Lecture 3: The pectoral region and shoulder
1/49
There's no tags or description
Looks like no tags are added yet.
Name | Mastery | Learn | Test | Matching | Spaced |
|---|
No study sessions yet.
50 Terms
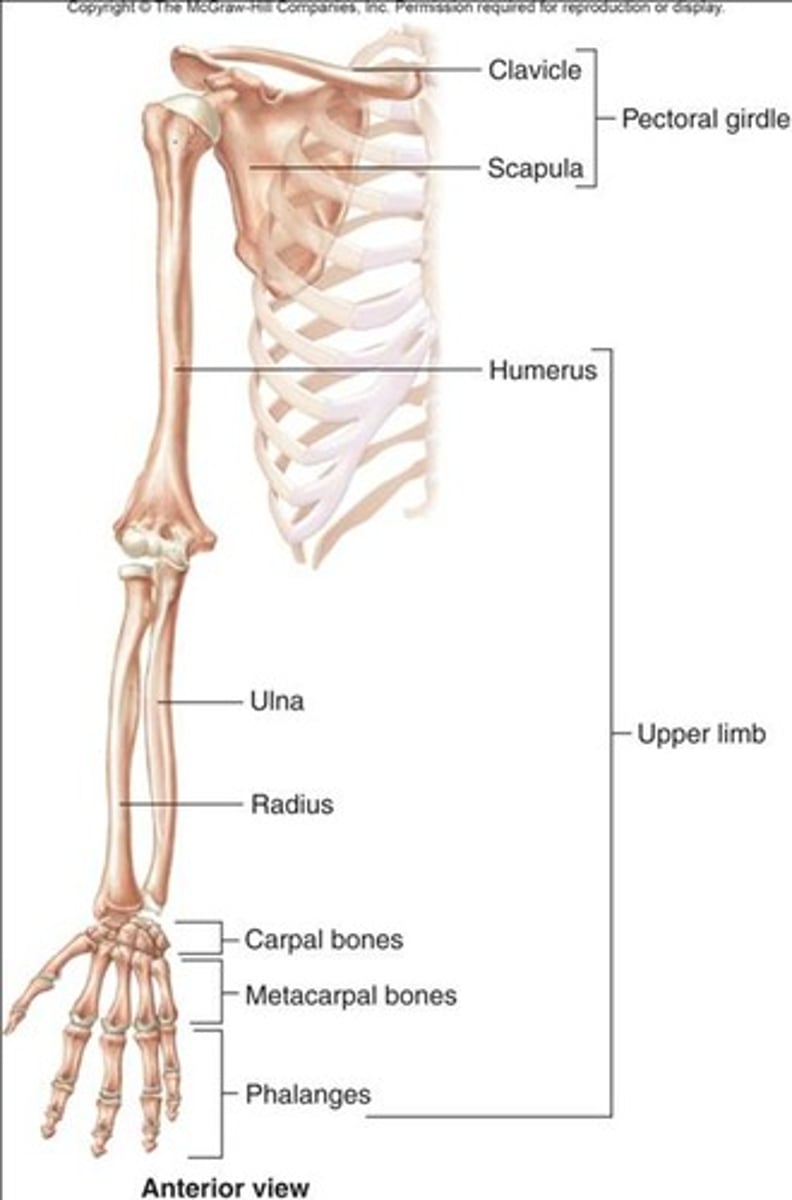
General Organization of the Upper Limb
Shoulder girdle
Arm
Forearm
Hand
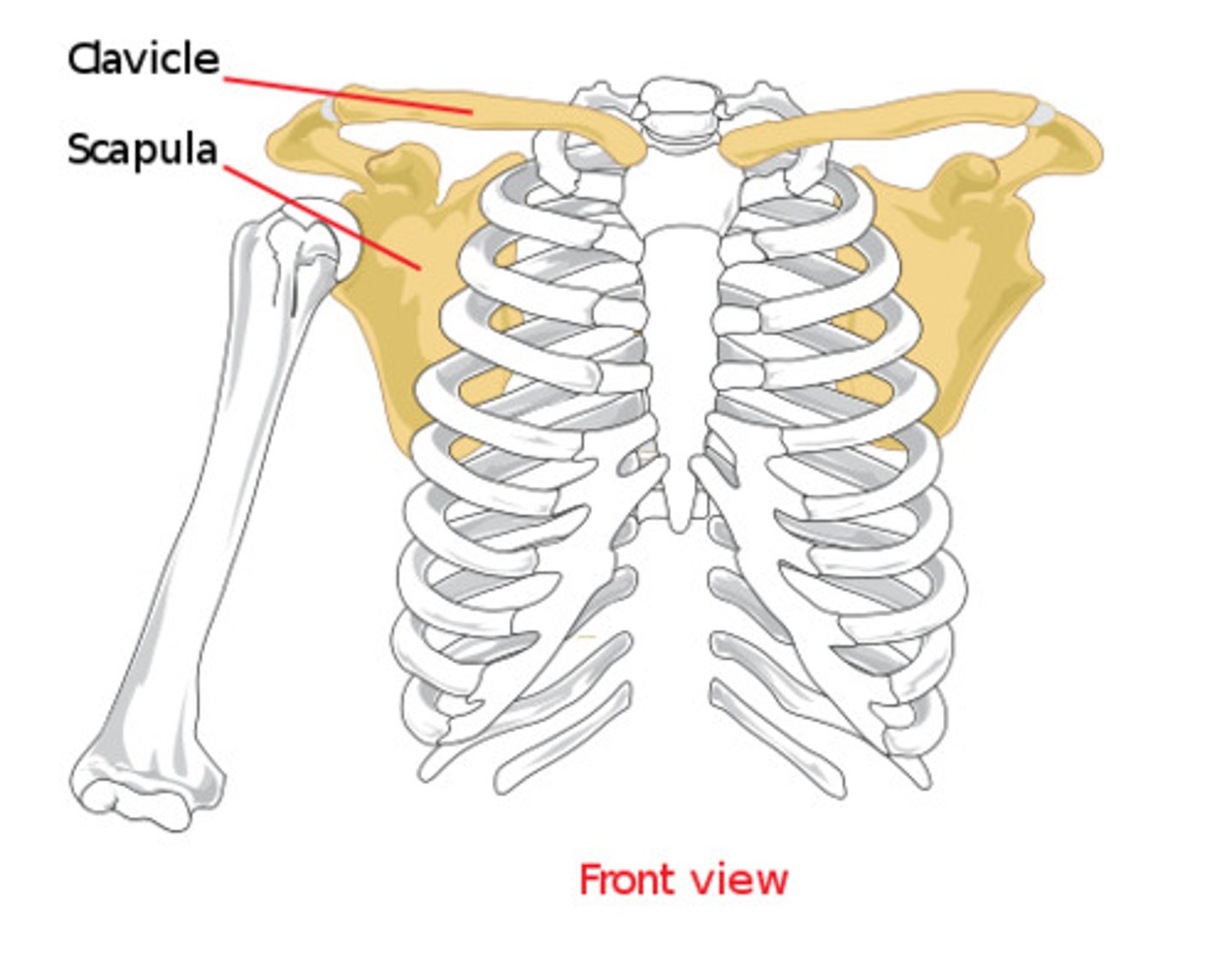
Shoulder Girdle (pectoral girdle)
between the axial skeleton and shoulder joint
Arm
between the shoulder joint and the elbow joint
Forearm
Between the elbow joint and wrist joint
hand
distal to the wrist joint
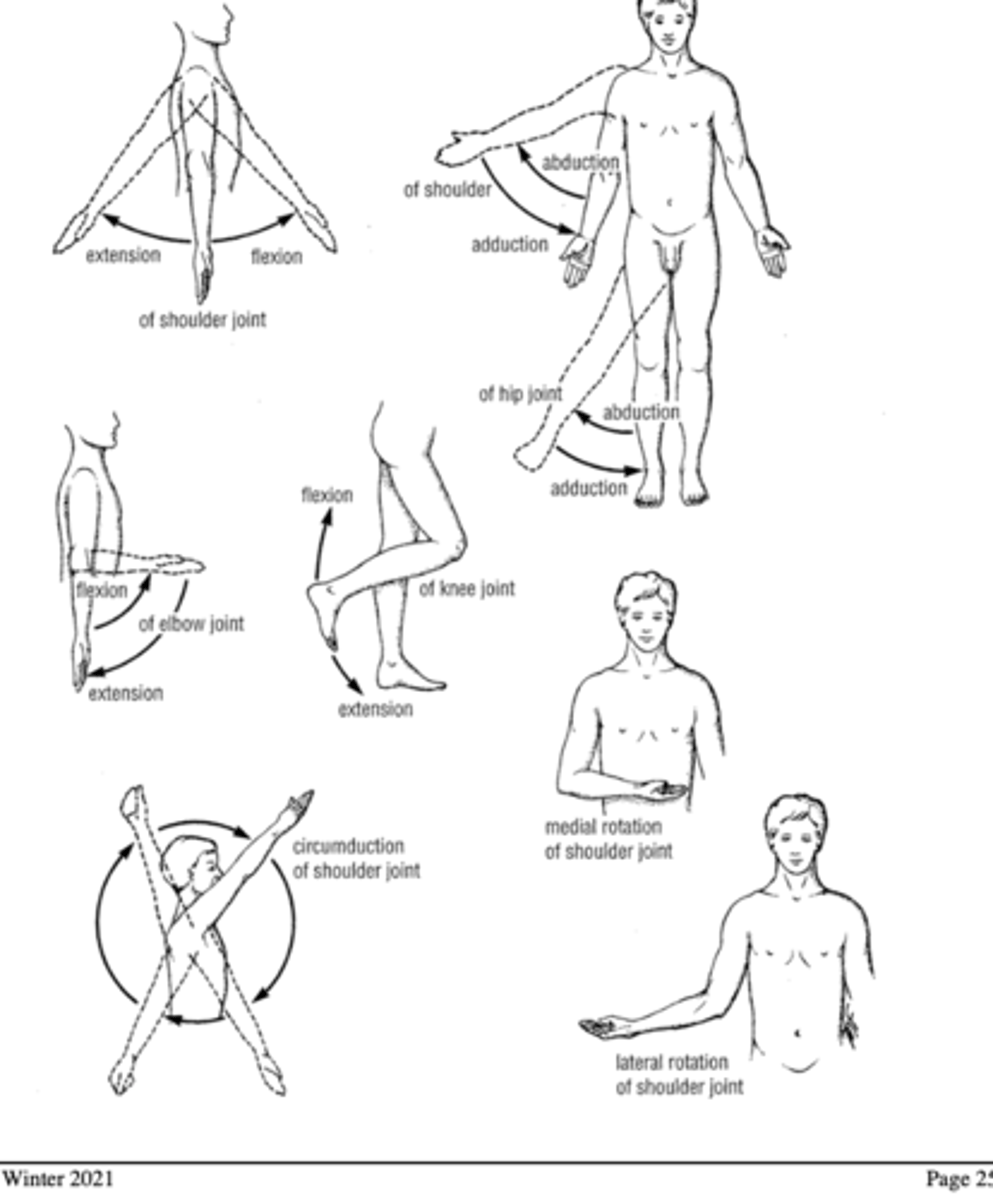
Terms Indicating Movement
Flexion
Extension
Adduction
Abduction
circumduction
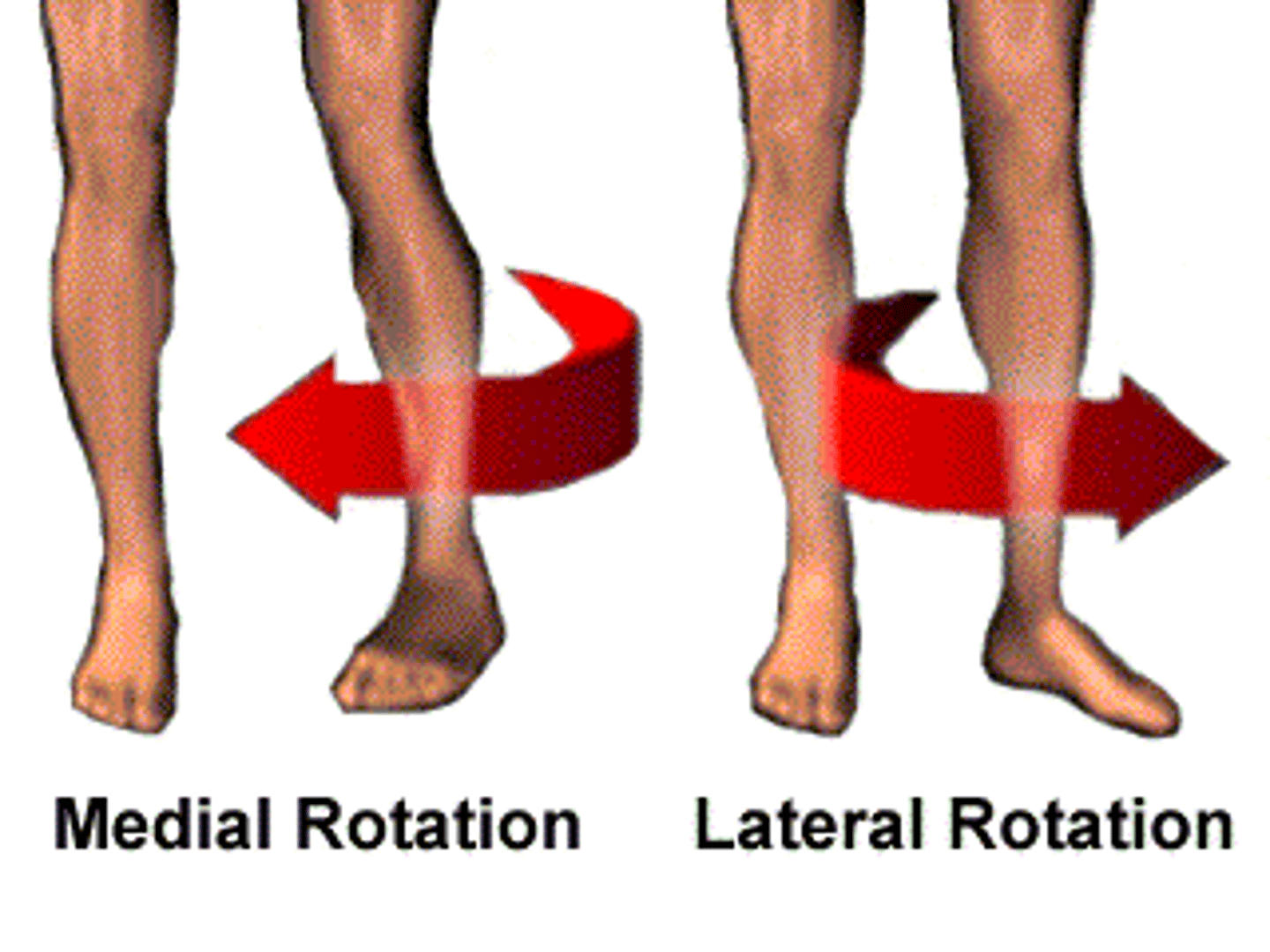
medial rotation
lateral rotation
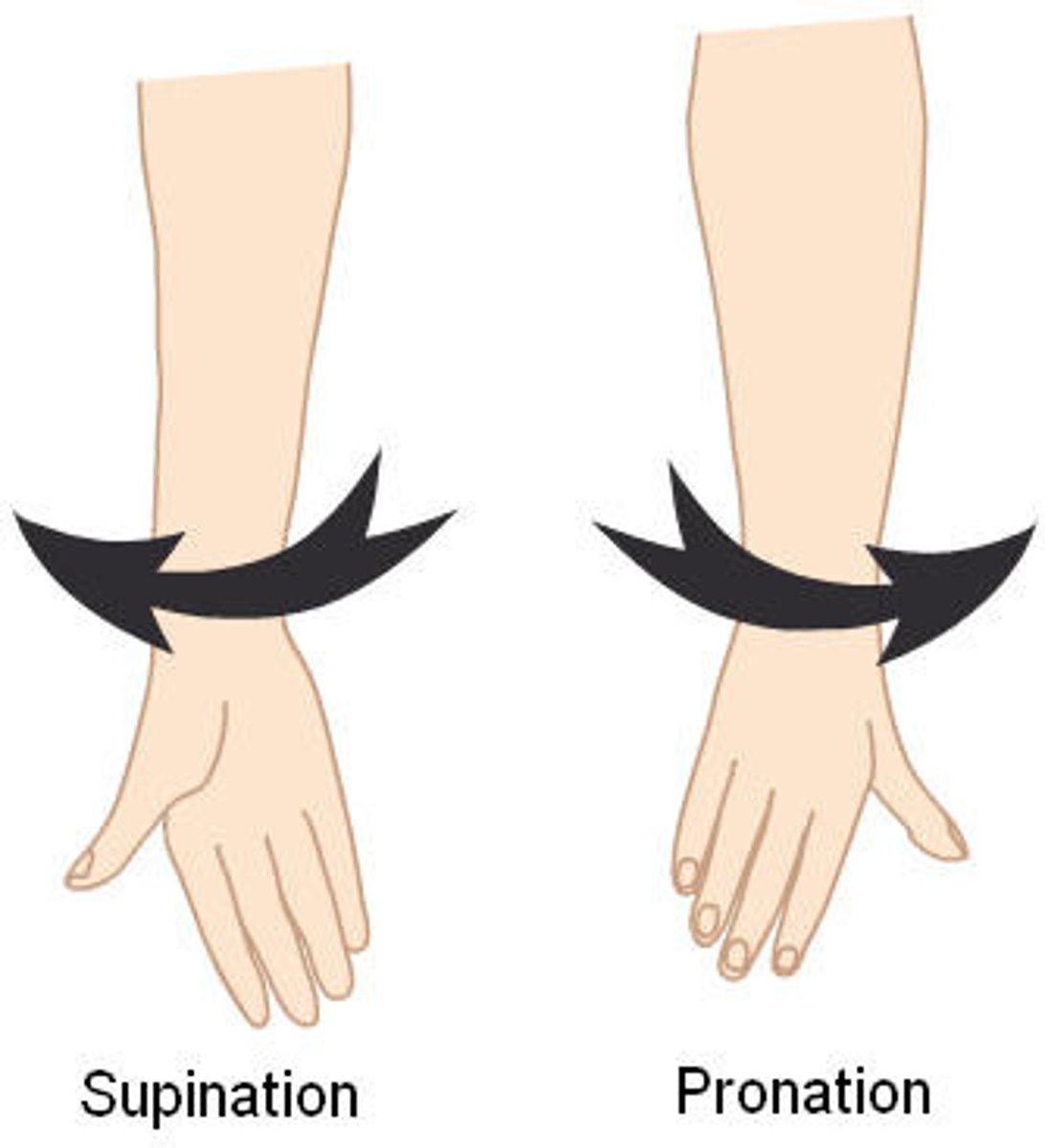
supination
pronation
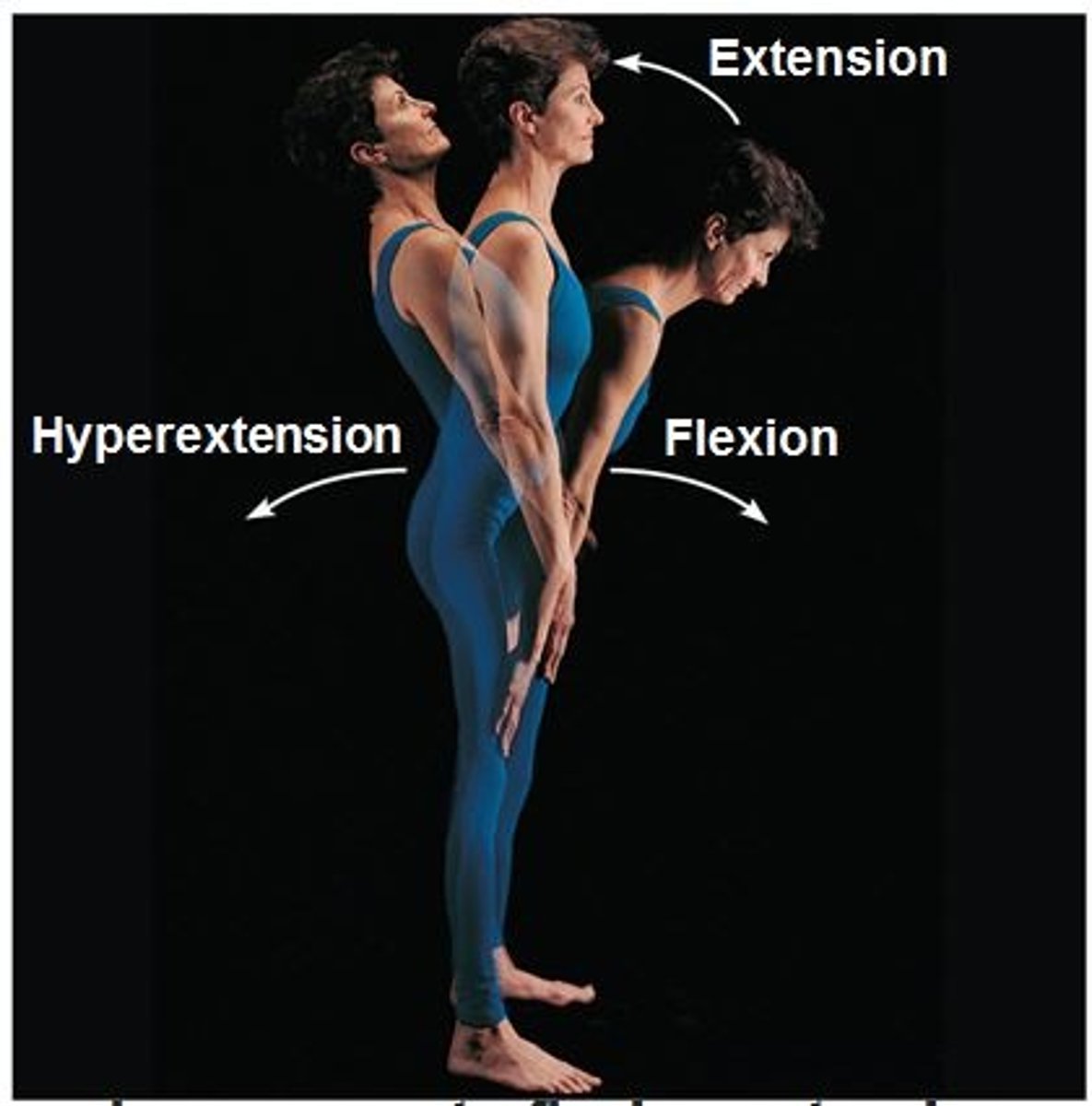
Flexion
Extension
Decreasing the angle in a joint
Increasing the angle in a joint
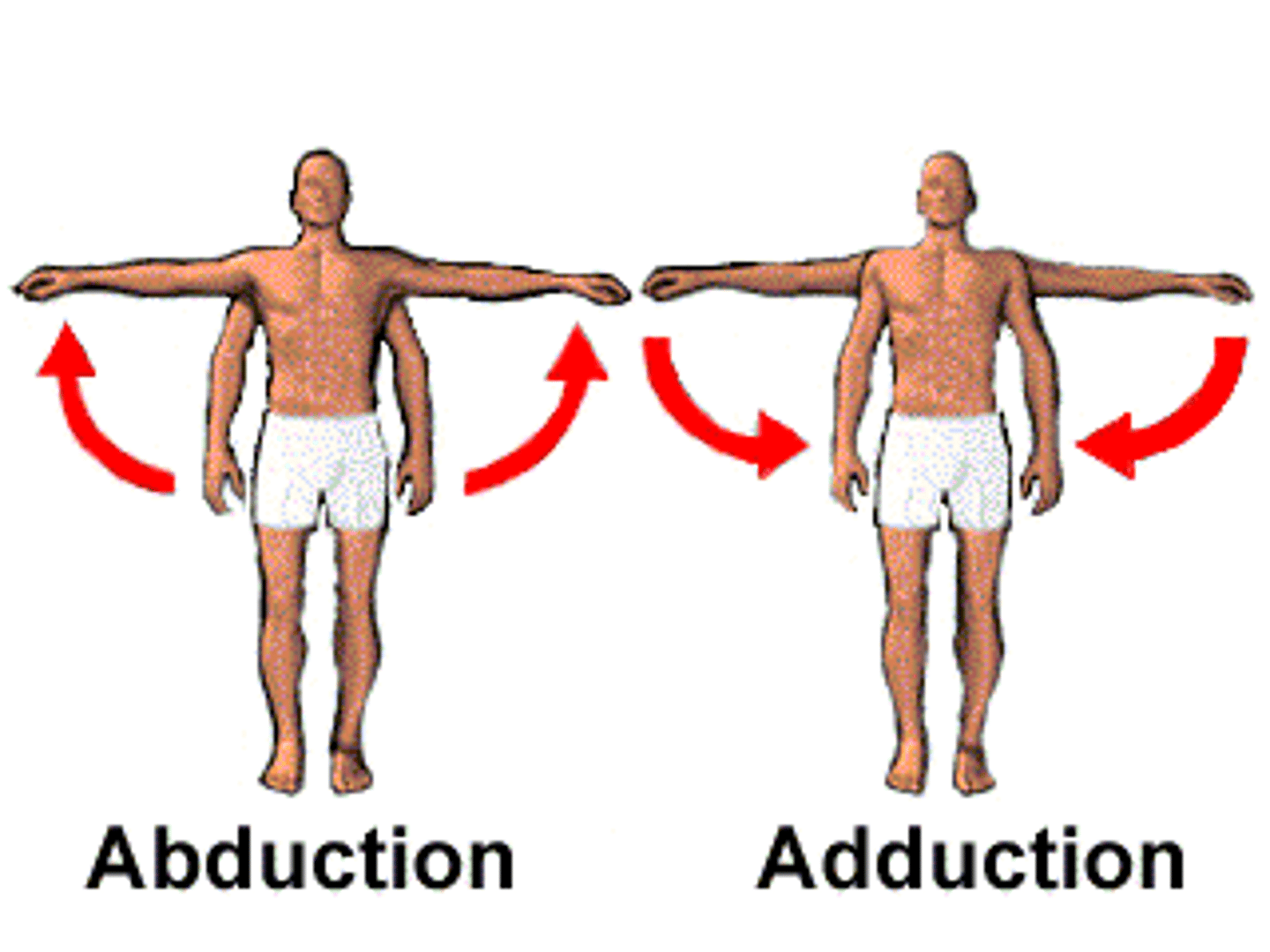
Adduction
Abduction
Movement closer to the medial plane
Movement away from the midline of the body
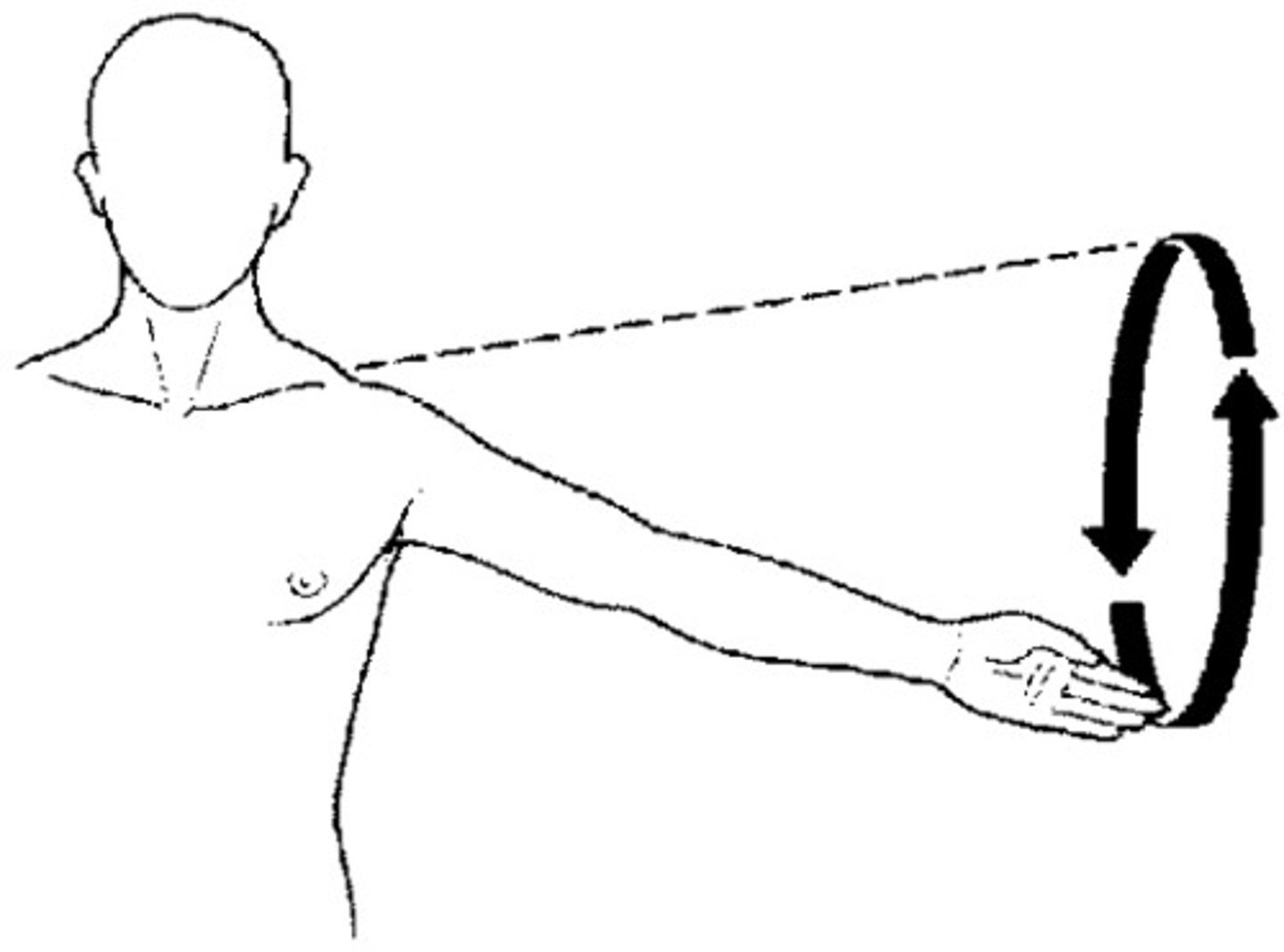
Circumduction
circular movement of a limb at the far end
Medial Rotation
Lateral Rotation
Rotation toward the midline
rotation away from the midline
Supination
Pronation
rotational movement, results in the palm facing upward
rotational movement, results in the palm facing downward
Myolog
study of muscles
Muscular Attachments
Origins
Insertions
Origins
Insertions
Usually less mobile and/or on the more proximal of a muscle's attachments
Usually more mobile and/or on the more distal of a muscle's attachments
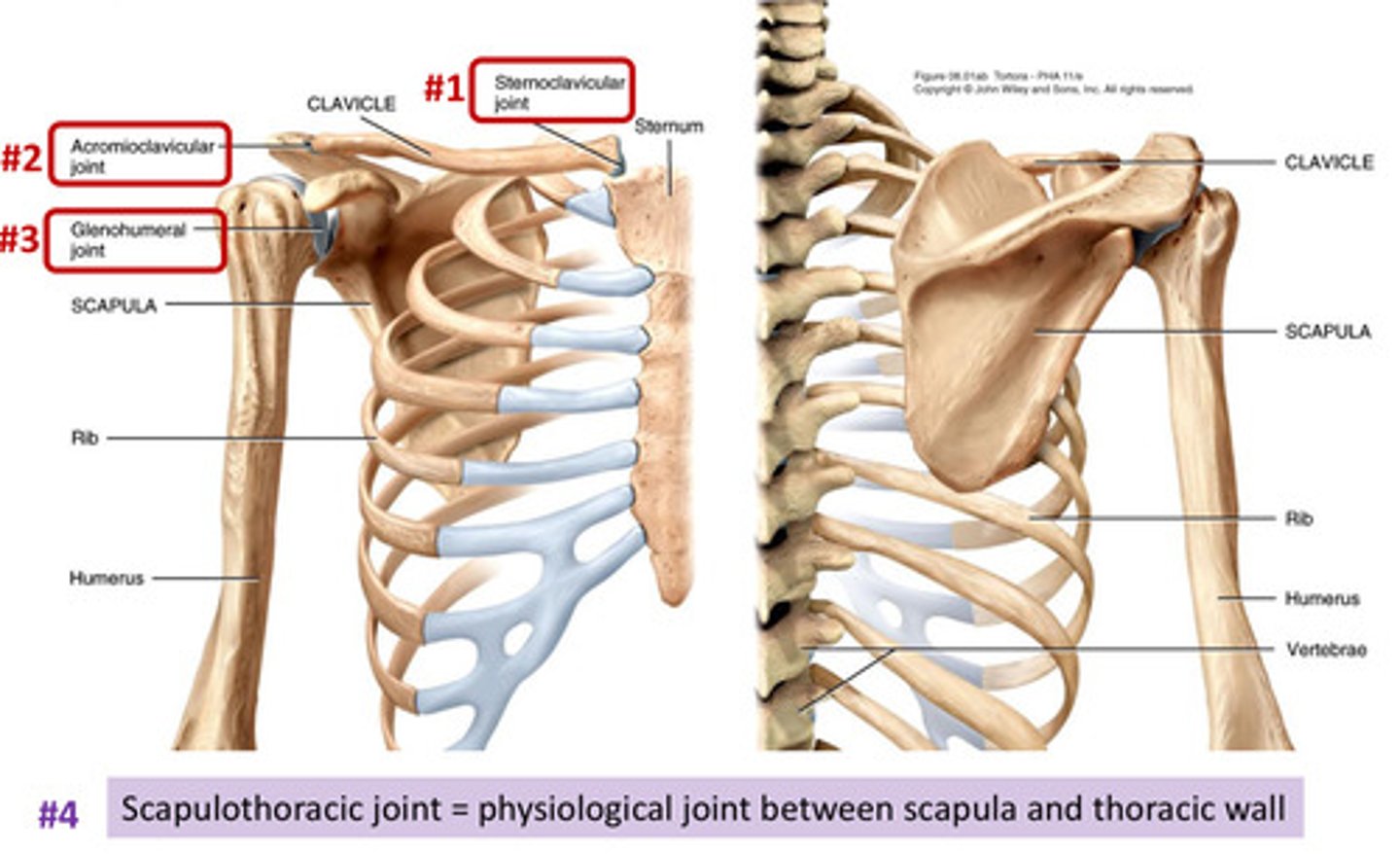
Pectoral Region; Bones
Scapula
Humerus
Clavicle
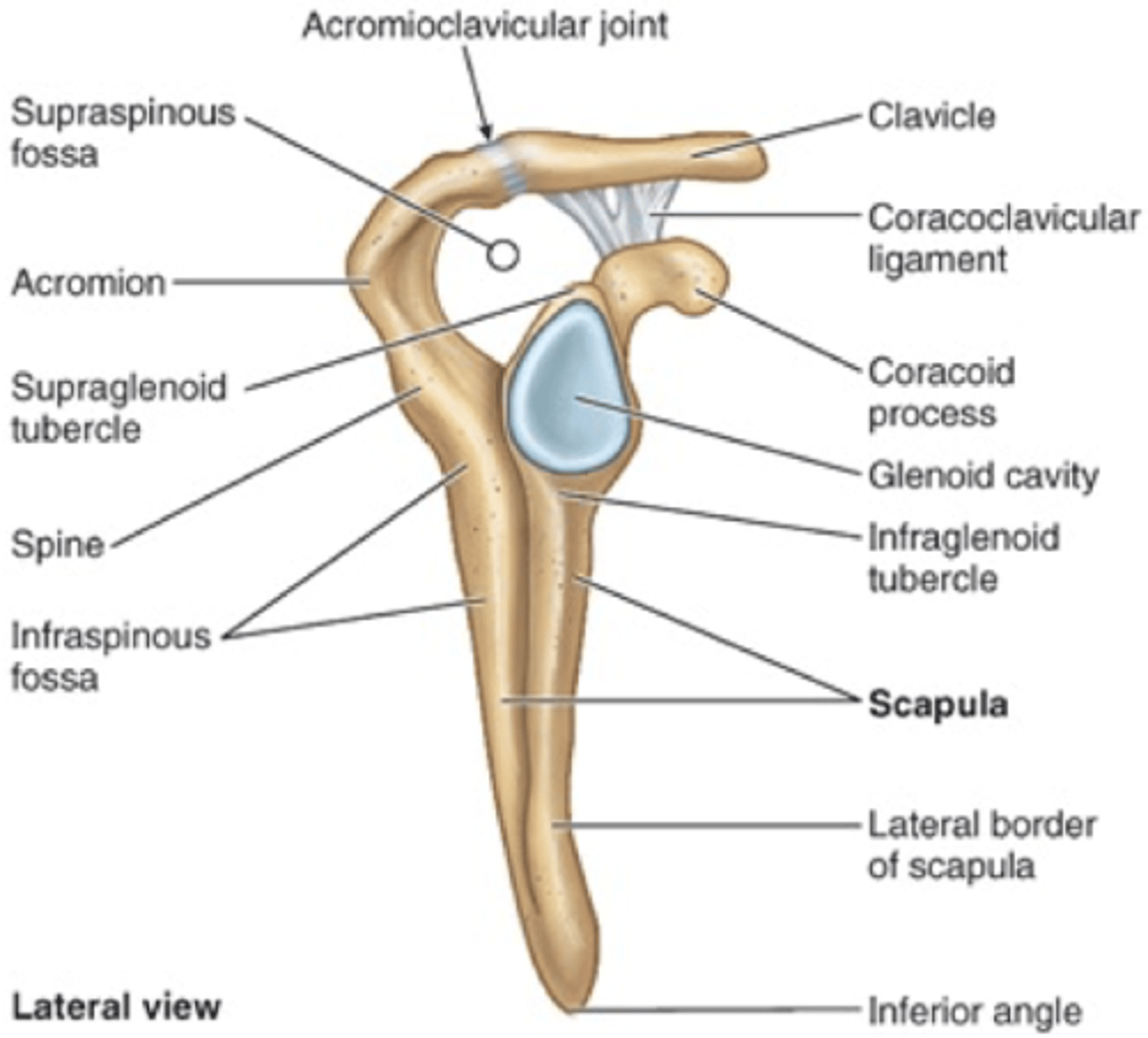
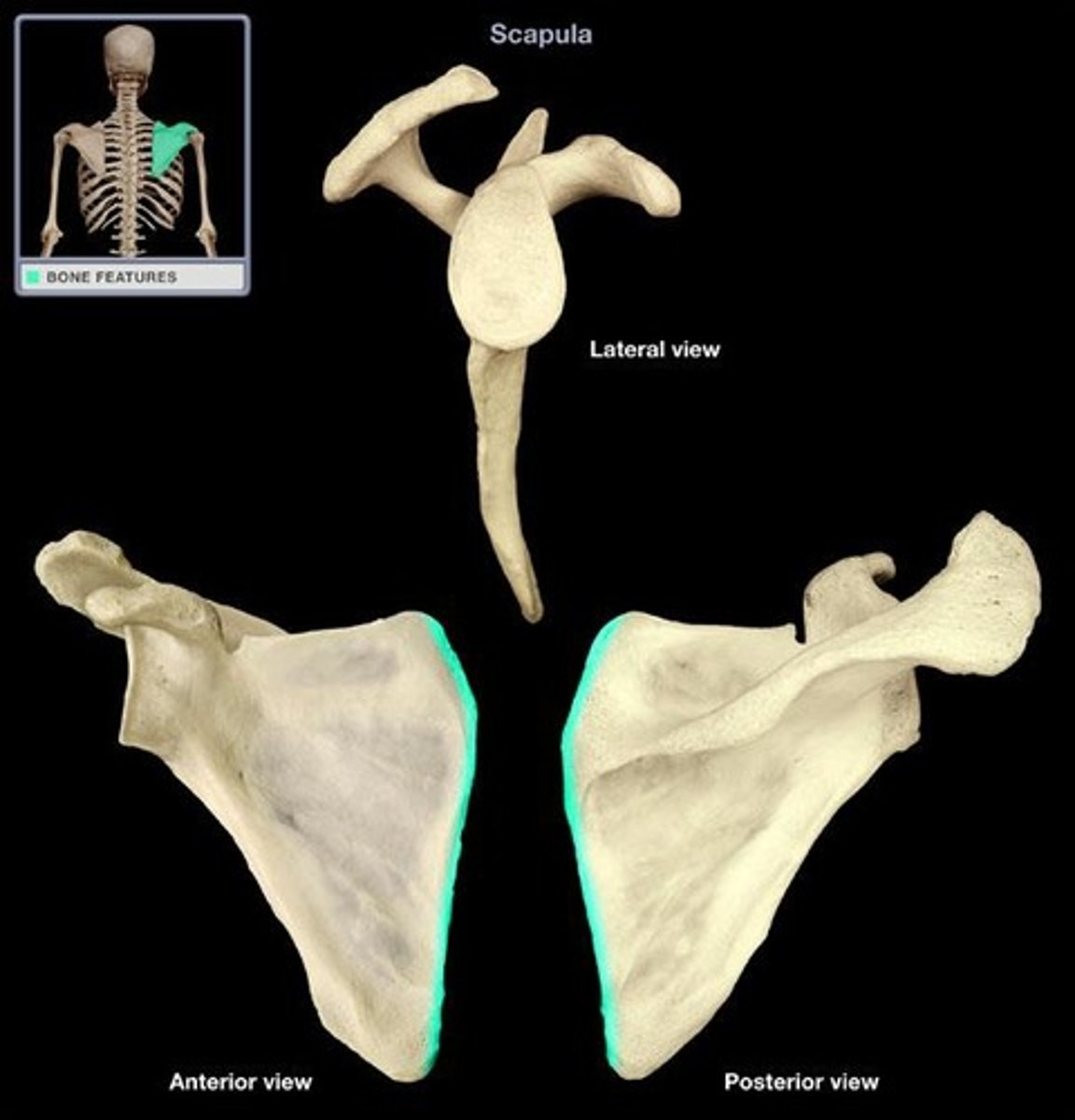
Scapula- breakdown
Coracoid process
glenoid cavity
scapular notch
scapular spine
acromion
inferior angle
medial border
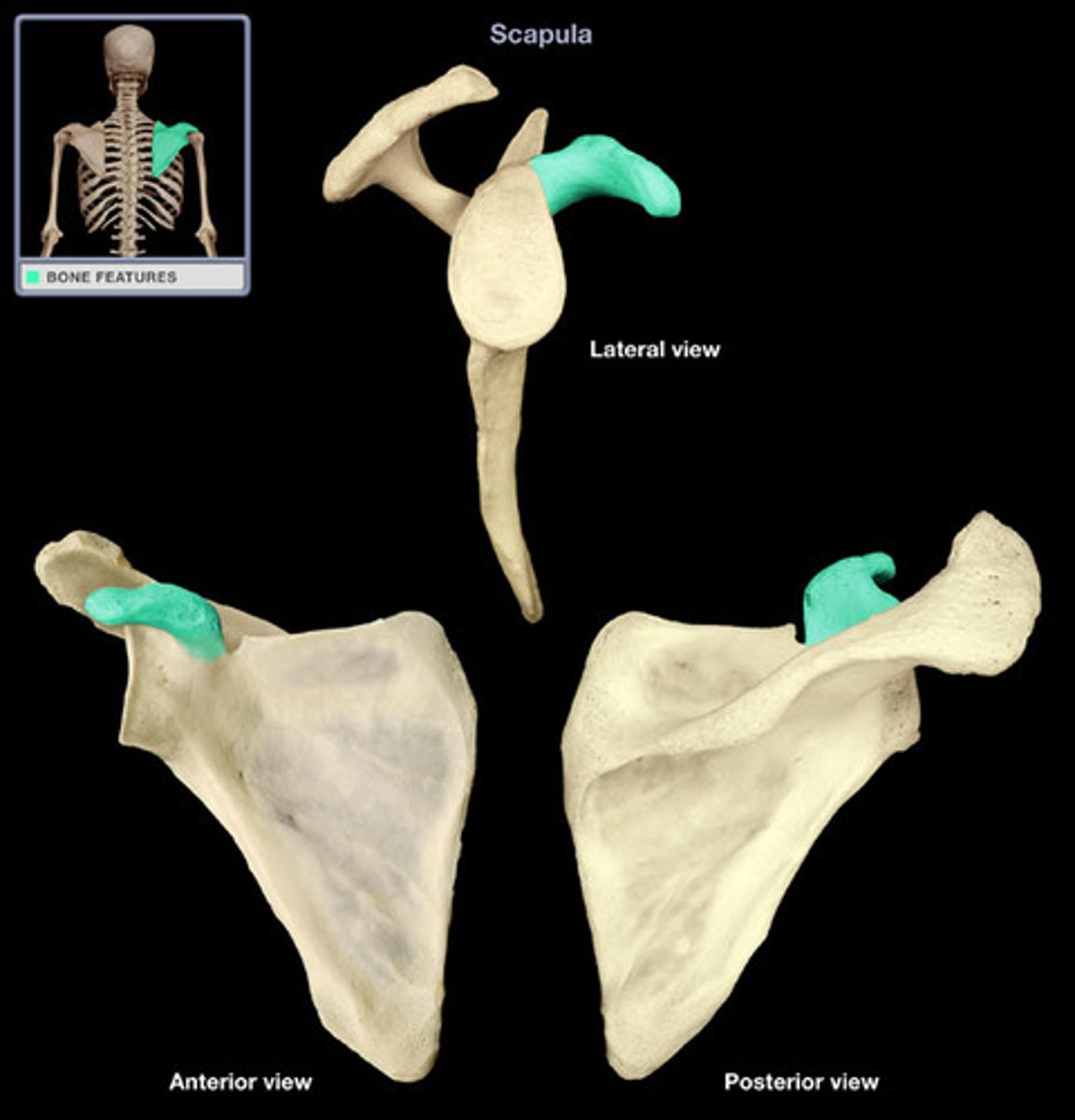
Coracoid process
a major point of weight/stress transfer from the arm to the shoulder; it also helps shelter the superior aspect of the shoulder joint
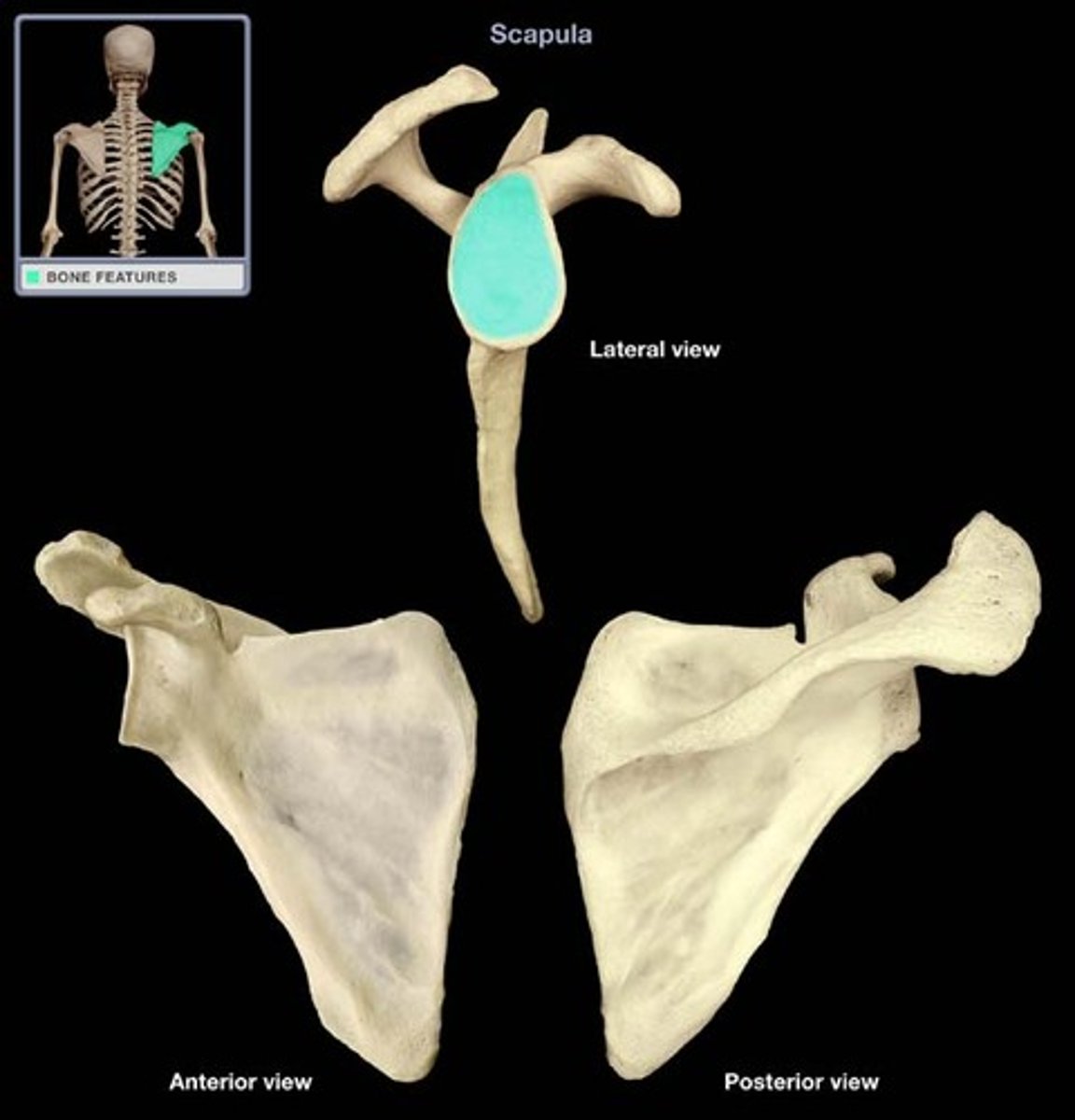
Glenoid Cavity
proximal part of the shoulder joint that receives the humeral head
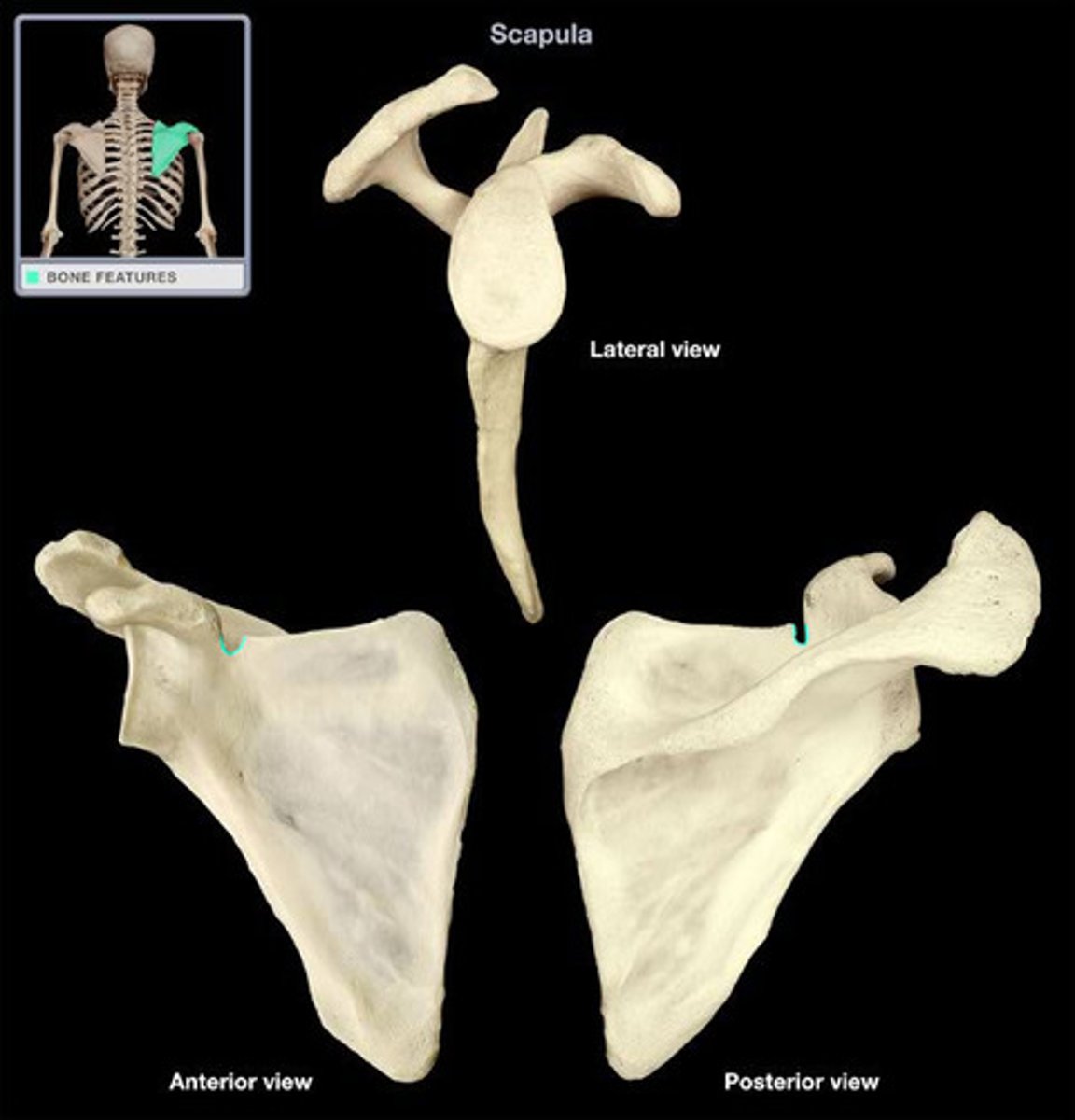
Scapular notch
crossed by the suprascapular artery and nerve
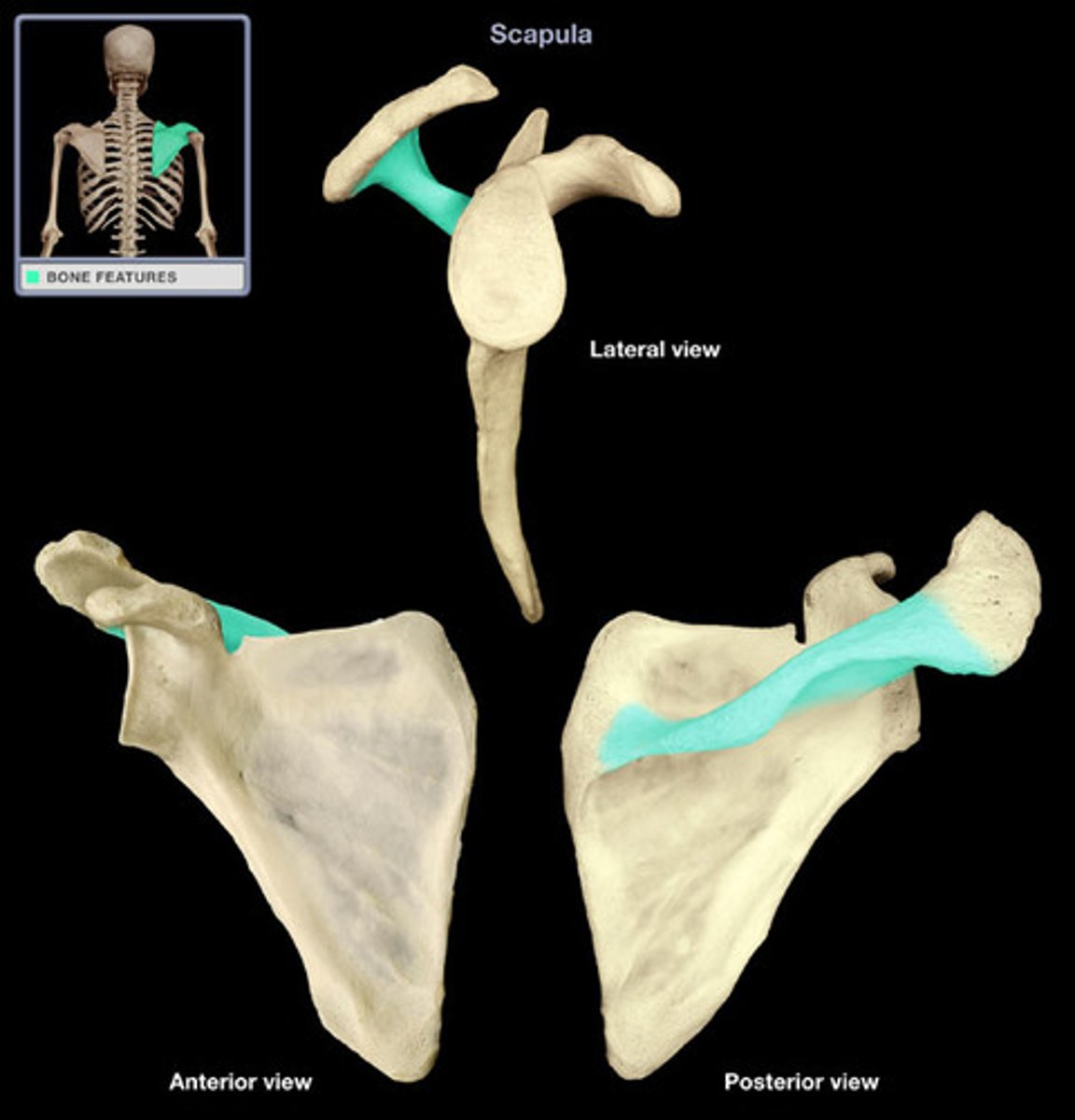
Scapular Spine
divides back of the scapula into supraspinous and infraspinous fossae
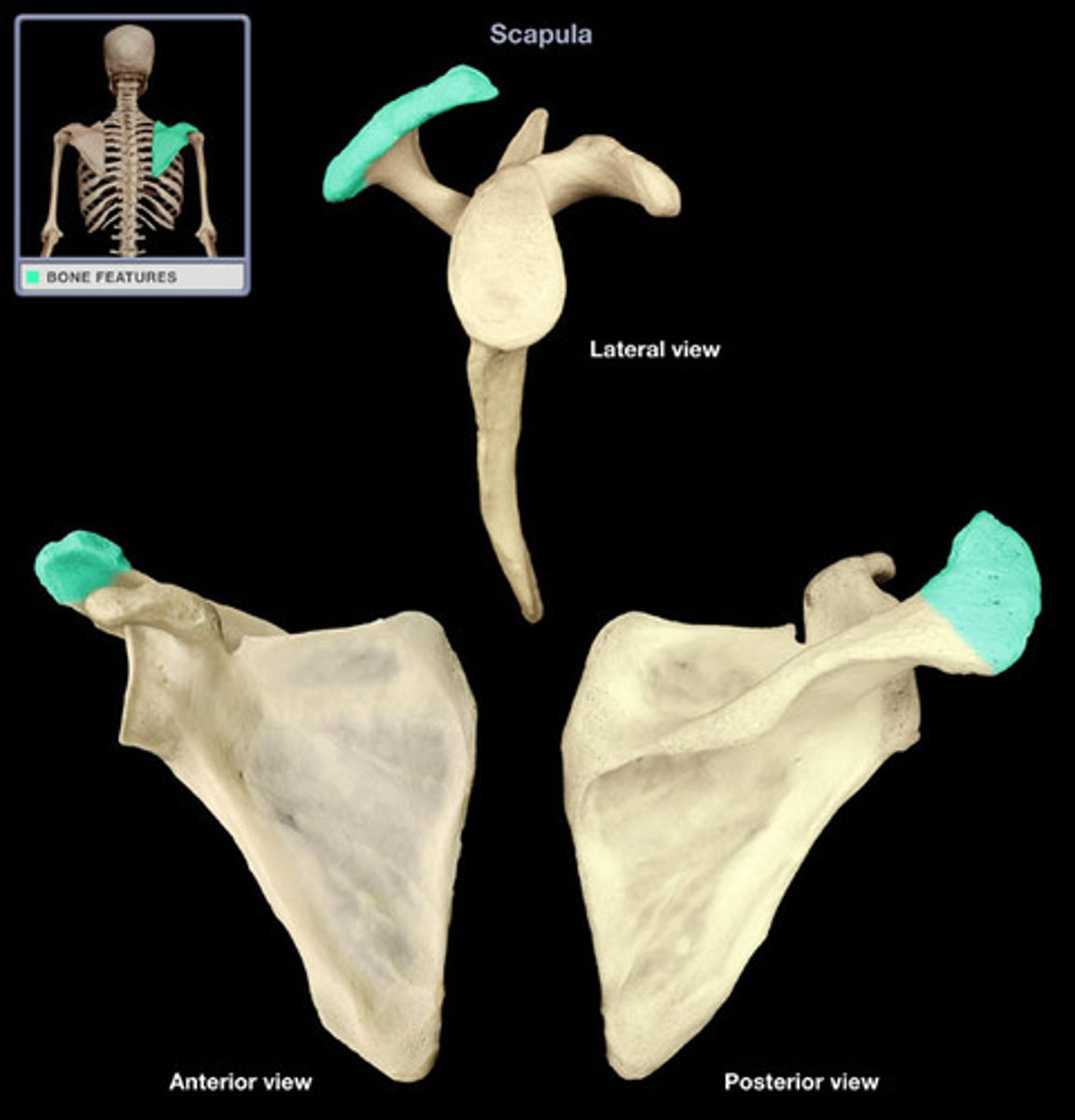
Acromion
"point" of the shoulder' distal end of scapular spine; lateral projection
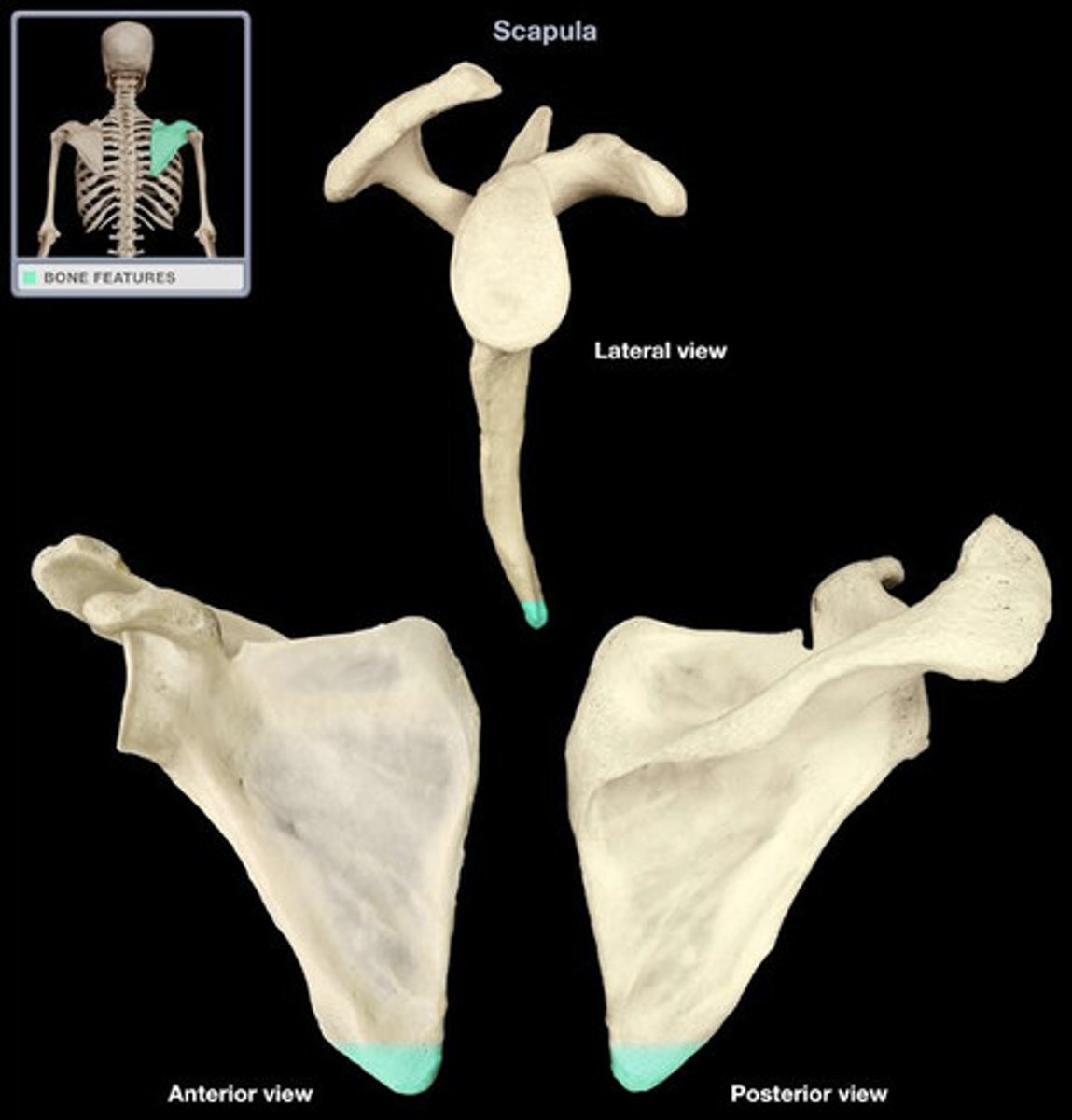
Inferior angle
bottom point of scapula
Medial Border
Inner edge of the scapula
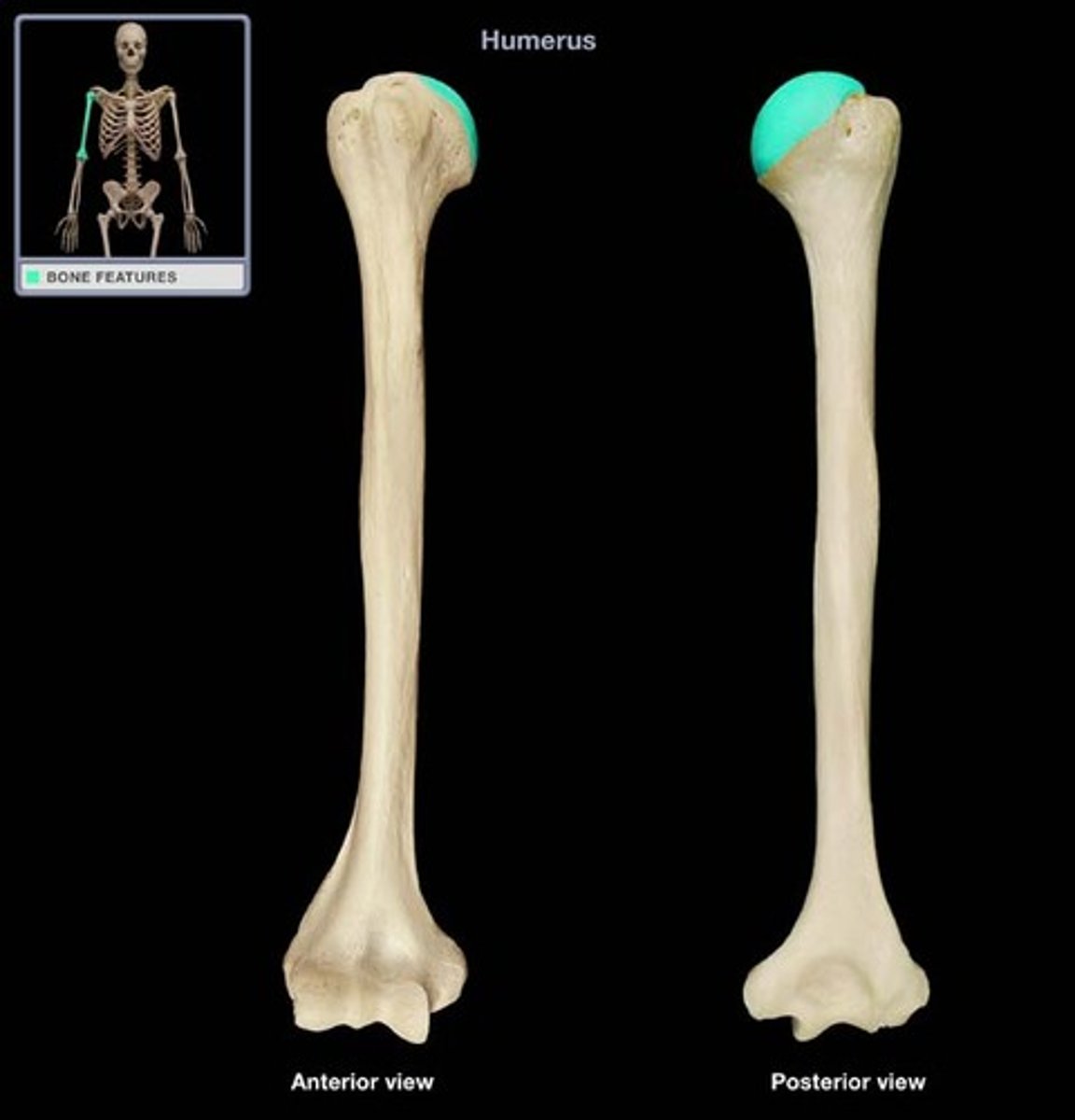
Humerus; breakdown
head
anatomical neck
surgical neck
greater tubercles
lesser tubercles
intertubercular groove
Shaft
deltoid tuberosity
Head
Enlarged proximal part of the humerus that articulates with the glenoid cavity
Anatomical neck
Base of the head
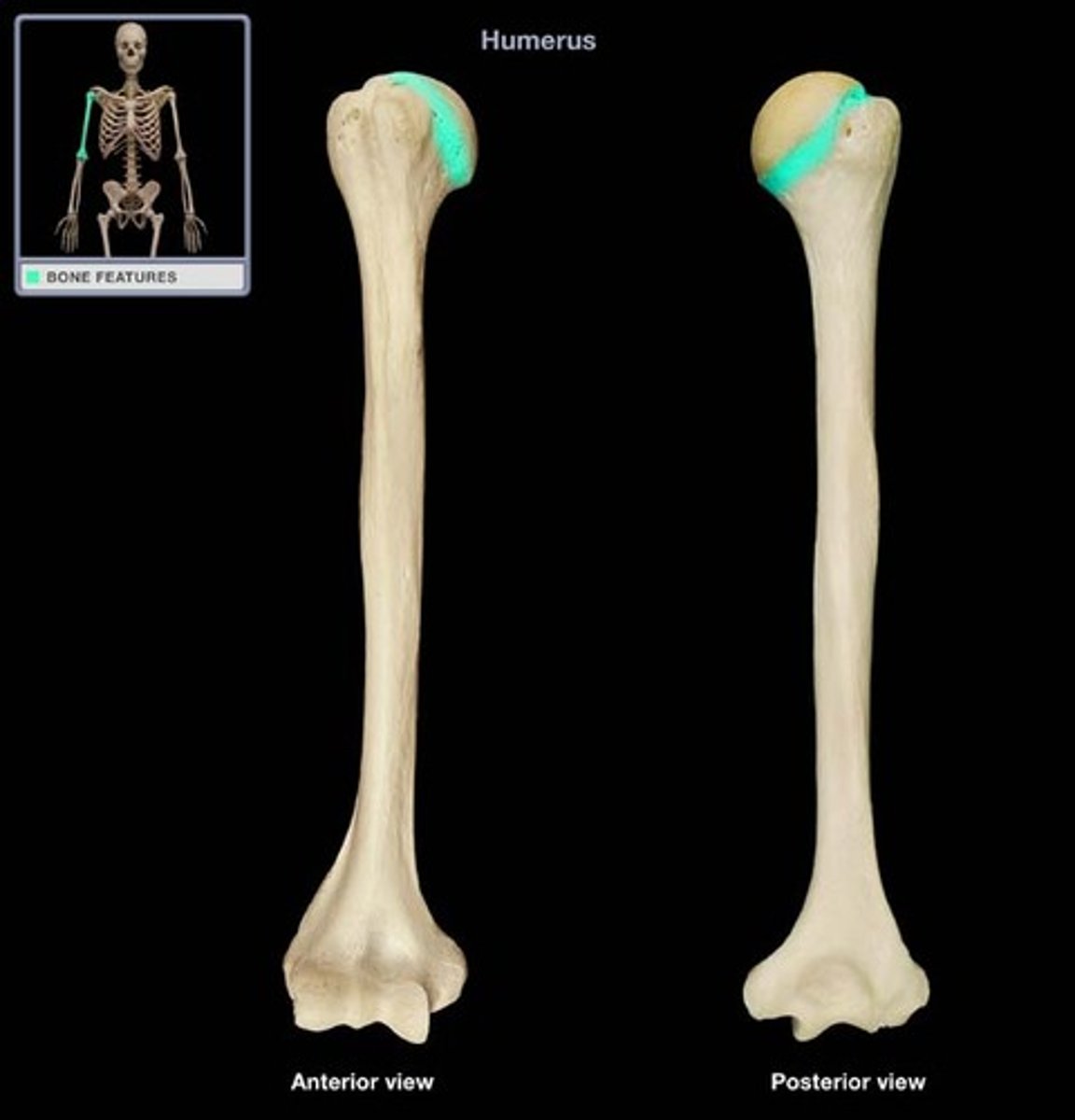
Surgical Neck
Lower than the Anatomical neck, on the shaft of the bone
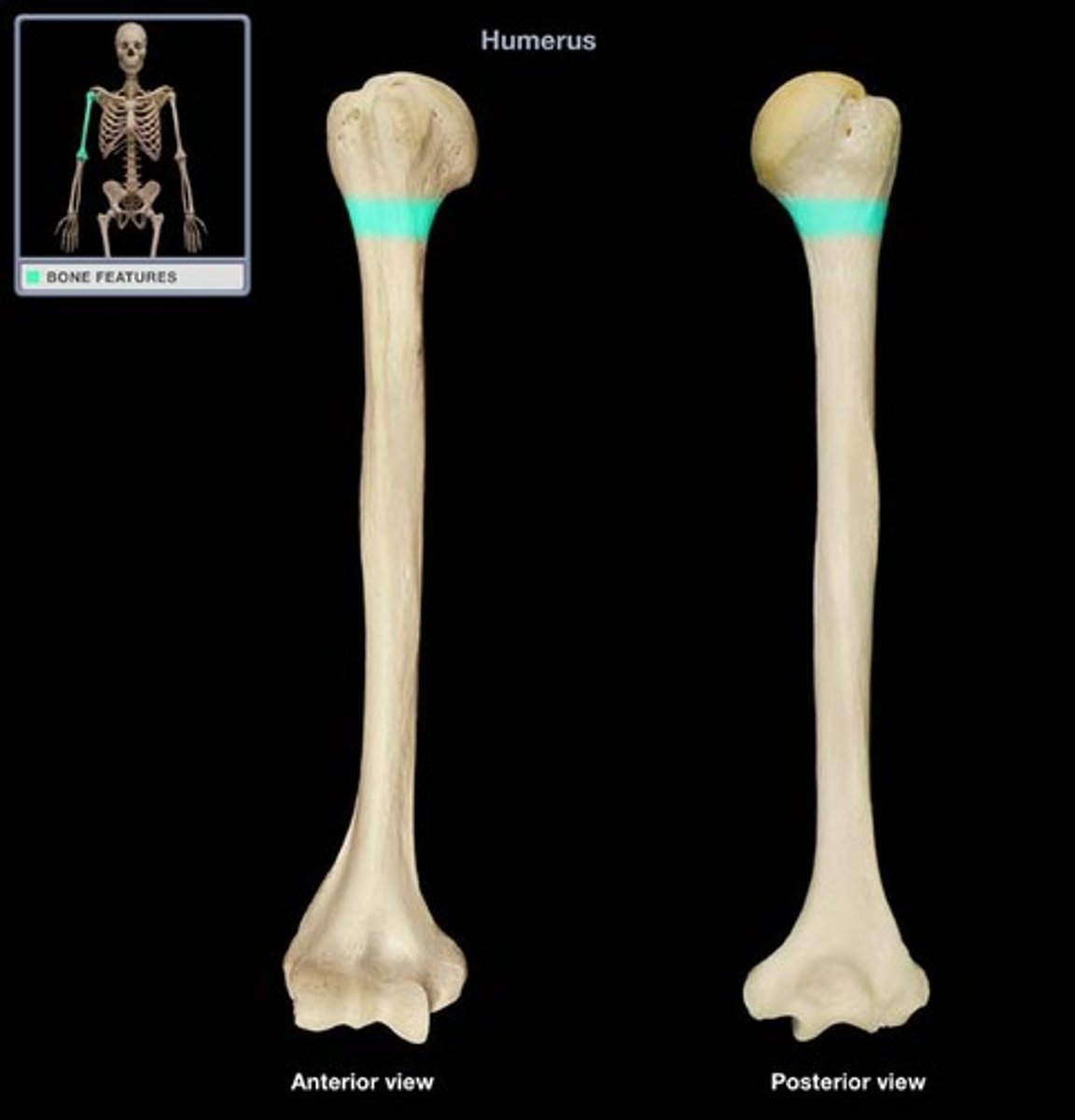
Greater Tubercles
sites of attachment for the rotator cuff muscles at the upper end of the humerus
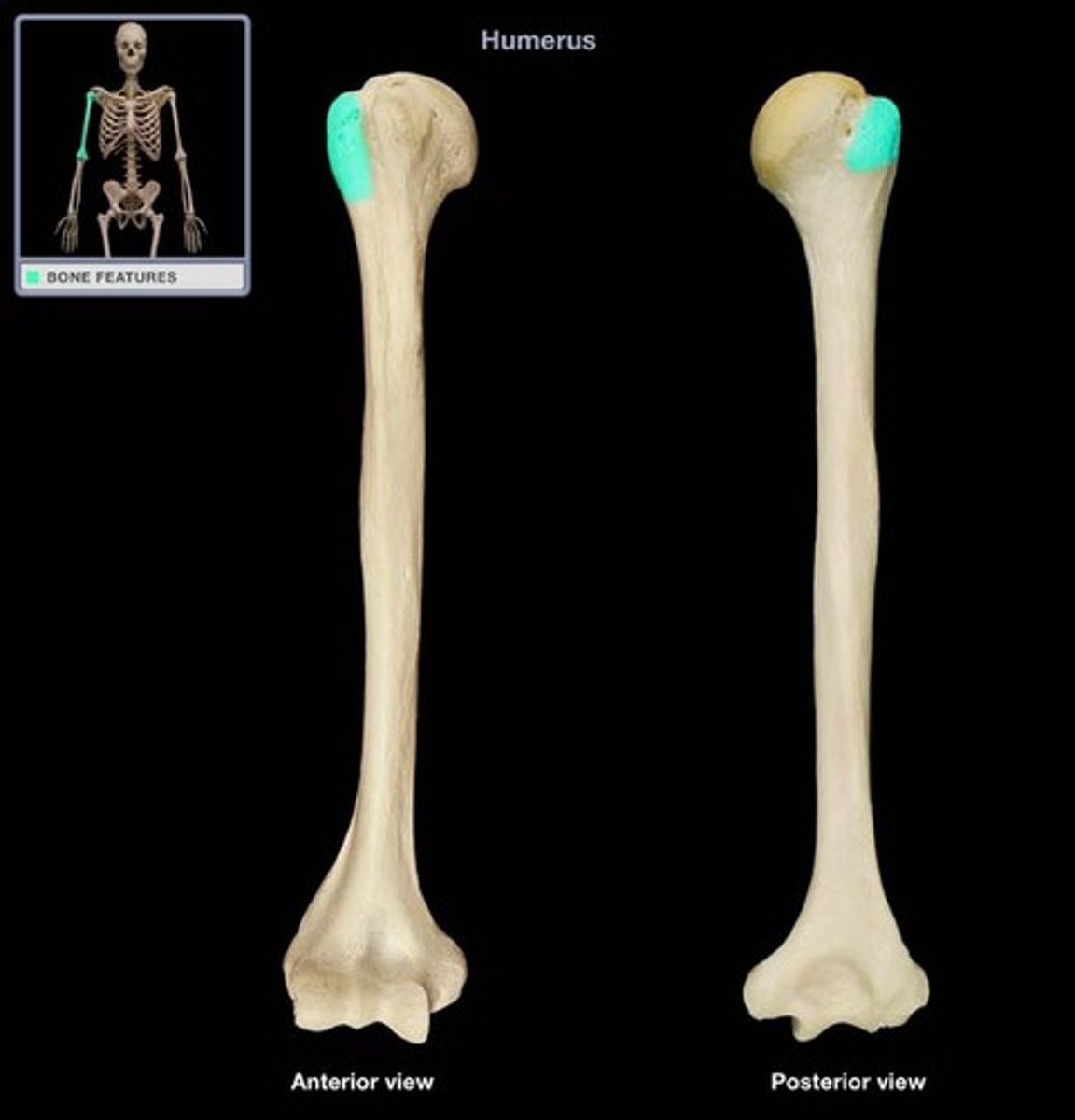
Lesser Tubercles
bony projection site of muscle attachment in the humorous
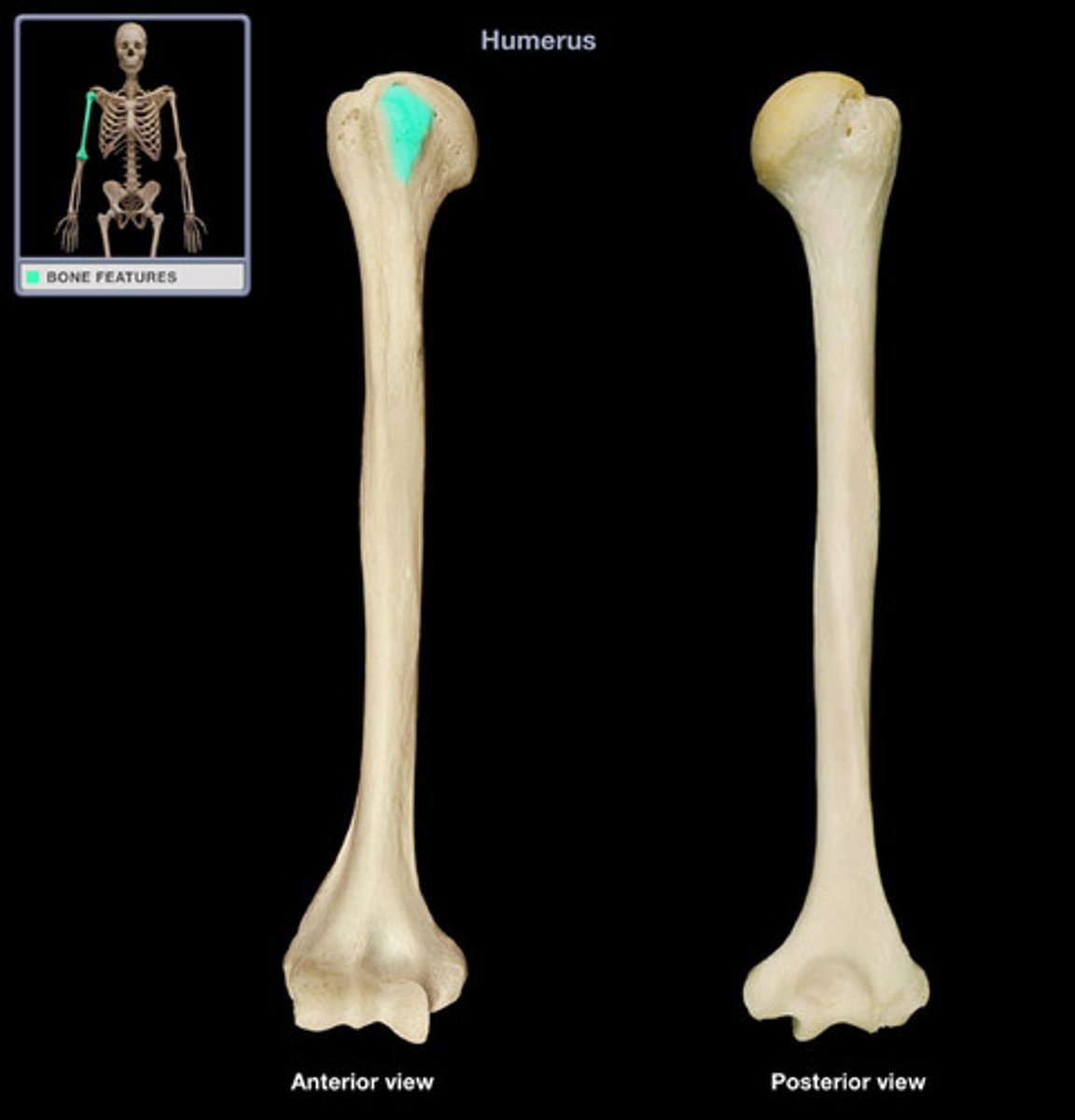
intertub
groove between the greater and lesser tubercles of the humerus
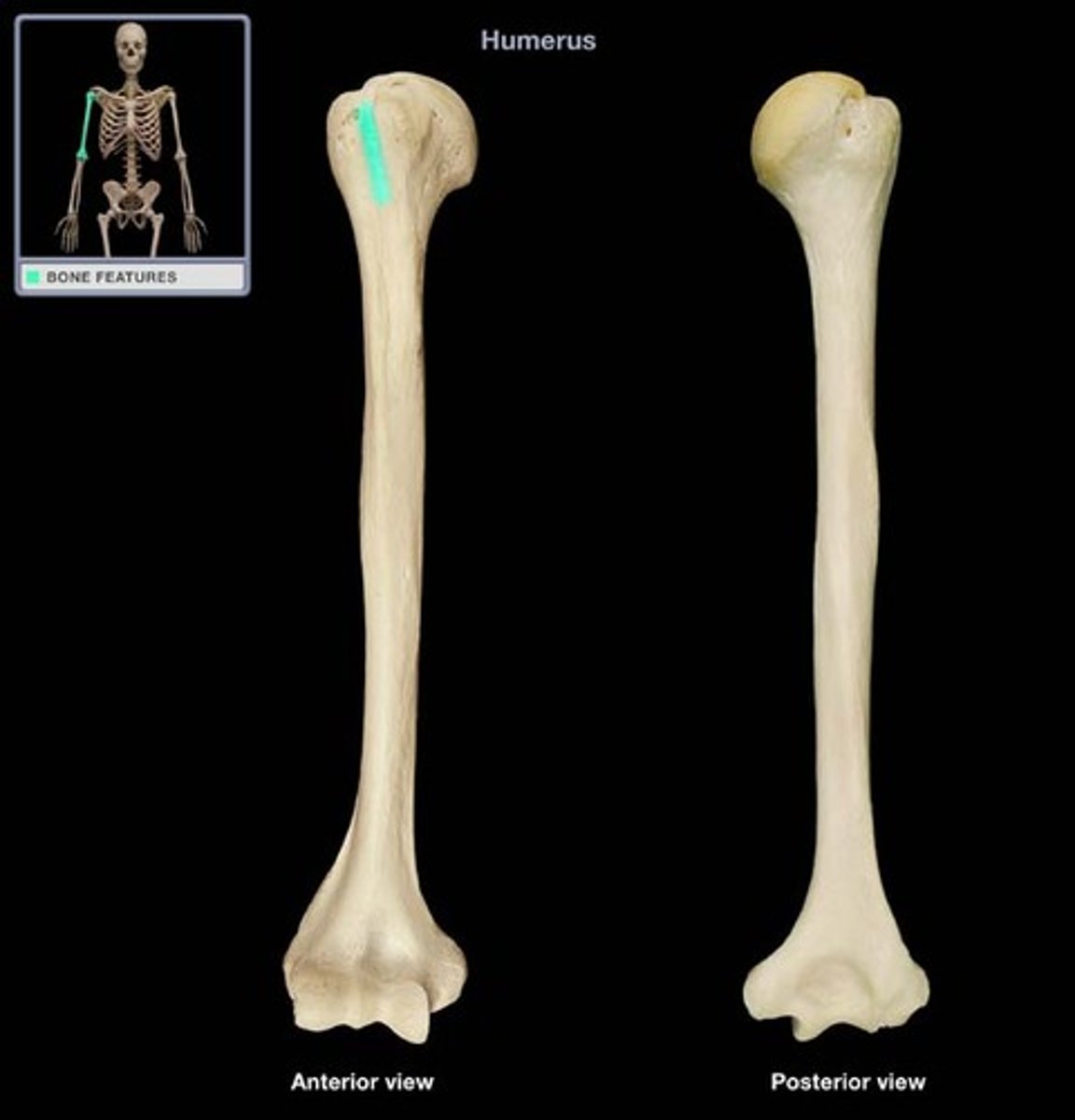
Shaft
Long, slender portion of a long bone
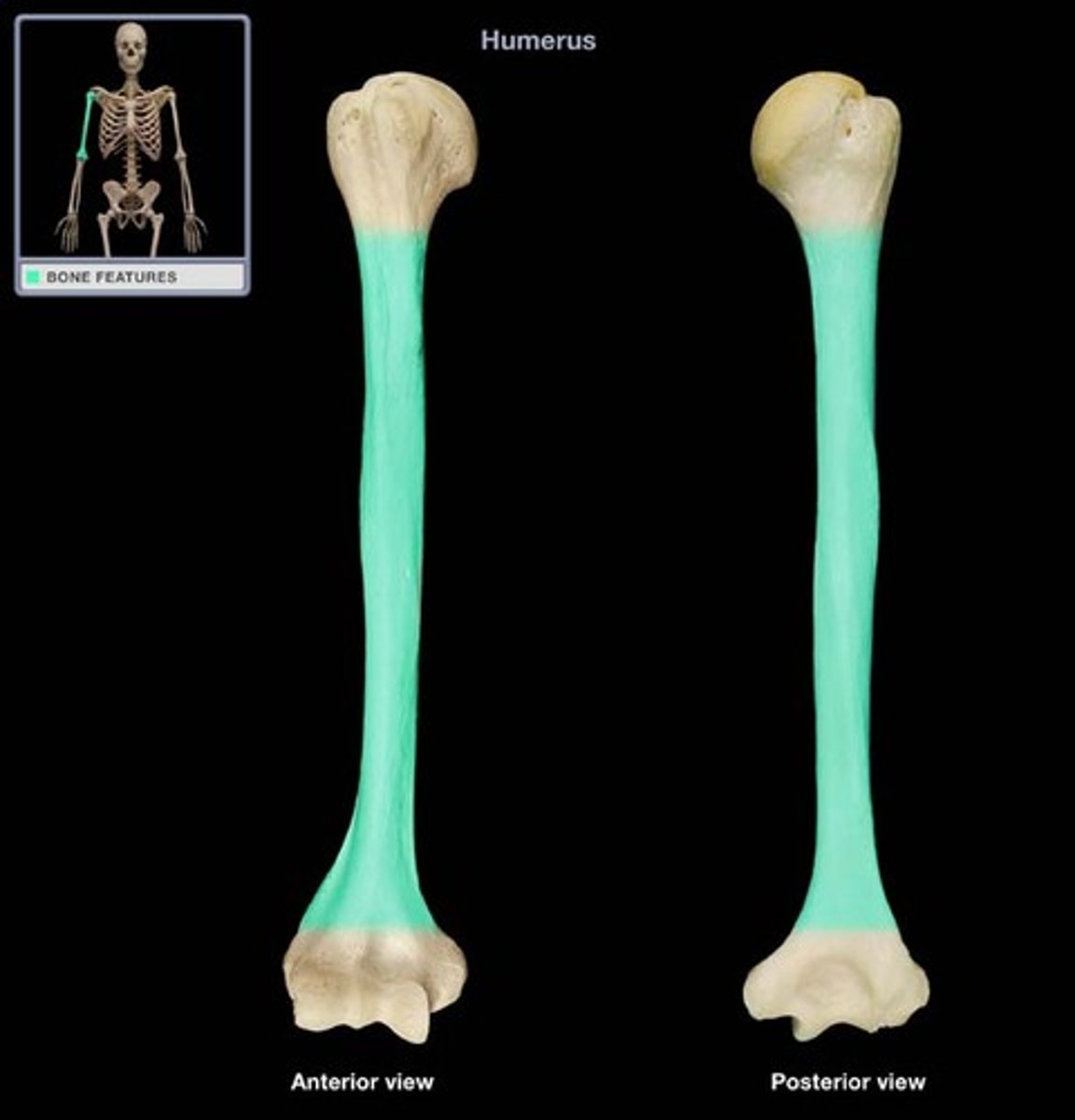
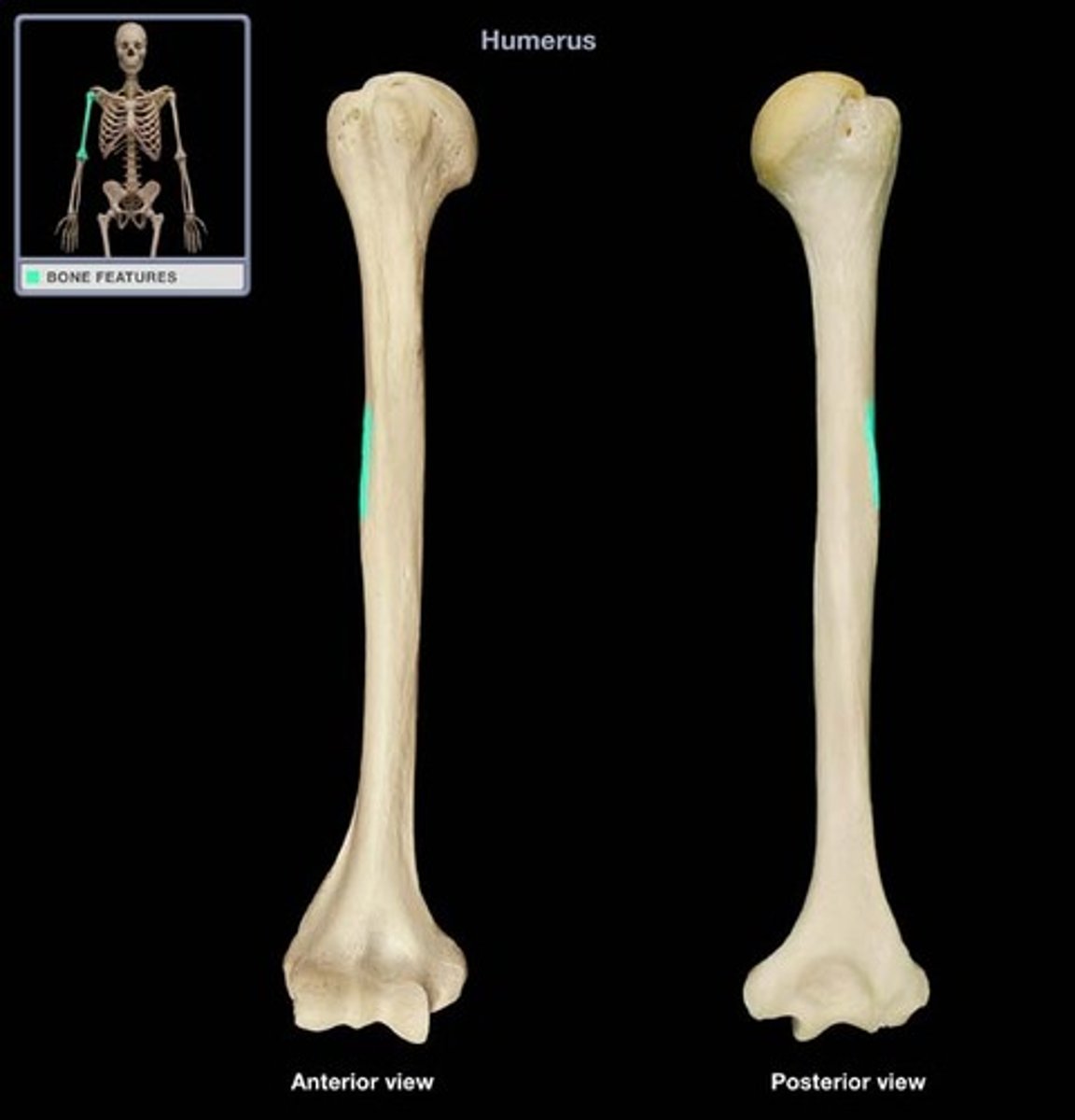
Deltoid tuberosity
raised area on lateral surface of humerus to which deltoid muscle attaches
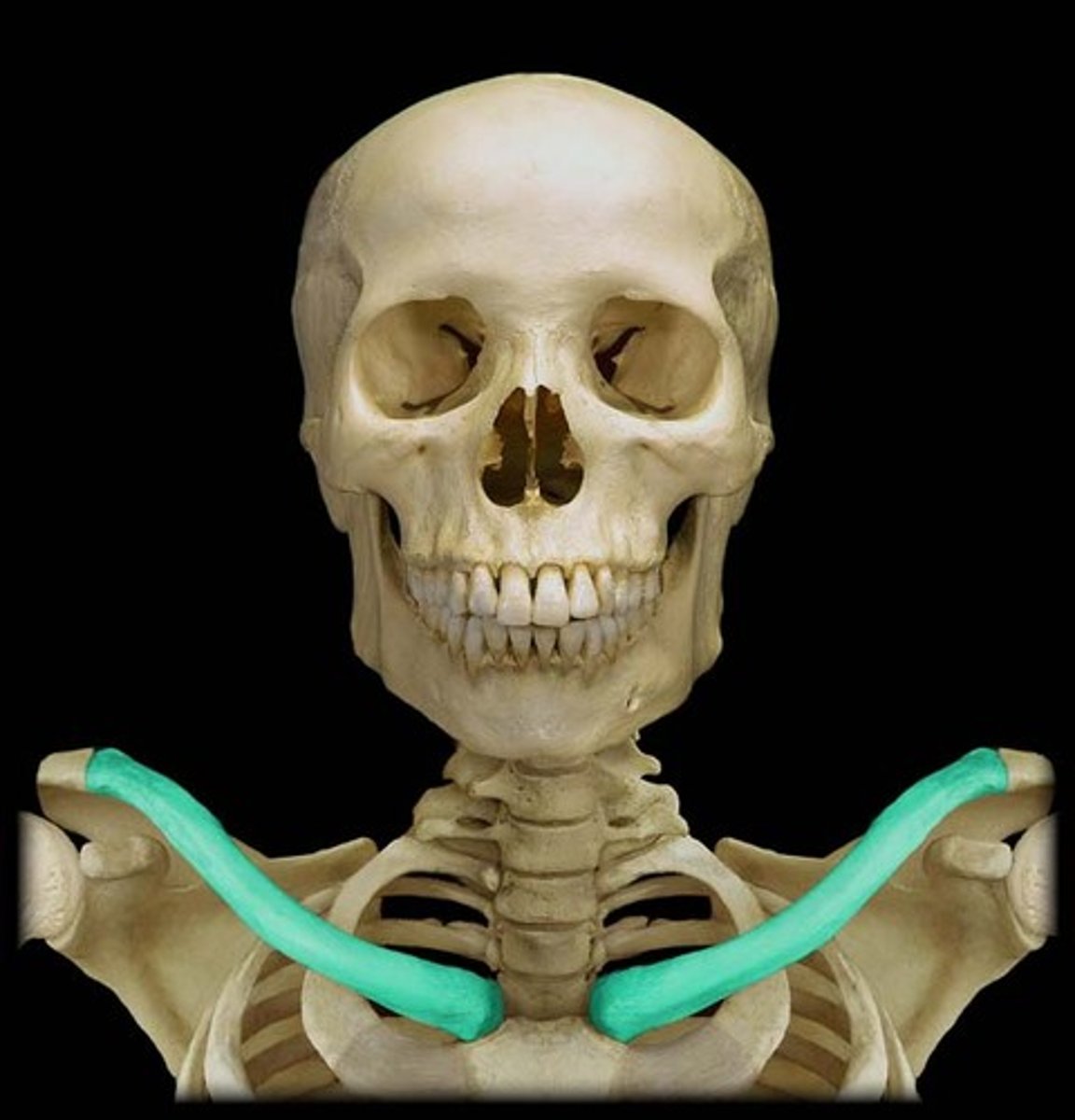
Clavicle
a strut that keeps the upper limb from the thorax to allow for maximum mobility
transmits forces from the arm to the axial skeleton
one of the most commonly fractured bones in the body
has 2 joints-
sternoclavicular joint
acromioclavicular joint
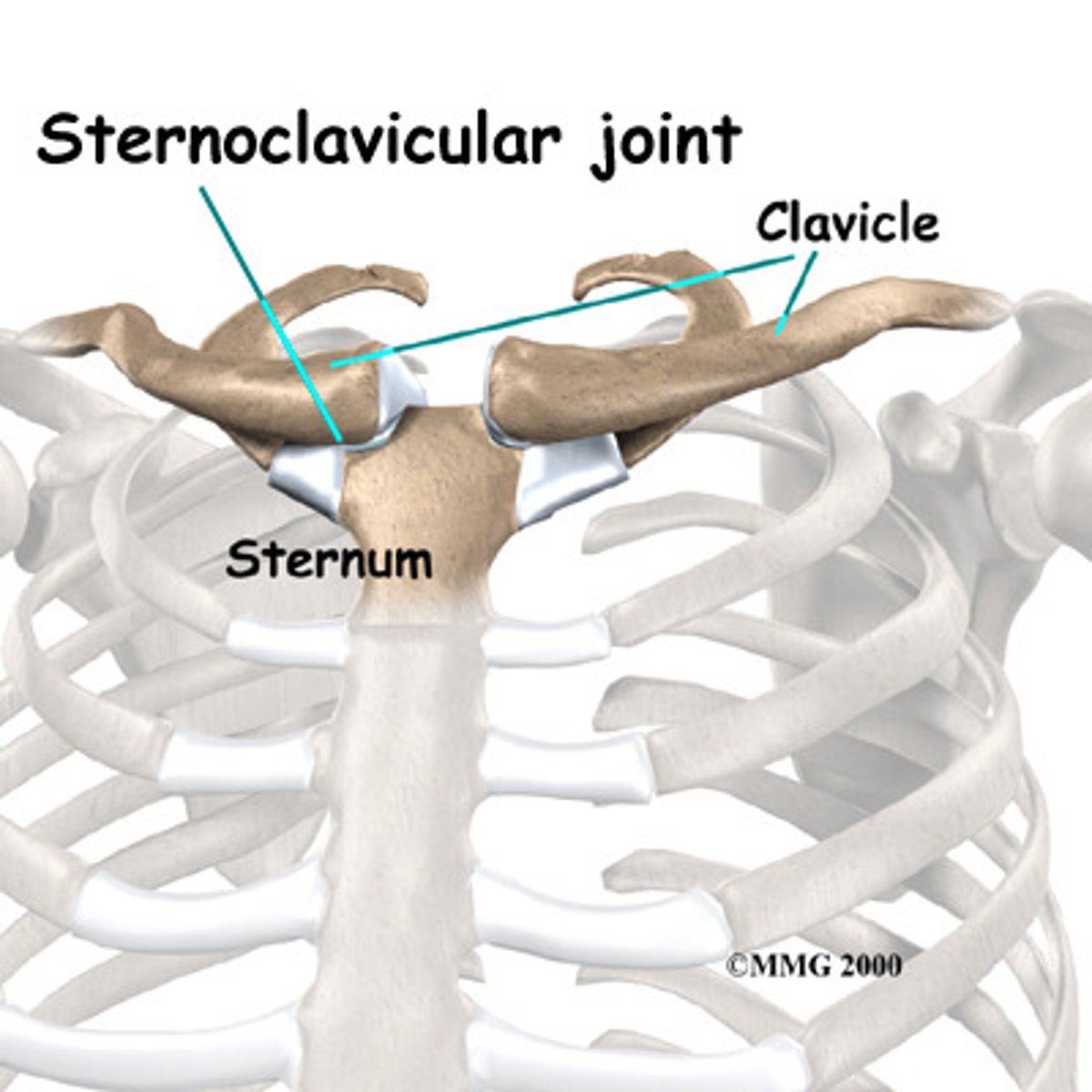
Sternoclavicular Joint
Articulation between the clavicle and the sternum
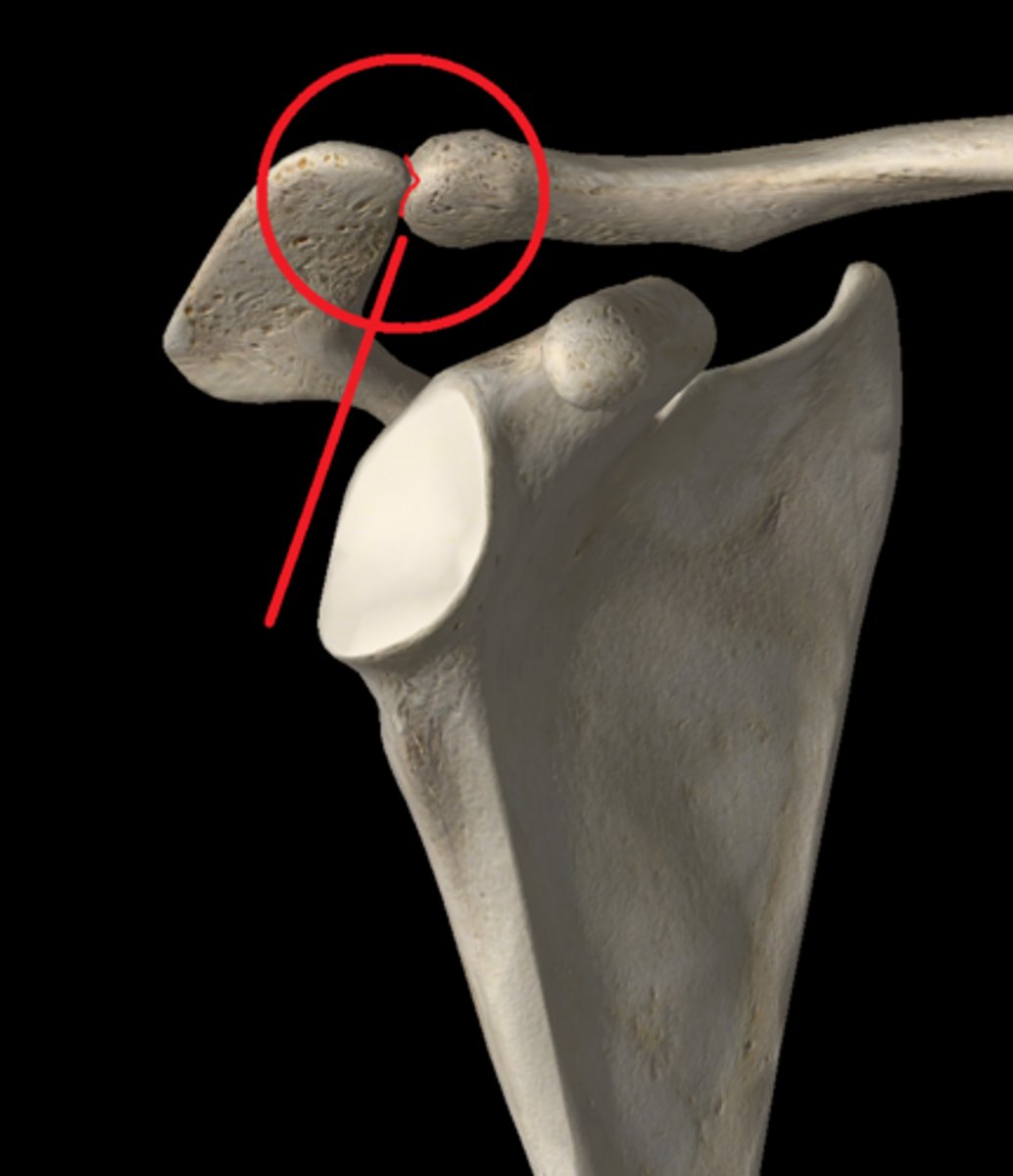
acromioclavicular joint
the joint formed by the acromion of the scapula and the clavicle
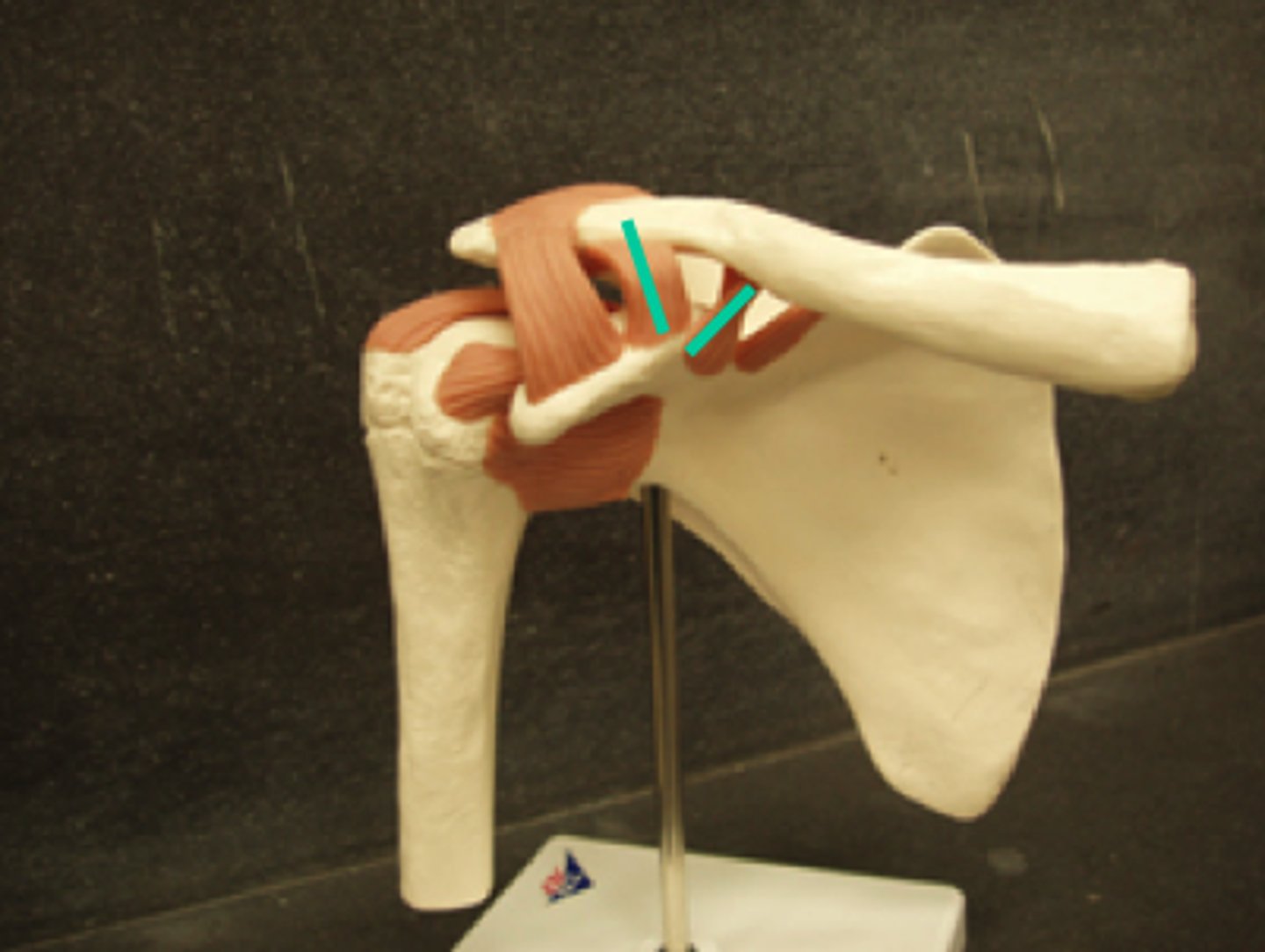
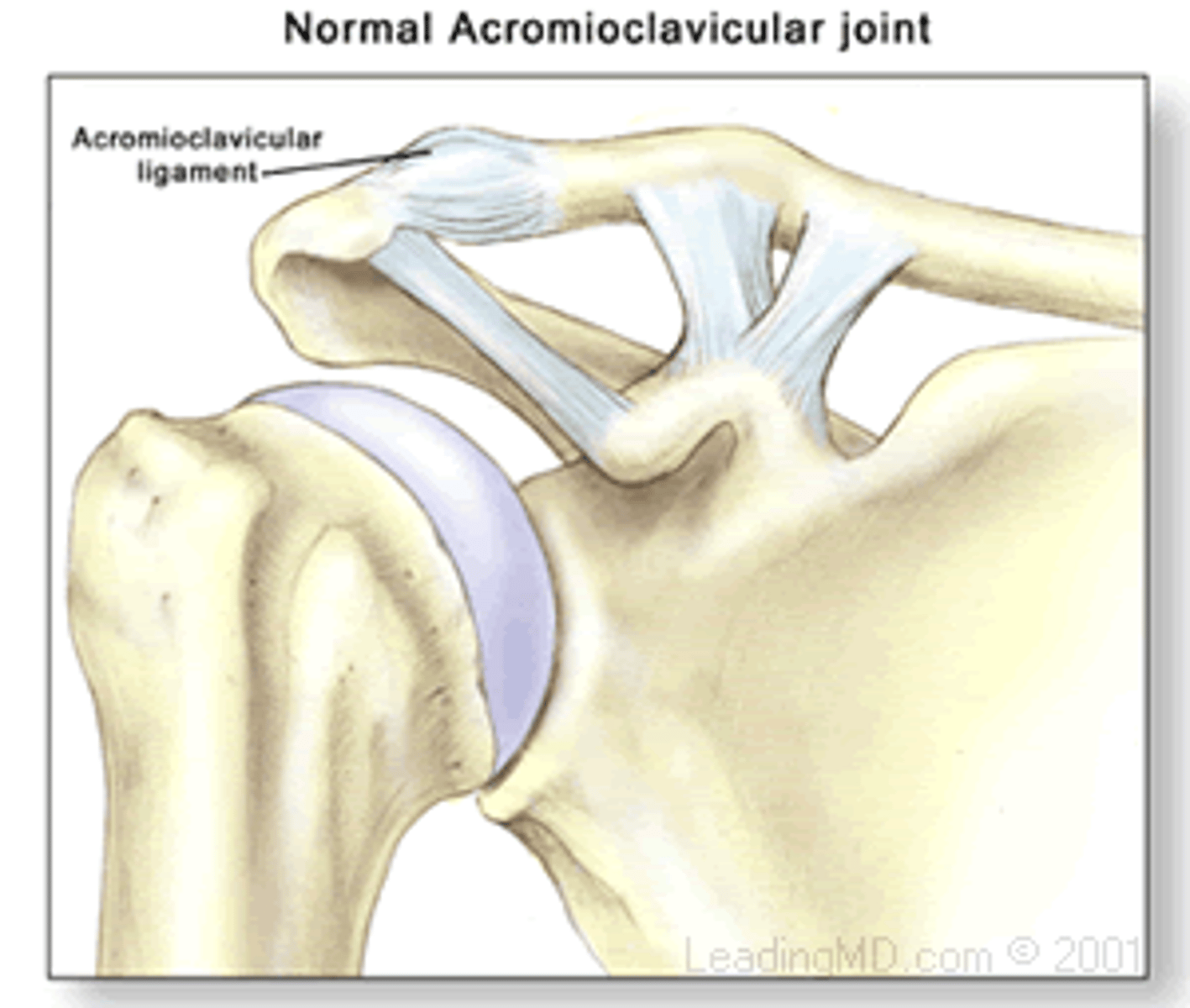
Pectoral Region- Ligaments
Coracoclavicular ligament
Acromioclavicular ligament
Coracoacromial Ligament
Coracoclavicular ligament
connects the clavicle to the coracoid process
Acromioclavicular ligament
connects the clavicle to the acromion
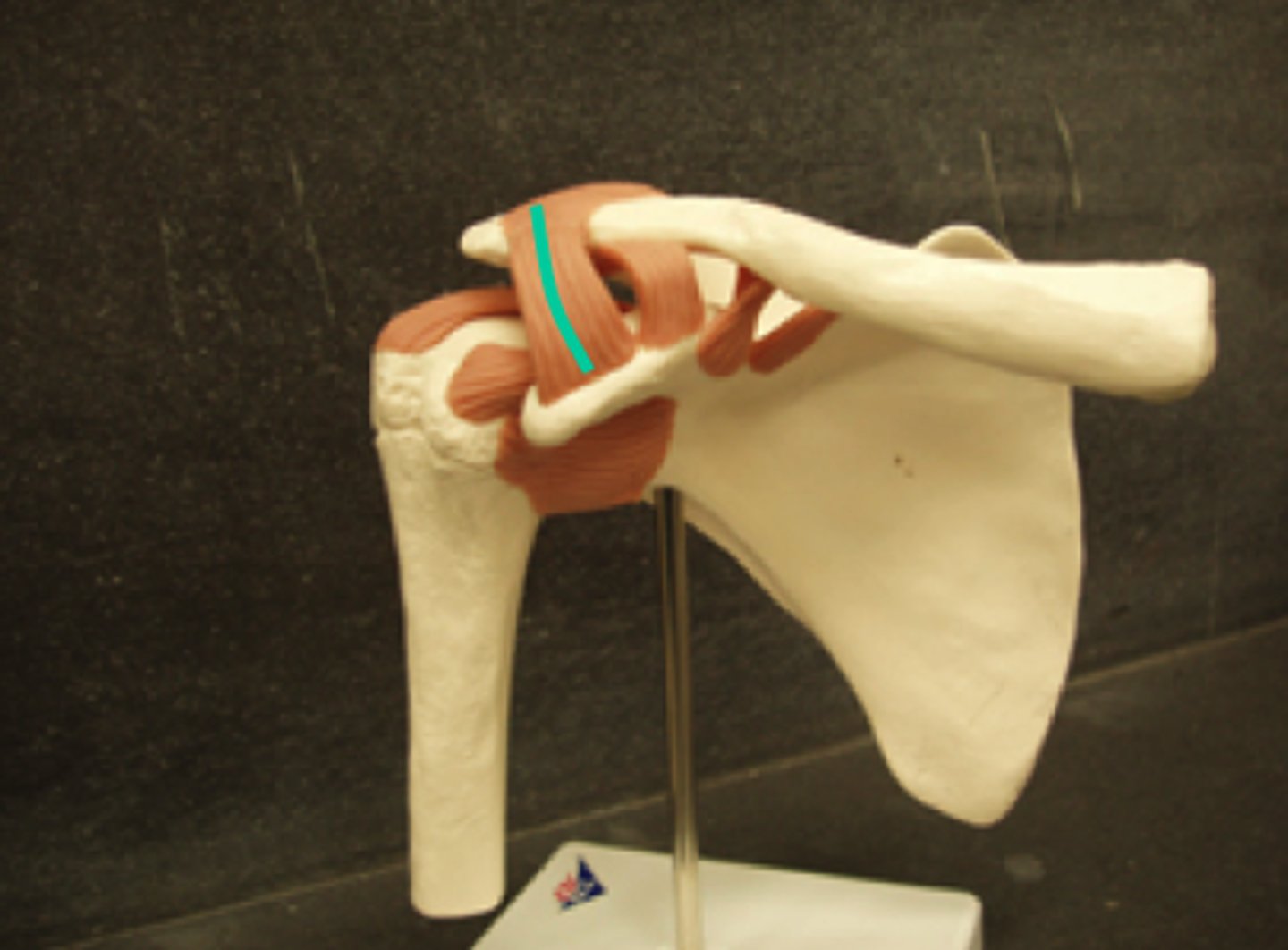
Coracoacromial Ligament
connects coracoid process and acromion
Pectoral Region- Muscules
Pectoralis Major
Pectoralis Minor
Serratus Anterior
Pectoralis Major
Origin- medial 1/2 of the clavicle, sternum, ribs 1-6
Insertion- upper anterior humerus/intertubercular groove
Innervation- medial and lateral pectoral nerves
Major Actions- Adduction and medical rotation of the arm
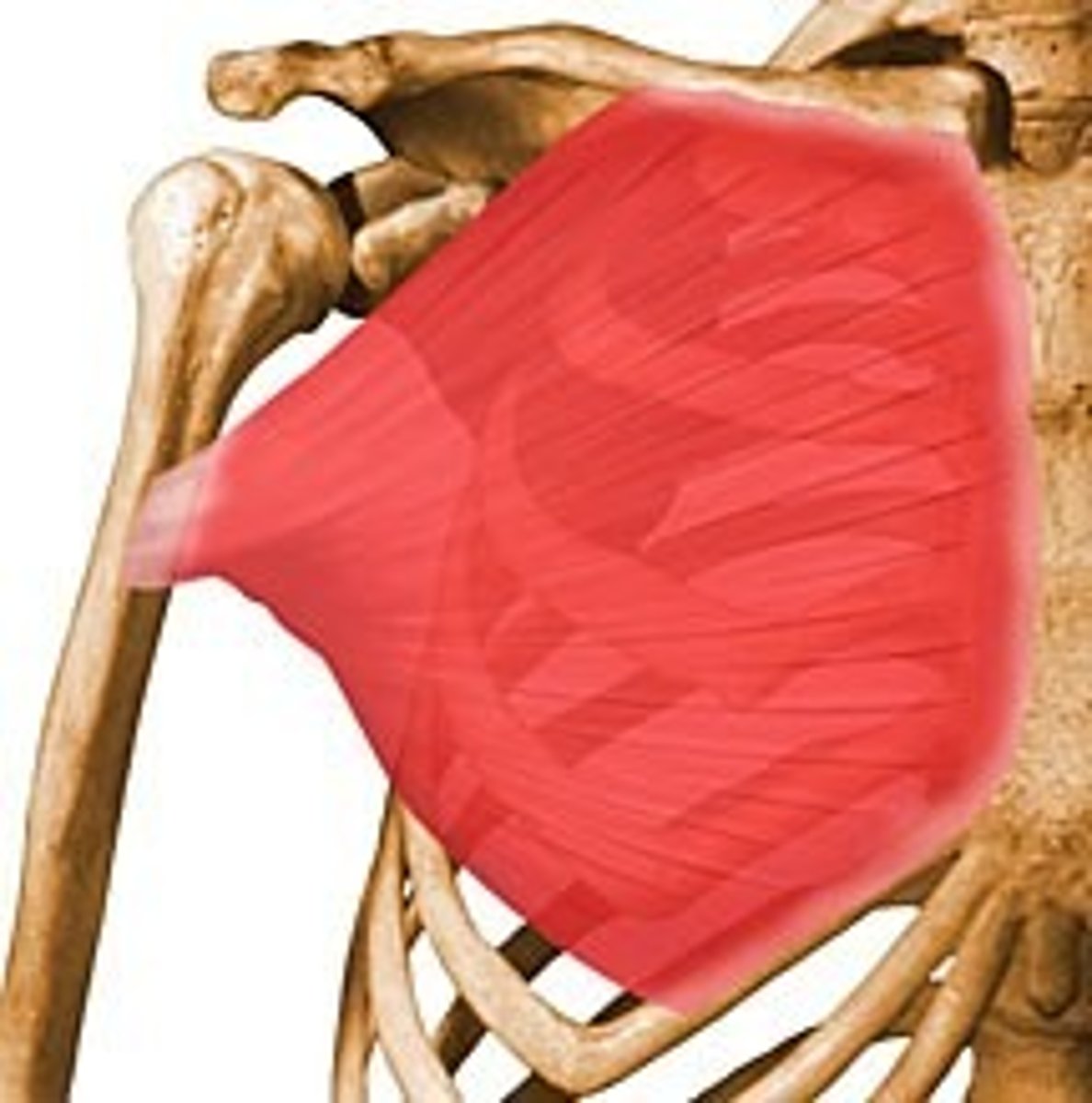
Pectoralis Minor
Origin- ribs 3-5
Insertion- coracoid process of the scapula
Innervation- medial pectoral nerve
Major Actions- stabilizes scapula against thoracic wall; medial rotation of scapula
deep to pectoralis major
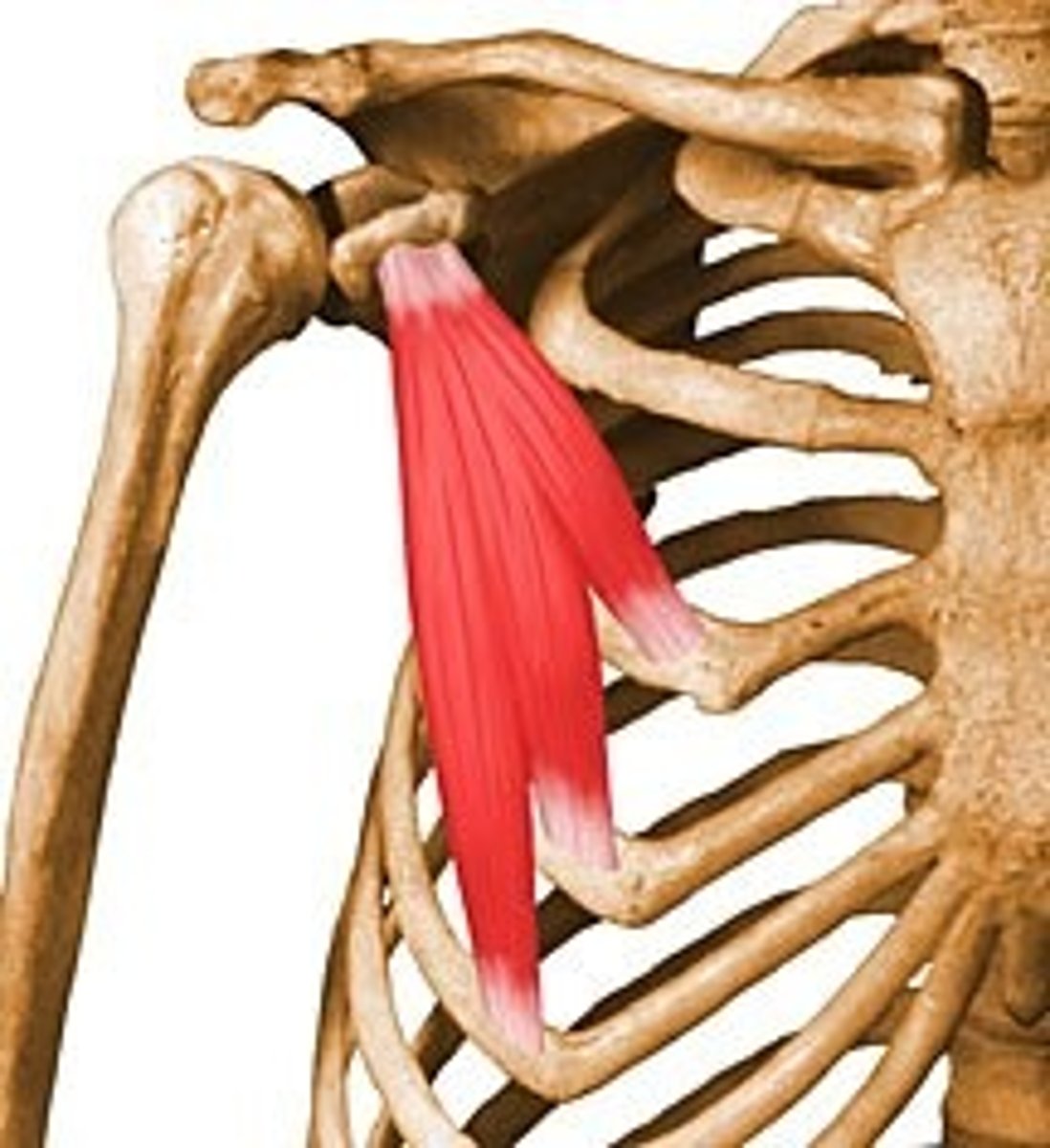
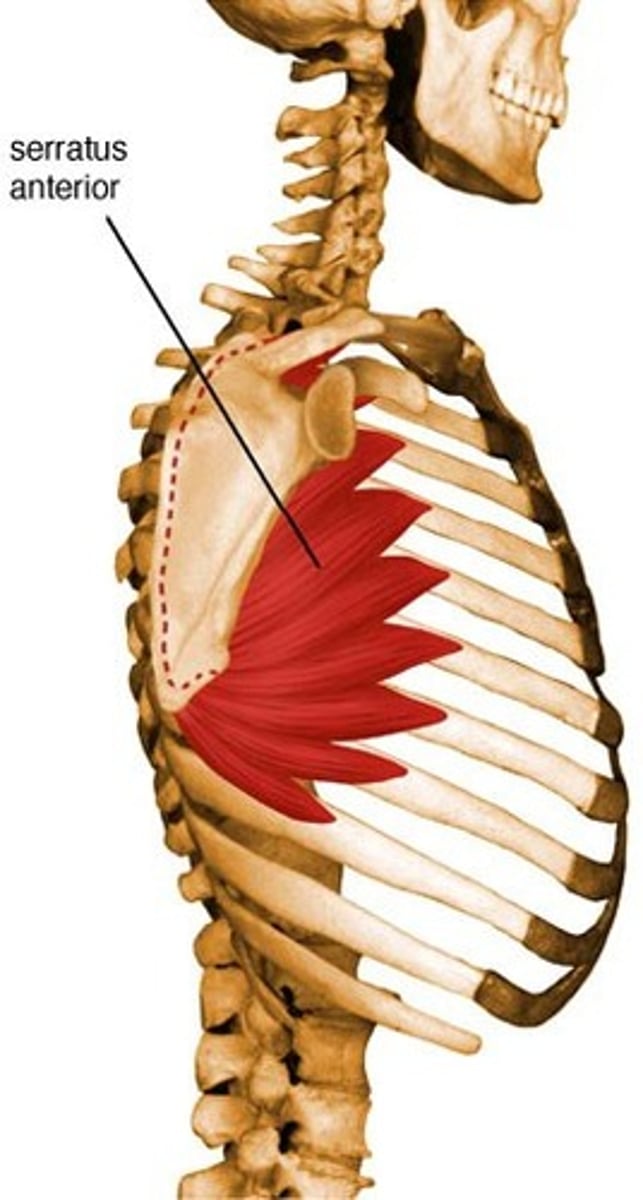
Serratus Anterior
Origin- Ribs 1-8
Insertion- medial border of the Scapula
Innervation- Long thoracic nerve
Major Actions- stabilizes scapula against thoracic wall; lateral rotation of scapula beyond 90*
Scapular Winging
occurs when an injury to the long thoracic nerve weakens or paralyzes the serratus anterior muscle, causing the medial border of the scapula to rise away from the rib cage
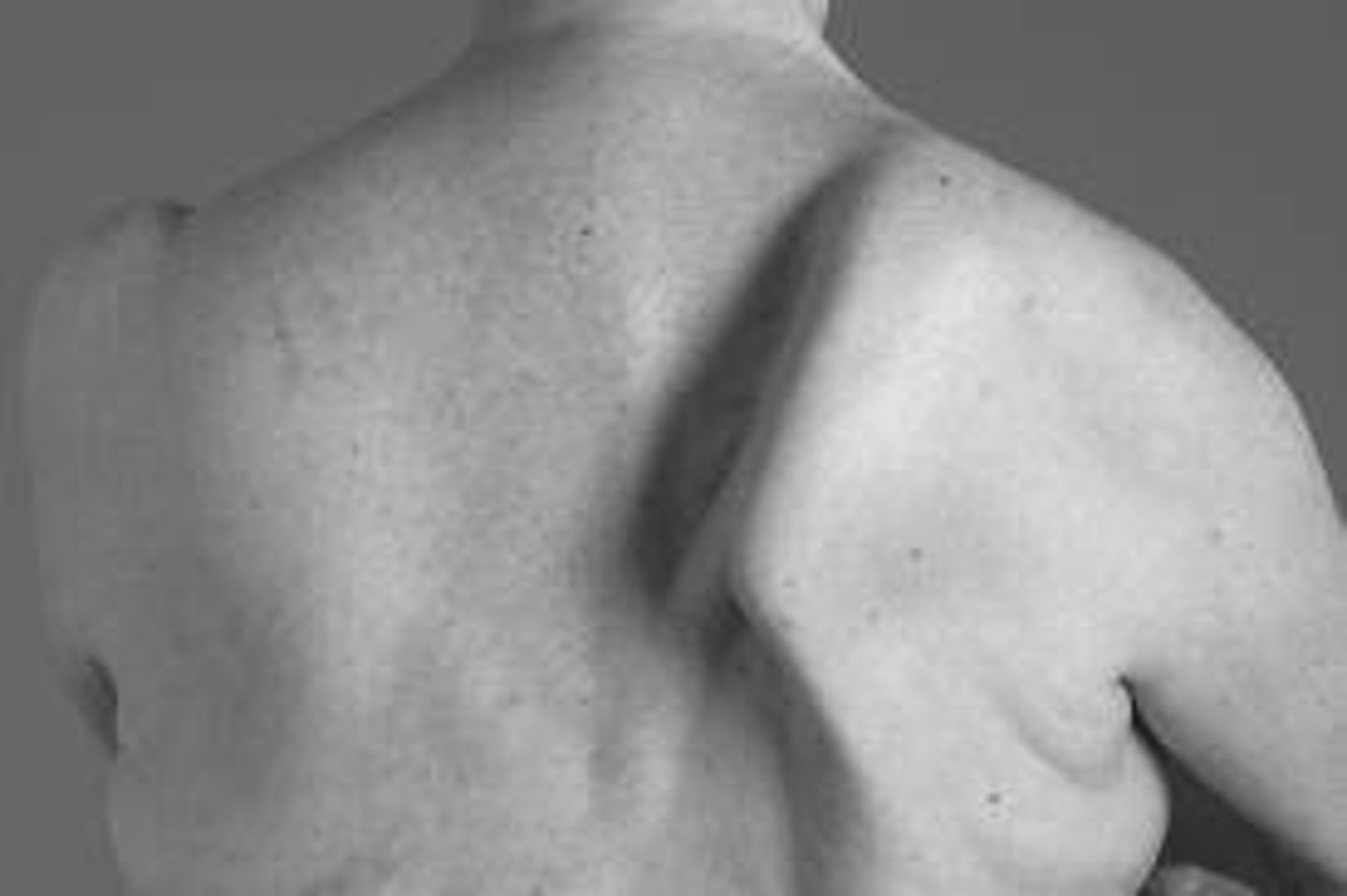
Shoulder Region- Muscules
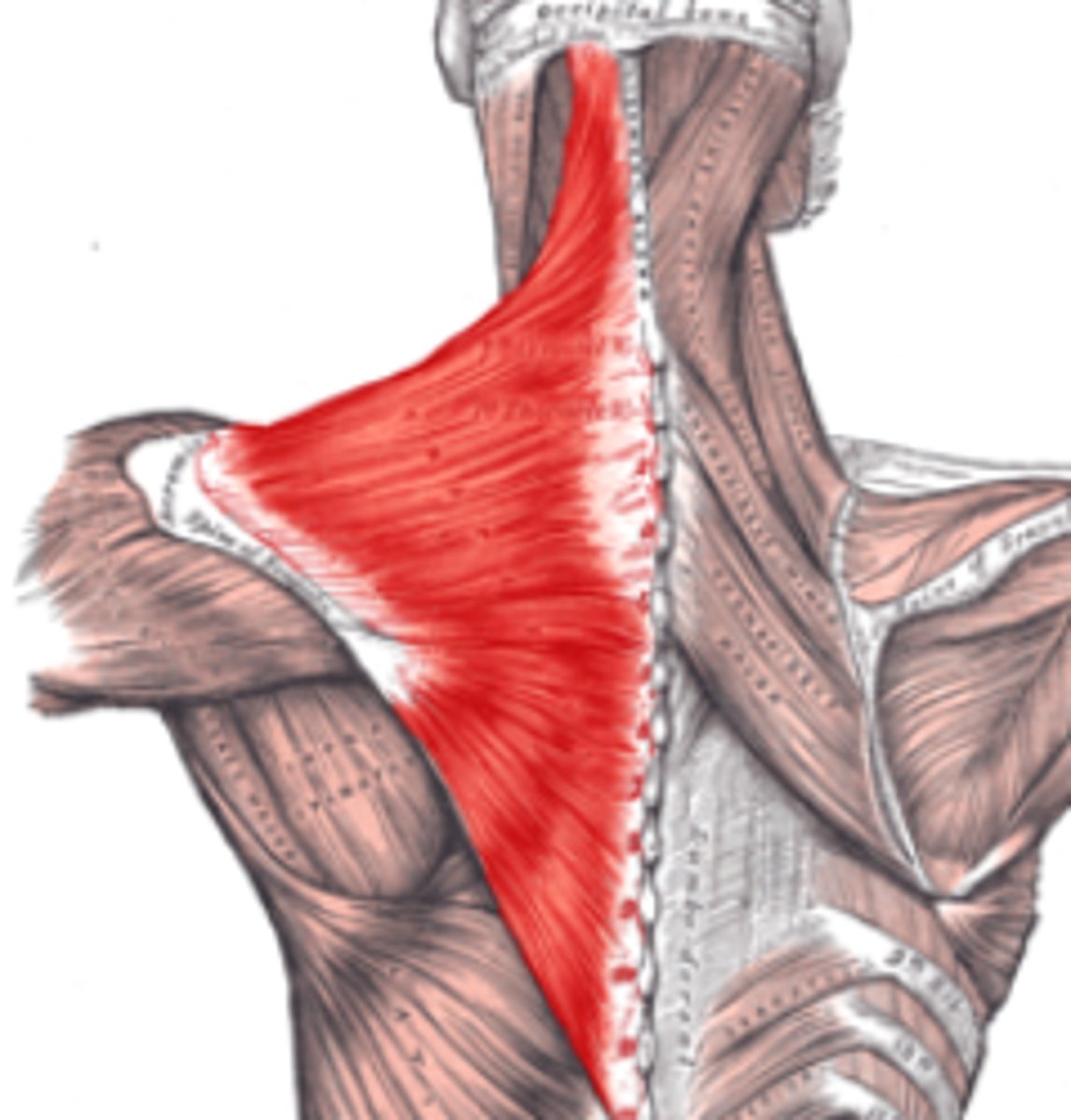
Trapezius
Latissimus Dorsi
Levator Scapulae
Rhomboid Major
Rhomboid Minor
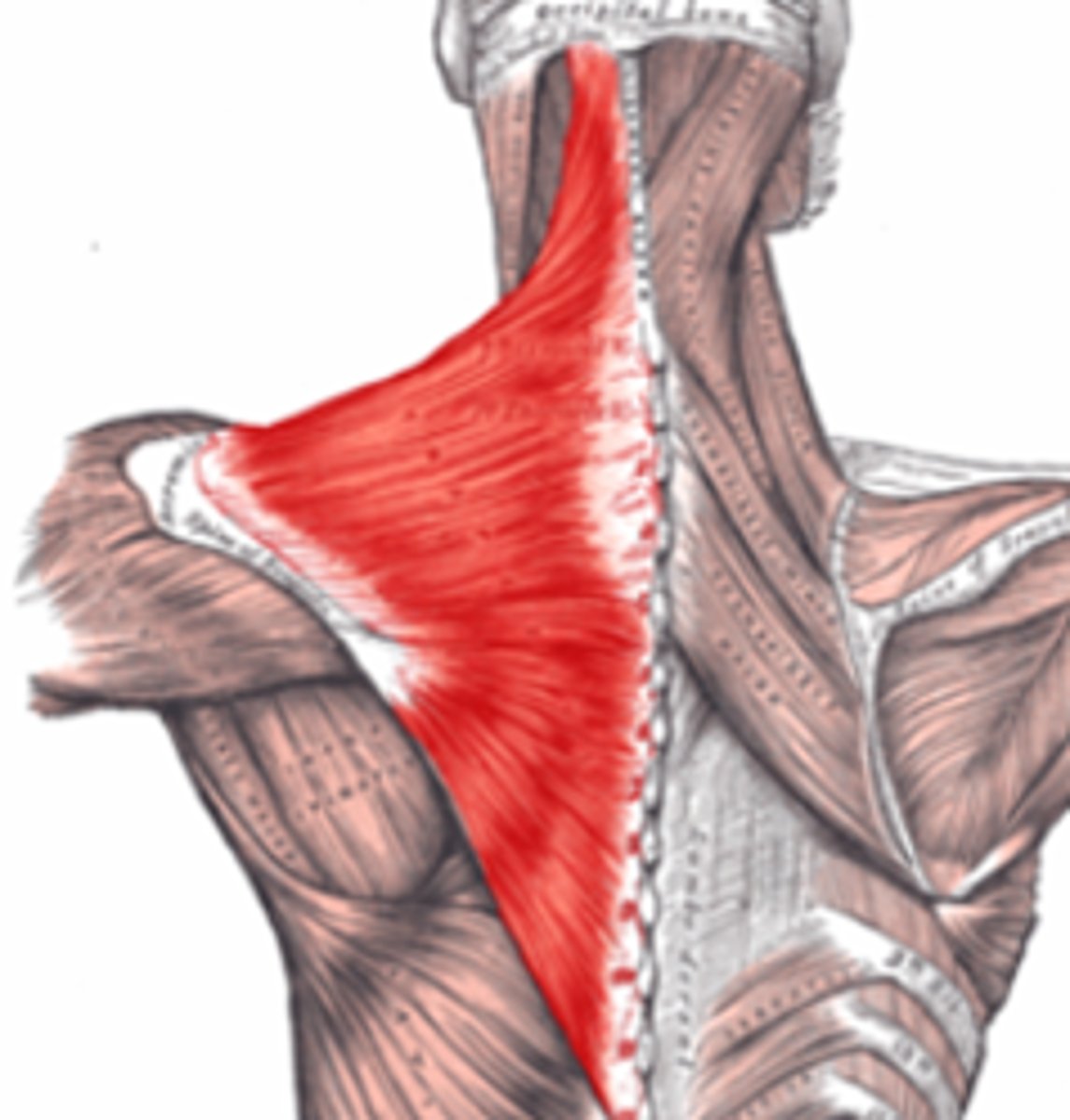
Trapezuis
Origin- Occipital bone and C7-T12 vertebral spines
Insertion- lateral 1/3 of the clavicle, acromion, and the Scapular spine
Innervation- Accessory Nerve
Major Actions- Elevates, Depresses, Retracts and rotates the scapula
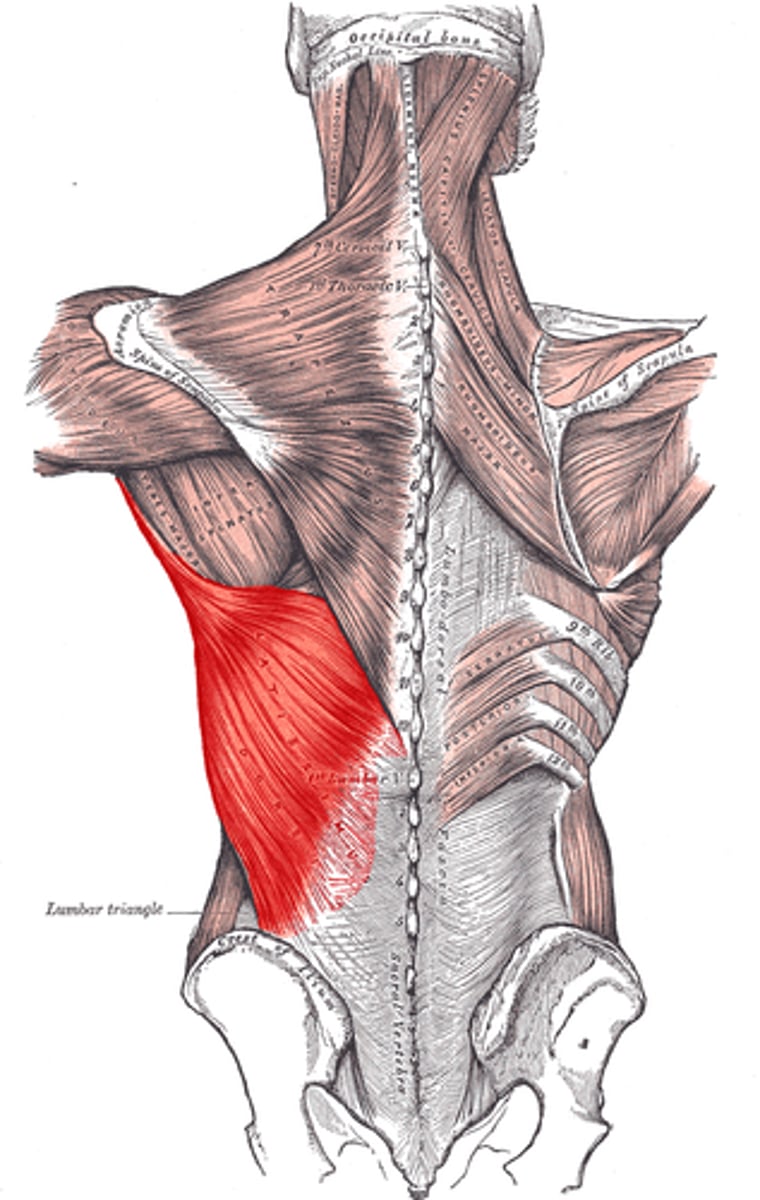
Latissimus Dorsi
Origin- T7-T12 vertebral spines. iliac crest, inferior ribs
Insertion- intertubercular groove
Innervation- thoracodorsal nerve
Major Actions- Extends,adducts, and medically rotates the humerus
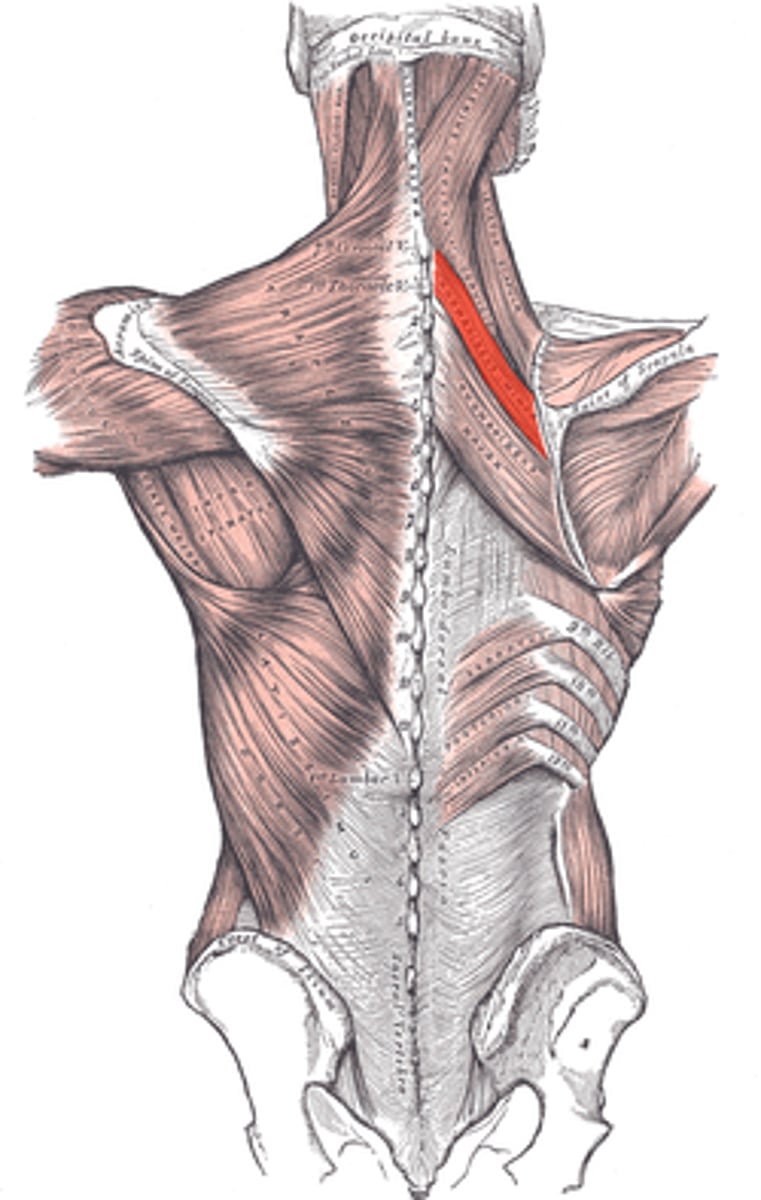
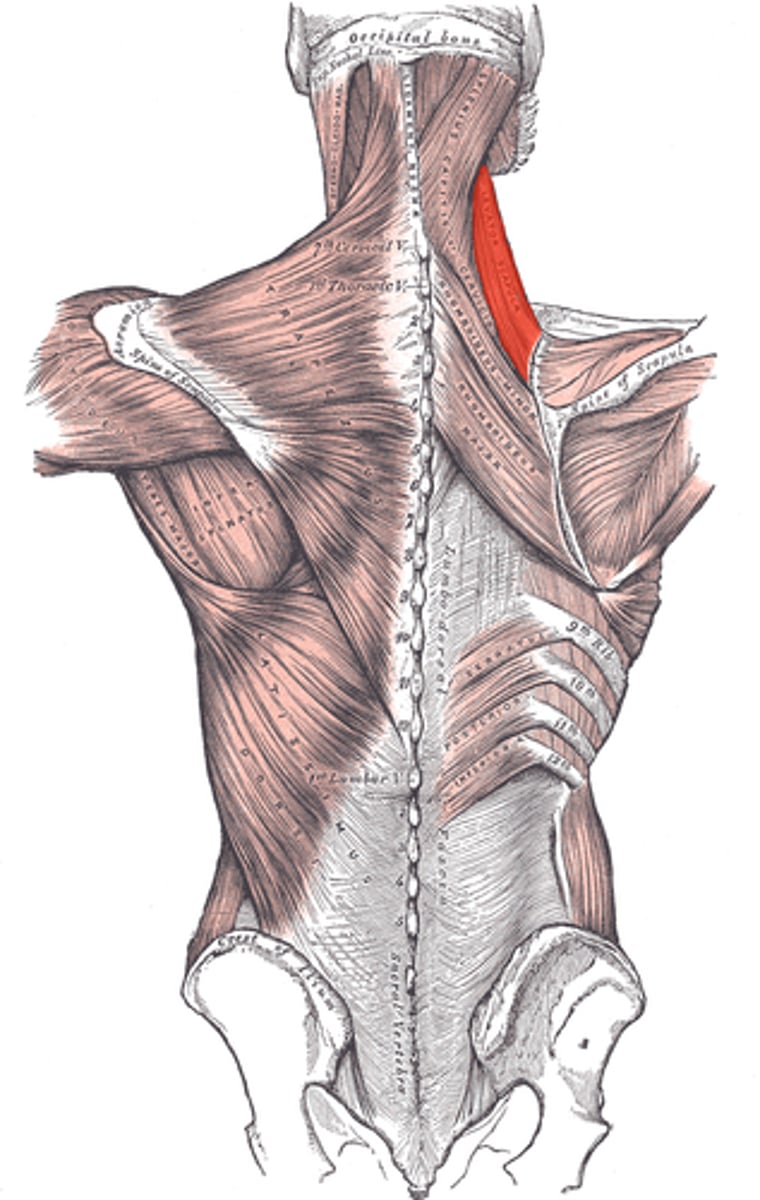
Levator Scapulae
Origin- Vertebrae C1-C4
Insertion- medial scapular border, above the base of the scapular spine
Innervation- dorsal scapular nerve
Major Actions- Elevates and medially rotates the scapula
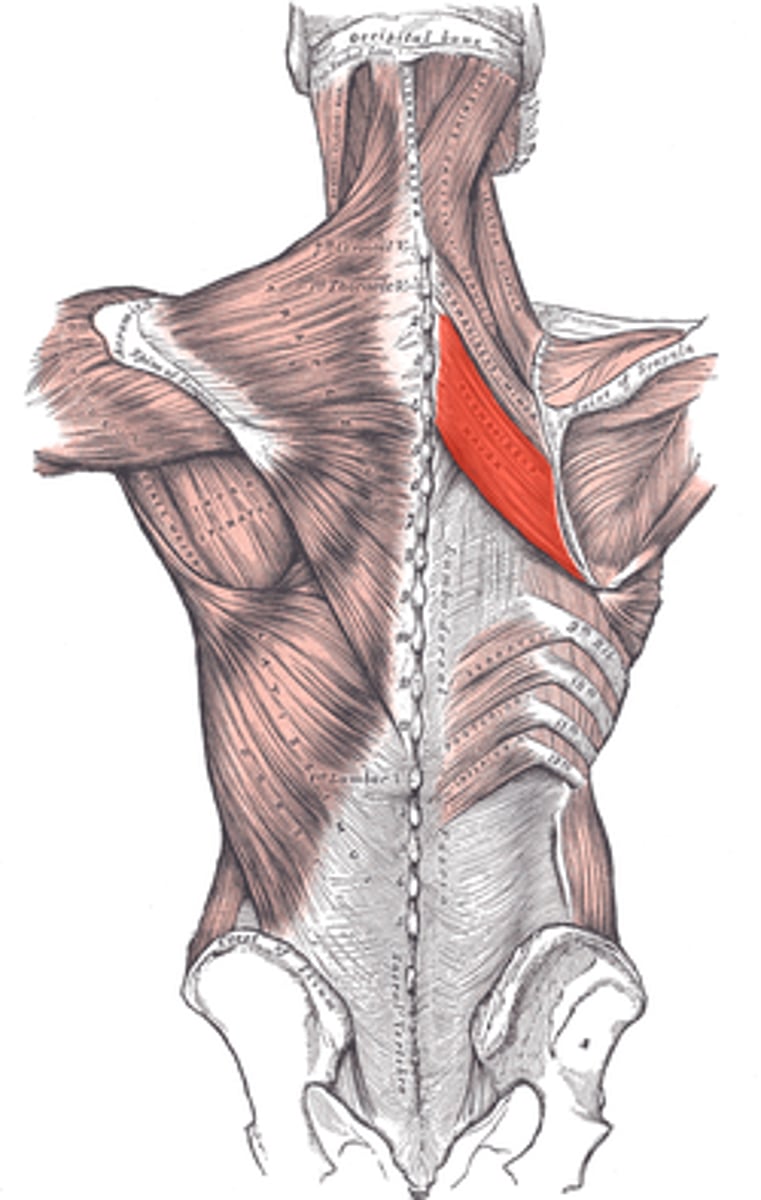
Rhomboid Major
Origin- upper thoracic spines
Insertion- medial scapular border, below the base of the scapular spine
Innervation- dorsal scapular nerve
Major Actions- retracts and medially rotates scapula
Rhomboid Minor
Origin- vertebrae C7-T1
Insertion- medial scapular border, at the base of the scapular spine
Innervation- dorsal scapular nerve
Major Actions- stabilizes, retracts, and medially rotates scapula