ANTH 103 Final Exam
1/63
There's no tags or description
Looks like no tags are added yet.
Name | Mastery | Learn | Test | Matching | Spaced | Call with Kai |
|---|
No analytics yet
Send a link to your students to track their progress
64 Terms
consanguineal kin
biologically related relatives, commonly referred to as blood relatives (mothers sisters daughter)
affinial relations
Kin relations grounded in cultural conventions
Biological Kin Types
Description of actual genealogical relationships.
- Etic
- Biological
- Universal
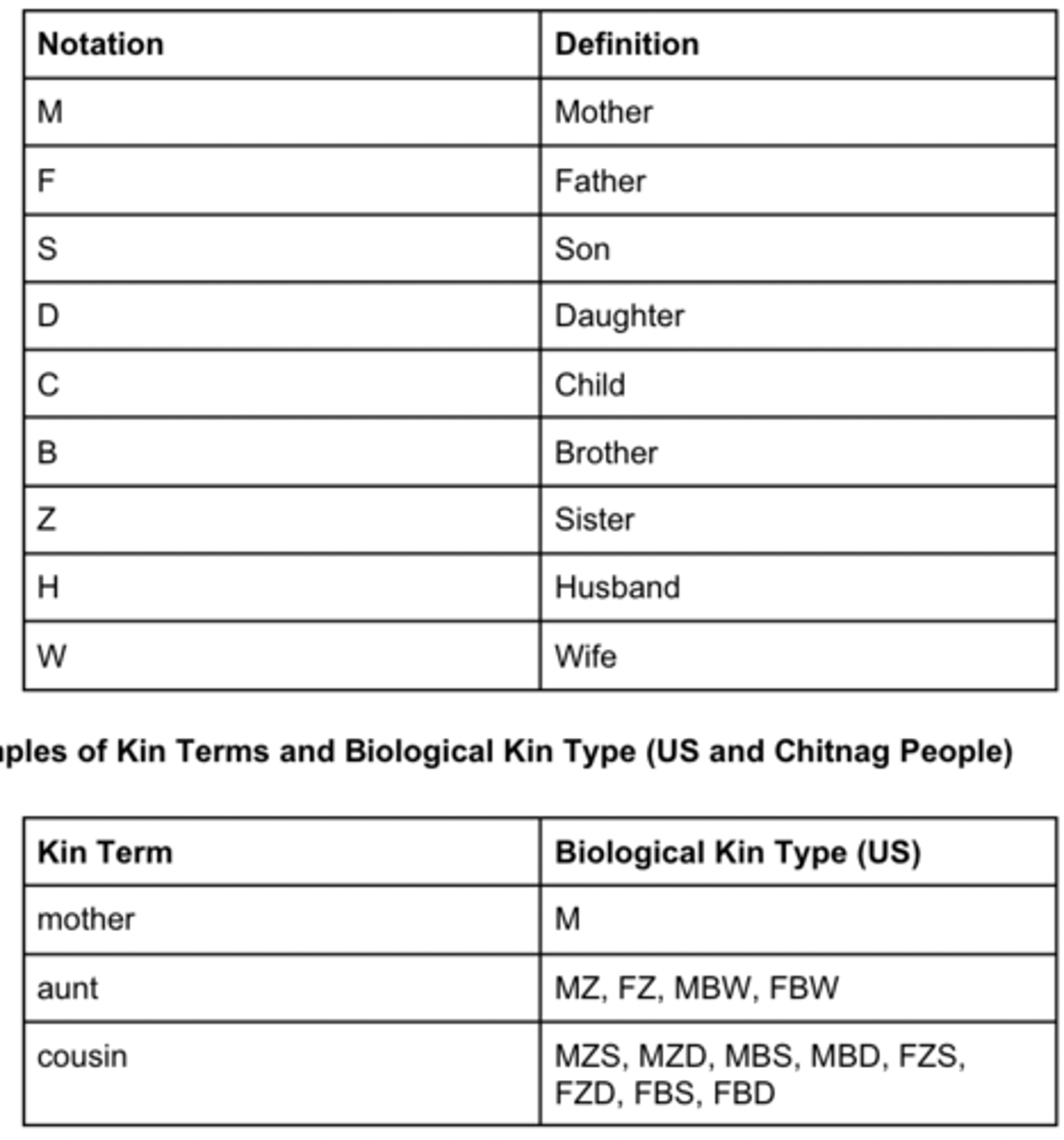
kin terms
How different societies label/classify kin relations
- Emic
- Cultural
Polygyny
One male, several females.

Polyandry
One female, several males.

descent
the system by which members of a society trace kinship over generations
lineage
People who can trace back to a common focal ancestor
- Demonstrated descent: Being able to trace/prove your ancestor or geneology
clans
Lineages that go further back in time, more inclusive, and may include groups of related families.
- Stipulated descent: Not being able to prove your relation to a common ancestor, but claiming it nonetheless.

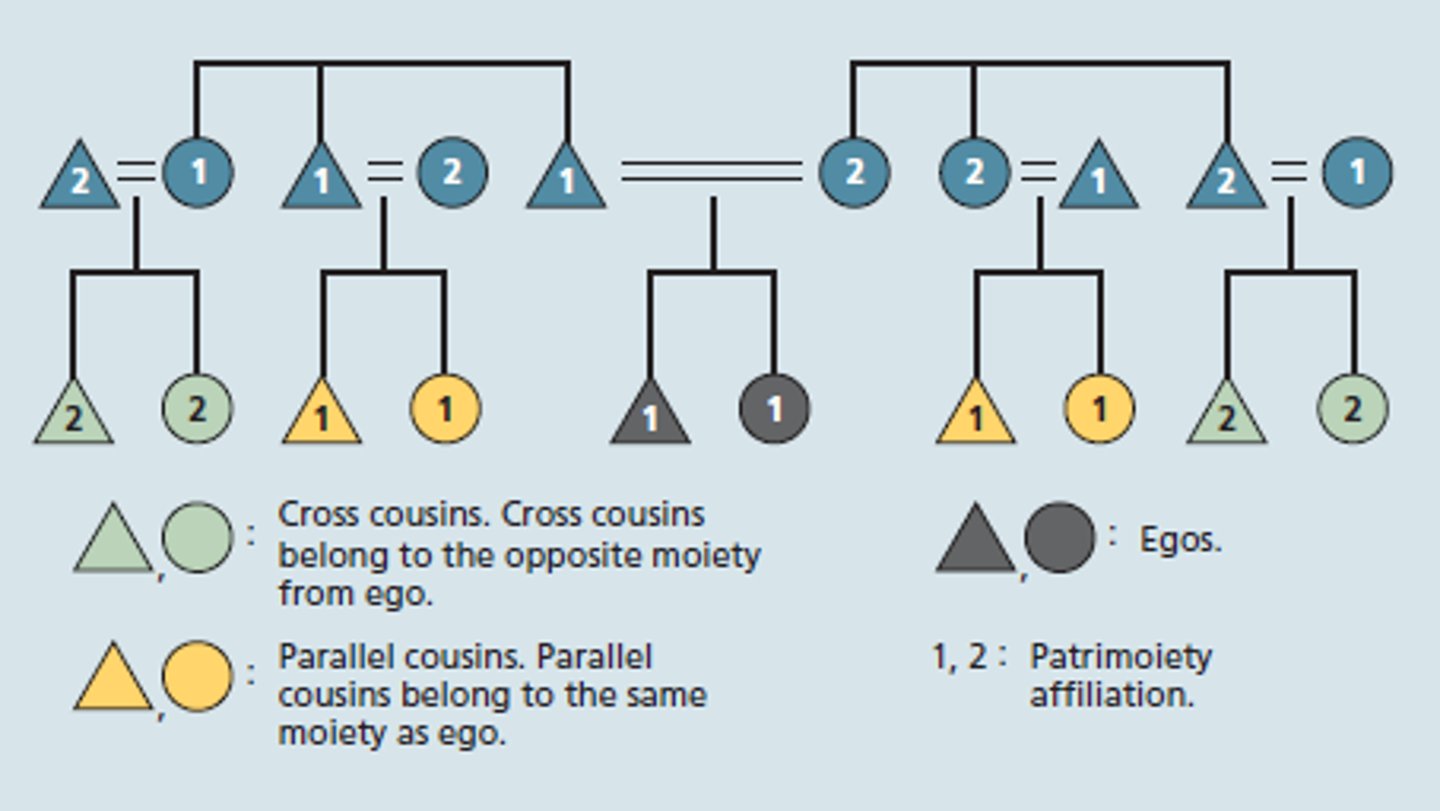
cross cousins
The children of a person's parents' opposite-gender siblings (a father's sister's children or a mother's brother's children).
- Depending on system of descent (patrilineal or matrineal) impacts relations with cousins
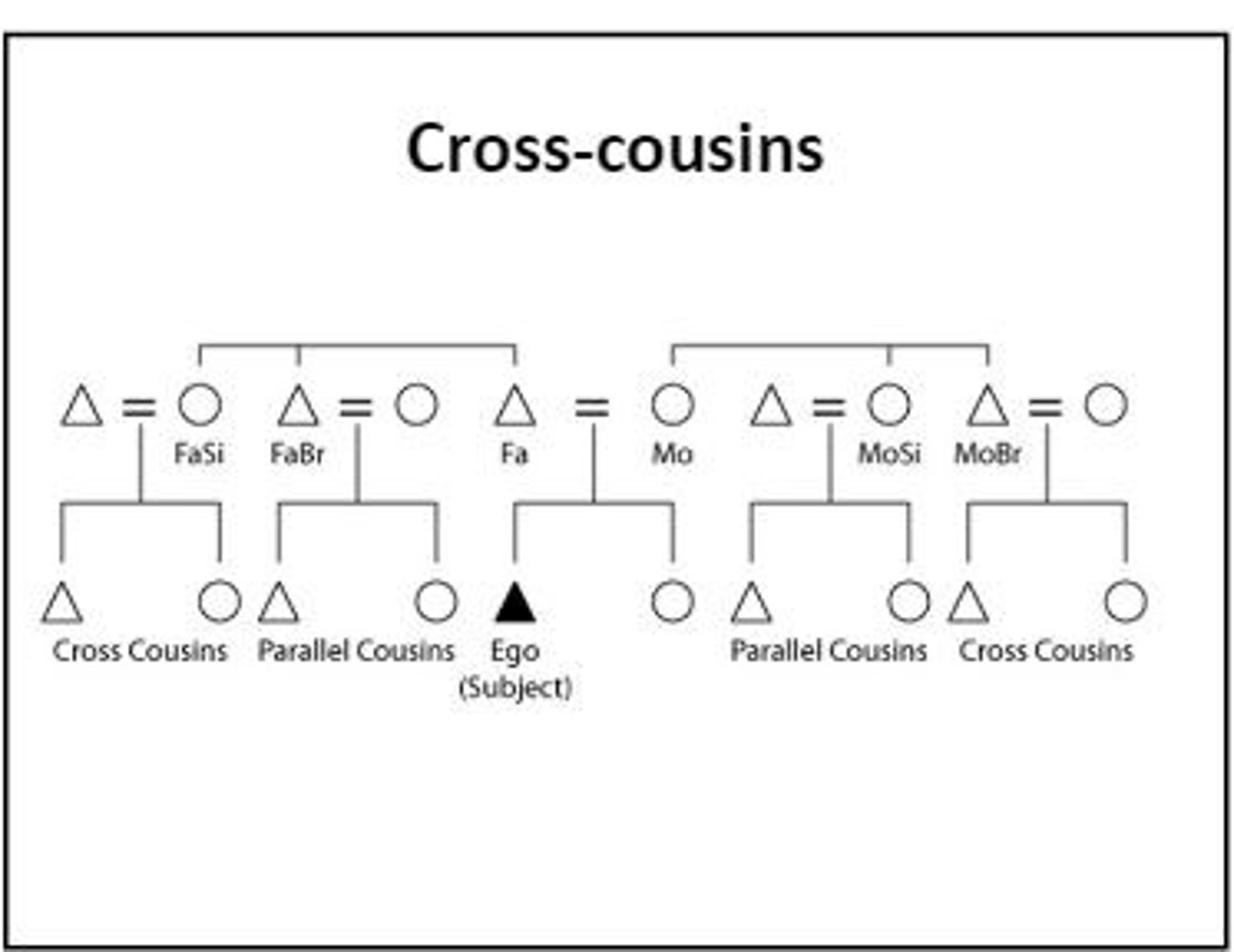
parallel cousins
children of two brothers or two sisters (moms sister)
fictive kinship
kin relations developed through cultural ties
- Compradrazgo
- Expands the web of kinship
- Intensifies friend relations
compradazgo
Spiritual parenthood, fictive kin amongst the Runa. Kinda like godparents
Endogamy
marriage between people of the same social category

Exogamy
marriage outside the tribe, caste, or social group
- More common in patralineal societies
Post-Marital Residence
Rules that specify where a person resides after marriage and, accordingly, influence the structure and size of household units.
- Patrilocal, matrilocal, neo-local
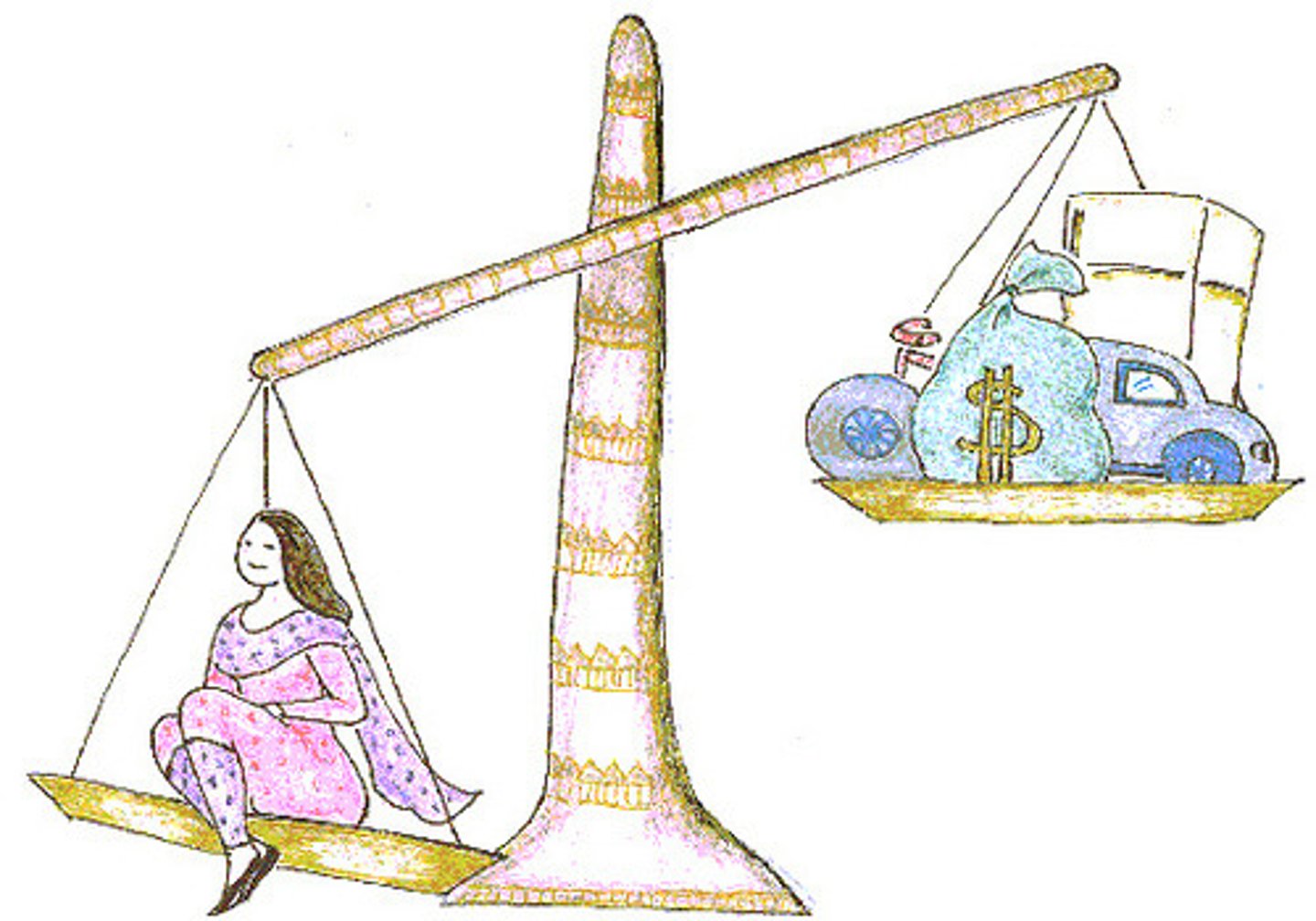
Dowry/Bridewealth
strategies to establish rights over labor and reproductive
Levirate
Custom by which a widow marries the brother of her deceased husband
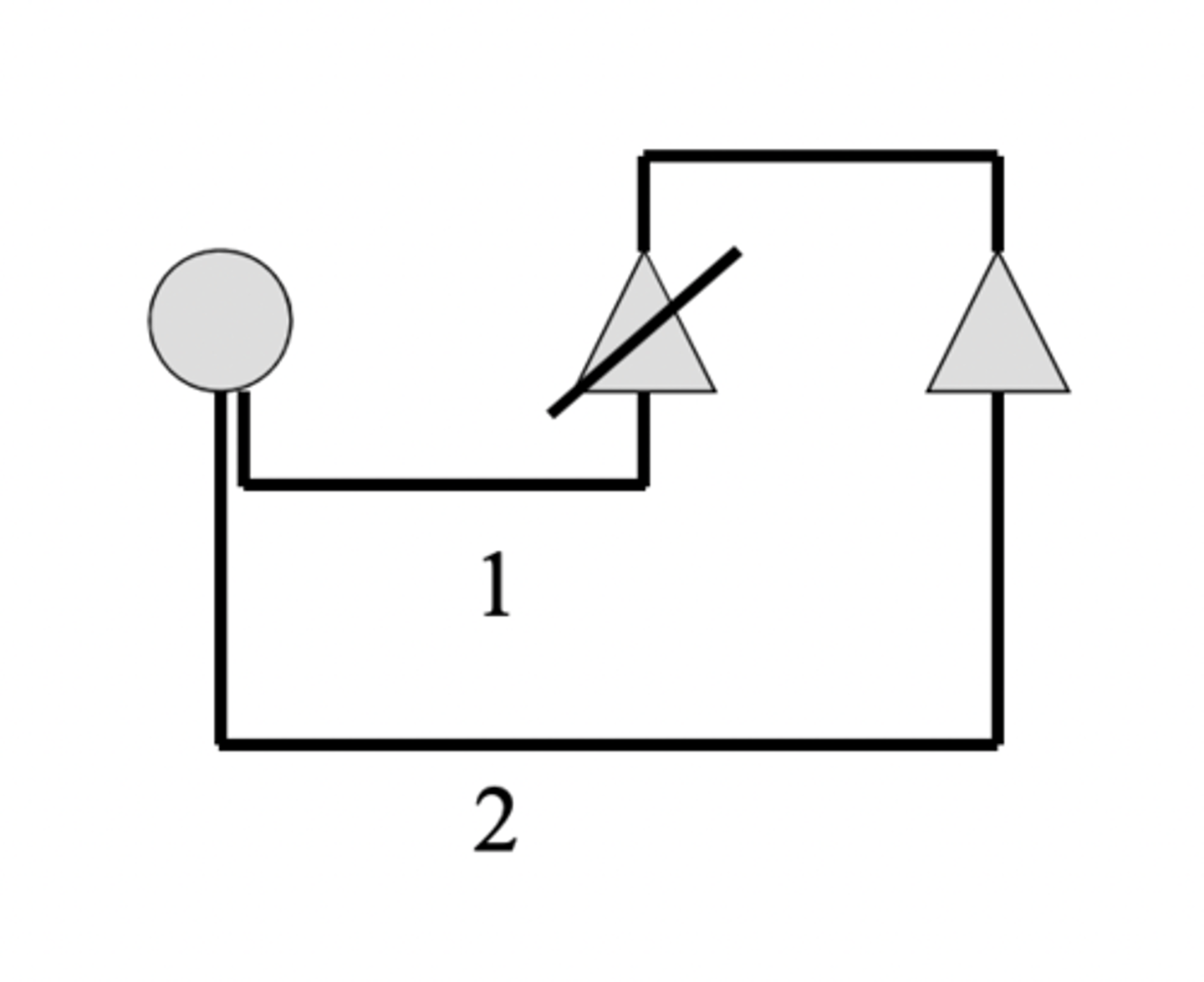
Sororate
the custom whereby, when a man's wife dies, her sister is given to him as a wife
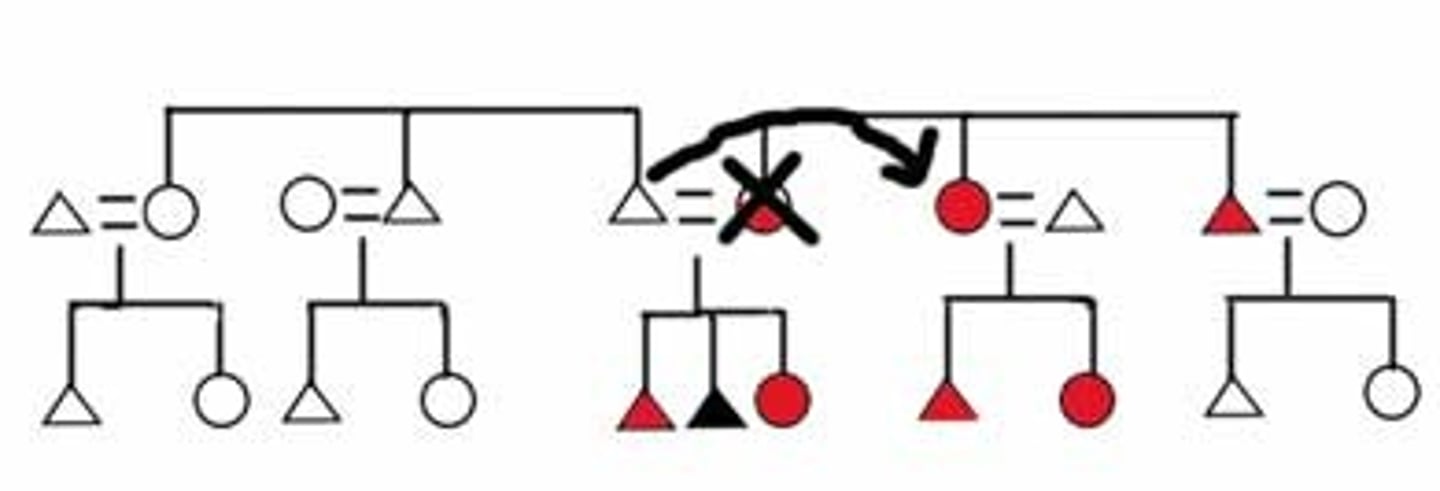
Andes Marriage
- Patrilocal post marital residence
- Community (aylu) endogamy
- Creates unequal relationship with in laws (son-in-law is expected to perform minka labor)
nuer marriage
bride price cattle; oldest son marries first, next son can't marry till cows are replished
social structure
A process of patterned interrelationships of social groups and "persons"
- How people inhabit social roles, conventions, and expectations
achieved/ascribed status
Achieved: Things you have done
Ascribed: Things you were assigned/born into.
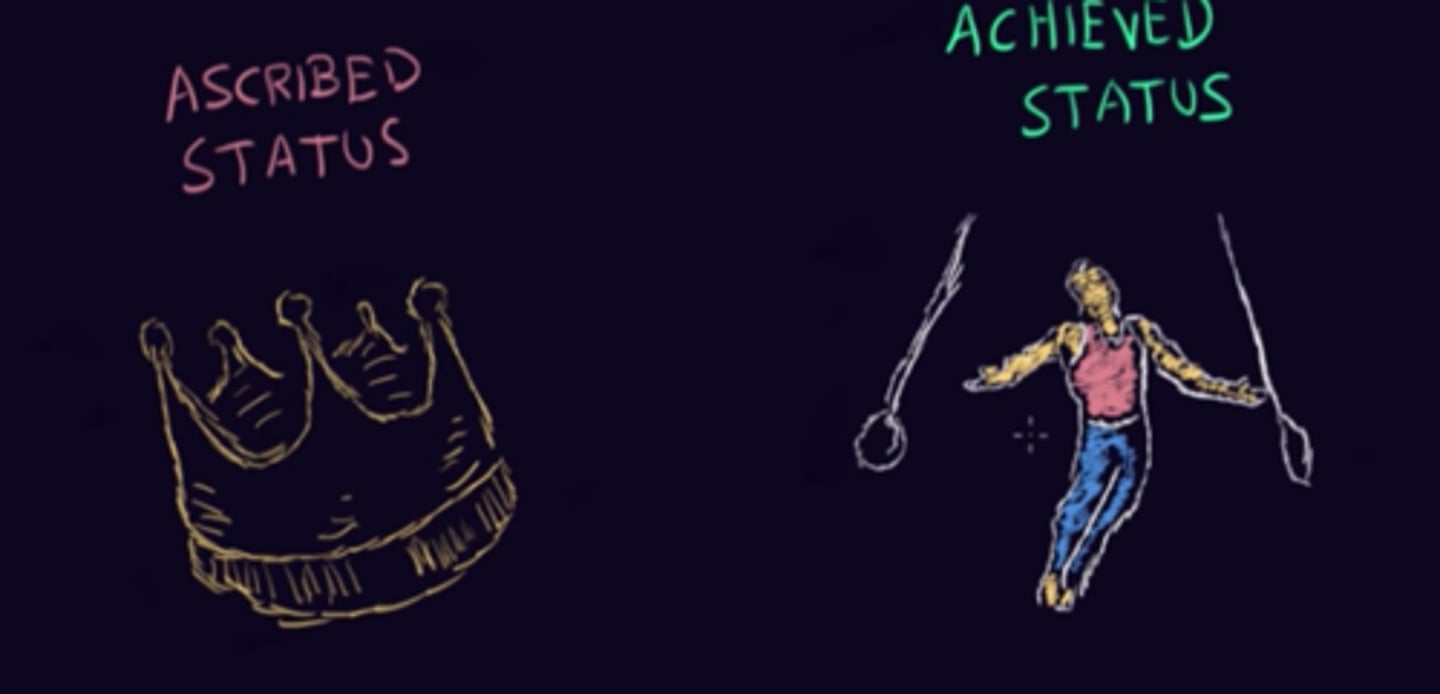
Structural Functionalism
More distant, systematic view of analyzing society by looking at institutions
- Marriage is capitalism
persons
Not the same as individuals. How people inhabit socially assigned roles.
age sets
Sets of different ages that work together to maintain the tribe; have different jobs
age grades
Reaching a certain age as milestones
- Fiesta cargo
culture and the body
The way that we use our bodies are shaped by culture
- Bodies are the raw material through which we experience culture
habitus
Cultural habits that seem like second nature
- Andean people expected to enter a room and greet everyone
- Linked to hegemony
hegemony
domination over others that advantages one social group

sex
"Biological" physical differences perceived as distinguishing males and females
- Sexual dimorphism
- Binary framework that doesn't neatly match the realities of biological variation
gender
Meanings, practices, stereotypes, expectations of a particular sex
- Systematic: Intertwined with other areas in society
- Also interacts with adaptive strategies, beliefs, residence patterns (women staying in the house)
sexuality
Ethnographic research suggests wide variation in actual behavior and categorical systems in which societies classify behavior
- Matti women: Black, working class Surinamese women who form intimate bonds with other women, but don't identify with the western label of lesbians
domestic/public dichotamy
What work done by which genders is valued
- Girls can cook, but men can be professional chefs
gender diversity
The real world of gender and sex in human societies is always more complicated than categories in a given culture
- Two-spirit
intersex
possessing biological sexual characteristics of both sexes
religion
dealing with universal existensial conditions
- Etic, deeply connected with economics and politics
- During enlightenment, switch to rational thought. Religions was considered as a bad science, rather than a way of teaching morals
functionalism
how a practice links to a cultural whole, with respect to individuals
- How cultural practices meet individual needs (basic/derived)
- Malinowski: Magic is a way of controlling the uncontrollable, used for when there's more danger
- Evans Pritchard: witchcraft among the Azande is not illogical, it has it's own logic as a way of settling conflicts
ritual
highly formalized event in which the implicit is made explicit
- Fiesta-Cargo (Andean): Sequence of ladders of community service obligations through which all members of society are expected to pass
- Carnival (Andean): Has roots in Catholicism. Symbolic alignment with flowering of crops
Ritual symbol
Signifies
- Association: Relationship between symbol and what it represents (coca in the Andes)
- Resemblance: Similarity w/ what is being signified (dressing up a sheep for a wedding)
- Convention: Shared cultural understandings, other cultural meanings, associated cultural values
salvage anthropology
the idea that small scale societies are threatened of disappearing due to globalization and modernity
- flawed
World Systems Theory
Variety of political, economic, and social relations of interdependence among different societies within the world
- Core and periphery: Maintains hierarchy and stratification
- Not naturally found in the world, result of legacies of colonization
colonialism
Transforms both EuroAmerican societies and periphery colonies
- Western sense of "self" vs colonized groups
- Part of globalization 1.0
Modernization theory
Making less-developed societies like those in the west. Similar to unilineal cultural evolution
- West as civilized, periphery as unhygenic and barbaric
globalization 2.0
Intensification of cultural processes and connections through technology from 1980 beyond
- Culture isn't just defined by territory, you can participate in it from afar
- Assimilation is no longer the norm
global and local
Global- Interconnection of social life on the planet
Local- Specific settings of everyday life
cultural imperialism
The dominance of one culture over another.
Fordism
System of standardized mass production attributed to Henry Ford.
- Made in America, core countries
financialization
Creating value through financial engineering, not making an actual product
-

political anthropology
How structures of power are organized and reproduced. Emerged after WWII
power and authority
The ability to influence what others do. Located in particular institutions.
- Interacts w/ other dimensions of stratification: wealth, prestige
- Social norms/roles shape leadership.
Nuer
Pastoral, trans humanance. Located in South Sudan. Patrilineal descent is very important
- Cattle is important, plays a role in marriage exchange.
bands
Small group of hunters and gatherers who hunt and gather for a living over territory
tribes
Populations descended from a common ancestor,
- Nowadays is usually used to describe an Indigenous group with its own leadership existing outside a state
chiefdoms
Autonomous political unit composed of a number of communities living under a chief
state
autonomous regional structure of political, economic, and military rule with a central gov.
- Modern Western State: Control over clearly marked territory. Part of global system of state.
- Anthropologists view the state as a complex cultural process that is carried out everyday
non-state actors
groups other than nation-states that attempt to play a role in the international system.
- World bank, IMF, NGO's, criminal orgs.,
- All have influence beyond the nation state
Underdifferentiation
Seeing all "less developed countries" the same
- ROW: Rest of the world
- WEIRD: Western, educated, industrial, rich, democratic
overinnovation
When people in Western nations (think peace corp volunteers) make projects that aren't really suited for the people who live there.
- Good intent, bad practice.
collaborative research
an approach to learning about culture that involves anthropologists working with members of the study population as partners and participants rather than as "subjects"
- Emic approach
- PRATEC: NGO devoted to researching Andean technologies, that counters Western idea that Indigenous people are something of the past.
medical anthropology
Differential impact of disease and other health-related issues,
- How different populations concerive of "health" "wellness" and "disease"
- Analyzing Western biomedical knowledge
- Biomedical understanding AS cultural understanding
Biomedicine vs. Ethnomedicine
Biomedicine is medical science that applies biological and other natural-science principles to clinical practice.
Ethnomedicine is traditional medicine practiced by various ethnic groups, and especially by indigenous peoples. The word ethnomedicine is sometimes used as a synonym for traditional medicine.
human microbiome
Our health is connected to the people around us
business anthropology
Business practices as an object of ethnographic study
- Business practices aren't just money making machines, but social institutions
- Communication across cultural boundaries
- The stock market isn't as sure as something like gravity, but we often act like it is.