Pelvis and ligaments of pelvis
1/61
There's no tags or description
Looks like no tags are added yet.
Name | Mastery | Learn | Test | Matching | Spaced |
|---|
No study sessions yet.
62 Terms
function of pelvis
support bladder, rectum, anal canal and reproductive organs
anchors root of external genitalia
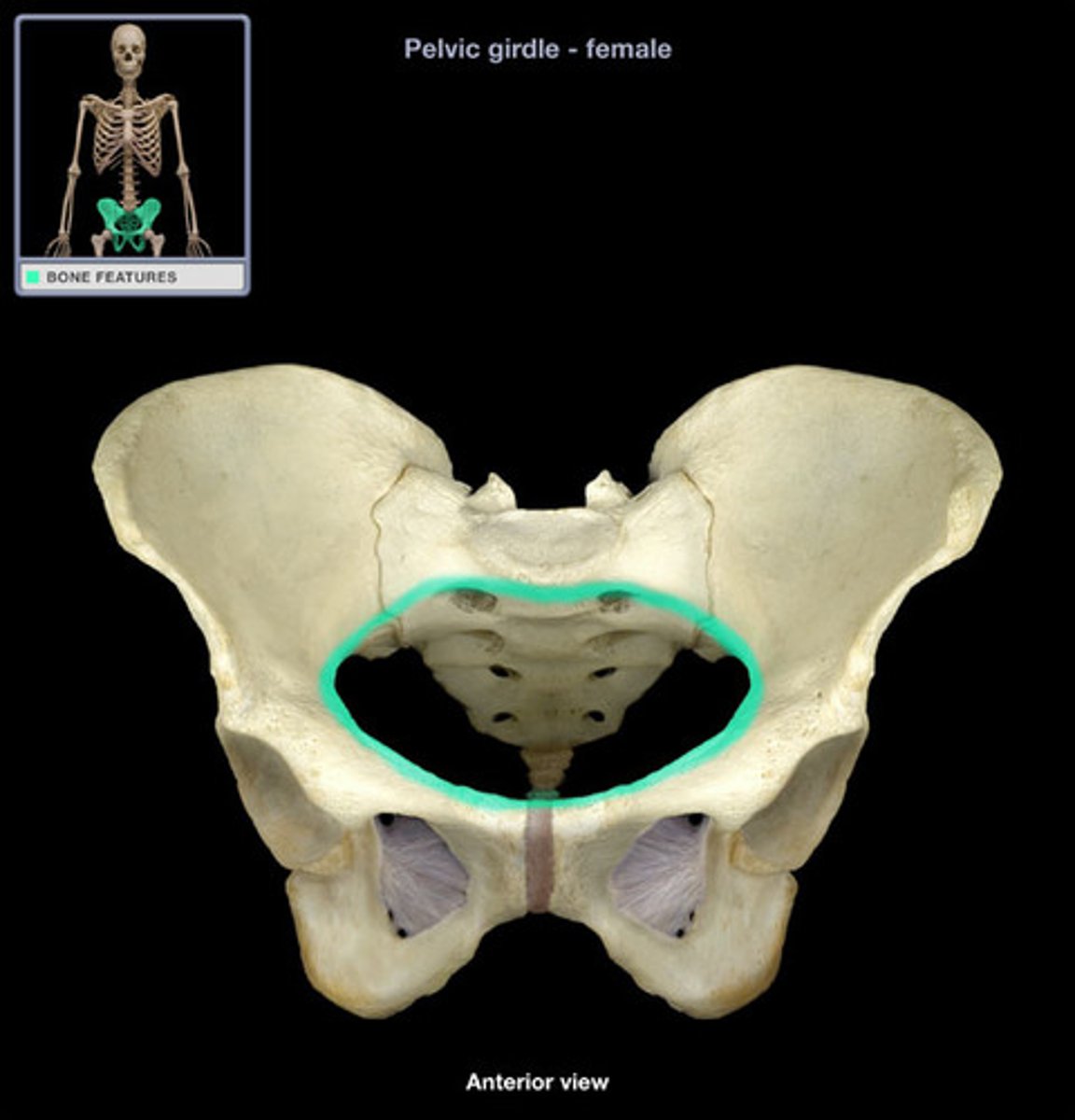
terminal line of pelvis
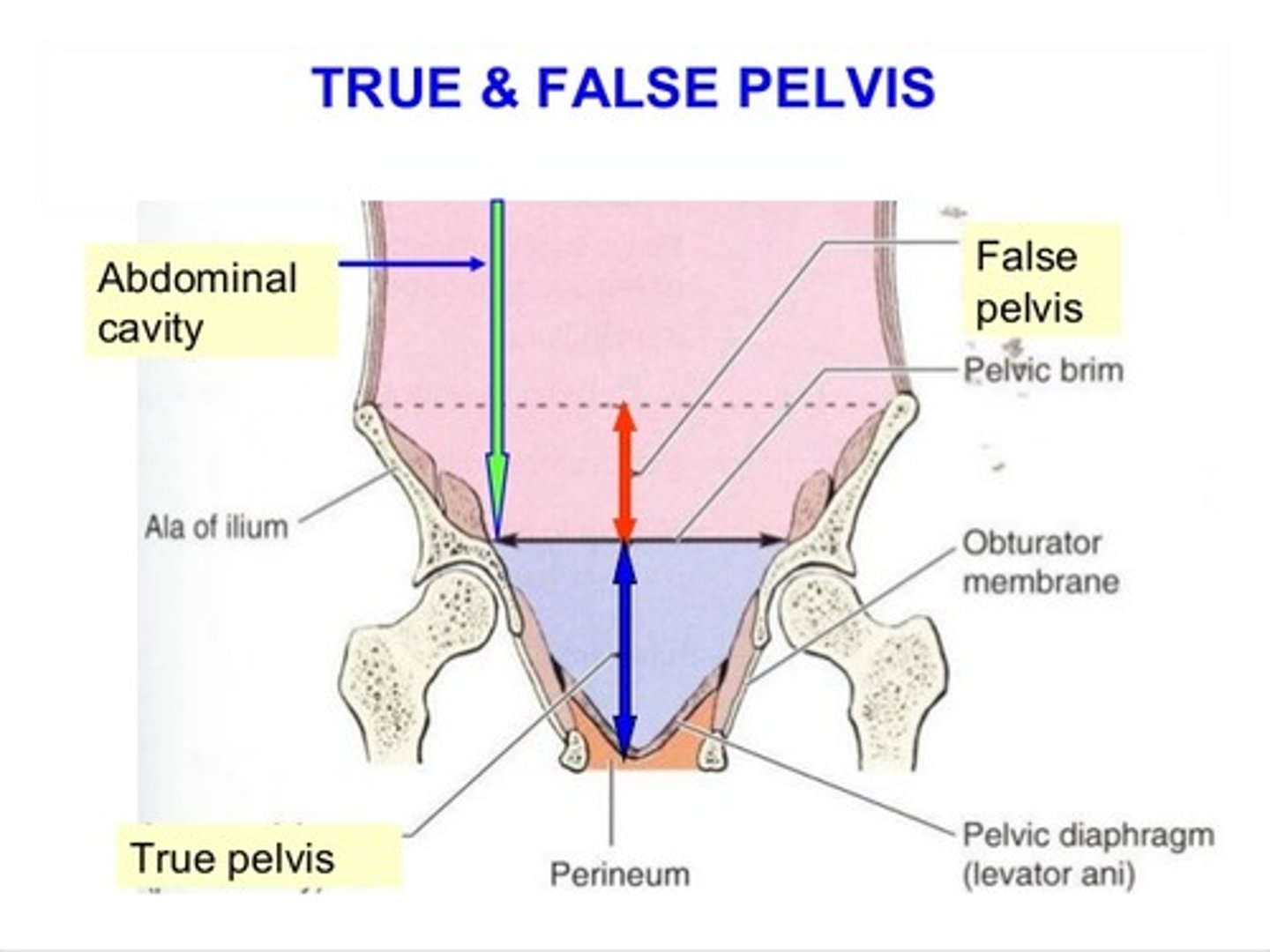
false (greater) pelvis
bounded by wings of the iliac and superior margin of pubis
provides support of the lower abdominal viscera
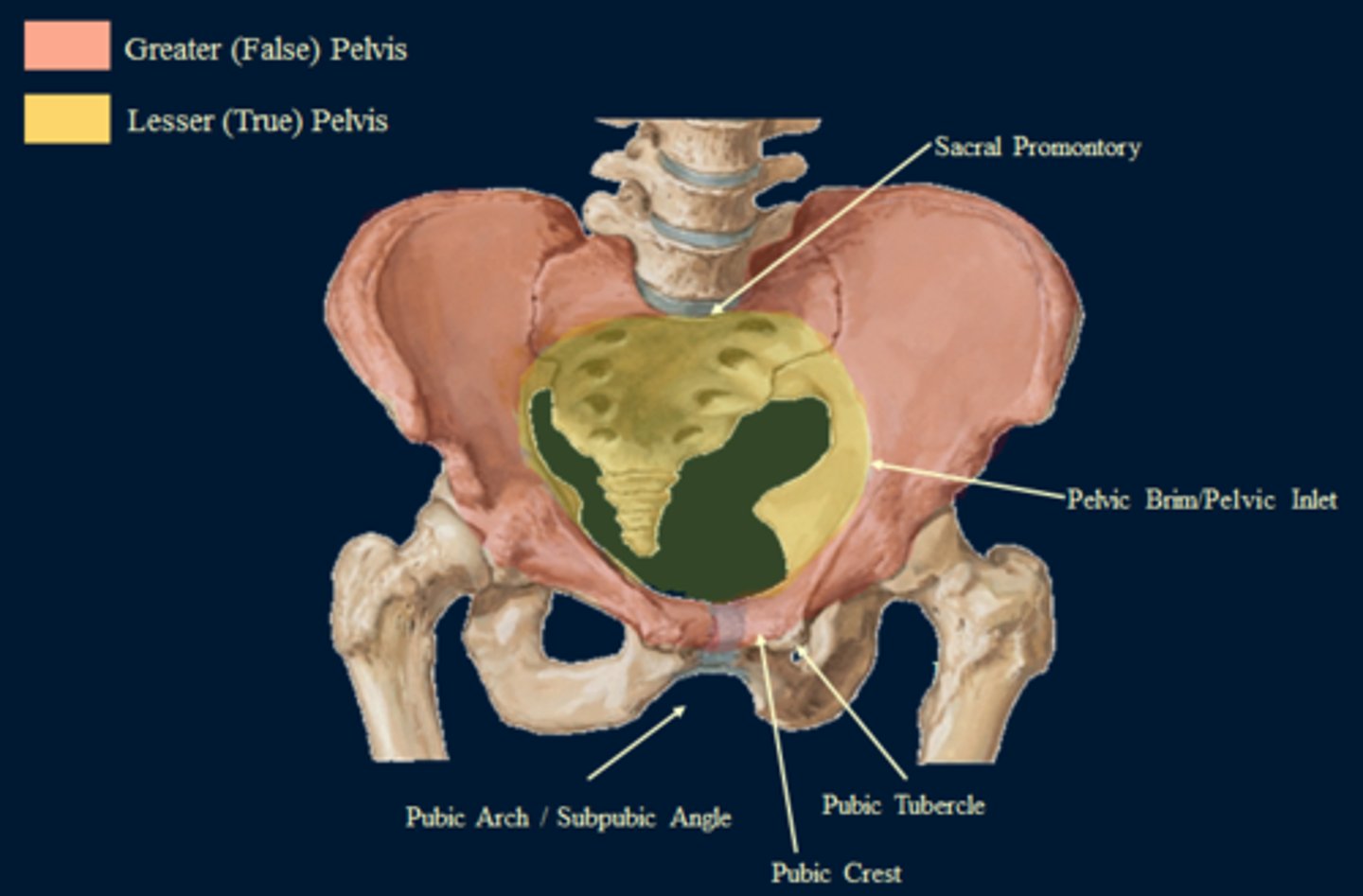
true (lesser) pelvis
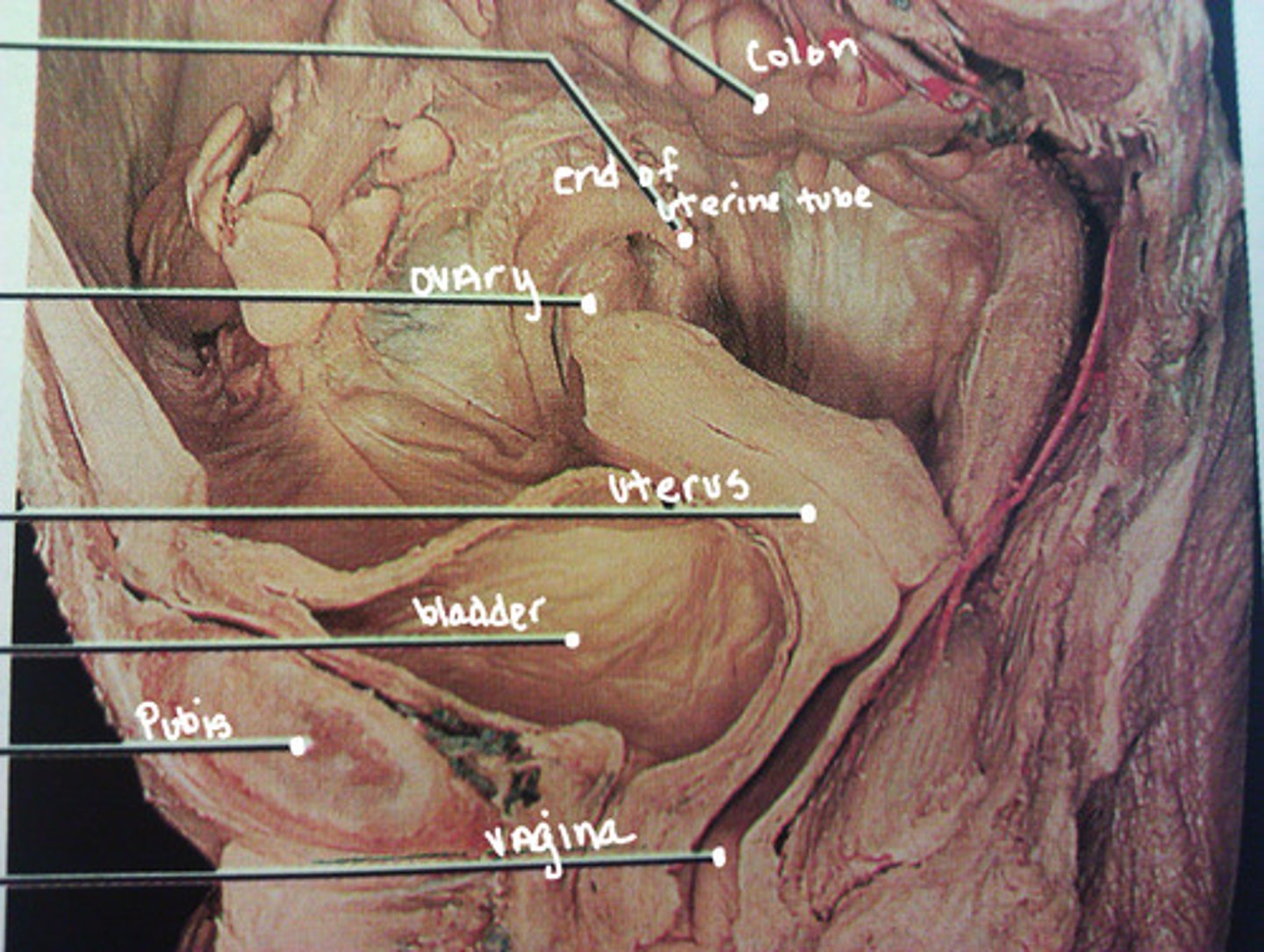
forms a bowl containing the pelvic organs: elements of urinary, gastrointestinal and reproductive systems
has an inlet, walls, outlet and a floor
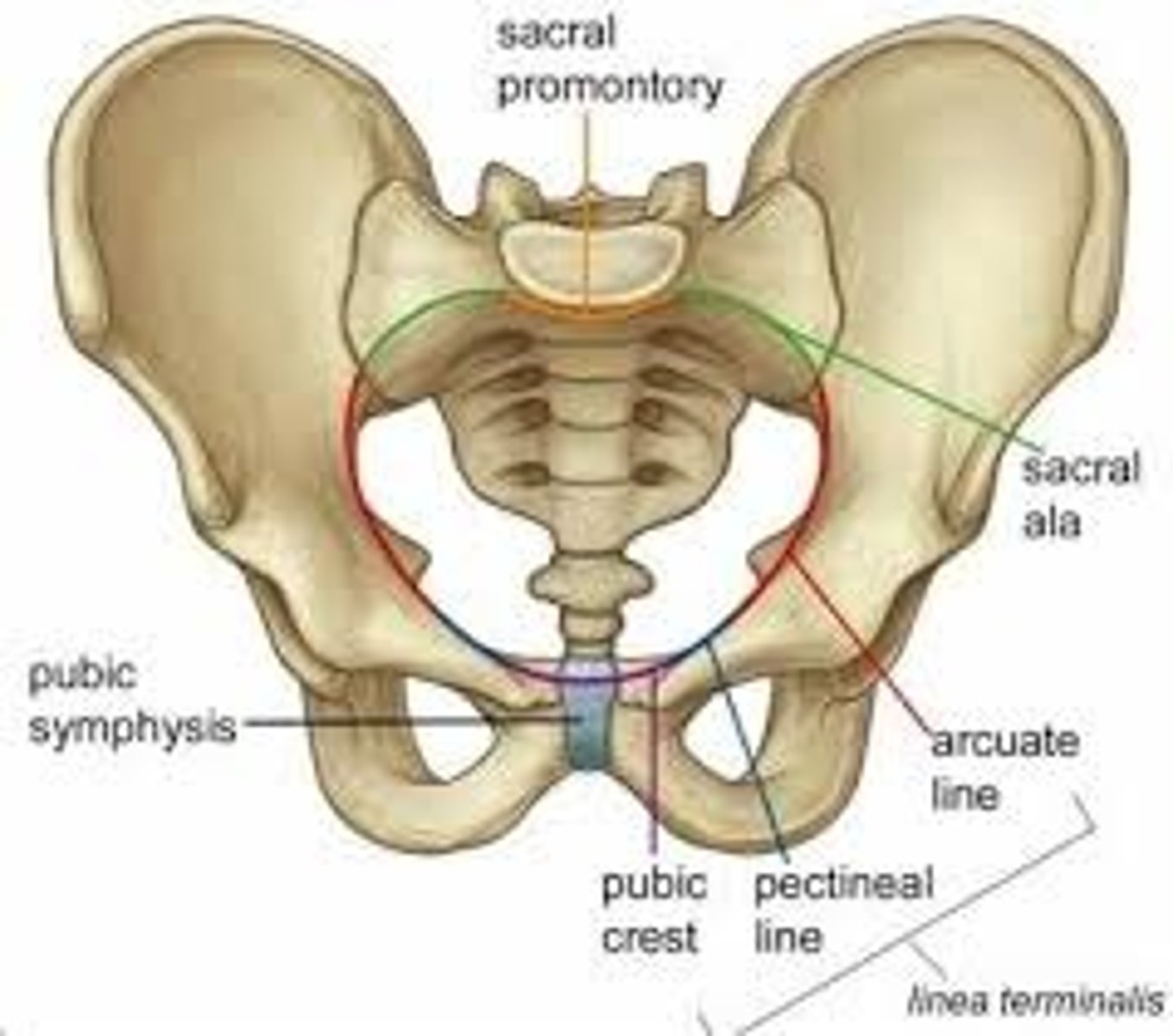
pelvic inlet (brim)
a line from the sacral promontory to the upper part of the pubic symphysis
the junction between the greater and lesser pelvis
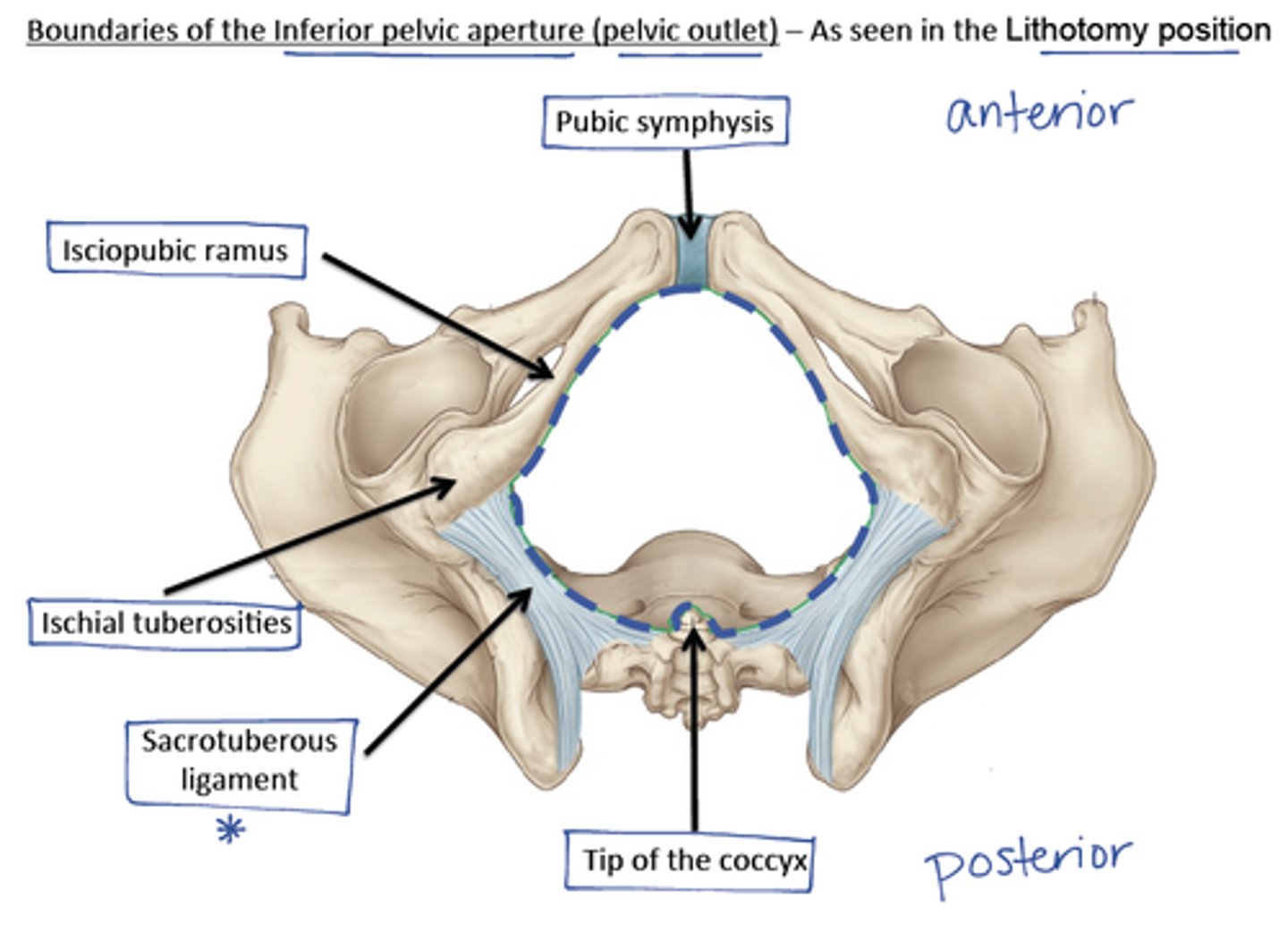
pelvic outlet
inferior opening of the true pelvis
a line from the lower border of sacrum to lower part of pubic symphysis
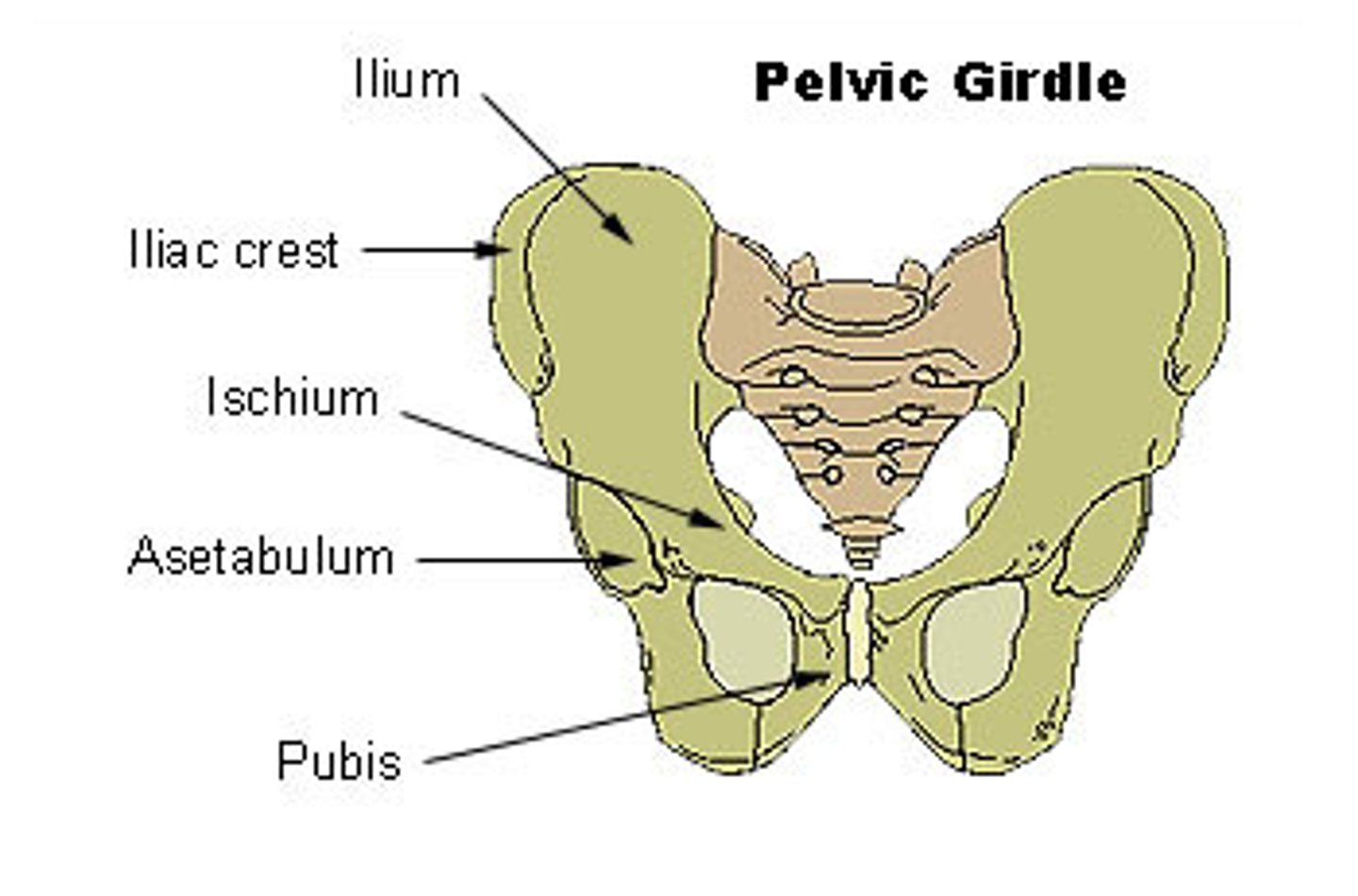
Bones of the pelvis
ilium, ischium, pubis
lumbosacral joint
sacrum S1 articulates superiorly with lumbar spine L5
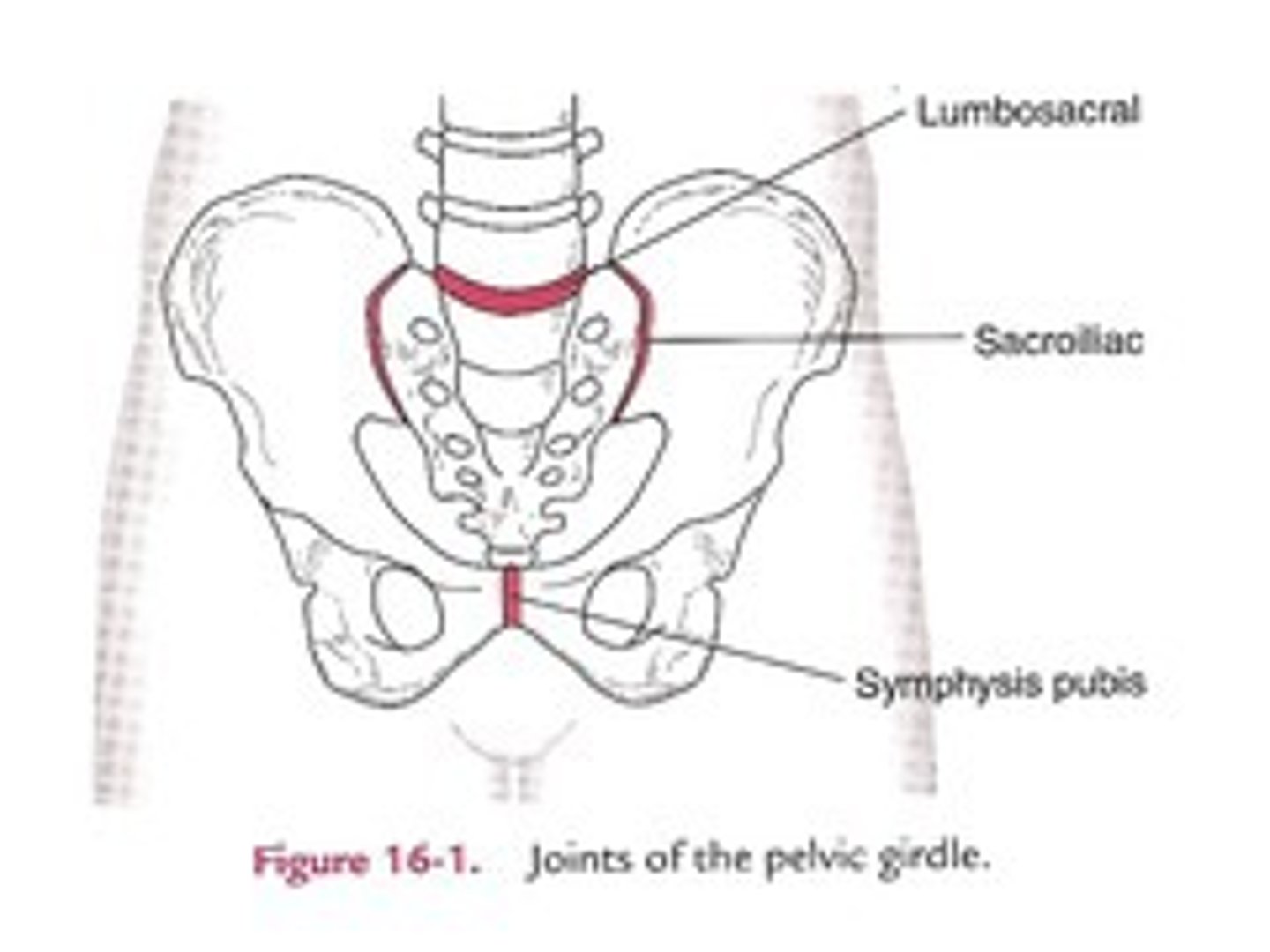
Pelvic Joints
- lumbosacral
- sacrococcygeal
- sacroiliac (SI)
- pubic symphysis
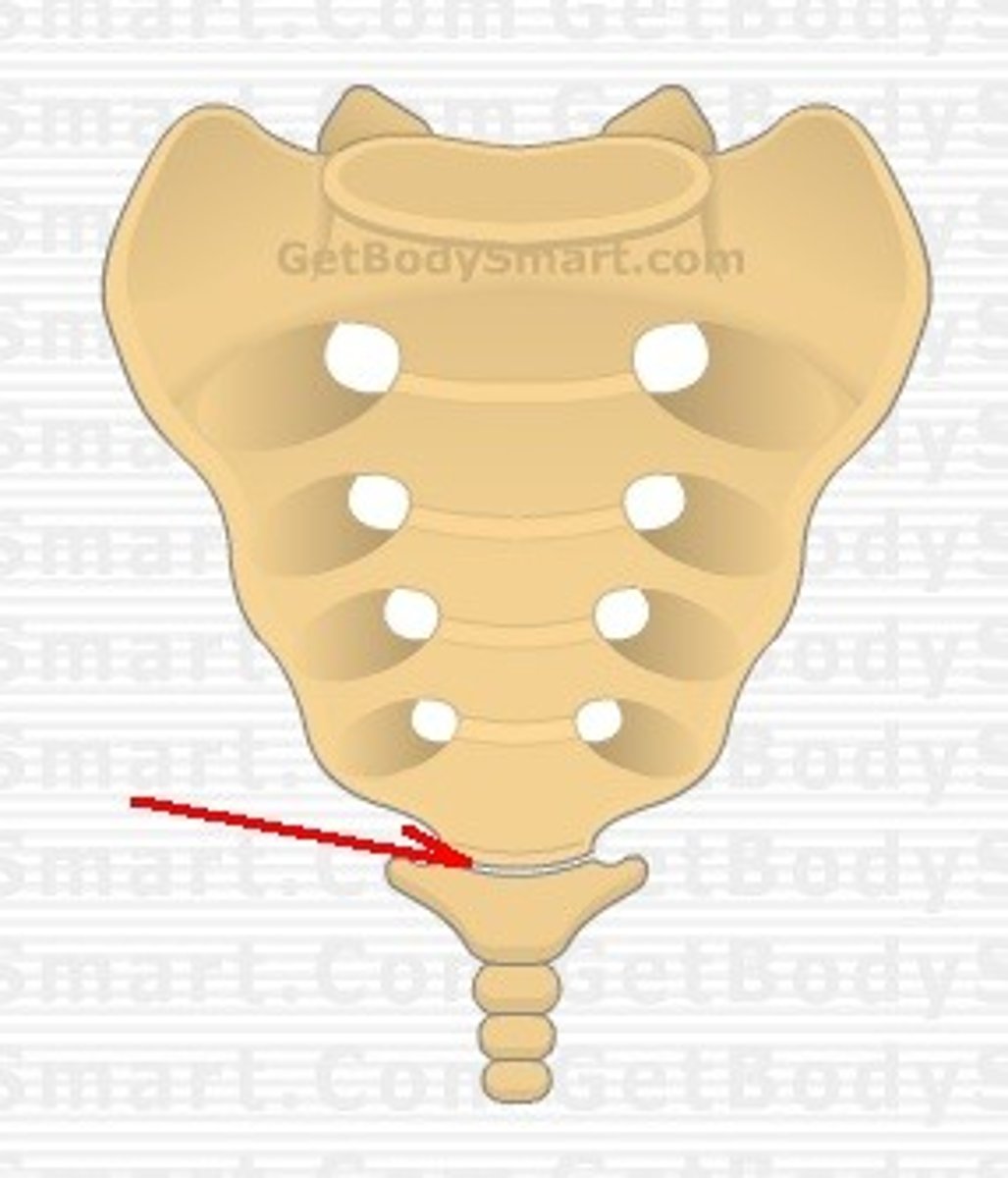
sacrococcygeal joint
between sacrum and coccyx
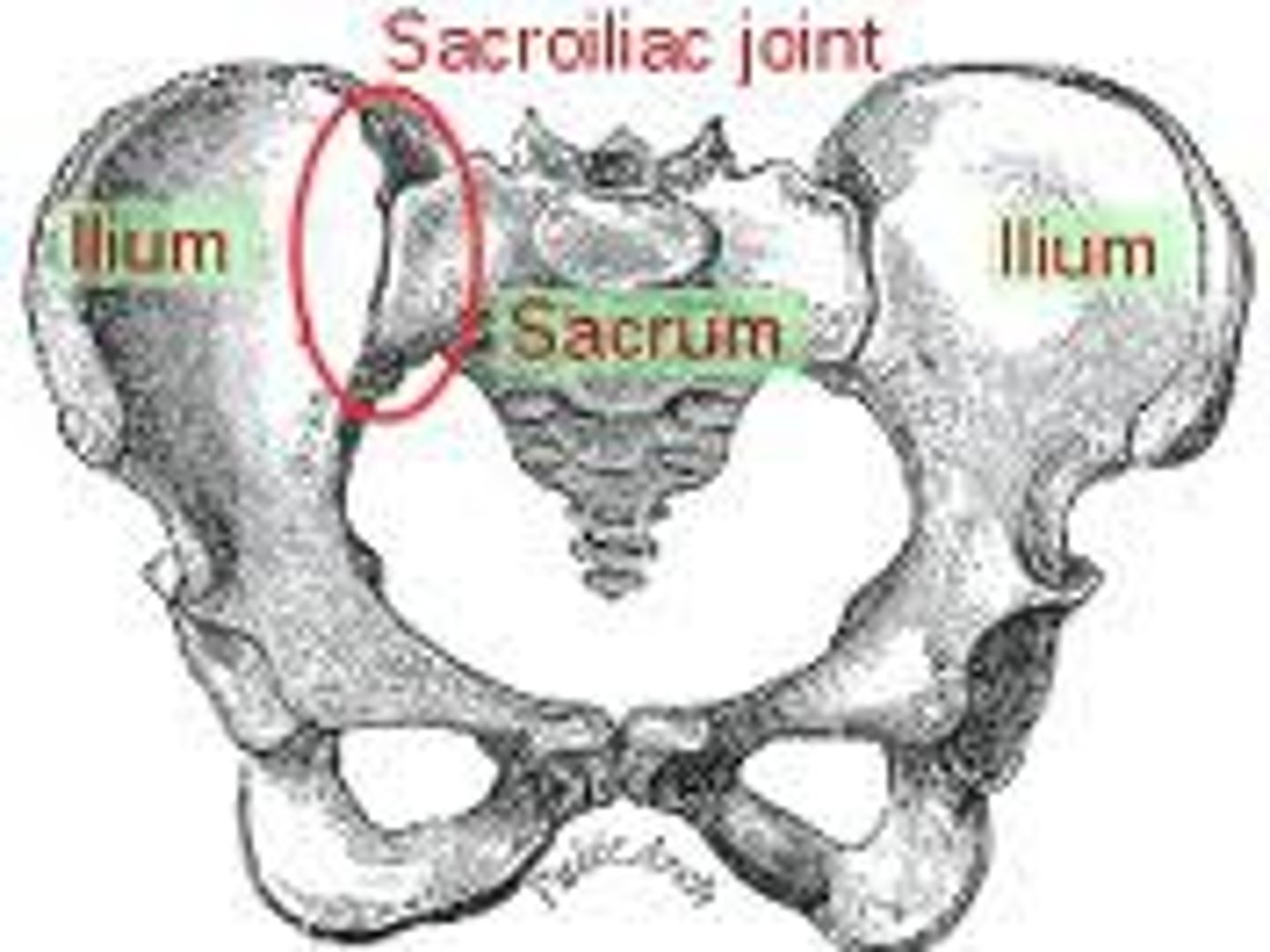
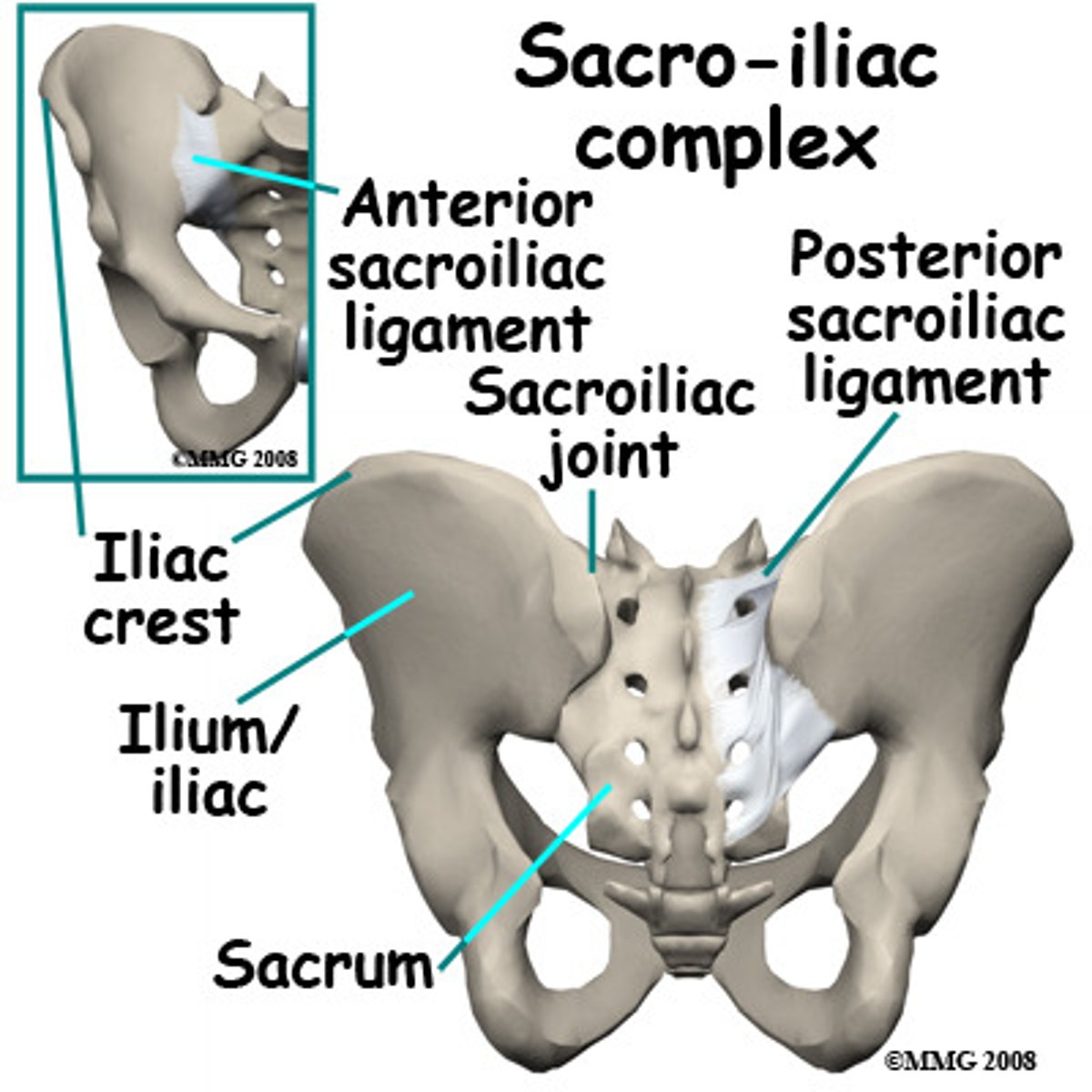
sacroiliac (SI) joint
ilium of pelvic bones and facets (articular surfaces) of sacrum
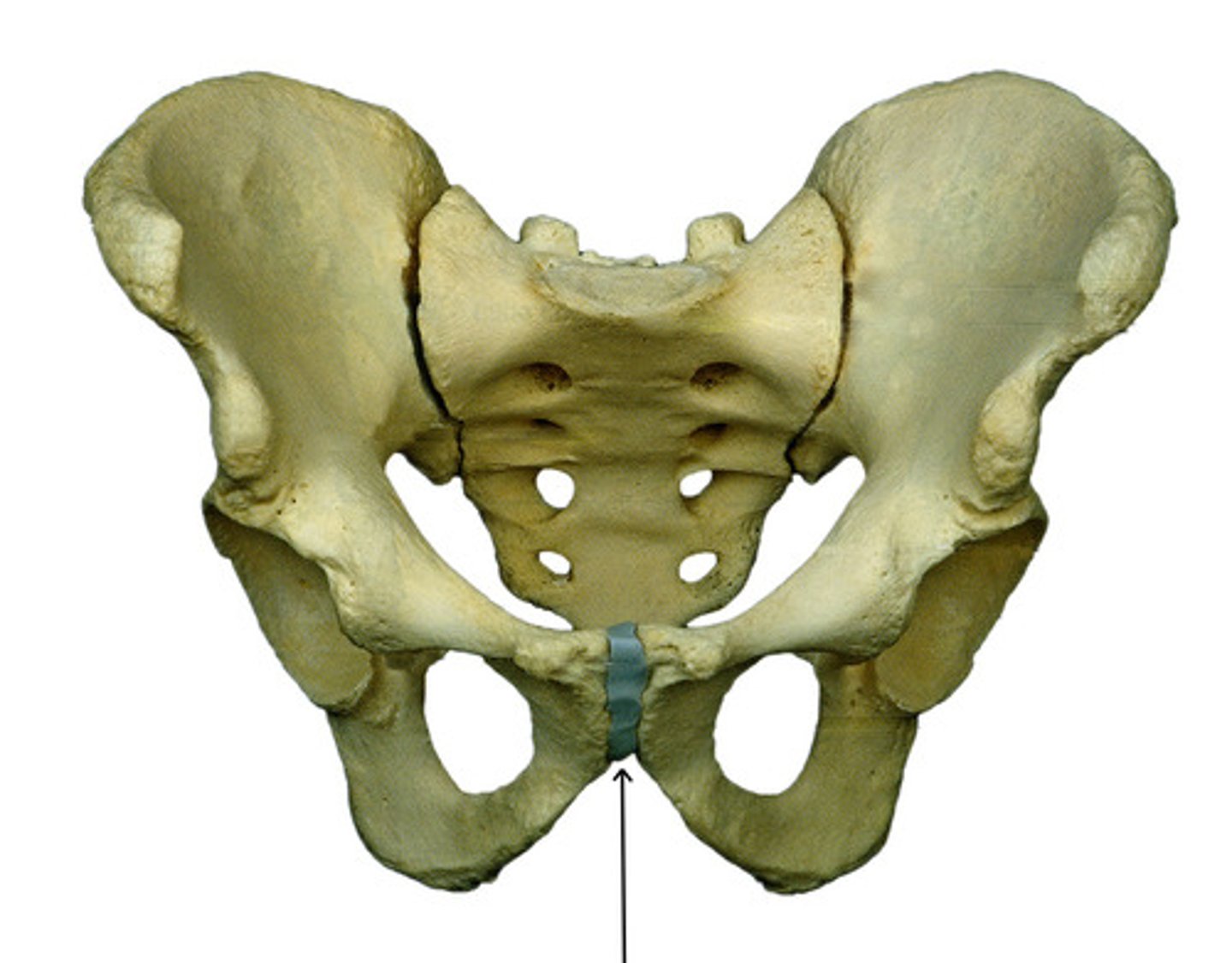
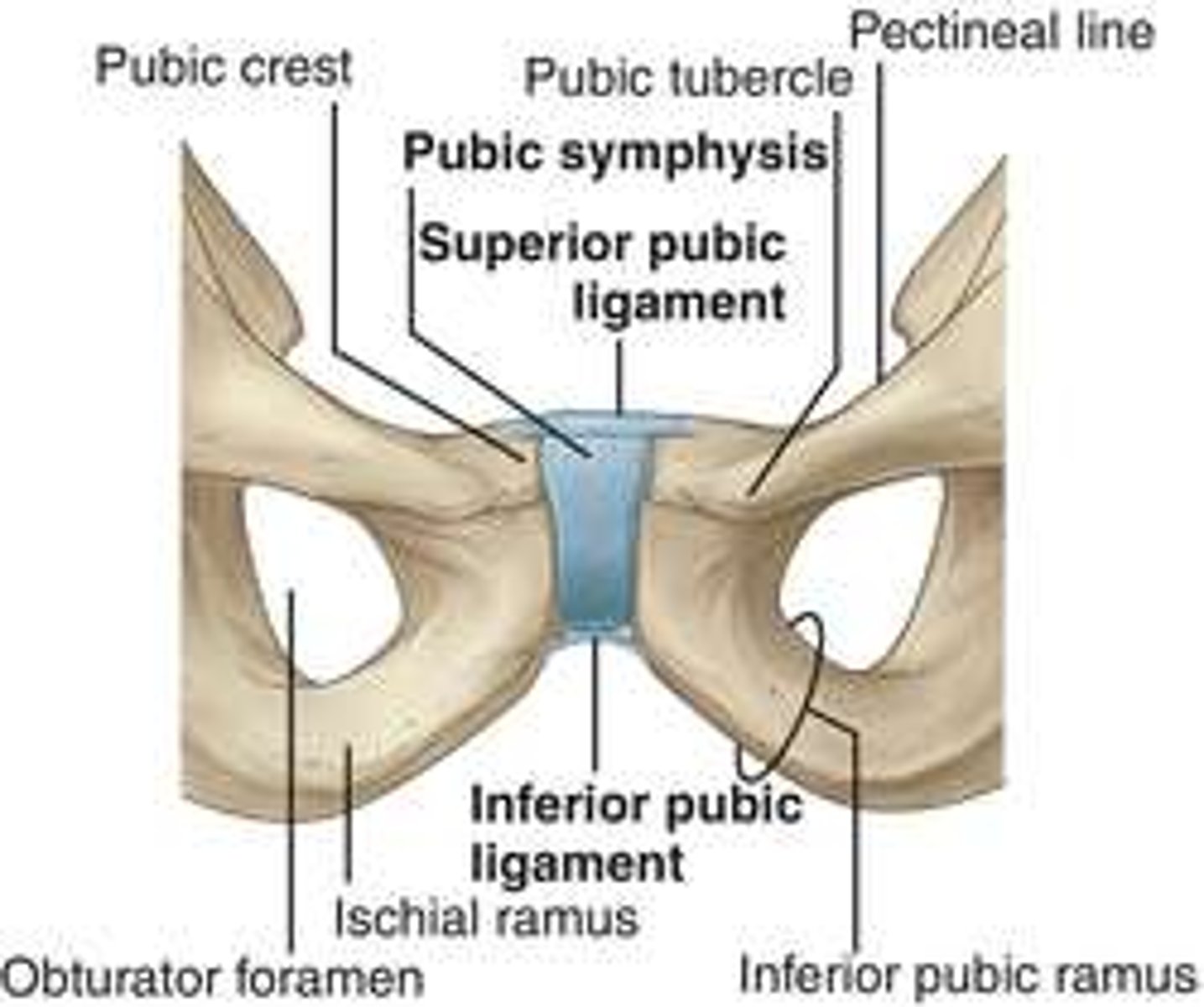
pubic symphysis joint
pelvic bones articulating anteriorly
ilium bone
wing + body
ilium function
expands to form the ala (wing) - provides support for lower abdomen
attachment for lower limb muscles
iliac fossa
anterior concavity surface of ilium wing
iliac crest
upper margin of the ilium
muscle attachment site
auricular surface of ilium
anterior superior iliac spine (ASIS)
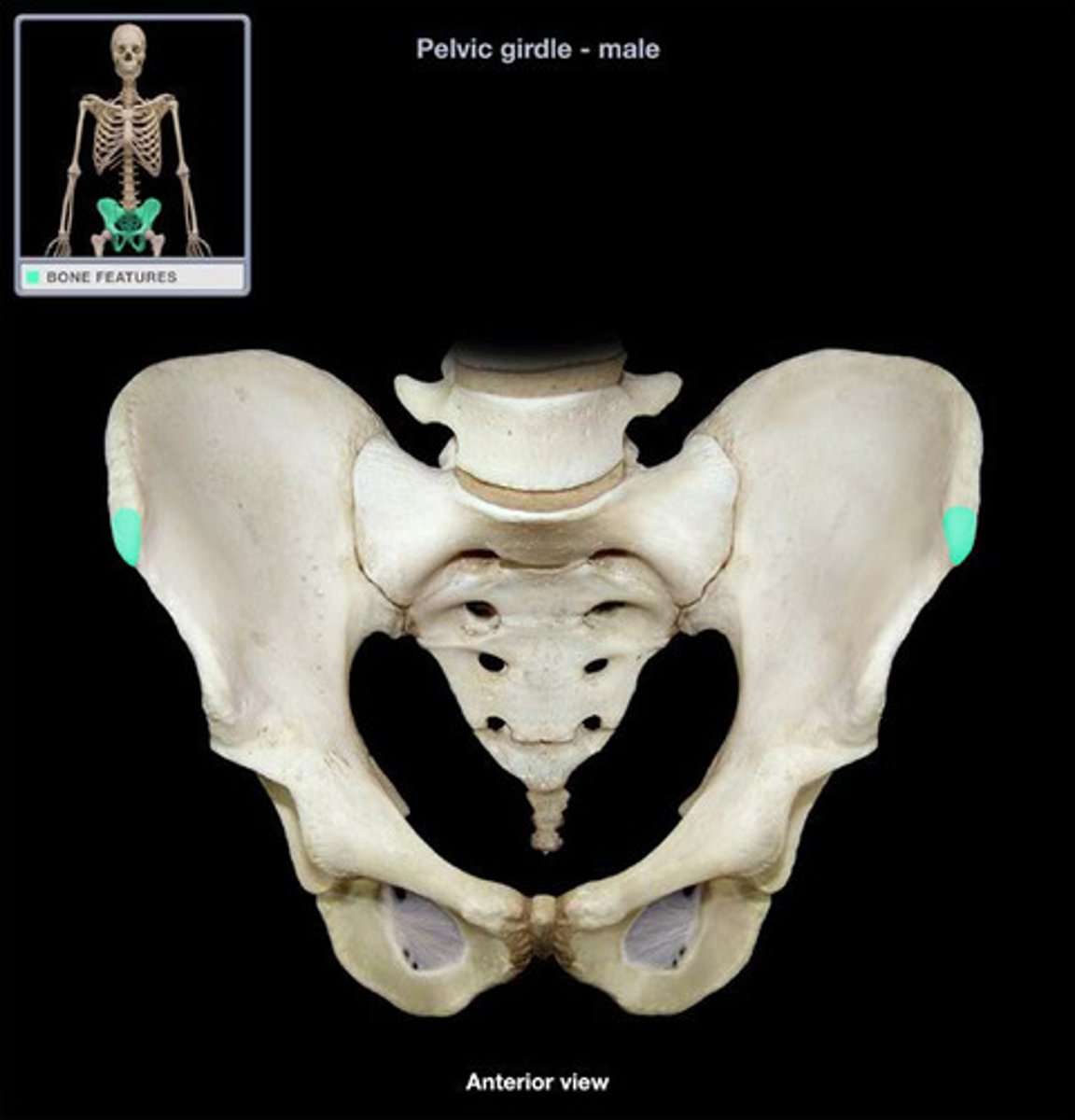
anterior inferior iliac spine (AIIS)
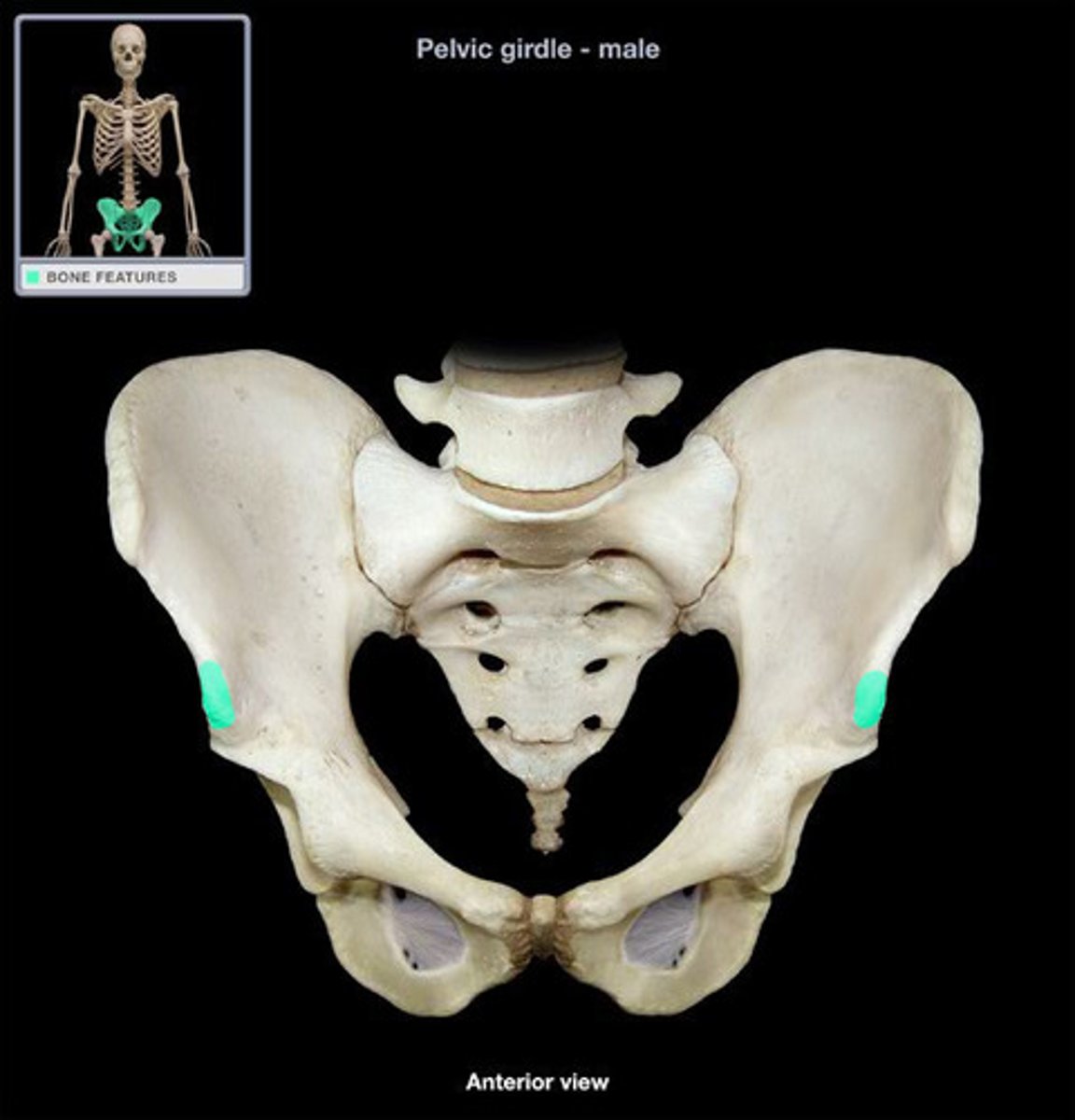
Posterior Superior Iliac Spine (PSIS)
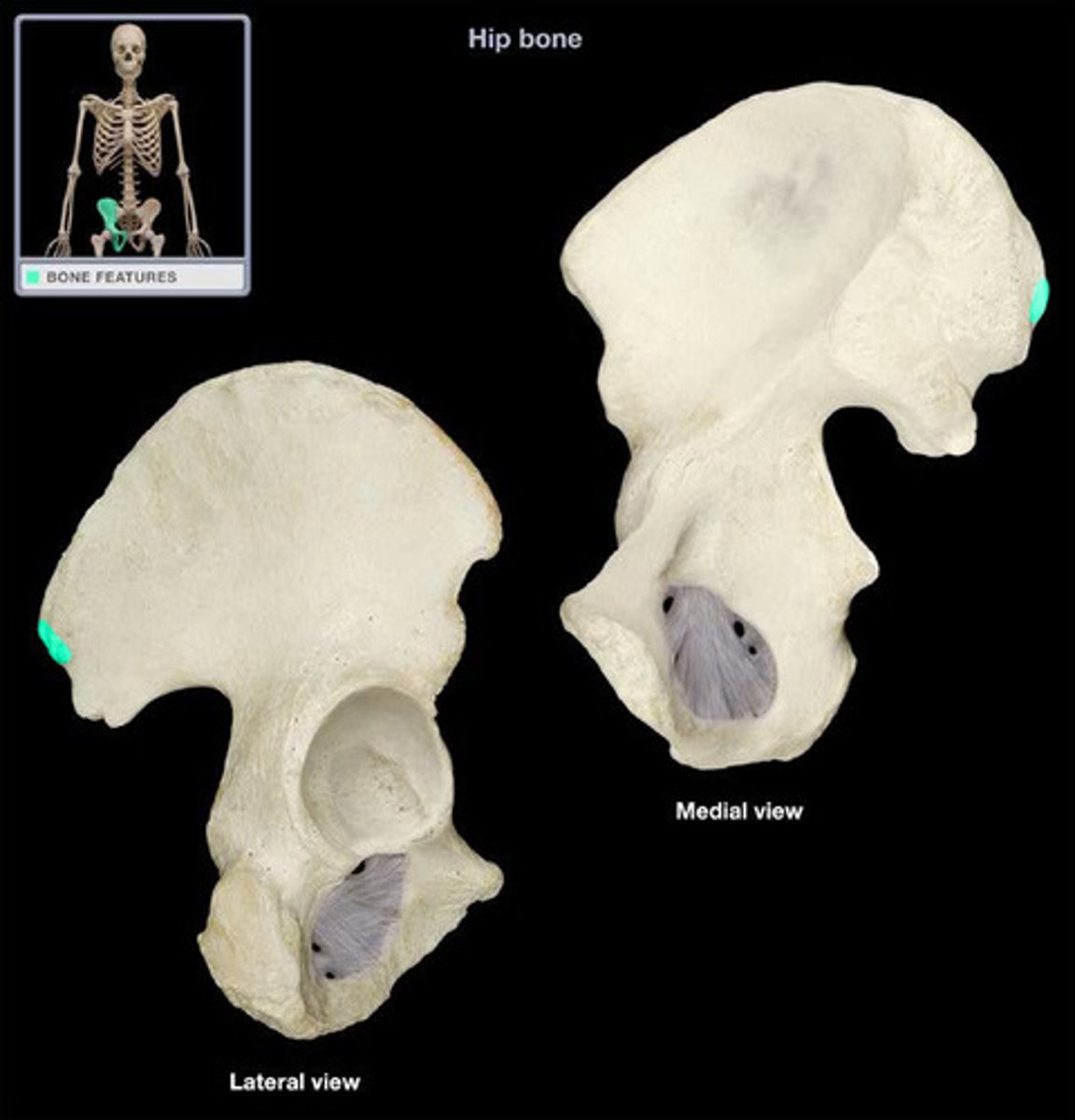
posterior inferior iliac spine (PIIS)
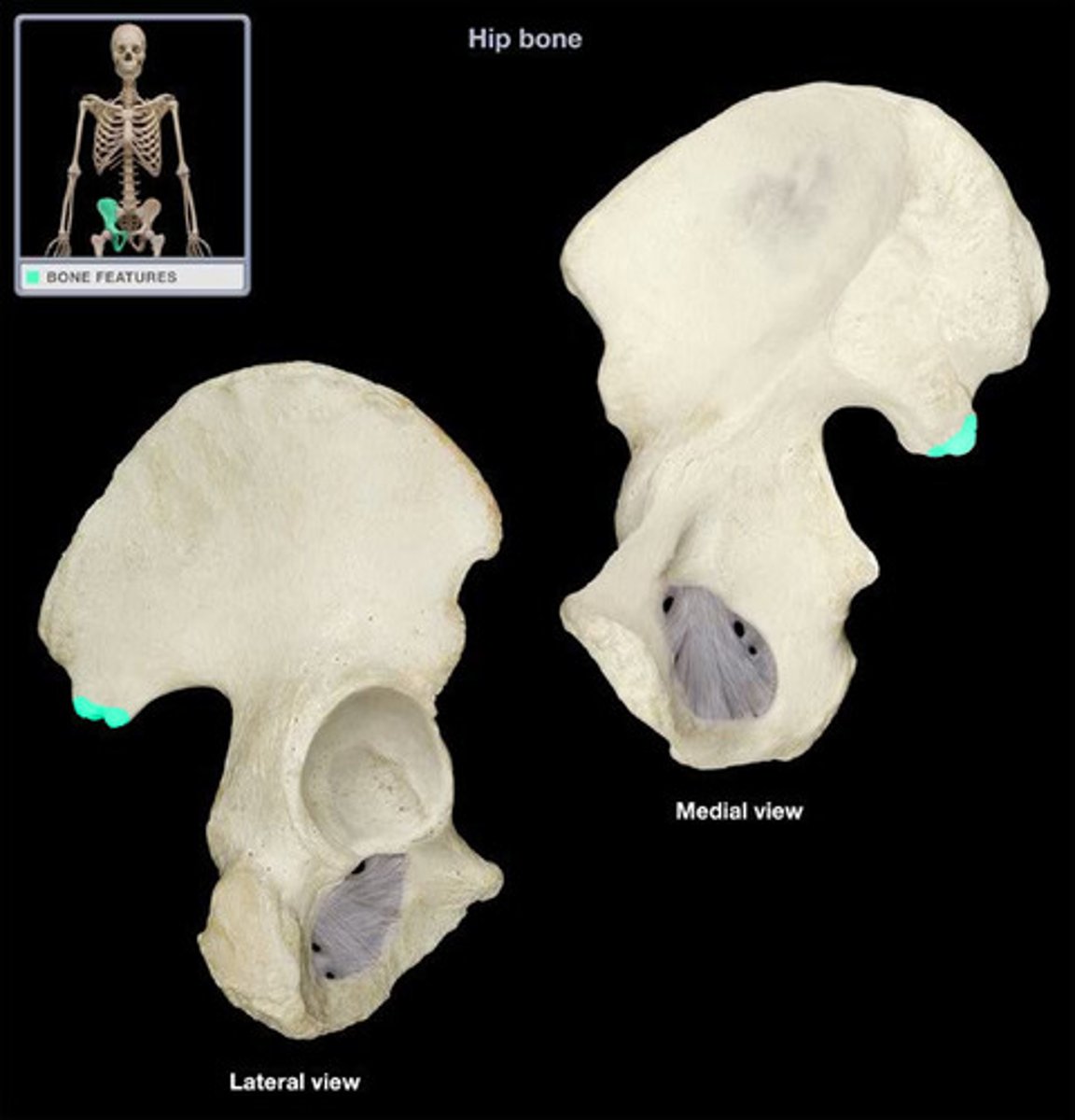
arcuate line
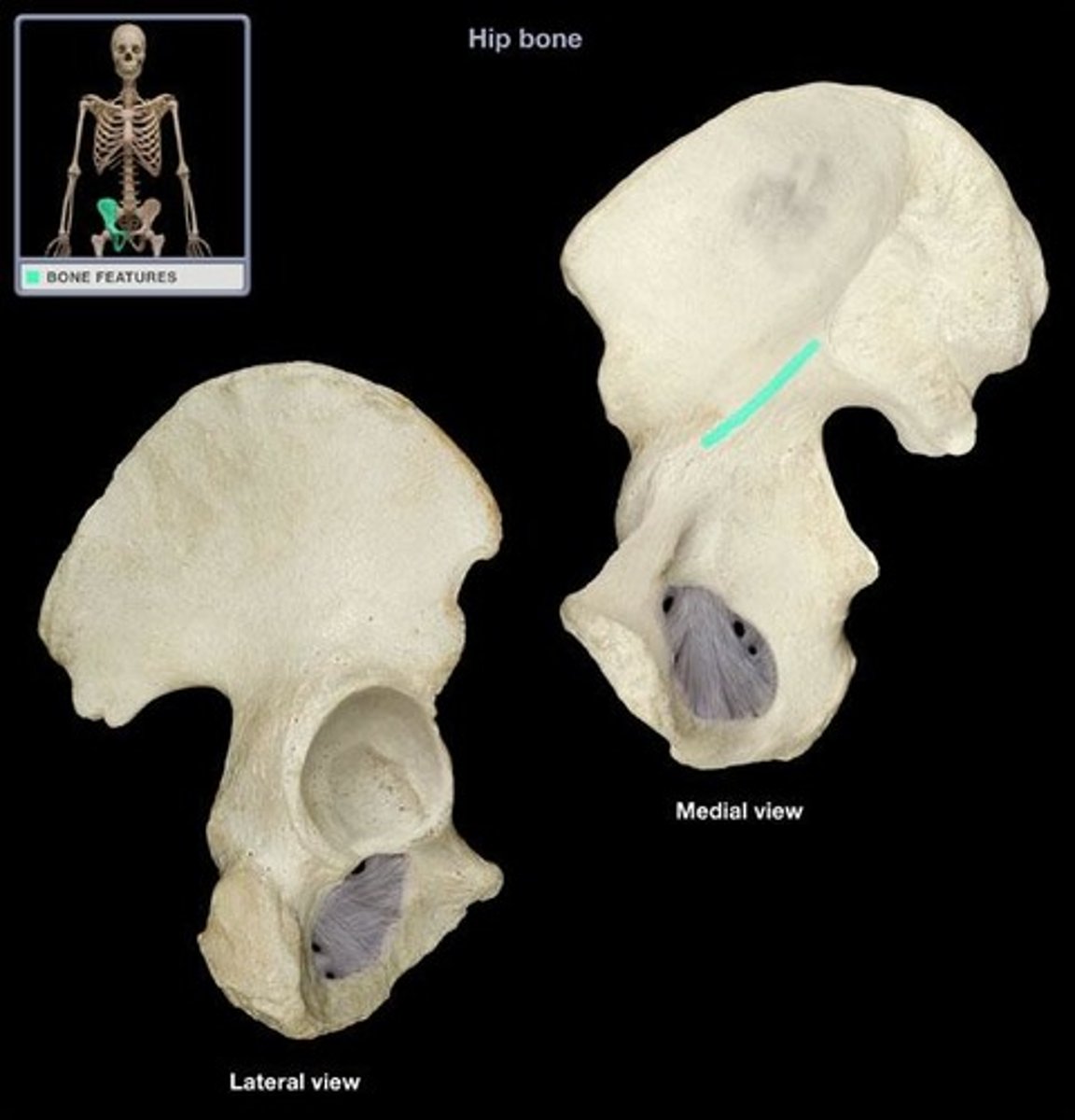
ischium bone
(sit bones) the lower, posterior portions of the pelvis
body + ramus
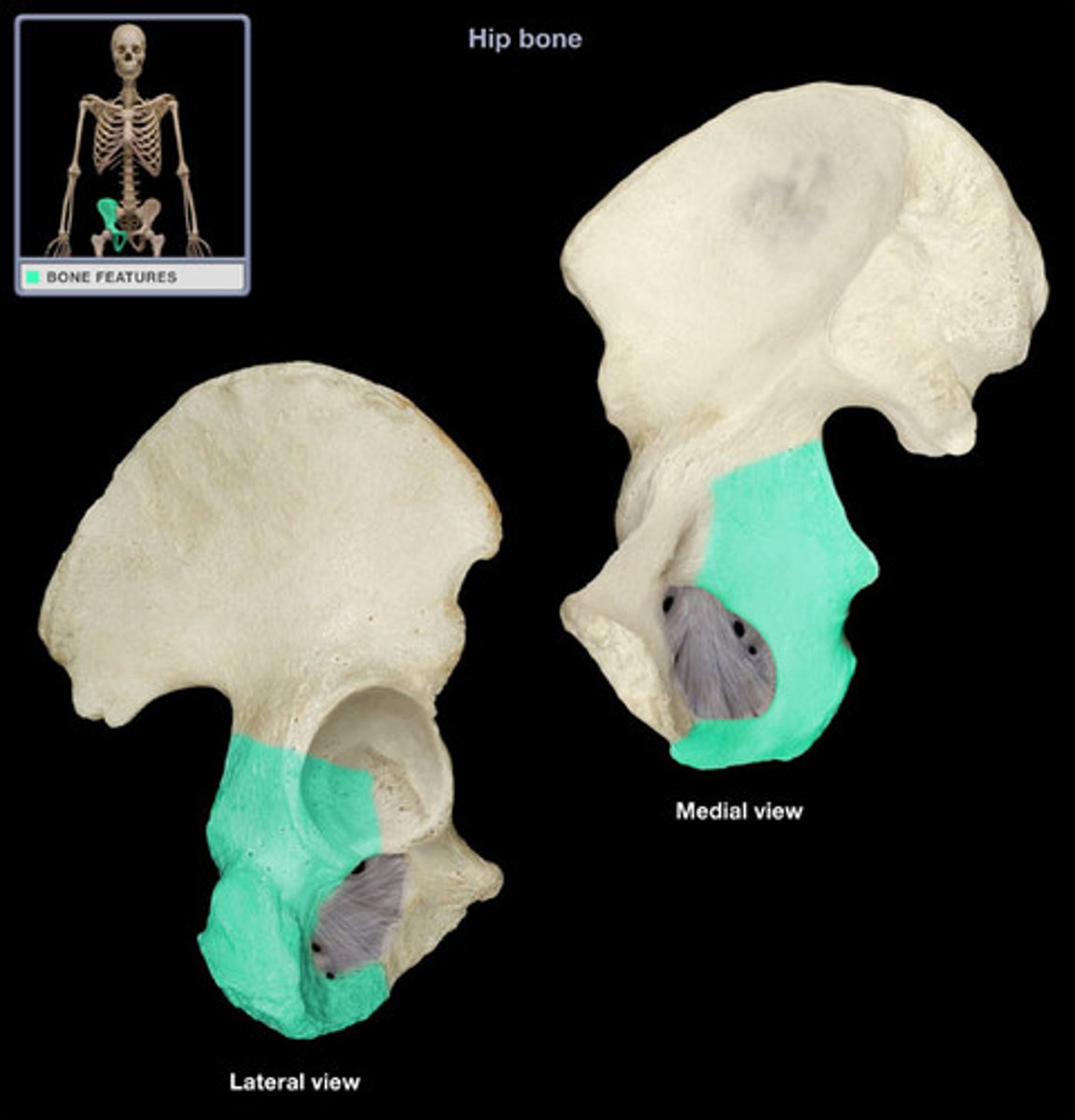
gluteal surface of ilium
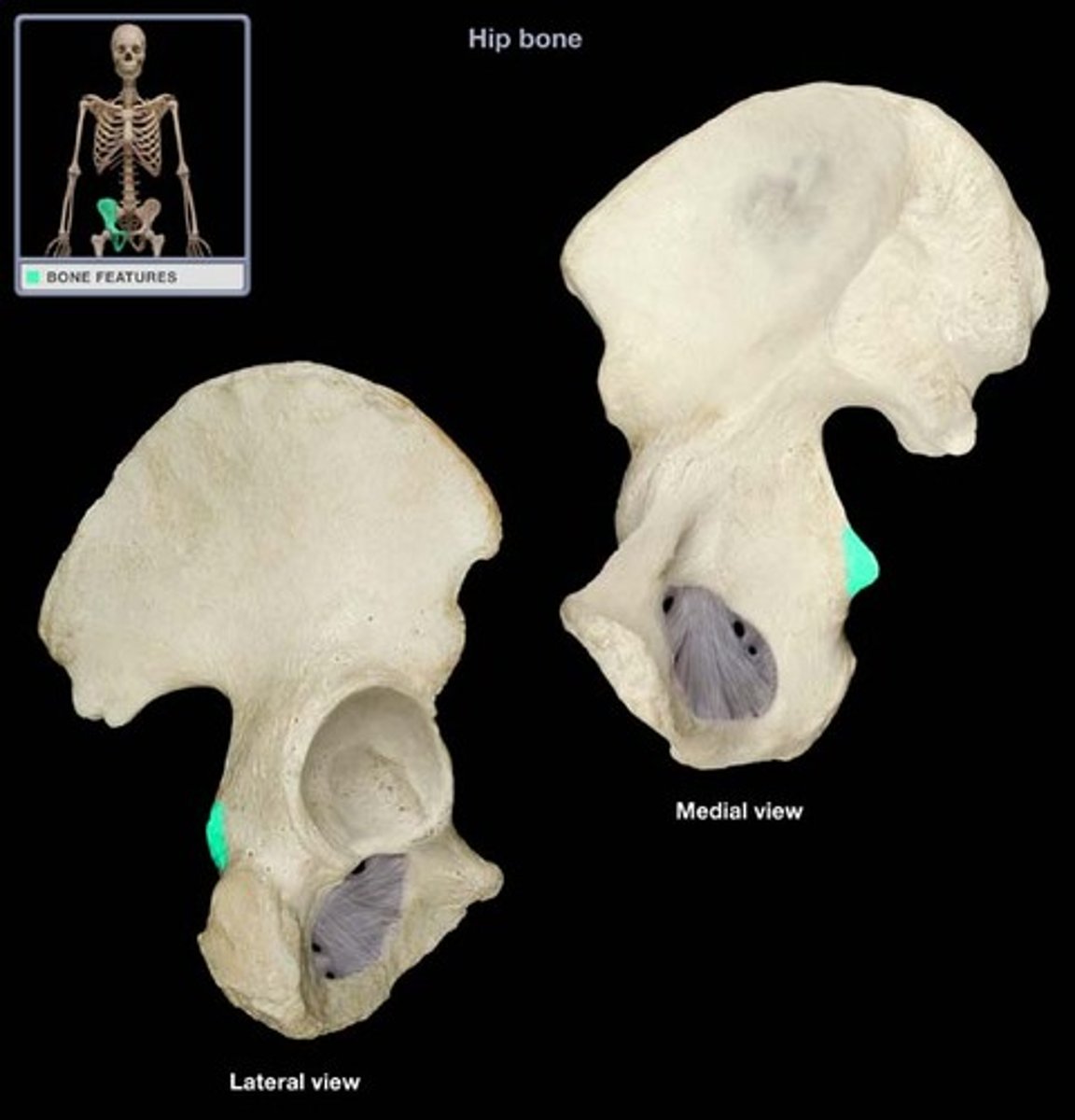
ischial spine
ischial tuberosity
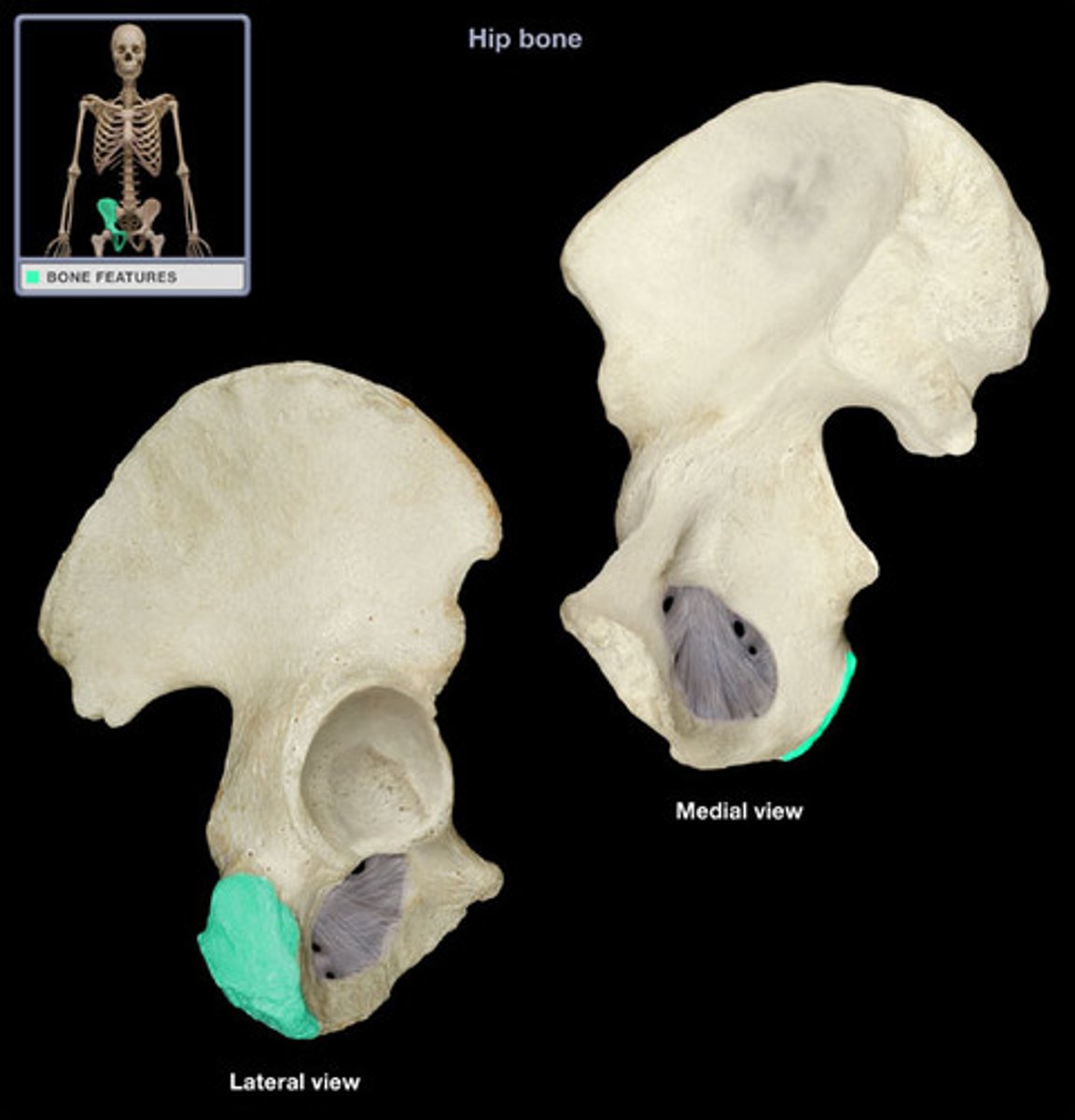
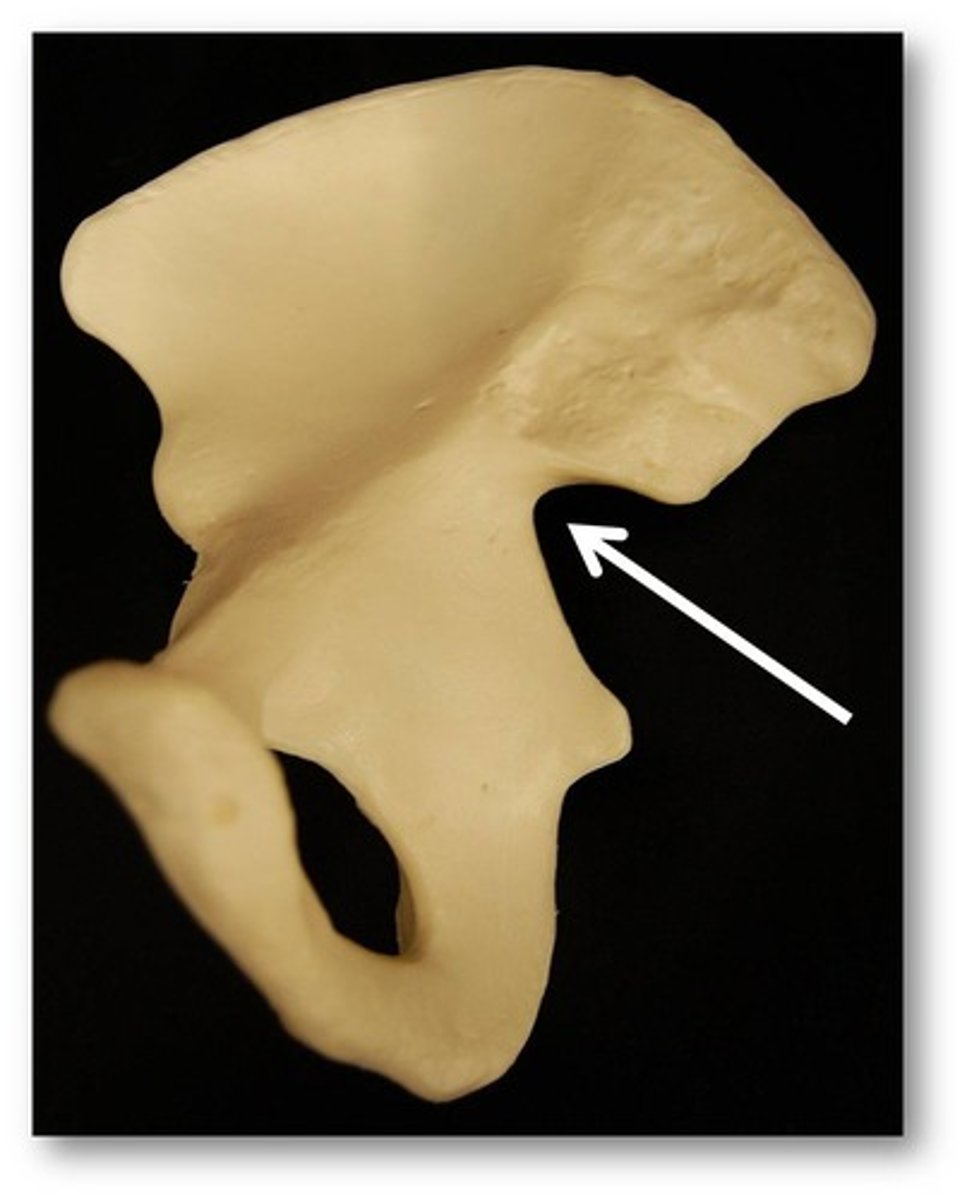
greater sciatic notch
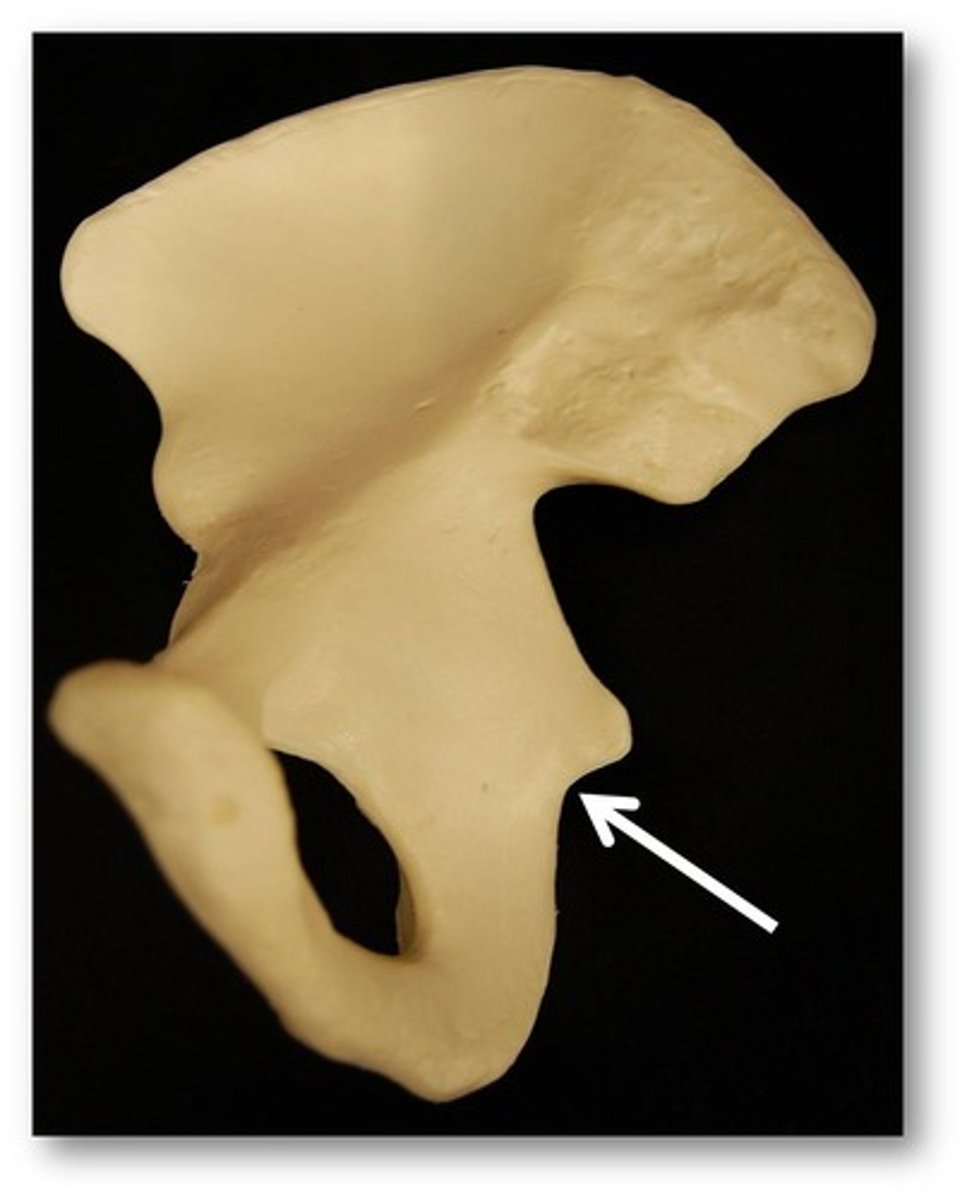
lesser sciatic notch
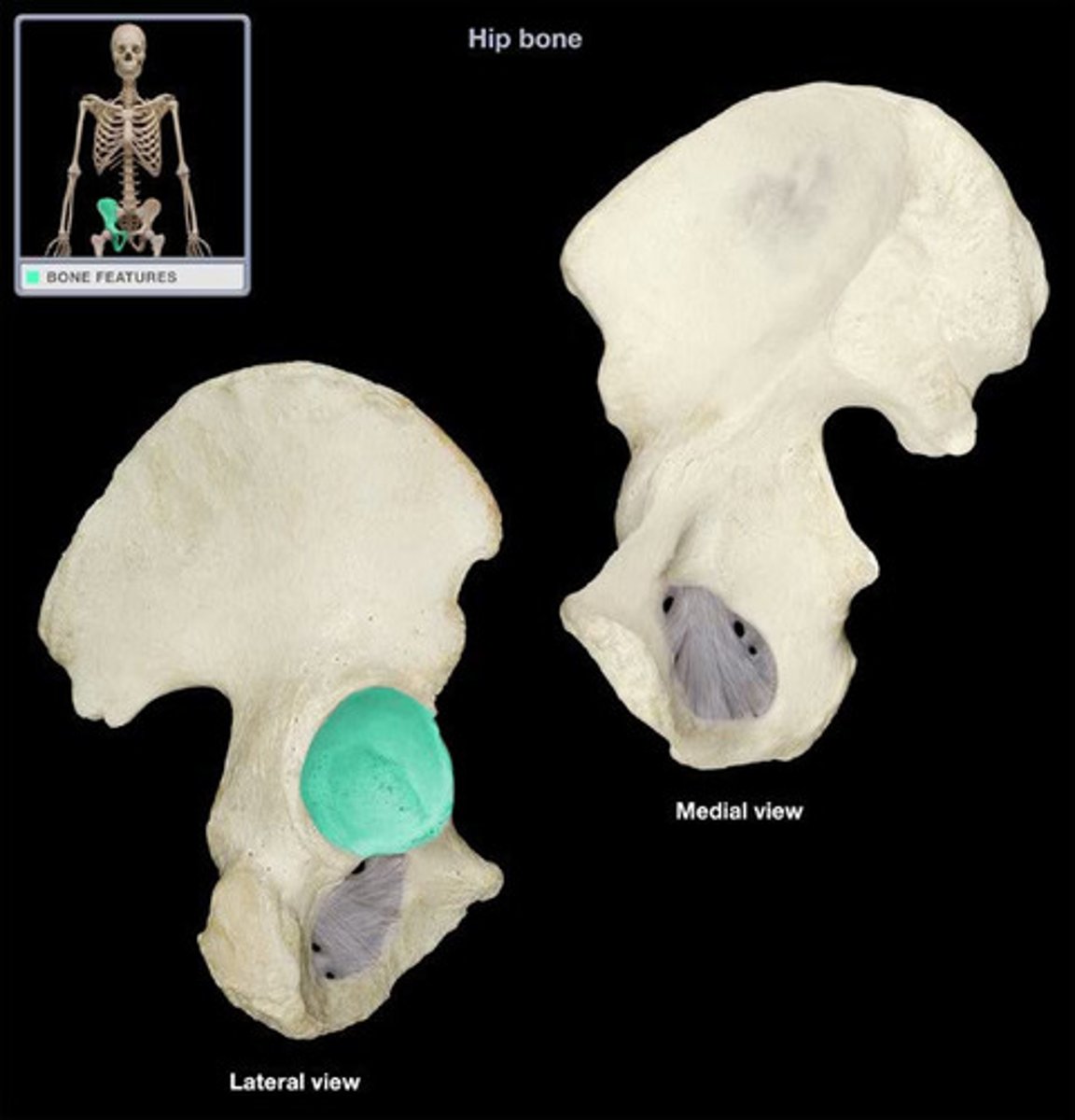
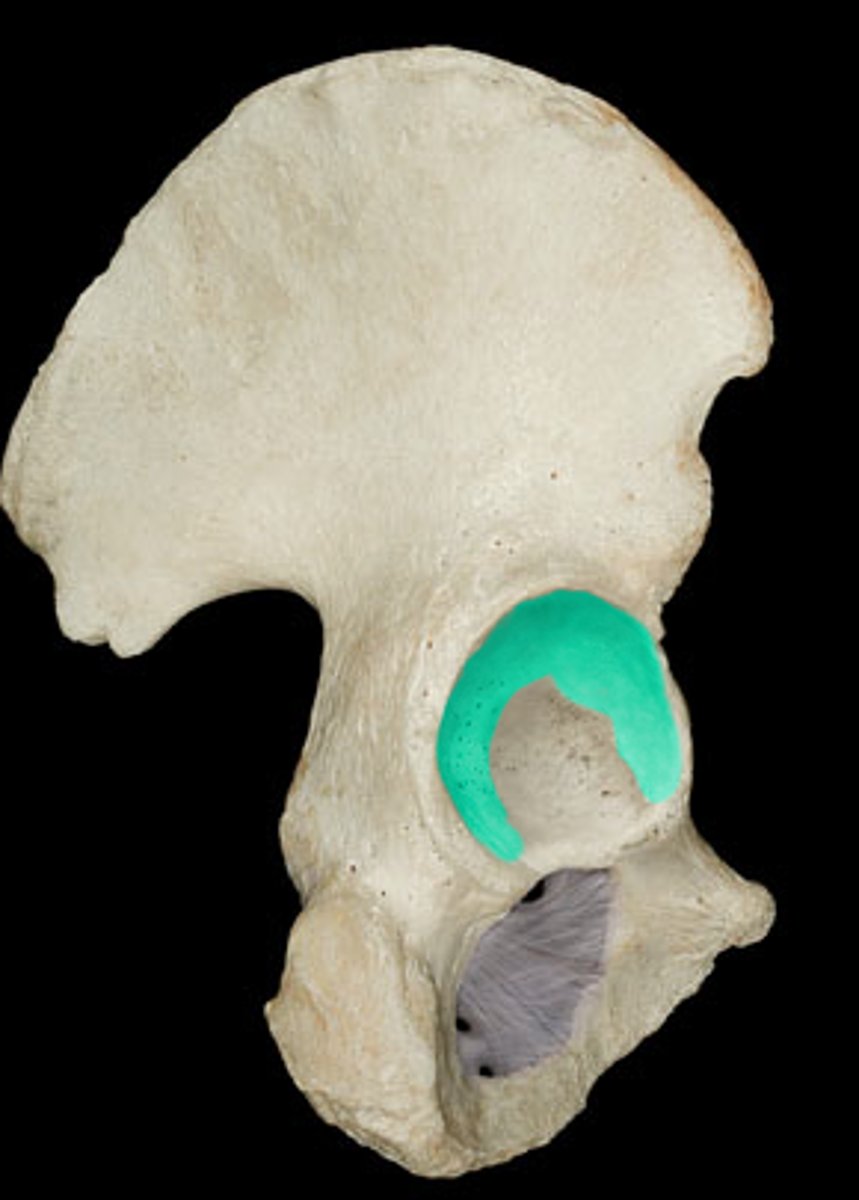
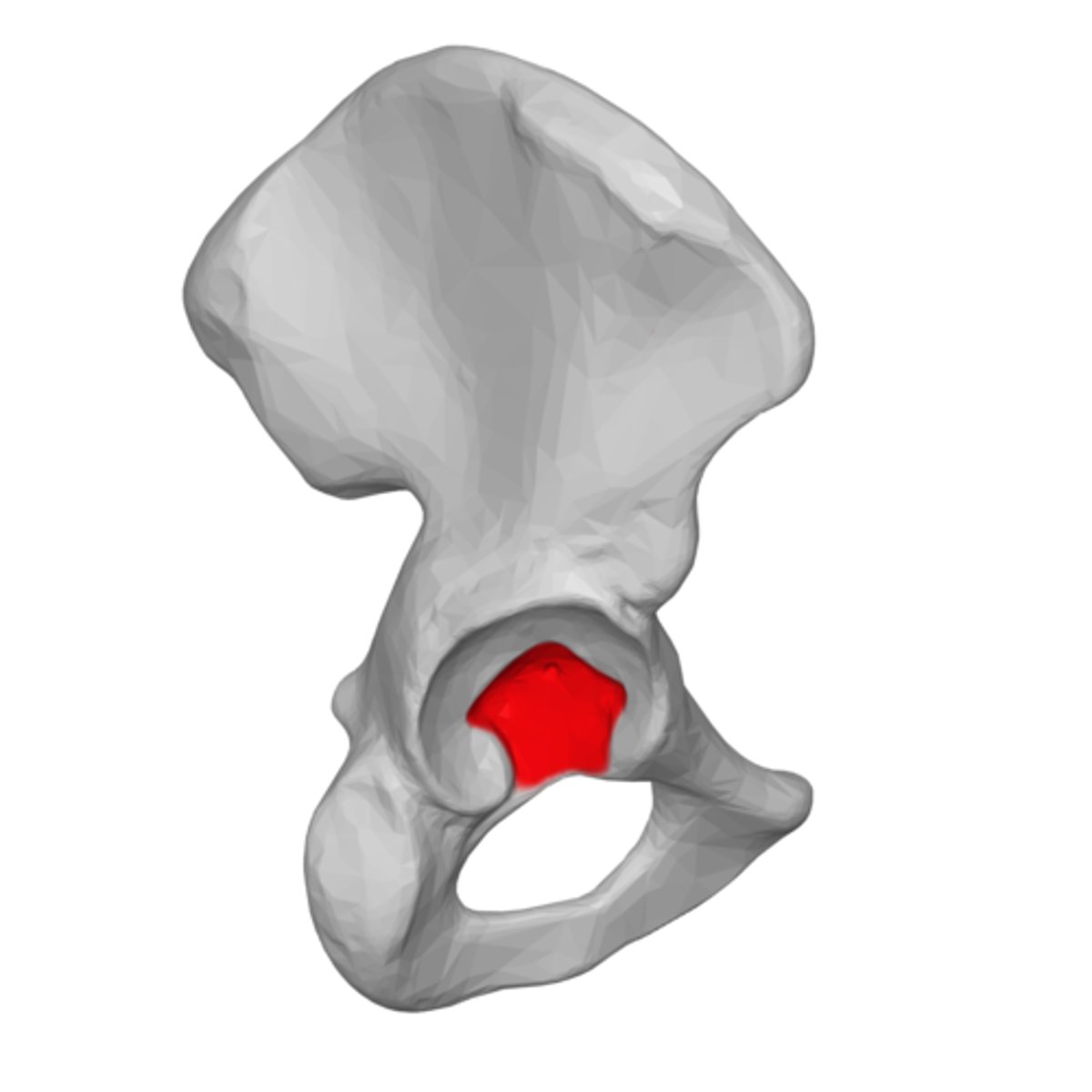
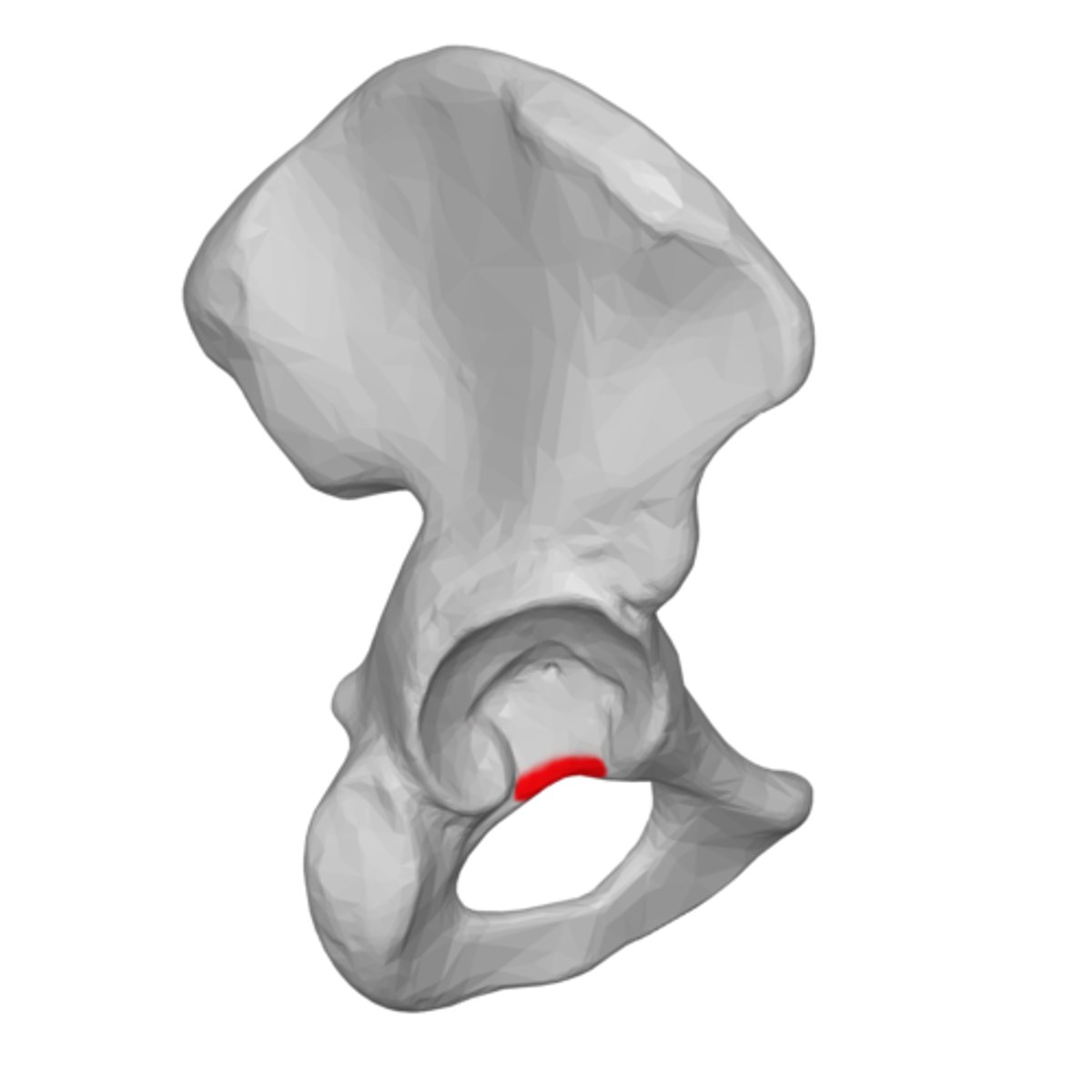
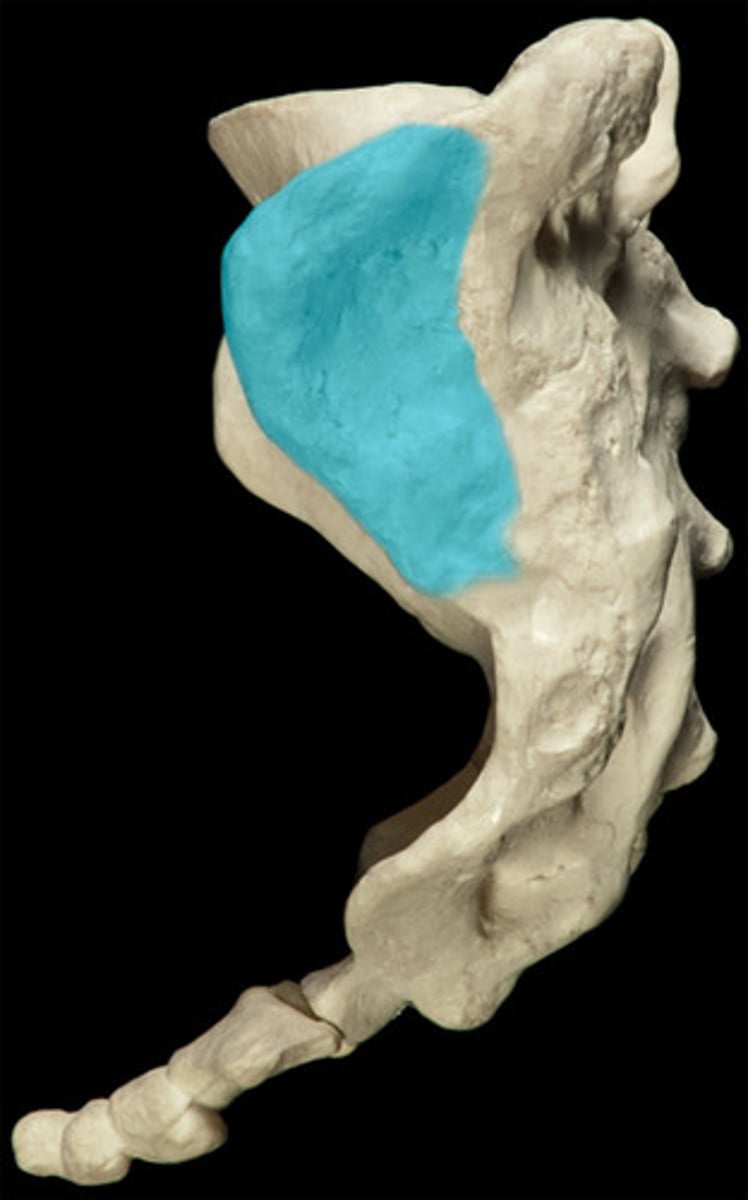
Acetabulum
large socket on lateral surface of the pelvic bone for the head of the femur - forms hip joint
acetabular margin
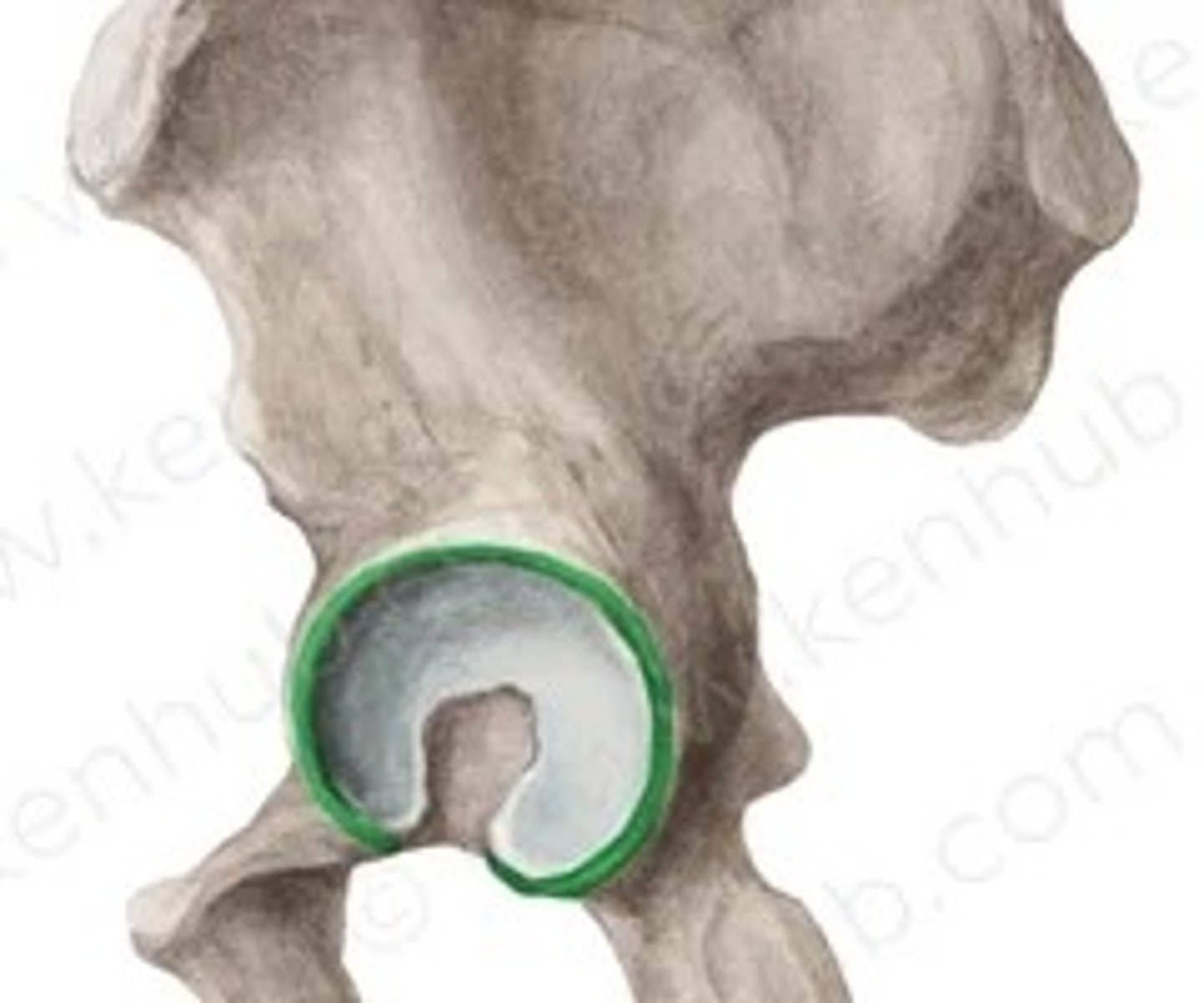
lunate surface of acetabulum
acetabular fossa
acetabular notch
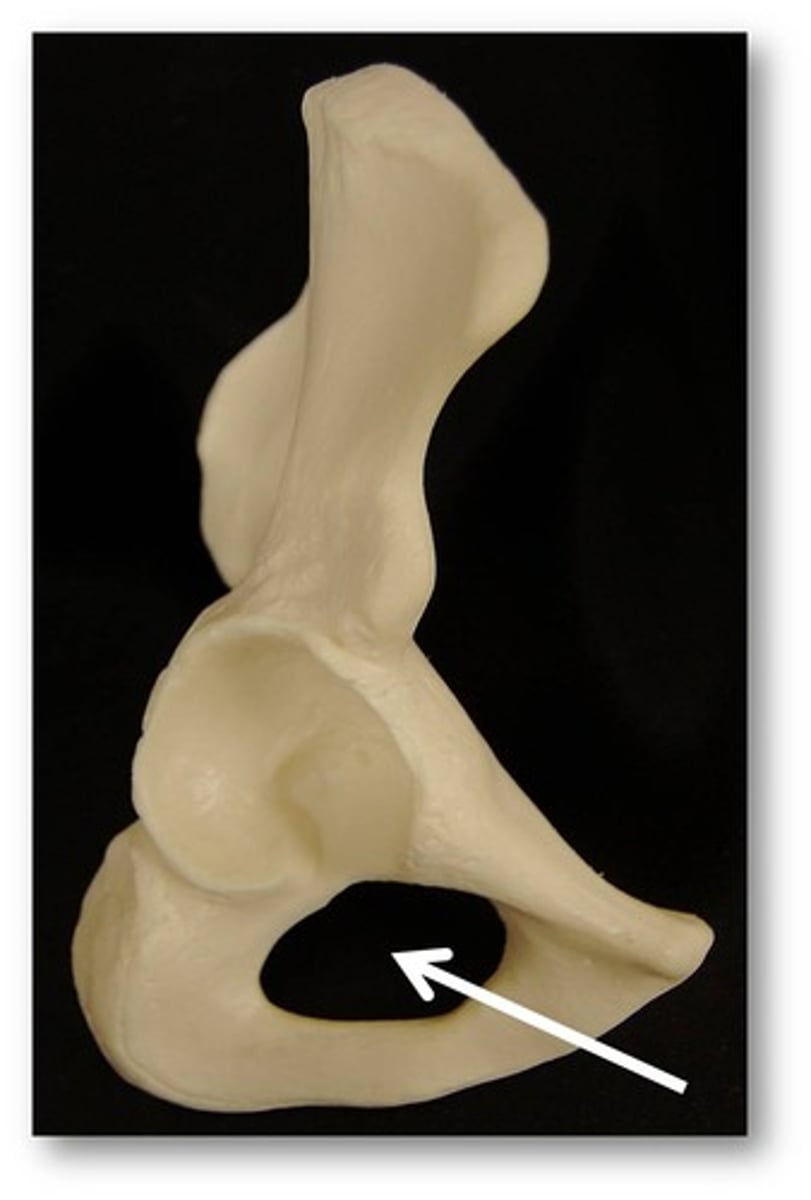
obturator foramen
opening in hip bone formed by the pubic and ischial rami
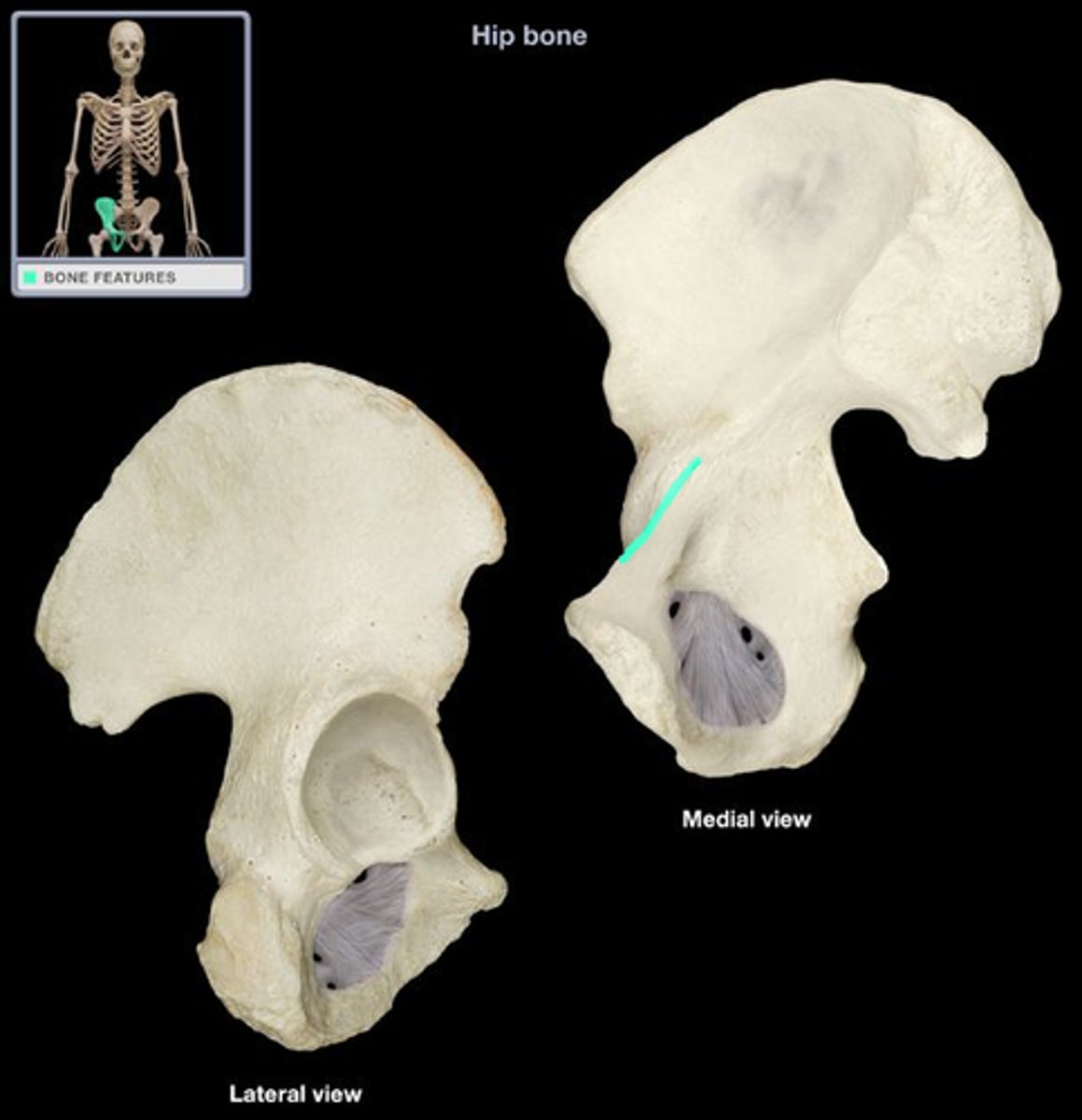
Pubis bone
body + 2 rami
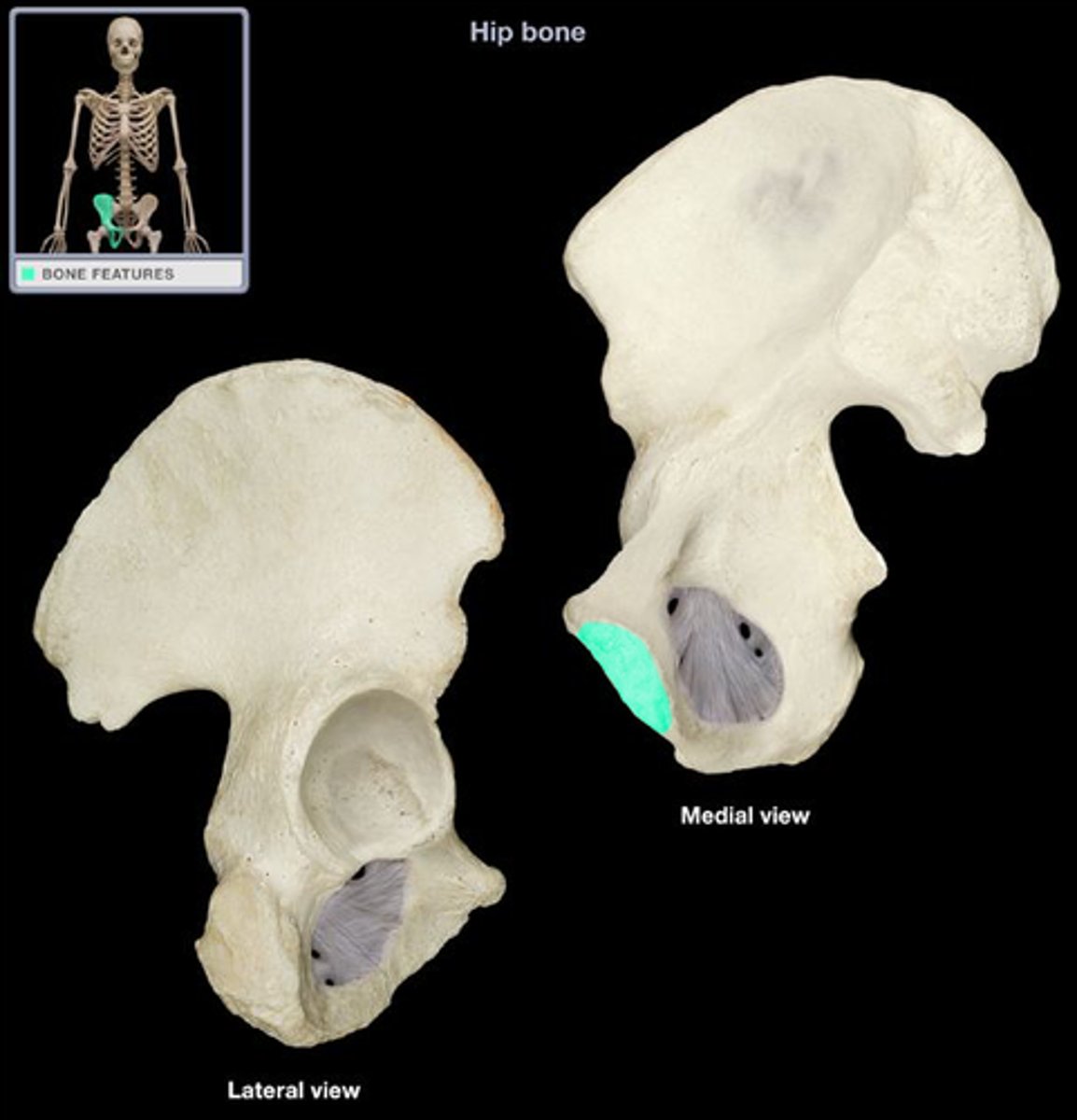
pectineal line of pubis
symphysis surface
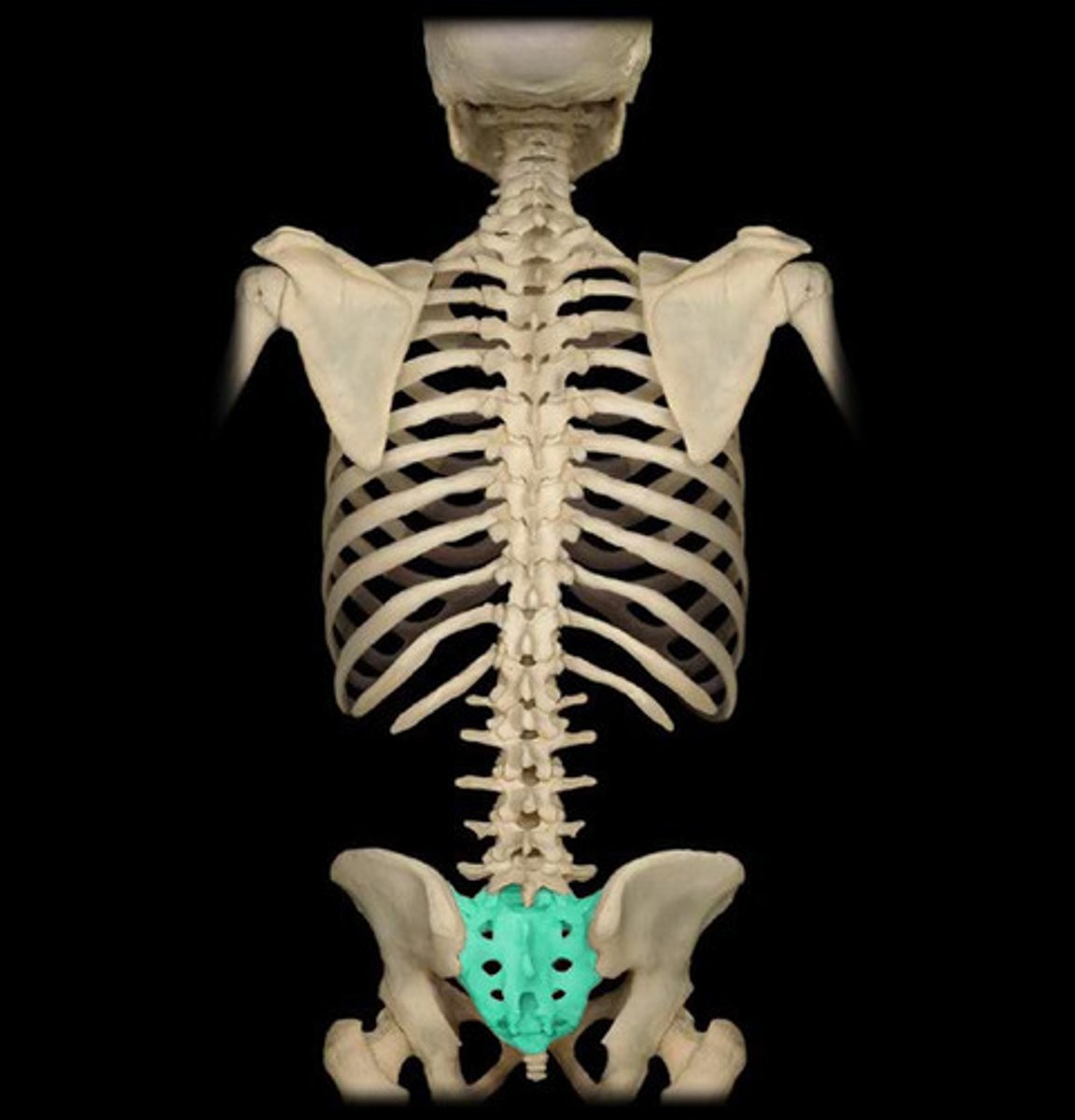
Sacrum
bone formed from five vertebrae fused together
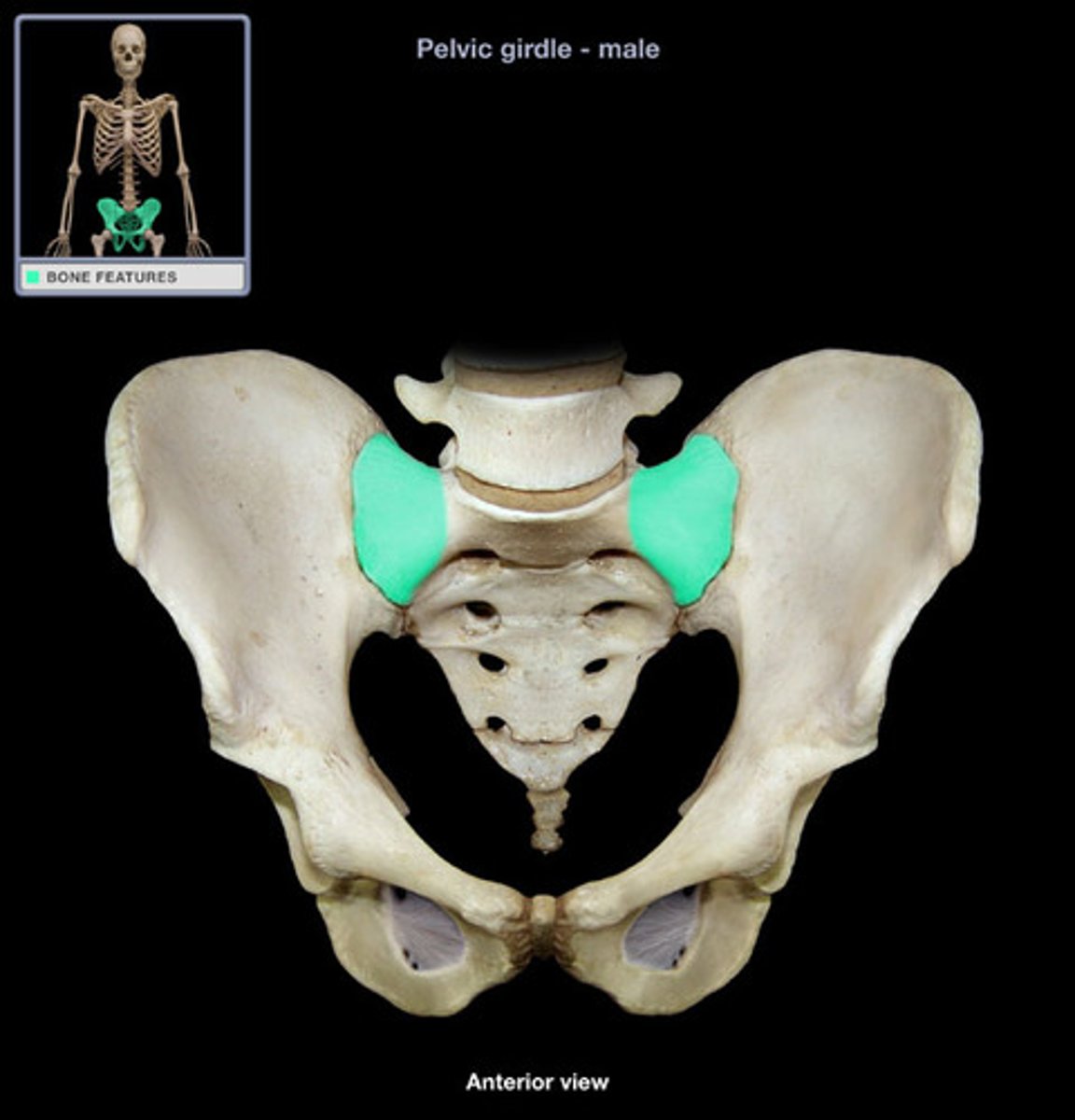
Wings of the sacrum
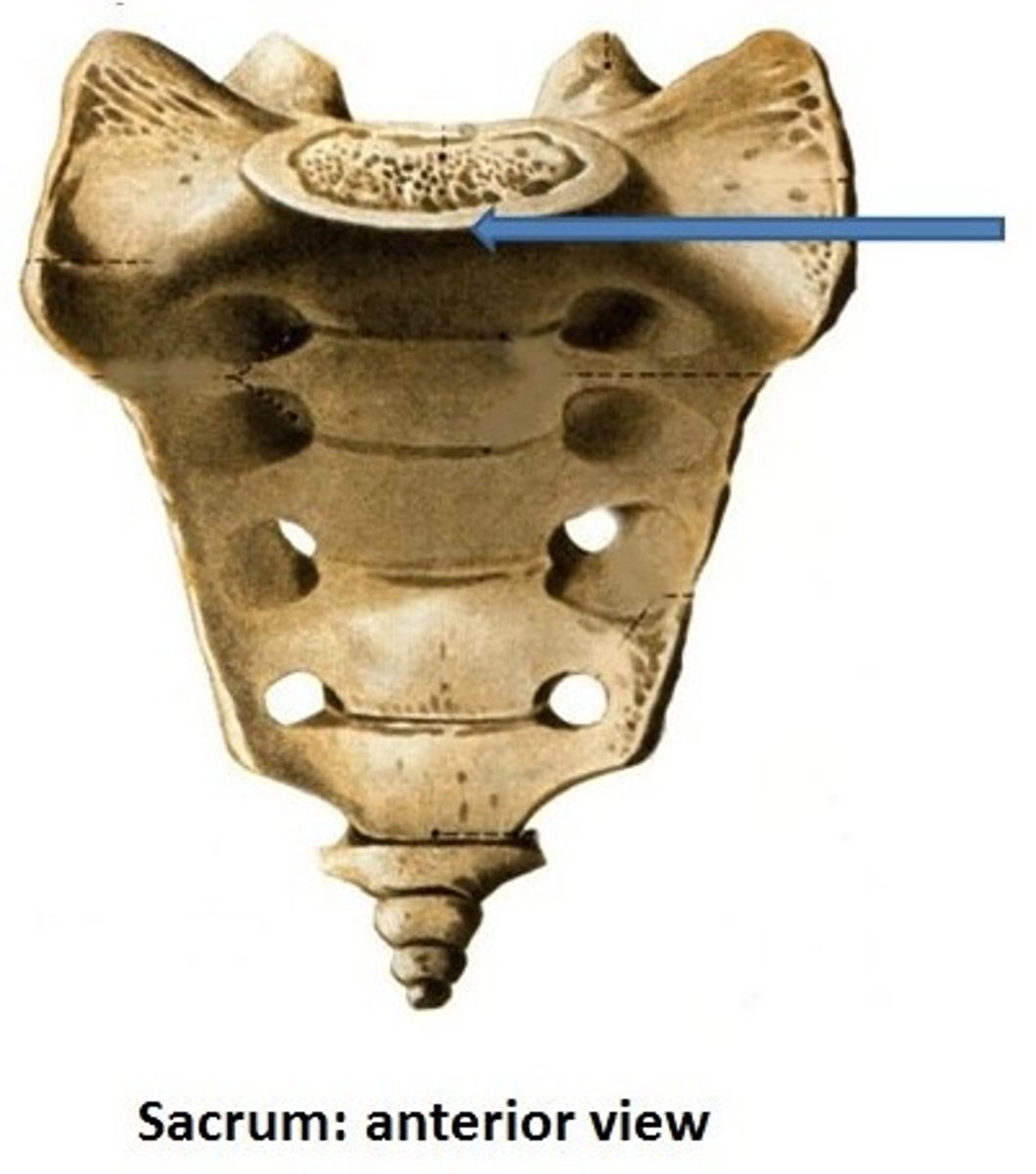
sacral promontory
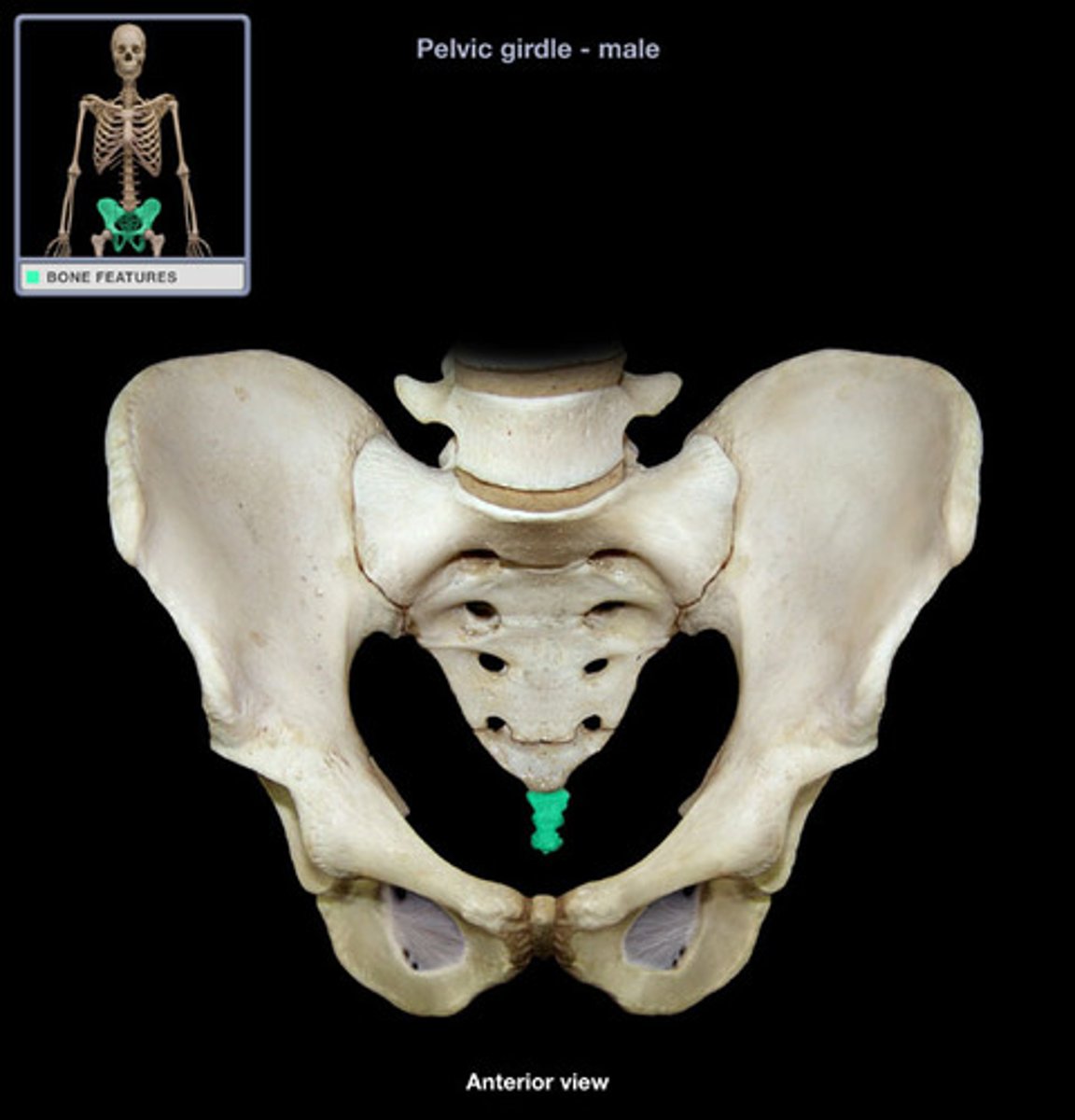
Coccyx
four vertebrae fused together to form the tailbone
auricular surface of sacrum
lateral sacral crest
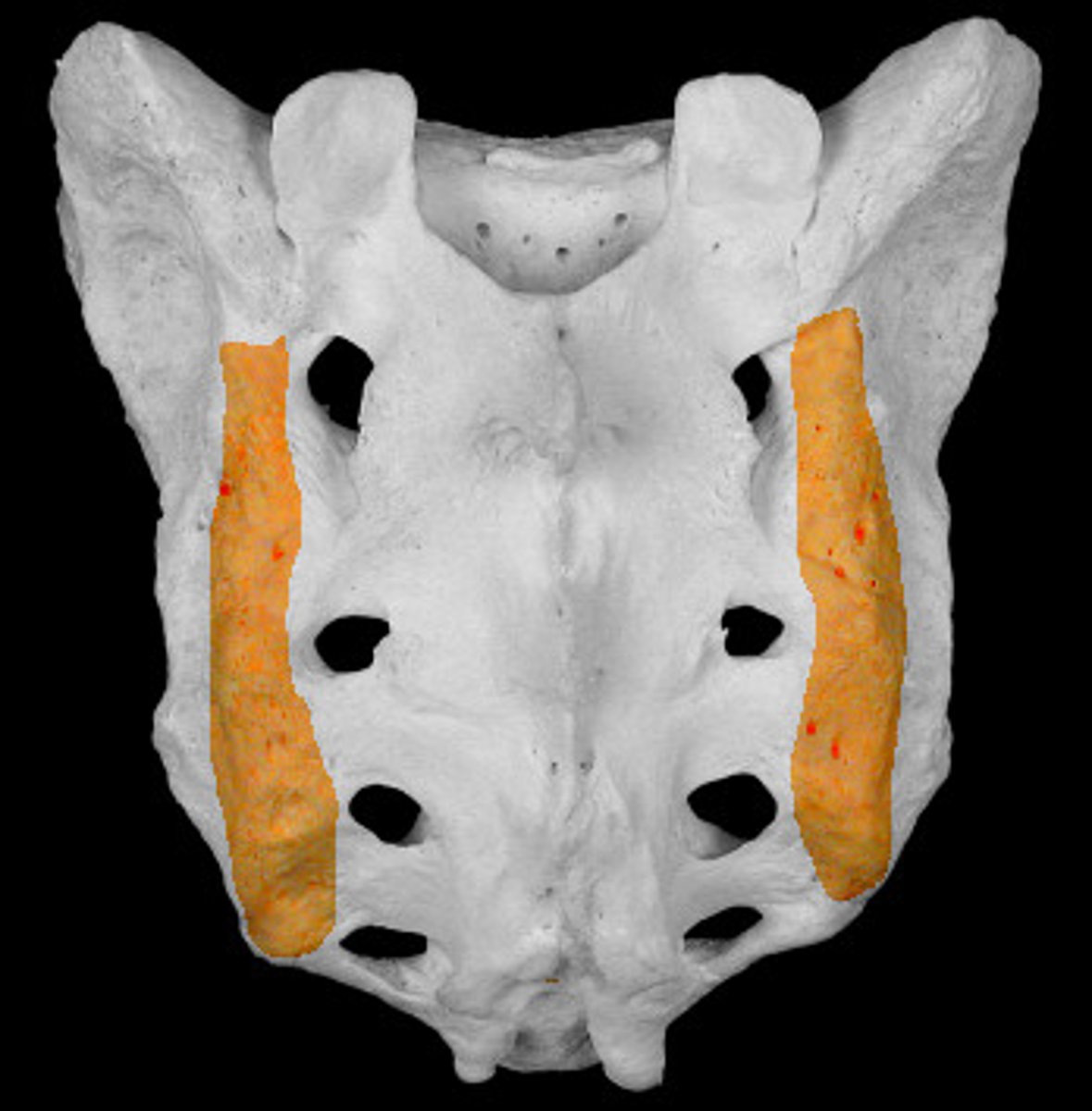
medial sacral crest
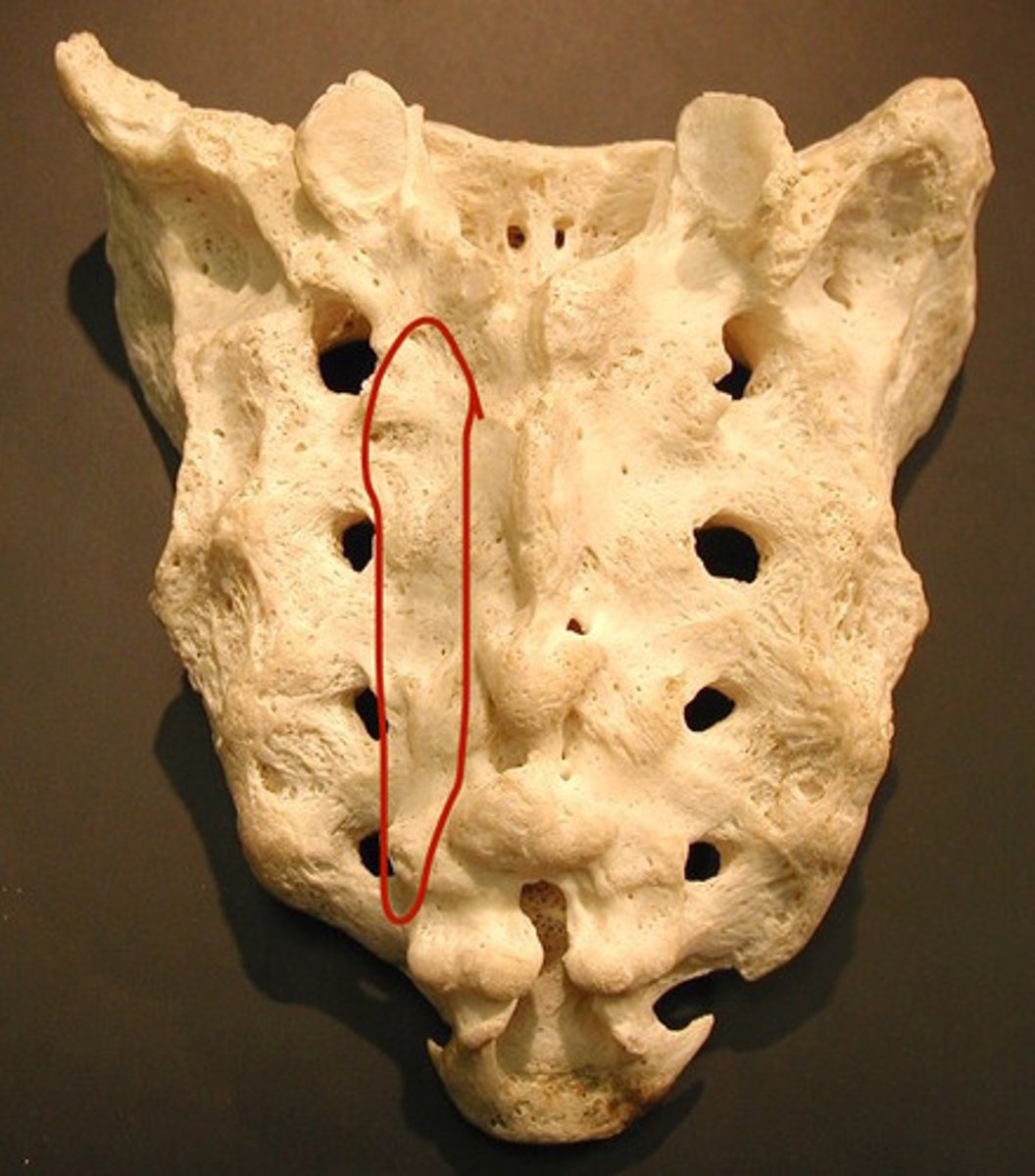
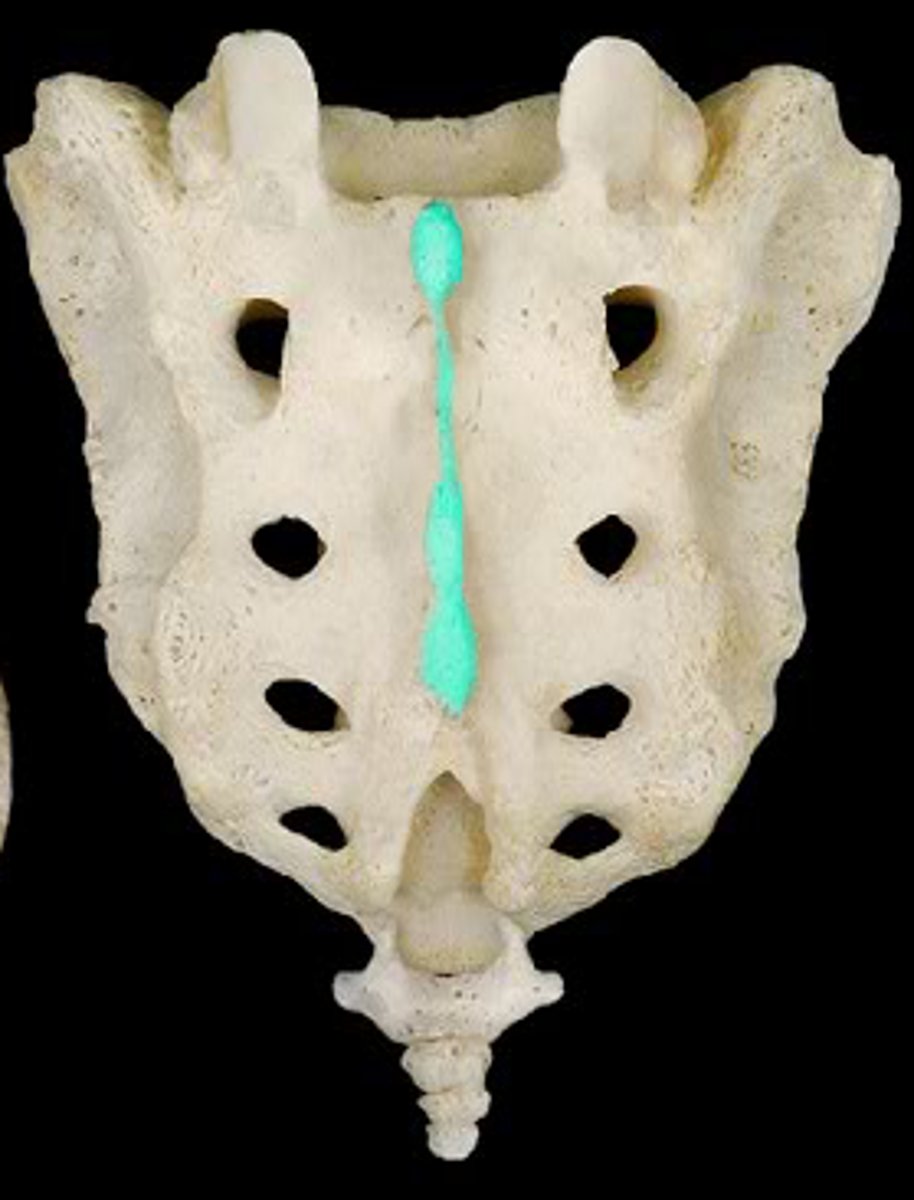
median sacral crest
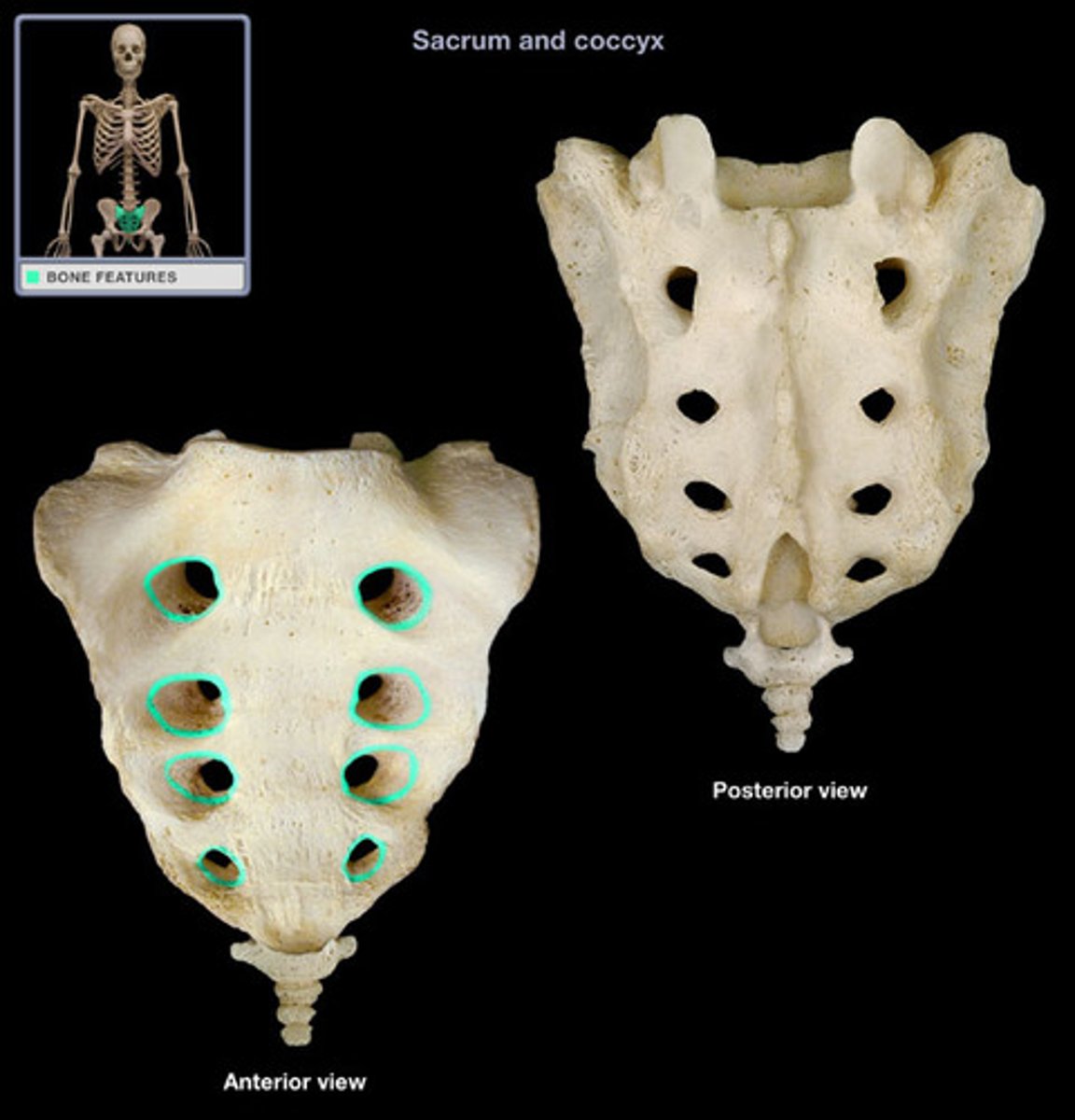
sacral foramina
holes in sacrum for passage of blood vessels and nerves (S1-S4)
4 pairs anteriorly
4 pairs posteriorly
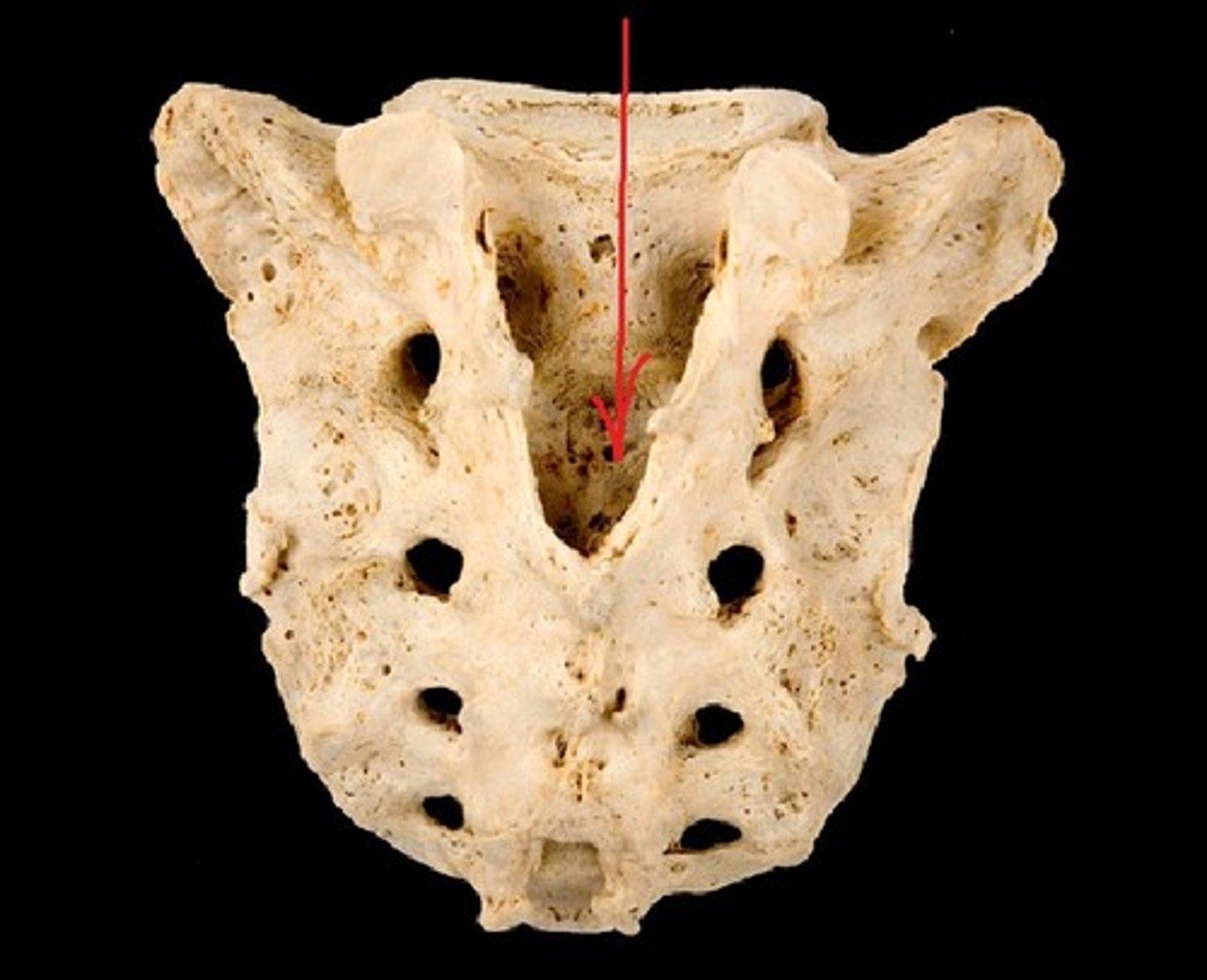
sacral canal
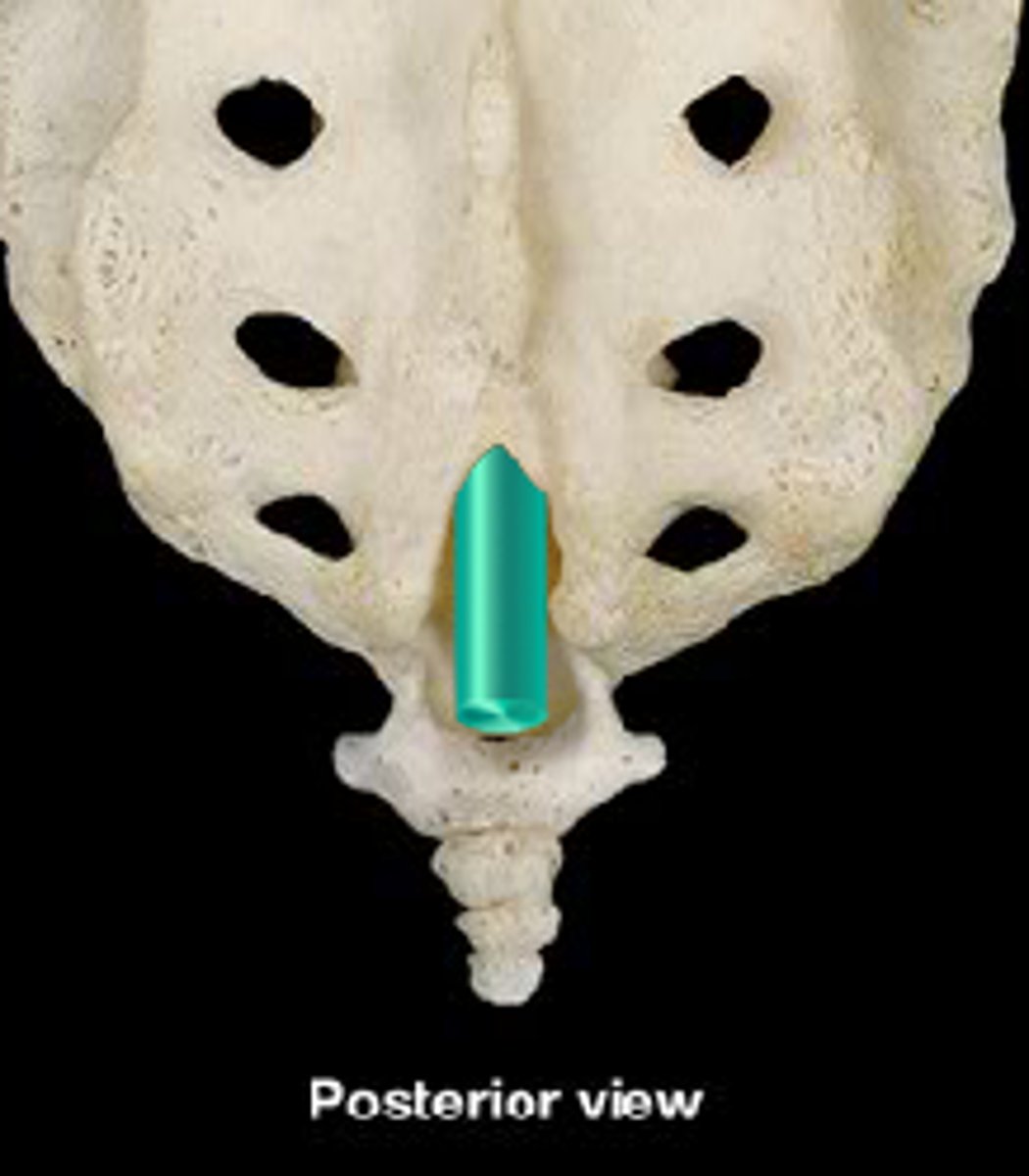
sacral hiatus of sacrum
inferior opening of the sacral canal
iliolumbar ligament
connects the transverse process of L5 and iliac crest
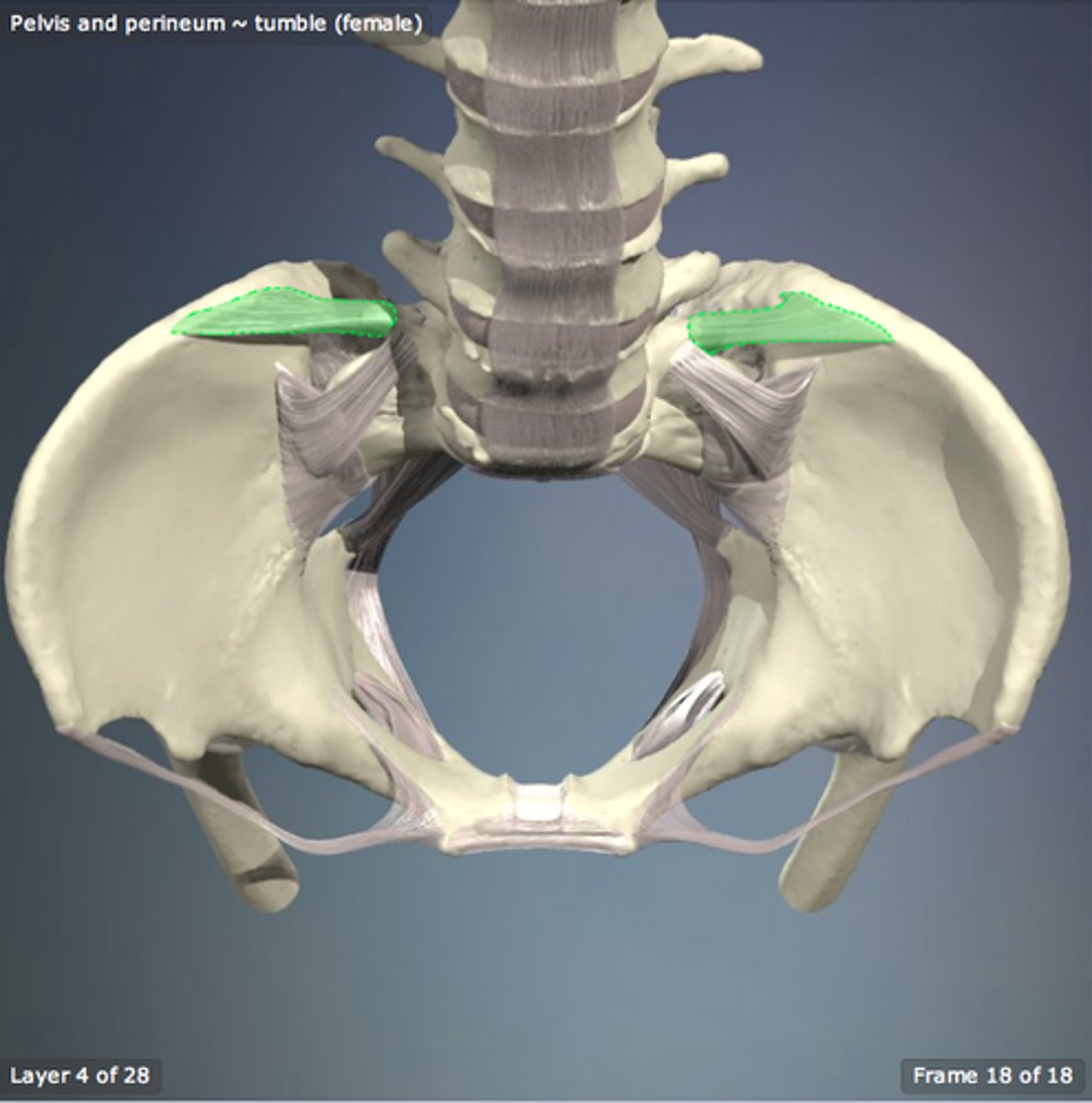
Lumbosacral ligament
connects transverse process of L5 and wing of ilium
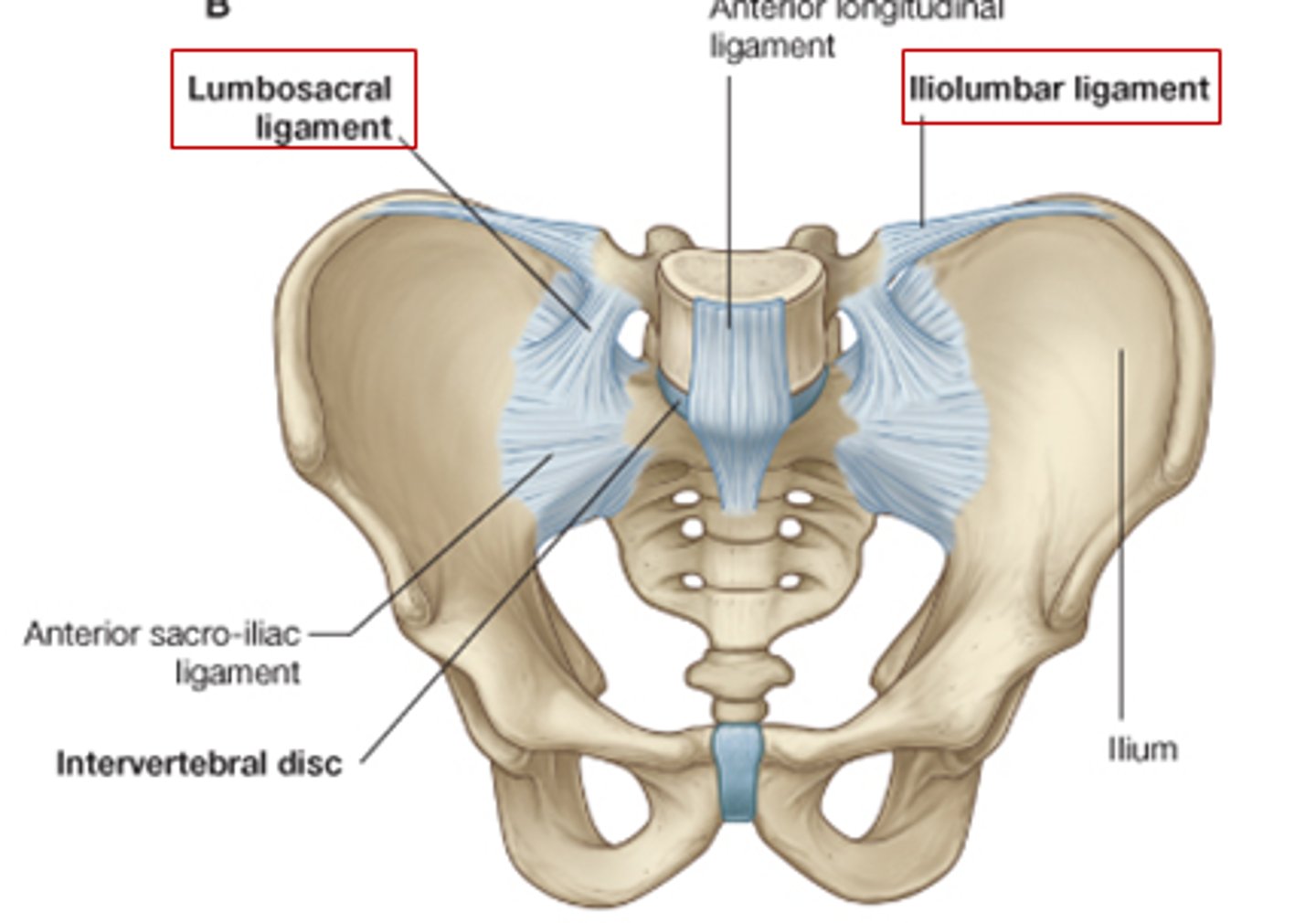
sacroiliac ligament (anterior and posterior)
attaches sacrum to ilium
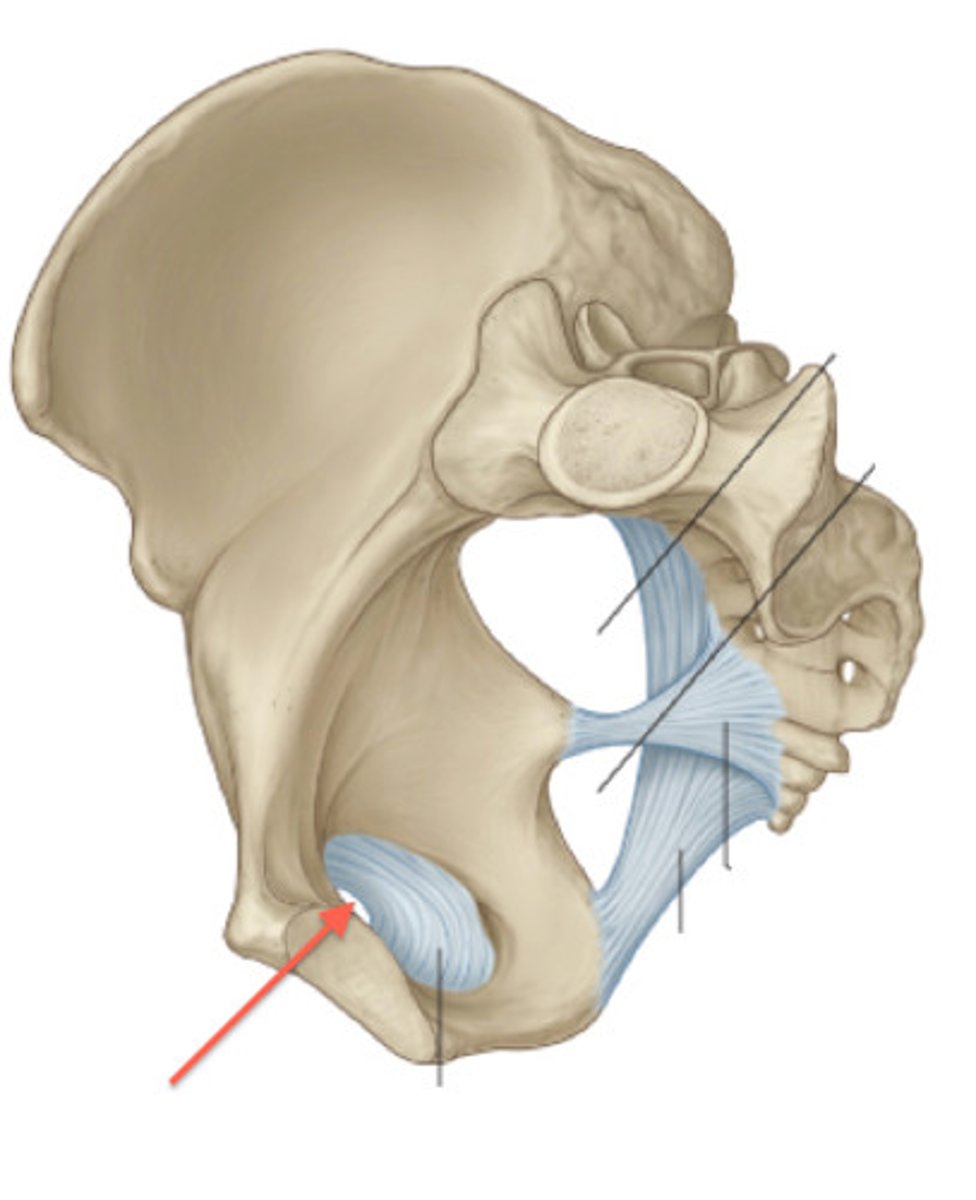
obturator membrane
covers most of obturator foramen
Pubis symphysis ligaments (superior and inferior)
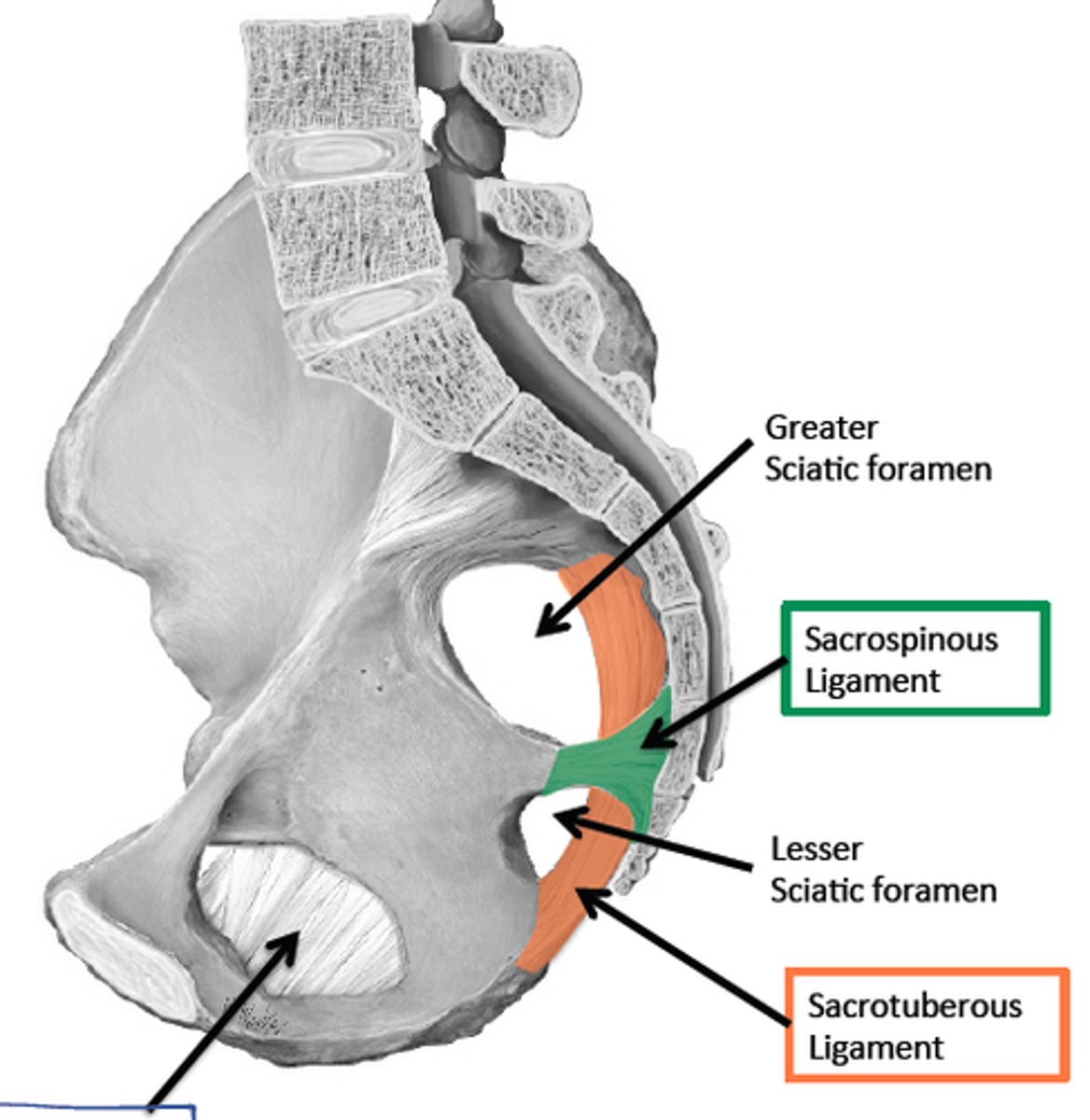
sacrotuberous ligament
sacrum to ischial tuberosity
C
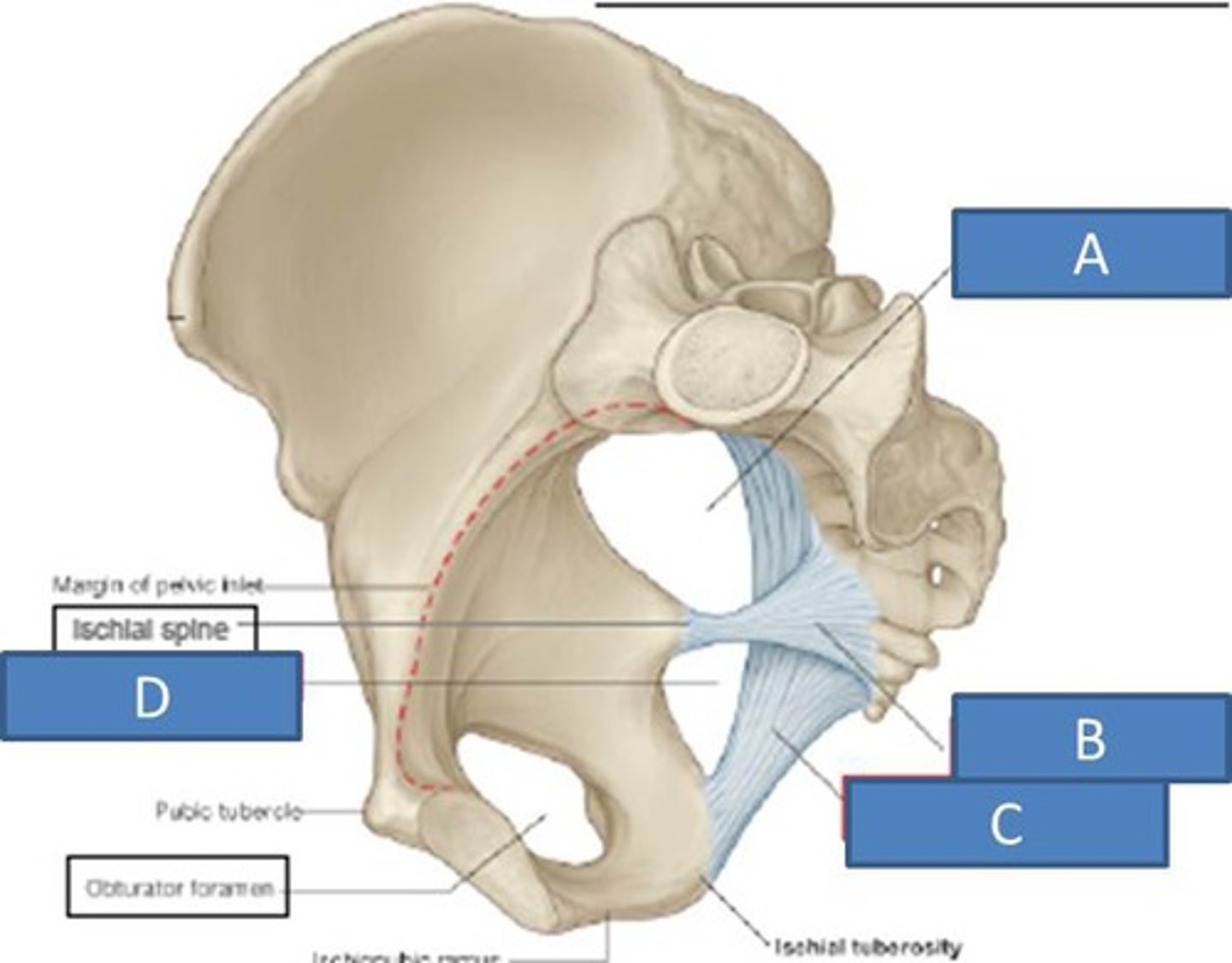
sacrospinous ligament
sacrum to ischial spine
B
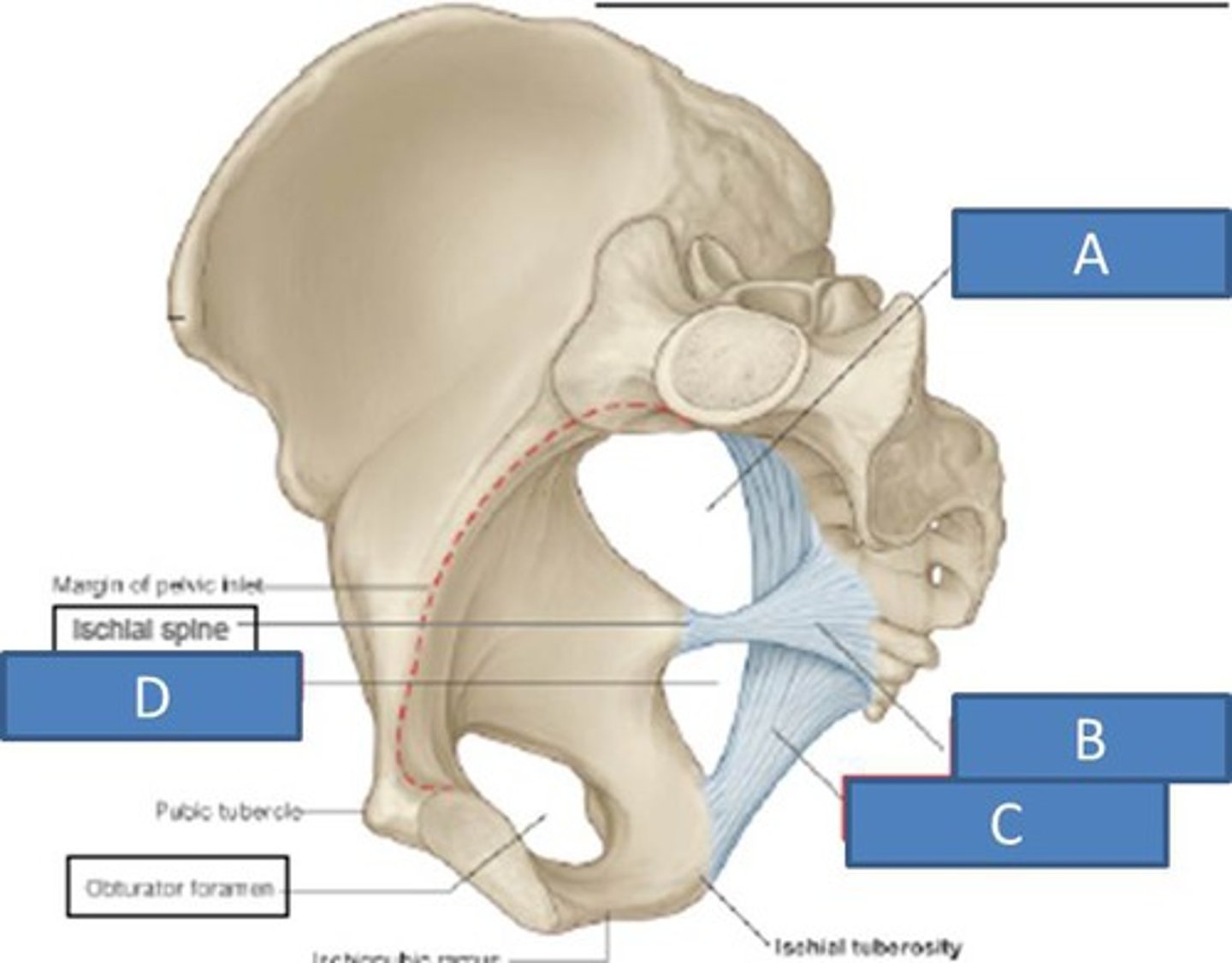
inguinal ligament
ASIS and pubic tubercle
greater sciatic foramen
pelvic opening formed by the greater sciatic notch of the hip bone, the sacrum, and the sacrospinous ligament
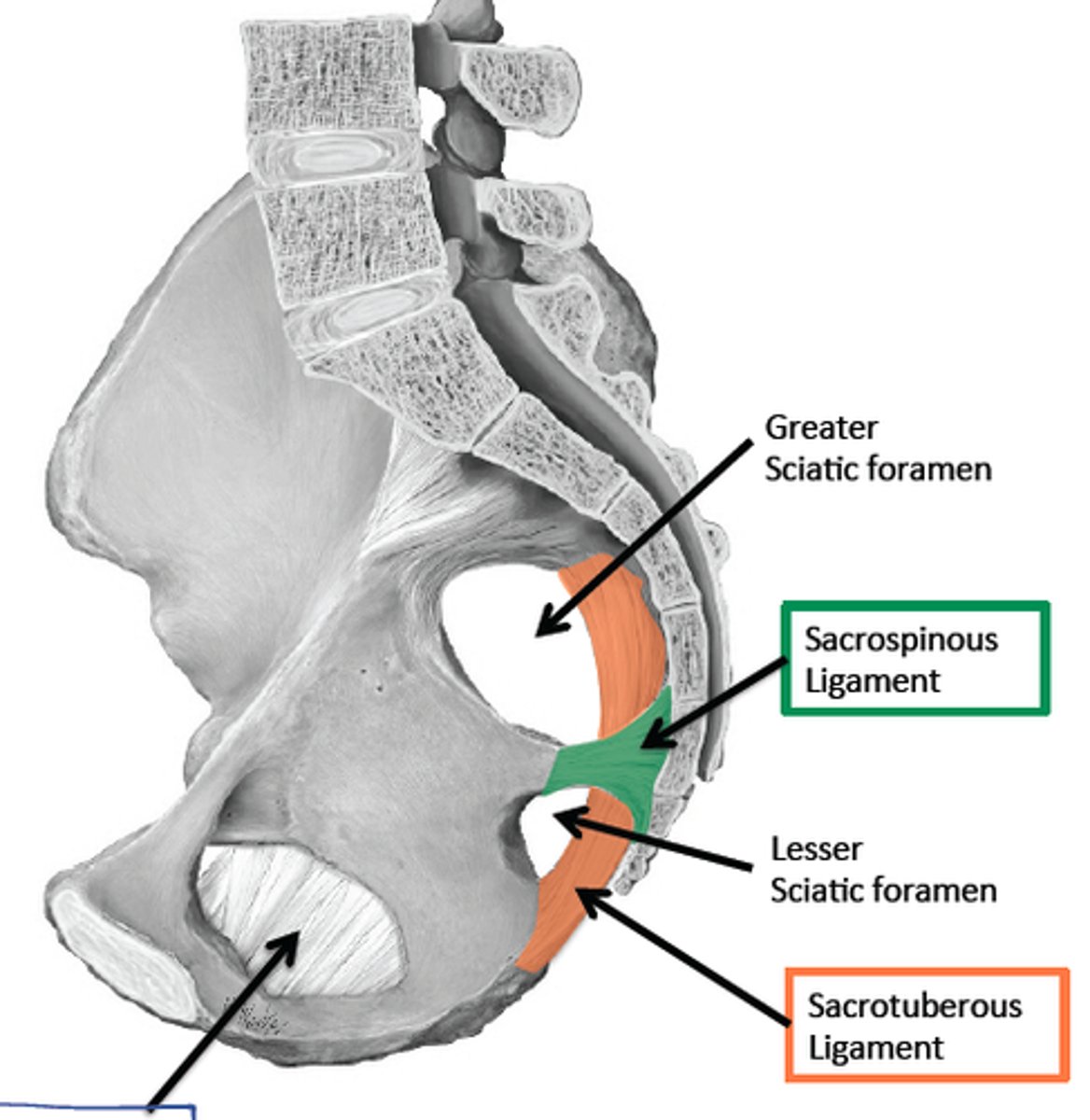
lesser sciatic foramen
pelvic opening formed by the lesser sciatic notch of the hip bone, the sacrospinous ligament, and the sacrotuberous ligament
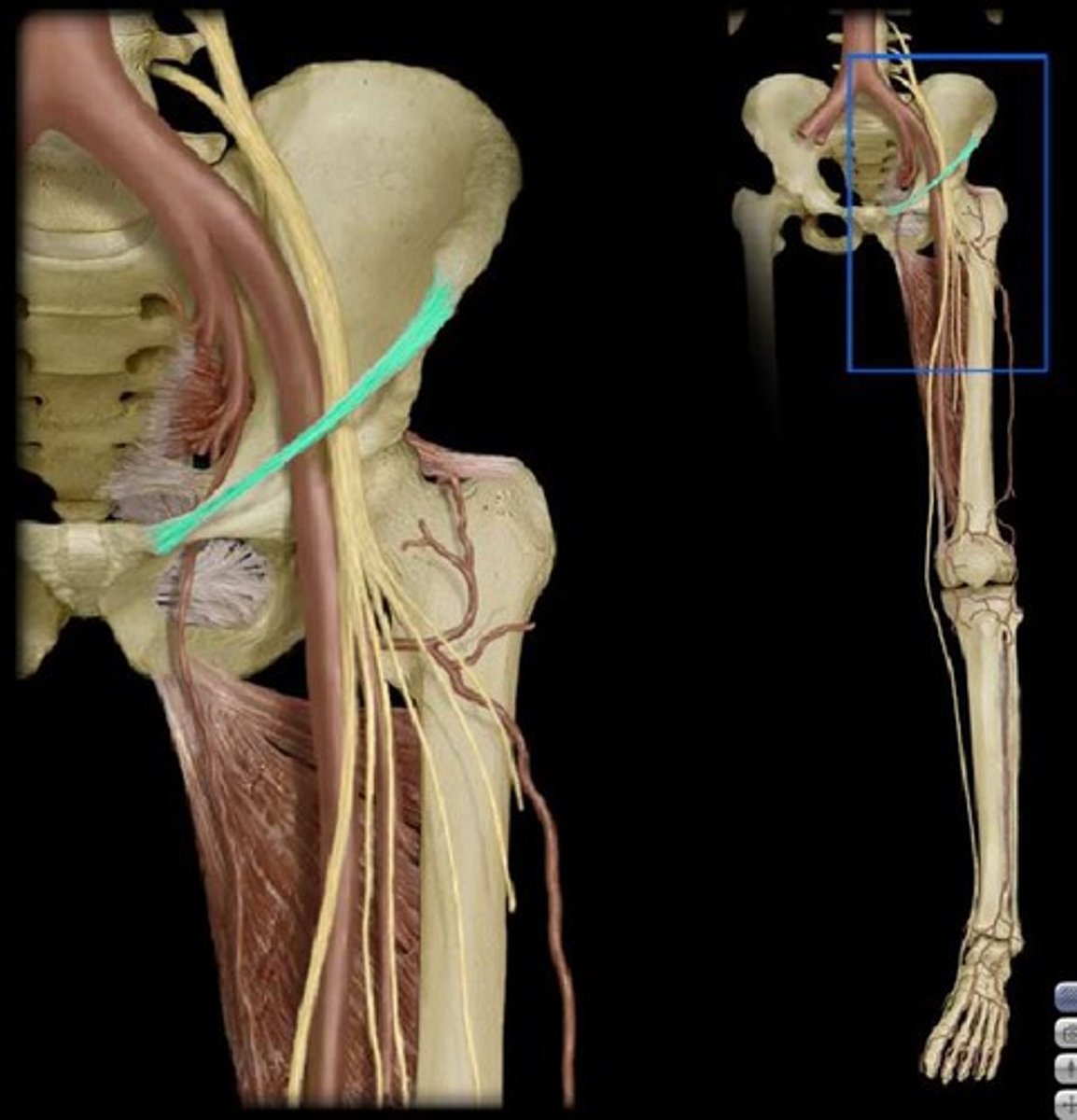
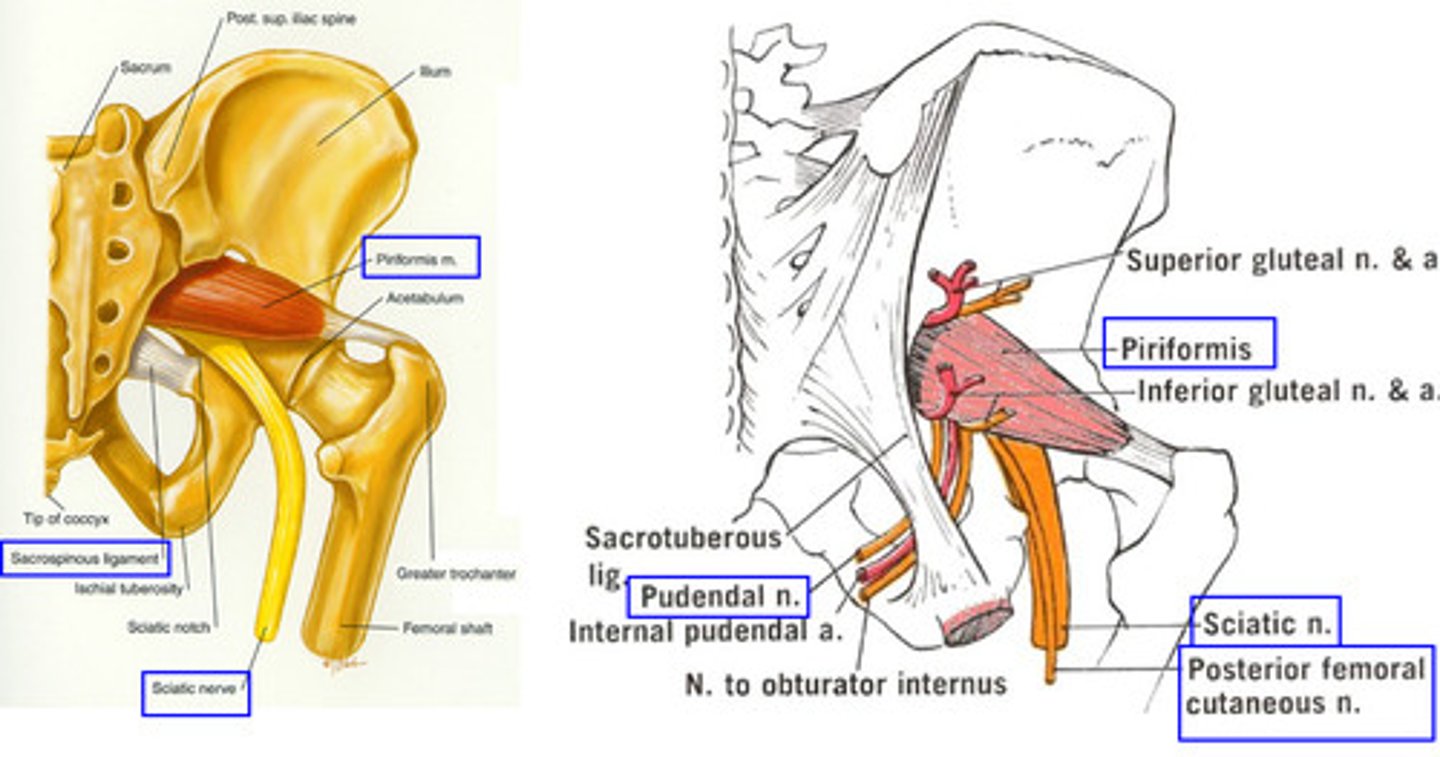
Where does the sciatic nerve exit the pelvis?
greater sciatic foramen inferior to piriformis
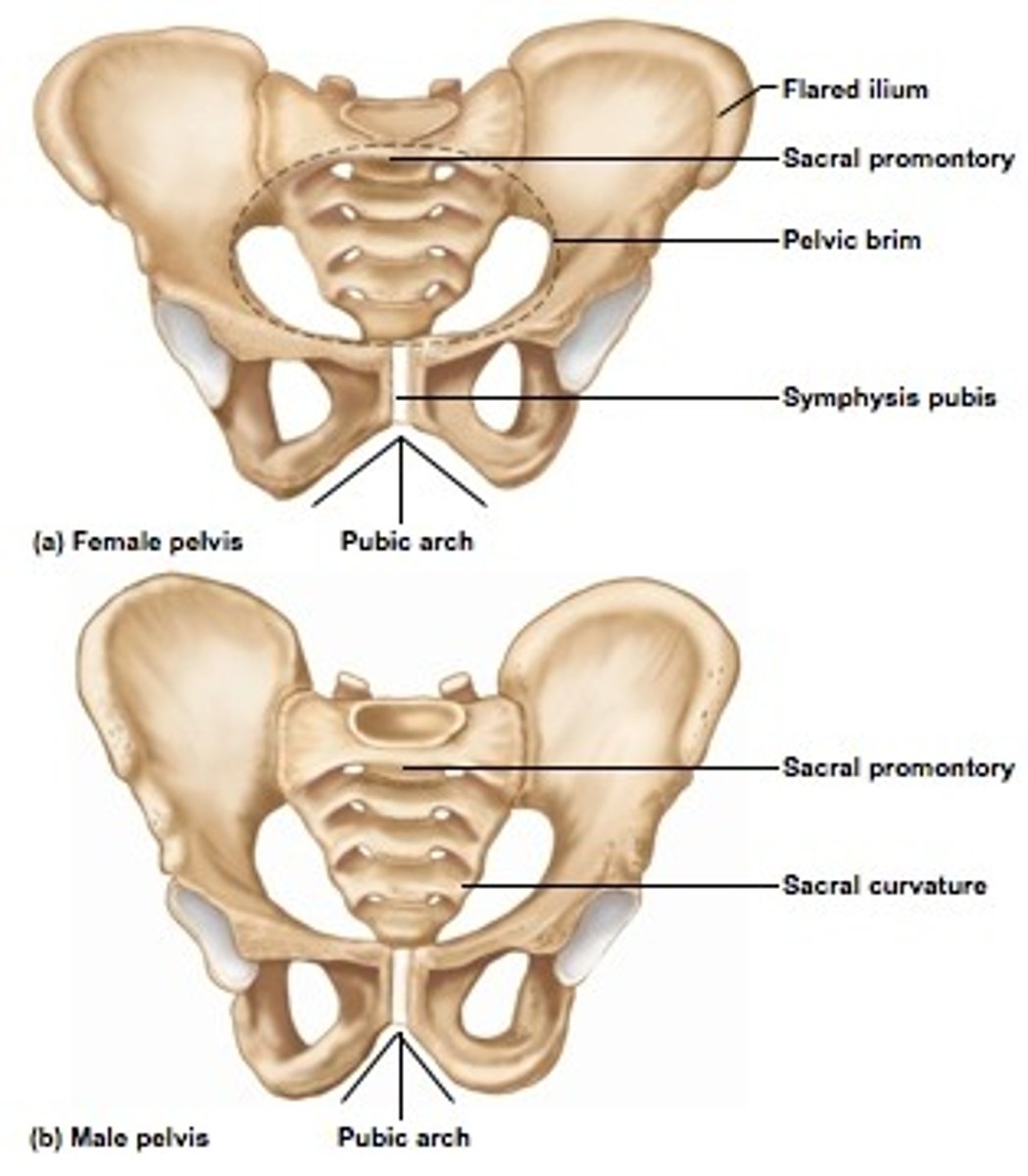
Female & Male Pelvis Differences
Static of pelvis
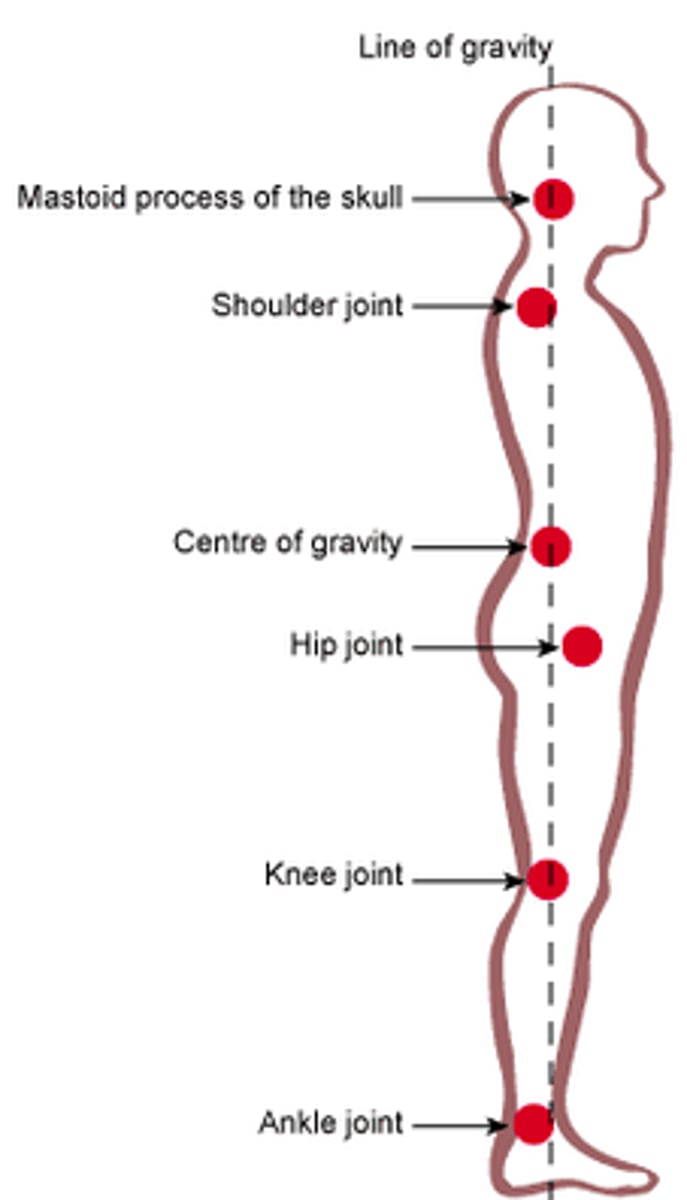
Center of gravity passes through: atlanto-occipital joint, lower lumbar vertebrae, anterior to promontory, head of femur, highest point of plantar arch
Pelvic inclination: 60-65 degrees
ASIS and symphysis are on the same frontal plane, sacrum is nearly vertical
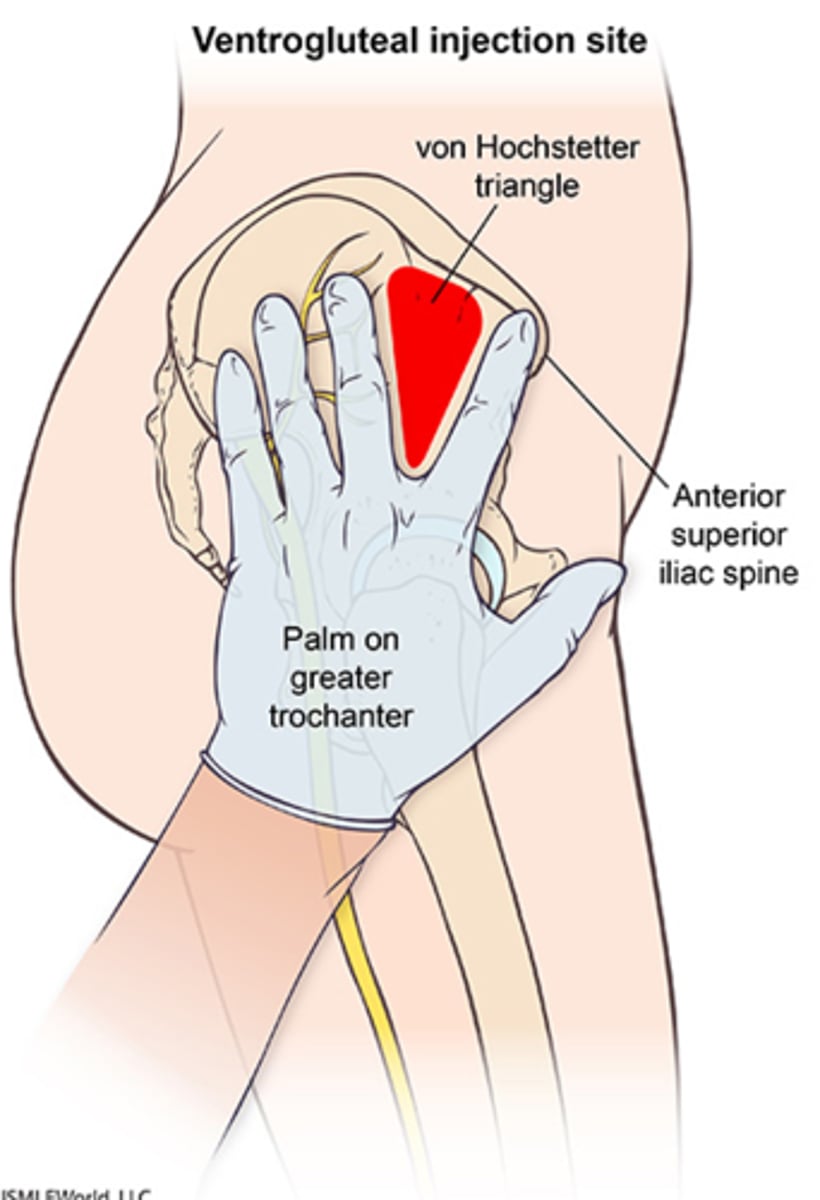
Intragluteal injections