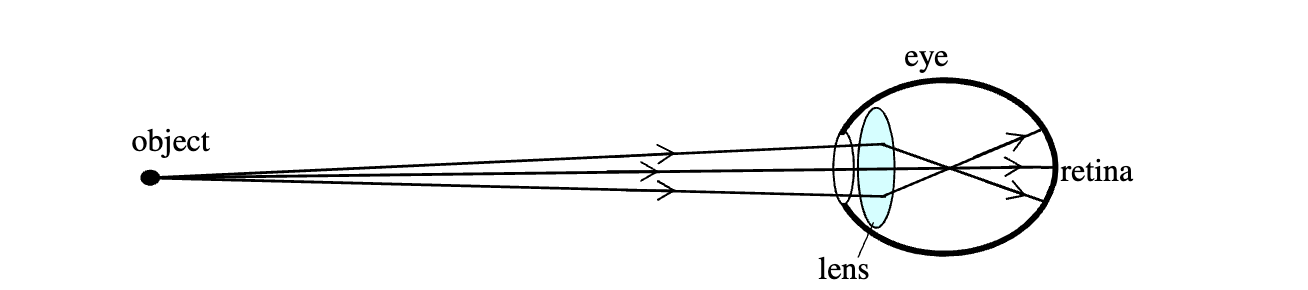
The following diagram shows the light rays for nearsighted people attempting to see an object beyond their far point. To correct their vision, a concave(i.e., diverging) lens should be used.
true
The intermediate image of a compound microscope (the image created by the objective lens) is a real inverted image.
true
Due to diffraction limitation, we can see red objects in greater detail than blue objects when we view them through a given telescope (recall λred >
λblue)
false
When 1.0 × 10^6 electrons are removed from an initially electrically neutral object, the net charge on the object is +1.6 × 10^−13 C.
true
The electric potential energy due to two point charges that are separated by a distance of d is U. When the distance between the charges is increased to 2d, the electric potential energy of the charges is 1/4 U.
false
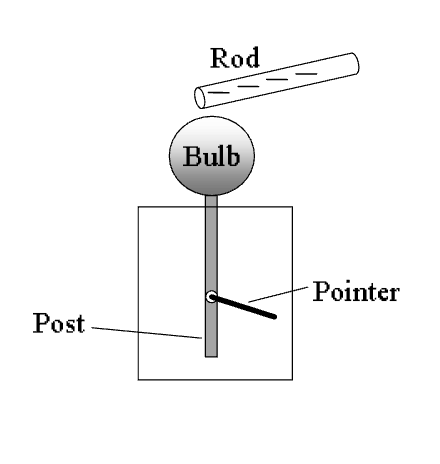
Consider an initially uncharged electroscope.
A negatively charged rod is placed close to
he electroscope bulb (but not touching, so
that no charge is transferred to the electro-
scope), causing its needle on the electroscope
to deflect. In this situation, the bulb is pos-
itively charged, and the post and pointer
both are negatively charged.
true
A person has a near point that is 25 cm from his eyes. He examines an object that is at the focal point of a magnifying glass (so that the image
is at infinity). If the power of the magnifying glass is +10 D, what is the angular magnification?
2.5
A farsighted woman wears contact lenses of power +2.0 D to see objects that are a close as 1/4 m away from her. What is her near point? (Remember, you want the lens to create, for an object at 1/4 m, a virtual image of at the
person’s near point.)
0.5m
A student wears eyeglasses of power −1.0 D to correct nearsightedness. The glasses are designed to be worn a distance of 0.20 m in front of her eye. What is her far point distance? Hint: Her far point distance is the distance from her eye to the image of an object at infinity.
1.2m
In a basic compound microscope,
both the objective and eyepiece are are converging(convex) lens
To obtain an angular magnification of magnitude 5× in an astronomical telescope, if an eyepiece lens of focal length 10 cm is used, the objective lens should have a focal length of?
50cm
When you view an object through an astronomical telescope, the image that you see as you look through the eyepiece is?
virtual and inverted
A telescope has a angular magnification of magnitude 20×. If it is used to view an object that has a size of 6 × 102 km that is the 6 × 105 km away, the angle subtended by the object when viewed through the telescope is (hint: use the small angle approximation θ ≈ h/d)
2 × 10^−2 rad
Two point charges, separated by a distance d, exert a force of magnitude F on each other. To increase the magnitude of the force to 4F , the separation of the charges should be changed to
1/2d
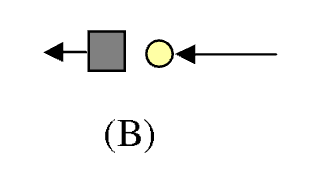
A square object has a charge of −1 × 10^−9 C and a round object has a charge of +2 × 10^−9 C. They are placed close to each other. Which of the
following figures best indicates the directions and magnitudes (indicated by the length of the vectors) of the electric forces of the objects on one another?
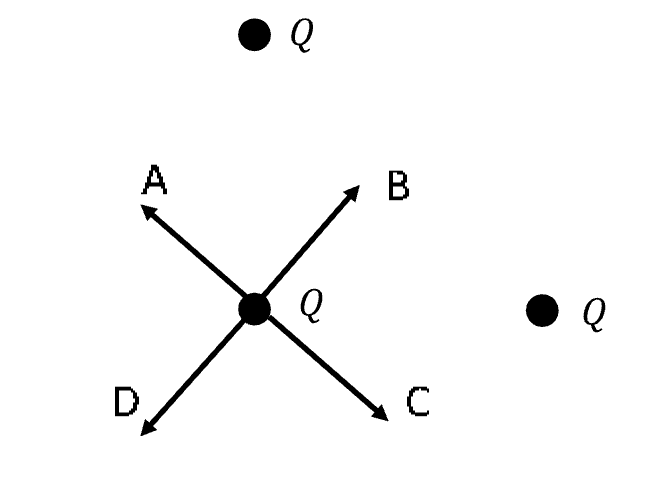
Three positive point charges of equal magnitude are placed as indicated by the black dots in the figure below. On the charge that is marked with
arrows, which arrow best indicates the net force on that charge due to the other two charges?
B

The figure below shows a charge dipole (an object with a positive charge at one end and an equal magnitude of negative charge at the other) in a region with electric field lines. The positive and negative charges are indicated by “+” and “−”, respectively. In which direction is the net force of the electric field on the dipole?
no net force
In a region of space, there is a constant electric field of 100 N/C pointing to the right. When an object is placed in that region, it experiences a force of 10 N, pointing to the left due to that electric field. What is the charge on that object?
+10C
In a region of space, the electric potential is constant at 20 V. If a charge of 1 × 10^−2 C is placed in this region, what is the magnitude of the electric force on this charge? (Hint: |~E| = ∆V /∆x.)
2 × 10^3 N
A point +1 μC charge and another point charge Q are 40 cm apart. At the point along the line joining the two charges that is 10 cm from the +1 μC charge (and hence 30 cm from charge Q), the net electric field is zero. What is the charge Q?
-3uC
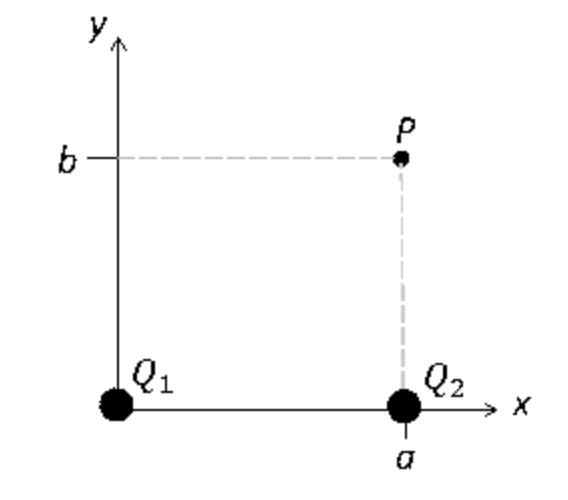
Charge Q1 is located at the coordinate system origin, while charge Q2 is located at (a, 0). The point P has coordinates (a, b). What is the electric
potential (i.e., voltage) at point P ? (Hint: Use Pythagoras’ theorem to determine the distance of P from Q1.) Here, k = 9.0 × 109 N · m2/C2.
Assume the electric potential is zero at infinity.
k Q1/a + b − k Q2/√a2 + b2
Consider two parallel plates, one with negative and the other with positive charge. An electron that placed in between the plates is at the lowest electric potential (i.e., voltage) near the (i) plate, and has the lowest electric potential energy near the (ii) plate.
(i) negative; (ii) positive
Suppose you have two parallel conducting plates having a potential difference between them of 4 V. If the electric field between the plates is 20 V/m,
what is the separation between the plates?
5m
An alpha particle has 2 protons and no electrons. It starts at a point where the electric potential is 20 V and ends at a point where the electric potential is −10 V. If its initial kinetic energy is 100 eV, what is its final kinetic energy? (Assume the only force acting on the alpha particle is that of the electric field.)
70eV
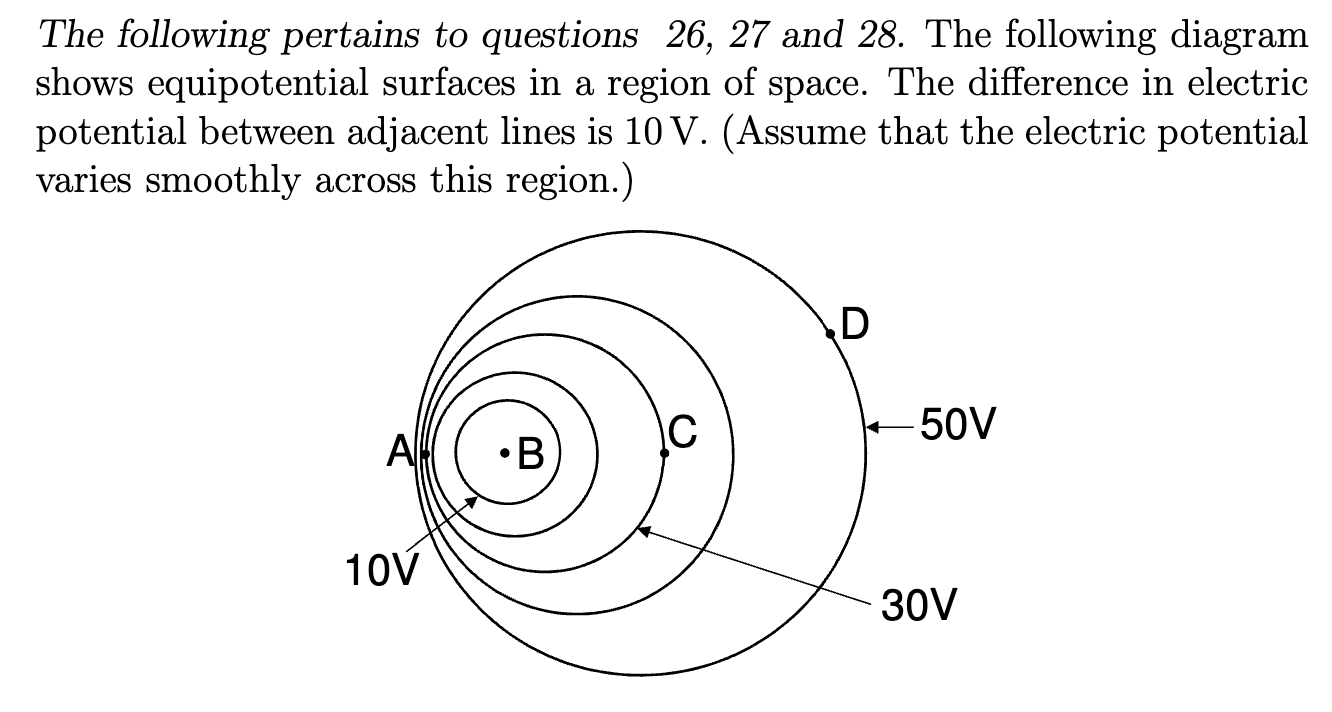
What is the direction of the electric field at point C?
←
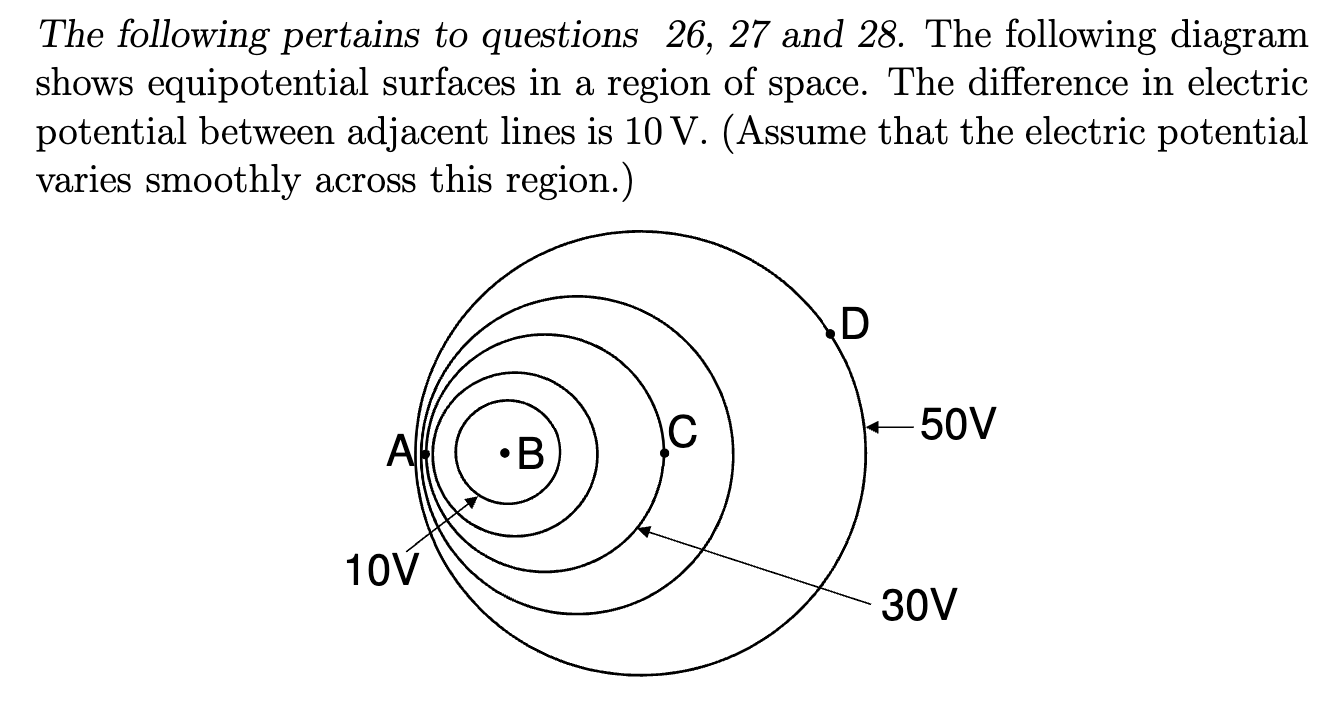
At which point in the electric field the strongest?
A
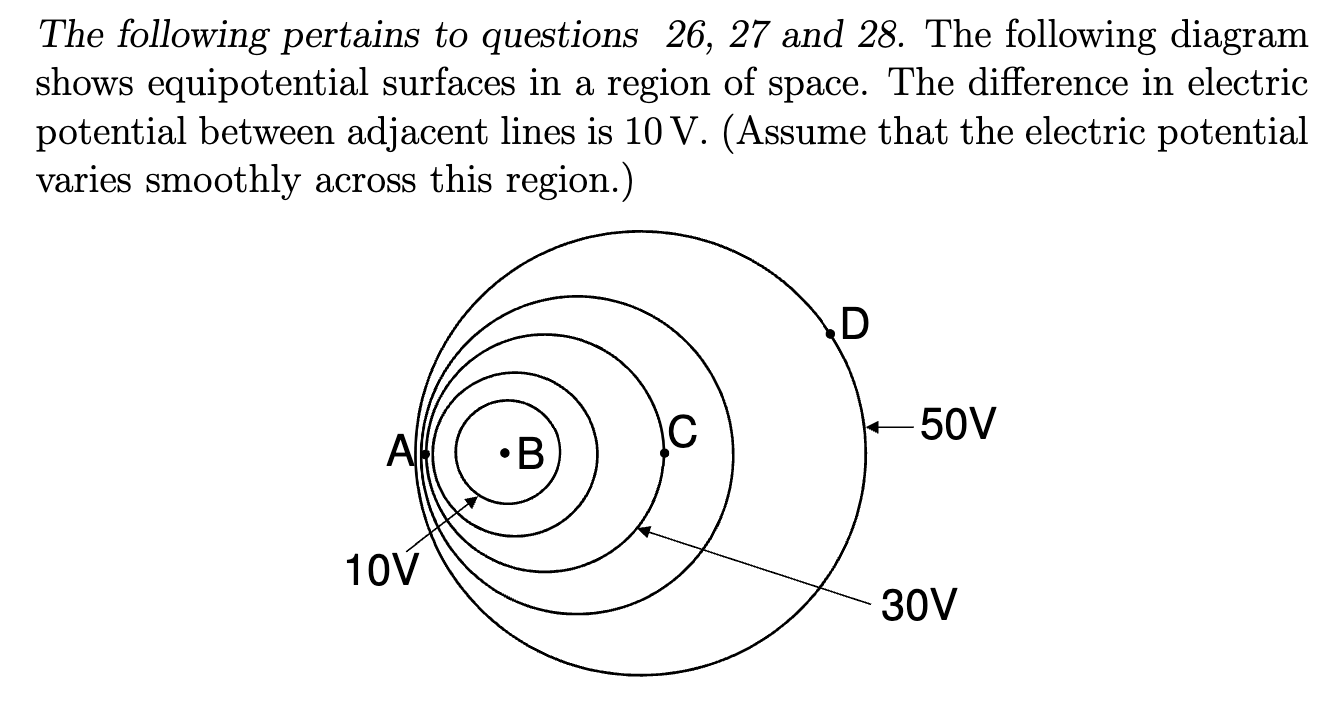
What is the change in the electric potential energy of a −2 C charge when it is moved from D to C? (Remember that the change is defined to be the
final value minus the initial value.)
40J