Vitamin D (mine)
1/158
There's no tags or description
Looks like no tags are added yet.
Name | Mastery | Learn | Test | Matching | Spaced | Call with Kai |
|---|
No analytics yet
Send a link to your students to track their progress
159 Terms
vit D is a
prohormone
vitamin D is derived from
cholesterol
how we make it from scratch
is in every cell of the body
vit D can be synthesized from
sun exposure
insufficient sun exposure is why vit D
is essential vit D
vit D synthesis is activated by ____ in ____ and_______
enzymes
liver and kidneys
what are the 2 main organs needed for synthesis of vit D in active form?
kidney and liver
vit D deficiency can cause (general)
diseases
what form of vit D do we get from plant foods
ergosterol
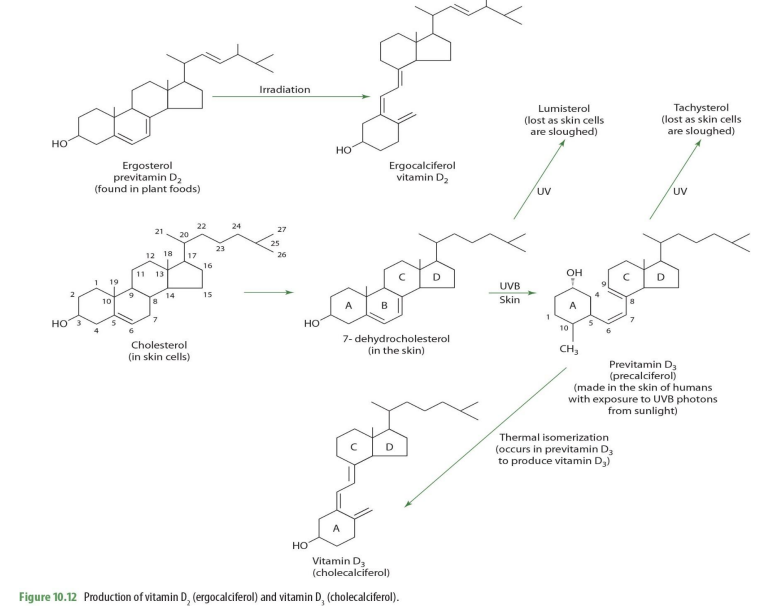
ergosterol (previt D2) —> _____
ergocalciferol (D2)
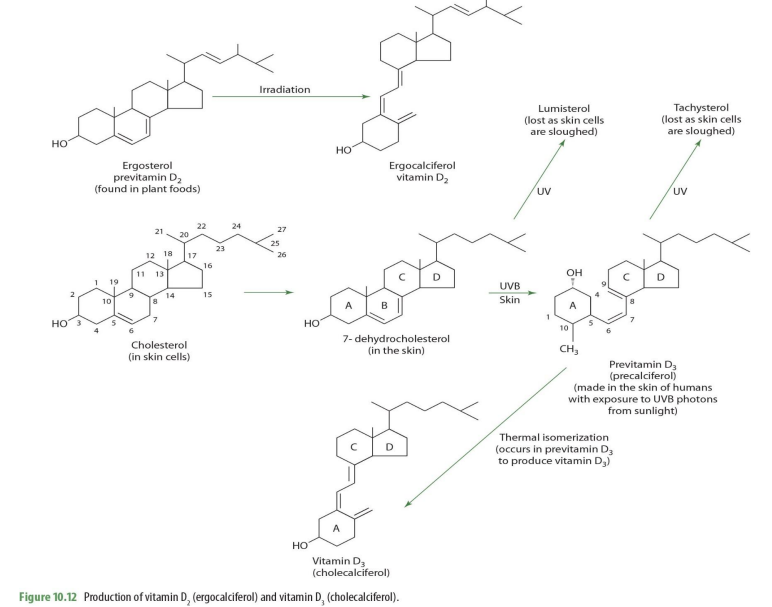
In our bodies, we derive vit D from
cholesterol
cholesterol on skin cells becomes what?
7-dehydrocholesterol
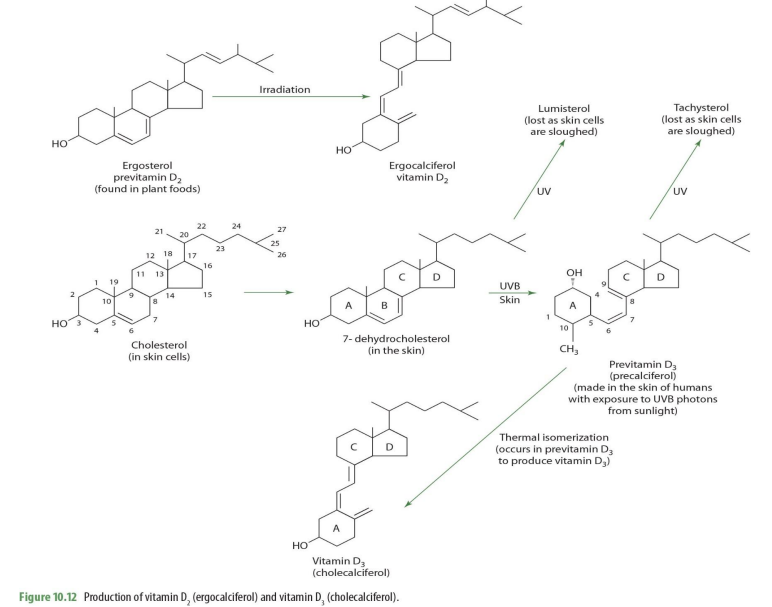
7-dehydrocholesterol exposed to UV becomes
lumisterol (lost as skin cells sloughed off)
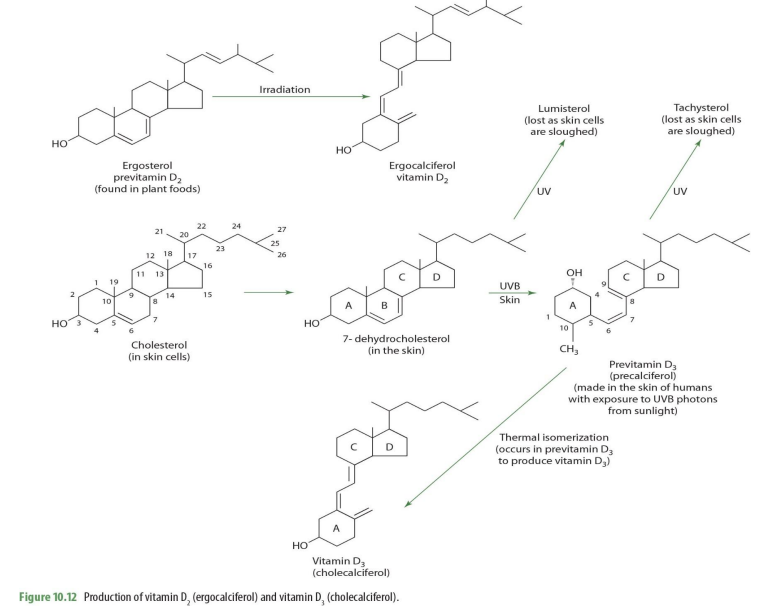
7-dehydrocholesterol exposed to UVB on skin becomes
previtamin D3 (precalciferol)
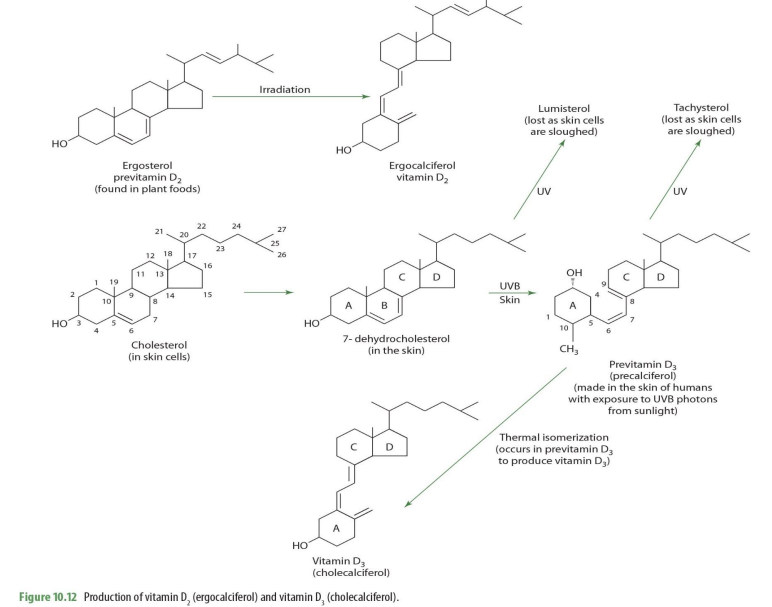
precalceferol (previt D3) exposed to UV becomes
tachysterol (lost as skin cells are sloughed off)
precalceferol (previt D3) when undergoes thermal isomerization becomes
cholecalciferol (D3)
is cholecalciferol the active form of VitD?
nope
what does the subscript 3 in D3 mean? D2?
3 represents what is produce by human/animal sources
2 means originates from plants
which form of vit D is from plant sources?
ergosterol (converts into ergocalciferol)
D2 vs D3 bioavailability
D2 is almost equivalent to D3
supplements tend to be D2
__% of vitamin D is absorbed
50%
where is rate of absorption the highest? & where is most absorption?
rate is highest in duodenum/jejunum BUT
most absorption occurs in distal SI
vitamin D is incorporated into___ & transported through____
chylomicron
lymphatic system & then blood
chylomicrons transport ___% of cholecalciferol in the blood
40%
some (60%) of vit D transport involves what?
vit D binding protein (DBP)
aka transcalciferin
what tissues take vit D from chylomicron transport
adipose, muscle & other tissues
where is storage higher & when
adipose; when more fat is present
who requires a higher intake of vit D & to maintain what
obese individuals
to maintain blood concentration (in comparison to normal wt individuals)
in contrast to dietary vit D, vit D synthesized by the skin (cholecalciferol) goes into blood how?
diffuses slowly
vitamin synthesized by the skin is picked up by the ______ in the blood
hepatic DBP
DBP can transport the vitamin primarily to ___ (other tissues take as needed)
liver
plasma transport involves ____% bound to ____
60% ; DBP (transcalciferin)
VIT D METABOLISM
what form of vit D diffuses into the blood?
cholecalciferol
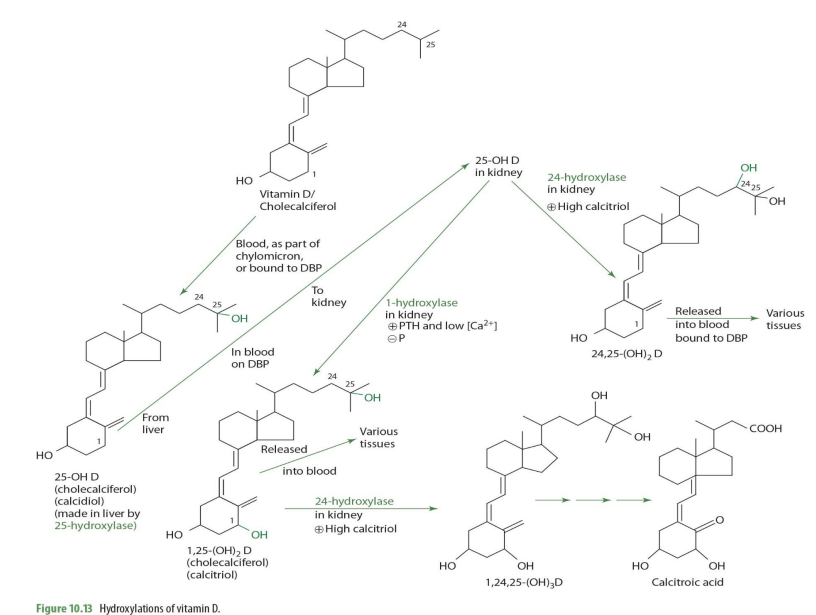
Cholecalciferol diffuses from skin into blood & is picked up by ____ for transport
vitamin-D binding protein (DBP) —> aka transcalciferin
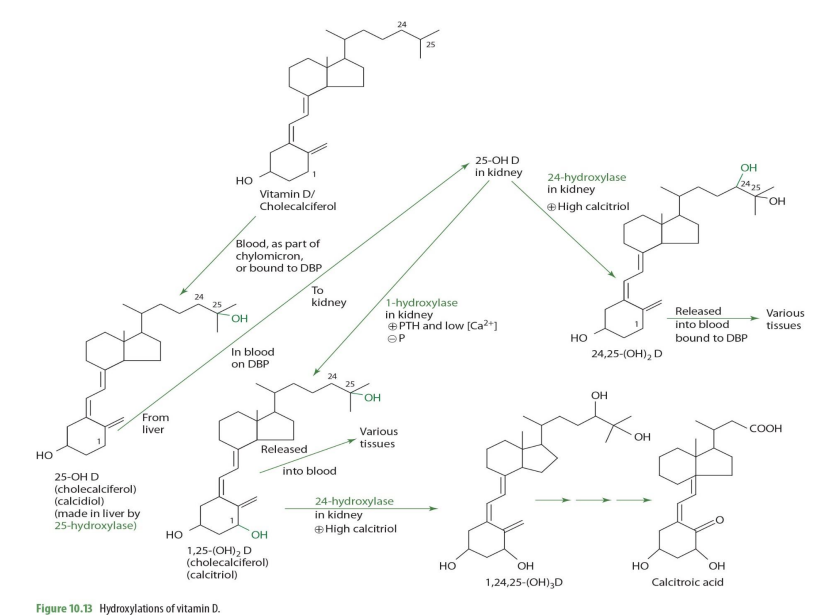
Vitamin D/cholecalciferol travels through blood as part of ___ or bound to ___
chylomicron ; DBP (transcalciferin)
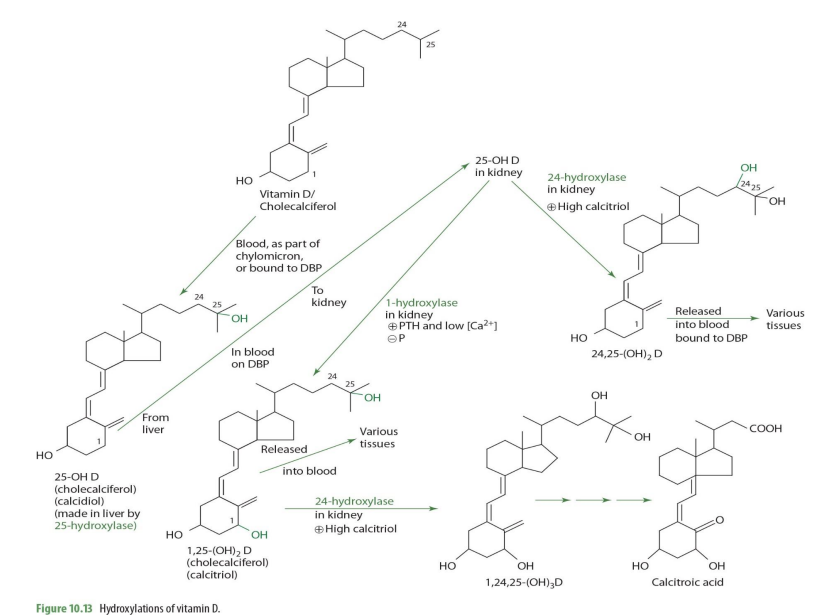
cholecalciferol is metabolized into what form in the liver?
25-OH D (calcidiol)
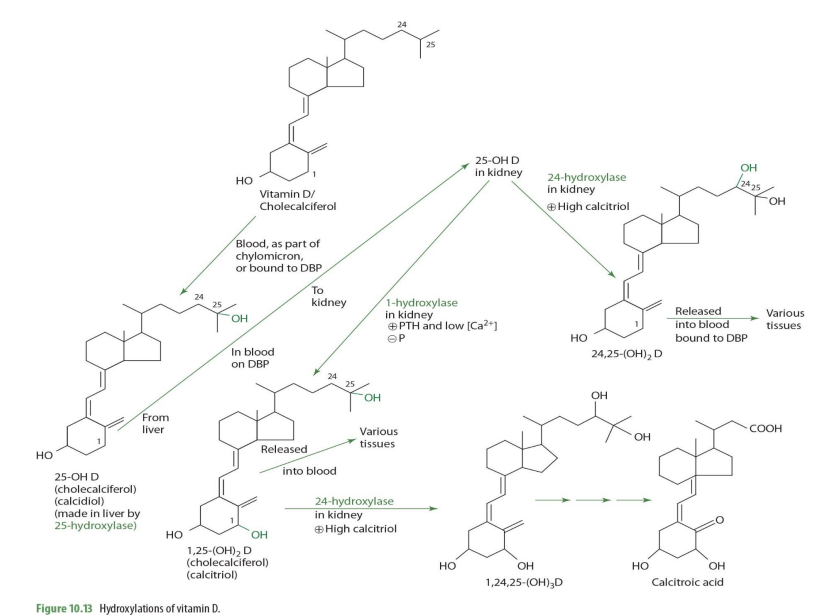
cholecalciferol —> 25-OH D (calcidiol) via what enzyme? coenzyme?
25 hydroxylase (NADPH)
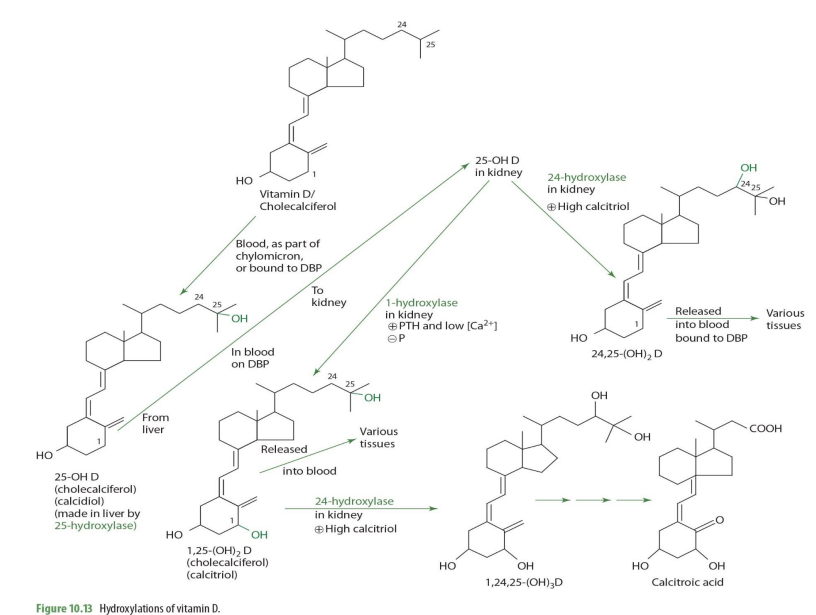
cholecalciferol —> 25-OH D (calcidiol) occurs where in the cell?
mitochondria
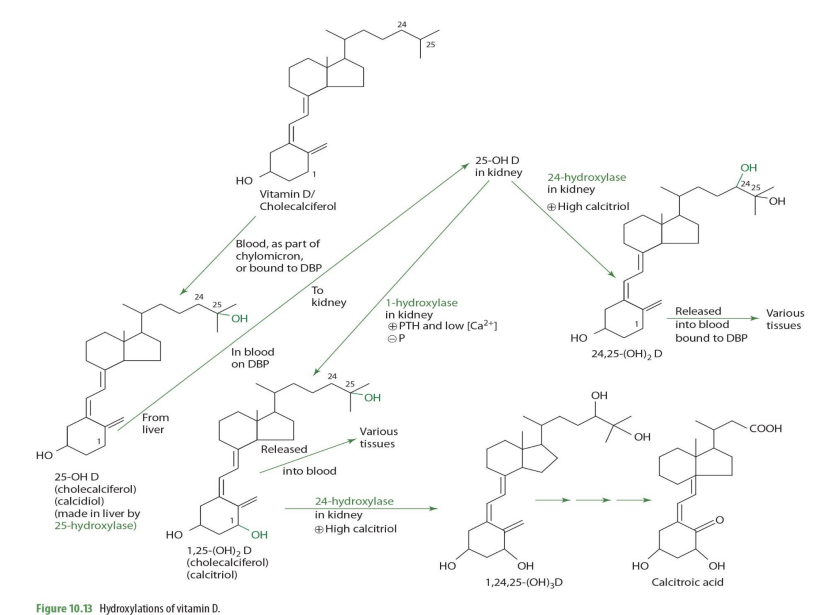
majority of 25-OH D (calcidiol) is secreted into __
blood
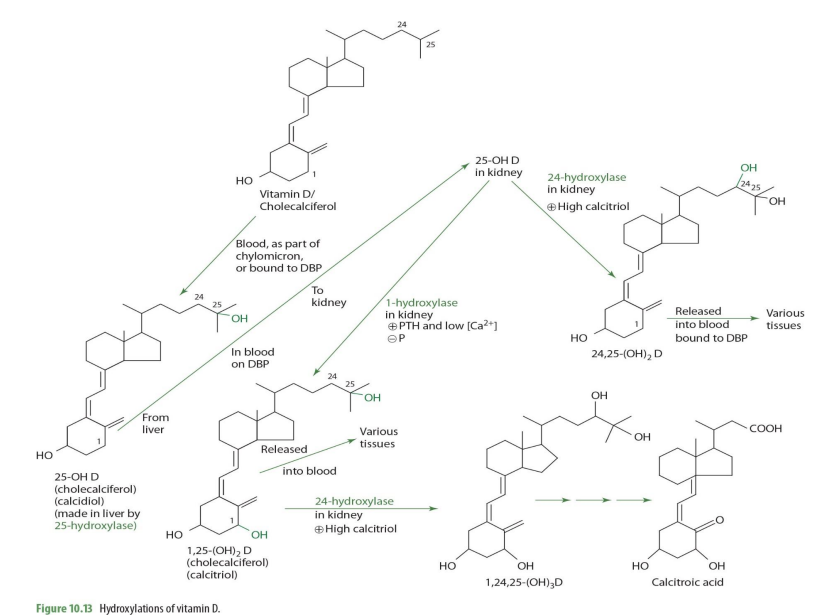
majority of 25-OH D (calcidiol) is transported by
DBP (transcalciferin)
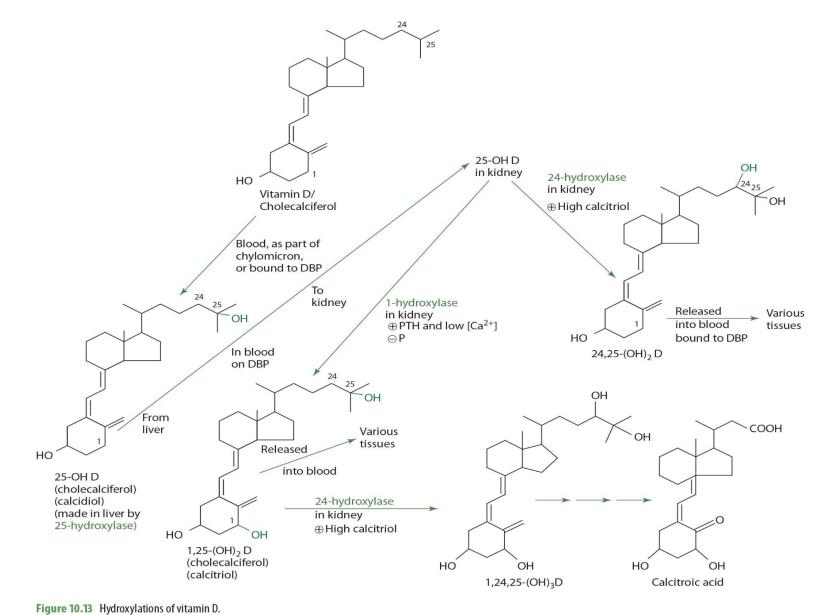
half life of 25-OH D (calcidiol)
2-3wks
normal serum concentrations of 25-OH D (know this**)
30-40ng/mL (ng = nanogram= 9 decimal places)
very very little amount… yet around 15% is suboptimal
From blood, 25-OH-D is taken up by (mostly ____) in response to increases in ______ concentration.
kidney
increase in parathyroid hormone (PTH)
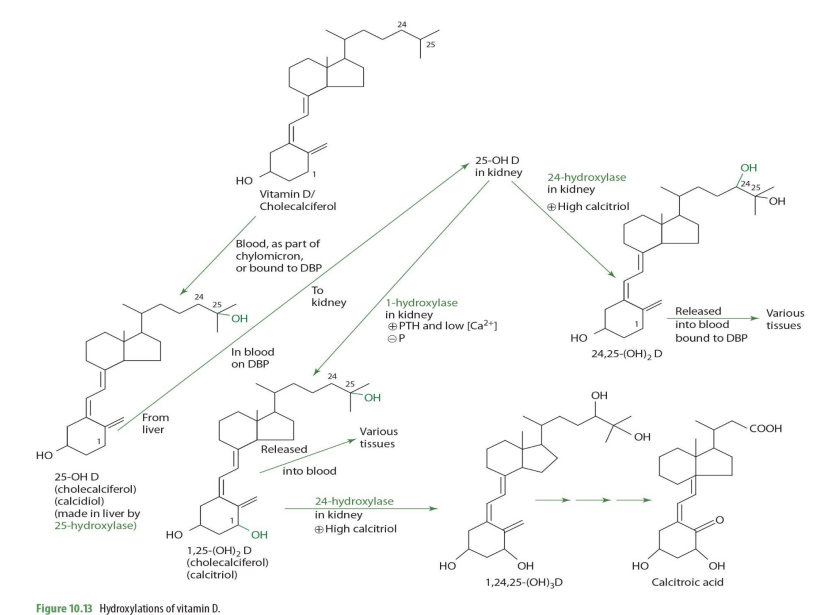
In the kidney proximal tubules, 25-OH-D and DBP bind to a ____________ to form a complex.
cubulin-megalin membrane receptor
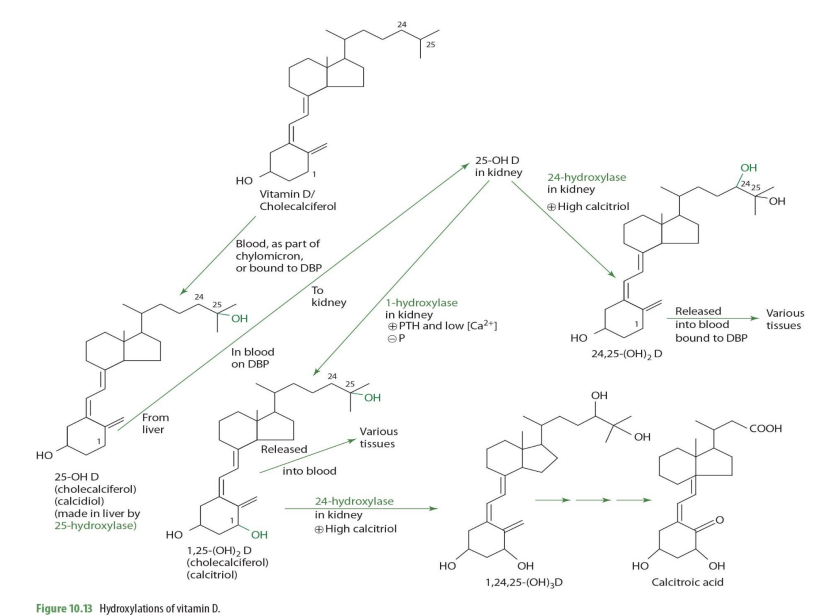
The complex is internalized through _______
endocytosis
once in the kidney, 25-OH-D can be converted into ___________ or ___________—
1,25OH2D (calcitriol) OR 24,25-(OH)2D
what kidney enzyme will convert 25-OH-D into 1,25(OH)2D (calcitriol)?
1-alpha hydroxylase (NADPH dependent)
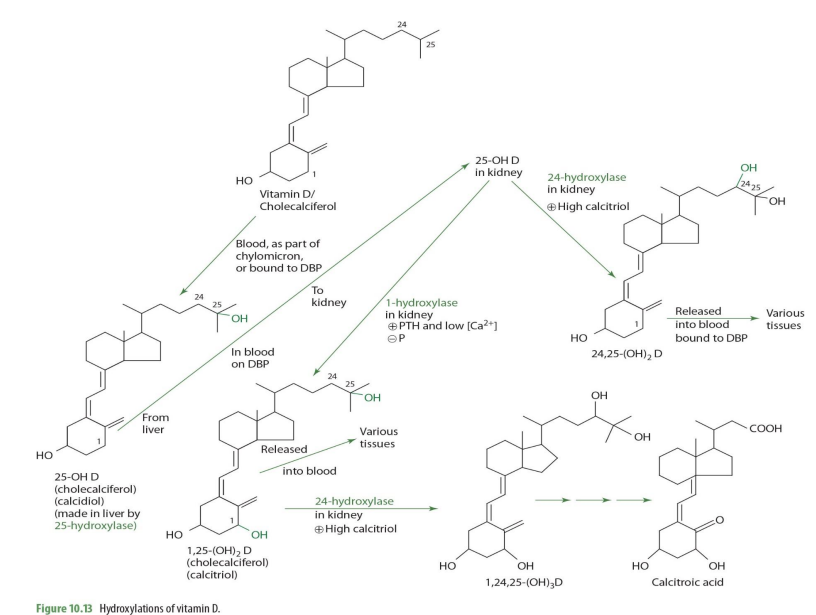
1-alpha hydroxylase is also known as what names?
1-hydrolase
alpha-hydrolase
Majority of 1-alpha hydroxylase is found in the ______with smaller amounts in ......
kidney ; bone, skin, intestine, etc
Renal production of 1,25-OH2 D is tightly regulated by what 2 hormones
PTH and fibroblast-like growth factor (FGF)
PTH ) is produced by
fibroblast-like growth factor (FGF) is produced by
parathyroid gland
bone cells
when will 25-OH-D be converted into 1,25(OH)2D (calcitriol) by 1-a hydrolase?
when high PTH and low calcium

1,25-(OH)2D (calcitriol) can be converted further into other molecules via what enzyme and into what when calcitriol is high?
24-hydrolase
making 1,24,25(OH)2D
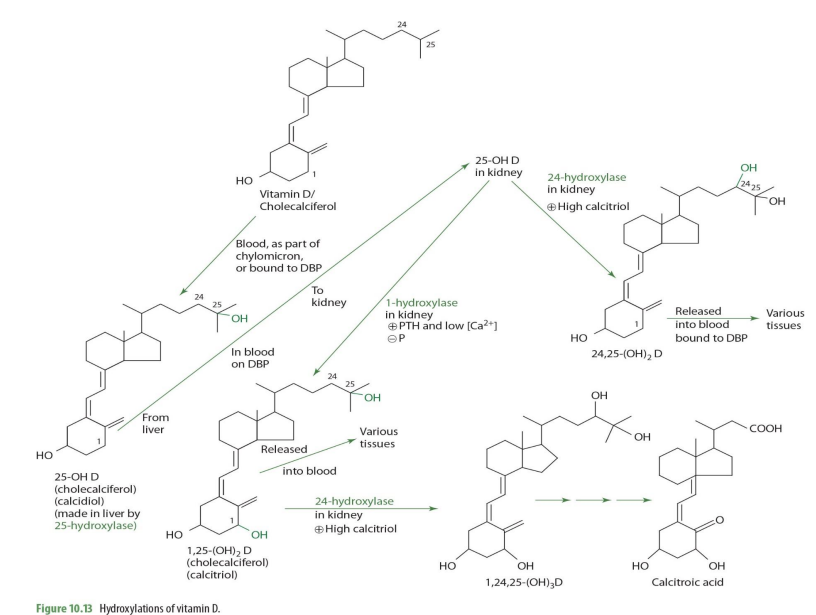
1,25-(OH)2D (calcitriol) acted upon 24-hydrolase occurs in what tissue?
kidney
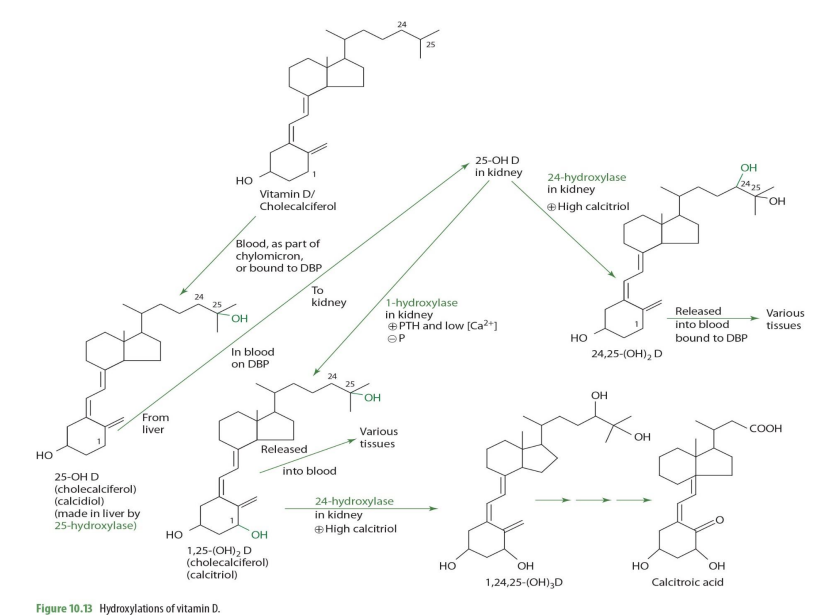
1,25-(OH)2D + 24-hydroxylase -> what eventual compound
calcitroic acid
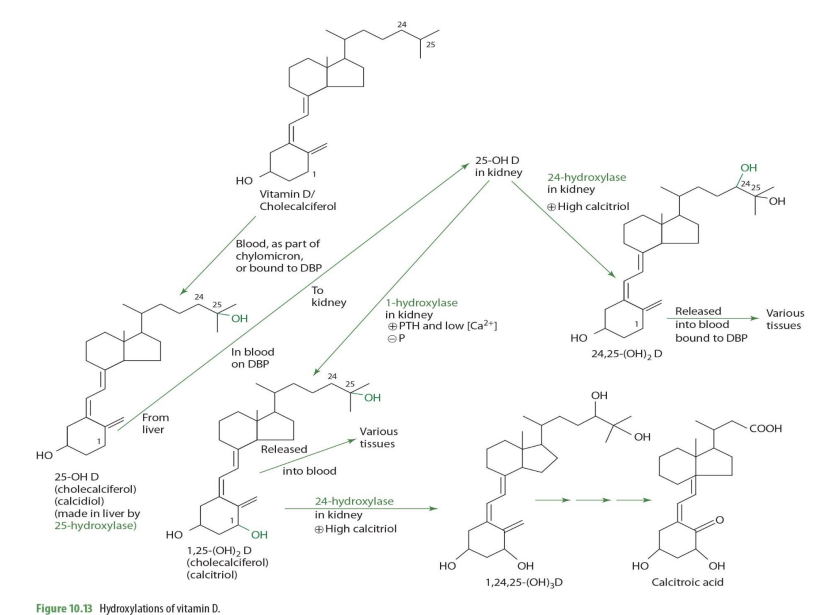
calcitroic acid can be used as a .....
secondary maker for assessment (excreted in urine)
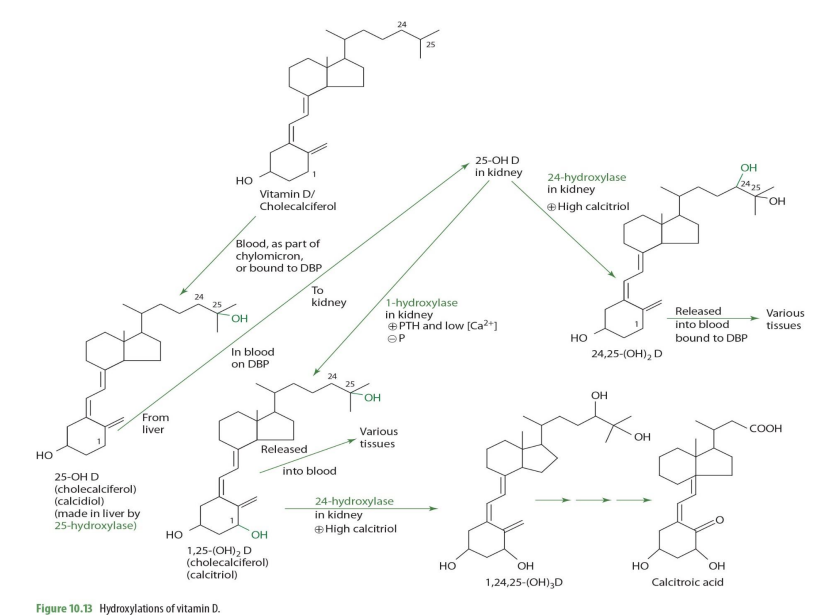
what is primary marker for assessment?
25(OH)D (calcidiol)
when would 25(OH)2D (calcidiol) be converted into 24,25(OH)2D instead of 1,25(OH)2D
When Calcitriol is high

how is 25-OH D —> 24,25-(OH)2D (enzyme?)
24-hydroxylase
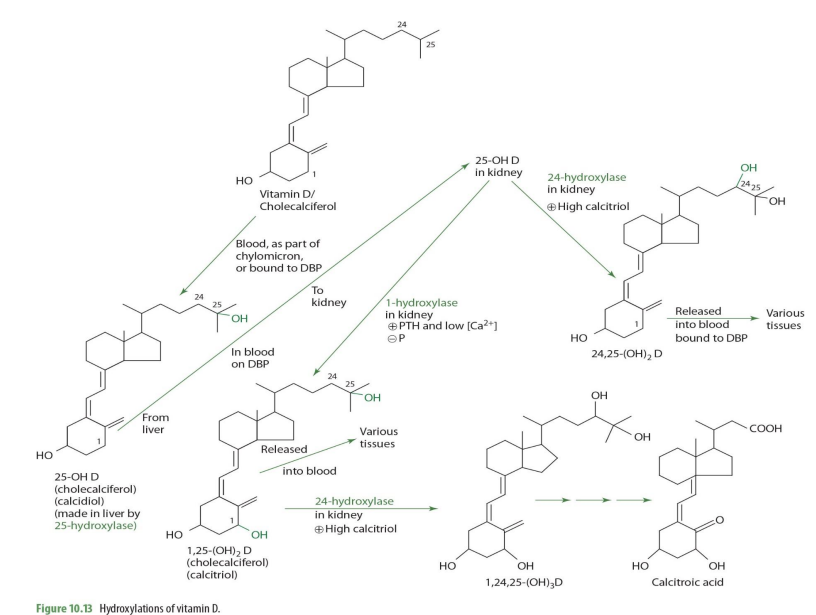
24,25-(OH)2D can then ...
release to blood bound to DBP to be carried to various tissues
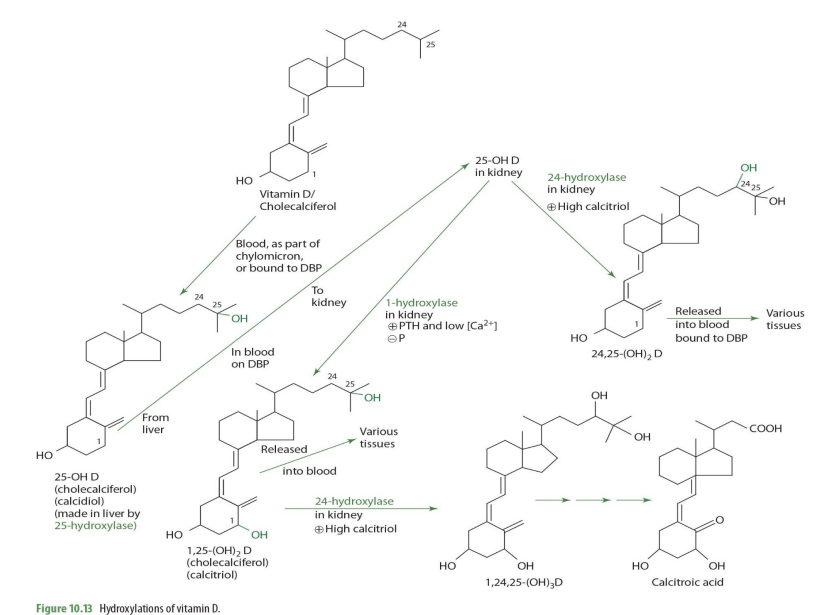
what is the major circulating form of vit D
25-OH Vitamin D

what is 25-OH vit D used for?
measured for assessment and deficiency determination (primary assessment measure)
active form of vit D
1,25(OH)2
1,25(OH)2 half life & normal range
2-6 hours
normal range of 20-40 pg/dL (12 decimal places)
why is 25(OH)D used for assessment vs 1,25(OH)D?
because 1,25(OH)D has shorter half life AND smaller adequate range (pico vs nanograms) so 25(OH)D is easier to measure and can be done in most labs
Vitamin D binding protein responsible for .....
transport
vitamin D binding protein is also known as ***
Transcalciferin
ACTIVATION, TRANSPORT, STORAGE
Activation of vit D occurs by what tissues.....
liver & kidneys
vit D is stored in
liver & fat tissue
increased activation of D is linked to .....
Ca inadequacy, metabolism, & homeostasis
excretion of D mainly via
bile
VIT D ROLES AND ACTIONS
genomic action of Vit D involved what form?
1,25(OH)2D
1,25(OH)2D goes where for genomic action?
travels to nucleus of its target tissue cells
In the nucleus, 1,25(OH)2D binds to a ____
protein receptor
the complex (1,25(OH)2D with protein receptor) bind to what?
binds directly to DNA
the complex (1,25(OH)2D with protein receptor) binding to DNA, causes what?
increase or decrease gene transcription
in gene expression, calcitriol binds to
vitamin D receptor (VDR)

vit D receptor (VDR)-calcitriol forms heterodimer how?
with retinoid X receptor
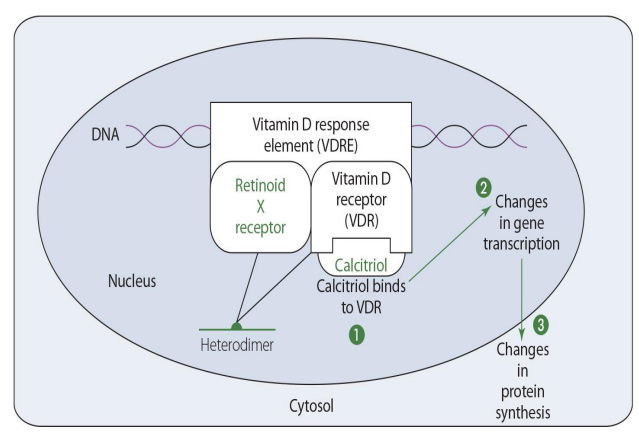
VDR and RXR form what?
vitamin D response element (VDRE)
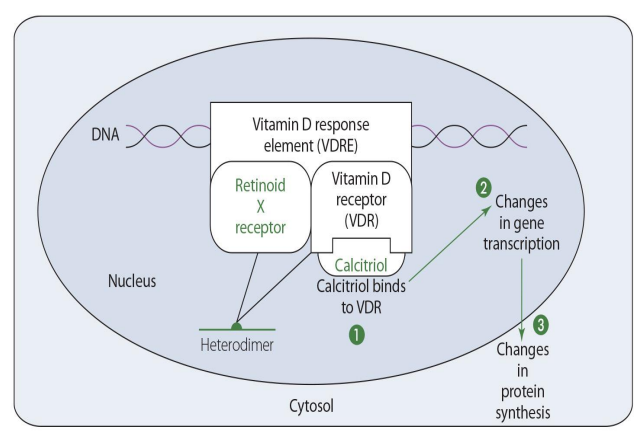
vitamin D response element (VDRE) then proceeds to ____ & then ____
changes in gene transcription
changes in protein synthesis
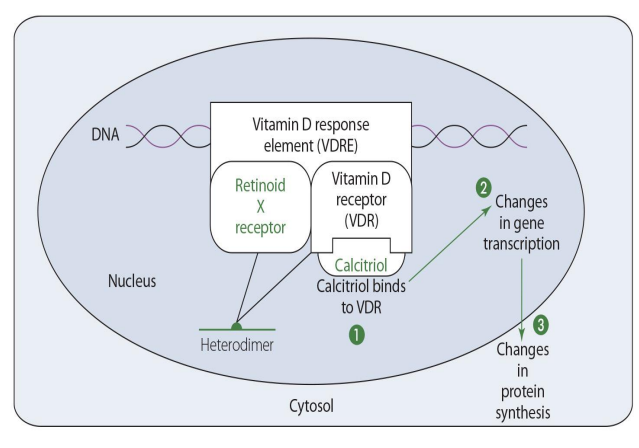
Vit D plays a role in making
important calcium binding proteins
vit D influences 2 important calcium binding proteins how?
its nuclear response element (VDRE) in the transcription machinery
Vitamin D via its nuclear response element in the transcription machinery influences what 2 important Ca binding proteins
calbindin & calmodulin
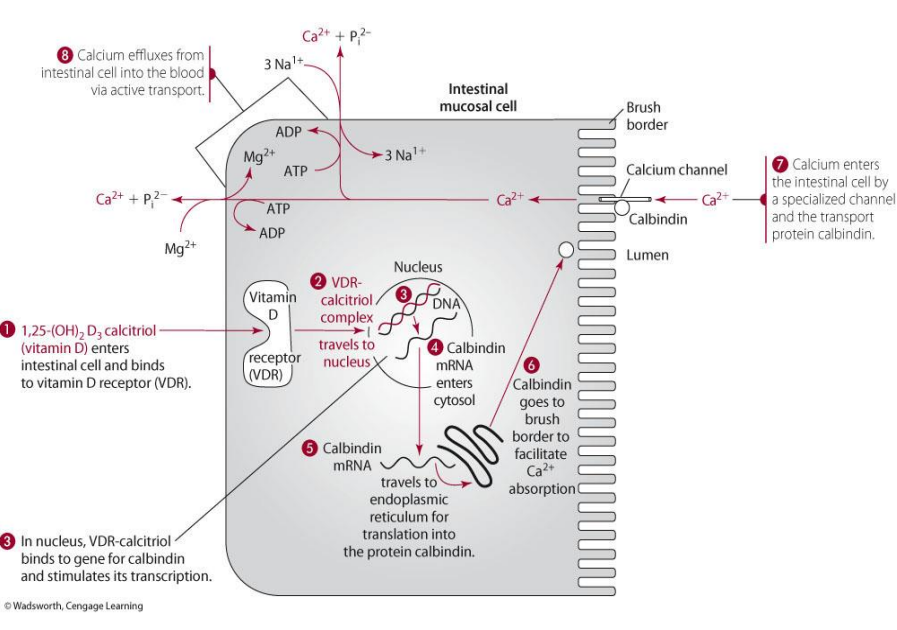
calbindin vs calmodulin
calbindin is the INTESTINAL binding protein
calmodulin is the intercellular binding protein (within in all cells)
what does calbindin do? where found?
found: found in the intestinal brush border
function: brings in calcium into the intestinal cell
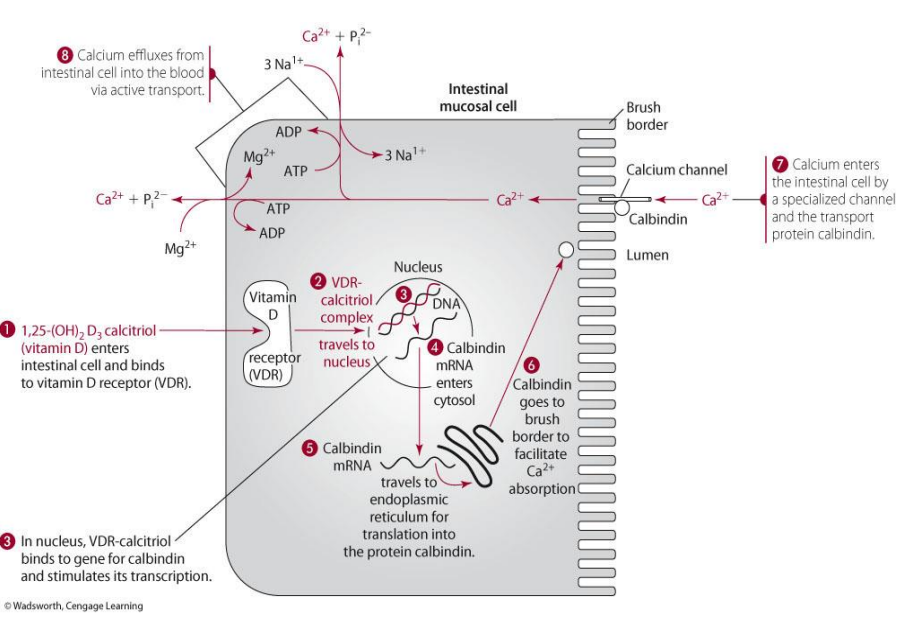
for calcium-binding action, what form of Vit D is used?
1,25(OH)2D (calcitriol)

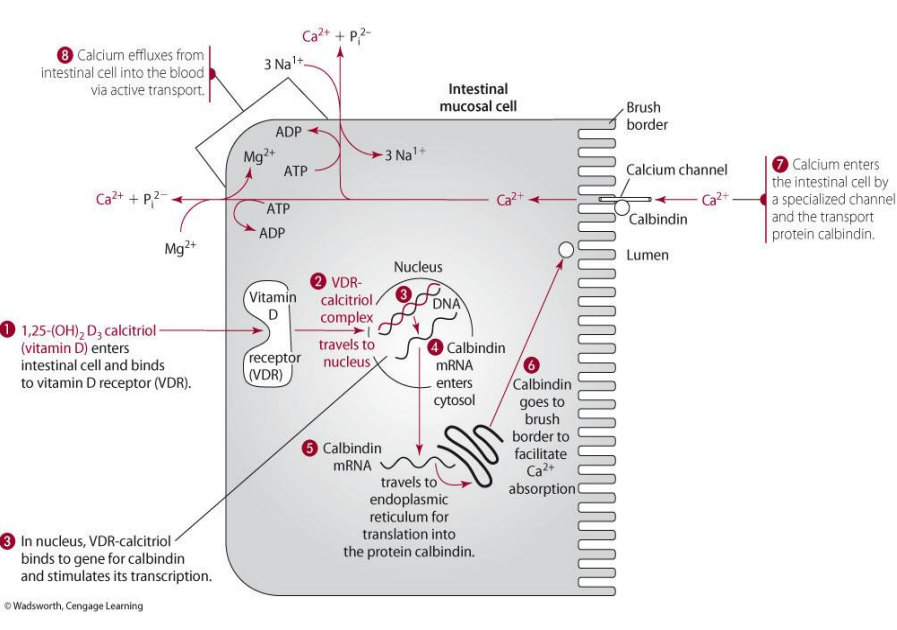
how does vit D play a role in calbindin? (think illustration)
1,25(OH)2D goes into intestinal cell as will bind to VDR to form complex—> goes to nucleus to make calbindin mRNA which will then go to cytosol to ER and be made into calbindin
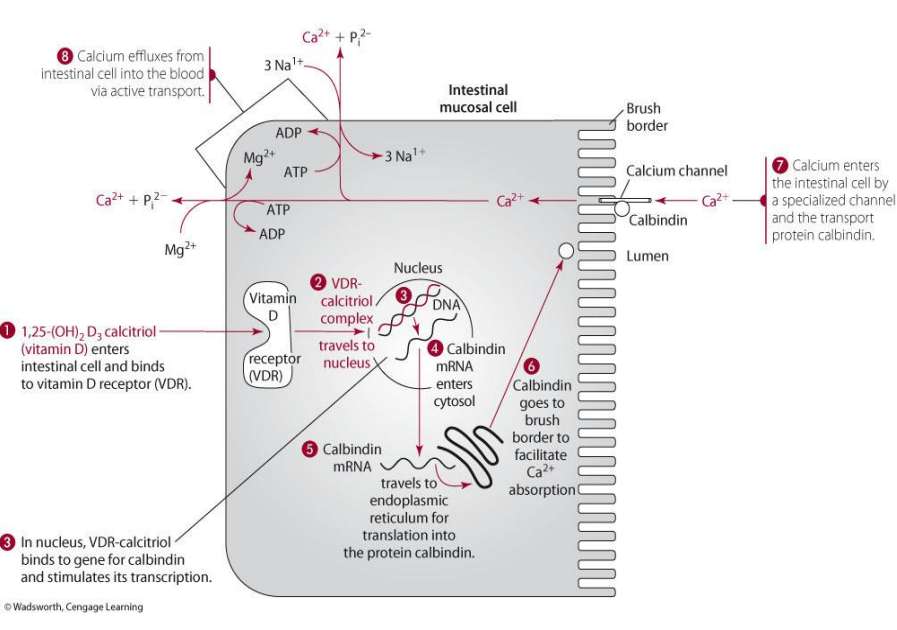
calbindin made then does what?
goes to brush border and functions to allow calcium absorption in the intestine
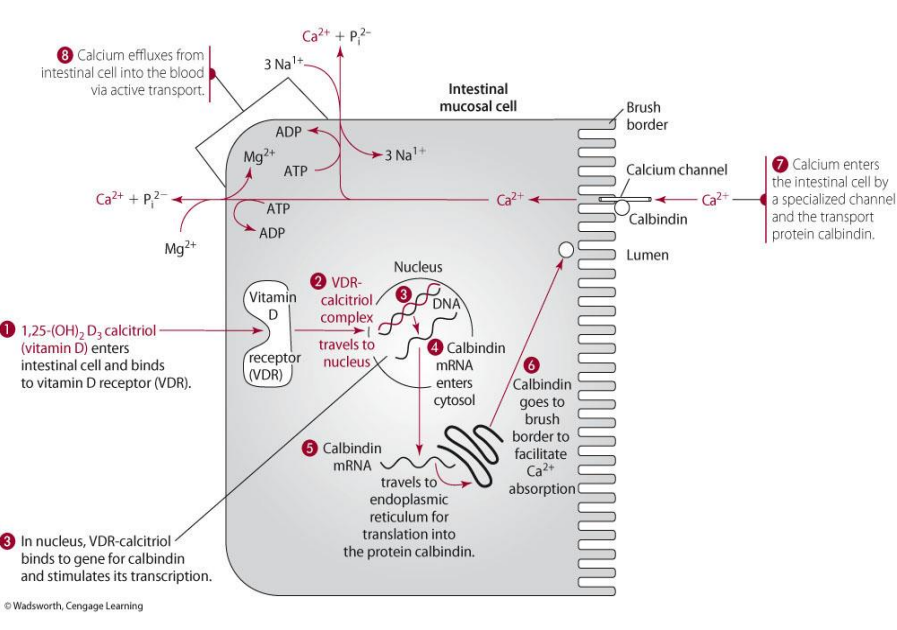
how does calcium enter the intestinal cell?
via specialized channel and the transport of calbindin
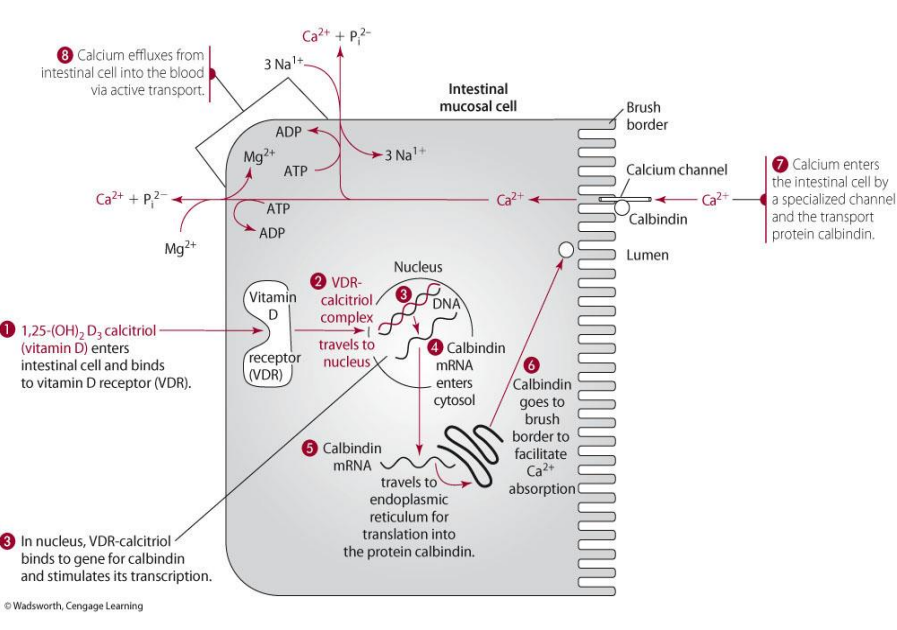
calcium exits the intestinal cell via
active transport
non-genomic actions of 1,25(OH)2D involves
Intracellular signaling (signal transduction pathways)
what 3 things does vit D do through signal transduction pathways?
increased calcium uptake
increased intracellular concentration
transcellular calcium flux in enterocytes, osteoblasts, adipocytes, and skeletal muscle.
Primary function of active D (1,25(OH)2D
maintain an optimal serum Ca level (8.5-10.5mg/dL)
how does active D maintain optimal serum Ca level (3 things)
-Increasing Ca absorption from intestine
-Increasing Ca reabsorption from kidney
-Increasing Ca resorption from bone
1,25(OH)2D functions in what tissues for calcium levels (3)
intestine, kidney, bone
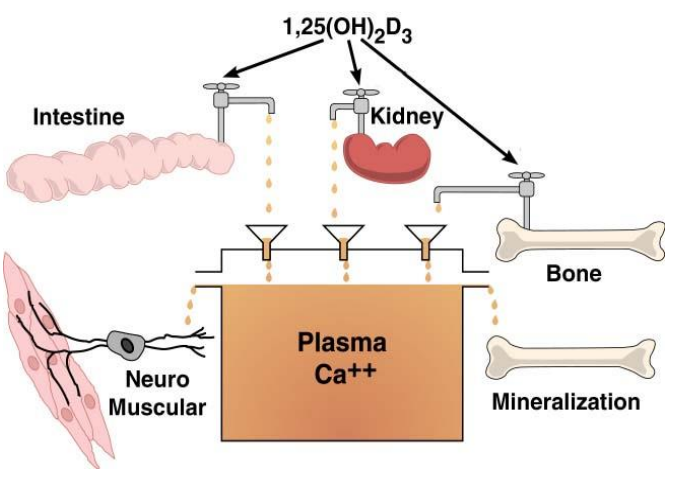
intestine, kidney, bone contribute to ....
plasma Ca++
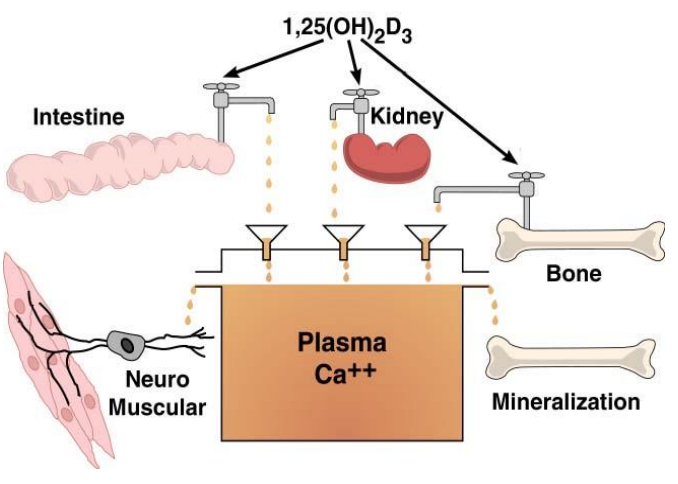
plasma Ca++ contributes to
mineralization & neuromuscular function
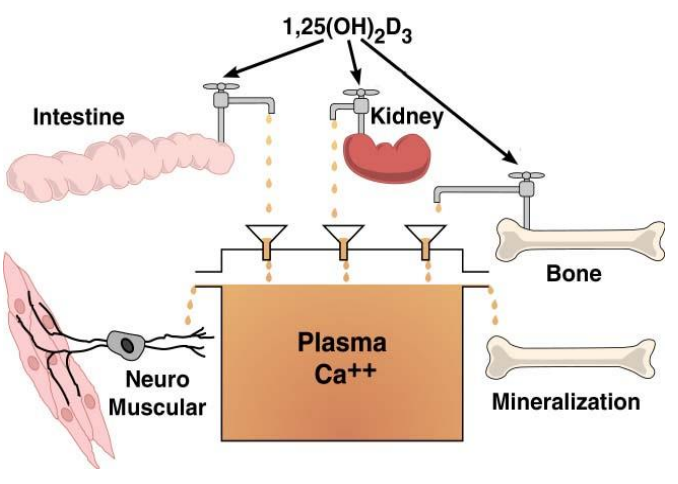
1,25(OH)2D is ____
extremely potent