[CC-LAB] Lactate Dehydrogenase and Creatine Kinase
1/74
There's no tags or description
Looks like no tags are added yet.
Name | Mastery | Learn | Test | Matching | Spaced |
|---|
No study sessions yet.
75 Terms
Lactate + NAD ⇌ Pyruvate + NADH
Reaction for Lactate Dehydrogenase
Lactate Dehydrogenase
It is a zinc-containing enzyme that is part of the glycolytic pathway and Krebs cycle.
Four subunits of two possible forms .
(H and M)
Tetrameric molecule of Lactate Dehydrogenase contains ____.
Lactate Dehydrogenase
Referred to as tissue non-specific marker of inflammation.
100 - 255 u/L
Reference Range for Forward Reaction in Lactate Dehydrogenase
[Good to know lang]
80 - 280 u/L
Reference Range for Reverse Reaction in Lactate Dehydrogenase
[Good to know lang]
LD1
LD2
LD3
LD4
LD5
Isoenzymes of Lactate Dehydrogenase
LD1
Fastest Isoenzyme towards Anode of Lactate Dehydrogenase
(Most Negatively Charged)
LD5 > LD4 > LD3 > LD2 > LD1
Migration of Lactate Dehydrogenase Isoenzymes
(Positive to Negatively Charged)
LD2
Highest Concentration in Serum of Lactate Dehydrogenase Isoenzymes
LD2 > LD1 > LD3 > LD4 > LD5
Concentration Levels in Serum of Lactate Dehydrogenase Isoenzymes
LD4 and LD5
Lactate Dehydrogenase Isoenzymes that are cold-labile
Alpha-hydroxybutyric Dehydrogenase (HBD)
Has the same kinetic properties as LD1, but does not act on the substrate lactate.
The substrate used is ketobutyrate instead of lactate
Main difference between Alpha-hydroxybutyric Dehydrogenase and LD1
Rosalki-Wilkinson Method
Method used in measuring Alpha-hydroxybutyric Dehydrogenase
Ketobutyrate + NAD ⇌ Pyruvate + NADH
Reaction for Alpha-hydroxybutyric Dehydrogenase
LD6
Lactate Dehydrogenase Isoenzyme that denotes the presence of the alcohol dehydrogenase enzyme.
Drug Hepatotoxicity
Obstructive Jaundice
Alcohol dehydrogenase is the 6th band in electrophoresis, usually elevated in cases of ____ and ___.
ADD INFO: Another form of LD composed of four C subunits is found in spermatozoa and in semen b
ADD INFO: Another form of LD composed of four C subunits is found in spermatozoa and in semen b
REMEMBER:
REMEMBER:
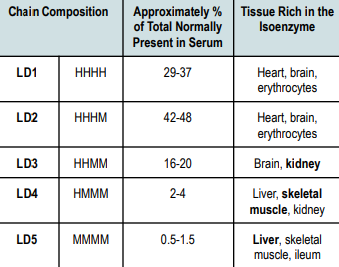
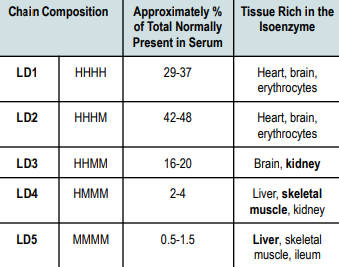
HHHH
Chain Composition of LD1
Heart
Brain
Erythrocytes
Tissue Rich in LD1
HHHM
Chain Composition of LD2
Heart
Brain
Erythrocytes
Tissue Rich in LD2
HHMM
Chain Composition of LD3
Brain
Kidney
Tissue Rich in LD3
HMMM
Chain Composition of LD4
Liver
Skeletal Muscle
Kidney
Tissue Rich in LD4
MMMM
Chain Composition of LD5
Liver
Skeletal Muscle
Ileum
Tissue Rich in LD5
Pernicious Anemia or Megaloblastic Anemia
Pronounced elevation of Lactate Dehydrogenase is observed in ____.
Myoglobin
Troponin I
Creatine Kinase
Aspartate Transferase
Lactate Dehydrogenase
Cardiac Markers (My TropiCAL)
12 to 24 hours
Lactate Dehydrogenase increase at ____ after the onset of AMI.
48 to 72 hours
Lactate Dehydrogenase peaks at ____ after the onset of AMI.
10 to 14 days
Lactate Dehydrogenase returns to normal at ___.
LD Flip Pattern
The concentration of LD1 increases compared to LD2.
Megaloblastic Anemia
Widespread Carcinomatosis (Metastases)
Systemic Shock and Hypoxia
Hepatitis
Renal Infarction
Conditions with Pronounced Elevation (5 or more times normal)
Myocardial Infarction
Pulmonary Infarction
Hemolytic Conditions
Leukemia
Infectious Mononucleosis
Delirium tremens
Muscular Dystrophy
Conditions with Moderate Elevation (3 to 5 times normal)
Most Liver Diseases
Nephrotic Syndrome
Hypothyroidism
Cholangitis
Conditions with Slight Elevation (Up to 3 times normal)
REMEMBER: Serum is preferred for Lactate Dehydrogenase
REMEMBER: Serum is preferred for Lactate Dehydrogenase
Wacker Method (Forward Reaction)
Measures enzymatic activity as lactate is converted to pyruvate
340 nm
In Kinetic for Lactate Dehydrogenase:
Measures the increase in absorbance at ___ nm as NAD is converted to NADH.
Phenazine Methosulfate
Nitroblue Tetrazolium
In Colorimetric for Lactate Dehydrogenase:
Add ____ and ____.
Phenylhydrazone
In Colorimetric for Lactate Dehydrogenase:
Add Phenazine Methosulfate and Nitroblue Tetrazolium to produce ____.
440 nm or 525 nm.
In Colorimetric for Lactate Dehydrogenase:
Add Phenazine Methosulfate and Nitroblue Tetrazolium producing Phenylhdrazone measured at ____ or ___ nm.
Wrobleuski-La Due (Reverse Reaction)
Measures enzymatic activity as pyruvate is converted to lactate
REMEMBER: Wroblueski-La Due is 3 times faster than Wacker
REMEMBER: Wroblueski-La Due is 3 times faster than Wacker
Creatine Kinase
Catalyzes the transfer of phosphate groups from creatine to form creatine phosphate.
Creatine + ATP ⇌ Creatine Phosphate + ADP
Reaction for Creatine Kinase
Magnesium
Thiol Surface
Creatine Kinase requires ___ and ___.
Zinc
Manganese
Creatine Kinase is inhibited by ___ and ___.
Dimeric
(M and B)
Creatine Kinase is a ___ molecule and composed of two different monomers.
Brain
Skeletal Muscle
Cardiac Muscle
Major Tissue Sources of Creatine Kinase
CK-BB (Brain Type)
CK-BM (Hybrid Type)
CK-MM (Muscle Type)
Isoenzymes for Creatine Kinase
95%
____ of total CK activity is derived from CK-MM
2 to 3 hours
Half-life of CK-BB
15 hours
Half-life of CK-MM
12 hours
Half-life of CK-MB
Mitochondrial CK
CK found within the mitochondria of the cell. It does not appear in the circulation unless more severe cellular damage takes place.
CK-BB
Fastest Isoenzyme of Creatine Kinase
Intramitochondrial CK
It is also known as the MtCK or non-muscle/ubiquitous mitochondrial CK.
Sarcomeric Muscle CK
Acts to support structure and contractility of muscle.
4 to 8 hours
Creatine Kinase-MB increase at ____ after the onset of AMI.
12 to 24 hours
Creatine Kinase peaks at ____.
48 to 72 hours
Creatine Kinase returns to normal at ____.
Duchenne’s Muscular Dystrophy
Highest elevation of CK is found in ___.
REMEMBER: CK is not present in Liver
REMEMBER: CK is not present in Liver
Duchenne’s Muscular Dystrophy
Polymyositis
Dermatomyositis
Myocardial Infarction
[Creatine Kinase]
Conditions with Pronounced Elevation (5 or more times normal)
Severe Exercise, Trauma, Surgical Procedure
Intramuscular Injection
Delirium Tremens
Alcoholic Myopathy
Severe Ischemic Injury
Pulmonary Infarction
Pulmonary Edema
Hypothyroidism
Acute Agitated Psychoses
[Creatine Kinase]
Conditions with Mild or Moderate Elevation (2 to 4 times normal)
ADD INFO: Aldolase is progressive muscular dystrophy, CK is Duchenne’s muscular dystrophy.
ADD INFO: Aldolase is progressive muscular dystrophy, CK is Duchenne’s muscular dystrophy.
Increases
Hemolysis falsely ___ Creatine Kinase.
Adenylate Kinase
____ catalyzes a similar reaction as that of Creatine Kinase.
Adenosine Monophosphate
Binds adenylate kinase
Tanzer-Gilbarg
Forward reaction for Creatine Kinase
Oliver-Rosalki or Rosalki-Hess
Reverse reaction for Creatine Kinase