Pre-Clinical Pediatric Dentistry- Combined
1/573
There's no tags or description
Looks like no tags are added yet.
Name | Mastery | Learn | Test | Matching | Spaced | Call with Kai |
|---|
No analytics yet
Send a link to your students to track their progress
574 Terms
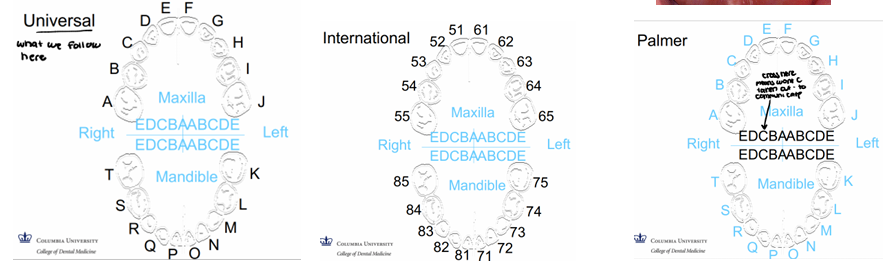
numbering systems
-Palmer used in ortho
-Universal system used most commonly
eruption of primary dentition
-teething
-drooling, desire to bite or chew, mild pain/discomfort
-no evidence of high fever, diarrhea, or sleep problems → pick up disease from more frequently putting hands/items in mouth
-permanent teeth develop lingual/palatal to primary dentition
-posterior permanent teeth develop in furcations
eruption patterns of primary teeth
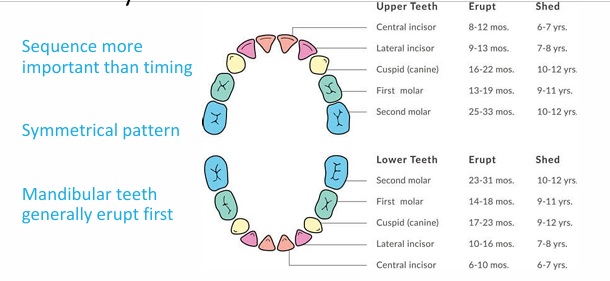
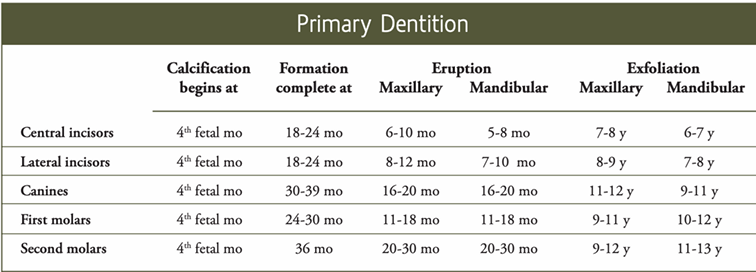
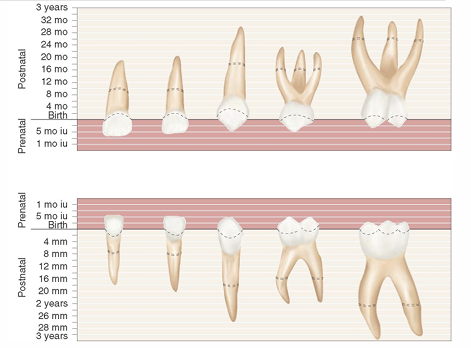
primary dentition calcification, eruption, exfoliation
common eruption findings- eruption cyst
-fluid accumulation within a follicular space of an erupting tooth
-no treatment needed
-will rupture on their own
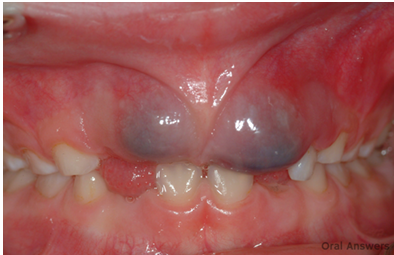
common eruption findings- eruption hematoma
-eruption cyst where blood fills the follicular space
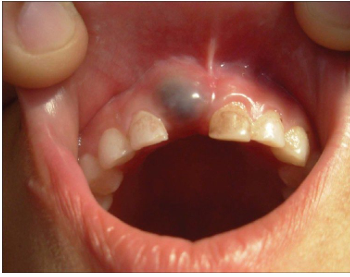
common eruption findings- ectopic eruption
-see especially in mandibular teeth (most commonly anterior)
-assess mobility of primary teeth, encourage child to wiggle, watch and wait approach
-more concerning in maxilla → can lock teeth into an anterior crossbite due to lack of tongue force/strength pushing into occlusion
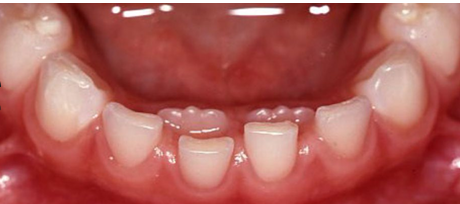
permanent dentition calcification, crown completion, root completion, eruption
crown of primary teeth
-shorter
-narrower occlusal table
-constricted in cervical portion
-thinner enamel and dentin layers
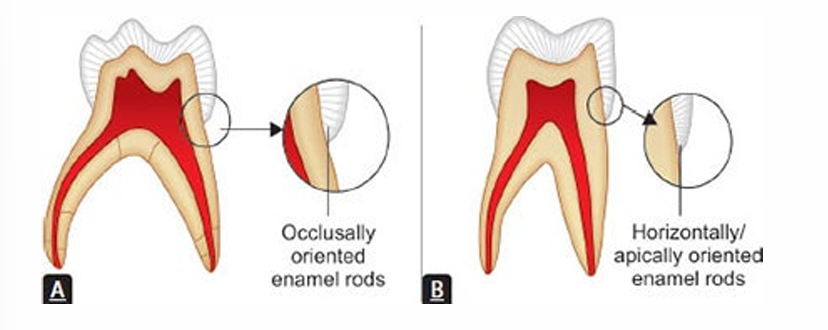
-enamel rods in the cervical area directed occlusally (opposite of permanent dentition)
-broad and flat contacts
-color usually lighter
-prominent mesio-buccal cervical bulge seen in primary molars
-incisors have no developmental grooves or mammelons
crown of primary teeth- posterior teeth
-microscopically, enamel rods slope occlusally
-compared to permanent dentition where enamel rods are perpendicular or slope apically
-won’t have unsupported enamel in preps as with permanent dentition preps → less use (if any) of hand instruments
primary crown anatomy- mandibular incisors
-mandibular central incisors: symmetrically flat when viewed from buccal, crown about 1/3 length of root
-mandibular lateral incisors: similar form to central, usually longer, incisal edges slopes towards distal and DI angle more rounded
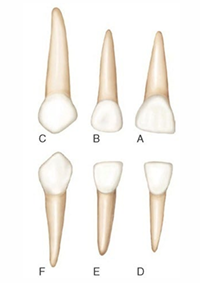
primary crown anatomy- maxillary incisors
-maxillary central incisor: only tooth that has a greater mesiodistal width than height
-maxillary lateral incisor: similar form to central, smaller and DI angle rounded
primary crown anatomy- canines
-maxillary canine: crown constricted at cervical region, well-developed, sharp cusp, long root
-mandibular canine: similar form to maxillary, crown shorter and narrower labiolingually
primary crown anatomy- first molars
-maxillary first molar: unique appearance, 3 cusps- MB/DB/Lingual, prominent MB cervical bulge
-mandibular first molar: unique in appearance, 4 cusps- MB/DB/ML/DL, prominent MB cervical bulge, transverse ridge
primary crown anatomy- second molar
-maxillary second molar: resembles permanent maxillary first molar but smaller
-mandibular second molar: resembles permanent mandibular first molar but smaller
pulp of primary teeth
-relatively larger
-pulp horns closer to outer surface
-great variation in size and location
-mesial pulp horn is higher
-form of the pulp follows the external anatomy
-usually a pulp horn under each cusp
roots of primary teeth
-roots of anterior teeth narrower mesiodistally than permanent teeth
-posterior teeth have longer and more slender roots in relation to crown size
-molar roots flare more as they approach the apex
-apical foramina may be larger and accessory canals often larger and more numerous
implications of primary tooth morphology
-thinner enamel and dentin leading to faster progression of caries
-high mesial pulp horn to be aware of during restorative procedures
-numerous accessory canals making pulpectomies more difficult and less reliable in primary teeth, especially primary first molars
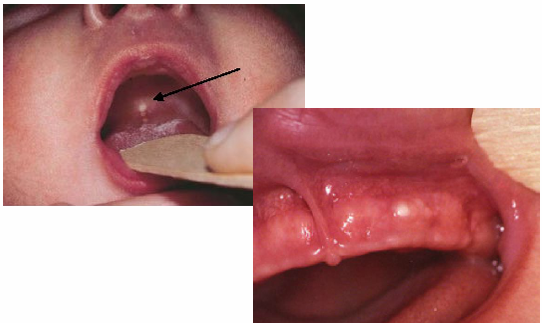
infant oral health- inclusion cysts
-often seen at birth
-Epstein’s pearls: midpalatal raphe, epithelial remnant, no tx
-Bohn’s nodules: side of alveolar ridge, mucous gland remnant, no tx
-Dental lamina cyst: crest of alveolar ridge, odontogenic epithelial remnant, no tx
natal and neonatal teeth
-natal teeth: present at birth
-neonatal teeth: erupts within first 30 days of life
-usually the primary teeth
-no tx indicated unless interfering with feeding or aspiration risk
-if aspiration risk concern: extraction with gauze, practically no force needed
-if feeding interference: can smooth down if necessary
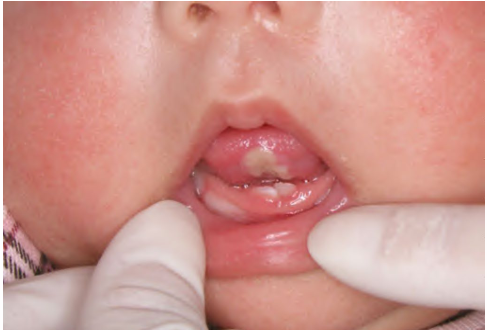
-Riga Fede
-tooth irritating tissue and causing ulceration of tongue
early childhood caries (ECC)
-presence of one or more decayed, missing, or filled tooth surfaces (dmft) in any primary tooth in a child under six
-decay can be noncavitated or cavitated
-missing due to caries (not due to trauma)
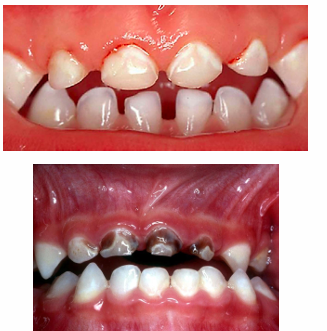
severe childhood caries (S-ECC)
-under 3 years old- any sign of smooth surface caries
-3-5 years old- dmft of 1 greater than the child’s age
caries factors
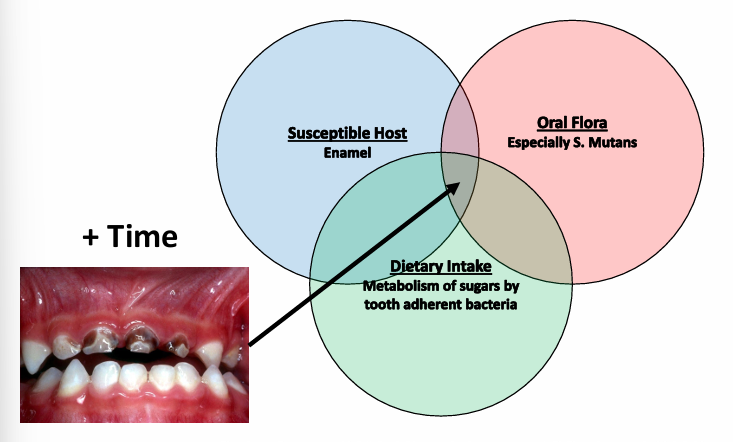
first dental visit
-within 6 months of the first tooth erupting or first birthday- whichever is first
-exam
-caries risk assessment
-toothbrush prophylaxis
-fluoride application depending on risk
-**anticipatory guidance
anticipatory guidance
-information provided to child and family about the child’s current oral health and what to expect as the child enters the next phase of development
-teething, eruption, exfoliation, trauma, diet, hygiene, habits
diet/behaviors
-acids produced by bacteria after sugar intake persist for 20-40 minutes
-frequency of sugar ingestion is more important than quantity
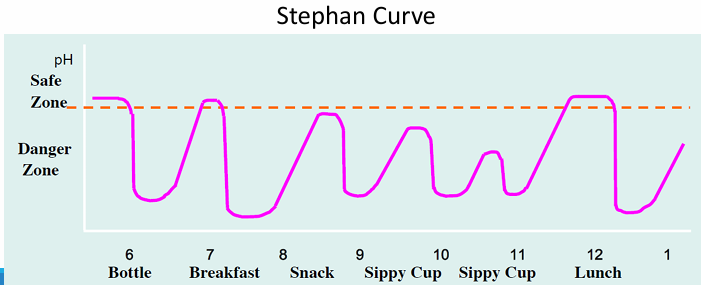
diet
-caries promoted by carbohydrates, which breakdown to acid
-acid causes demineralization of enamel
-frequent snacking promotes acid attack
-foods with complex carbohydrates (breads, cereals, pastas) are major sources of “hidden” sugars
-high sugar content in sodas is a source of substrates
oral hygiene- fluoride toothpaste
-recommend use of fluoride toothpaste twice a day as soon as first teeth begin to erupt
-”smear” <3 years old
-”pea size” 3-6 years old
-regular use associated with reduction in caries, relatively greater in higher risk children
-greater effect (prevention) with increased concentration, frequency of use, and supervised brushing
fluoride’s MOA
-topical effect: inhibits demineralization, enhances re-mineralization, antibacterial → concentrates in plaques, disrupts bacterial enzyme systems
-systemic (weaker evidence): improves enamel structure, reduces acid solubility, improves tooth morphology
sources of fluoride
-public drinking water
-processed beverages and foods (“halo effect”)
-dentrifices
-mouth rinses
-dietary supplements
-fluoride gel
-fluoride foam
-fluoride varnish
water fluoridation
-ideal situation: effective, inexpensive, does not require conscious daily cooperation from patients
-optimal water fluoridation level = 0.7ppm
-62.8% of US population receiving fluoridated water- difficult to go above this, ~25% of population uses well water
-F already in water, more of a F “optimization”- some locations have too much Fl in water naturally
-F supplements should be considered for all children drinking fluoride-deficient (<0.6ppm F) water; all possible sources of F exposure should be considered prior to prescribing (test well water, consider school, other care settings, etc.)
dietary supplement recommendations
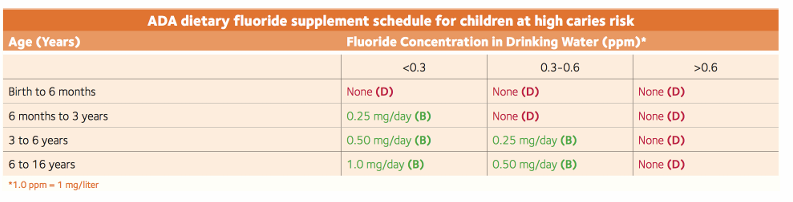
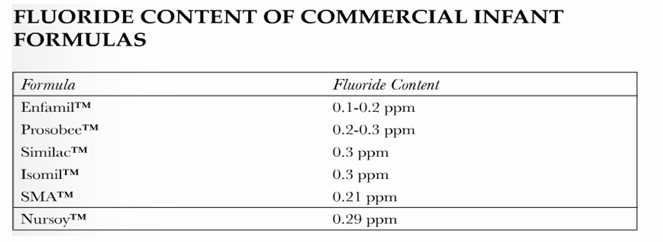
fluoride in infant formula
-recommend using low fluoride or fluoride free water to prepare fluoride
toothpaste
-95% of toothpastes have fluoride
-0.1-0.15% fluoride content (1000ppm-1500ppm); 1g of toothpaste has 1mg of F
-parents must supervise small children
-higher concentration prescription options available: 0.5% F content
mouth rinse
-OTC: 0.05% NaF (1mg/5mL)
-Rx: 0.2% NaF (weekly use; 4mg/5mL)
-indications: orthodontics, radiation therapy to head/face/neck, prosthetic appliances, high sucrose diet, high caries risk
fluoride varnish
-5% NaF varnish- 2.2%F = 22,500ppm = 22.5mg/mL
-applied by healthcare provider every 3-6 months in high risk population
-instructions/recommendations: dry teeth, very small amount used, no eating or drinking for 30min-1hr following application (check manufacturer’s instructions), advise parent and child of film on teeth
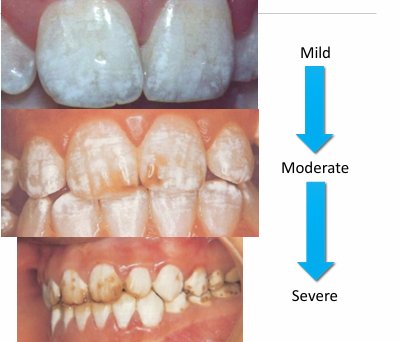
enamel fluorosis
-white-to-brown discoloration of enamel (varies from mild to severe)
-associated with cumulative fluoride intake during enamel development
-increase in prevalence because of increased ambient fluoride
-severity determined by: dose, timing, duration
fluoride toxicity- acute
-probable toxic dose 5mg F/kg
-probable lethal dose 15mg F/kg
-symptoms of overdose: n/v, diarrhea, abdominal pain, seizures, coma, cardiac arrhythmias
-treatment: bind F- <8mg F/kg use milk or activated charcoal and observe for 6hrs, >8mg F/kg use milk and refer for emergency care (gastric lavage, CaCl2, MgSO4)
ingestion of toothpaste
-most OTC toothpaste = 0.243% NaF, 0.15% F, 1100ppm F
-1.1mg of F in 1g of toothpaste
-average amount of toothpaste in smear = 0.1mg, pea size amount = 0.25mg
-tube of toothpaste 4.6oz (130g): 143.3mg of F = probable lethal dose for <9.5kg child (~2 years old), probable toxic dose for <28.6kg child (~8 years old)
risk factors- transmission
-if parents, siblings, etc. have caries, can transmit to pt
-inadequate cleaning of utensils, pacifiers, etc. can pass bacteria associated with caries
non-nutritive sucking habits
-pacifier or fingers
-ideally stop by 3 years
caries risk assessment
-determination of likelihood of incidence of caries during a certain time period or the likelihood that there will be a change in the size or activity of lesions already present
-purpose: focus on tx of disease v. outcome of disease, individualizes treatment plan, focus on prevention, anticipates progression or stabilization of caries
-categories: biological, protective, clinical findings
caries risk assessment forms
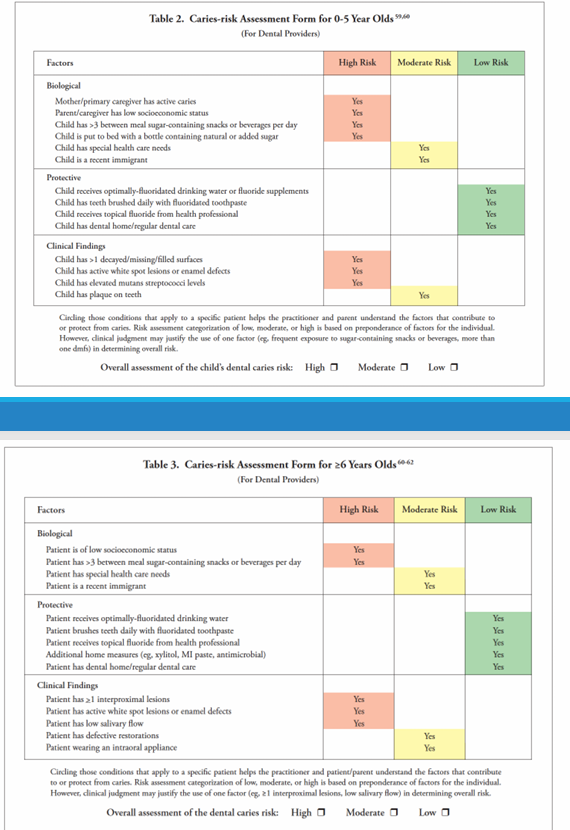
biological risk factors
-in adults, best tool to predict future caries is past caries experience, BUT not as useful in children
-important to determine caries risk before disease manifests
-diet
protective factors
-fluoride
-sugar substitutes: xylitol can reduce levels of S. mutans in plaque and saliva
-tooth brushing: weak relationship between brushing and dental caries reduction, unclear if due to fluoride application or mechanical removal of plaque
-dental home: known benefit of establishing regular dental visits and dental home at an early age
clinical findings
-in young children 0-3, plaque accumulation and white spot lesions are indicative of caries activity and should place them in high risk categories
-elevated S. mutans is most valuable when assessing preschool aged children because it is indicative of when patient is colonized
caries management protocols
-utilize risk assessment tool to aid in clinical decision making
-help provider create a more individualized treatment plan
-individualized treatment and prevention plan
caries management protocol for 1-2 year olds
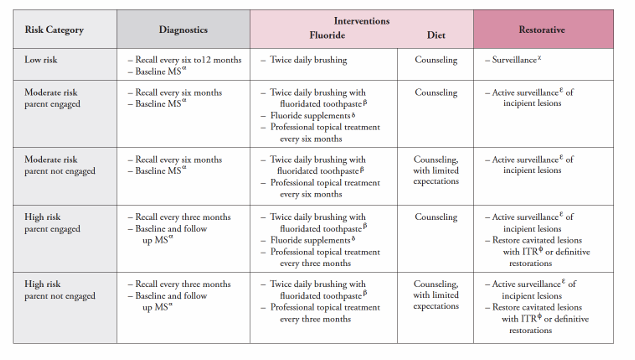
caries management protocol for 3-5 year olds
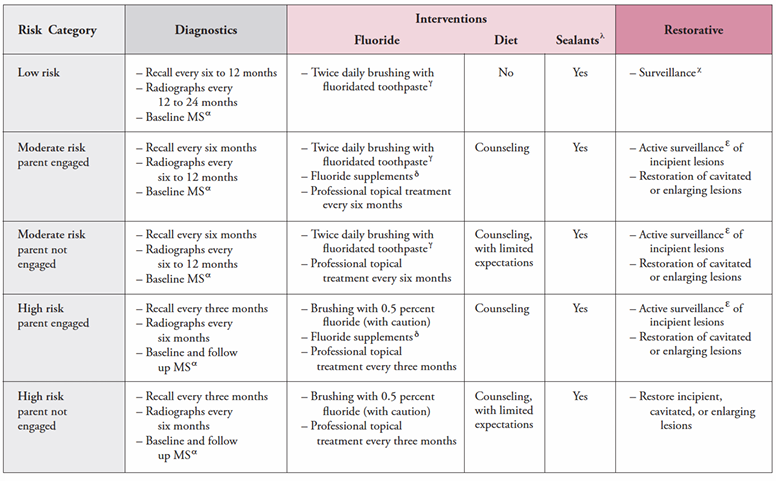
caries management protocol for >6 year olds
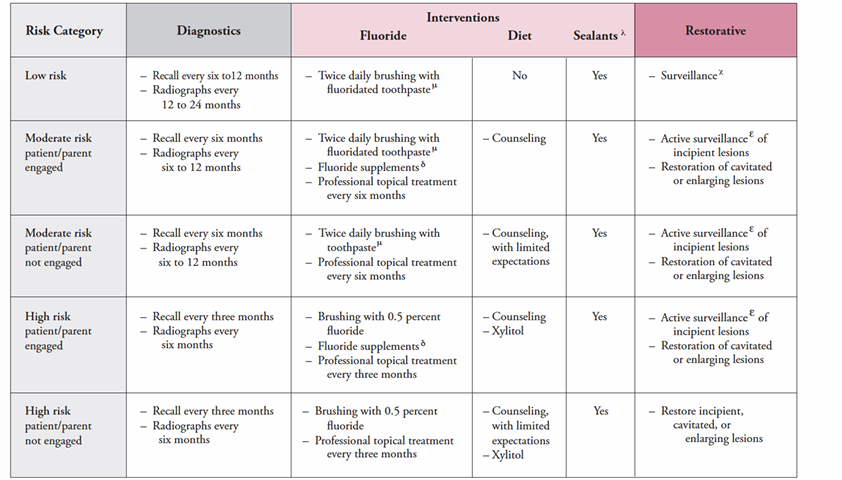
managing dental caries
-old philosophy: surgical intervention is required for all carious lesions
-new philosophy: surgical intervention alone will NOT STOP the disease process- caries management is required with surgical repair
information to collect to create a differential dx and develop tx plan options
-med history: ROS, meds, allergies, sx history
-dental history: previous dental visits (continuity of care), caries experience, trauma, family dental history (caries risk assessment, malocclusion, environmental risk factors, attitudes towards dentistry), oral hygiene practices, diet, fluoride exposure
-clinical exam: intraoral and extraoral
-radiographic exam
-caries risk assessment
radiographic assessment of pediatric patients
-radiographs should be taken based on individual considerations- there is no set frequency that applies to all pts
-considerations in determining radiology prescription:
-risk assessment: caries history, fluoride status, diet
-trauma
-anomalies (supernumerary, missing permanent teeth, mesiodents)
-absence or presence of contacts (kids have generalized spacing→when first permanent molars erupt, they push teeth forward which creates contacts)
-active decay
children should take over brushing at age
-~8
child preparation and management for radiographs
-euphemisms (camera, selfie)
-role models
-contour film- not possible with digital sensors, can damage phosphor plates
-”edge ease” (cushions that go around sensor)
-distraction
-parental help
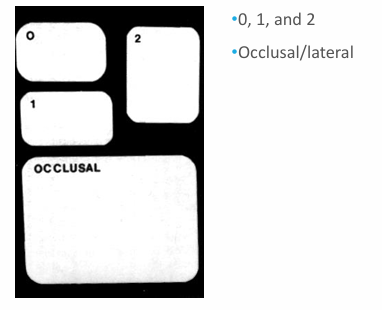
film sizes
-generally use 2 in adults
-0-1 in kids
radiographic tools
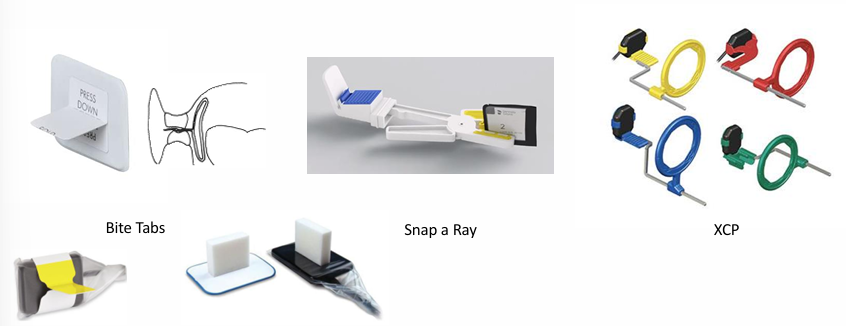
radiographic techniques
-bite wings
-periapicals
-maxillary and mandibular occlusals
-extraoral/lateral film
-soft tissue radiograph
-panoramic radiographs
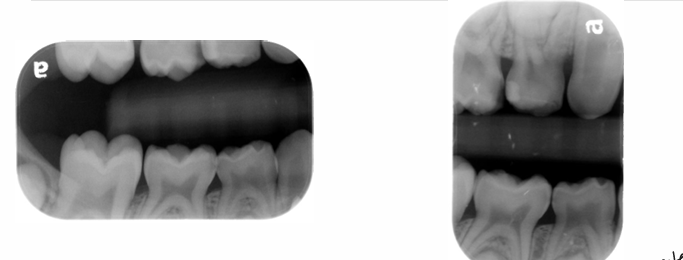
bite wing radiograph
-mesial surface of canine to distal surface of 1st permanent molar
-distal contact of canine to mesial contact of last tooth in arch
horizontal v. vertical bitewing
-vertical easier to tolerate for pts who gag
occlusal radiographs
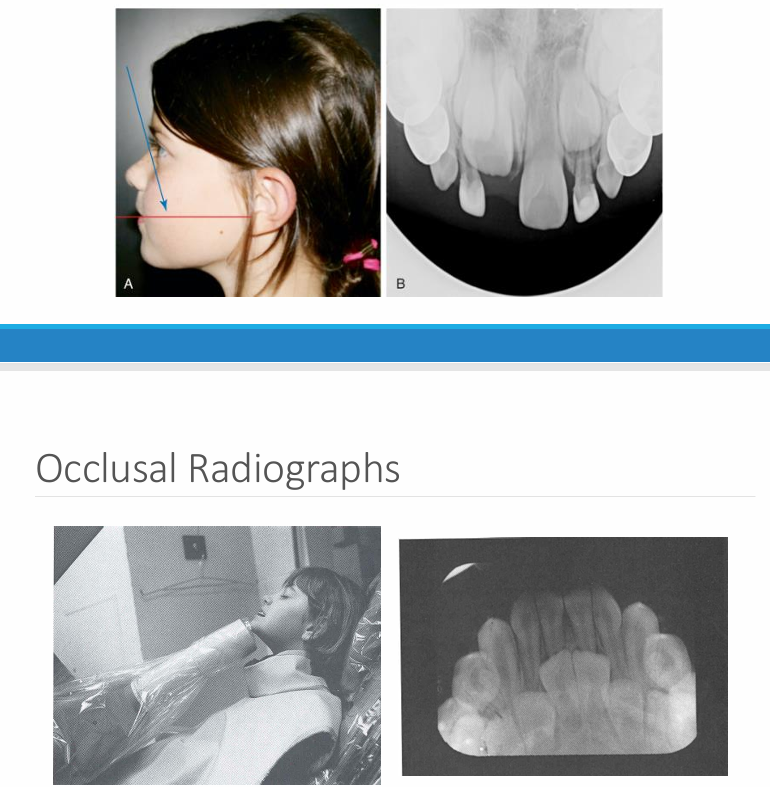
occlusal v. periapical radiographs
-occlusal: can often visualize the whole arch, angulation can vary
-periapical: a section of the arch that shows the whole tooth crown to apex- position film as if taking an occlusal
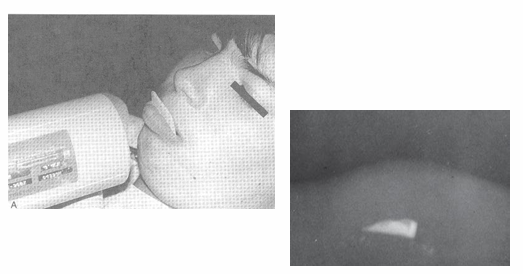
trauma
-soft tissue radiograph
-indicated after trauma to locate piece(s) of fractured tooth
panoramic radiograph
-evaluate growth and development
-take pans in children if unerupted teeth exist that should be erupted
-some practitioners say every 3 yrs starting at age 6
-look at overall development of child
-23, 24, 25, 26, 1st year molars present = good time to take pan
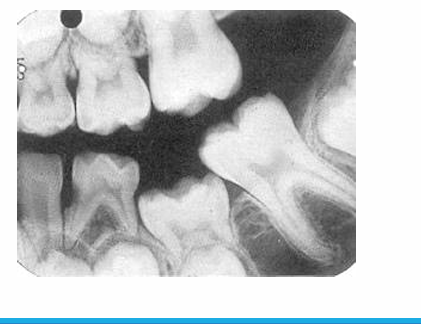
-anomaly: ankylosis
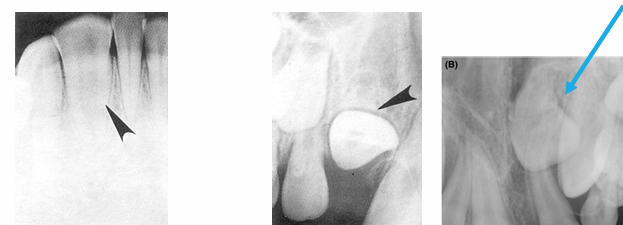
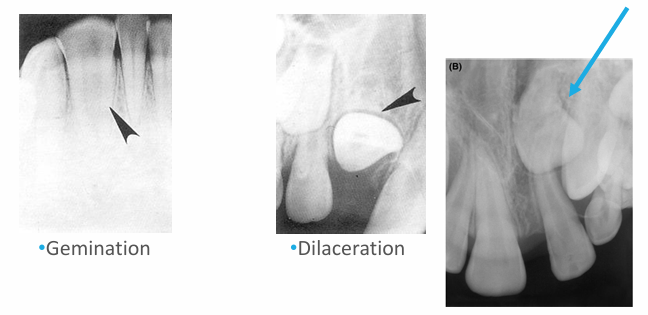
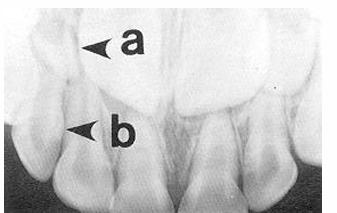
-peg lateral
-supernumerary primary lateral
-count the teeth
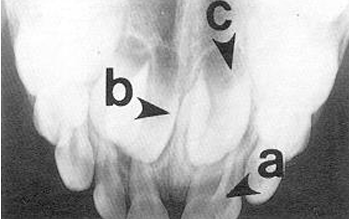
-fusion
-supernumerary tooth
-missing lateral
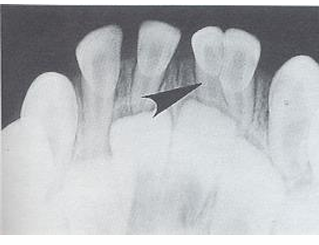
-concrescence: cementum fuses together
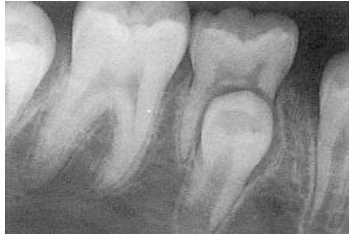
-unfavorable resorption pattern of roots
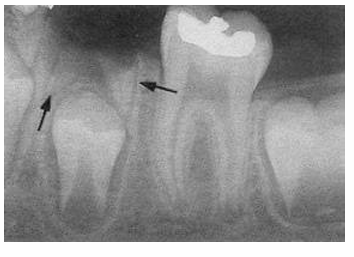
-retained primary root tips
-common in kids with high caries → don’t get tx and teeth just crumble
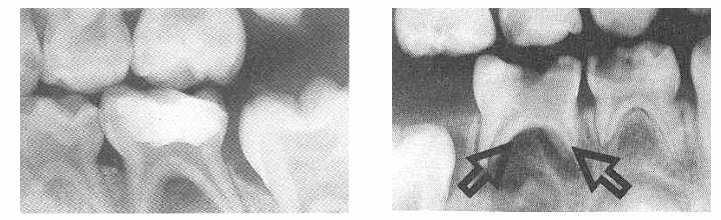
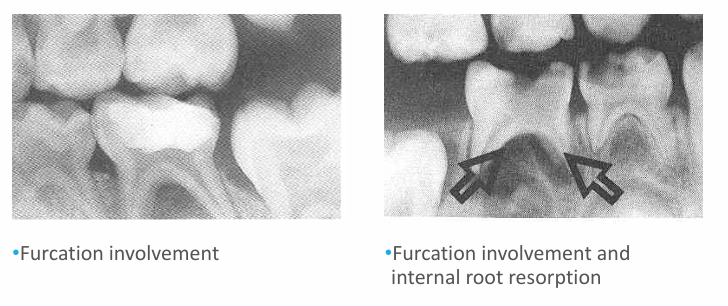
may take ____ demineralization to occur before it will be evident radiographically
-30-70%
dental erosion
-progressive irreversible loss of dental hard tissue that is chemically etched away from the tooth surface by intrinsic and/or extrinsic process that does not involve bacteria
-consequences of dental erosion: lack of enamel, hypersensitivity, discoloration, crazing/fractures, increased wear, restorations
signs of enamel erosion
-broad concavities on cusp tips (mandibular molars)
-smooth silky glazed appearance
-increased incisal translucency
-”raised” amalgam restorations (enamel wears away but amalgam does not)
-loss of surface anatomy in young children
-hypersensitivity
dental erosion as a sign of systemic disease
-bulimia nervosa: lingual surfaces of anterior teeth
-GERD
titratable acidity
-critical pH of enamel = 5.5
-measure of the amount of alkali which needs to be added to an acid in order to neutralize at pH 7.0
-indicates the amount of available acid, both bound and free hydrogen ions; erosive potential of a substance
dental caries
-disease of microbial origin
-communicable
-largely preventable
-described as a “silent epidemic”: 5x more common than asthma
dental caries- bacteria and biofilm
-initiated by pathogenic bacteria- Streptococcus mutans, Lactobacilli, and Streptococcus sobrinus
-formation of a complex structure called biofilms
-dental plaque biofilm: unremoved plaque promotes the caries process
-can explain biofilm as “teeth wearing sweaters”, “sugar bugs”, “sugar bug nest”
early signs of decay
-white spot lesions
-not as visible when dry → become chalky
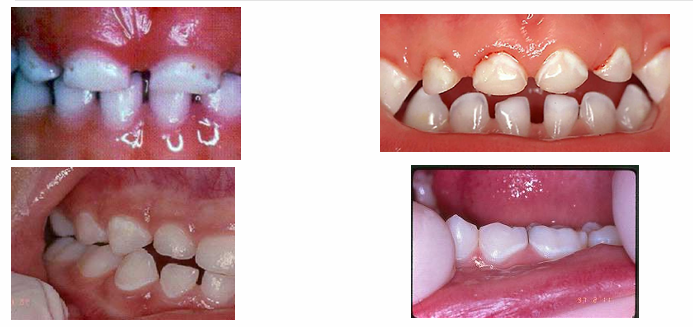
later signs of decay
-enamel breakdown
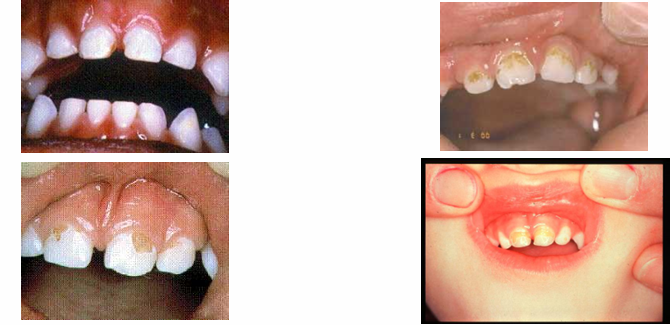
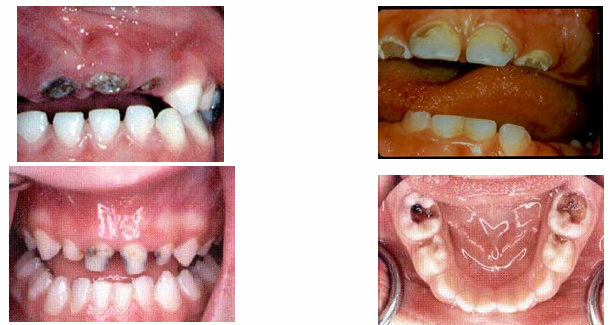
advanced/severe decay
-decay that extends all the way to the gingiva anteriorly or very extensively occlusally in the posterior
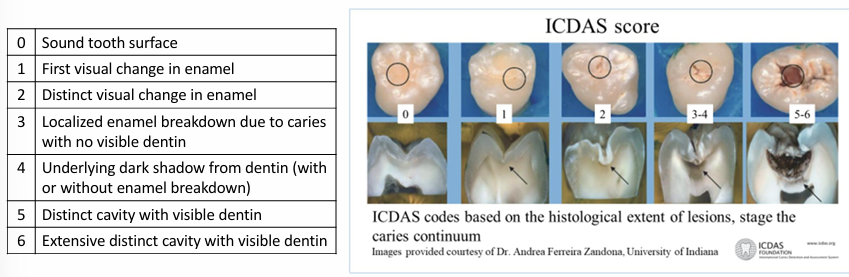
ICDAS score
sequalae of ECC
-extreme pain
-spread of infection
-difficulty chewing
-poor weight gain
-extensive and costly dental treatment
-risk of dental decay in permanent dentition
-malocclusion
-missed school and work days
-impaired language development
-inability to concentrate in school
-reduced self-esteem
-possible facial cellulitis requiring hospitalization
-possible systemic illness
-death
dental infections
-can spread more quickly in children → tissues more compliant
high risk groups
-children with special health care needs
-children from low socioeconomic and ethnocultural groups
-children with suboptimal exposure to topical or systemic fluoride
-children with poor dietary and feeding habits
-children whose caregivers and/or siblings have caries
-children with visible caries, white spots, plaque, or decay
caries prevention- fluoride varnish
-5% NaF or 2.26% fluoride in a viscous resinous base in an alcoholic suspension with flavoring agent
-has not been associated with fluorosis
-application does not replace the dental home or is equivalent to comprehensive dental care
-ensure teeth are super dry before applying- otherwise will just slide off the teeth
additional fluoride exposures
-fluoride mouthwashes, Rx toothpastes and gels
-reservoir in saliva/vestibule → don’t want to eat/drink & have reservoir deplete
caries prevention- flossing
-once a day, preferably at night
-whenever any two teeth touch
dental sealants
-noninvasive procedures
-helps prevent pit and fissure caries (account for almost 80% of all dental caries in children)
-seals deep, narrow grooves
-BEWARE of the poorly placed sealant → can create a plaque trap
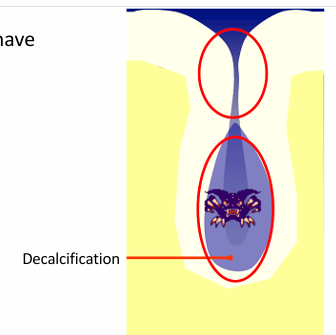
fissures caries model
-once the organic plug fails, bacteria have access to the depths of the fissure
-fissure walls are in close apposition
-unable to detect caries
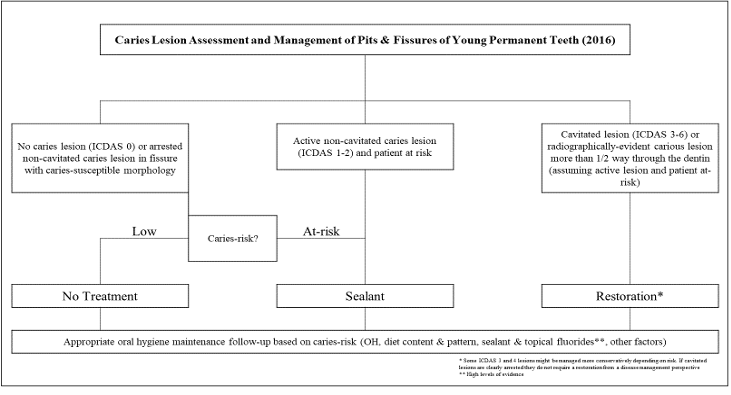
clinical pathway for occlusal surface management
restorative dentistry
-adhesive dentistry: retention and resistance forms of cavity preparation do not apply, therefore more conservative, isolation is CRITICAL (moisture makes composite fail)
-amalgam restorations: follow GV Black’s principles of cavity preparation, less conservative (need bulk of amalgam to ensure success), more forgiving in terms of moisture control
-full coverage restorations: stainless steel crowns, preformed ceramic crowns
-other tools: silver diamine fluoride (SDF)
preventive resin restorations (PRR)
-a single or multiple, small, discontinuous, carious pits or fissures
-may extend into enamel, dentin, or DEJ
-excavated and restored with resin
-occlusal surface sealed for prevention
composite/resin restorations
-involves the excavation of a single, larger carious lesion followed by restoration with a resin based material
bonding tips
-etch for the appropriate length of time: too long = etch patterns that extend too deeply causing adhesives to not be able to penetrate the demineralized zone; usually 15-20 seconds
-ensure ideal dentin moisture conditions: ethanol adhesives do not require as much moisture, apply indirect air to dry, do not dessicate
-pay attention to application time and technique: watch the clock to avoid counting too fast
-scrub adhesive when recommended by manufacturer: usually scrub dentin to increase bond strength, scrubbing enamel will usually decrease bond strength, treat enamel more delicately and dentin more aggressively
-thin and dry the adhesive properly: gentle air spray at half an inch from the surface
-light cure close to the surface with a compatible light
-first increment of composite in a thin layer (0.2mm)
-thoroughly clean contamination: if contamination during bonding, clean and re-etch for 5 seconds
resin based composites- resin matrix (Bis-GMA) with inorganic filler particles
-filler content: filled v. unfilled, flowable (less filler) v. packable (more filler), anterior v. posterior composite
-particle size: macro, microfilled, and hybrids
-BPA = endocrine disruptor? → scrub top of composite with water
glass ionomer cements
-fluorosilicate glass powder (base) combined with a water soluble polymer (acid)
-set via chemical rxn
-contain fluoride
-Ketac cement, Fuji II or IX, Fuji Triage- used as sealants
resin-modified glass ionomer (RMGI)
-glass ionomers with a light polymerized resin component
-dual cure
-increased mechanical properties
-physiochemically bonds to tooth structure
-biocompatible, moisture
-similar coefficient of thermal expansion as dentin (good dentin replacement material)
-ion leachability- fluoride release (anti-cariogenic)
-minimal polymerization shrinkage