C4.1 Electrolysis
1/18
There's no tags or description
Looks like no tags are added yet.
Name | Mastery | Learn | Test | Matching | Spaced |
|---|
No study sessions yet.
19 Terms
What is electrolysis?
The decomposition of an ionic compound when molten or dissolved in an aqueous solution by the passage of an electric current
Only occurs in ionic compounds
What is required for electrolysis to occur?
Power source
Electrode
Electrolyte
What is an electrode and what are they usually made of?
Solid, conductive substance through which electric current enters or leaves the electrolytic cell
Usually made of graphite or platinum, which are inert substances
What is an inert substance?
A substance that does not react chemically with other substances
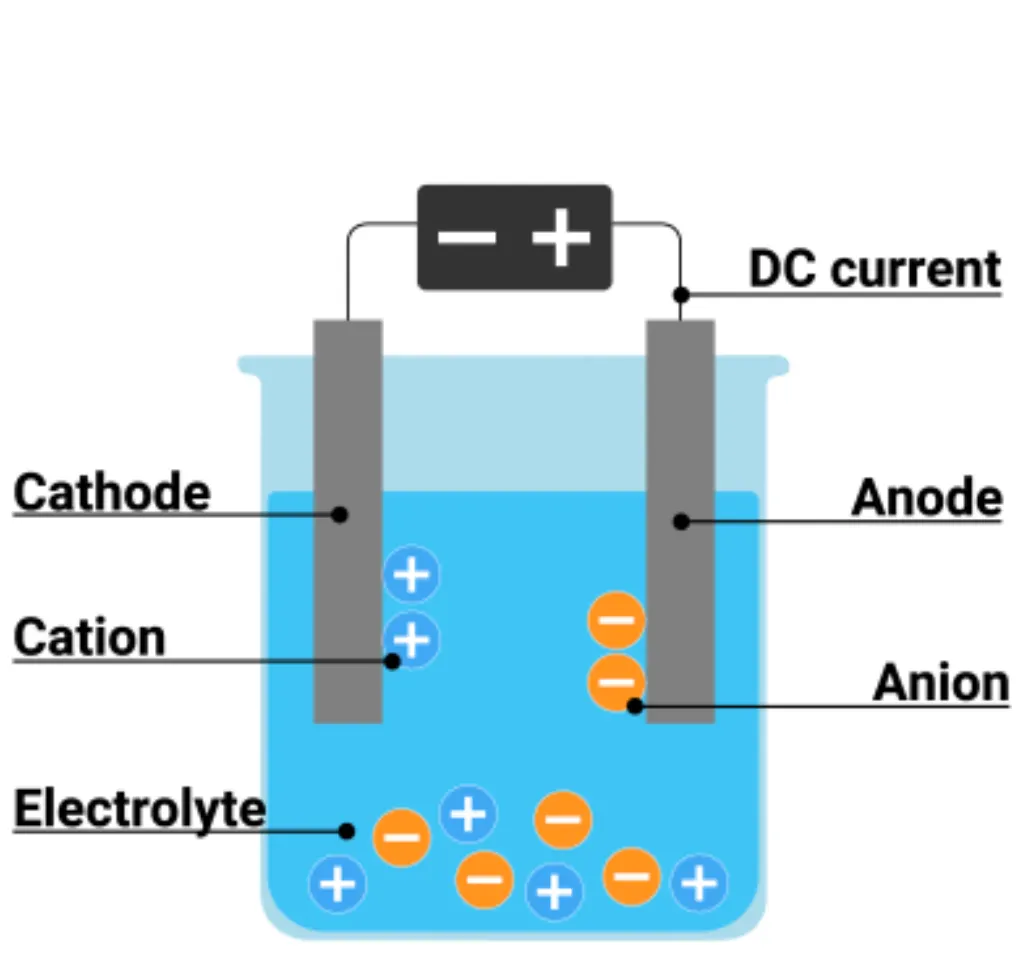
What is an electrolyte?
An ionic compound that has been molten or dissolved in water, which contains free ions which can easily move to conduct electricity
What is the cathode and the anode and what do each of them attract? In which one does reduction/oxidation occur?
Cathode: negative electrode
Attracts cations (positive ions)
Reduction occurs at the cathode (electrons gained)
Anode: positive electrode
Attracts anions (negative ions)
Oxidation occurs at the anode (electrons lost)
In which direction do electrons flow in an electrolytic cell?
From the cathode to anode through the external circuit in the wires
Label the parts of an electrolytic cell in a diagram
What are the general products formed at the cathode and anode during electrolysis?
Cathode: metals or hydrogen
The product depends on the reactivity series
If the metal is less reactive than hydrogen, the metal is produced
If the metal is more reactive than hydrogen, hydrogen is produced
Anode: non-metals except hydrogen
If there is an element from group 7, that will be formed
If there is no element from group 7, oxygen is formed
Predict the identity of the products at each electrode for the electrolysis of a binary compound in the molten state
The cation forms a metal at the cathode
The anion forms a non-metal at the anode
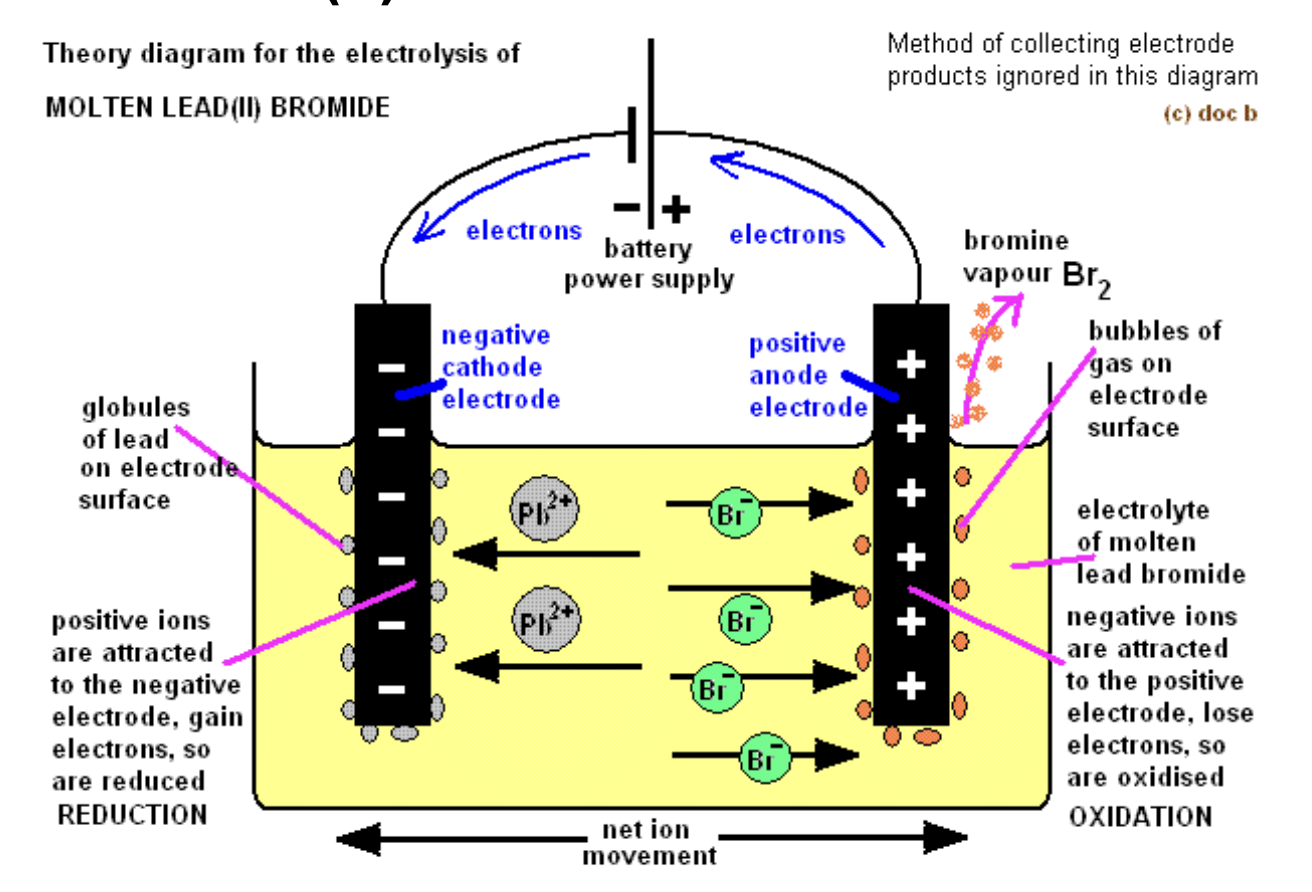
What are the products and observations for molten lead (II) bromide or Molten PbBr₂?
Product at cathode: Pb, grey metal deposit
Product at anode: Br2 (brown gas)
Observations: simple decomposition of molten ionic compound
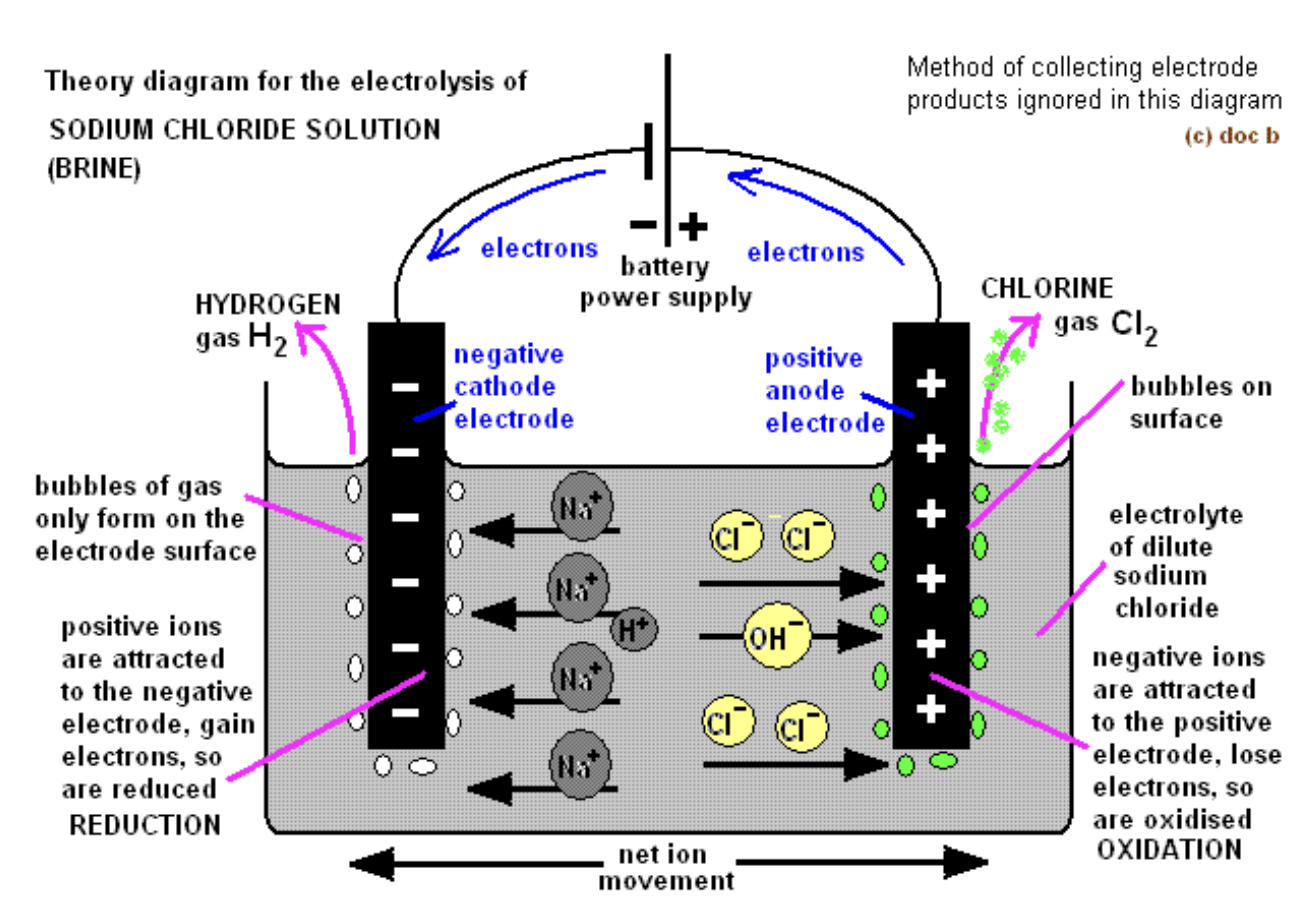
What are the products and observations for concentrated aqueous sodium chloride or Conc. NaCl (aq)?
Products at cathode: H2 (bubbles)
Products at anode: Cl2 (greenish-yellow gas, smell)
Observations: solution becomes alkaline (NaOH formed)
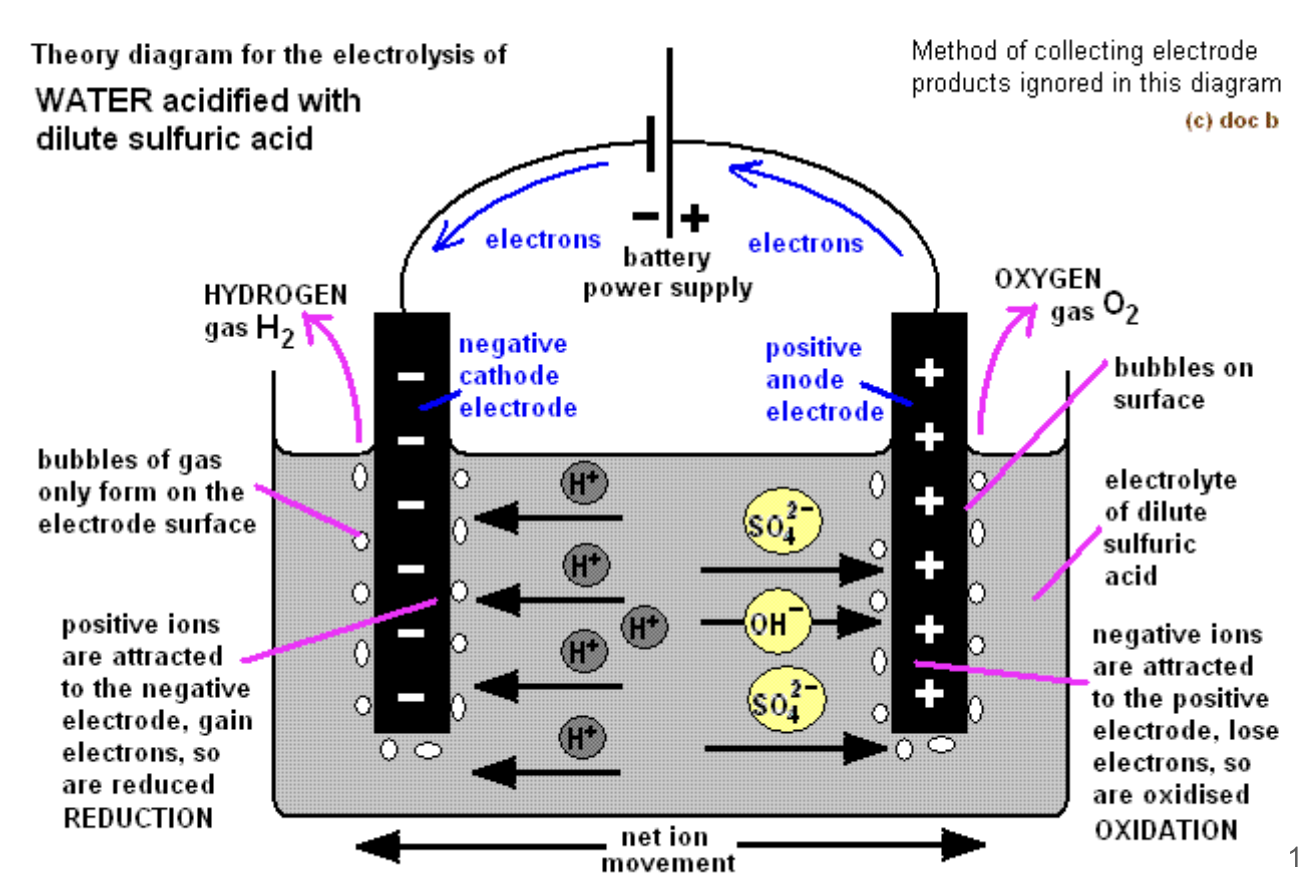
What are the products and observations for dilute sulfuric acid or Dilute H₂SO₄ (aq)?
Products at cathode: H2 (bubbles)
Products at anode: O2 (bubbles)
Observations: water decomposes → 2H₂ + O₂
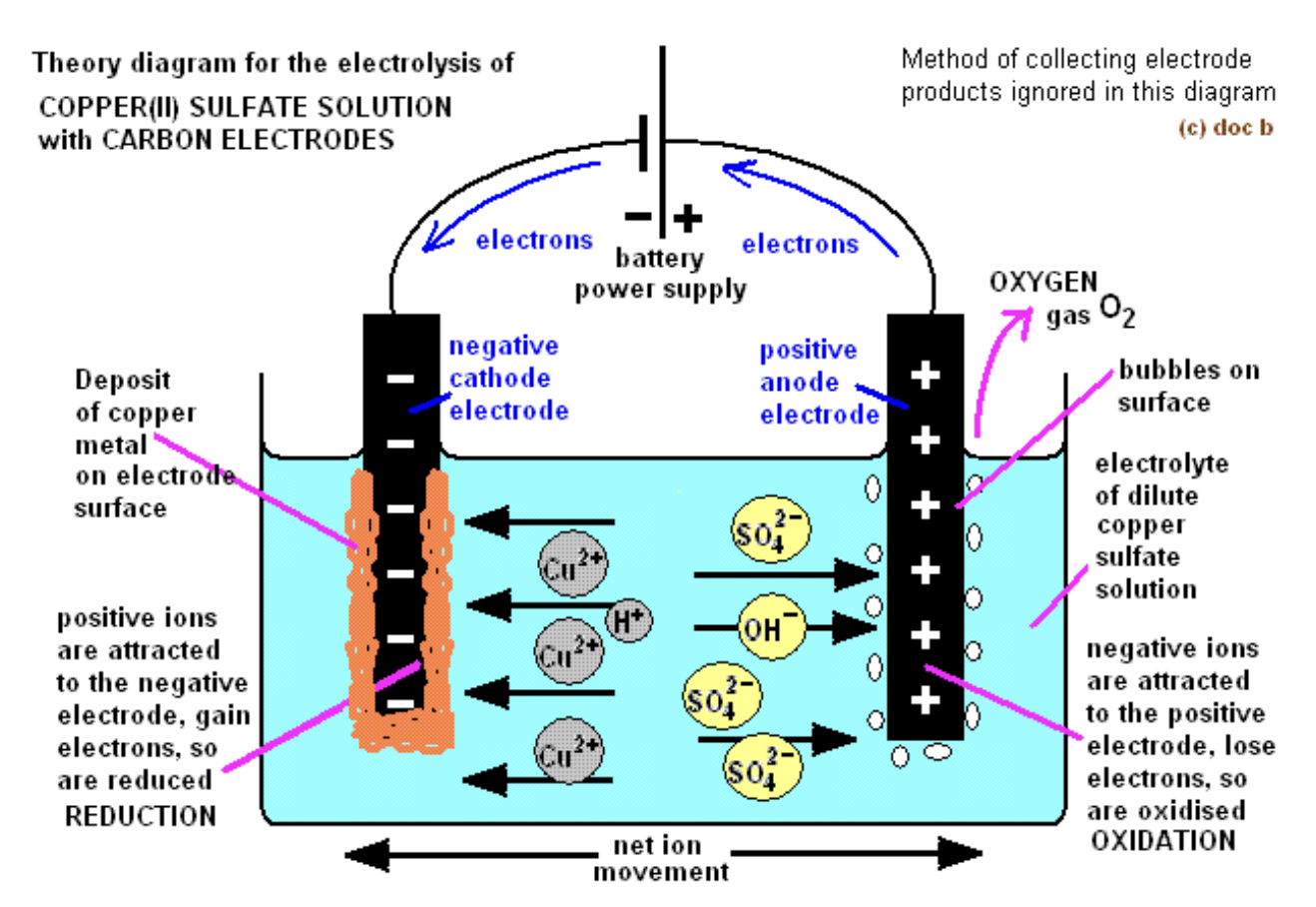
What are the products and observations for aqueous copper(II) sulfate or CuSO4 with graphite electrodes?
Products at cathode: Cu (reddish-brown deposit)
Products at anode: O2 (bubbles)
Observations: Blue solution slowly fades
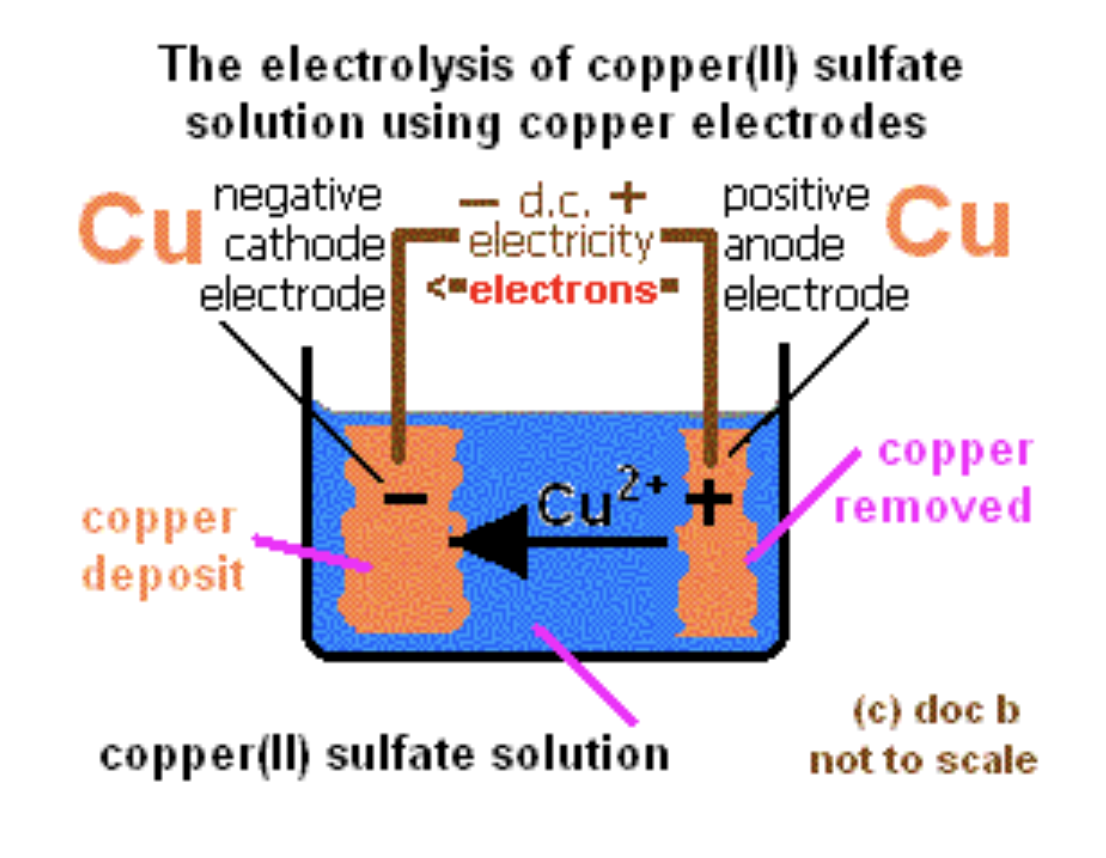
What are the products and observations for aqueous copper(II) sulfate or CuSO4 with copper electrodes?
Products at cathode: Cu (reddish-brown deposit)
Products at anode: Cu dissolves into solution (Cu²⁺ ions)
Observations: Mass of cathode ↑, anode ↓ (used in electroplating/purification)
What ions does water split up into in solutions?
H2O → H+ + OH-
What usually happens in electrolysis if reactive electrodes are involved?
The electrode element participates in the reaction
It typically dissolves in the anode, while the expected reduction occurs at the cathode
How do hydrogen-oxygen fuel cells produce electricity? What is the overall reaction?
They use hydrogen and oxygen to produce electricity, and the only chemical product is water
Reaction: 2H2+O2 → 2H2O
Describe the advantages and disadvantages of using hydrogen–oxygen fuel cells in comparison with gasoline/petrol engines in vehicles
Advantages of fuel cells:
Only water produced (no CO₂).
Efficient energy conversion.
Renewable hydrogen possible.
Disadvantages of fuel cells:
Hydrogen storage is difficult and expensive.
Hydrogen production may rely on fossil fuels.
Fuel cell technology is costly.