Cell Structure & Function Chapter 12
1/28
There's no tags or description
Looks like no tags are added yet.
Name | Mastery | Learn | Test | Matching | Spaced |
|---|
No study sessions yet.
29 Terms
Endoplasmic Reticulum
Protein Synthesis, sorting
Golgi Complex
protein processing, and sorting
Endosomes
Carry and sort material brought into the cell
Lysosomes
Digest ingested material and unneeded cellular components
Peroxisomes
Lipid metabolism and scavenging of reactive oxygen species
Rough ER
Characterized by ribosomes on the cytosolic side of the membrane
Large flattened sheets
Smooth ER
Lacks ribosomes and has other roles in the cell involving the processing and storage of nonproteins
Tubular membranes
Differences between ER
Rough ER membrane - large flattened sheet
Smooth ER membrane - tubular structures
Transitional elements (ER exit sites) of the rough ER are an exception as they resemble the smooth ER.
The lumenal spaces of rough and smooth ER are continuous.
Cells involved in synthesis of secretory proteins have prominent rough E R networks.
Cells producing steroid hormones tend to have extensive networks of smooth E R.
Rough ER Function
Membrane protein synthesis through cotranslational insertion into the ER through a pore complex as they are synthesized.
The initial steps of addition of carbohydrates to glycoproteins
Folding of polypeptides
Recognition and removal of misfolded proteins
Assembly of multimeric proteins
Smooth ER Function
Drug detoxification - store enzymes for drug hydroxylation
Certain carbohydrate metabolism - glycogen breakdown
Calcium Storage - muscle contraction
Steroid Biosynthesis - steroid hormone synthesis
Drug Detoxification (Smooth ER)
involves hydroxylation
Adding hydroxyl groups increases their solubility making them easier to excrete
Catalyzed by a member of the cytochrome P-450 family of proteins (monooxygenases)
Hydroxylation Occurs via Electron Transport
Electrons transferred to a heme group in cytochrome P-450
Electron donated to O2, one oxygen atom forms H2O and the other is added to the substrate as a hydroxyl group.
R is drug being hydroxylated
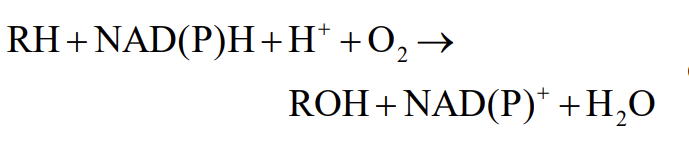
Pharmacogenetics
Investigates how inherited differences in genes, like P-450, can lead to differential responses to drugs and medications.
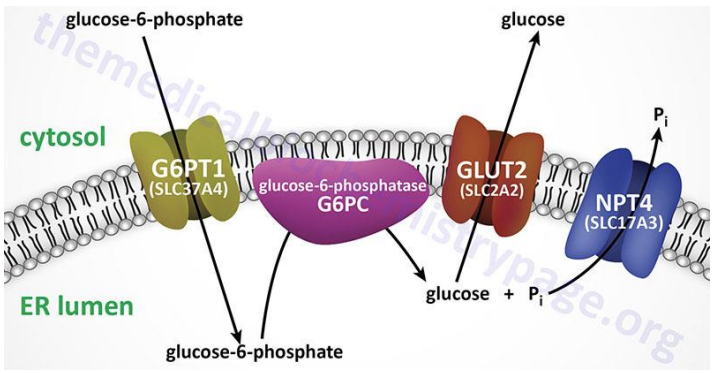
Carbohydrate Metabolism (Smooth ER)
Smooth ER in liver cells breakdown the stored glycogen; it contains glucose 6 phosphatase, an enzyme unique to smooth ER
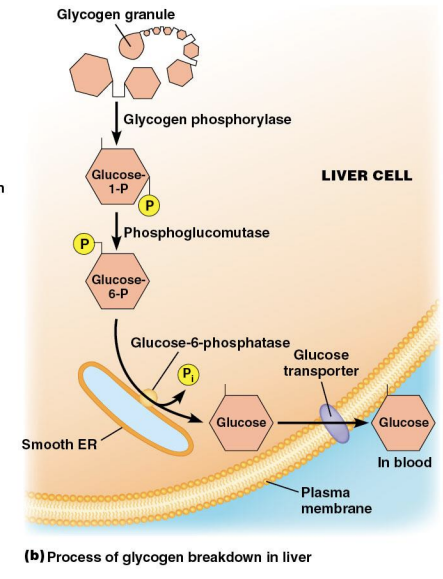
Glycogen Metabolism
Glycogen is not stored in the ER, rather, G6P is transported into the ER lumen where G6Pase is bound
Calcium Storage (Smooth ER)
Sarcoplasmic reticulum (calcium storage) of muscle cells is an example of Smooth ER
ER lumen contains high concentrations of calcium binding proteins
Controlling muscle contraction by regulated calcium release.
Steroid Biosynthesis (Smooth ER)
Synthesis of steroids and cholesterol
Utilizes enzymes such as HMG-CoA reductase, the committed step in cholesterol biosynthesis.
Found in smooth ER of liver cells and is targeted by cholesterol-lowering drugs called statins.
Biosynthesis of Membranes
Mitochondria synthesize phosphatidylethanolamine.
Peroxisomes synthesize cholesterol.
From precursors from ER
Chloroplasts contain enzymes for chloroplast-specific lipids.
ER primary source of membrane lipids.
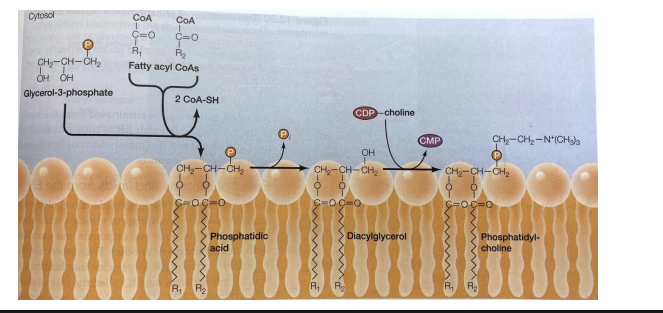
Membrane Lipid Biosynthesis in the ER
Fatty acids synthesized in the cytosol are inserted into the cytosolic leaflet of the ER membrane.
Phospholipid translocators (flippases) transfer specific phospholipids to the lumenal leaflet, generating membrane asymmetry.
Distinct composition of cytosolic and lumenal monolayers established in the E R is transferred to other cellular membranes.
Phospholipid exchange proteins - convey specific phospholipids to chloroplasts, mitochondria, or peroxisomes
Sorting Signals
A linear sequence of amino acids (signal sequence)
protein translocation into organelles
Signal Patch - specific three dimensional arrangement of amino acids
Nuclear and vesicular transport
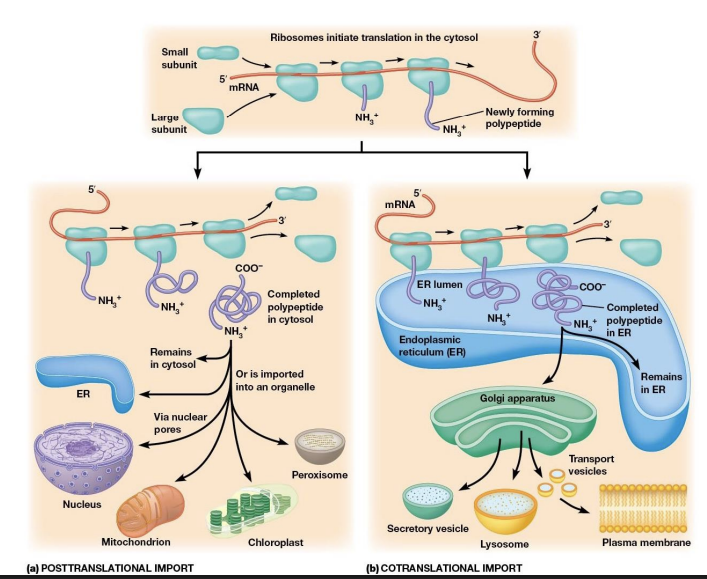
Intracellular Sorting of Proteins
Tags determine the fate or proteins after translation.
ER Signaling Sequences
Proteins destined for secretion or membranes possess an N-terminal ER signal sequence (15-30 amino acids) with three domains: a positively charged N-terminal region, a hydrophobic core, and a polar region near the cleavage site.
Signal hypothesis
For polypeptides destined for the E R, the N-terminus contains an E R signal sequence that directs ribosome-mRNA-polypeptide complexes to the surface of the rough ER.
Signal Recognition Particle (SRP)
Contact of the ribosome with the E R is mediated by SRP
SRP recognizes and binds to the E R signal sequence and then binds to the E R membrane.
SRP Mechanism
mRNA binds to a free ribosome. The polypeptide is synthesized until the E R signal sequence has been formed
SRP binds the ER signal sequence and blocks translation
The SRP binds the ribosome to a translocon in the ER membrane.
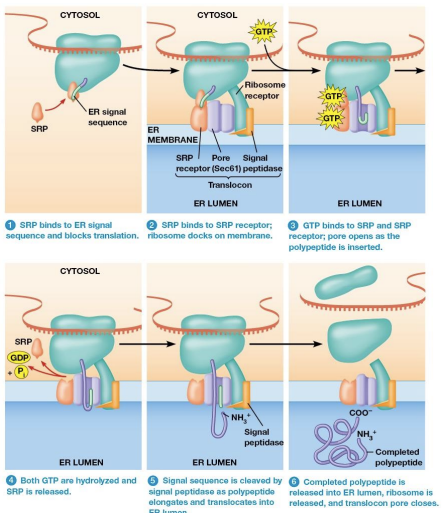
Translocon
Protein Complex made of:
SRP receptor which SPR binds
Ribosome Receptor - holds ribosome in place
Pore protein - Forms a channel for the growing polypeptide to enter the ER lumen
Signal peptidase -