A2.3: Viruses
1/29
There's no tags or description
Looks like no tags are added yet.
Name | Mastery | Learn | Test | Matching | Spaced |
|---|
No study sessions yet.
30 Terms
Structure of Viruses (5)
Small Size: need to be small to enter host (20-300 nm)
Fixed Size: Do not grow, assembled in full size in host
Nucleic Acid as Genetic Material: either single/double stranded DNA/RNA, hosts machinery must read it to make proteins
Capsid: Protein coat that encloses genetic material
No cytoplasm, very few enzymes: Relies on hosts metabolism. Own enzymes used to replicate genetic material and infect/burst host
Genetic Material Basics
Single or double-stranded DNA or RNA
Circular or linear
Genetic material varies greatly in length
Positive-Sense RNA Virus
Genes are used directly as mRNA
Positive-sense is the complement to template/antisense strand, therefore looks like mRNA
Negative-Sense RNA Virus
Genes need to be transcribed to mRNA
Retrovirus
RNA gene changes to double-stranded DNA (w/ Reverse Transcriptase), then to mRNA
Drawing of DNA to Showcase Template vs. Nontemplate
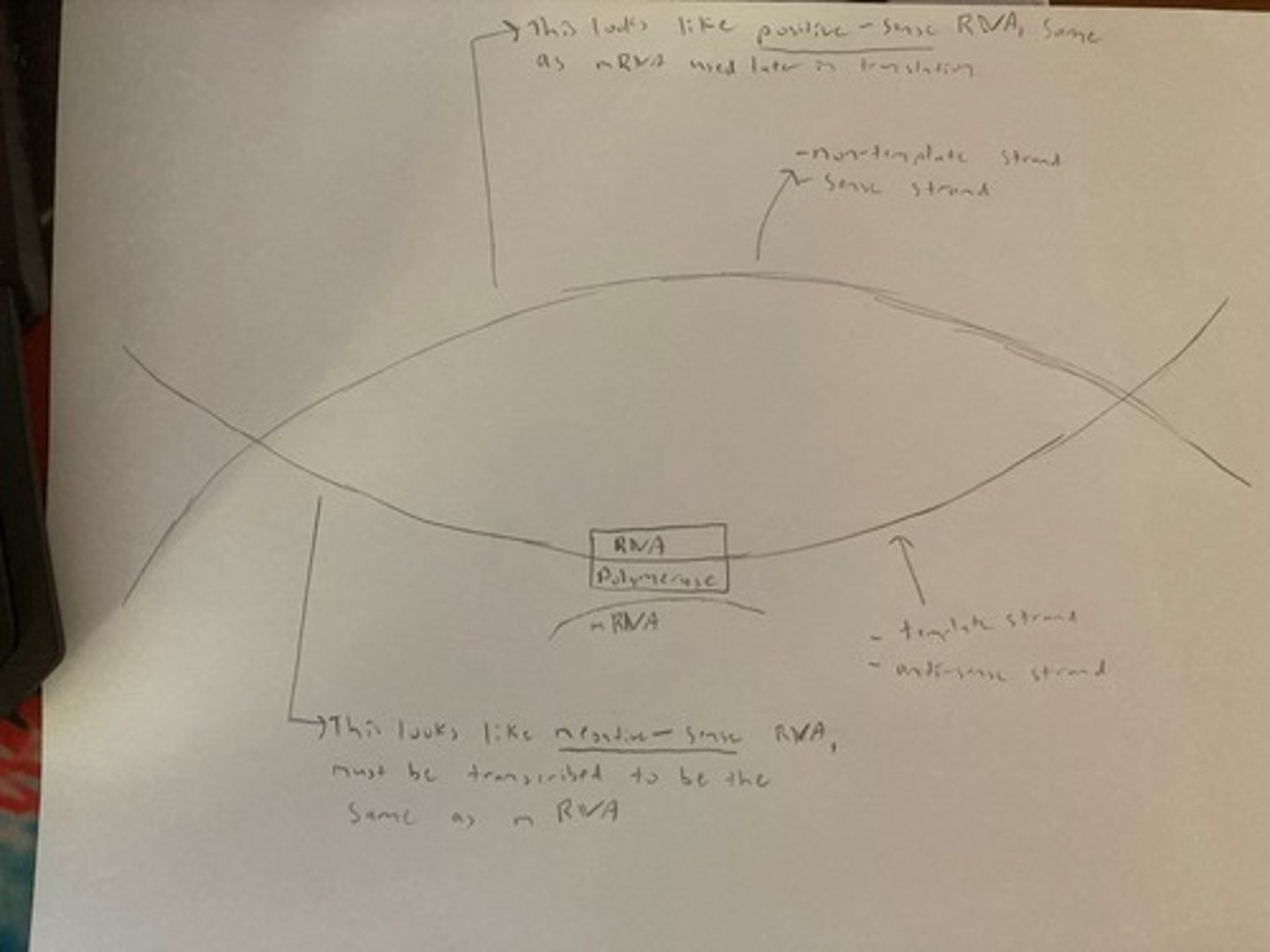
Envelope in Viruses
-Envelope is membrane acquired during lysis, or bursting process
-Takes plasma membrane of animal cell host
-helps make contact w/ other hosts (b/c looks similar to disguise itself)
Enveloped Viruses
Infect Animal cells
Non-enveloped Viruses
Infect bacteria or plant cells
Lose envelope as break through cell wall
Bacteriophage Lambda Characteristics (5)
Type: DNA Virus
Envelope: Non-envelope
Genetic Material: one double-stranded, positive & negative sense DNA (AKA regular DNA)
32 Genes code for 29 proteins, 4 enzymes
Features: can engage in lytic and lysogenic cycles
Host: Escherichia coli (E. coli)
HIV (human immunodeficiency virus) Characteristics (5)
Type: Retrovirus
Envelope: Enveloped
Genetic Material: Two single-stranded positive-sense RNA (but must be reverse-transcribed)
9 Genes or 15 proteins, 4 enzymes
Features: Contains reverse transcriptase, makes DNA from RNA
Host: Human Helper T Cell
Lytic Cycle Characteristics
Virus is virulent, or kills host, spreads extremely fast from host to host
Disease becomes more severe as it spreads
Disadvantages: Host can produce antibodies to destroy the virus, may kill host to fast and not be able to replicate
Lytic Cycle Process (in Bacteriophage Lambda) (7)
Attachment: proteins on virus tail bind to maltoporin on host's (E. coli) membrane
DNA entry - viral DNA enters host
DNA replication - linear, viral DNA turns circular and replicates
DNA Transcription - mRNA produced
Protein Synthesis - Host ribosomes synthesize viral proteins, head and tail proteins self-assemble into capsid
Lysis - Viral proteins puncture host's cell wall
Spread - Host bursts, releasing about 100 viruses
Lytic Cycle Process Image
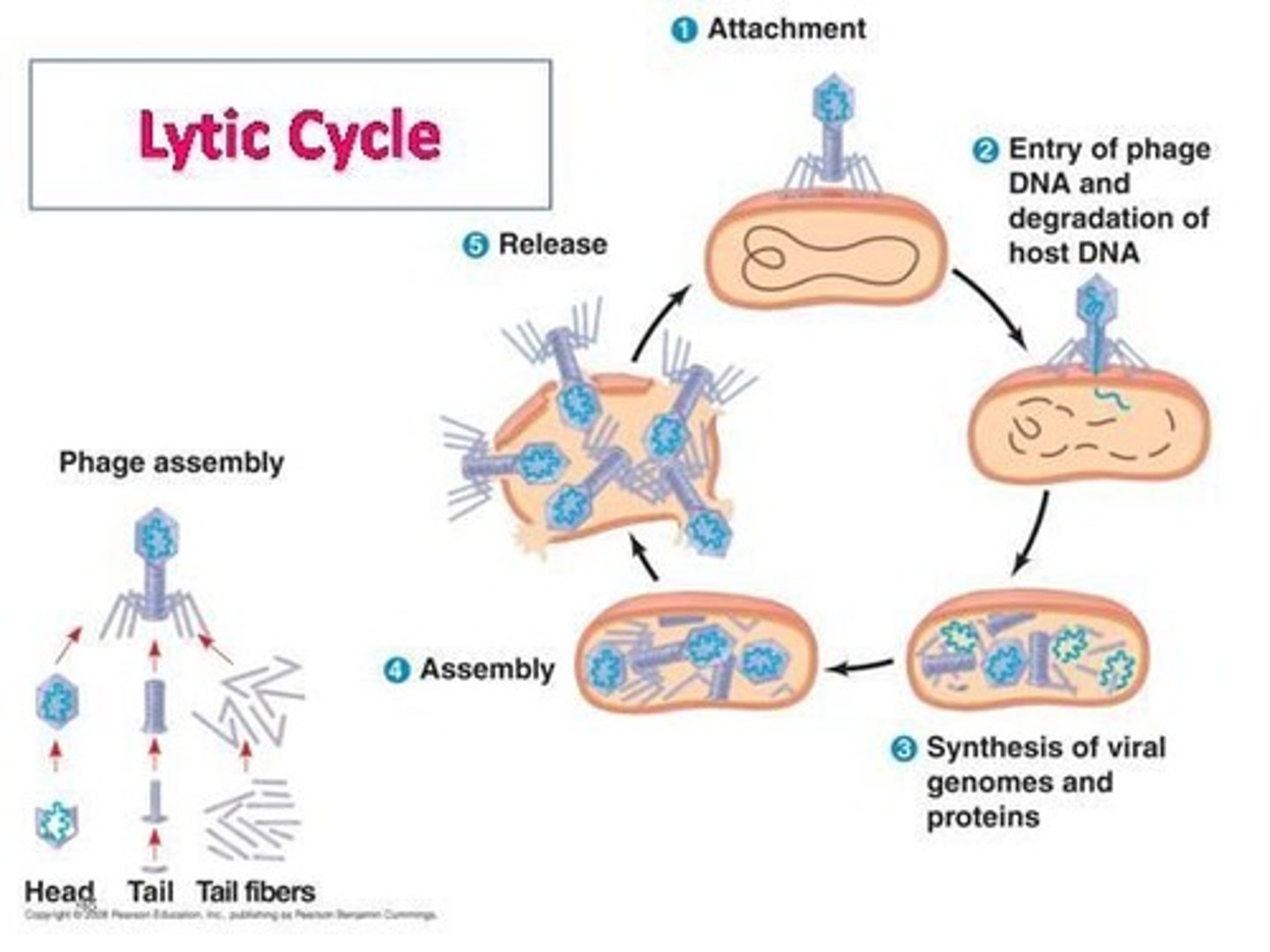
Lysogenic Cycle Characteristics
Virus is temperate, so host is not destroyed
-remains this way until lytic cycle induced, this occurs when a stimulate activates viral genes
Benefit to Host: due to prophage (viral + bacterial DNA), new host can receive previous host's DNA
-this increased bacterial genetic diversity
*Typically used w/ hosts w/ longer lifespans so the virus doesn't go through the host population too quickly and kill off all it's potential hosts*
Lysogenic Cycle Process (in Bacteriophage Lambda (4)
Attachment, DNA Entry (same as Lytic)
Integration - linear, viral DNA turns circular
-enzyme Integrase inserts DNA into specific location in bacterial DNA
-now viral DNA only exists as prophage, or part of bacterial DNA
Cell Division: bacterial cell divides as normal, and prophage (viral genes) copy as well
Lysogenic Cycle Image
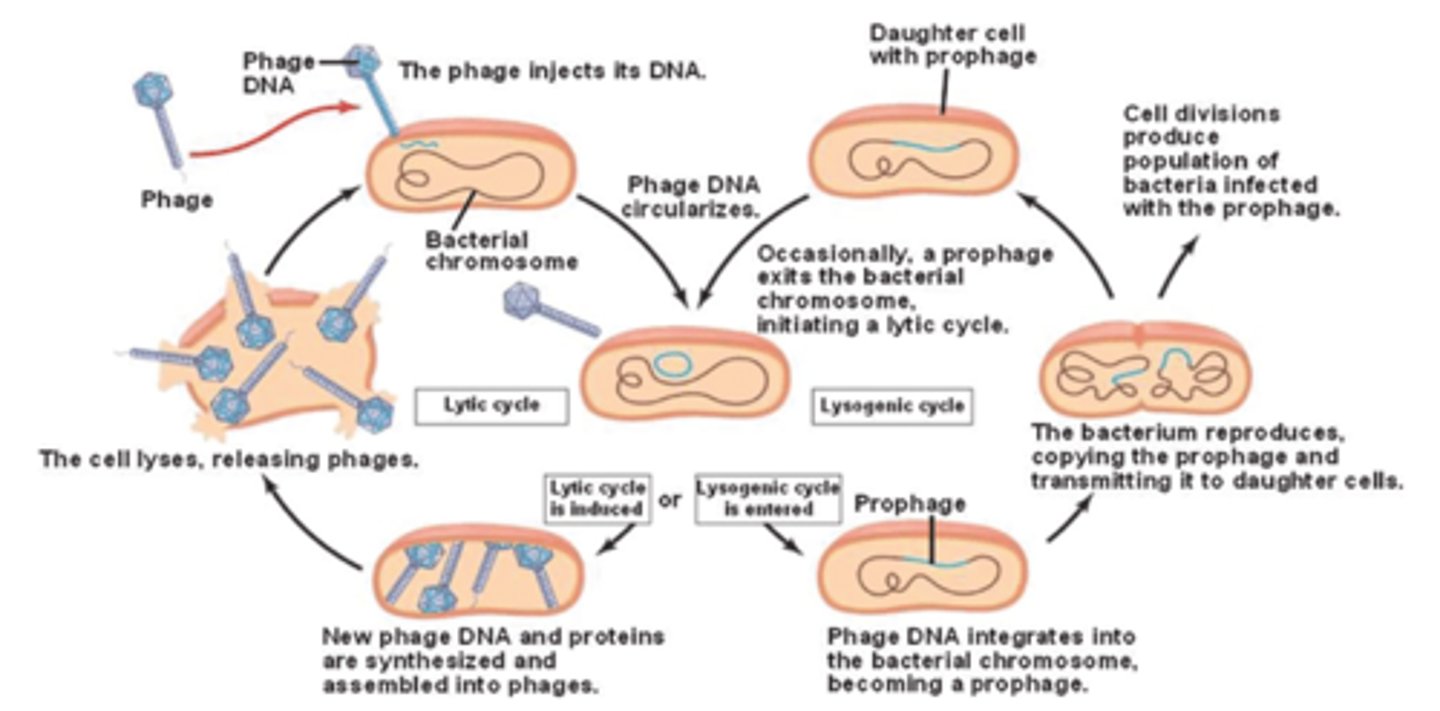
Viral Evolution
Viruses must have evolved from cells
Viruses evolved through convergent evolution (not common ancestor)
-bc high structural and genetic diversity suggests multiple origins
Obligate Parasite
What a virus is, means that it requires a host to replicate
Progressive Hypothesis
Viruses developed from cells via modification
Evidence: cells contain virus-like components such as retrotransposons
Retrotransposons
-Sequence of nucleotides common in DNA
-Transcribed into mRNA, then translated into several enzymes
-Enzymes make copies of the transposon DNA in reverse transcription (similar to revers transcriptase)
-Transposon copies inserted into various chromosomes at random places, similar to HIV, a retrovirus
*basically just copies DNA to RNA, then back to DNA and put in random place*
Regressive Hypothesis
Virus developed from cells via loss (basically just remove everything unnecessary in cell)
Evidence: Viruses vary regarding complexity and self-reliance
-ex. some larger/complex viruses (smallpox) perform host functions
Rapid Evolution of Viruses Causes (3)
Quick Generation Time, High Mutation Rate, High Intensity for Natural Selection
Quick Generation Time
Evolution occurs between generations, each virus generation is about 1 hour (very fast)
High Mutation Rate
Variation must exist for evolution, RNA Polymerase doesn't proofread replication errors, leads to lots of variation
High Intensity for Natural Selection
-Host has immune mechanisms for detection and disposal of viruses
-host's antibodies target viruses' antigens
-Viruses w/ new antigens can survive (leads to very fast natural selection)
Influenza Virus Characteristics
Enveloped virus w/ negative-sense, single stranded RNA w/ a HIGH MUTATION RATE
Transmitted between species
Why does Influenza mutate quickly? (6)
-Genome exists as 8 separate molecules
-Has two antigens on membrane surface:
-hemagglutinin - binds to host
-neuraminidase - used to break free form host
New strain/mutation surfaces if new combinations of genome or antigen evolve
Allows for high potential for a pandemic
HIV (human immunodeficiency virus) Characteristics Part II
Retrovirus w/ reverse-transcriptase that converts single-stranded RNA into DNA
HIGH MUTATION RATE
Why does HIV mutate quickly? (4)
-Reverse transcriptase does not proofread
-HIV affected by cytidine deaminase, enzyme in host that converts cytosine to uracil (relevant b/c viral DNA can be mutated more when incorporated into host DNA)
-env gene - surface protein used to enter host, mutations in it allow it to enter different human cells
-New strain surfaces from any different combinations, leads to resistance to antiretroviral drugs