W3 Measure and Development of Vision
1/16
There's no tags or description
Looks like no tags are added yet.
Name | Mastery | Learn | Test | Matching | Spaced | Call with Kai |
|---|
No analytics yet
Send a link to your students to track their progress
17 Terms
What is amblyopia?
Lazy eye
What is visual development at birth like?
Incomplete- maturation of the visual system is influenced by factors such as prenatal and postnatal nutrition and postnatal visual stimulation
How are abnormalities in visual development caused?
Abnormal visual input such as amblyopia or ocular misalignment leads to abnormalities including abnormal eye growth and neurological changes- if left untreated can lead to long term or permanent visual impairment
How does nutrition play a role in visual development?
Formula containing nutrients like omega-3 and omega-6 may protect non breastfed infants
What do infants see at birth?
Acuity at birth is 6/300, this rapidly improves over the first 6-8 months of age
Why is it important to know what infants see?
To understand medical implications (critical period, amblyopia) and to further understand how the visual system works
What is critical period?
During early childhood and the visual system is highly sensitive to visual experience and can only develop normally if it receives clear, balanced and focused input from both eyes- if not, permanent visual deficits can occur
What may happen if visual deprivation occurs during the critical period?
Amblyopia- lazy eye- factors influencing this include optical errors of the eye, muscle imbalance (strabismus) or other (drooping lids)
When is the critical period for humans?
From shortly after birth and ends around 8 years of age
What is the most well known critical period in infant visual development?
Development of stereopsis- depth perception. The brains learns to integrate and process vision from both eyes, enabling perception of depth and 3D space?
What happens if the development of stereopsis is missed or disrupted?
It can lead to visual impairments such as amblyopia
When does the development of visual acuity occur?
That critical period begins shortly after birth and continues into the first few years of life where infants gradually refine their ability to see fine detail
What are modifications to visual input they may lead to reduced vision?
Optical errors- leading to refractive amblyopia
Eye muscle errors- leading to strabismic amblyopia
Light deprivation- leading to deprivation amblyopia
How do you assess infant vision?
Preferential looking- behavioural measure
Visual evoked response (VEP’S)- electrophysiological measure
OR response to light/tracking object movement
How does preferential looking work?
By recording how an infants eye fixations vary for different stimuli, a researcher can infer what an infant may be able to see
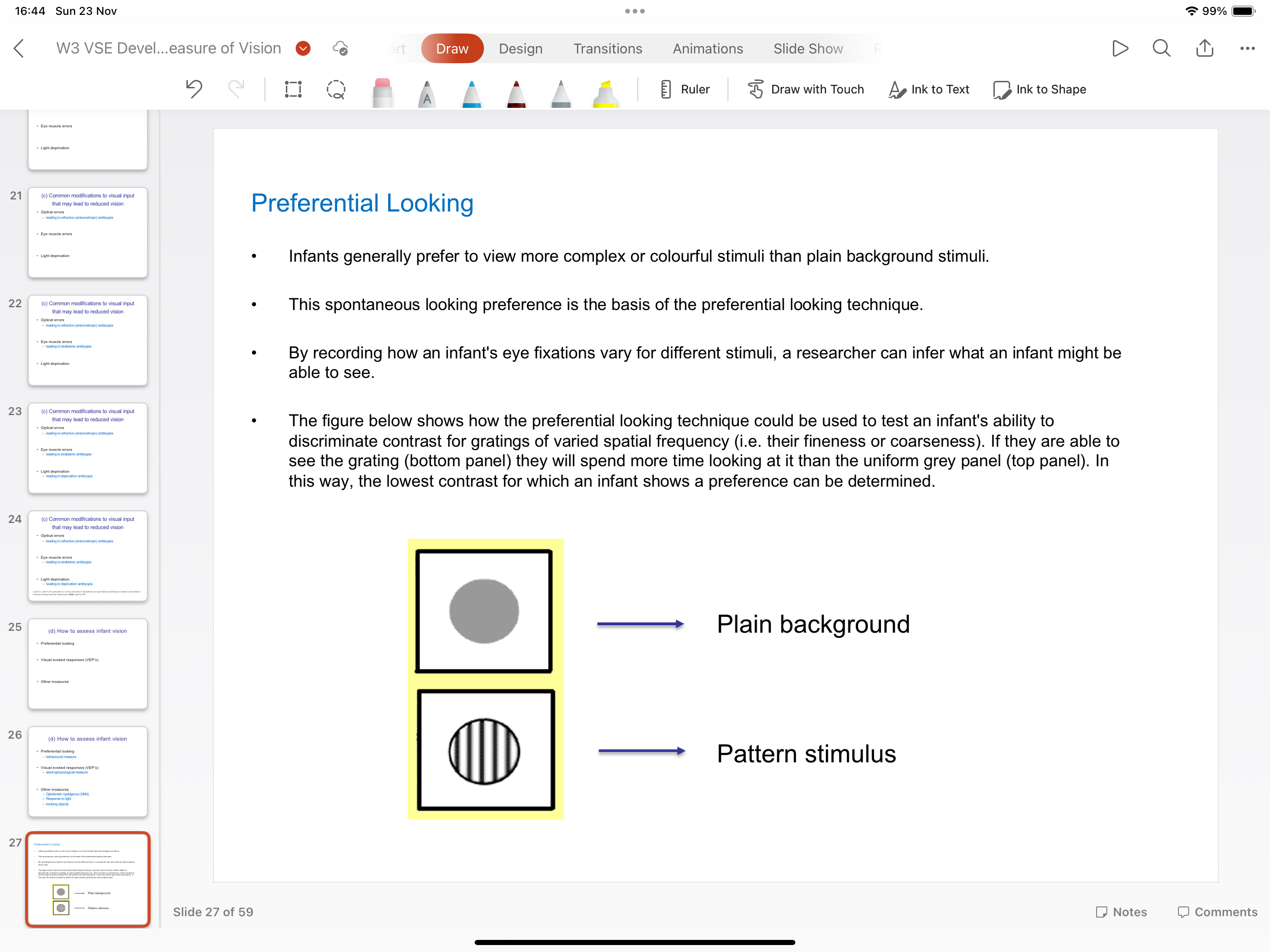
What are the 4 methods of preferential looking?
Visual stimuli- 2 varying stimuli are presented simultaneously with one blank one side by side
Eye tracking- Infants eye/head movements are observed and recording when observing stimuli
Preference measurement- researcher analyses head movement of stimuli- they are unaware of which side of the stimulus is presented
Assessment- if an infant consistently looks at a high contrast striped pattern, researcher can infer the infant has the ability to perceive the pattern