4.9 & 4.10 APHG Challenges to Sovereignty and Centripetal/Centrifugal
1/40
There's no tags or description
Looks like no tags are added yet.
Name | Mastery | Learn | Test | Matching | Spaced | Call with Kai |
|---|
No study sessions yet.
41 Terms
devolution
the process by which a country's government cedes power to a sub-national group or area, or an area breaks away and forms a new state
how the internet contributes to devolution
used to disseminate the beliefs of devolutionary groups, attract new members, and communicate with the outside world

how social media contributes to devolution
used to help groups organize protests and communicate quickly during protests

how cell phone video contributes to devolution
used by protesters to show abuses by government forces to gain sympathy for the protesters

supranationalism
when several countries form an organization to achieve common goals and benefits for all the countries

Types of supranational organizations
political, military, economic, or environmental
United Nations
The United Nations (UN) is an international organization formed in 1945 to increase political and economic cooperation among member countries. The organization works on economic and social development programs, improving human rights and reducing global conflicts.

African Union
organization formed in 2002 to promote unity among African states and to foster development and end poverty (replaces the Organization of African Unity (1963-1999)

European Union
an organization of European states that cooperate in trade and political areas and have their own currency

Euro
the basic monetary unit of most members of the European Union (introduced in 1999)

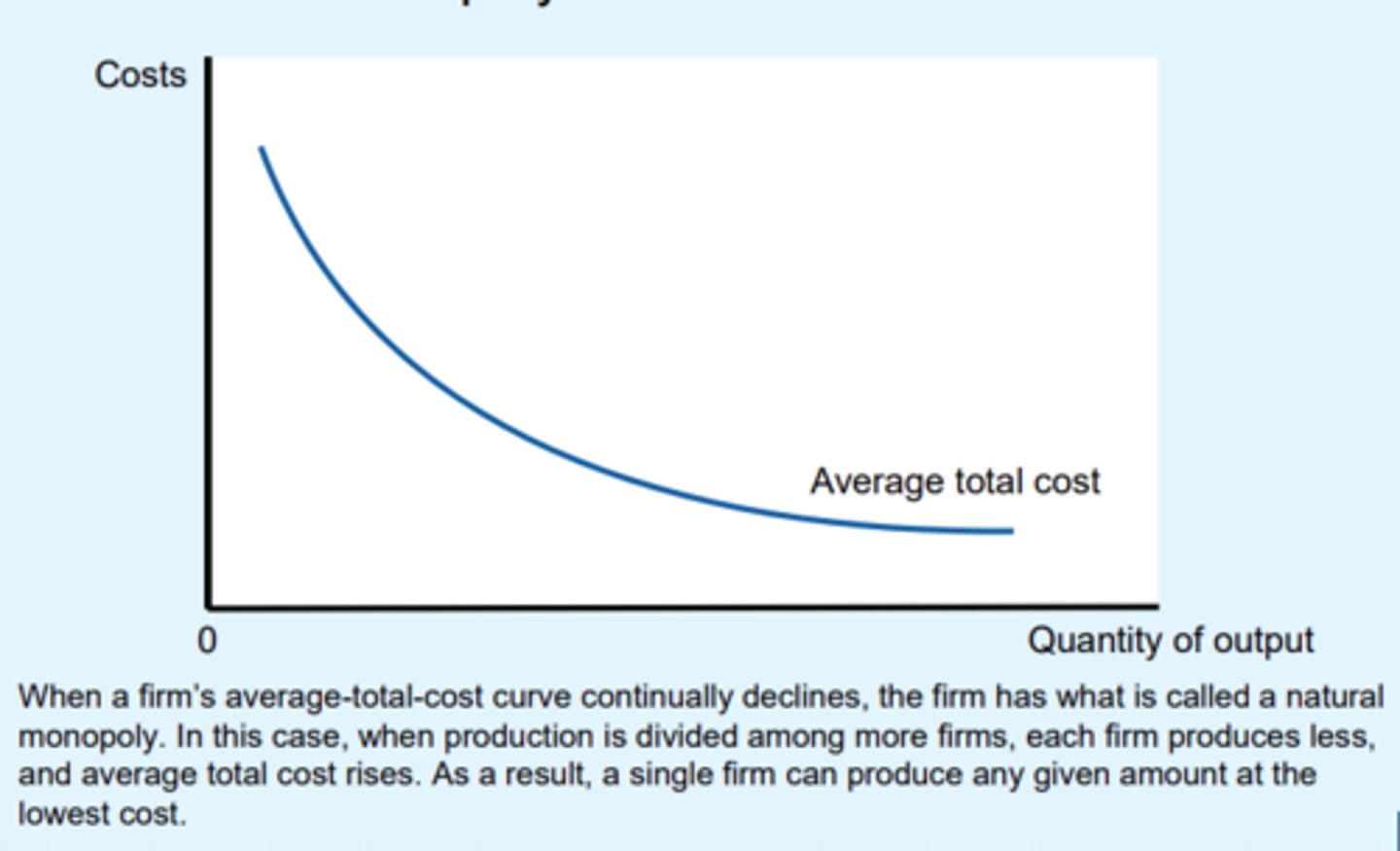
economy of scale
the more you produce, the lower the cost per unit
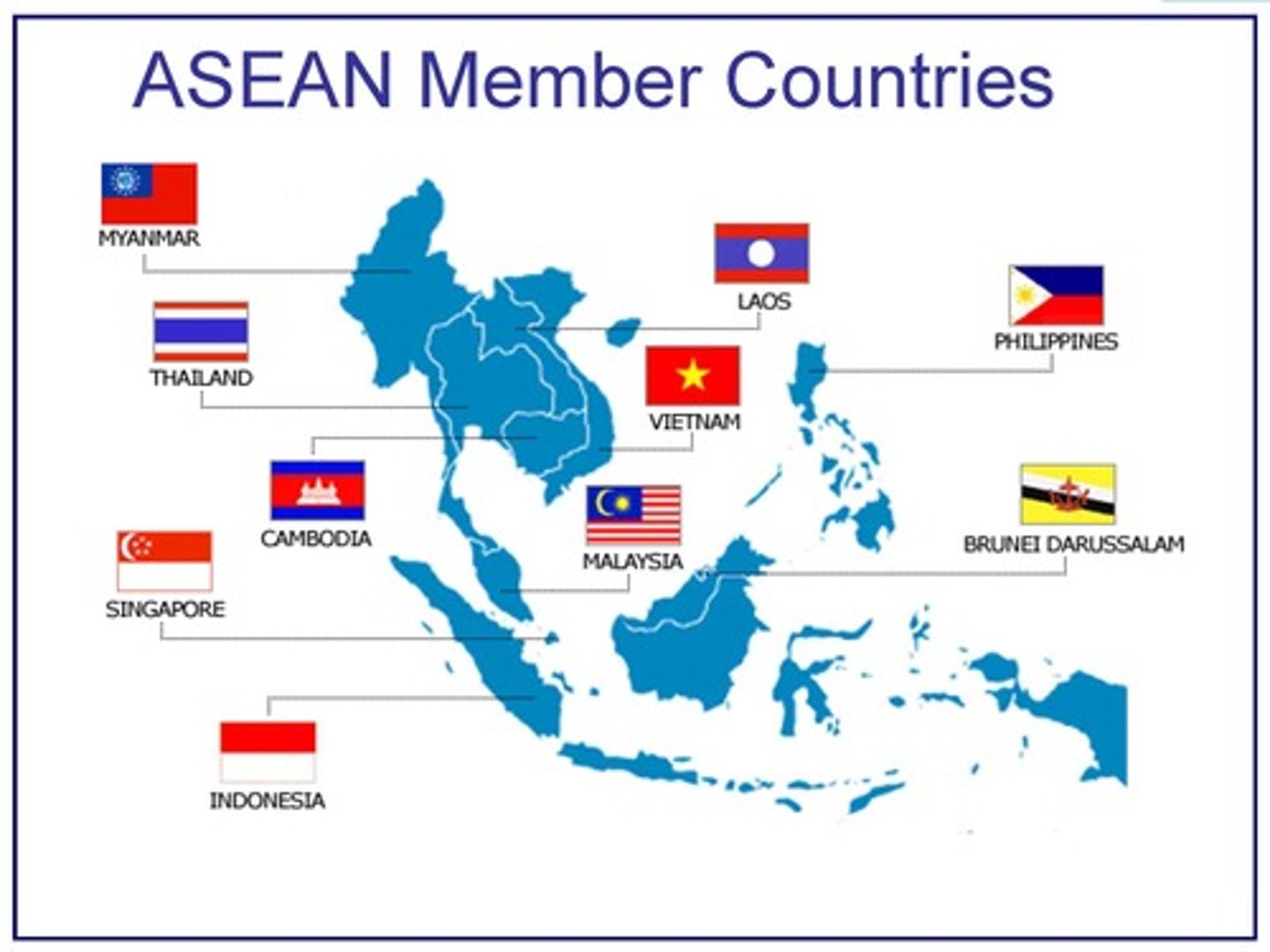
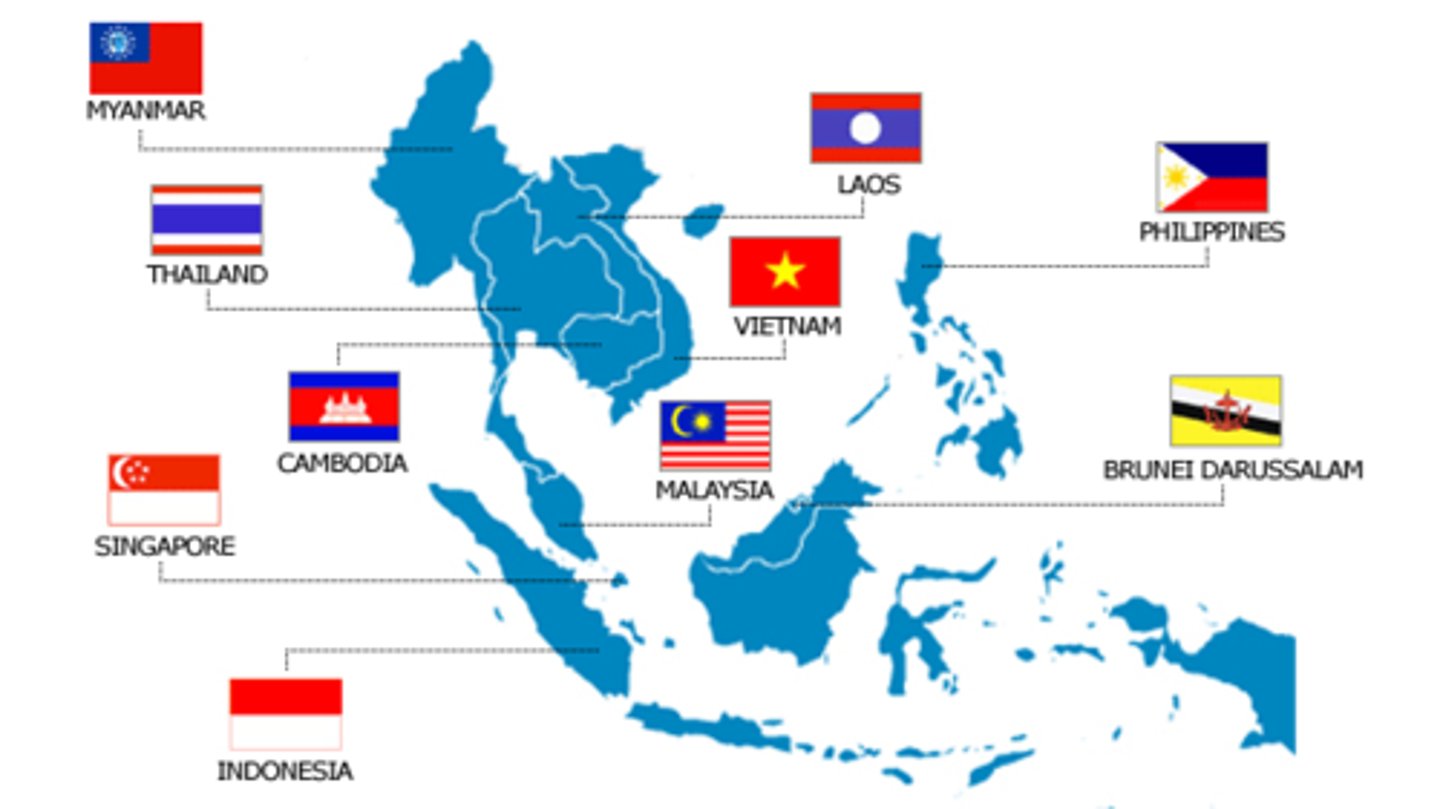
ASEAN (Association of Southeast Asian Nations)
An international organization linking together the 10 most important countries of Southeast Asia
NATO
an international organization created in 1949 for purposes of collective security; includes the US, France UK, and several more western countries
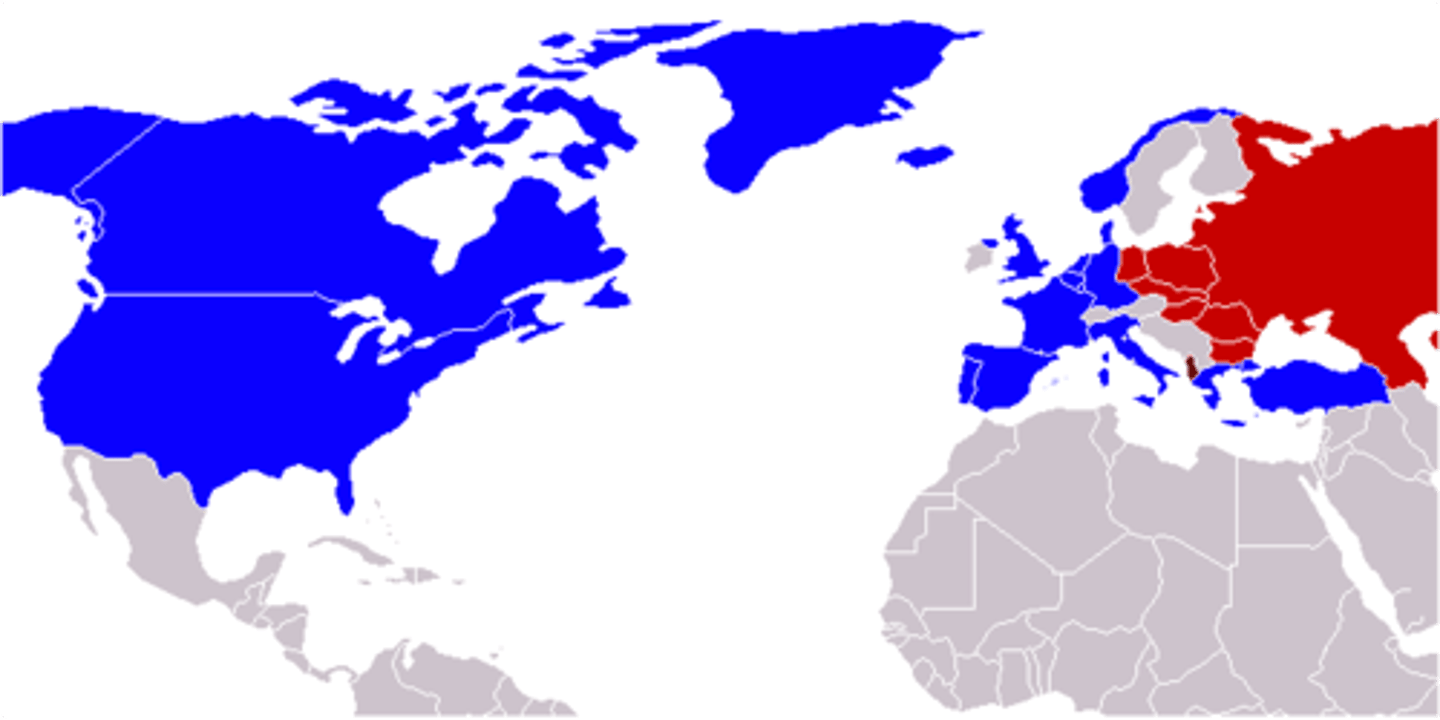
Arctic Council
: A multilateral organization composed of representatives
from the eight circumpolar states (US, Canada, Finland, Norway, Sweden, Russia, Iceland, Denmark) and six indigenous organizations.

Kyoto Protocol
Countries which ratify this protocol commit to reduce their emissions of carbon dioxide.

Brexit
The British Exit from the European Union

free trade
the movement of goods and services among nations without political or economic barriers

OPEC
An organization of countries formed in 1961 to agree on a common policy for the production and sale of petroleum. (Organization of Petroleum Exporting Countries)
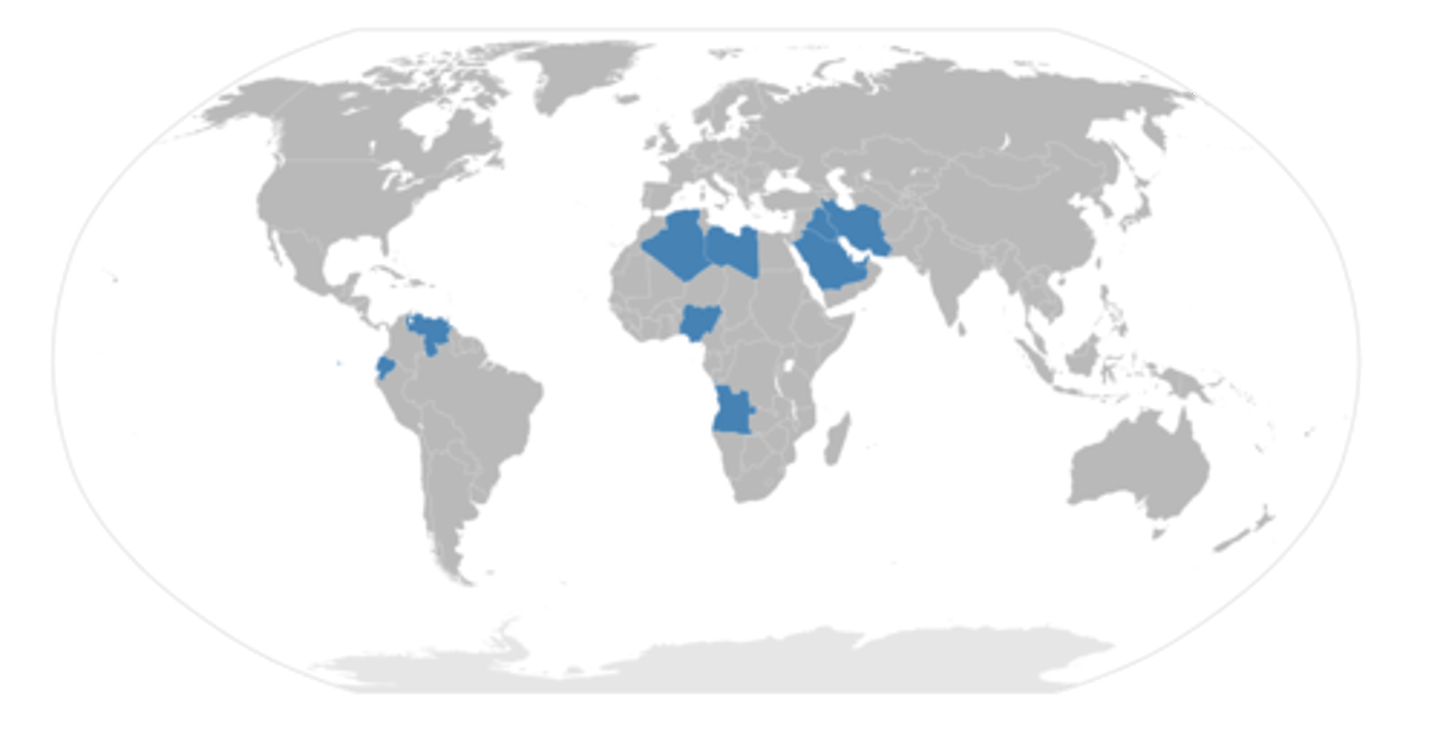
Paris Climate Accord
An agreement within the United Nations to deal with greenhouse gas emissions mitigation, adaptation, and finance starting in the year 2020
Effects of Communication on Supranationalism
connect people and countries faster across time and space; efficiently link countries involved in military alliances; link markets and banks

Effects of Communication on Deomcratization
bring outside information to people in autocratic countries; make it easier for groups to send information and gets support from outside forces.
Economic Supranationalism
countries joined together to cooperate economically

advantages of economic supranationalism
common regulations; lower tariffs; trade more freely withing their trade zone; specialization in certain sectors of the economy
environmental supranationalism
countries join together to cooperate on environmental issues

reasons for environmental supranationalism
work together to set limits for air and water pollution; work together to protect animal species from overharvest or endangerment; work together to manage local environmental issues complicated by political borders

Effects of Supranationalism
countries may have to cede some sovereignty to the organization
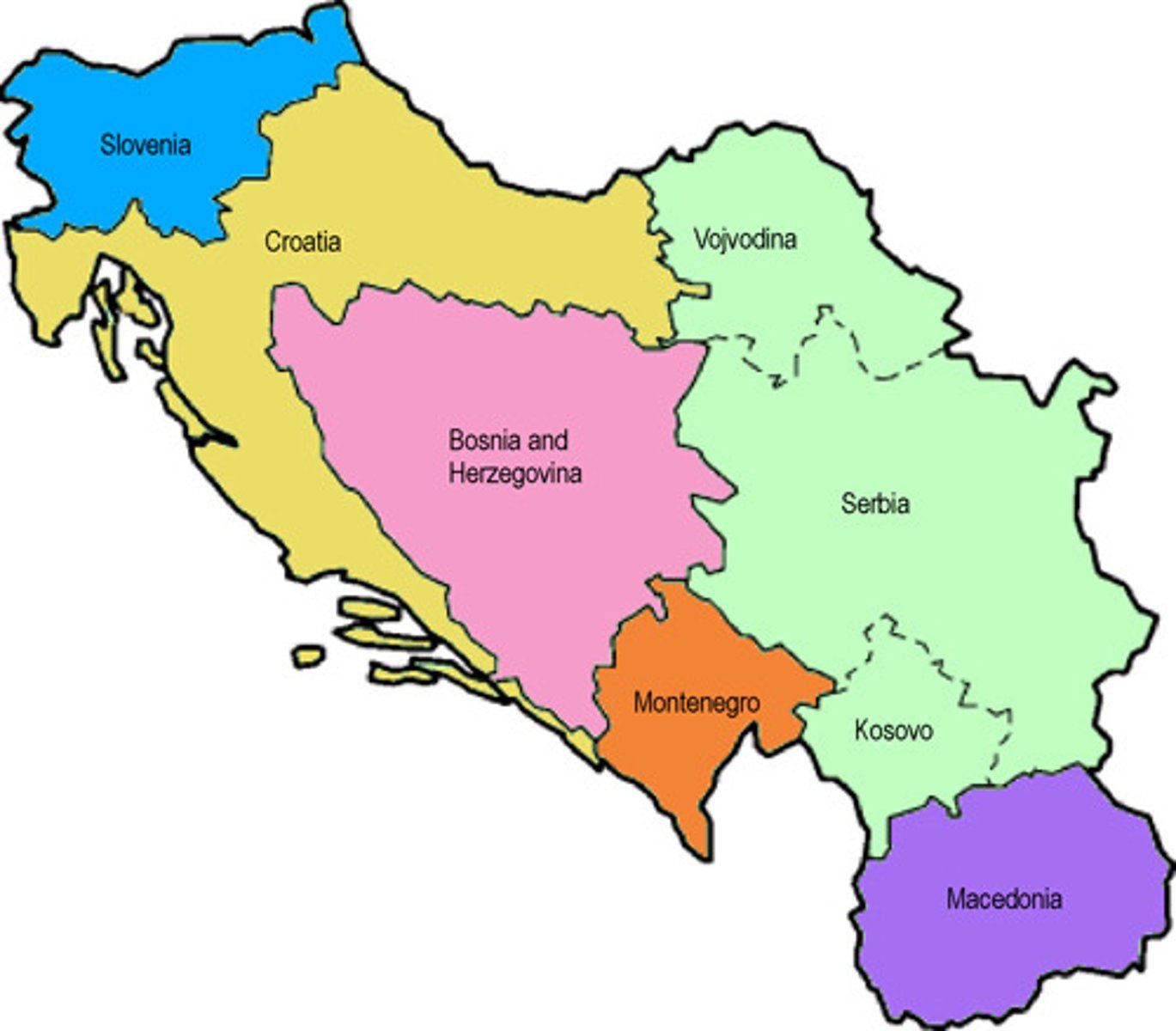
centrifugal forces
Forces that tend to divide a country.
causes of centrifugal forces
multiple ethnicities/nationalities; economic inequality; territorial disputes; lack of infrastructure

consequences of centrifugal forces
failed states; uneven development; stateless nations
failed state
a state whose political or economic system has become so weak that the government is no longer in control.

uneven development
The increasing gap in economic conditions between core and peripheral regions as a result of the globalization of the economy.

stateless nation
A nation that is fighting to establish their own state

Palestinians
A displaced group of Arabs who lived or still live in the area formerly called Palestine and now called Israel
Ethnic Nationalist Movement
a movement devoted to the independence of a cultural, ethnic, or linguistic community.

centripetal force
An attitude that tends to unify people and enhance support for a state

examples of centripetal forces
educational institutions, development of national identity, transportation infrastructure, outside threats to a country; strong national government; common culture

possible consequences of centripetal forces
ethnonationalism; infrastructure development; increased cultural cohesion
ethnonationalism
linking of national identity to a particular ethnicity

Hindu Nationalism
A contemporary religious and political movement that promotes Hindu values as the essential—and exclusive—fabric of Indian society; villainizes Hindus

MAGA
a nationalist movement in the United States that started in 2016 based on the "America First" doctrine of Donald Trump (centrifugal force)

Black Lives Matter
Civil rights movement sparked by a series of incidents of police brutality and lethal force against people of color. Became a centrifugal force in the summer of 2020
