[BOTAONE-LE2] cell division
1/50
Name | Mastery | Learn | Test | Matching | Spaced | Call with Kai |
|---|
No analytics yet
Send a link to your students to track their progress
51 Terms
Cell division
is an integral part of the cycle, the life of a cell from formation to its own division.
The ability of organisms to reproduce best distinguishes living things from non-living matter.
The continuity of life is based upon the reproduction of cells or cell division.
Unicellular organisms
Division of one cell reproduces the entire organism.
Multi cellular eukaryotes
They depend on cell division for the development of a fertilized cell, growth, and repair.
Meiosis & mitosis
2 types of cell division
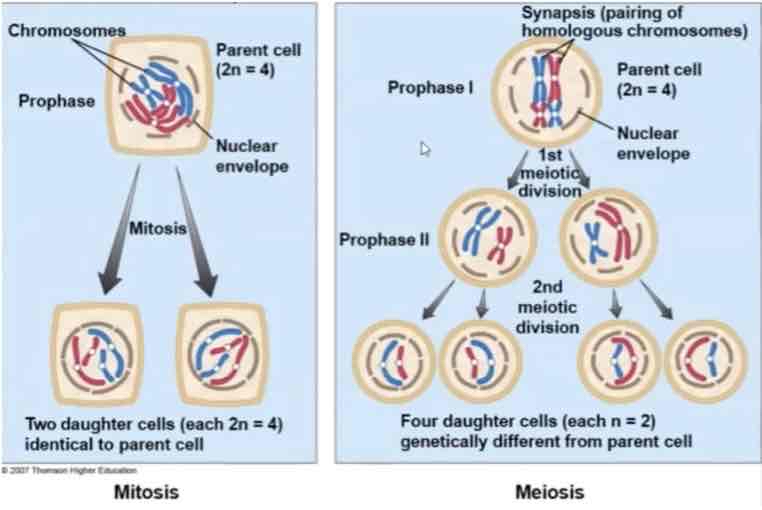
Mitosis
retains the number of chromosomes in the dividing cells.
Meiosis
reduces the chromosome # of the dividing cells into half.
→ E.g. from diploid (2n) to haploid (n)
Binary fission
In prokaryotes, An asexual type of reproduction where DNA is copied and the cell splits. Usually for bacteria
Chromosomes
DNA in cells is divided into long chains called..
Histones
What is wrapped around chromosome DNA to organize it
Nucleosome
What is the unit of DNA wrapped around histones called
simplest packing strand of DNA
146 bp (base pair) DNA wrapped around histone octamer
chromatin
“thin” genetic material
chromosomes are spread out & not identifiable
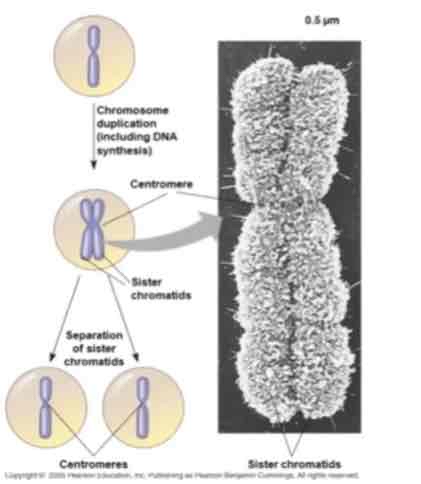
Sister chromatids
At the start of mitosis they condense & take the form shown
The replicated chromosomes stay together and are called
are attached at the centromere by proteins called cohesins
The other side of the centromeres contain other proteins called kinetochore
Interphase
A cell performs all of its regular functions & gets ready to divide
> metabolic activity is very high
The longest out of all the cell cycles
interphase, G0, G1, S, G2
the cell cycle
G1 (Gap)
cells are recovering from an earlier cell division and are synthesizing components for cell growth and DNA synthesis.
S (Synthesis)
- DNA replication occurs
G2 (Gap)
cells are making gure all the DNA was replicated correctly.
(checking)
→A little more growth, the chromosomes start to undergo condensation, becoming tightly coiled
MITOSIS
for growth, development, and repair
Asexual reproduction (yields genetically identical cells)
Occurs in somatic (body) cells
Is divided into four phases:
Prophase, Metaphase, Anaphase, Telophase
Prophase
Chromosomes shorten and become visible.
Centrioles move to opposite sides of the animal cell.
Nuclear envelope disappears
Spindle Apparatus begins to form.
Metaphase
Chromosomes line up along the center of the cell called the "metaphase plate"
Chromosomes attach to spindle fibers.
Spindle fibers are now clearly visible.
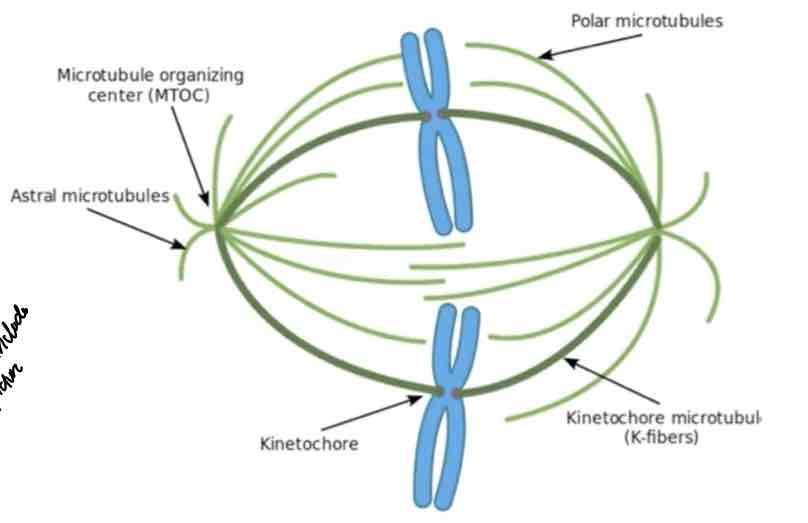
Spindle Apparatus
consists of two distinct sets of microtubules.
→ Each set extends from one of the cell poles.
→ Two sets overlap at the spindle equator.
Moves chromosomes during mitosis.
Phragmoplast
In animal spindle fibers originate from centrioles. in plant cells, what forms like a scaffold for cell plate assembly
G1
Any cell that is going to divide must enter this phase
This is the period before DNA synthesis begins
G stands for gap and the number refers to the gap between cell division and DNA synthesis
Here the cell makes ER, ribosomes, and cytosol to make 2 functional cells
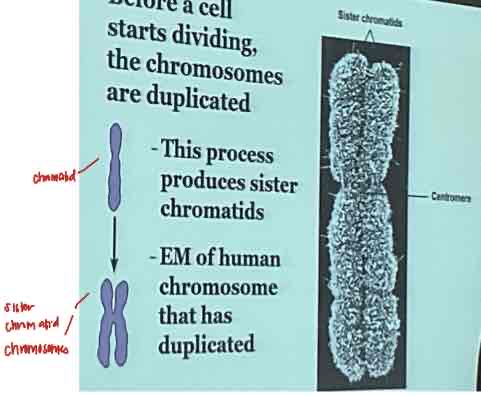
before a cell starts dividing, the chromosomes are duplicated
This process produces sister chromatids
Homologous chromosomes are identical pairs of chromosomes.
One inherited from mother and one from father
made up of sister chromatids joined at the centromere.
What are the 3 main points to describe the structure of chromosomes
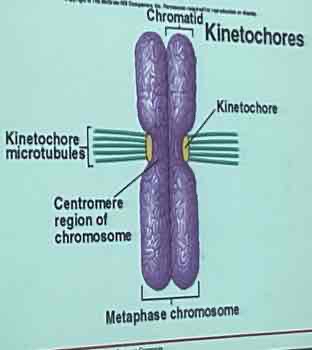
chromatid, kinetochore, microtubules, sister chromatid, chromosome, centromere
Parts of a chromosome (5-6 enumerate)
G2
This phase spans the time from the completion of
DNA synthesis to the onset of cell division
• Following DNA replication, the cell spends about
2-5 hours making proteins prior to entering the M phase
Function of proteins works: as enzymes
M phase
This is the process that separates the duplicated sister chromatids of the parental cell into 2 nuclei
Mitosis refers specifically to the division of the nucleus of the cell
preprophase band
The orientation of the division plane is determined by a band of cytoskeletal elements called the ..
In plant cell instead of centrioles they have thickening of cytoplasm (guide for cell division)
Prophase
nuclear membrane disintegrates
nucleolus disappears
chromosomes condense
mitotic spindie begins to form between centrioles
kinetochores begin to mature and attach to spindle
nucleus disappears
Nuclear membrane disappears in plant cells
Metaphase
kinetochores attach chromosomes to mittic spindle and align them along metaphase plate at equator of cell
Anaphase
When the cell divides, the sister chromatids separate
Two daughter cells are produced
Each has a complete and identical set of chromosomes
kinetochore microtubules shorten, separating chromosomes to opposite poles
polar microtubules elongate, preparing cell for cytokinesis
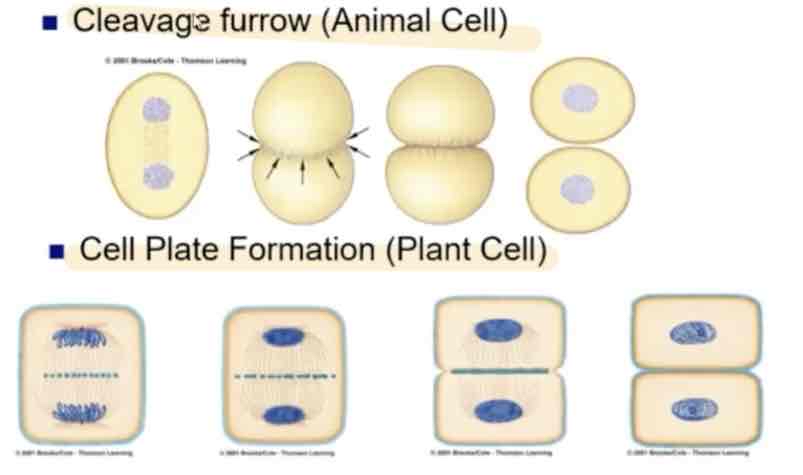
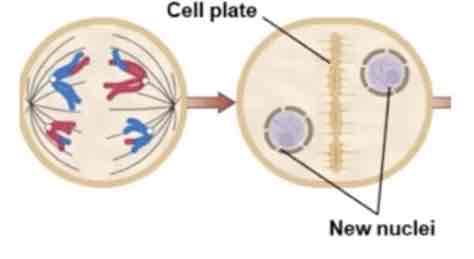
Vesicles containing cell wall material
Cell plate formation
New cell wall
Then finally daughter cells
In plant cells they conduct telophase like:
(note: that there will be a size difference)
Telophase (cytokinesis)
Nuclear envelope forms around both sets of chromosomes.
DNA uncoils
Spindle and Astral fibers completely disappear
Cytokinesis happens with most (but not all) cells Cytoplasm and organelles move (mostly equally) to either side of the cell.
Cell membrane "pinches" to form two separate cells.
Meiosis
Similar in many ways to mitosis.
Several differences
Occurs only in sex cells
Yields gametes (= eggs and sperm or spores)
Involves two cell devisions (meiosis 1 & 2)
Results in four haploid cells
Leads to genetic variations
Meiosis 1 (prophase 1, metaphase 1, anaphase 1, telophase 1)
First cell division for gametes
Meiosis 2 (prophase 2, metaphase 2, anaphase 2, telophase 2)
Second cell division for gametes
MEIOSIS I: PROPHASE I
Synapsis and crossing over occurs
Areas of homologous chromosomes connect in areas called chiasmata.
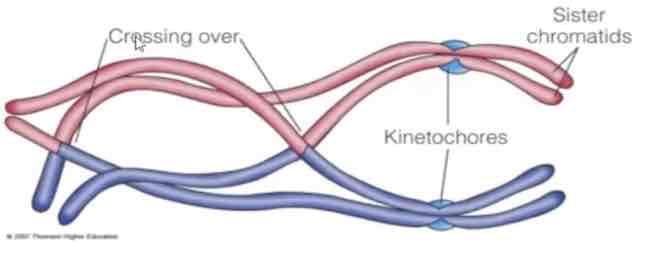
Synapsis
pairing of homologous chromosomes
Crossing over
exchange of segments of homologous chromsomes
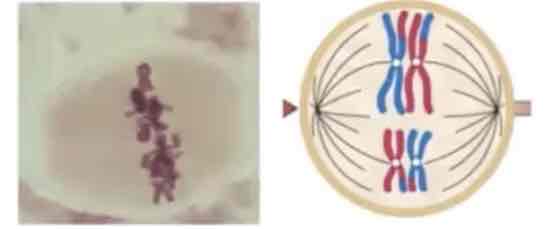
MEIOSIS I: METAPHASE I
Alignment of pairs of homologous chromosomes at the metaphase plate.
MEIOSIS I: ANAPHASE I
Splitting of the pairs of homologous chromosomes and subsequent movement to opposite poles
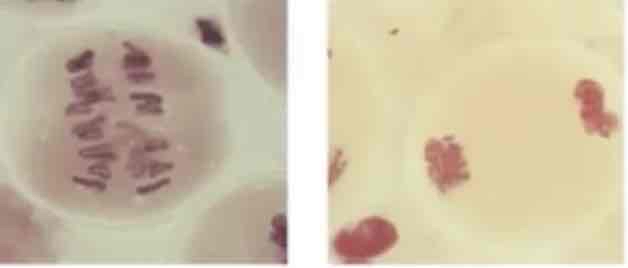
MEIOSIS I: TELOPHASE I
Cytokinesis results in two haploid cells (n)
MEIOSIS II
DNA does not double
Stages occur like regular mitosis (Prophase Il, Metaphase II, Anaphase Il, Telophase Il)
Cytokinesis results to four haploid cells (n)
Cells are not identical in this phase due to the crossing over that happened during meiosis 1.
CELL CYCLE CONTROL SYSTEM
the cell cycle appears to be driven by specific chemical signals present in the cytoplasm.
The sequential events of the cell cycle are directed by a distinct cell cycle control system, which is similar to a clock.
The clock has specific checkpoints where the cell cycle stops until a go-ahead signal is received.
complete the S, G2, and M phases and divide.
If a cell receives a go-ahead signal at the G1 checkpoint, it will usually….
exit the cycle, switching into a nondividing state called the G0 phase
If the cell does not receive the go-ahead signal, it will
Cyclins
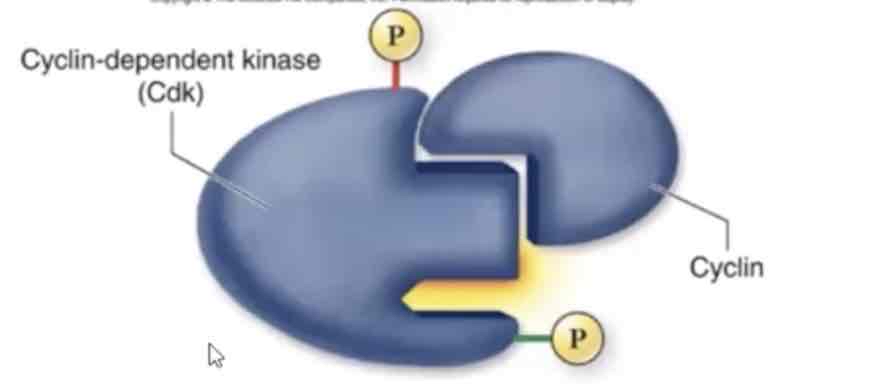
Cyclin dependent kinases (Cdks)
Two types of regulatory proteins are involved in cell cycle control:
Cyclins
Proteins produced in synchrony with the cell cycle.
Regulate passage of the cell through cell cycle checkpoints.
Cyclin-dependent kinases (Cdks)
Enzymes that drive the cell cycle
Activated only when bound by a cyclin
The activity of this regulatory progein rises and falls with changes in concentration of its cyclin partner
Malnutrition-promoting factor (MPF)
Is a cyclin-Cdk complex that triggers a cell's passage past the G2 checkpoint into the M phase.