PKPD Final Questions Practice
1/83
There's no tags or description
Looks like no tags are added yet.
Name | Mastery | Learn | Test | Matching | Spaced | Call with Kai |
|---|
No analytics yet
Send a link to your students to track their progress
84 Terms
False
(True/False) A correct definition of a drug is — A chemical substance that interacts with a receptor to produce a beneficial therapeutic effect.
D (All of the Above)
Therapeutic Drug Monitoring is important for:
A. For clinical decisions
B. Avoid Toxicity
C. Assess medication compliance
D. All of the Above
True
(True/False) Enzymes (cytochrome P-450) is an important enzyme in pharmacokinetics
D (Lower drug dose, increase dose interval or both)
The best way to manage patients with reduced GFR
A. Give cytochrome inhibitors
B. Use higher dose drug
C. IV administration
D. Lower drug dose, increase dose interval or both
True
(True/False) The reabsorption of drugs that are acids or weak bases is influenced by the pH of the fluid in the renal tubule (i.e. urine pH) and pKa of the drug.
D (Both A and B)
Among the following statements on drugs effect on renal reabsorption select the appropriate answer
A. Drugs such as ascorbic acid and antacids such as sodium carbonate may decrease (acidify) or increase (alkalinize) the urinary pH, respectively, when administered in large quantities.
B. most important changes in urinary pH are caused by fluids administered intravenously
C. None of the above
D. Both A and B
A (IV)
Which route has the highest bioavailability?
A. IV
B. Oral
C. Transdermal
D. IM
B (Capillaries of the CNS a have tight junctions that limit para cellular movement of drugs)
Which of the following statements regarding the blood-brain barrier is true
A. The membranes between the blood-brain barrier have a large number of pores
B. Capillaries of the CNS a have tight junctions that limit para cellular movement of drugs
C. All polar materials can easily pass through the blood-brain barrier
D. Both B and C
B (Increased volume of distribution or decreased clearance)
The half life of a drug eliminated by first order elimination kinetics will be LONGER in individuals who have an:
A. Increased volume of distribution or increased clearance
B. Increased volume of distribution or decreased clearance
C. decreased volume of distribution or increased clearance
D. decreased volume of distribution or decreased clearance
True
(True/False) A fundamental characteristic of all first order pharmacokinetic processes is that the rate of the process is proportional to drug concentration
D (A&B)
Passive transport is
A. The movement of molecules through the membrane in which no energy is require.
B. The molecules move in response to a concentration gradient.
C. ATP is required for the transport.
D. A&B
A, B, C, D
Select all correct answers Passive transport is -
A. The movement of a molecule from high to low concentration with the help of a carrier protein.
B. Specific
C. ATP Independent
D. Saturates when all carriers are occupied
C (p-glycoprotein (MDR1))
The major proteins that are responsible for multi-drug resistance
A. SLC6
B. OCT1
C. P-glycoprotein (MDR1)
D. SGLT2
Uptake (Influx)
The transport of a molecule from outside the cell to inside is called ________.
B (Efflux)
Most ABC superfamily members are __________ transporter
A. An influx
B. Efflux
C. Uptake
D. None
A (An Influx)
Most SLC superfamily members are _________ transporters
A. An influx
B. Efflux
C. Active
D. None
True
(True/False) If a new molecular entity (NME) does not inhibit OCT2-mediated uptake in the in vitro assays at therapeutic concentrations, the guidance does not recommend a clinical study
B (Duodenum)
Most of the organ drug absorption occurs in -
A. Ileum
B. Duodenum
C. Colon
D. Liver
True
(True/False) Absorption of drugs through the lymphatic system bypasses the liver and avoids the first-pass effect due to liver metabolism.
True
(True/False) In the case of high motility in the intestinal tract, as in diarrhea, the drug has a very brief residence time and less opportunity for adequate absorption
B (6 to 6.5)
What s the pH of duodenum?
A. 1.5 to 2
B. 6 to 6.5
C. 3 - 3.4
D. 9 to 10
D (all of the above)
Which statement is true for receptors?
A. Receptors have a life cycle
B. In normal physiology there is an equilibrium between active an inactive states
C. Binding of ligand to receptor is only temporary
D. all of the above
D (Intrinsic Activity)
A true antagonist of a receptor lacks the following:
A. Affinity to the receptor
B. Ability to recycle the receptor
C. Ability to desensitize the receptor
D. Intrinsic activity
D (All of the Above)
Please select all the correct statements for semi log graded dose-response curve:
A. In this relationship response is plotted against the log dose of the drug
B. We can derive the relationship between drug dose, receptor occupancy and the magnitude of the resulting physiologic effect
C. It follows from receptor theory that the maximal response to a drug occurs when all receptors that can be occupied by that drug
D. All of the above
B (Drug B has higher margin of safety than Drug A)
Drug A and Drug B were developed by the pharmaceutical industry. Their therapeutic indices are 4 and 125, respectively. The following is true for their relative safety.
A. Information is not sufficient
B. Drug B has higher margin of safety than Drug A
C. Drug B is toxic
D. All the above
D (A receptor without a well defined ligand or function)
What is an orphan receptor?
A. A receptor with no co-receptor
B. A receptor with no closely related receptors
C. The only receptor within a family
D. A receptor without a well defined ligand or function
True
(True/False) Binding ligands to each subunit of 3TM ion channel linked receptors will result in increased conductance, opening the channel to higher conductance level.
D (All of the Above)
Which of the following is true of receptor tyrosine kinases?
A. They are membrane receptors
B. They have tyrosine kinase activity after ligand induced activation
C. Lead to Downstream Ras-MAP kinase pathway
D. All the above
A (Cancer)
Generally speaking, kinase inhibitors are most frequently used to treat what type of disease:
A. Cancer
B. Inflammatory disease
C. Neurological diseases
D. Obesity/Diabetes
D (All of the Above)
Which of the following is true of receptor tyrosine kinases?
A. They are membrane receptors
B. They have tyrosine kinase activity after ligand induced activation
C. Lead to Downstream Ras-MAP kinase pathway
D. All the above
D (All of the Above)
What is appropriate regarding G-proteins
A. G protein is a protein that can bind to guanine nucleotides and has GTPase activity.
B. It is composed of α subunit, β subunit and γ subunit.
C. G protein binds to the cytoplasmic domain of GPCR
D. All of the above
D (All of the Above)
Which statements are true for GPCRs
A. Response depends on type of G-protein and type of effector
B. Single ligand can activate multiple GPCR pathways
C. Responses can be regulated by altering receptor numbers
D. All of the above
D (All of the Above)
Which statements are true for opioid receptors?
A. Pain is modulated by endogenous opioid peptides
B. Belongs to GPCR superfamily
C. Exogenous opioids are effective analgesic agents
D. All of the above
True
(True/False) DBD (DNA Binding Domain) of nuclear receptors associate with the Hormone response elements (HRE) in DNA
B (They are structurally diverse, but all bind to the LBD of estrogen receptor)
Which of the following is true of selective estrogen receptor modulators
A. They are all close derivatives of estradiol
B. They are structurally diverse, but all bind to the LBD of estrogen receptor
C. They are structurally diverse, but generally bind to the kinase domain of estrogen receptor
D. They all prevent estrogen receptor - dimer formation as a general mechanism of action
True
(True/False) Compounds or drugs that contain certain types of functional groups can be directly conjugated (do not Require Phase I metabolism)
False
(True/False) Phase I reaction always precedes Phase II reaction during biotransformation
True
(True/False) Phase II conjugation often creates polar or ionic metabolites that are then efficiently excreted.
False
(True/False) Phase II reactions are always regarded as detoxifying pathway, and attenuating pharmacological reactivity and toxicity
True
(True/False) The rate of elimination of xenobiotics whose excretion depends on biotransformation by CYPs following by Phase II conjugation is determined by the first reaction
False
(True/False) All Phase II reactions need formation of cofactor
A (Convert drugs into forms that are ready for elimination)
What is the major biological object of drug metabolism?
A. Convert drugs into forms that are ready for elimination
B. Generate energy from Drugs
C. All of the Above
D. None of the above
A
Which glucose derivative is involved in synthesis of UDPG? (Just enter the letter)
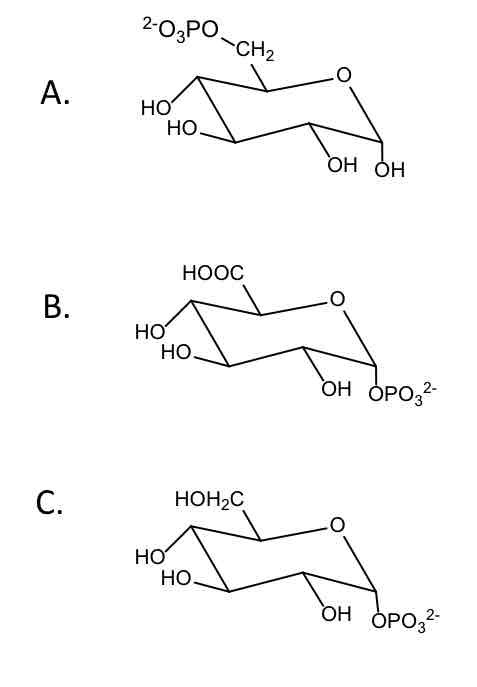
D
Which of the following is the cofactor from which glucuronic acid is transferred to substrate in glucruonidation? (Just type the letter)
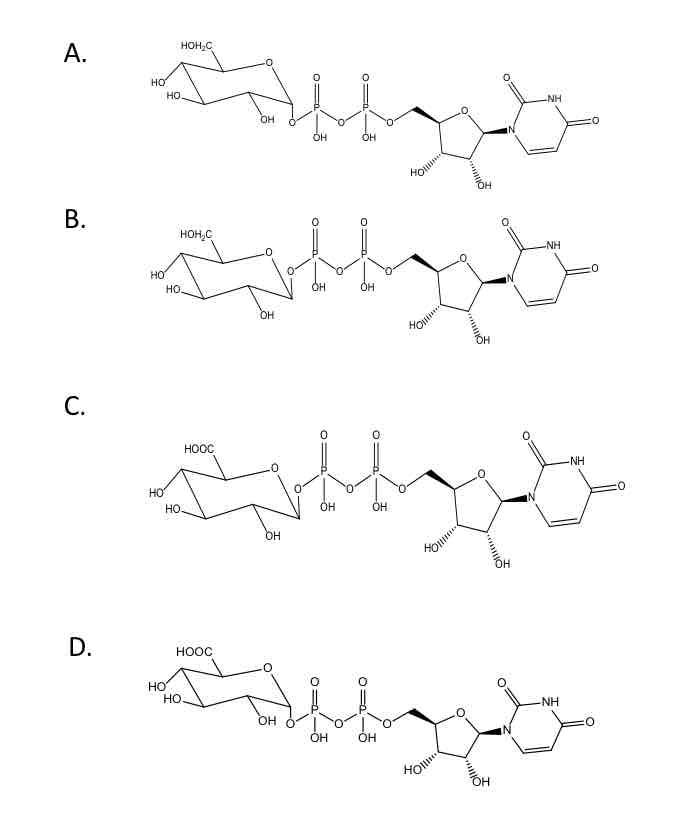
D
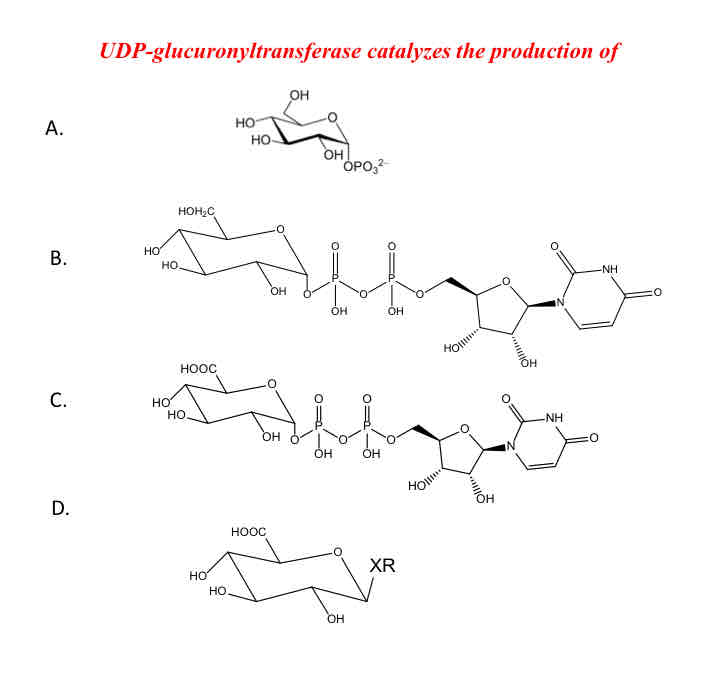
UDP-glucuronyltransferase catalyzed the production of… (just type the letter)
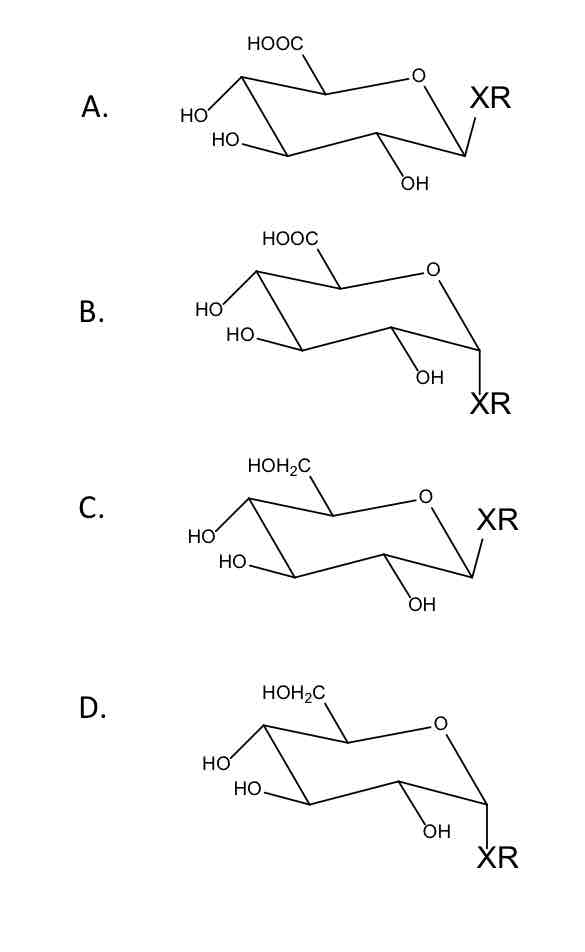
A (Beta configuration)
Which of the following correctly represents the conjugated product of glucuronidation? (Just type the letter)
A (C1)
In glucuronide, which C atom of glucuronic acid forms covalent bond with substrate?
A. C1
B. C3
C. C5
D. C6
C (UDP-glucuronyltransferase)
Which enzyme catalyzes the last step of glucuronidation?
A. UDP-glucose pyrophosphorylase
B. UDPG Dehydrogenase
C. UDP-glucuronyltransferase
A
Indicate which group is transferred to substrate in the last step of glucuronidation.
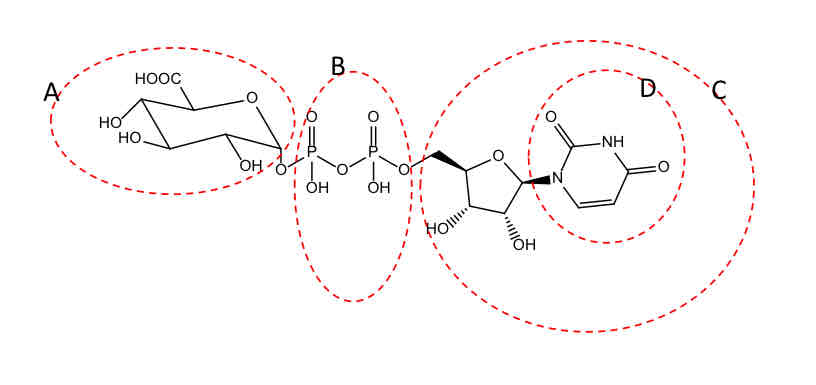
C (UDPG has beta linkage at C1)
Which of the following statements if FALSE?
A. The cofactor of glucuronidation reaction has an alpha linkage at C1
B. All glucuronide conjugated products have a beta-linkage at C1
C. UDPG has a beta linkage at C1
A (inability to glucuronidate chloramphenicol)
The cause of gray baby syndrome is:
A. Inability to glucuronidate chloramphenicol
B. Inability to glucuronidate bilirubin
ER
What is the subcellular localization of Glucuronidation?
A
Given the Structure of N-hydroxy-2-acetyl-amino fluorine.
Which of the following structure represents the correct glucuronidation product? (Just type the letter)
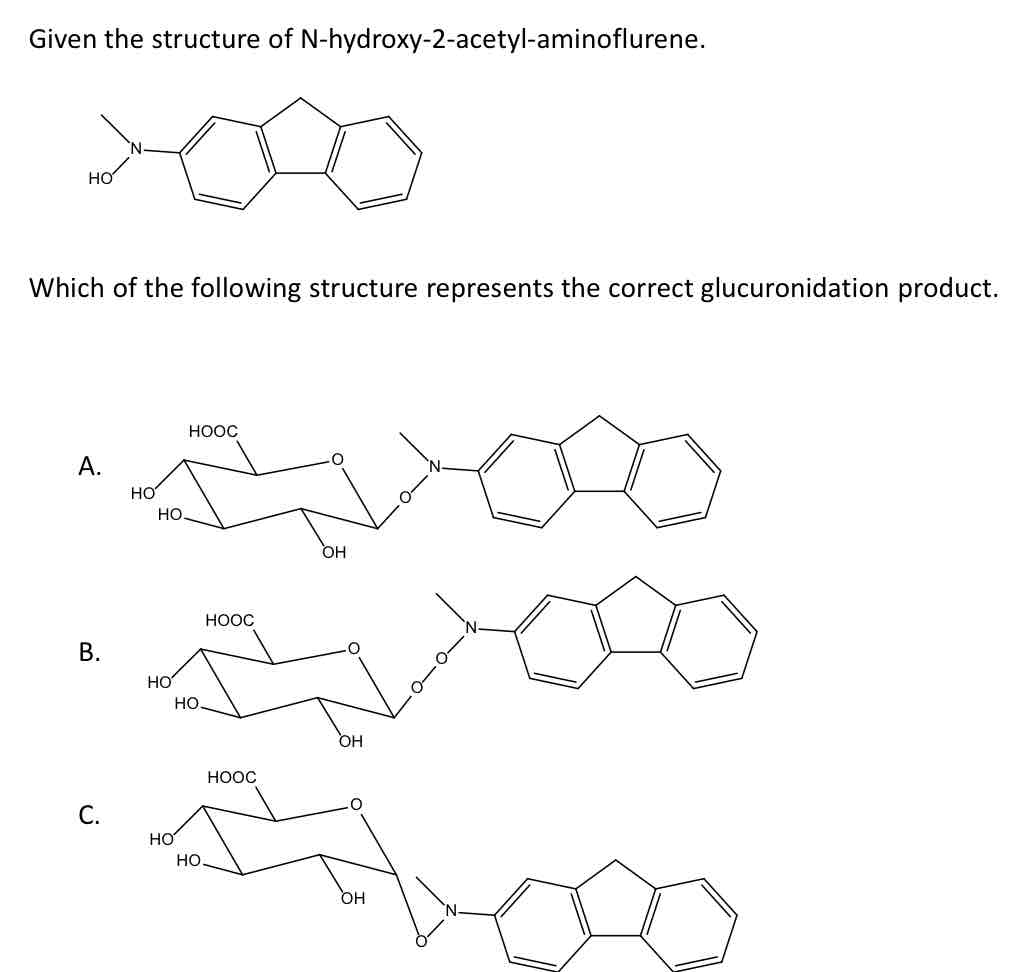
C
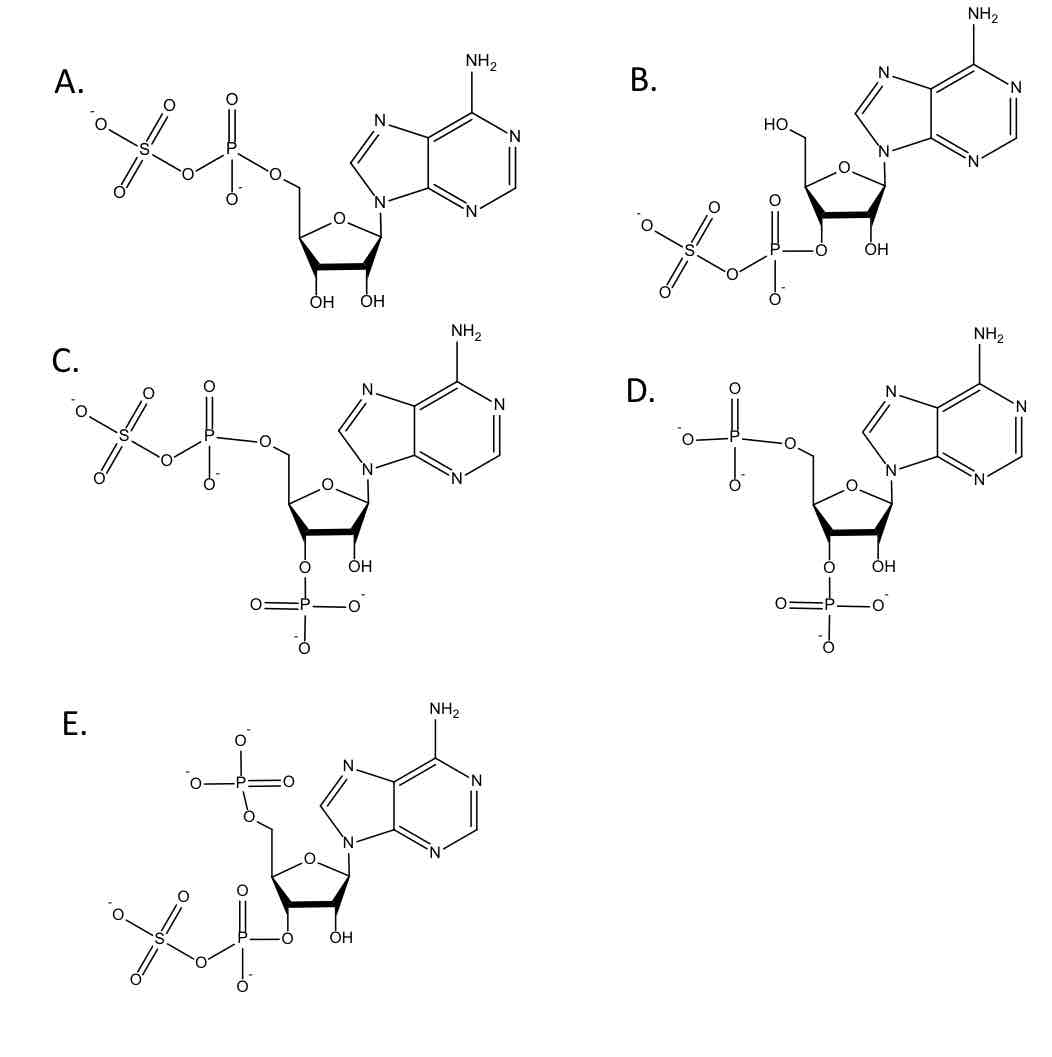
Give a logical prediction of the function group that most likely undergo glucuronidation. (Just type the letter)
Cytosol
What is the subcellular localization of Sulfation
C
Which is the co-factor for Sulfation reactions?
C (Sulfotransferase)
Which enzyme catalyzed the last step of Sulfation reactions?
A. ATP-sulfurylase
B. Sulfatase
C. Sulfotransferase
D. APS-Kinase
A
In infants, the major urinary metabolite of the analgesic acetaminophen is:
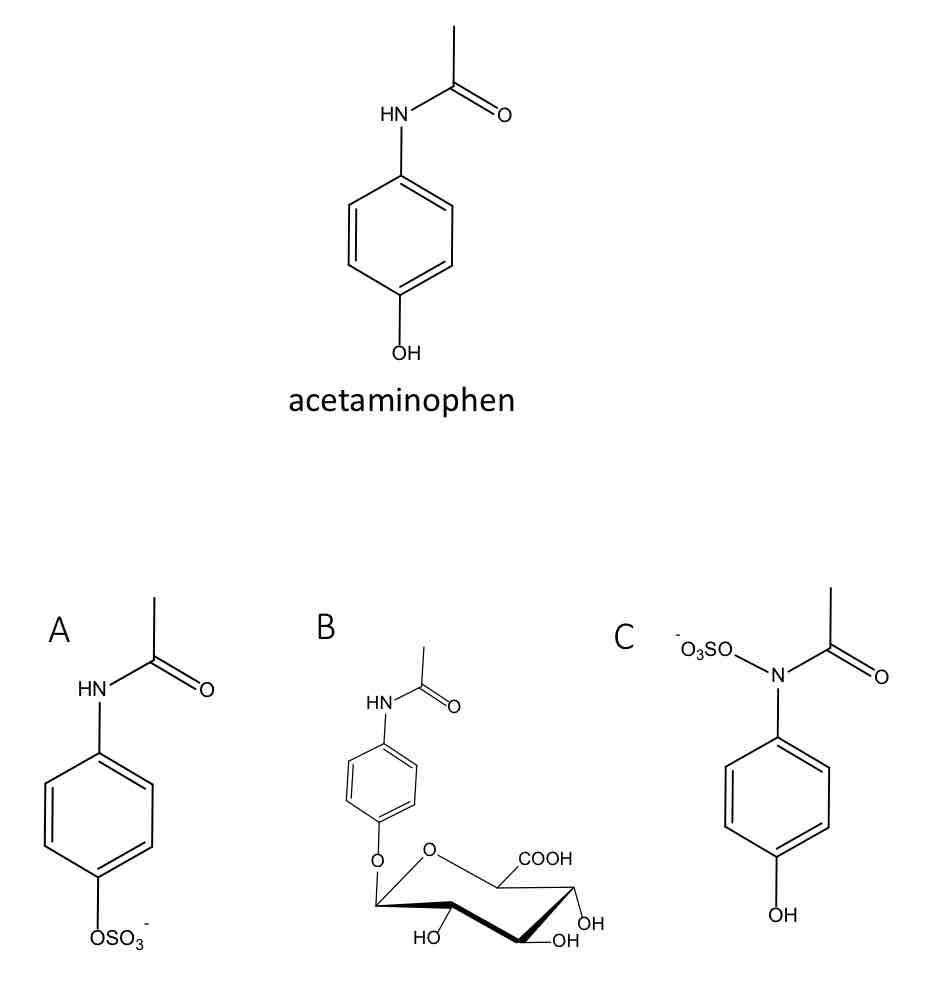
B
In adults, the major urinary metabolite of the analgesic acetaminophen is:
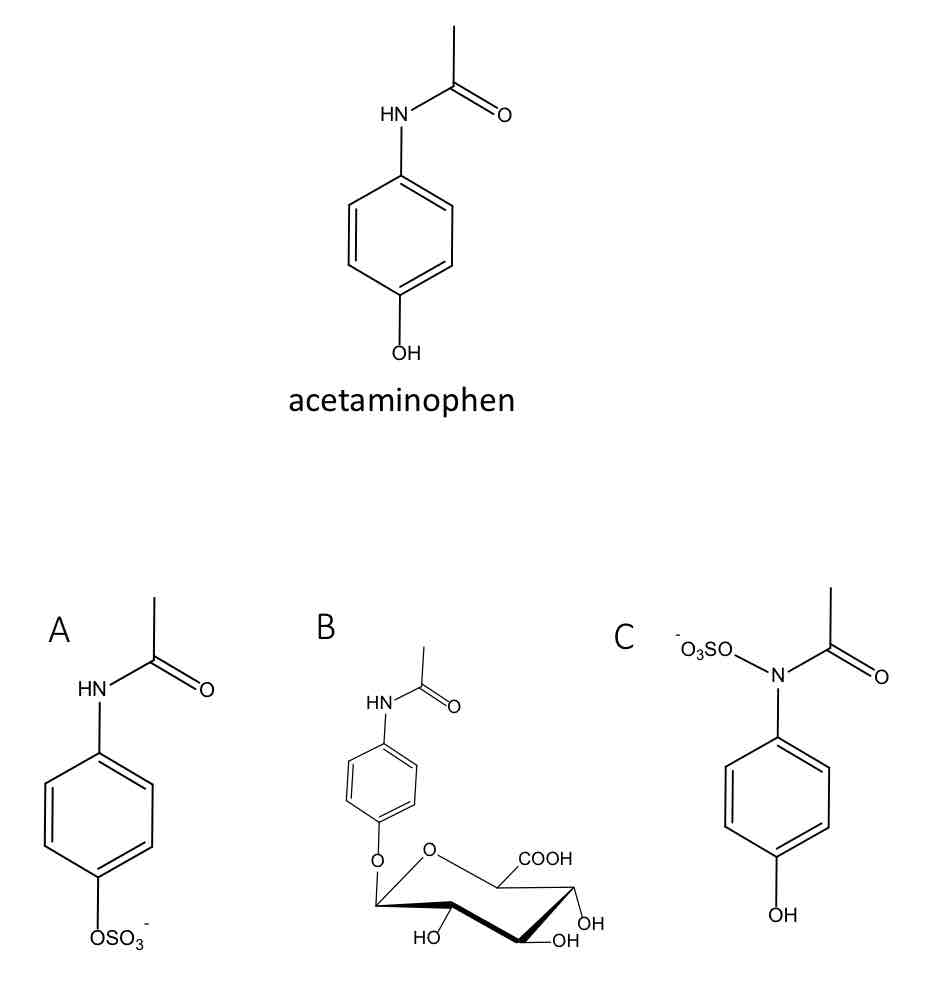
B
Terbutaline undergoes extensive sulfation even in adult.
Based on what learned in class, predict the most likely structure of the Terbutaline metabolite after sulfation.
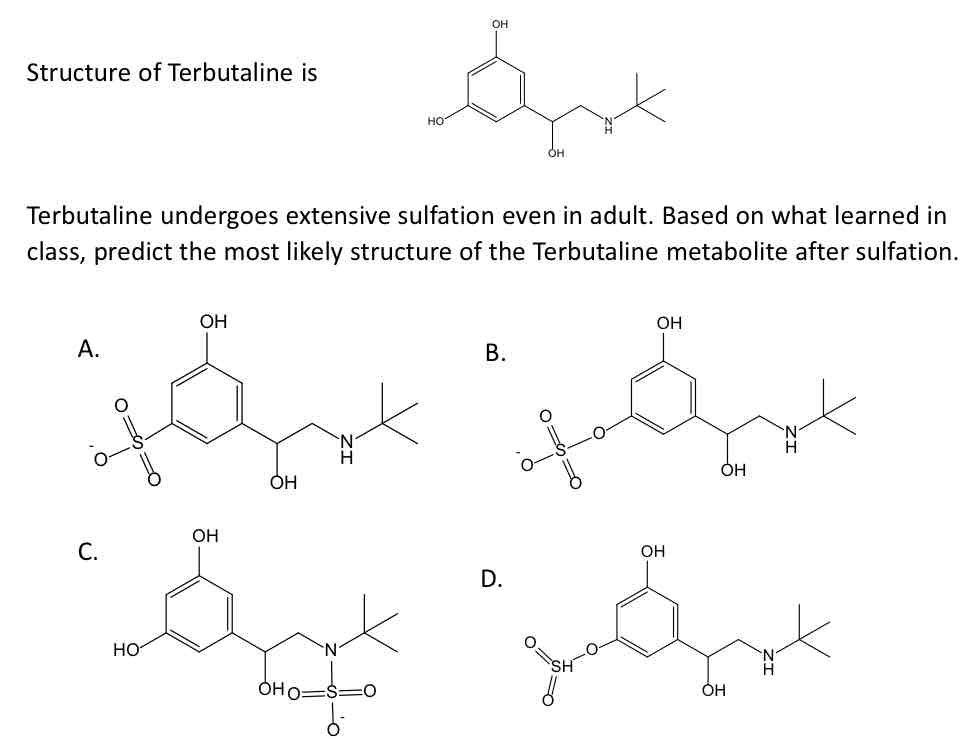
False (prefers urine b/c sulfate can only slightly increase molecular weight)
(True/False) Sulfate metabolites are mostly excreted by the bile
A (ATP-sulfurylase)
Which enzyme is required to form the following structure in Sulfation reaction?
A. ATP-sulfurylase
B. APS-Kinase
C. Sulfotransferase
D. Sulfatase
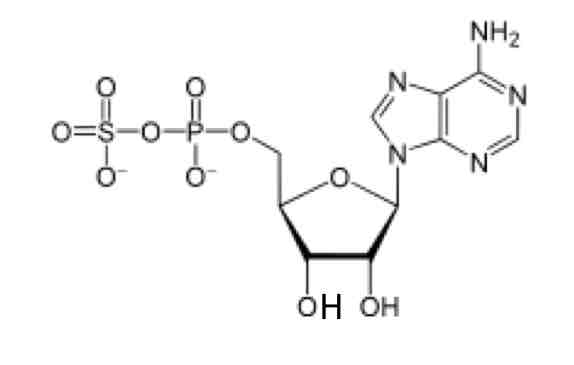
Mitochondria
Where is the sub cellular localization of amino acid conjugation of drugs?
A, B
Which of the following are examples of compound undergoing glycine conjugation?
A. Salicylic acid
B. Benzoic Acid
C. Histamine
D. Sulfonamides
Hydrolysis
Name the reaction (#1)
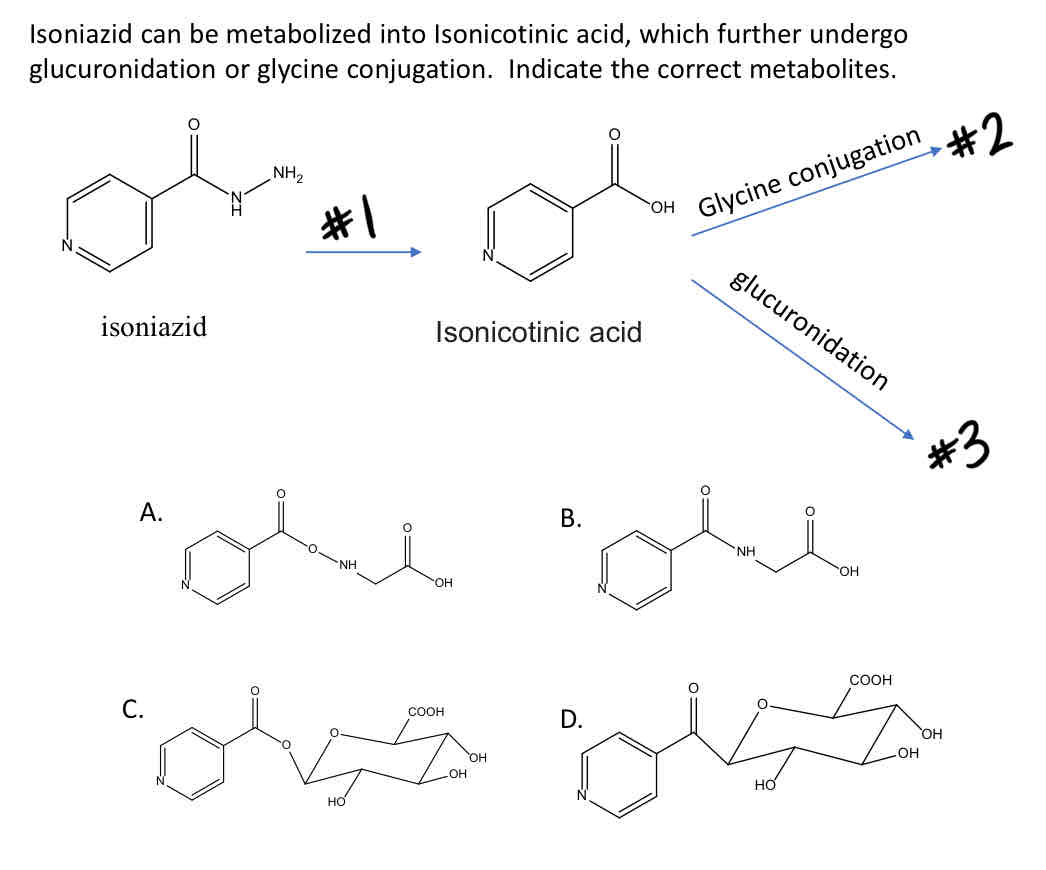
B
Name the product (A, B, C, or D) of #2
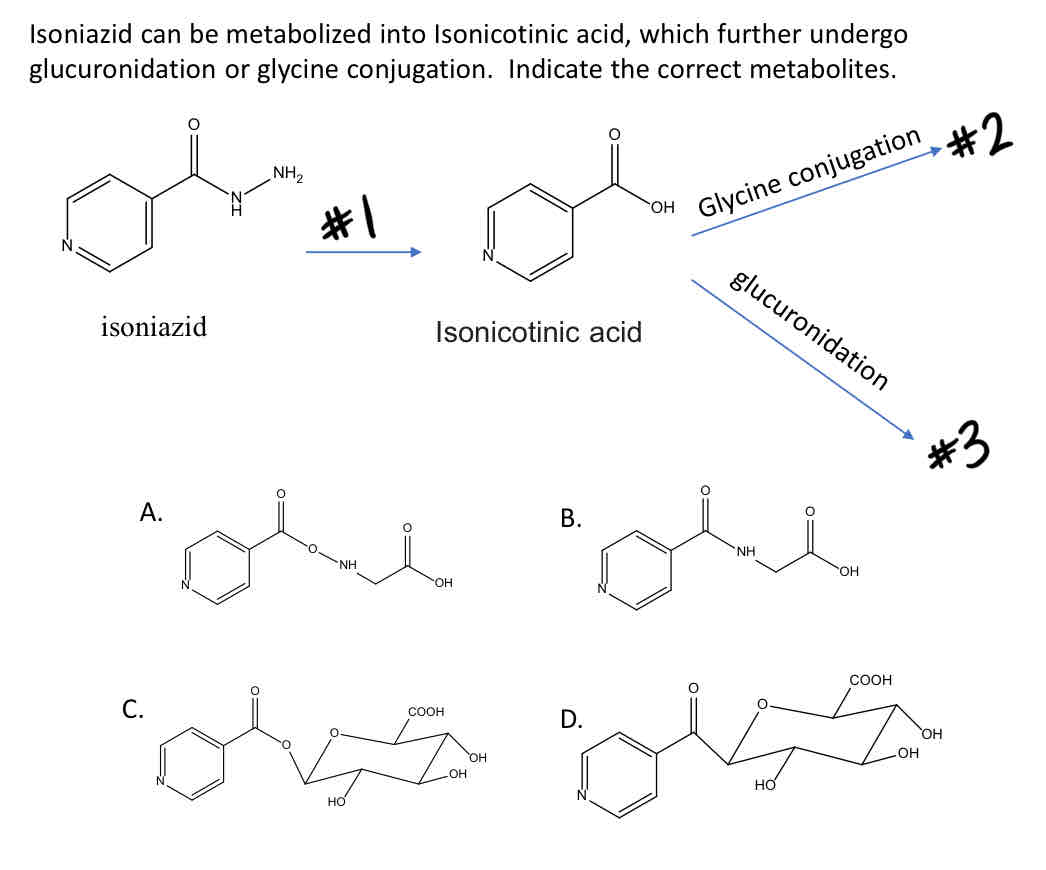
C
Name the product (A, B, C, or D) of #3
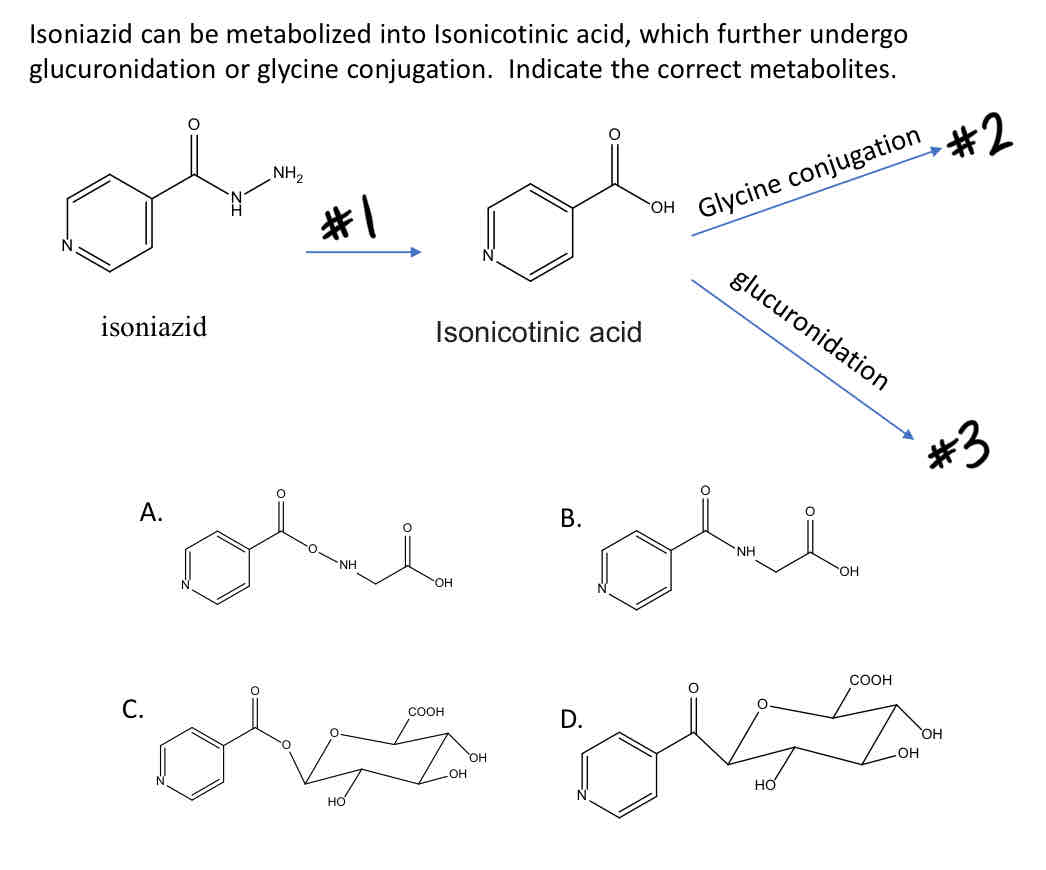
Hydrolysis
Name the reaction responsible for Metabolite I
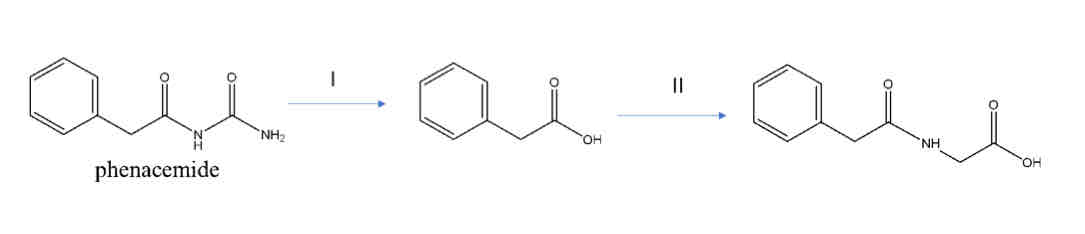
Glycine Conjugation
Name the reaction responsible for Metabolite II
Cytosol
Where is the subcellular localization of acetylation?
D
Which functional group of Sulfamethoxazole undergoes acetylation?
B (requires acetyl CoA synthetase to transfer acetyl to drugs with primary amines)
select INCORRECT answer about Acetylation
A. Acetylation rate shows polymorphism in human population
B. Requires acetyl CoA synthetase to transfer acetyl to drugs with primary amines.
C. Leads to formation of amide derivative
A, B, E, G
Select all that apply:
Which Phase II reactions increase water solubility?
A. Glucuronidation
B. Sulfation
C. Acetylation
D. Methylation
E. Amino Acid Conjugation
F. Glutathione Conjugation
G. Mercapturic Acid Transformation of Glutathione Conjugates
C, D
Select all that apply:
Which Phase II reactions DO NOT increase water solubility?
A. Glucuronidation
B. Sulfation
C. Acetylation
D. Methylation
E. Amino Acid Conjugation
F. Glutathione Conjugation
G. Mercapturic Acid Transformation of Glutathione Conjugates
Glucuronidation
What is the most common and most important Phase II reaction?
A, B, C, D, E
Select all that apply:
Which Phase II reactions inactivate the substrate?
A. Glucuronidation
B. Sulfation
C. Acetylation
D. Methylation
E. Amino Acid Conjugation
F. Glutathione Conjugation
G. Mercapturic Acid Transformation of Glutathione Conjugates
A, B, E
Select all that apply:
Which Phase II reactions prevent reabsorption?
A. Glucuronidation
B. Sulfation
C. Acetylation
D. Methylation
E. Amino Acid Conjugation
F. Glutathione Conjugation
G. Mercapturic Acid Transformation of Glutathione Conjugates
Sulfation
What phase II reaction is low capacity and age dependent
Amino Acid Conjugation
What Phase II reaction is low capacity?
Strong
GSH is a _________ (strong/weak) nucleophile
Glutathione conjugation
Which Phase II reaction is an important detoxification mechanism that neutralizes electrophiles.
Acetaminophen
Sulfation generates major urine metabolite of _____________ in neonates.
A
What is the correct definition of Pharmacokinetics?
A. The fate of a drug within the body.
B. The biochemical, physiologic, and molecular effects of drugs on the body.
B
What is the correct definition of Pharmacodynamics?
A. The fate of a drug within the body.
B. The biochemical, physiologic, and molecular effects of drugs on the body.