Social Determinants of Health in Occupational Therapy
1/57
There's no tags or description
Looks like no tags are added yet.
Name | Mastery | Learn | Test | Matching | Spaced | Call with Kai |
|---|
No analytics yet
Send a link to your students to track their progress
58 Terms
Equality
the quality or state of being equal
Equity
justice according to natural law or right

Inequity
an instance of injustice or unfairness
Disparity
a noticeable & usually significant difference or dissimilarity
Social Determinants of Health (SDOH)
conditions in which people are born, grow, live, work, and age that affect health outcomes
Social
of or relating to human society, the interaction of the individual & the group, or the welfare of human beings as members of society
Determinant
an element that identifies or determines the nature of something or that fixes or conditions an outcome
Health
condition of being sound in body, mind, or spirit
Health (expanded definition)
state of complete physical, mental, & social well-being, & not merely the absence of disease or infirmity (OTPF-4)
Culture
the customary beliefs, social forms, & material traits of a racial, religious, or social group
Culture (expanded definition)
the set of shared attitudes, values, goals, & practices that characterizes an institution or organization
Culture (further definition)
the set of values, conventions, or social practices associated with a particular field, activity, or societal characteristic
Health Disparities
a particular type of health difference that is closely linked with social, economic, &/or environmental disadvantage (Gillen & Brown, p. 861)
Healthy People 2030
A framework that can be used to address & assess outcomes of programs & policies that aim to improve the health & well-being of populations living in the US
Healthy People objectives
were first released in 1980 to decrease mortality in infants, children, adolescents, & adults, & increase independence among older adults
Vision of Healthy People 2030
a society in which all people can achieve their full potential for health & well-being across the lifespan
Foundational principles of Healthy People 2030
Overarching goals and plan of action for improving health outcomes
Indicators of Health Disparities
Metrics such as infant mortality, life expectancy, cardiovascular disease, cancer, diabetes, chronic obstructive pulmonary disease (COPD), HIV/AIDS, healthcare access & utilization, health insurance, disability, mental health, preventative health services, smoking, obesity, substance use, suicide, homicide, and unintentional injuries.
West Virginia
Highest rate of people with disabilities in the nation, with 20% of the population reporting some form of disability.
Visual Impairment in West Virginia
Residents with severe visual impairment were more likely to have diabetes, arthritis, & mobility issues.
Poor Health Reporting
Severe visual impairment was higher in those reporting poor health (17% vs 5% good health).
Education and Visual Impairment
Severe visual impairment was higher in those with less than high school education (10% vs 6% high school education & above).
Urban Population in West Virginia
Third lowest urban population in the U.S., lower population density, & higher levels of poverty compared to other states.
Infrastructure in West Virginia
Ranks 50th in terms of infrastructure, with internet access & road quality the worst in the nation.
SDOH
Conditions in the environments where people are born, live, learn, work, play, worship, and age that affect a wide range of health, functioning, and quality-of-life outcomes and risks.

5 SDOH
Conditions that affect health outcomes as defined by the US Department of Health and Human Services (DHHS) and the Centers for Disease Control and Prevention (CDC).
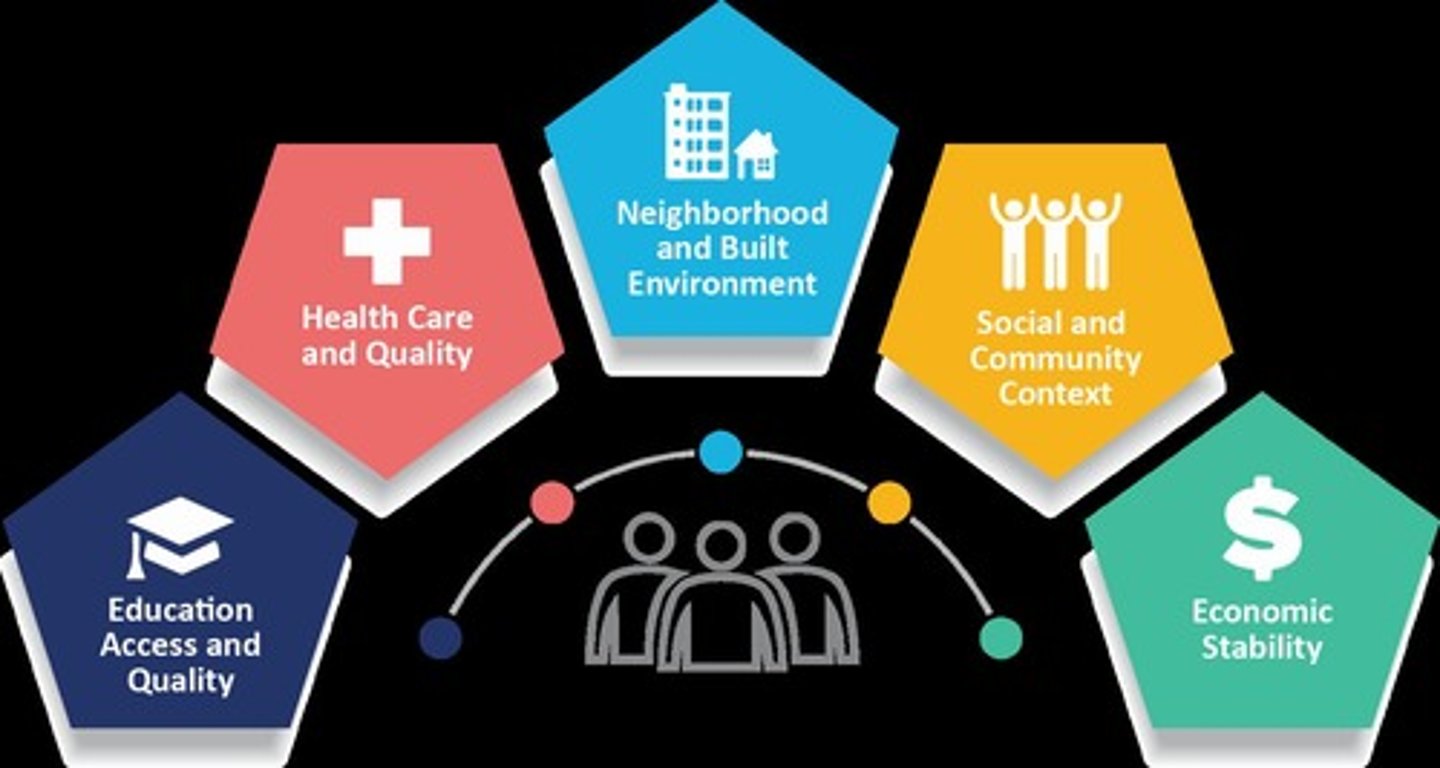
Economic Policies & Systems
Factors that influence health outcomes as part of the social determinants of health.
Social Norms
Cultural expectations that can influence health outcomes.
Racism
A social determinant that affects health outcomes and equity.
Climate Change
A factor influencing health outcomes as part of the social determinants of health.
Political Systems
Structures that can affect health outcomes and access to resources.
CDC's Work on SDOH
Focuses on the interplay of social & structural conditions contributing to overall equity.

Policy & Law in SDOH
Identifying evidence, tools, & resources to enhance communication about policies affecting SDOH.
Data & Surveillance in SDOH
Embedding a consistent SDOH approach to standardization, collection, analysis, & dissemination of data.
Evaluation & Evidence Building in SDOH
Advancing evaluation & building evidence for strategies that address SDOH to reduce disparities.
Partnerships & Collaborations in SDOH
Establishing criteria and actionable steps for partnerships that improve health outcomes.
Community Engagement in SDOH
Fostering meaningful, sustained community engagement across all phases of intervention planning.
Infrastructure & Capacity in SDOH
Strengthening infrastructure such as workforce, training, & access to financial resources to address SDOH.
WHO on SDOH
Defines the non-medical factors that influence health outcomes.
Importance of SDOH
Research shows that the social determinants can be more important than health care or lifestyle choices in influencing health.
WHO Critical Actions
Three areas for critical action identified in the report of the Global Commission on Social Determinants of Health: Improve daily living conditions, tackle the inequitable distribution of power, money & resources, measure & understand the problem & assess the impact of action.
Daily Living Conditions
The circumstances in which people are born, grow, live, work & age.
Inequitable Distribution
The structural drivers of those conditions of daily life, such as macroeconomic & urbanization policies & governance.
Knowledge Base Expansion
Expand the knowledge base, develop a workforce that is trained in the social determinants of health, & raise public awareness about the SDOH.
Universal Action Requirement
Scaled up & systematic action is required that is universal but proportionate to the disadvantage across the social gradient.
Public Health Services
10 Essential Public Health Services as outlined by the CDC.
Occupational Deprivation
Lack of access to engagement in an array of occupations that have meaning to the individual, family, or community, which may result in ill health & occupational injustice.
Protective Social Factors
Social support, self-esteem, & self-efficacy that may mitigate the deleterious effects of adverse social conditions.
Income Impact on Health
Income may have less health impact where there is less social stigma associated with having limited economic means.
Genetic Vulnerability
Genetics may play a role in an individual's vulnerability or resilience to socioeconomic adversity.
Vision Loss and SDOH
Research has shown that SDOH are also linked to vision loss, with individuals reporting visual difficulty more likely to have lower education levels, Medicaid coverage, food insecurity, and trouble finding a doctor.

Occupational Therapy Perspective
Not what is 'normal' or 'typical', but rather what supports and limits occupational performance.
Engagement and SDOH
Questions regarding whether SDOH support or inhibit engagement and if they can shift/change for individuals, groups, or populations.
Community Mapping Activity
An activity focused on understanding and visualizing the social determinants of health in a community.
Role Play Activity
An activity designed to explore the implications of social determinants of health through interactive scenarios.
Occupational Therapy/Occupational Science (OT/OS)
A field that examines how social determinants affect occupational engagement and health outcomes.
Social Gradient
The concept that health inequities are related to the social and economic conditions of individuals.
Ill Health and Occupational Injustice
The result of occupational deprivation, leading to negative health outcomes and social inequities.