People Society Midterm #2
1/10
Earn XP
Description and Tags
Important People
Name | Mastery | Learn | Test | Matching | Spaced |
|---|
No study sessions yet.
11 Terms
Eric Wold
Creator of Political Ecology, former student of Julian Steward (CE). Created it after seeing the dynamics of land and resource ownership in the Swiss Alps
Gander Frank
An influential figure in urban sociology, known for his research on community development and social change, particularly how urban environments impact social structures.
Wrote about dependency theory, how the Global North made the Global South dependent on them via reorienting their economies to meet European needs (cash crops), and in doing so, limited thier growth.
Wallerstein
Adding a spatial element to Gander Frank’s ideas — world divided into core, semi-periphery, and periphery. Periphery are locked into this role, and cannot break out as Rostow predicted.
Rostow
Modernization Theory: A nation's linear progression from a traditional society to a modern, consumer-driven economy. The stages are: Traditional Society (subsistence agriculture), Pre-Conditions for Take-Off (infrastructure development), Take-Off (rapid industrialization), Drive to Maturity (diversified economy), and Age of High Mass Consumption (consumer-oriented economy).
Gilbert White
1940s, big hazard guy, says it is humans fault because they dont realize its dangerous. Hydraulic infrastructure and technology that are meant to allow people to live in dangerous areas are just bandaids. When something goes wrong, it goes way wrong.
Michael Watts
1980s, claims PE plays a big rolls in hazards, people know about the hazards, but the PE forces them to live there. Two main arguments:
Behavior is shaped by socioeconomic status
Natural events don’t always create disasters (flooding of fields in midwest is good)
Benjamin Chavis
Environmental hazards affect people of color disproportionately
Robert Bullard
Coined the term Environmental Justice in 1990s
Disadvantaged groups often bear the least responsibility, but bear the greatest consequences — Ej is achieved when everyone enjoys the same protection from hazards
Equal participation of all in development/ enforcement of environmental laws.
Jack Hollander
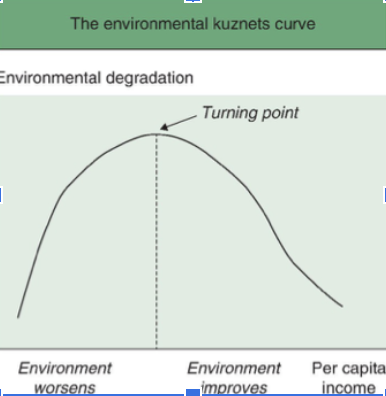
2004 — argues that poor communities should accept pollution industries if they offer opportunities for employment. Makes his case with the Environmental Kuznets Curve.
Cedric J. Robinson
Racial Capitalism: The accumulation of wealth is the goal of capitalism, and this profit is generated by targeting/ exploiting people who suffer from inequality. This is linked to the origins of capitalism through enclosures and the transatlantic slave trade.
Blaike and Brookfield
Linked the marginalization of farmers to the Global North.