Unit 2 - Energy Changes, Thermochemistry & Rates of Reaction
1/23
There's no tags or description
Looks like no tags are added yet.
Name | Mastery | Learn | Test | Matching | Spaced | Call with Kai |
|---|
No analytics yet
Send a link to your students to track their progress
24 Terms
Bond dissociation energy (BDE) equation
Bonds BROKEN - Bonds FORMED or…
-bonds FORMED + bonds BROKEN
Finds total energy change

Sublimation
Solid to gas
Desublimation
Gas to solid
Fusion
Solid to liquid
Solidification
Liquid to solid
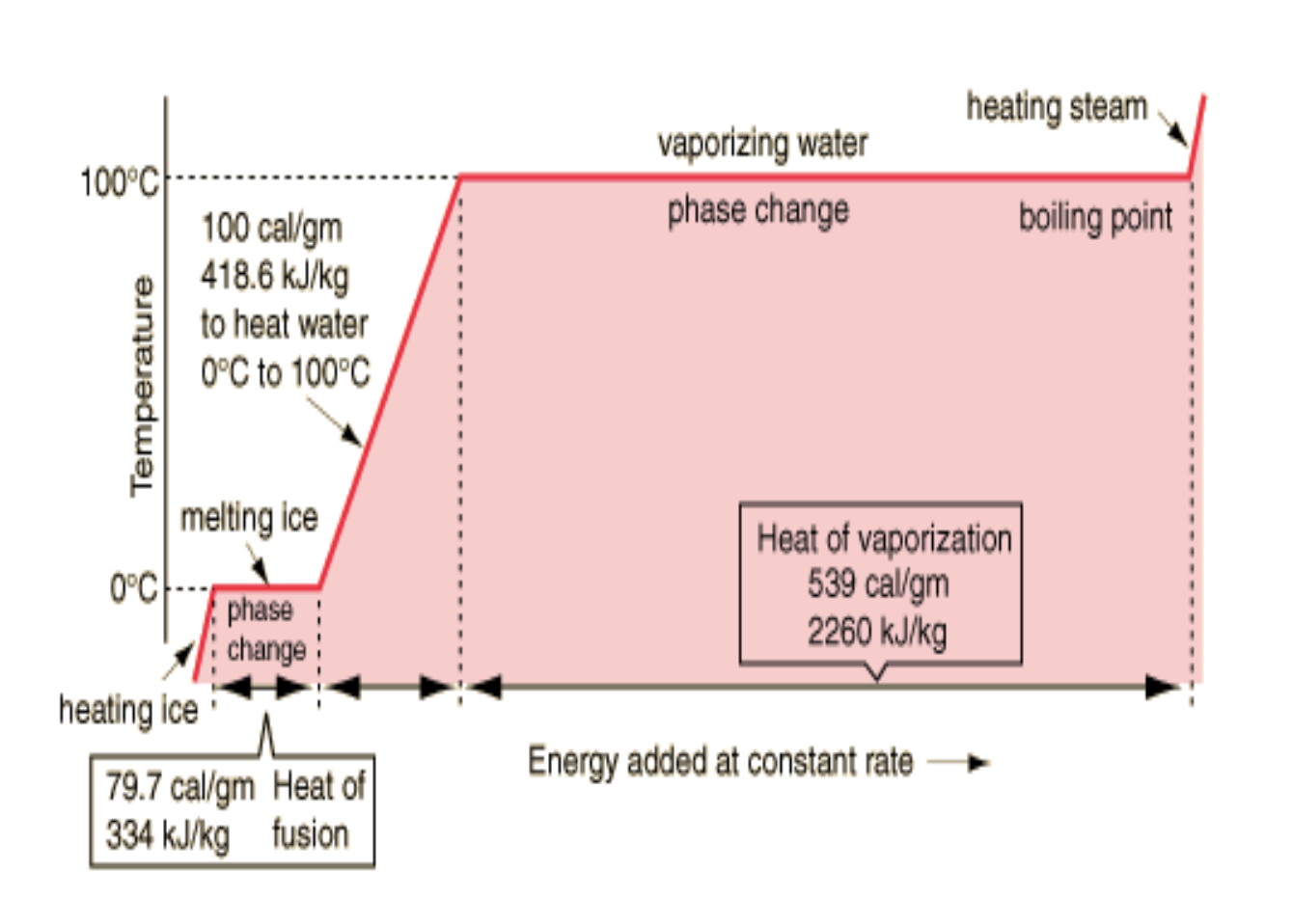
Why doesn’t temperature change when reactant is changing states?
Energy goes into breaking intermolecular bonds between particles instead of increasing kinetic energy
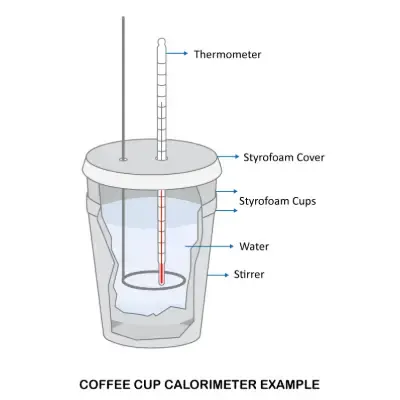
Calorimeter constant equation
Ccal = qcal / 𝝙T
Gibb’s Free Energy Equation
𝝙G = 𝝙H - T𝝙S (kJ or J)
Entropy of SURROUNDINGS equation
-𝝙H/T (J/K)
What 𝝙G value signifies a spontaneous reaction? What does a 𝝙G of 0 mean?
When 𝝙G < 0, rxn is spontaneous
When 𝝙G = 0, rxn is at equilibrium; neither occuring in forward or reverse directions
Entropy equation
S = k ln W (J/K) where:
S = entropy
k = Boltzmann constant
W = microstates
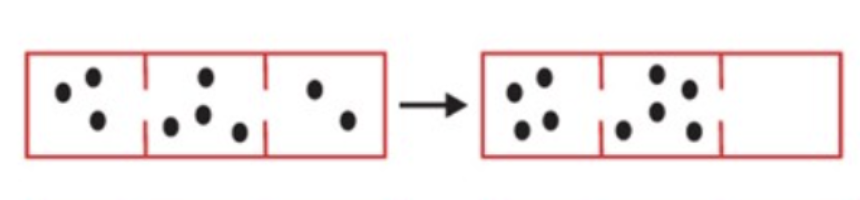
Is the 𝝙S greater, lesser, or equal to zero?
𝝙S < 0
What factors increase entropy and why?
Volume - more spatial configurations, more possible ways to distribute E
Temperature - more kinetic E, more possible ways it can be partitioned
# of molecules (MATTERS MORE THAN COMPLEXITY) - more molecules, more possible arrangements in space
Complexity - more complex molecule, more degrees of freedom, more microstates
Enthalpy of formation definition
Energy change when one mol of product is generated from its elements in standard state.
Bond Energy definition
Energy required to break one mol of bond within a gaseous substance.
What is suggested about the entropy and enthalpy of this rxn if it’s spontaneous?
Entropy:
𝝙S approx equal to 0 or a little larger than zero
Molecules amount or complexity does not change dramatically
Enthalpy:
𝝙H likely negative (exothermic)
Probably largest contributing factor to spontaneity of this rxn
What is a reaction that is spontaneous where 𝝙G < 0 called?
EXERGONIC
What is a reaction that is not spontaneous where 𝝙G > 0 called?
ENDERGONIC
What factors affect rate of reaction?
Relating to collision theory:
Concentration (more particles, more successful collisions, faster rxn)
Surface Area (more reactant particles "exposed” to collide, faster rxn)
Temperature (more kinetic E, more high E collisions, chance particles surpass EA)
Catalyst (lowers EA, faster rxn)
Collision theory
For a rxn to occur, particles must collide with the proper:
Energy (greater than EA)
Orientation (collision geometry)
Average rate formula
Slope of concentration-time graph:
-(𝝙[A] / 𝝙T)
negative bc 𝝙[A] is negative, but rate is traditionally positive.
![<p>Slope of concentration-time graph:</p><ul><li><p>-(𝝙[A] / 𝝙T)</p></li></ul><p><em>negative bc 𝝙[A] is negative, but rate is traditionally positive.</em></p><p></p>](https://knowt-user-attachments.s3.amazonaws.com/1f190826-d68a-4339-9168-1f6e4dd49a0a.png)
Rate law equation
Rate = k[A]x[B]y
where:
Rate in mol/(L x S)
k = rate constant
[A] and [B] = reactant concentration (mol/L)
x and y = reactant order, NOT stoich coeff
Why does the rate constant k depend on temperature?
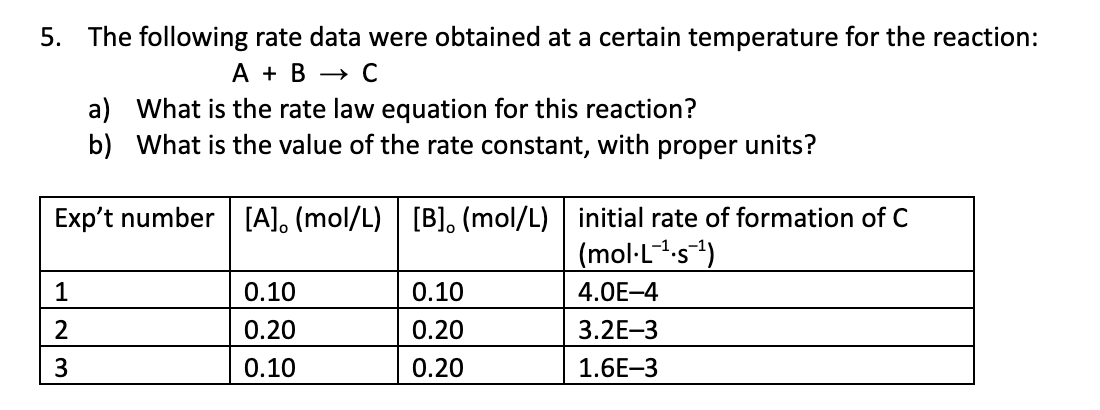
Define rate law and units of k for this reaction, where A + B → C
Rate law: rate = k[A]1[B]2
k = L2/(mol2 x S)