B5 homeostasis and responsewhat is homeostasis
1/43
There's no tags or description
Looks like no tags are added yet.
Name | Mastery | Learn | Test | Matching | Spaced |
|---|
No study sessions yet.
44 Terms
what is homeostasis?
The regulation of internal conditions of a cell or organisms to maintain optimum conditions for function, in response to internal or external changes
Name three things that are controlled by homeostasis?
blood glucose concentration
body temperature
water levels
Homeostasis is a voluntary/involuntary system that involves ____ or ___ responses
involuntary
chemical or nervous
what is the role of the receptor?(example)
detect stimulus (specialised cells)
what are the roles of the control centres?
To receive and process information (brain,spinal cord, pancreas)
What is the role of the effectors?
to bring about responses to restore optimum levels.(muscles,glands)
what is the role of the nervous system?
to enable us to react to our surroundings and coordinate our behaviour.
what does CNS stand for and what two organs make up the CNS?
Central Nervous System
spinal cord and brain
what is the function of the nerve cell?
to carry electrical impulses rapidly around the body
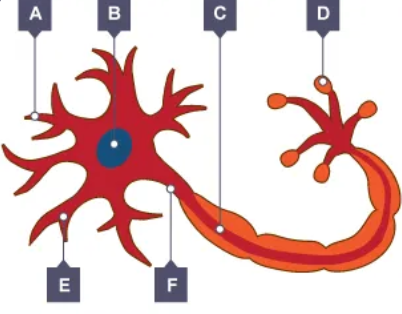
label the nerve cell
A - dendrites
B- nucleus
C- meylin sheath
D- synapse
E- cell body
F- axon
explain how the nerve cell is adapted to its function.
it has lots of dendrites so that it can make a lot of connections to other nerve cells.
the axon is very long to carry the nerve impulse a long way.
the axon is also insulated so the impulses travel rapidly
the synapses have a lot of mitochondria to transfer the energy needed to make transmitter chemicals.
what is the flow diagram of the nervous system?
stimulus → receptor → sensory neurone → relay neurone in CNS → motor neurone → receptor
why are reflexes important?
they happen automatically and rapidly to avoid harm
they take care of your body systems like breathing and circulating blood so you don’t have to think about them all the time.
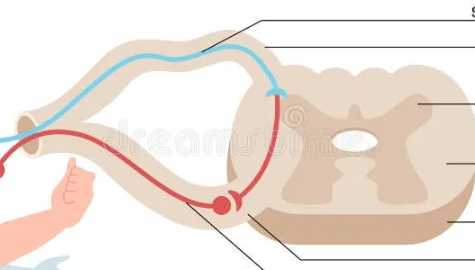
label the reflex arc.
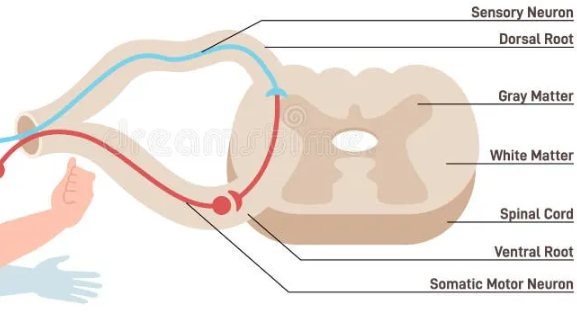
Explain how the reflex arc works.
the receptor detects a stimulus
an electrical impulse travels along the sensory neurone to the relay neurone in the CNS
at the synapse, a chemical is released and it diffuses along the synapse and triggers an electrical impulse in the relay neuron.
the impulse then travels along the motor neurone
and then reaches the effector muscle or glands
which hormone is released by the adrenal gland?
adrenaline
when is adrenaline produced?
when you are scared or stressed.
what are the effects of adrenaline?
increase heart rate
increase breathing rate
prepares your body for fight or flight
explain how the endocrine system produces a response to a stimulus.
the endocrine system produces a chemical response to the stimulus. The glands of the endocrine system secrete hormones into the blood stream.
The blood carries the hormones to organs who have the receptors to pick up those hormones, this causes them to respond.
compare the hormonal effects with the response of the nervous system.
Hormonal effects are much slower than the nervous system but last for longer.
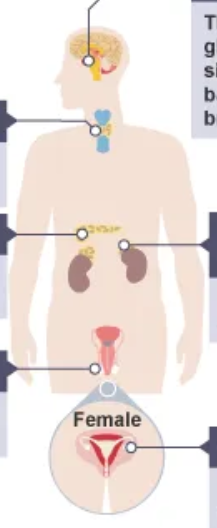
label the endocrine glands.
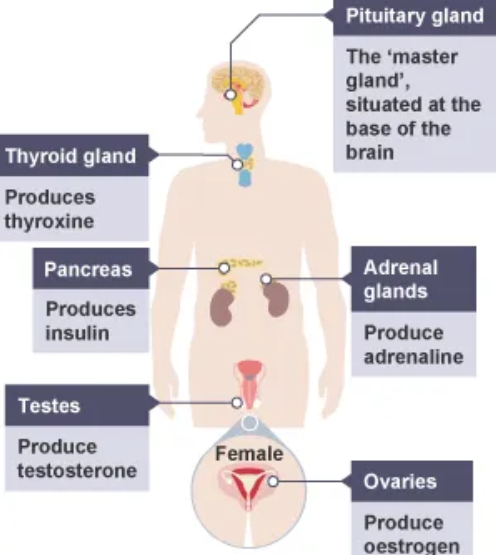
where is the hormone thyroxine produced ?
thyroid gland
what is the role of thyroxine in the body?
it controls the basal metabolic rate and is important in growth and repair.
How is the level of thyroxine controlled?
a negative feedback system keeps the amount of thyroxine in the blood at the right level
if the level is higher than normal the secretion of the TSH from the pituitary gland is stopped.
this reduces the level of thyroxine in the blood so it can go back to normal